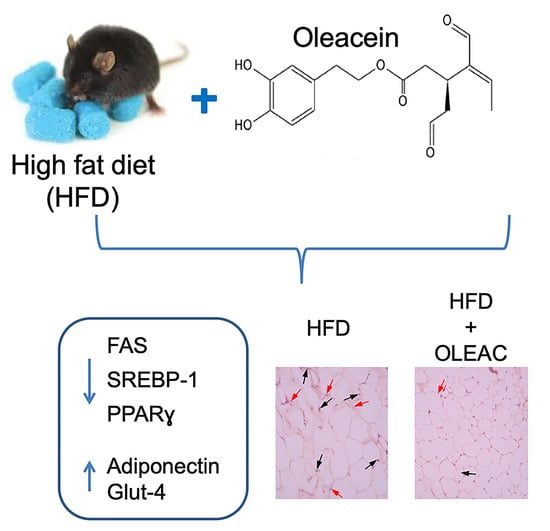
Oleacein Prevents High Fat Diet-Induced Adiposity and Ameliorates Some Biochemical Parameters of Insulin Sensitivity in Mice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animal Care and Experimental Protocol
2.2. Histological Analysis
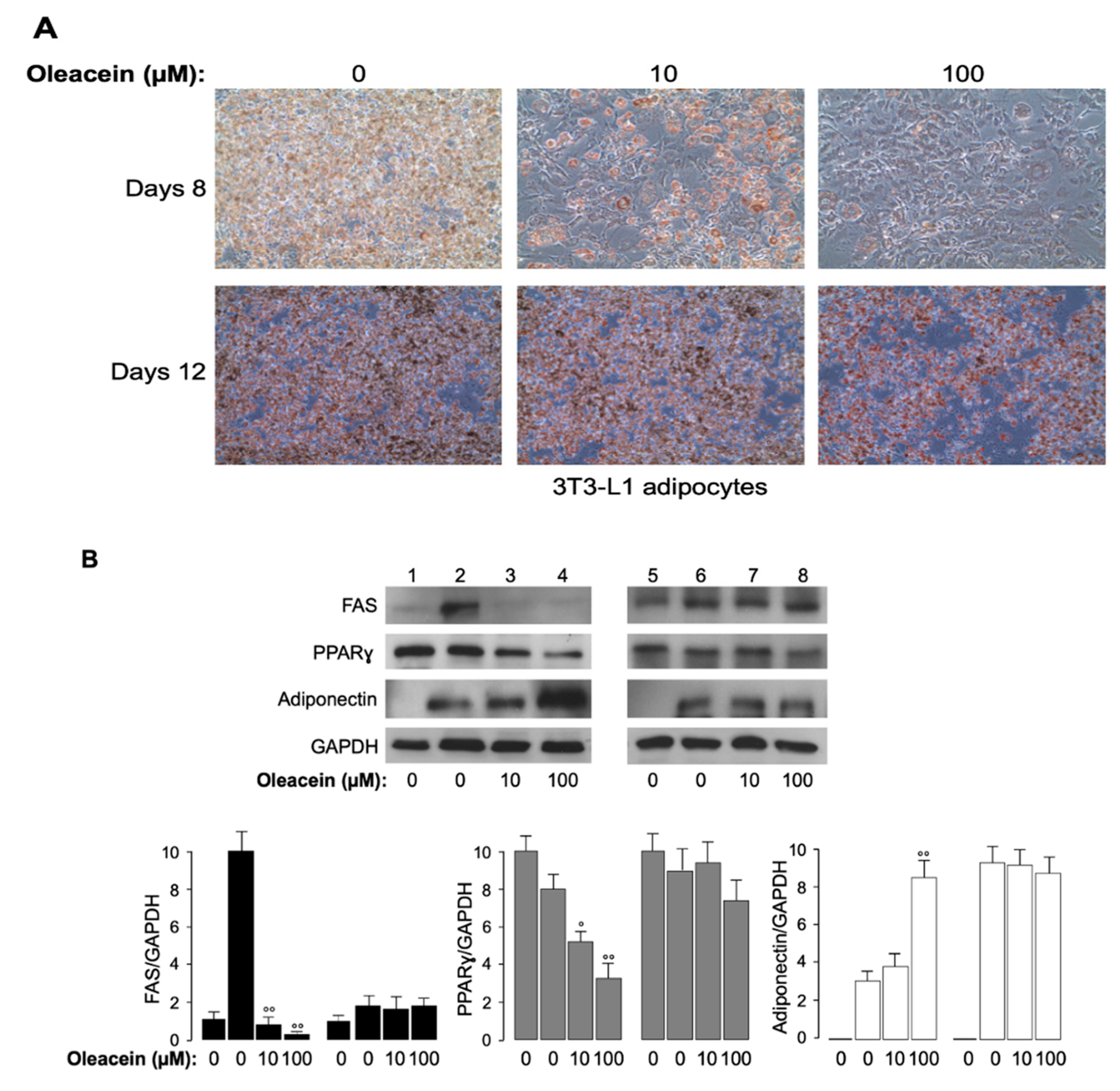
2.3. Cell Culture, Differentiation and Oil Red O Staining
2.4. Protein Extraction, Western Blot Analysis and RT-PCR
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
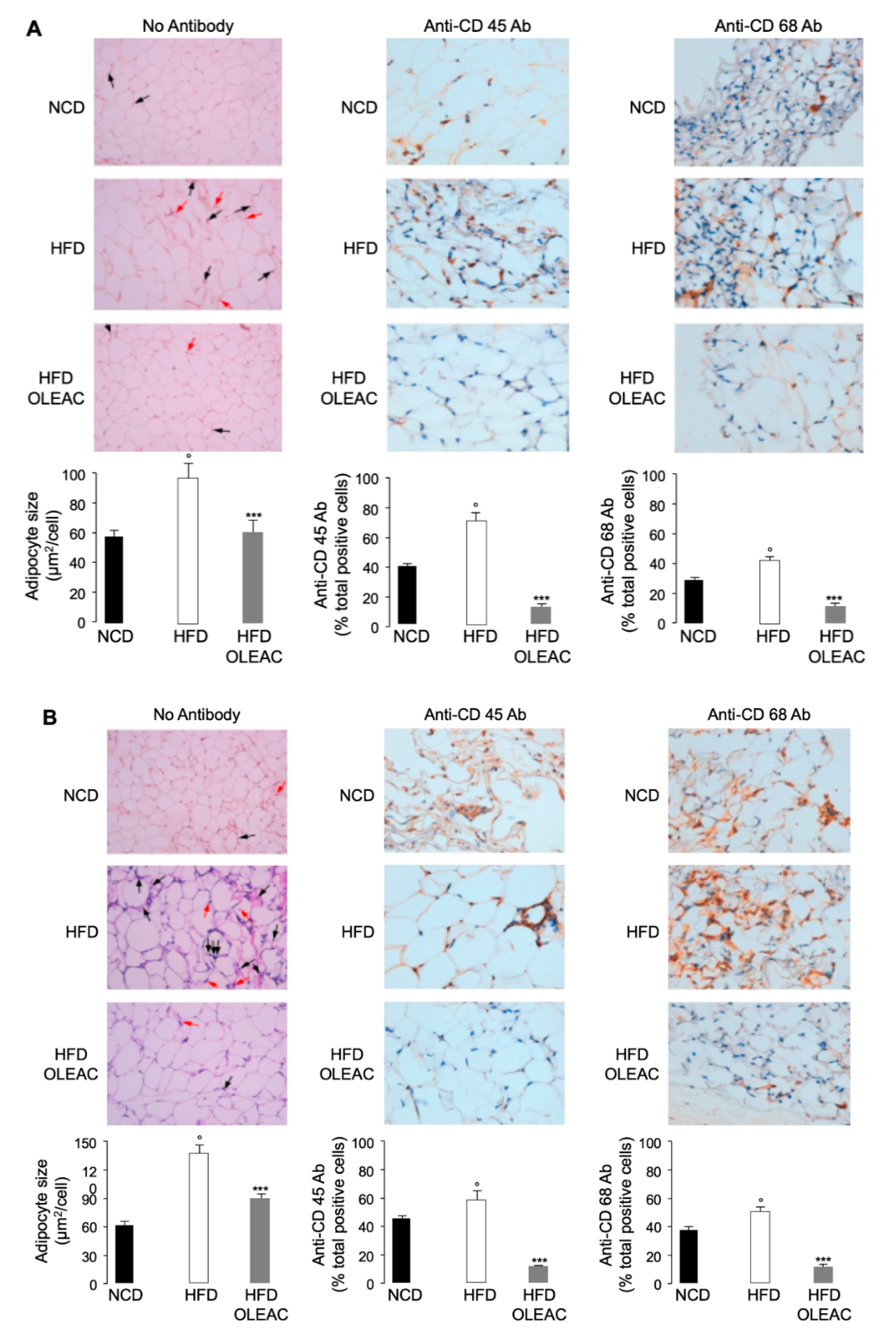
3.1. Effects of Oleacein on Adipose Tissue In Vivo
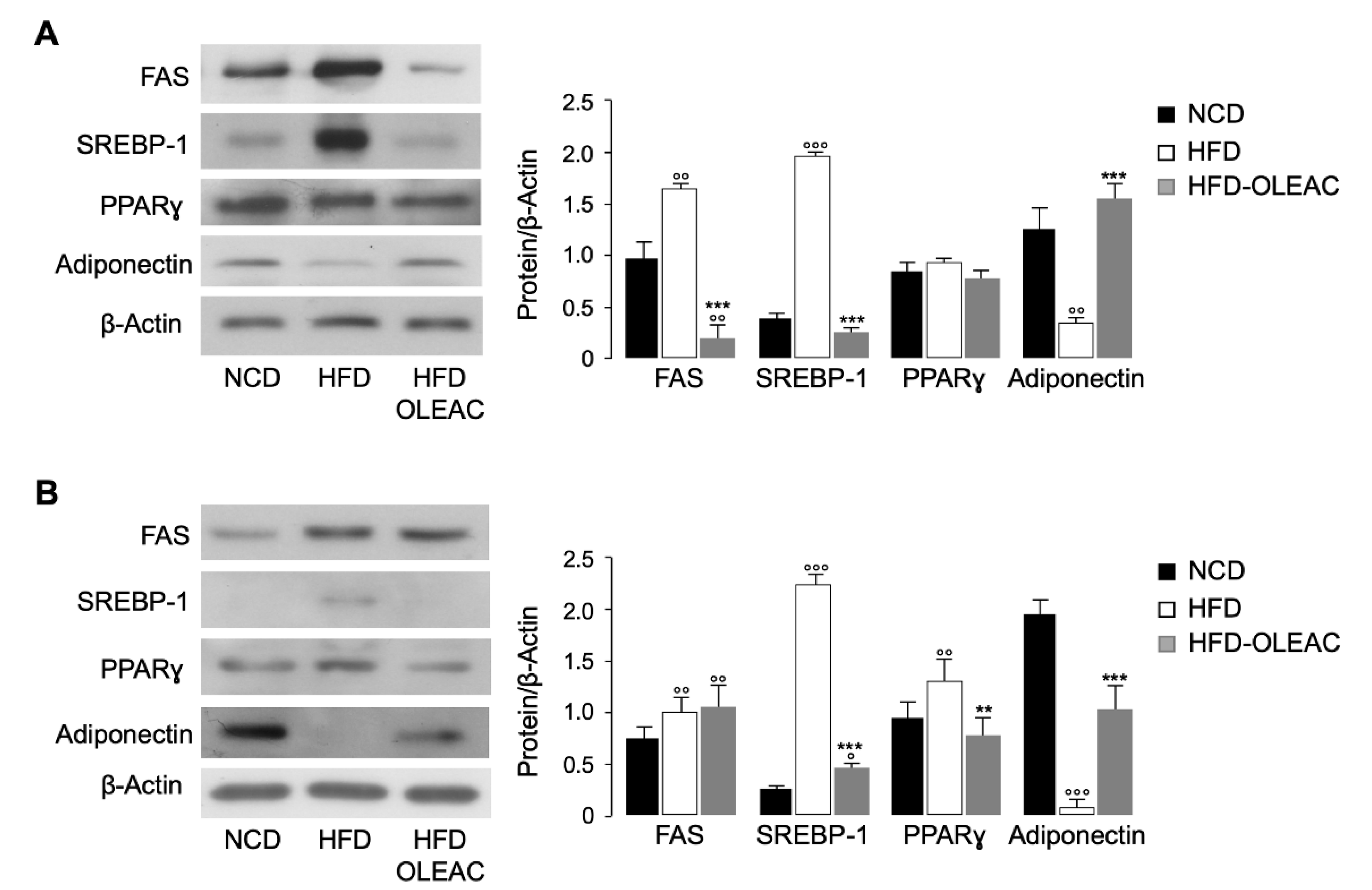
3.2. Oleacein Regulates Markers of Adipogenesis In Vivo
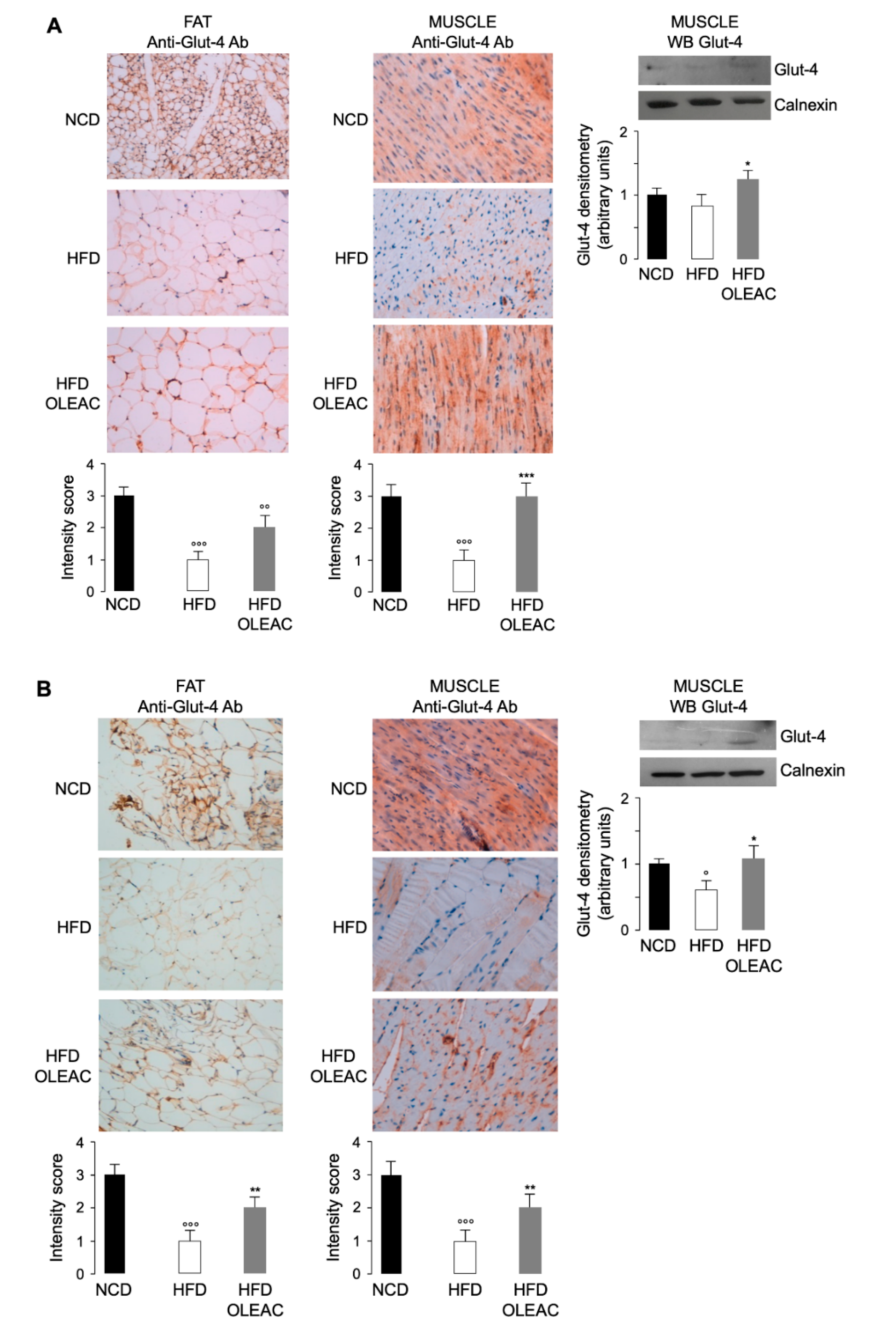
3.3. Effects of Oleacein on Glut-4 Expression In Vivo
3.4. Effects of Oleacein in 3T3-L1 Cells
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gluvic, Z.; Zaric, B.; Resanovic, I.; Obradovic, M.; Mitrovic, A.; Radak, D.; Isenovic, E.R. Link between Metabolic Syndrome and Insulin Resistance. Curr. Vasc. Pharmacol. 2017, 15, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foti, D.; Chiefari, E.; Fedele, M.; Iuliano, R.; Brunetti, L.; Paonessa, F.; Manfioletti, G.; Barbetti, F.; Brunetti, A.; Croce, C.M.; et al. Lack of the architectural factor HMGA1 causes insulin resistance and diabetes in humans and mice. Nat. Med. 2005, 11, 765–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunetti, A.; Brunetti, L.; Foti, D.; Accili, D.; Goldfine, I.D. Human diabetes associated with defects in nuclear regulatory proteins for the insulin receptor gene. J. Clin. Investig. 1996, 97, 258–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahyoun, N.R.; Sankavaram, K. Historical origins of the Mediterranean Diet, Regional Dietary Profiles, and the Development of the Dietary Guidelines. In Mediterranean Diet; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 43–56. [Google Scholar]
- Bulotta, S.; Celano, M.; Lepore, S.M.; Montalcini, T.; Pujia, A.; Russo, D. Beneficial effects of the olive oil phenolic components oleuropein and hydroxytyrosol: Focus on protection against cardiovascular and metabolic diseases. J. Transl. Med. 2014, 12, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parkinson, L.; Cicerale, S. The Health Benefiting Mechanisms of Virgin Olive Oil Phenolic Compounds. Molecules 2016, 21, 1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorzynik-Debicka, M.; Przychodzen, P.; Cappello, F.; Kuban-Jankowska, A.; Marino Gammazza, A.; Knap, N.; Wozniak, M.; Gorska-Ponikowska, M. Potential Health Benefits of Olive Oil and Plant Polyphenols. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cicerale, S.; Lucas, L.; Keast, R. Biological activities of phenolic compounds present in virgin olive oil. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2010, 11, 458–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martín-Peláez, S.; Covas, M.I.; Fitó, M.; Kušar, A.; Pravst, I. Health effects of olive oil polyphenols: Recent advances and possibilities for the use of health claims. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2013, 57, 760–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celano, M.; Maggisano, V.; Lepore, S.M.; Russo, D.; Bulotta, S. Secoiridoids of olive and derivatives as potential coadjuvant drugs in cancer: A critical analysis of experimental studies. Pharmacol. Res. 2019, 142, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montedoro, G.; Servili, M.; Baldioli, M.; Selvaggini, R.; Miniati, E.; Macchioni, A. Simple and hydrolyzable compounds in virgin olive oil. 3. Spectroscopic characterizations of the secoiridoid derivatives. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1993, 41, 2228–2234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czerwińska, M.; Kiss, A.K.; Naruszewicz, M. A comparison of antioxidant activities of oleuropein and its dialdehydic derivative from olive oil, oleacein. Food Chem. 2012, 131, 940–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sindona, G.; Caruso, A.; Cozza, A.; Fiorentini, S.; Lorusso, B.; Marini, E.; Nardi, M.; Procopio, A.; Zicari, S. Anti-inflammatory effect of 3,4-DHPEA-EDA[2-(3,4-hydroxyphenyl)ethyl(3S,4E)-4-formyl-3-(2-oxoethyl) hex-4-enoate] on primary human vascular endothelial cells. Curr. Med. Chem. 2012, 19, 4006–4013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filipek, A.; Czerwińska, M.E.; Kiss, A.K.; Wrzosek, M.; Naruszewicz, M. Oleacein enhances anti-inflammatory activity of human macrophages by increasing CD163 receptor expression. Phytomedicine 2015, 22, 1255–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lombardo, G.E.; Lepore, S.M.; Morittu, V.M.; Arcidiacono, B.; Colica, C.; Procopio, A.; Maggisano, V.; Bulotta, S.; Costa, N.; Mignogna, C.; et al. Effects of Oleacein on High-Fat Diet-Dependent Steatosis, Weight Gain, and Insulin Resistance in Mice. Front. Endocrinol. (Lausanne) 2018, 9, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collins, T.J. Image J for microscopy. Biotechniques 2007, 43, S25–S32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arcidiacono, B.; Chiefari, E.; Laria, A.E.; Messineo, S.; Bilotta, F.L.; Britti, D.; Foti, D.P.; Foryst-Ludwig, A.; Kintscher, U.; Brunetti, A. Expression of matrix metalloproteinase-11 is inceased under conditions of insulin resistance. World J. Diabetes 2017, 8, 422–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunetti, A.; Foti, D.; Goldfine, I.D. Identification of unique nuclear regulatory proteins for the insulin receptor gene, which appear during myocyte and adipocyte differentiation. J. Clin. Investig. 1993, 92, 1288–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laria, A.E.; Messineo, S.; Arcidiacono, B.; Varano, M.; Chiefari, E.; Semple, R.K.; Rocha, N.; Russo, D.; Cuda, G.; Gaspari, M.; et al. Secretome Analysis of Hypoxia-Induced 3T3-L1 Adipocytes Uncovers Novel Proteins Potentially Involved in Obesity. Proteomics 2018, 18, e1700260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombardo, G.E.; Arcidiacono, B.; De Rose, R.F.; Lepore, S.M.; Costa, N.; Montalcini, T.; Brunetti, A.; Russo, D.; De Sarro, G.; Celano, M. Normocaloric Diet Restores Weight Gain and Insulin Sensitivity in Obese Mice. Front. Endocrinol. (Lausanne) 2016, 7, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iiritano, S.; Chiefari, E.; Ventura, V.; Arcidiacono, B.; Possidente, K.; Nocera, A.; Nevolo, M.T.; Fedele, M.; Greco, A.; Greco, M.; et al. The HMGA1-IGF-I/IGFBP system: A novel pathway for modulating glucose uptake. Mol. Endocrinol. 2012, 26, 1578–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Chiefari, E.; Nevolo, M.T.; Arcidiacono, B.; Maurizio, E.; Nocera, A.; Iiritano, S.; Sgarra, R.; Possidente, K.; Palmieri, C.; Paonessa, P.; et al. HMGA1 is a novel downstream nuclear target of the insulin receptor signaling pathway. Sci. Rep. 2012, 2, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffin, M.J.; Sul, H.S. Insulin regulation of fatty acid synthase gene transcription: Roles of USF and SREBP-1c. IUBMB Life 2004, 56, 595–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, V.; Foti, D.; Paonessa, F.; Chiefari, E.; Palaia, L.; Brunetti, G.; Gulletta, E.; Fusco, A.; Brunetti, A. The insulin receptor: A new anticancer target for peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ (PPARγ) and thiazolidinedione-PPARγ agonists. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2008, 15, 325–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lepore, S.M.; Morittu, V.M.; Celano, M.; Trimboli, F.; Oliverio, M.; Procopio, A.; Di Loreto, C.; Damante, G.; Britti, D.; Bulotta, S.; et al. Oral Administration of Oleuropein and Its Semisynthetic Peracetylated Derivative Prevents Hepatic Steatosis, Hyperinsulinemia, and Weight Gain in Mice Fed with High Fat Cafeteria Diet. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2015, 2015, 431453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.; Choi, Y.; Um, S.J.; Yoon, S.K.; Park, T. Oleuropein attenuates hepatic steatosis induced by high-fat diet in mice. J. Hepathol. 2011, 54, 984–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Y.; Soong, S.J.; Keum, N.; Park, T. Olive leaf extract attenuates obesity in high-fat diet-fed mice by modulating the expression of molecules involved in adipogenesis and thermogenesis. Evid. Based Complement Alter. Med. 2014, 2014, 971890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Stelt, I.; Hoek-van den Hil, E.F.; Swarts, H.J.; Vervoort, J.J.; Hoving, L.; Skaltsounis, L.; Lemonakis, N.; Andreadou, I.; van Schothorst, E.M.; Keijer, J. Nutraceutical oleuropein supplementation prevents high fat diet-induced adiposity in mice. J. Funct. Foods 2015, 14, 702–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Choi, Y.; Park, T. Hepatoprotective effect of oleuropein in mice: Mechanisms uncovered by gene expression profiling. Biotechnol. J. 2010, 5, 950–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costanzo, P.; Bonacci, S.; Cariati, L.; Nardi, M.; Oliverio, M.; Procopio, A. Simple and efficient sustainable semi-synthesis of oleacein [2-(3,4-hydroxyphenyl) ethyl (3S,4E)-4-formyl-3-(2-oxoethyl)hex-4-enoate] as potential additive for edible oils. Food Chem. 2018, 245, 410–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svobodova, M.; Andreadou, I.; Skaltsounis, A.L.; Kopecky, J.; Flachs, P. Oleuropein as an inhibitor of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma. Genes Nutr. 2014, 9, 376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuem, N.; Song, S.J.; Yu, R.; Yun, J.W.; Park, T. Oleuropein attenuates visceral adiposity in high-fat diet-induced obese mice through the modulation of WNT10b- and galanin-mediated signalings. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2014, 58, 2166–2176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yaribeygi, H.; Farrokhi, F.R.; Butler, A.E.; Sahebkar, A. Insulin resistance: Reviewof the underlying molecular mechanisms. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 8152–8161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiefari, E.; Paonessa, F.; Iiritano, S.; Le Pera, I.; Palmieri, D.; Brunetti, G.; Lupo, A.; Colantuoni, V.; Foti, D.; Gulletta, E.; et al. The cAMP-HMGA1-RBP4 system: A novel biochemical pathway for modulating glucose homeostasis. BMC Biol. 2009, 7, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lepore, S.M.; Maggisano, V.; Bulotta, S.; Mignogna, C.; Arcidiacono, B.; Procopio, A.; Brunetti, A.; Russo, D.; Celano, M. Oleacein Prevents High Fat Diet-Induced Adiposity and Ameliorates Some Biochemical Parameters of Insulin Sensitivity in Mice. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1829. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11081829
Lepore SM, Maggisano V, Bulotta S, Mignogna C, Arcidiacono B, Procopio A, Brunetti A, Russo D, Celano M. Oleacein Prevents High Fat Diet-Induced Adiposity and Ameliorates Some Biochemical Parameters of Insulin Sensitivity in Mice. Nutrients. 2019; 11(8):1829. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11081829
Chicago/Turabian StyleLepore, Saverio Massimo, Valentina Maggisano, Stefania Bulotta, Chiara Mignogna, Biagio Arcidiacono, Antonio Procopio, Antonio Brunetti, Diego Russo, and Marilena Celano. 2019. "Oleacein Prevents High Fat Diet-Induced Adiposity and Ameliorates Some Biochemical Parameters of Insulin Sensitivity in Mice" Nutrients 11, no. 8: 1829. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11081829
APA StyleLepore, S. M., Maggisano, V., Bulotta, S., Mignogna, C., Arcidiacono, B., Procopio, A., Brunetti, A., Russo, D., & Celano, M. (2019). Oleacein Prevents High Fat Diet-Induced Adiposity and Ameliorates Some Biochemical Parameters of Insulin Sensitivity in Mice. Nutrients, 11(8), 1829. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11081829