Decreased PEDF Promotes Hepatic Fatty Acid Uptake and Lipid Droplet Formation in the Pathogenesis of NAFLD
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animal Experiments
2.2. Histological Analysis
2.3. Cell Culture and Treatments
2.4. Fatty Acid Preparation
2.5. Quantitative RT-PCR
2.6. Immunoblotting
2.7. Lipid Staining and Imaging
2.8. RNA Sequencing Analysis
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. PEDF Expression Is Decreased in a Diet-Induced NAFLD Mouse Model
3.2. Decreased PEDF Is Associated with Increased Lipid Accumulation
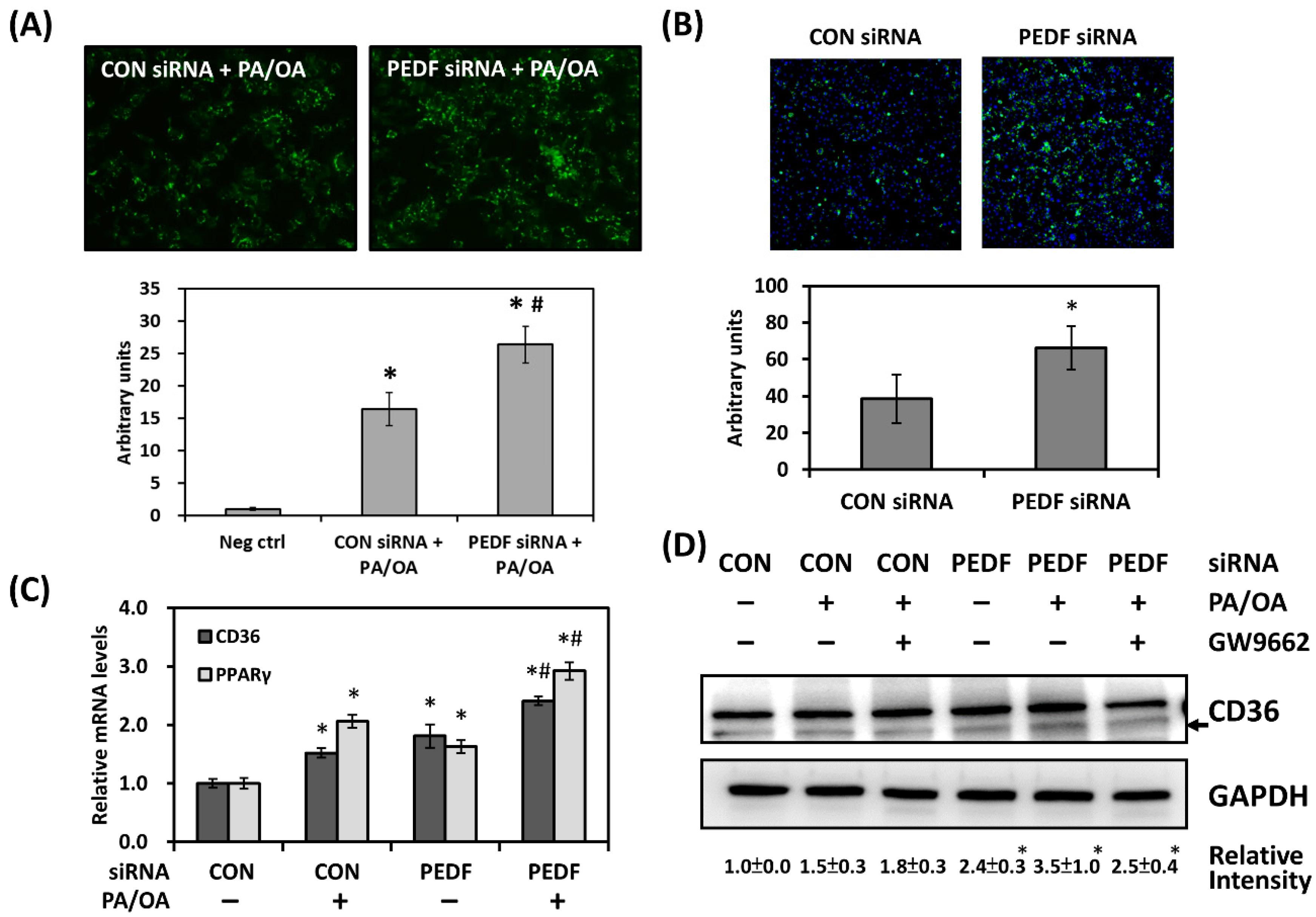
3.3. Decreased PEDF Alters Cellular Fatty Acid Mobilization
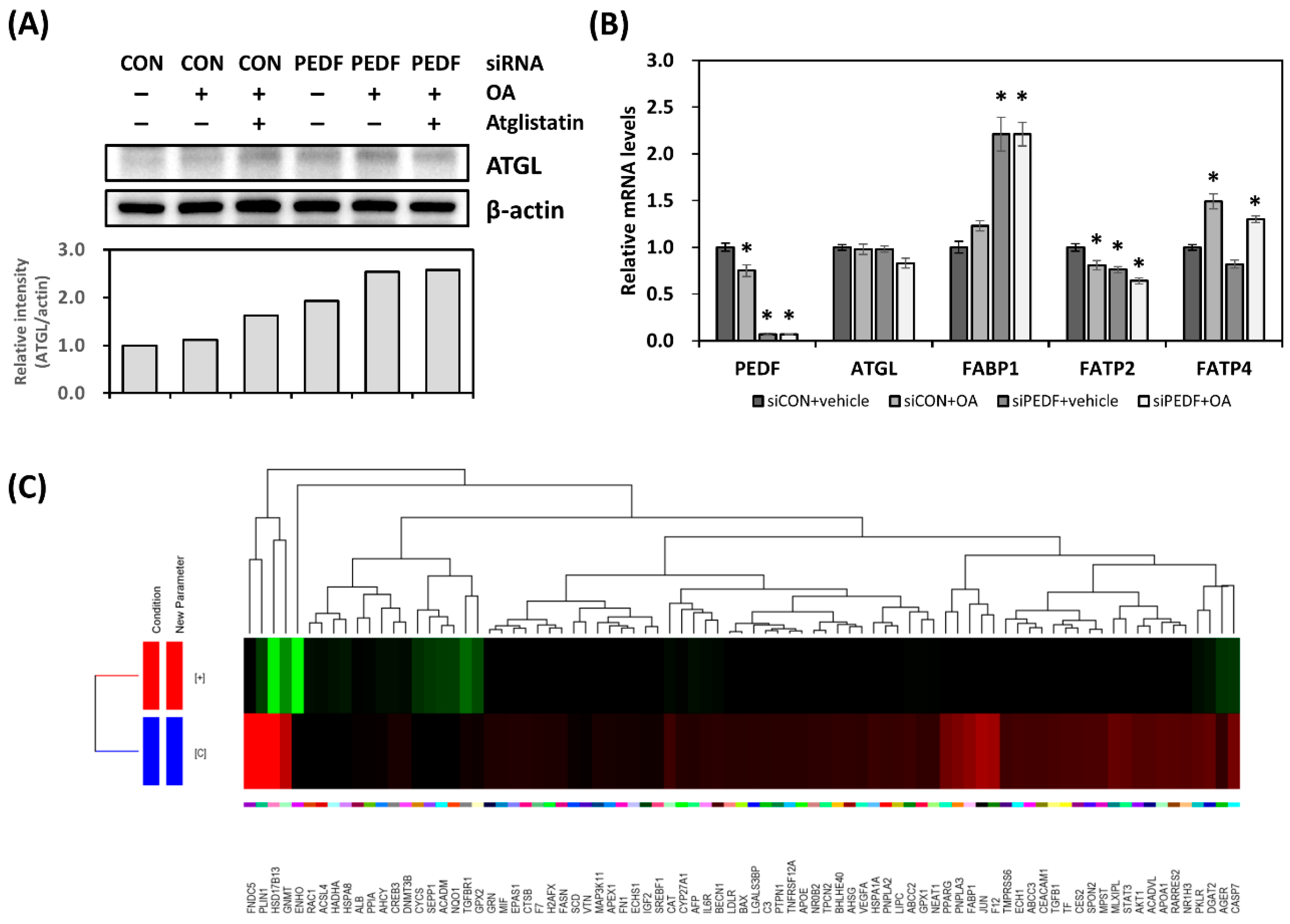
3.4. Decreased PEDF Results in Gene Expression Changes toward Hepatic Lipid Accumulation
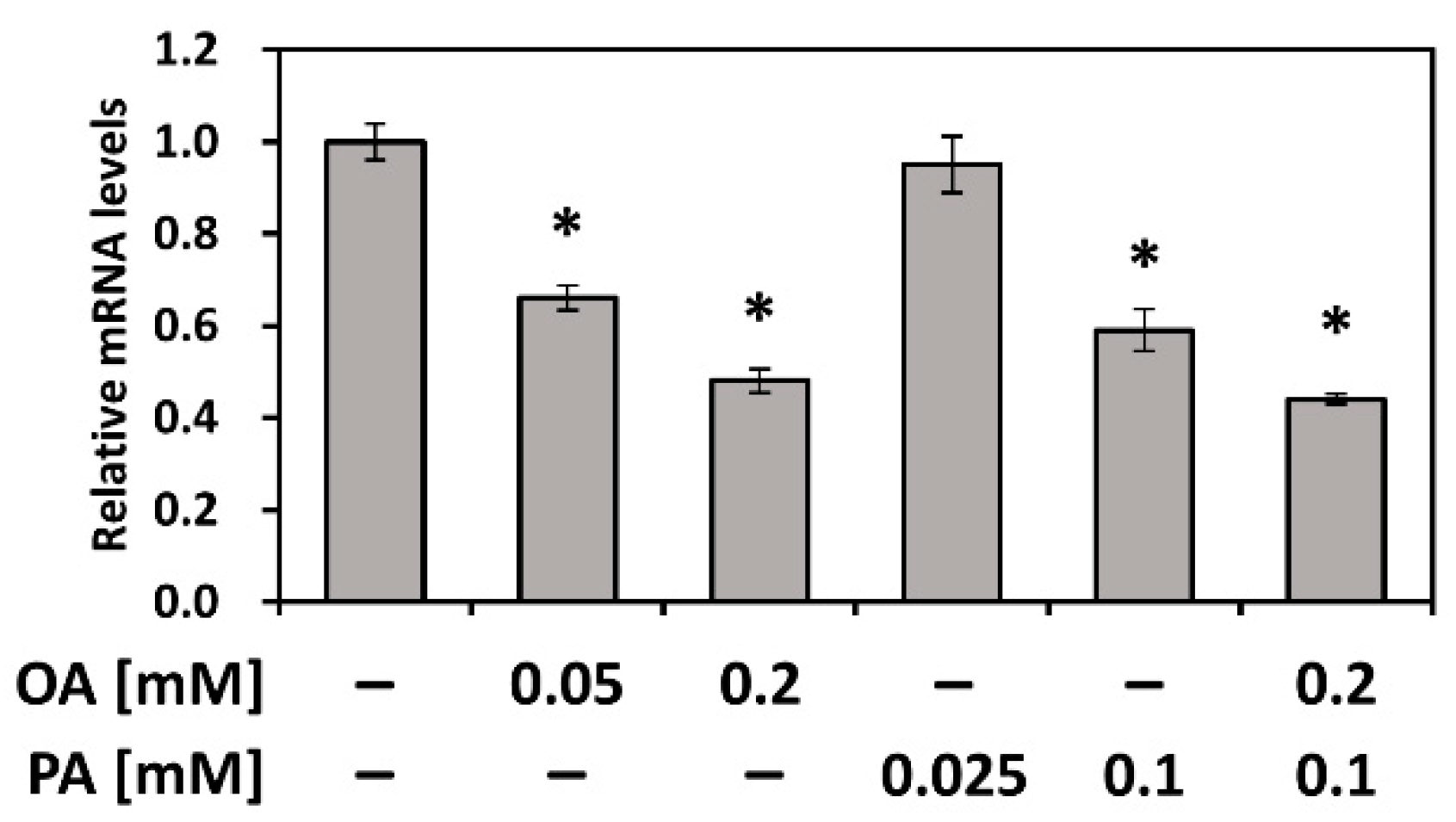
3.5. PEDF Is Downregulated by Fatty Acids PA and OA
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chalasani, N.; Younossi, Z.; Lavine, J.E.; Charlton, M.; Cusi, K.; Rinella, M.; Harrison, S.A.; Brunt, E.M.; Sanyal, A.J. The diagnosis and management of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Practice guidance from the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Hepatology 2018, 67, 328–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demir, M.; Lang, S.; Steffen, H.M. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease—Current status and future directions. J. Dig. Dis. 2015, 16, 541–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Younossi, Z.M.; Koenig, A.B.; Abdelatif, D.; Fazel, Y.; Henry, L.; Wymer, M. Global epidemiology of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease-Meta-analytic assessment of prevalence, incidence, and outcomes. Hepatology 2016, 64, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drew, L. Fighting the fatty liver. Nature 2017, 550, S102–S103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ascha, M.S.; Hanouneh, I.A.; Lopez, R.; Tamimi, T.A.; Feldstein, A.F.; Zein, N.N. The incidence and risk factors of hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Hepatology 2010, 51, 1972–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellentani, S. The epidemiology of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Liver Int. 2017, 37 (Suppl. 1), 81–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tombran-Tink, J.; Chader, G.G.; Johnson, L.V. PEDF: A pigment epithelium-derived factor with potent neuronal differentiative activity. Exp. Eye Res. 1991, 53, 411–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, C.; Doll, J.A.; Gattu, A.K.; Shugrue, C.; Cornwell, M.; Fitchev, P.; Crawford, S.E. Anti-angiogenic pigment epithelium-derived factor regulates hepatocyte triglyceride content through adipose triglyceride lipase (ATGL). J. Hepatol. 2008, 48, 471–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Notari, L.; Baladron, V.; Aroca-Aguilar, J.D.; Balko, N.; Heredia, R.; Meyer, C.; Notario, P.M.; Saravanamuthu, S.; Nueda, M.L.; Sanchez-Sanchez, F.; et al. Identification of a lipase-linked cell membrane receptor for pigment epithelium-derived factor. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 38022–38037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabater, M.; Moreno-Navarrete, J.M.; Ortega, F.J.; Pardo, G.; Salvador, J.; Ricart, W.; Fruhbeck, G.; Fernandez-Real, J.M. Circulating pigment epithelium-derived factor levels are associated with insulin resistance and decrease after weight loss. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2010, 95, 4720–4728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamagishi, S.; Adachi, H.; Abe, A.; Yashiro, T.; Enomoto, M.; Furuki, K.; Hino, A.; Jinnouchi, Y.; Takenaka, K.; Matsui, T.; et al. Elevated serum levels of pigment epithelium-derived factor in the metabolic syndrome. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2006, 91, 2447–2450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crowe, S.; Wu, L.E.; Economou, C.; Turpin, S.M.; Matzaris, M.; Hoehn, K.L.; Hevener, A.L.; James, D.E.; Duh, E.J.; Watt, M.J. Pigment epithelium-derived factor contributes to insulin resistance in obesity. Cell Metab. 2009, 10, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, Z.; Zhou, T.; Li, C.; Qi, W.; Mao, Y.; Lu, J.; Yao, Y.; Li, L.; Zhang, T.; Hong, H.; et al. Intracellular pigment epithelium-derived factor contributes to triglyceride degradation. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2013, 45, 2076–2086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adak, M.; Das, D.; Niyogi, S.; Nagalakshmi, C.; Ray, D.; Chakrabarti, P. Inflammasome activation in Kupffer cells confers a protective response in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis through pigment epithelium-derived factor expression. FASEB J. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.C.; Lee, T.Y.; Leu, Y.L.; Wang, S.H. Pigment epithelium-derived factor inhibits adipogenesis in 3T3-L1 adipocytes and protects against high-fat diet-induced obesity and metabolic disorders in mice. Transl. Res. 2019, 210, 26–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, T.; Akiba, J.; Matsui, T.; Nakamura, K.; Hisamoto, T.; Abe, M.; Ikezono, Y.; Wada, F.; Iwamoto, H.; Nakamura, T.; et al. Pigment Epithelium-Derived Factor (PEDF) Prevents Hepatic Fat Storage, Inflammation, and Fibrosis in Dietary Steatohepatitis of Mice. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2017, 62, 1527–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.T.; Hsu, L.W.; Chen, K.D.; Kung, C.P.; Goto, S.; Chen, C.L. Decreased PEDF Expression Promotes Adipogenic Differentiation through the Up-Regulation of CD36. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.D.; Huang, K.T.; Lin, C.C.; Weng, W.T.; Hsu, L.W.; Goto, S.; Nakano, T.; Lai, C.Y.; Kung, C.P.; Chiu, K.W.; et al. MicroRNA-27b Enhances the Hepatic Regenerative Properties of Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Mol. Nucleic Acids 2016, 5, e285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodama, Y.; Kisseleva, T.; Iwaisako, K.; Miura, K.; Taura, K.; De Minicis, S.; Osterreicher, C.H.; Schnabl, B.; Seki, E.; Brenner, D.A. c-Jun N-terminal kinase-1 from hematopoietic cells mediates progression from hepatic steatosis to steatohepatitis and fibrosis in mice. Gastroenterology 2009, 137, 1467–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakano, T.; Cheng, Y.F.; Lai, C.Y.; Hsu, L.W.; Chang, Y.C.; Deng, J.Y.; Huang, Y.Z.; Honda, H.; Chen, K.D.; Wang, C.C.; et al. Impact of artificial sunlight therapy on the progress of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in rats. J. Hepatol. 2011, 55, 415–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Febbraio, M.; Wada, T.; Zhai, Y.; Kuruba, R.; He, J.; Lee, J.H.; Khadem, S.; Ren, S.; Li, S.; et al. Hepatic fatty acid transporter Cd36 is a common target of LXR, PXR, and PPARgamma in promoting steatosis. Gastroenterology 2008, 134, 556–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, M.; Niyogi, S.; Bhattacharyya, M.; Adak, M.; Nayak, D.K.; Chakrabarti, S.; Chakrabarti, P. Ubiquitin Ligase COP1 Controls Hepatic Fat Metabolism by Targeting ATGL for Degradation. Diabetes 2016, 65, 3561–3572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rambold, A.S.; Cohen, S.; Lippincott-Schwartz, J. Fatty acid trafficking in starved cells: Regulation by lipid droplet lipolysis, autophagy, and mitochondrial fusion dynamics. Dev. Cell 2015, 32, 678–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palomer, X.; Pizarro-Delgado, J.; Barroso, E.; Vazquez-Carrera, M. Palmitic and Oleic Acid: The Yin and Yang of Fatty Acids in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2018, 29, 178–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trauner, M.; Arrese, M.; Wagner, M. Fatty liver and lipotoxicity. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2010, 1801, 299–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glatz, J.F.; Luiken, J.J. From fat to FAT (CD36/SR-B2): Understanding the regulation of cellular fatty acid uptake. Biochimie 2017, 136, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosui, A.; Tatsumi, T.; Hikita, H.; Saito, Y.; Hiramatsu, N.; Tsujii, M.; Hennighausen, L.; Takehara, T. Signal transducer and activator of transcription 5 plays a crucial role in hepatic lipid metabolism through regulation of CD36 expression. Hepatol. Res. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheedfar, F.; Sung, M.M.; Aparicio-Vergara, M.; Kloosterhuis, N.J.; Miquilena-Colina, M.E.; Vargas-Castrillon, J.; Febbraio, M.; Jacobs, R.L.; de Bruin, A.; Vinciguerra, M.; et al. Increased hepatic CD36 expression with age is associated with enhanced susceptibility to nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Aging 2014, 6, 281–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, J.F.; Walewski, J.L.; Anglade, D.; Berk, P.D. Regulation of Hepatocellular Fatty Acid Uptake in Mouse Models of Fatty Liver Disease with and without Functional Leptin Signaling: Roles of NfKB and SREBP-1C and the Effects of Spexin. Semin. Liver Dis. 2016, 36, 360–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Zhou, J.; Han, N.; Liu, Z.; Xiao, B.; Yin, J. Beneficial effects of neomangiferin on high fat diet-induced nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in rats. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2015, 25, 218–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroeder, F.; McIntosh, A.L.; Martin, G.G.; Huang, H.; Landrock, D.; Chung, S.; Landrock, K.K.; Dangott, L.J.; Li, S.; Kaczocha, M.; et al. Fatty Acid Binding Protein-1 (FABP1) and the Human FABP1 T94A Variant: Roles in the Endocannabinoid System and Dyslipidemias. Lipids 2016, 51, 655–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolfrum, C.; Buhlmann, C.; Rolf, B.; Borchers, T.; Spener, F. Variation of liver-type fatty acid binding protein content in the human hepatoma cell line HepG2 by peroxisome proliferators and antisense RNA affects the rate of fatty acid uptake. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1999, 1437, 194–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zechner, R. FAT FLUX: Enzymes, regulators, and pathophysiology of intracellular lipolysis. EMBO Mol. Med. 2015, 7, 359–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niyogi, S.; Ghosh, M.; Adak, M.; Chakrabarti, P. PEDF promotes nuclear degradation of ATGL through COP1. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2019, 512, 806–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.; Fornes, O.; Stigliani, A.; Gheorghe, M.; Castro-Mondragon, J.A.; van der Lee, R.; Bessy, A.; Cheneby, J.; Kulkarni, S.R.; Tan, G.; et al. JASPAR 2018: Update of the open-access database of transcription factor binding profiles and its web framework. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, D260–D266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; McIntosh, A.L.; Martin, G.G.; Petrescu, A.D.; Landrock, K.K.; Landrock, D.; Kier, A.B.; Schroeder, F. Inhibitors of Fatty Acid Synthesis Induce PPAR alpha -Regulated Fatty Acid beta -Oxidative Genes: Synergistic Roles of L-FABP and Glucose. PPAR Res. 2013, 2013, 865604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrescu, A.D.; McIntosh, A.L.; Storey, S.M.; Huang, H.; Martin, G.G.; Landrock, D.; Kier, A.B.; Schroeder, F. High glucose potentiates L-FABP mediated fibrate induction of PPARalpha in mouse hepatocytes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1831, 1412–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Famulla, S.; Lamers, D.; Hartwig, S.; Passlack, W.; Horrighs, A.; Cramer, A.; Lehr, S.; Sell, H.; Eckel, J. Pigment epithelium-derived factor (PEDF) is one of the most abundant proteins secreted by human adipocytes and induces insulin resistance and inflammatory signaling in muscle and fat cells. Int J. Obes. 2011, 35, 762–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Navarrete, J.M.; Touskova, V.; Sabater, M.; Mraz, M.; Drapalova, J.; Ortega, F.; Serrano, M.; Catalan, V.; Gomez-Ambrosi, J.; Ortiz, M.R.; et al. Liver, but not adipose tissue PEDF gene expression is associated with insulin resistance. Int. J. Obes. 2013, 37, 1230–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]


© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, K.-T.; Chen, K.-D.; Hsu, L.-W.; Kung, C.-P.; Li, S.-R.; Chen, C.-C.; Chiu, K.-W.; Goto, S.; Chen, C.-L. Decreased PEDF Promotes Hepatic Fatty Acid Uptake and Lipid Droplet Formation in the Pathogenesis of NAFLD. Nutrients 2020, 12, 270. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12010270
Huang K-T, Chen K-D, Hsu L-W, Kung C-P, Li S-R, Chen C-C, Chiu K-W, Goto S, Chen C-L. Decreased PEDF Promotes Hepatic Fatty Acid Uptake and Lipid Droplet Formation in the Pathogenesis of NAFLD. Nutrients. 2020; 12(1):270. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12010270
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Kuang-Tzu, Kuang-Den Chen, Li-Wen Hsu, Chao-Pin Kung, Shu-Rong Li, Chien-Chih Chen, King-Wah Chiu, Shigeru Goto, and Chao-Long Chen. 2020. "Decreased PEDF Promotes Hepatic Fatty Acid Uptake and Lipid Droplet Formation in the Pathogenesis of NAFLD" Nutrients 12, no. 1: 270. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12010270
APA StyleHuang, K.-T., Chen, K.-D., Hsu, L.-W., Kung, C.-P., Li, S.-R., Chen, C.-C., Chiu, K.-W., Goto, S., & Chen, C.-L. (2020). Decreased PEDF Promotes Hepatic Fatty Acid Uptake and Lipid Droplet Formation in the Pathogenesis of NAFLD. Nutrients, 12(1), 270. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12010270




