Nutritional Outcome in Home Gastrostomy-Fed Children with Chronic Diseases
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Patients and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Participants
2.3. GT Placement and Nutrition Support Mode
2.4. Anthropometric Evaluation
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Anthropometric Outcomes following GT Placement
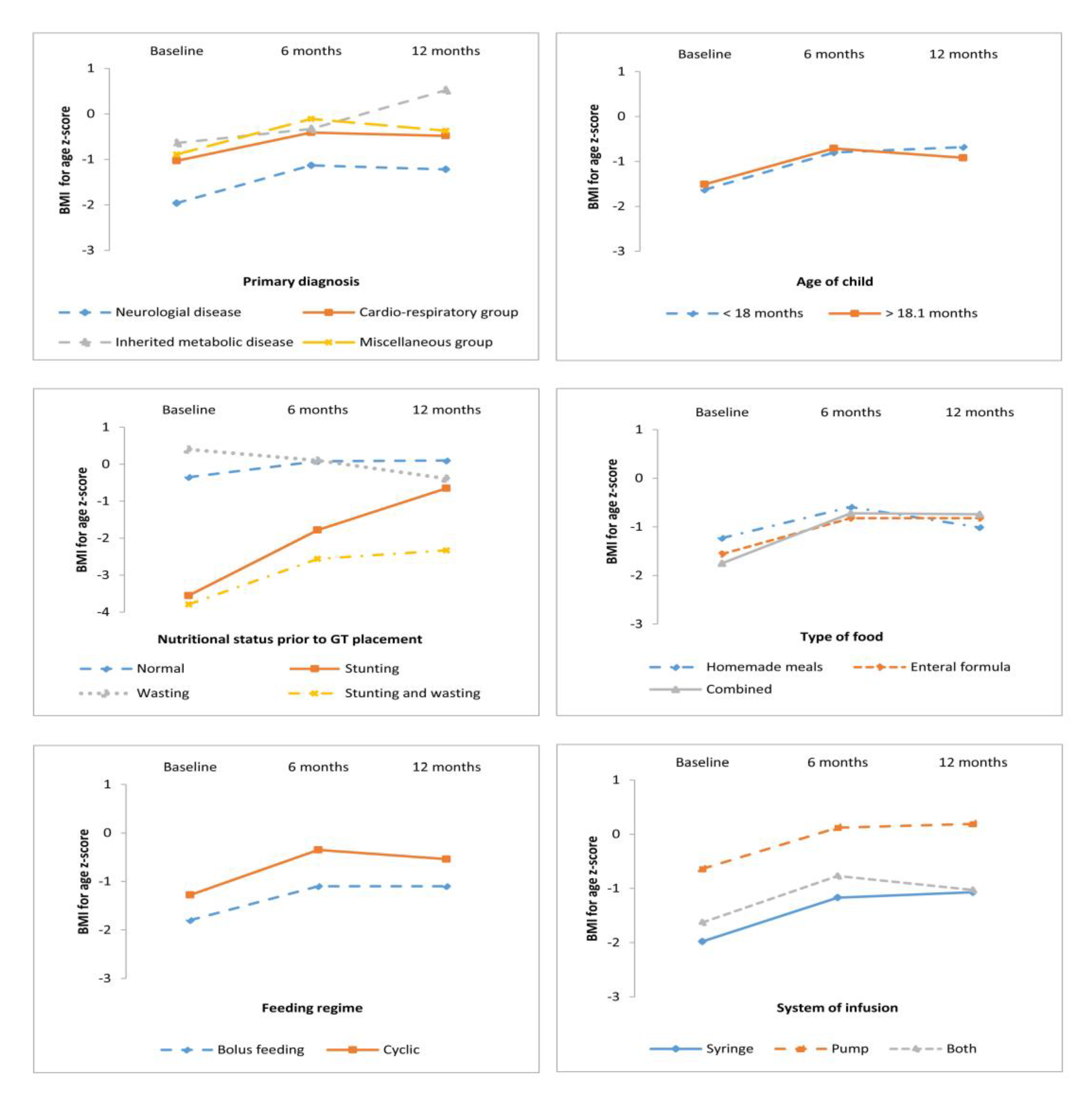
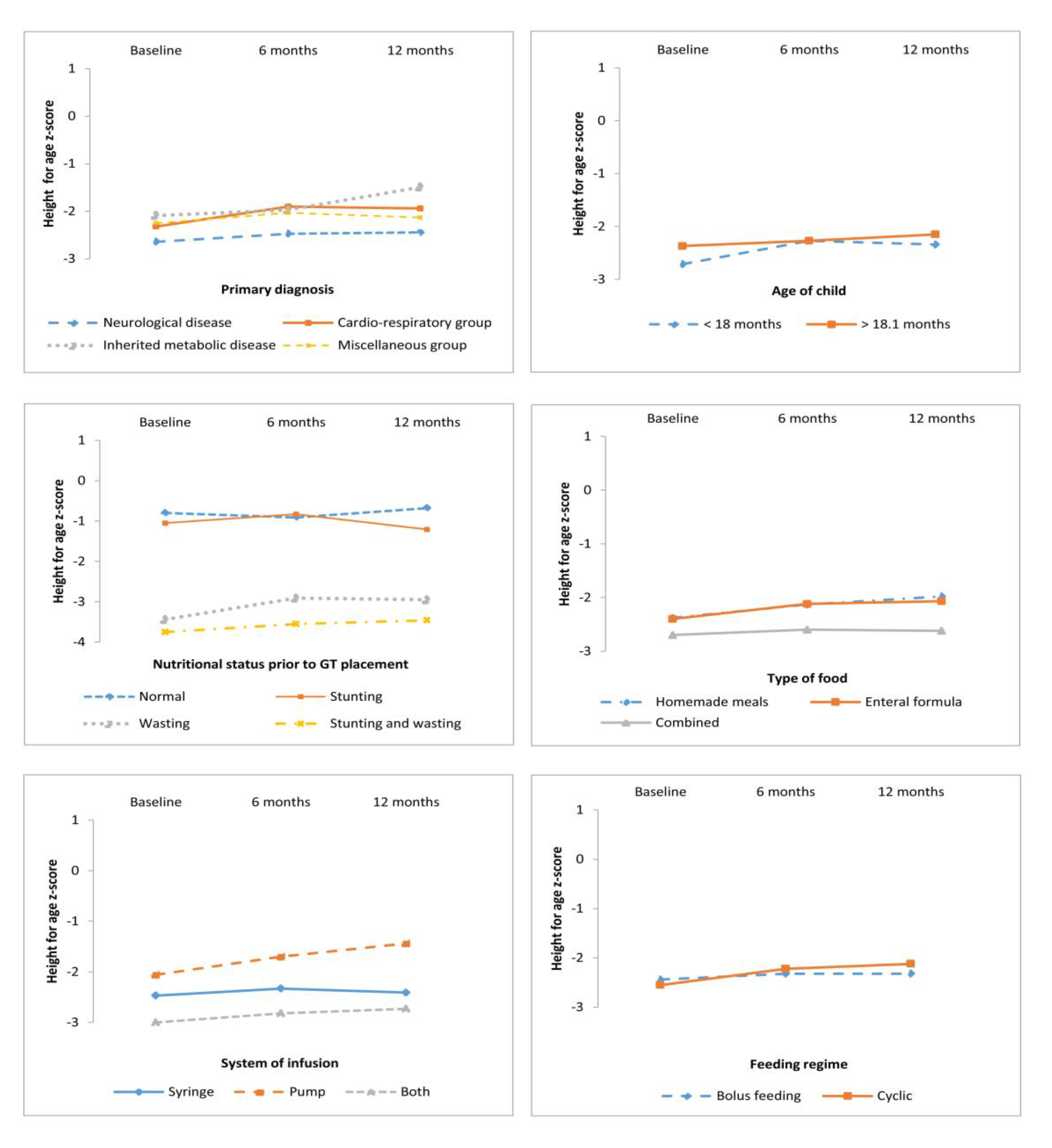
3.2. Anthropometric Outcomes According to Primary Diagnosis, Age, and Nutrition Status at GT Placement
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sullivan, P.B.; Juszczak, E.; Bachlet, A.M.E.; Lambert, B.; Vernon-Roberts, A.; Grant, H.W.; Eltumi, M.; McLean, L.; Alder, N.; Thomas, A.G. Gastrostomy tube feeding in children with cerebral palsy: A prospective, longitudinal study. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2005, 47, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuperminc, M.N.; Stevenson, R.D. Growth and nutrition disorders in children with cerebral palsy. Dev. Disabil. Res. Rev. 2008, 14, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vickers, D.W.; Maynard, L.C. Balancing biomedical, care, and support needs in the technology dependent child. Arch. Dis. Child. 2006, 91, 458–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kilpinen-Loisa, P.; Pihko, H.; Vesander, U.; Paganus, A.; Ritanen, U.; Mäkitie, O. Insufficient energy and nutrient intake in children with motor disability. Acta Paediatr. 2009, 98, 1329–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heuschkel, R.B.; Gottrand, F.; Devarajan, K.; Poole, H.; Callan, J.; Dias, J.A.; Karkelis, S.; Papadopoulou, A.; Husby, S.; Ruemmele, F.; et al. ESPGHAN position paper on management of percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy in children and adolescents. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2015, 60, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craig, G.M.; Carr, L.J.; Cass, H.; Hastings, R.P.; Lawson, M.; Reilly, S.; Ryan, M.; Townsend, J.; Spitz, L. Medical, surgical, and health outcomes of gastrostomy feeding. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2006, 48, 353–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradley, G.M.; Carson, K.A.; Leonard, A.R.; Mogayzel, P.J.; Oliva-Hemker, M. Nutritional outcomes following gastrostomy in children with cystic fibrosis. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2012, 47, 743–748. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3343175/ (accessed on 20 February 2019). [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, R.; Irvine, T.; Dalzell, M. Indications for percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy and procedure-related outcome. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2009, 49, 584–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedrón-Giner, C.; Navas-López, V.M.; Martínez-Zazo, A.B.; Martínez-Costa, C.; Sánchez-Valverde, F.; Blasco-Alonso, J.; Moreno-Villares, J.M.; Redecillas-Ferreiro, S.; Canals-Badía, M.J.; Rosell-Camps, A.; et al. Analysis of the Spanish national registry for pediatric home enteral nutrition (NEPAD): Implementation rates and observed trends during the past 8 years. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2013, 67, 318–323. Available online: https://www.nature.com/articles/ejcn20138 (accessed on 30 January 2018). [CrossRef]
- Daveluy, W.; Guimber, D.; Uhlen, S.; Lescut, D.; Michaud, L.; Turck, D.; Gottrand, F. Dramatic changes in home-based enteral nutrition practices in children during an 11-year period. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2006, 43, 240–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romano, C.; van Wynckel, M.; Hulst, J.; Broekaert, I.; Bronsky, J.; Dall’Oglio, L.; Mis, N.F.; Hojsak, I.; Orel, R.; Papadopoulou, A.; et al. European Society for Paediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition Guidelines for the Evaluation and Treatment of Gastrointestinal and Nutritional Complications in Children With Neurological Impairment. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2017, 65, 242–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, J.; Day, S.; Shavelle, R.; Strauss, D. Low weight, morbidity, and mortality in children with cerebral palsy: New clinical growth charts. Pediatrics. 2011, 128, e299–e307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapadia, M.Z.; Joachim, K.C.; Balasingham, C.; Cohen, E.; Mahant, S.; Nelson, K.; Maguire, J.L.; Guttmann, A.; Offringa, M. A Core Outcome Set for Children With Feeding Tubes and Neurologic Impairment: A Systematic Review. Pediatrics 2016, 138, e20153967. Available online: https://pediatrics.aappublications.org/content/138/1/e20153967.long (accessed on 15 February 2018). [CrossRef]
- Thomas, H.; Yole, J.; Livingston, M.H.; Bailey, K.; Cameron, B.H.; VanHouwelingen, L. Replacing gastrostomy tubes with collapsible bumpers in pediatric patients: Is it safe to ‘cut’ the tube and allow the bumper to pass enterally? J. Pediatr. Surg. 2018, 53, 942–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balogh, B.; Kovács, T.; Saxena, A.K. Complications in children with percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy (PEG) placement. World J. Pediatr. 2019, 15, 12–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Costa, C.; Borraz, S.; Benlloch, C.; López-Sáiz, A.; Sanchiz, V.; Brines, J. Early decision of gastrostomy tube insertion in children with severe developmental disability: A current dilemma. J. Hum. Nutr. Diet. 2011, 24, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avitsland, T.L.; Faugli, A.; Pripp, A.H.; Malt, U.F.; Bjørnland, K.; Emblem, R. Maternal psychological distress and parenting stress after gastrostomy placement in children. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2012, 55, 562–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Costa, C.; Calderón, C.; Pedrón-Giner, C.; Borraz, S.; Gómez-López, L. Psychometric properties of the structured Satisfaction Questionnaire with Gastrostomy Feeding (SAGA-8) for caregivers of children with gastrostomy tube nutritional support. J. Hum. Nutr. Diet. 2013, 26, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palisano, R.; Rosenbaum, P.; Walter, S.; Russell, D.; Wood, E.; Galuppi, B. Development and reliability of a system to classify gross motor function in children with cerebral palsy. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 1997, 39, 214–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gauderer, M.W.; Ponsky, J.L.; Izant, R.J. Gastrostomy without laparotomy: A percutaneous endoscopic technique. J. Pediatr. Surg. 1980, 15, 872–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novotny, N.M.; Vegeler, R.C.; Breckler, F.D.; Rescorla, F.J. Percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy buttons in children: Superior to tubes. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2009, 44, 1193–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO | The WHO Child Growth Standards [Internet]. WHO. Available online: http://www.who.int/childgrowth/standards/en/ (accessed on 19 March 2019).
- WHO | Growth Reference Data for 5–19 Years [Internet]. WHO. Available online: https://www.who.int/growthref/en/. (accessed on 19 March 2019).
- World Health Organization. International Classification of Diseases 11th Revision-Beta Browser [Internet]. Available online: http://apps.who.int/classifications/ icd11/browse/l-m/en (accessed on 10 January 2018).
- Dipasquale, V.; Catena, M.A.; Cardile, S.; Romano, C. Standard Polymeric Formula Tube Feeding in Neurologically Impaired Children: A Five-Year Retrospective Study. Nutrients 2018, 10, 684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalanne, A.; Gottrand, F.; Salleron, J.; Puybasset-Jonquez, A.L.; Guimber, D.; Turck, D.; Michaud, L. Long-term outcome of children receiving percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy feeding. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2014, 59, 172–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, A.; Zamora, S.A.; Scott, R.B.; Parsons, H.G. Catch-up growth in children treated with home enteral nutrition. Pediatrics 1998, 102, 951–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kansu, A.; Durmaz Ugurcan, O.; Arslan, D.; Unalp, A.; Celtik, C.; Sarıoglu, A.A.; ANTK Study Group; Tolan, H.; Gulerman, F.; Ince, H.; et al. High-fibre enteral feeding results in improved anthropometrics and favourable gastrointestinal tolerance in malnourished children with growth failure. Acta Paediatr. 2018, 107, 1036–1042. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5969084/ (accessed on 10 January 2019). [CrossRef]
- Seguy, D.; Michaud, L.; Guimber, D.; Cuisset, J.M.; Devos, P.; Turck, D.; Gottrand, F. Efficacy and tolerance of gastrostomy feeding in pediatric forms of neuromuscular diseases. J. Parenter. Enteral. Nutr. 2002, 26, 298–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuperminc, M.N.; Gottrand, F.; Samson-Fang, L.; Arvedson, J.; Bell, K.; Craig, G.M.; Sullivan, P.B. Nutritional management of children with cerebral palsy: A practical guide. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2013, 67, S21–S23. Available online: https://www.nature.com/articles/ejcn2013227 (accessed on 10 January 2018). [CrossRef]
- Sienna, J.L.; Saqan, R.; Teh, J.C.; Frieling, M.L.; Secker, D.; Cornelius, V.; Geary, D.F. Body size in children with chronic kidney disease after gastrostomy tube feeding. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2010, 25, 2115–2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barron, M.A.; Duncan, D.S.; Green, G.J.; Modrusan, D.; Connolly, B.; Chait, P.; Saunders, E.F.; Greenberg, M. Efficacy and safety of radiologically placed gastrostomy tubes in paediatric haematology/oncology patients. Med. Pediatr. Oncol. 2000, 34, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, B. Feeding method and health outcomes of children with cerebral palsy. J. Pediatr. 2004, 145, S28–S32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brotherton, A.M.; Abbott, J.; Aggett, P.J. The impact of percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy feeding in children; the parental perspective. Child Care Health Dev. 2007, 33, 539–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Costa, C.; Calderón, C.; Gómez-López, L.; Borraz, S.; Pedrón-Giner, C. Satisfaction with gastrostomy feeding in caregivers of children with home enteral nutrition; application of the SAGA-8 questionnaire and analysis of involved factors. Nutr. Hosp. 2013, 28, 1121–1128. Available online: http://www.nutricionhospitalaria.com/pdf/6555.pdf (accessed on 10 January 2018). [PubMed]
- Zettle, S. Deconstructing Pediatric Blenderized Tube Feeding: Getting Started and Problem Solving Common Concerns. Nutr. Clin. Pract. 2016, 31, 773–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coad, J.; Toft, A.; Lapwood, S.; Manning, J.; Hunter, M.; Jenkins, H.; Sadlier, C.; Hammonds, J.; Kennedy, A.; Murch, S.; et al. Blended foods for tube-fed children: A safe and realistic option? A rapid review of the evidence. Arch. Dis. Child. 2017, 102, 274–278. Available online: https://adc.bmj.com/content/102/3/274.long (accessed on 10 March 2019). [CrossRef]
- Epp, L.; Lammert, L.; Vallumsetla, N.; Hurt, R.T.; Mundi, M.S. Use of Blenderized Tube Feeding in Adult and Pediatric Home Enteral Nutrition Patients. Nutr. Clin. Pract. 2017, 32, 201–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Anthropometry z-score * | n | Baseline M ± SD | 6 months M ± SD | 12 months M ± SD | F | p |
| BMI-for-age | 65 | −1.56 ± 1.95 | −0.74 ± 1.62 | −0.83 ± 1.42 | 22.344 | 0.0001 |
| Height-for-age | 65 | −2.50 ± 1.62 | −2.27 ± 1.50 | −2.22 ± 1.64 | 6.078 | 0.016 |
| Anthropometry z-score * | Comparison * | Mean difference | p | 95% CI of the difference | ||
| Lower | Upper | |||||
| BMI-for-age | Baseline vs. 6 months | −0.81 | 0.001 | −0.48 | 1.14 | |
| Baseline vs. 12 months | −0.72 | 0.001 | −1.20 | 0.24 | ||
| 6 months vs. 12 months | 0.09 | 1.000 | −0.25 | 0.43 | ||
| Height-for-age | Baseline vs. 6 months | −0.22 | 0.031 | −0.43 | −0.02 | |
| Baseline vs. 12 months | −0.27 | 0.049 | −0.54 | 0.00 | ||
| 6 months vs. 12 months | −0.05 | 1.000 | −0.24 | 0.15 | ||
| Variables | n | % | BMI-for-Age z-Score | Height-for-Age z-Score | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | 6 Months | 12 Months | Baseline | 6 Months | 12 Months | |||
| M (SD) | M (SD) | M (SD) | M (SD) | M (SD) | M (SD) | |||
| Primary Diagnosis | ||||||||
| Neurological disease | 40 | 61.5 | −1.96 (2.12) | −1.13 (1.68) | −1.22 (1.51) | −2.64 (1.76) | −2.47 (1.56) | −2.44 (1.45) |
| Cardio-respiratory disease | 14 | 21.5 | −1.03 (1.43) | −0.41 (1.55) | −0.48 (1.01) | −2.32 (1.39) | −1.90 (1.47) | −1.94 (2.10) |
| Inherited metabolic disease | 6 | 9.3 | −0.64 (1.04) | −0.33 (0.78) | 0.52 (0.50) | −2.09 (1.81) | −1.97 (1.65) | −1.49 (2.11) |
| Miscellaneous group a | 5 | 7.7 | −0.89 (2.16) | 0.11 (1.19) | −0.37 (1.08) | −2.25 (1.01) | −2.03 (0.83) | −2.13 (1.01) |
| Age of Child | ||||||||
| <18 months | 24 | 36.9 | −1.63 (2.00) | −0.80 (1.58) | −0.68 (1.26) | −2.71 (1.50) | −2.27 (1.49) | −2.34 (1.61) |
| >18.1 months | 41 | 63.1 | −1.51 (1.94) | −0.71 (1.67) | −0.92 (1.51) | −2.37 (1.70) | −2.27 (1.53) | −2.15 (1.67) |
| Nutritional Status | ||||||||
| Normal nutritional status | 20 | 30.8 | −0.35 (0.99) | 0.08 (1.01) | −0.10 (1.01) | −0.80 (0.93) | −0.91 (0.82) | −0.68 (1.16) |
| Acute malnutrition (wasting) | 6 | 9.3 | −3.55 (1.27) | −1.78 (1.07) | −0.65 (0.81) | −1.05 (0.66) | −0.83 (0.96) | −1.21 (0.75) |
| Chronic malnutrition (stunting) | 22 | 33.7 | 0.40 (1.06) | 0.10 (0.95) | −0.39 (1.01) | −3.44 (1.00) | −2.91 (1.01) | −2.95 (0.96) |
| Stunting and wasting | 17 | 26.2 | −3.76 (1.30) | −2.56 (1.26) | −2.33 (1.40) | −3.75 (0.92) | −3.55 (1.10) | −3.46 (1.44) |
| Type of Food | ||||||||
| Homemade meals | 13 | 20.0 | −1.23 (1.82) | −0.59 (1.58) | −1.01 (1.48) | −2.38 (2.34) | −2.13 (1.95) | −1.98 (2.20) |
| Enteral formula | 32 | 49.2 | −1.56 (1.91) | −0.82 (1.64) | −0.82 (1.37) | −2.40 (1.50) | −2.12 (1.36) | −2.07 (1.43) |
| Combined | 20 | 30.8 | −1.75 (2.15) | −0.72 (1.69) | −0.74 (1.51) | −2.70 (1.29) | −2.60 (1.42) | −2.62 (1.56) |
| Feeding Regime | ||||||||
| Bolus feeding | 34 | 52.3 | −1.80 (2.20) | −1.10 (1.73) | −1.10 (1.53) | −2.44 (1.92) | −2.32 (1.66) | −2.32 (1.70) |
| Cyclic | 31 | 47.7 | −1.28 (1.63) | −0.35 (1.43) | −0.54 (1.24) | −2.55 (1.25) | −2.22 (1.34) | −2.12 (1.59) |
| System of Infusion | ||||||||
| Syringe | 34 | 52.3 | −1.98 (2.24) | −1.17 (1.75) | −1.07 (1.45) | −2.47 (1.94) | −2.33 (1.77) | −2.41 (1.93) |
| Pump | 17 | 26.2 | −0.64 (1.28) | 0.12 (1.09) | −0.19 (1.12) | −2.06 (1.23) | −1.70 (0.97) | −1.44 (1.13) |
| Combined | 14 | 21.5 | −1.63 (1.53) | −0.77 (1.51) | −1.03 (1.51) | −3.06 (1.01) | −2.82 (1.10) | −2.73 (1.05) |
| Variable | Source | BMI-for-Age z-score | Height-for-Age z-score | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F | p | F | p | ||
| Primary diagnosis | Within-subjects effects | 13.336 | <0.0001 | 4.668 | 0.035 |
| Interaction | 0.233 | 0.873 | 0.440 | 0.725 | |
| Between-groups effects | 2.900 | 0.042 | 0.612 | 0.610 | |
| Age of GT placement | Within-subjects effects | 18.858 | <0.0001 | 6.492 | 0.013 |
| Interaction | 0.816 | 0.370 | 4.600 | 0.036 | |
| Between-groups effects | 0.001 | 0.974 | 0,195 | 0.660 | |
| Nutritional status prior GT placement | Within-subjects effects | 14.928 | 0.001 | 2.329 | 0.132 |
| Interaction | 9.946 | 0.001 | 1.141 | 0.340 | |
| Between groups effects | 38.603 | 0.001 | 36.611 | 0.001 | |
| Type of food | Within-subjects effects | 21.194 | <0.0001 | 5.426 | 0.023 |
| Interaction | 0.975 | 0.383 | 0.691 | 0.505 | |
| Between-groups effects | 0.035 | 0.965 | 0.189 | 0.665 | |
| Feeding regime | Within-subjects effects | 22.882 | 0.001 | 6.480 | 0.013 |
| Interaction | 0.007 | 0.932 | 1.954 | 0.664 | |
| Between-groups effects | 2.677 | 0.107 | 0.189 | 0.664 | |
| System of infusion | Within-subjects effects | 22.392 | <0.0001 | 8.819 | 0.004 |
| Interaction | 0.526 | 0.593 | 2.435 | 0.096 | |
| Between-groups effects | 0.029 | 0.865 | 2.254 | 0.114 | |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Martínez-Costa, C.; Calderón, C.; Gómez-López, L.; Borraz, S.; Crehuá-Gaudiza, E.; Pedrón-Giner, C. Nutritional Outcome in Home Gastrostomy-Fed Children with Chronic Diseases. Nutrients 2019, 11, 956. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11050956
Martínez-Costa C, Calderón C, Gómez-López L, Borraz S, Crehuá-Gaudiza E, Pedrón-Giner C. Nutritional Outcome in Home Gastrostomy-Fed Children with Chronic Diseases. Nutrients. 2019; 11(5):956. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11050956
Chicago/Turabian StyleMartínez-Costa, Cecilia, Caterina Calderón, Lilianne Gómez-López, Soraya Borraz, Elena Crehuá-Gaudiza, and Consuelo Pedrón-Giner. 2019. "Nutritional Outcome in Home Gastrostomy-Fed Children with Chronic Diseases" Nutrients 11, no. 5: 956. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11050956
APA StyleMartínez-Costa, C., Calderón, C., Gómez-López, L., Borraz, S., Crehuá-Gaudiza, E., & Pedrón-Giner, C. (2019). Nutritional Outcome in Home Gastrostomy-Fed Children with Chronic Diseases. Nutrients, 11(5), 956. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11050956





