A Longitudinal Assessment of Diet Quality and Risks Associated with Malnutrition in Socioeconomic and Racially Diverse Adults
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
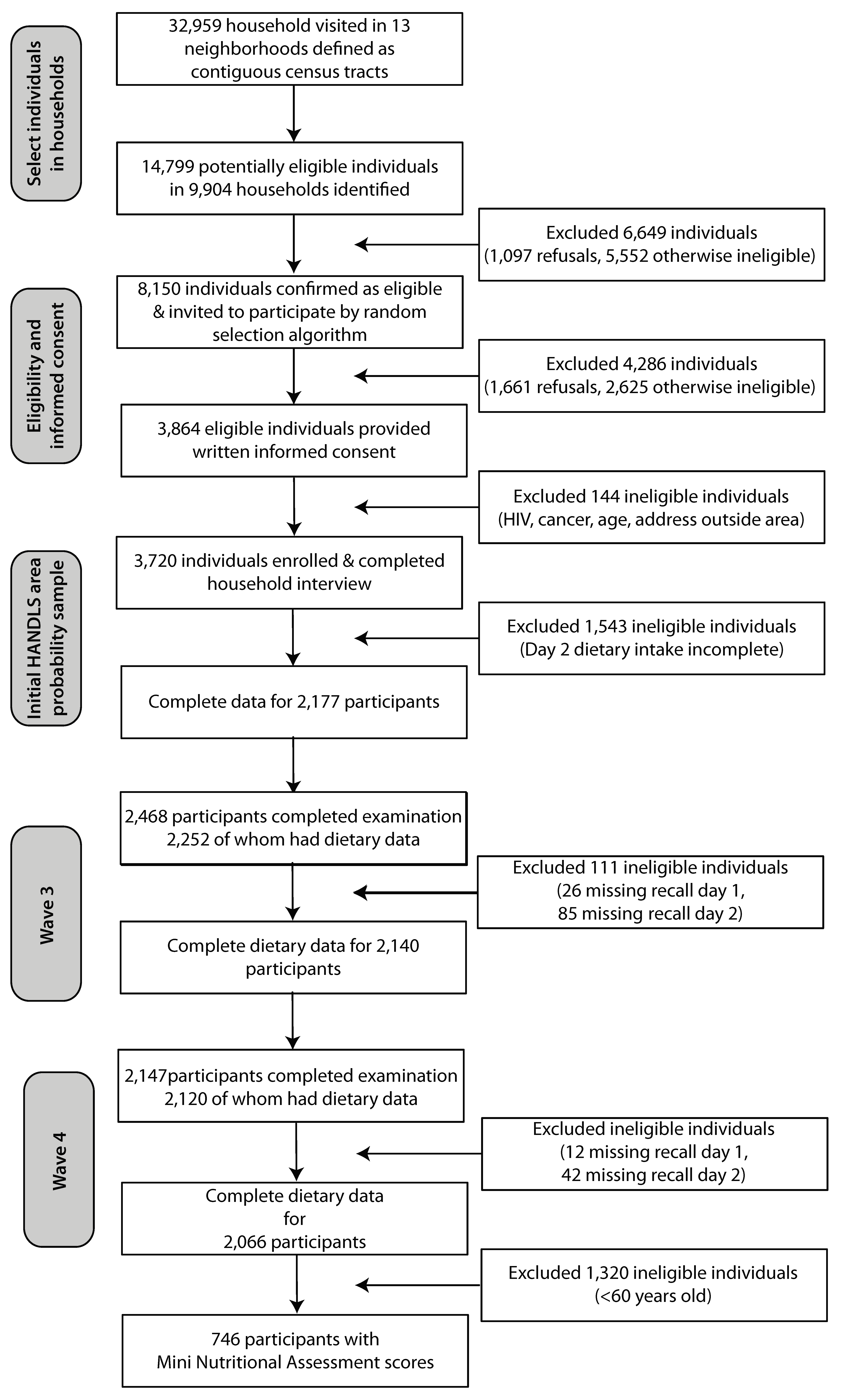
2.1. Background on Healthy Aging in Neighborhoods of Diversity across the Life Span (HANDLS) Study
2.2. Dietary Methods and Quality
2.3. Malnutrition Evaluation
2.4. Demographic and Health-Related Measures
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Population Characteristics
3.2. Comparison of Longitudinal Diet Quality of Younger and Older Cohorts
3.3. Characteristics of Persons aged ≥60 years at Wave 4 At-Risk for Malnutrition
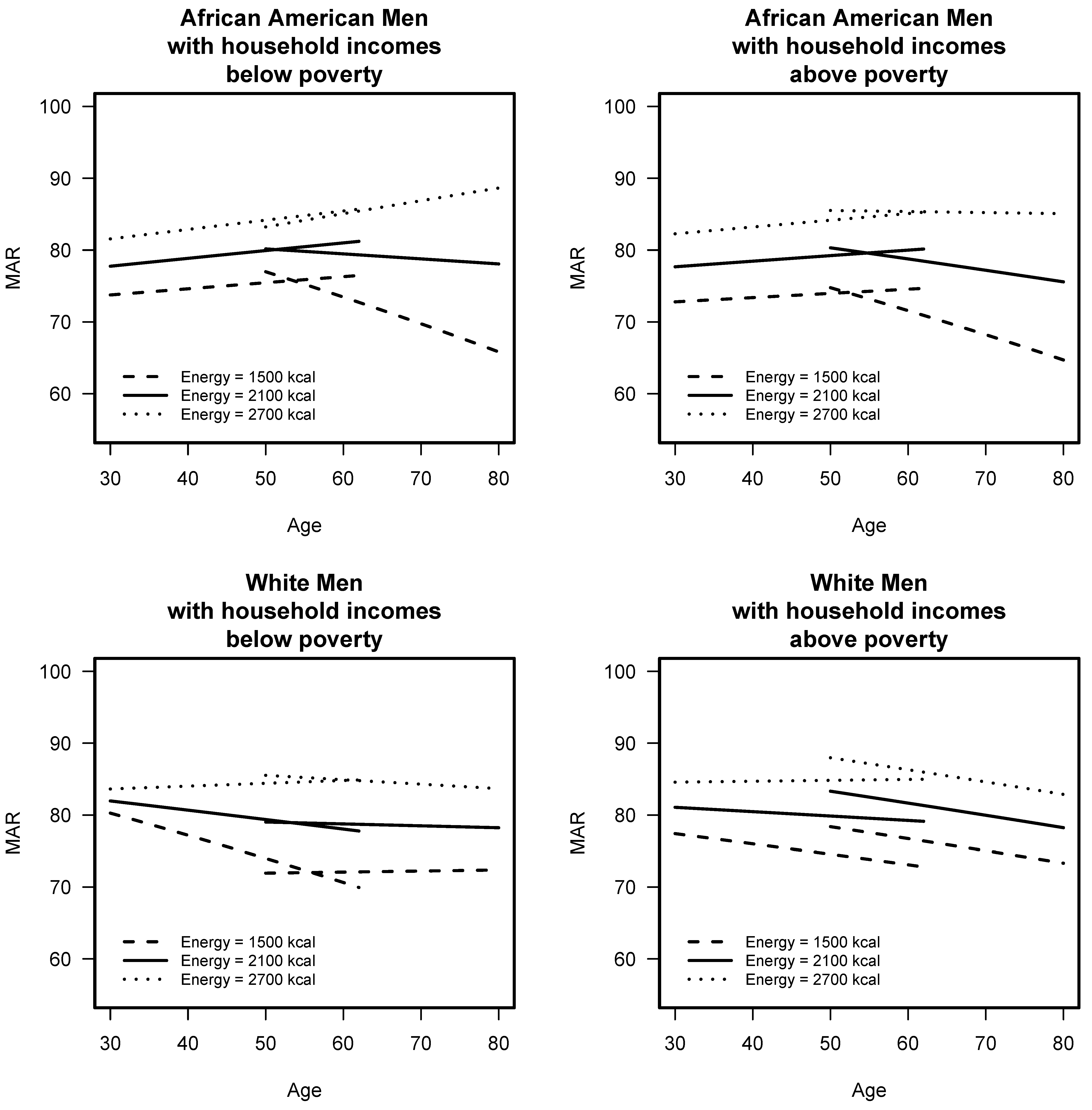
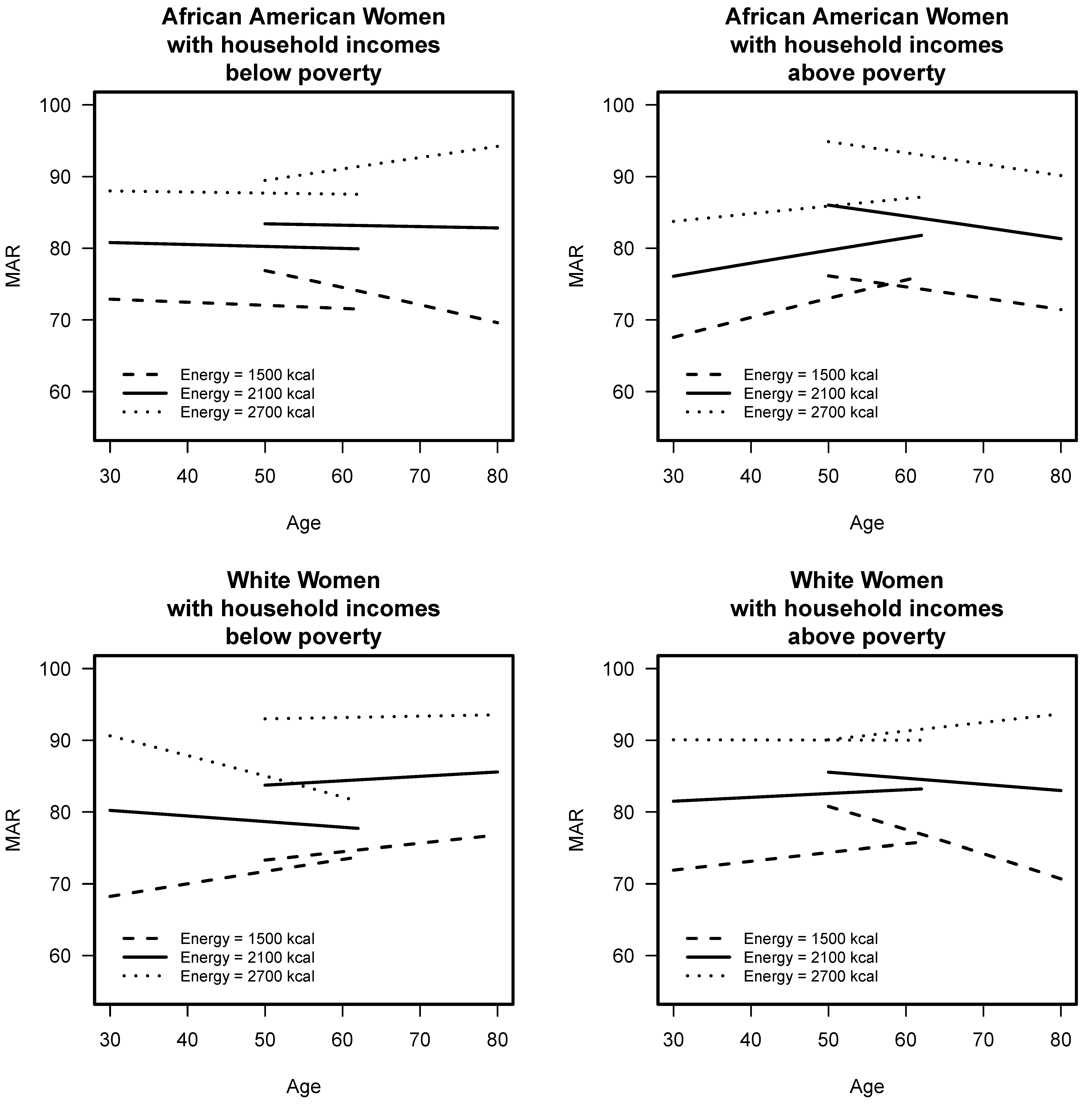
3.4. Association of Diet Quality with Malnutrition
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. Healthy Diet. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact- sheets/detail/healthy-diet (accessed on 7 August 2019).
- Scientific Report of the 2015 Dietary Guidelines Advisory Committee. Available online: https://health.gov/dietaryguidelines/2015-scientific-report/ (accessed on 25 March 2019).
- Alkerwi, A. Diet quality concept. Nutrition 2014, 30, 613–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dietary Reference Intakes Tables and Applications. Available online: http://nationalacademies.org/hmd/Activities/Nutrition/SummaryDRIs/DRI-Tables.aspx (accessed on 24 August 2019).
- International Dietary Data Expansion Project. Data4Diets. Available online: https://inddex.nutrition.tufts.edu/data4diets/indicator/mean-adequacy-ratio-mar (accessed on 7 August 2019).
- Wilson, M.M.; Reedy, J.; Krebs-Smith, S.M. American diet quality: Where it is, where it is heading, and what it could be. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2016, 116, 302–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.D.; Leung, C.W.; Li, Y.; Ding, E.L.; Chiuve, S.E.; Hu, F.B.; Willett, W.C. Trends in dietary quality among adults in the United States, 1999 through 2010. JAMA Intern. Med. 2014, 174, 1587–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baum, J.; Kim, I.-Y.; Wolfe, R. Protein consumption and the elderly: What is the optimal level of intake? Nutrients 2016, 8, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deutz, N.E.P.; Bauer, J.M.; Barazzoni, R.; Biolo, G.; Boirie, Y.; Bosy-Westphal, A.; Cederholm, T.; Cruz-Jentoft, A.; Krznariç, Z.; Nair, K.S.; et al. Protein intake and exercise for optimal muscle function with aging: Recommendations from the ESPEN expert group. Clin. Nutr. 2014, 33, 929–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauer, J.; Biolo, G.; Cederholm, T.; Cesari, M.; Cruz-Jentoft, A.J.; Morley, J.E.; Phillips, S.; Sieber, C.; Stehle, P.; Teta, D.; et al. Evidence-based recommendations for optimal dietary protein intake in older people: A position paper from the PROT-AGE study group. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2013, 14, 542–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, S.M.; Reginster, J.Y.; Rizzoli, R.; Shaw, S.C.; Kanis, J.A.; Bautmans, I.; Bischoff-Ferrari, H.; Bruyère, O.; Cesari, M.; Dawson-Hughes, B.; et al. Does nutrition play a role in the prevention and management of sarcopenia? Clin. Nutr. 2018, 37, 1121–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamberg-Allardt, C.; Brustad, M.; Meyer, H.E.; Steingrimsdottir, L. Vitamin D—A systematic literature review for the 5th edition of the nordic nutrition recommendations. Food Nutr. Res. 2013, 57, 22671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Healthy Eating Index. Available online: https://www.cnpp.usda.gov/healthyeatingindex (accessed on 25 March 2019).
- Hiza, H.A.B.; Casavale, K.O.; Guenther, P.M.; Davis, C.A. Diet quality of americans differs by age, sex, race/ethnicity, income, and education level. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2013, 113, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaccaro, J.A.; Huffman, F.G. Dietary risk factors by race/ethnicity, age-group, and gender in a representative sample of US older adults. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2017, 21, 704–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Demographics of an Aging Population. Available online: https://www.healthdesign.org/insights-solutions/demographics-aging-population (accessed on 25 March 2019).
- Ham, R.R. The Signs and symptoms of poor nutritional status. Primary Care 1994, 21, 33–54. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Soenen, S.; Chapman, I.M. Body weight, anorexia, and undernutrition in older people. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2013, 14, 642–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landi, F.; Calvani, R.; Tosato, M.; Martone, A.; Ortolani, E.; Savera, G.; Sisto, A.; Marzetti, E. Anorexia of aging: Risk factors, consequences, and potential treatments. Nutrients 2016, 8, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuel, L.J.; Szanton, S.L.; Weiss, C.O.; Thorpe, R.J.; Semba, R.D.; Fried, L.P. Financial strain is associated with malnutrition risk in community-dwelling older women. Epidemiol. Res. Int. 2012, 2012, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilcox, S.; Sharpe, P.A.; Liese, A.D.; Dunn, C.G.; Hutto, B. Socioeconomic factors associated with diet quality and meeting dietary guidelines in disadvantaged neighborhoods in the southeast United States. Ethn. Health 2018, 2, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laur, C.; Keller, H. Making the case for nutrition screening in older adults in primary care. Nutr. Today 2017, 52, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuervo, M.; Garca, A.; Ansorena, D.; Snchez-Villegas, A.; Martnez-Gonzlez, M.A.; Astiasarn, I.; Martnez, J.A. Nutritional assessment interpretation on 22 007 Spanish community-dwelling elders through the mini nutritional assessment test. Public Health Nutr. 2009, 12, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mowé, M.; Bøhmer, T.; Kindt, E. Reduced nutritional status in an elderly population (> 70 y) is probable before disease and possibly contributes to the development of disease. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1994, 59, 317–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cederholm, T.; Barazzoni, R.; Austin, P.; Ballmer, P.; Biolo, G.; Bischoff, S.C.; Compher, C.; Correia, I.; Higashiguchi, T.; Holst, M.; et al. ESPEN guidelines on definitions and terminology of clinical nutrition. Clin Nutr. 2017, 36, 49–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.C.-H.; Schilling, L.S.; Lyder, C.H. A concept analysis of malnutrition in the elderly. J. Adv. Nurs. 2001, 36, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fávaro-Moreira, N.C.; Krausch-Hofmann, S.; Matthys, C.; Vereecken, C.; Vanhauwaert, E.; Declercq, A.; Bekkering, G.E.; Duyck, J. Risk factors for malnutrition in older adults: A systematic review of the literature based on longitudinal data. Adv. Nutr. 2016, 7, 507–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verlaan, S.; Ligthart-Melis, G.C.; Wijers, S.L.J.; Cederholm, T.; Maier, A.B.; de van der Schueren, M.A.E. High prevalence of physical frailty among community-dwelling malnourished older adults–A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2017, 18, 374–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clegg, M.E.; Williams, E.A. Optimizing nutrition in older people. Maturitas 2018, 112, 34–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donini, L.M.; Scardella, P.; Piombo, L.; Neri, B.; Asprino, R.; Proietti, A.R.; Carcaterra, S.; Cava, E.; Cataldi, S.; Cucinotta, D.; et al. Malnutrition in elderly: Social and economic determinants. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2013, 17, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shlisky, J.; Bloom, D.E.; Beaudreault, A.R.; Tucker, K.L.; Keller, H.H.; Freund-Levi, Y.; Fielding, R.A.; Cheng, F.W.; Jensen, G.L.; Wu, D.; et al. Nutritional considerations for healthy aging and reduction in age-related chronic disease. Adv. Nutr. An Int. Rev. J. 2017, 8, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bloom, I.; Lawrence, W.; Barker, M.; Baird, J.; Dennison, E.; Sayer, A.A.; Cooper, C.; Robinson, S. What influences diet quality in older people? A qualitative study among community-dwelling older adults from the Hertfordshire cohort study, UK. Public Health Nutr. 2017, 20, 2685–2693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bloom, I.; Shand, C.; Cooper, C.; Robinson, S.; Baird, J. Diet quality and sarcopenia in older adults: A systematic review. Nutrients 2018, 10, 308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hengeveld, L.M.; Wijnhoven, H.A.H.; Olthof, M.R.; Brouwer, I.A.; Harris, T.B.; Kritchevsky, S.B.; Newman, A.B.; Visser, M. Prospective associations of poor diet quality with long-term incidence of protein-energy malnutrition in community-dwelling older adults: The health, aging, and body composition (Health ABC) study. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 107, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaiser, M.J.; Bauer, J.M.; Ramsch, C.; Uter, W.; Guigoz, Y.; Cederholm, T.; Thomas, D.R.; Anthony, P.; Charlton, K.E.; Maggio, M.; et al. Validation of the mini nutritional assessment short-form (MNA-SF): A practical tool for identification of nutritional status. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2009, 13, 782–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donini, L.M.; Marrocco, W.; Marocco, C.; Lenzi, A. Validity of the self-mini nutritional assessment (Self-MNA) for the evaluation of nutritional risk. A cross-sectional study conducted in general practice. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2018, 22, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, M.K.; Lepkowski, J.M.; Powe, N.R.; LaVeist, T.; Kuczmarski, M.F.; Zonderman, A.B. Healthy aging in neighborhoods of diversity across the life span (HANDLS): Overcoming barriers to implementing a longitudinal, epidemiologic, urban study of health, race, and socioeconomic status. Ethn. Dis. 2010, 20, 267–275. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Healthy Aging in Neighborhoods of Diversity across the Life Span. Available online: https://handls.nih.gov/06Coll-dataDoc.htm (accessed on 25 March 2019).
- Moshfegh, A.J.; Rhodes, D.G.; Baer, D.J.; Murayi, T.; Clemens, J.C.; Rumpler, W.V.; Paul, D.R.; Sebastian, R.S.; Kuczynski, K.J.; Ingwersen, L.A.; et al. The US department of agriculture automated multiple-pass method reduces bias in the collection of energy intakes. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2008, 88, 324–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raper, N.; Perloff, B.; Ingwersen, L.; Steinfeldt, L.; Anand, J. An overview of USDA’s dietary intake data system. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2004, 17, 545–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Food Surveys Research Group: Beltsville, MD. United States Department of Agriculture. Available online: https://www.ars.usda.gov/northeast-area/beltsville-md-bhnrc/beltsville-human-nutrition-research-center/food-surveys-research-group (accessed on 25 March 2019).
- Murphy, S.P.; Foote, J.A.; Wilkens, L.R.; Basiotis, P.P.; Carlson, A.; White, K.K.L.; Yonemori, K.M. Simple measures of dietary variety are associated with improved dietary quality. J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 2006, 106, 425–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fanelli Kuczmarski, M.; Mason, M.A.; Beydoun, M.A.; Allegro, D.; Zonderman, A.B.; Evans, M.K. Dietary patterns and sarcopenia in an urban African American and white population in the United States. J. Nutr. Gerontol. Geriatr. 2013, 32, 291–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Institute of Medicine. Dietary Reference Intakes for Vitamin C, Vitamin E, Selenium, and Carotenoids; National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, Chapter 5; 2000; p. 95. ISBN 978-0-309-06935-9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vellas, B.; Villars, H.; Abellan, G.; Soto, M.E.; Rolland, Y.; Guigoz, Y.; Morley, J.E.; Chumlea, W.; Salva, A.; Rubenstein, L.Z.; et al. Overview of the MNA—Its history and challenges. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2006, 10, 456–463. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Guigoz, Y. The Mini Nutritional Assessment (MNA) Review of the literature—What does it tell us? J. Nutr. Health Aging 2006, 10, 466–485; discussion 485–487. [Google Scholar]
- Cereda, E. Mini Nutritional Assessment. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2012, 15, 29–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mini Nutritional Assessment. Available online: https://www.mnaelderly.com/forms/mini/mna_mini_english.pdf (accessed on 25 March 2019).
- The 2004 HHS Poverty Guidelines. Available online: https://aspe.hhs.gov/2004-hhs-poverty-guidelines (accessed on 25 March 2019).
- National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases: Diabetes Tests & Diagnosis. Available online: https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/diabetes/overview/tests-diagnosis (accessed on 8 April 2019).
- The Seventh Report of the Joint National Committee on Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Pressure. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK9630/ (accessed on 25 March 2019).
- Whelton, P.K.; Carey, R.M.; Aronow, W.S.; Casey, D.E.; Collins, K.J.; Dennison Himmelfarb, C.; DePalma, S.M.; Gidding, S.; Jamerson, K.A.; Jones, D.W.; et al. 2017 ACC/AHA/AAPA/ABC/ACPM/AGS/APhA/ASH/ASPC/NMA/PCNA Guideline for the prevention, detection, evaluation, and management of high blood pressure in adults. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2018, 71, e127–e248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batis, C.; Sotres-Alvarez, D.; Gordon-Larsen, P.; Mendez, M.A.; Adair, L.; Popkin, B. Longitudinal analysis of dietary patterns in Chinese adults from 1991 to 2009. Br. J. Nutr. 2014, 111, 1441–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, J.; Shikany, J.; Barrett-Connor, E.; Marshall, L.; Bunker, C.; Chan, J.; Stone, K.; Orwoll, E. Demographic factors associated with the diet quality of older US men: Baseline data from the osteoporotic fractures in men (MrOS) study. Public Health Nutr. 2007, 10, 810–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrington, J.; Fitzgerald, A.P.; Layte, R.; Lutomski, J.; Molcho, M.; Perry, I.J. Sociodemographic, health and lifestyle predictors of poor diets. Public Health Nutr. 2011, 14, 2166–2175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crichton, M.; Craven, D.; Mackay, H.; Marx, W.; de van der Schueren, M.; Marshall, S. A systematic review, meta-analysis and meta-regression of the prevalence of protein-energy malnutrition: Associations with geographical region and sex. Age Ageing 2018, 48, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fanelli Kuczmarski, M.; Bodt, B.; Stave Shupe, E.; Zonderman, A.; Evans, M. Dietary patterns associated with lower 10-year atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease risk among urban African-American and white adults consuming western diets. Nutrients 2018, 10, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castro-Quezada, I.; Román-Viñas, B.; Serra-Majem, L. The Mediterranean diet and nutritional adequacy: A review. Nutrients 2014, 6, 231–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Troesch, B.; Hoeft, B.; McBurney, M.; Eggersdorfer, M.; Weber, P. Dietary surveys indicate vitamin intakes below recommendations are common in representative western countries. Br. J. Nutr. 2012, 108, 692–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaccaro, J.A.; Huffman, F.G. Race/Ethnicity-, gender- and age-specific differences in micronutrient intakes of US adults with and without diabetes. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2013, 64, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krzymińska-Siemaszko, R.; Mossakowska, M.; Skalska, A.; Klich-Rączka, A.; Tobis, S.; Szybalska, A.; Cylkowska-Nowak, M.; Olszanecka-Glinianowicz, M.; Chudek, J.; Wieczorowska-Tobis, K. Social and economic correlates of malnutrition in Polish elderly population: The results of PolSenior study. J. Nutr. Heal. Aging 2015, 19, 397–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirczak, A. Risk factors of malnutrition among the elderly living in rural areas. Environ. Med. 2014, 17, 68–75. [Google Scholar]
- Romero-Ortuno, R.; Casey, A.-M.; Cunningham, C.U.; Squires, S.; Prendergast, D.; Kenny, R.A.; Lawlor, B.A. Psychosocial and functional correlates of nutrition among community-dwelling older adults in Ireland. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2011, 15, 527–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miri, R.; Saadati, H.; Ardi, P.; Firuzi, O. Alterations in oxidative stress biomarkers associated with mild hyperlipidemia and smoking. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2012, 50, 920–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degens, H.; Gayan-Ramirez, G.; van Hees, H.W.H. Smoking-induced skeletal muscle dysfunction. From evidence to mechanisms. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2015, 191, 620–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smit, E.; Winters-Stone, K.M.; Loprinzi, P.D.; Tang, A.M.; Crespo, C.J. Lower nutritional status and higher food insufficiency in frail older US adults. Br. J. Nutr. 2013, 110, 172–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzo-López, L.; Maseda, A.; de Labra, C.; Regueiro-Folgueira, L.; Rodríguez-Villamil, J.L.; Millán-Calenti, J.C. Nutritional determinants of frailty in older adults: A systematic review. BMC Geriatr. 2017, 17, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halfon, M.; Phan, O.; Teta, D. Vitamin D: A review on its effects on muscle strength, the risk of fall, and frailty. Biomed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominguez, L.J.; Barbagallo, M.; Lauretani, F.; Bandinelli, S.; Bos, A.; Corsi, A.M.; Simonsick, E.M.; Ferrucci, L. Magnesium and muscle performance in older persons: The InCHIANTI study1–3. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2006, 84, 419–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonnefoy, M.; Berrut, G.; Lesourd, B.; Ferry, M.; Gilbert, T.; Guerin, O.; Hanon, O.; Jeandel, C.; Paillaud, E.; Raynaud-Simon, A.; et al. Frailty and nutrition: Searching for evidence. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2015, 19, 250–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, H.; Aihie Sayer, A.; Jameson, K.; Syddall, H.; Dennison, E.M.; Cooper, C.; Robinson, S. Does diet influence physical performance in community-dwelling older people? Findings from the Hertfordshire Cohort study. Age Ageing 2011, 40, 181–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.; Park, Y. Association between the dietary inflammatory index and risk of frailty in older individuals with poor nutritional status. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carriere, I.; Dupuy, A.-M.; Lacroux, A.; Cristol, J.-P.; Delcourt, C. Biomarkers of inflammation and malnutrition associated with early death in healthy elderly people. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2008, 56, 840–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibutani, M.; Maeda, K.; Nagahara, H.; Ohtani, H.; Iseki, Y.; Ikeya, T.; Sugano, K.; Hirakawa, K. The pretreatment albumin to globulin ratio predicts chemotherapeutic outcomes in patients with unresectable metastatic colorectal cancer. BMC Cancer 2015, 15, 347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Statovci, D.; Aguilera, M.; MacSharry, J.; Melgar, S. The impact of western diet and nutrients on the microbiota and immune response at mucosal interfaces. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naska, A.; Lagiou, A.; Lagiou, P. Dietary assessment methods in epidemiological research: Current state of the art and future prospects. F1000Research 2017, 6, 926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pooler, J.A.; Morgan, R.E.; Wong, K.; Wilkin, M.K.; Blitstein, J.L. Cooking matters for adults improves food resource management skills and self-confidence among low-income participants. J. Nutr. Educ. Behav. 2017, 49, 545–553.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Characteristics | Baseline Age <50 Years Younger Cohort | Baseline Age ≥50 Years Older Cohort | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | Wave 3 | Wave 4 | Baseline | Wave 3 | Wave 4 | |
| Demographics | n = 1194 | n = 1190 | n = 1198 | n = 983 | n = 950 | n = 870 |
| Age, X ± SE | 41.34 ± 0.16 a | 46.60 ± 0.16 b | 50.38 ± 0.17 c | 57.00 ± 0.14 a | 61.41 ± 0.14 b | 65.24 ± 0.15 c |
| African American, % | 59.1 a | 63.4 a | 63.1 a | 56.4 a | 59.1 a | 57.8 a |
| Men, % | 43.1 a | 40.9 a | 41.7 a | 43.8 a | 41.5 a | 40.2 a |
| Poverty, <125%, % | 45.3 a | 43.4 a | 45.3 a | 40.0 a | 35.3 ab | 34.5 b |
| Education, <12th grade, % | 33.7 a | 39.6 a | 39.3 a | 35.0 a | 35.3 a | 34.0 a |
| Smoker, % | 53.3 a | 48.0 b | 54.7 c | 42.2 a | 33.7 b | 34.8 b |
| Health Conditions | ||||||
| Diabetes, % | 11.4 a | 12.9 a | 19.8 b | 23.4 a | 25.9 ab | 30.7 b |
| Hypertension, % | 31.5 a | 42.2 b | 55.5 c | 63.9 a | 68.3 b | 77.5 c |
| BMI, kg/m2, X ± SE | 29.38 ± 0.23 a (n = 1192) | 30.69 ± 0.24 b (n = 1188) | 31.06 ± 0.24 b (n = 1190) | 30.34 ± 0.24 a (n = 982) | 30.74 ± 0.25 a (n = 948) | 30.77 ± 0.26 a (n = 860) |
| Diet-related Measures | ||||||
| MAR, X ± SE | 78.30 ± 0.54 a | 77.49 ± 0.40 a | 77.90 ± 0.41 a | 77.68 ± 0.60 a | 76.93 ± 0.45 a | 74.24 ± 0.51 b |
| Energy, kcal, X ± SE | 2121 ± 30 a | 2151 ± 26 a | 2088 ± 25 a | 1867 ± 28 a | 1867 ± 25 a | 1796 ± 24 a |
| Protein, <0.8 g/kg, % | 44.0 a (n = 1192) | 43.4 a (n = 1188) | 48.0 a (n = 1190) | 49.3 a (n = 982) | 51.2 ab (n = 948) | 55.5 b (n = 860) |
| Characteristics | Normal Nutrition Status (n = 435) | At-Risk for Malnutrition (n = 311) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Demographics | |||
| Age, years, X ± SE | 66.34 ± 0.19 | 65.81 ± 0.22 | 0.064 |
| Men, % | 38.9 | 41.3 | 0.492 |
| African American, % | 58.6 | 64.4 | 0.109 |
| Poverty <125%, % | 28.3 | 42.6 | <0.001 |
| Education, % <12th grade | 27.4 | 39.0 | 0.001 |
| Smoker, % | 28.9 | 45.2 | <0.001 |
| Health Conditions | |||
| BMI, kg/m2, X ± SE | 31.42 ± 0.31 | 30.15 ± 0.50 | 0.025 |
| CVD event since Baseline, % | 8.7 | 15.6 | 0.030 |
| Diabetes, % | 21.9 | 24.6 | 0.622 |
| Hypertension, % | 59.9 | 69.5 | 0.007 |
| Symptoms of depression, CES-D, % | 26.4 | 41.2 | <0.001 |
| Diagnosed depression, % | 26.0 | 44.2 | <0.001 |
| Diagnosed bipolar disorder, % | 2.8 | 6.5 | 0.015 |
| Diagnosed suicidal thoughts, % | 4.8 | 11.0 | 0.002 |
| Diagnosed anxiety disorder, % | 13.8 | 27.7 | <0.001 |
| Diet-related Measures | |||
| Food insecure, % | 15.0 | 24.6 | 0.002 |
| Not feel like eating, poor appetite most of the time, % | 3.3 | 8.1 | <0.001 |
| Energy, kcal, X ± SE | 1833 ± 32 | 1713 ± 40 | 0.017 |
| MAR Wave 4, X ± SE | 75.43 ± 0.70 | 72.69 ± 0.87 | 0.184 |
| NAR Vitamin C, X ± SE | 0.605 ± 0.017 | 0.553 ± 0.020 | 0.049 |
| NAR Thiamin, X ± SE | 0.887 ± 0.009 | 0.839 ± 0.012 | 0.001 |
| NAR Riboflavin, X ± SE | 0.938 ± 0.007 | 0.907 ± 0.009 | 0.005 |
| NAR Niacin, X ± SE | 0.946 ± 0.006 | 0.919 ± 0.009 | 0.011 |
| NAR Folate, X ± SE | 0.814 ± 0.011 | 0.775 ± 0.013 | 0.022 |
| NAR Copper, X ± SE | 0.881 ± 0.009 | 0.844 ± 0.011 | 0.007 |
| NAR Magnesium, X ± SE | 0.659 ± 0.010 | 0.607 ± 0.013 | 0.001 |
| NAR Selenium, X ± SE | 0.977 ± 0.004 | 0.960 ± 0.006 | 0.017 |
| NAR Zinc, X ± SE | 0.819 ± 0.010 | 0.775 ± 0.013 | 0.005 |
| Protein, gm/kg, X ± SE | 0.82 ± 0.02 | 0.83 ± 0.03 | 0.884 |
| Protein, % energy | 15.8 ± 0.2 | 15.5 ± 0.3 | 0.330 |
| Carbohydrate, % energy | 47.2 ± 0.5 | 48.7 ± 0.5 | 0.037 |
| Sugar, % energy | 21.8 ± 0.4 | 23.3 ± 0.5 | 0.022 |
| Total fat, % energy | 36.6 ± 0.4 | 35.7 ± 0.4 | 0.087 |
| Clinical and Physical Measures | |||
| Self-rated Health as poor/fair, % | 18.4 | 31.3 | <0.001 |
| Accomplished less due to health, most of the time, % | 8.2 | 16.9 | <0.001 |
| Health limits climbing stairs, a lot, % | 12.8 | 25.6 | <0.001 |
| Health limits moderate activities, a lot, % | 11.1 | 21.8 | <0.001 |
| Difficulty walking 1/4 mile; % | 23.6 | 35.9 | <0.001 |
| Difficulty walking up 10 stairs; % | 19.2 | 29.2 | 0.004 |
| Difficulty standing up from chair; % | 22.2 | 33.6 | 0.003 |
| Difficulty carrying 20 lbs, % | 13.4 | 20.3 | 0.068 |
| Difficulty using fingers, % | 17.8 | 26.6 | 0.004 |
| Biochemical Measures | |||
| Hs-CRP (mg/L), X ± SE | 4.84 ± 0.42 | 6.07 ± 0.67 | 0.102 |
| Albumin/Globulin ratio (g/dL); X ± SE | 1.42 ± 0.01 | 1.35 ± 0.02 | 0.002 |
| Albumin (g/dL), X ± SE | 4.25 ± 0.02 | 4.18 ± 0.02 | 0.005 |
| Potassium (mmol/L), X ± SE | 4.24 ± 0.02 | 4.13 ± 0.03 | 0.003 |
| Serum 25 OH Vitamin D (ng/mL), X ± SE | 31.17 ± 0.75 | 28.12 ± 0.89 | 0.009 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fanelli Kuczmarski, M.; Stave Shupe, E.; Pohlig, R.T.; Rawal, R.; Zonderman, A.B.; Evans, M.K. A Longitudinal Assessment of Diet Quality and Risks Associated with Malnutrition in Socioeconomic and Racially Diverse Adults. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2046. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11092046
Fanelli Kuczmarski M, Stave Shupe E, Pohlig RT, Rawal R, Zonderman AB, Evans MK. A Longitudinal Assessment of Diet Quality and Risks Associated with Malnutrition in Socioeconomic and Racially Diverse Adults. Nutrients. 2019; 11(9):2046. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11092046
Chicago/Turabian StyleFanelli Kuczmarski, Marie, Emily Stave Shupe, Ryan T. Pohlig, Rita Rawal, Alan B. Zonderman, and Michele K. Evans. 2019. "A Longitudinal Assessment of Diet Quality and Risks Associated with Malnutrition in Socioeconomic and Racially Diverse Adults" Nutrients 11, no. 9: 2046. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11092046
APA StyleFanelli Kuczmarski, M., Stave Shupe, E., Pohlig, R. T., Rawal, R., Zonderman, A. B., & Evans, M. K. (2019). A Longitudinal Assessment of Diet Quality and Risks Associated with Malnutrition in Socioeconomic and Racially Diverse Adults. Nutrients, 11(9), 2046. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11092046





