Significant Amounts of Functional Collagen Peptides Can Be Incorporated in the Diet While Maintaining Indispensable Amino Acid Balance
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Composition and Digestibility of the Standard American Diet
2.2. Composition and Digestibility of Collagen Peptides
2.3. Iterative PDCAAS Calculations
2.4. Collagen Consumption in the Standard American Diet
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Milner, J.A. Functional foods: the US perspective. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2000, 71, 1654S–1659S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norheim, F.; Gjelstad, I.M.F.; Hjorth, M.; Vinknes, K.J.; Langleite, T.M.; Holen, T.; Jensen, J.; Dalen, K.T.; Karlsen, A.S.; Kielland, A.; et al. Molecular nutrition research—The modern way of performing nutritional science. Nutrients 2012, 4, 1898–1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakrabarti, S.; Guha, S.; Majumder, K. Food-derived bioactive peptides in human health: Challenges and opportunities. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartmann, R.; Meisel, H. Food-derived peptides with biological activity: from research to food applications. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2007, 18, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Therkildsen, M.; Aluko, R.E.; Lametsch, R. Exploration of collagen recovered from animal by-products as a precursor of bioactive peptides: Successes and challenges. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2018, 2, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proksch, E.; Segger, D.; Degwert, J.; Schunck, M.; Zague, V.; Oesser, S. Oral supplementation of specific collagen peptides has beneficial effects on human skin physiology: A double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Skin. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2014, 27, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McAlindon, T.E.; Nuite, M.; Krishnan, N.; Ruthazer, R.; Price, L.L.; Burstein, D.; Griffith, J.; Flechsenhar, K. Change in knee osteoarthritis cartilage detected by delayed gadolinium enhanced magnetic resonance imaging following treatment with collagen hydrolysate: A pilot randomized controlled trial. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2011, 19, 399–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zdzieblik, D.; Oesser, S.; Gollhofer, A.; Koenig, D. Corrigendum: Improvement of activity-related knee joint discomfort following supplementation of specific collagen peptides. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 2017, 42, 1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, K.L.; Sebastianelli, W.; Flechsenhar, K.R.; Aukermann, D.F.; Meza, F.; Millard, R.L.; Deitch, J.R.; Sherbondy, P.S.; Albert, A. 24-Week study on the use of collagen hydrolysate as a dietary supplement in athletes with activity-related joint pain. Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 2008, 24, 1485–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Praet, S.F.E.; Purdam, C.R.; Welvaert, M.; Vlahovich, N.; Lovell, G.; Burke, L.M.; Gaida, J.E.; Manzanero, S.; Hughes, D.; Waddington, G. Oral supplementation of specific collagen peptides combined with calf-strengthening exercises enhances function and reduces pain in Achilles tendinopathy patients. Nutrients 2019, 11, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dressler, P.; Gehring, D.; Zdzieblik, D.; Oesser, S.; Gollhofer, A.; König, D. Improvement of functional ankle properties following supplementation with specific collagen peptides in athletes with chronic ankle instability. J. Sports Sci. Med. 2018, 17, 198–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, G.; Lee-Barthel, A.; Ross, M.L.R.; Wang, B.; Baar, K. Vitamin C–enriched gelatin supplementation before intermittent activity augments collagen synthesis. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 105, 136–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baar, K. Stress relaxation and targeted nutrition to treat patellar tendinopathy. Int. J. Sports Nutr. Exerc. Metab. 2019, 4, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zdzieblik, D.; Oesser, S.; Baumstark, M.W.; Gollhofer, A.; König, D. Collagen peptide supplementation in combination with resistance training improves body composition and increases muscle strength in elderly sarcopenic men: a randomised controlled trial. Br. J. Nutr. 2015, 114, 1237–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jendricke, P.; Centner, C.; Zdzieblik, D.; Gollhofer, A.; König, D. Specific collagen peptides in combination with resistance training improve body composition and regional muscle strength in premenopausal women: A randomized controlled trial. Nutrients 2019, 11, 892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- König, D.; Oesser, S.; Scharla, S.; Zdzieblik, D.; Gollhofer, A. Specific collagen peptides improve bone mineral density and bone markers in postmenopausal women-A randomized controlled study. Nutrients 2018, 10, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siebert, H.-C.; Burg-Roderfeld, M.; Eckert, T.; Stötzel, S.; Kirch, U.; Diercks, T.; Humphries, M.J.; Frank, M.; Wechselberger, R.; Tajkhorshid, E.; et al. Interaction of the α2A domain of integrin with small collagen fragments. Protein Cell 2010, 1, 393–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, Y.; Yin, Y.; Wu, G. Dietary essentiality of “nutritionally non-essential amino acids” for animals and humans. Exp. Biol. Med. 2015, 240, 997–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, G.; Bazer, F.W.; Burghard, R.C.; Johnson, G.A.; Kim, S.W.; Knabe, D.A.; Li, P.; Li, X.; McKnight, J.R.; Satterfield, M.C.; Spencer, T.E. Proline and hydroxyproline metabolism: implications for animal and human nutrition. Amino Acids 2011, 4, 1053–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meléndez-Hevia, E.; De Paz-Lugo, P.; Cornish-Bowden, A.; Cárdenas, M.L.; Paz-Lugo, P. A weak link in metabolism: the metabolic capacity for glycine biosynthesis does not satisfy the need for collagen synthesis. J. Biosci. 2009, 34, 853–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EFSA Panel on Dietetics Products, Nutrition and Allergies (NDA). Scientific opinion on dietary reference values for protein. EFSA J. 2012, 10, 2557–2623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO). Dietary protein quality evaluation in human nutrition: report of an FAO Expert Consultation. FAO Food Nutr. Pap. 2013, 92, 1–79. [Google Scholar]
- Leser, S. The 2013 FAO report on dietary protein quality evaluation in human nutrition: Recommendations and implications. Nutr. Bull. 2013, 38, 421–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinangeli, C.P.F.; House, J.D. Potential impact of the digestible indispensable amino acid score as a measure of protein quality on dietary regulations and health. Nutr. Rev. 2017, 75, 658–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United States Department of Agriculture. CSFII/DHKS 1994–1996 Data Set and Documentation: The 1994 Continuing Survey of Food Intakes by Individuals and the 1994–1996 Diet and Health Knowledge Survey; Agricultural Research Service: Riverdale, MD, USA, 1996.
- Protein and Amino Acid Requirements in Human Nutrition: Report of a Joint FAO/WHO/UNU Expert Consultation. Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/43411 (accessed on 25 March 2019).
- Ao, J.; Li, B. Amino acid composition and antioxidant activities of hydrolysates and peptide fractions from porcine collagen. Food Sci. Technol. Int. 2012, 18, 425–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Z.; Yang, P.; Zhou, C.; Li, S.; Hong, P. Marine collagen peptides from the skin of Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis Niloticus): Characterization and wound healing evaluation. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keith, M.O.; Bell, J.M. Digestibility of nitrogen and amino acids in selected protein sources fed to mice. J. Nutr. 1988, 118, 561–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Institute of Medicine. Dietary Reference Intakes for Energy, Carbohydrate, Fiber, Fat, Fatty Acids, Cholesterol, Protein and Amino Acids; National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES), 2001–2002. Available online: https://www.icpsr.umich.edu/icpsrweb/NACDA/studies/25502/version/5/publications (accessed on 25 March 2019).
- National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES), 2003–2004. Available online: https://www.icpsr.umich.edu/icpsrweb/NACDA/studies/25503/version/7/publications (accessed on 25 March 2019).
- Wright, J.D.; Wang, C.Y. Trends in intake of energy and macronutrients in adults from 1999–2000 through 2007–2008. NCHS Data Brief 2010, 49, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Phillips, S.M.; Chevalier, S.; Leidy, H.J. Protein “requirements” beyond the RDA: implications for optimizing health. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 2016, 41, 565–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moughan, P.J. Dietary protein for human health. Br. J. Nutr. 2012, 108, S1–S2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutherfurd-Markwick, K.J. Food proteins as a source of bioactive peptides with diverse functions. Br. J. Nutr. 2012, 108, S149–S157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, K.; Rennie, M.J. New approaches and recent results concerning human-tissue collagen synthesis. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2007, 10, 582–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.; Rebholz, C.M.; Caulfield, L.E.; Ramsing, R.; Nachman, K.E. Trends in types of protein in US adults: results from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 1999–2010. Public Health Nutr. 2018, 22, 191–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Commonly Consumed Dietary Sources of Collagen Peptides | PDCAAS Equals 1.0 (“High” Dietary Protein Quality) | PDCAAS Equals 0.75 (“Good” Dietary Protein Quality) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Collagen (%) | First Limiting Amino Acid | Collagen (%) | First Limiting Amino Acid | |
| Porcine, sample A [27] | 39% | Tryptophan | 54% | Tryptophan |
| Porcine, sample B [27] | 39% | Tryptophan | 54% | Tryptophan |
| Porcine, sample C [27] | 39% | Tryptophan | 54% | Tryptophan |
| Porcine, sample D [27] | 36% | Cysteine + methionine | 54% | Tryptophan |
| Bovine (GELITA AG) | 39% | Cysteine + methionine | 54% | Tryptophan |
| Marine [28] | 39% | Tryptophan | 54% | Tryptophan |
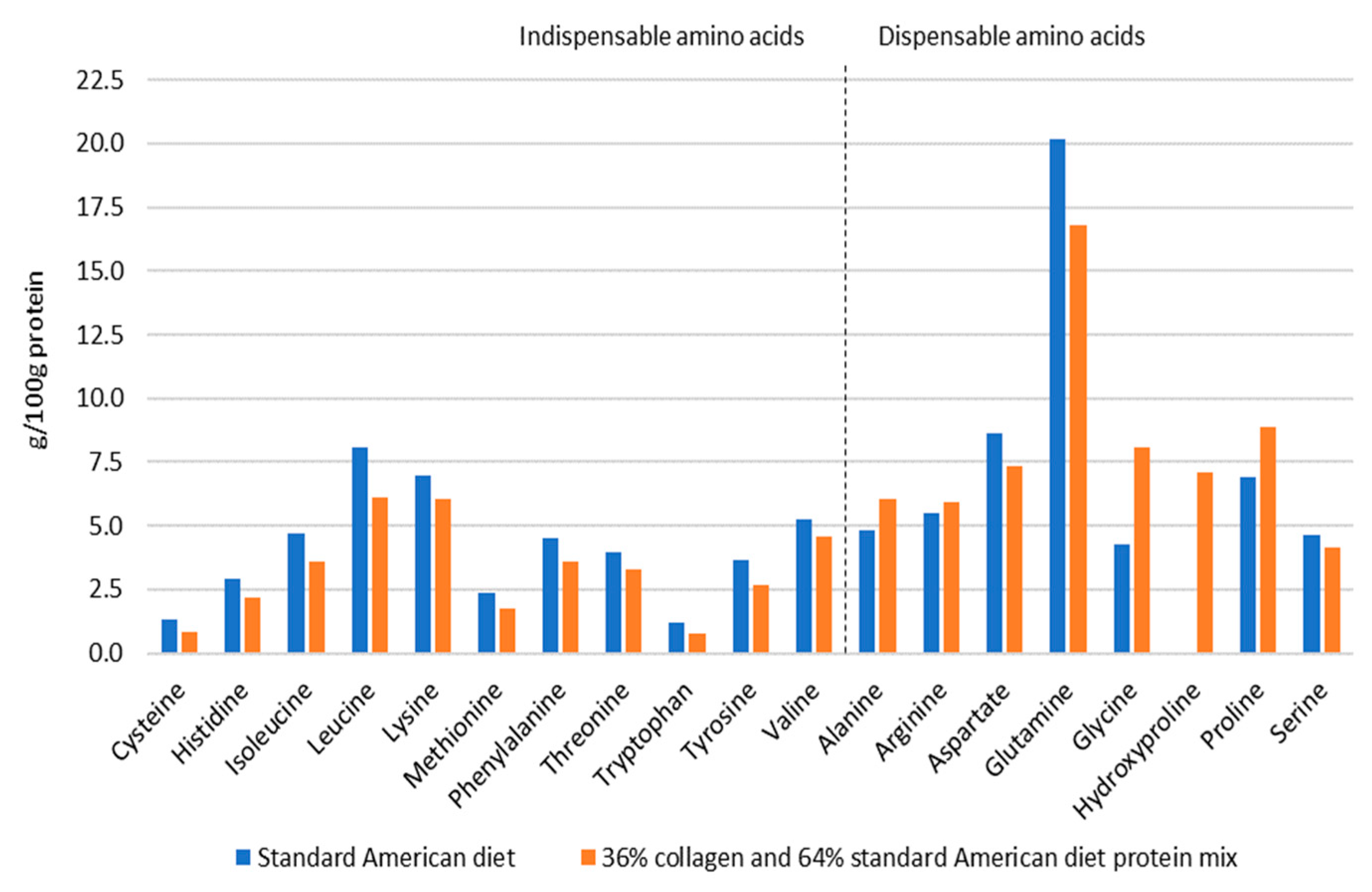
| Indispensable Amino Acids | Reference Amino Acid Requirement Pattern * (mg/g) | Standard American Diet Protein Mixture | Collagen Peptides (Porcine Origin, Sample D) | Daily Protein Mixture Containing 36% Collagen Peptides and 64% Standard American Diet Protein Mixture | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| g/100 g | g/100 g Corrected for 96% Digestibility | AAS | g/100 g | g/100 g Corrected for 98.4% Digestibility | AAS | g/100 g | mg/g | AAS | ||
| Cys+Met | 25 | 3.68 | 3.53 | 1.41 | 0.72 | 0.71 | 0.28 | 2.50 | 25.00 | 1.00 ** |
| Histidine | 18 | 2.91 | 2.79 | 1.55 | 0.85 | 0.83 | 0.46 | 2.08 | 20.78 | 1.15 |
| Isoleucine | 25 | 4.70 | 4.51 | 1.80 | 1.61 | 1.58 | 0.63 | 3.44 | 34.39 | 1.38 |
| Leucine | 55 | 8.07 | 7.75 | 1.41 | 2.51 | 2.46 | 0.45 | 5.82 | 58.18 | 1.06 |
| Lysine | 51 | 6.97 | 6.69 | 1.31 | 4.31 | 4.22 | 0.82 | 5.79 | 57.92 | 1.14 |
| Threonine | 27 | 4.00 | 3.84 | 1.42 | 1.96 | 1.92 | 0.71 | 3.14 | 31.37 | 1.16 |
| Tryptophan | 7 | 1.20 | 1.16 | 1.65 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.73 | 7.34 | 1.05 |
| Tyr + Phe | 47 | 8.19 | 7.86 | 1.67 | 2.97 | 2.91 | 0.62 | 6.05 | 60.55 | 1.29 |
| Valine | 32 | 5.28 | 5.07 | 1.58 | 3.22 | 3.16 | 0.99 | 4.37 | 43.70 | 1.37 |
| Main Food Groups Sources of Dietary Collagen Protein (NHANES 2001–2004) | Average Collagen Protein (% Dry Weight) | Average Daily Consumption | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Males | Females | ||||
| Food Group (g) | Collagen Protein (g) | Food Group (g) | Collagen Protein (g) | ||
| Beef, pork, veal, lamb, and game | 5.15 | 70.87 | 3.6 | 39.69 | 2.04 |
| Chicken, turkey, and other poultry | 1.40 | 42.52 | 0.6 | 34.02 | 0.48 |
| Seafood | 5.50 | 19.84 | 1.1 | 14.17 | 0.78 |
| Frankfurters, sausages and luncheon meats | 55.43 | 31.18 | 17.3 | 17.01 | 9.43 |
| Total, high consumers of frankfurters, sausages, and luncheon meats | 22.6 | 12.7 | |||
| Total, no consumers of frankfurters, sausages, and luncheon meats | 5.3 | 3.3 | |||
| Effective Daily Amounts of Functional Collagen Peptides | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Min 2.5 g | Max 15 g | ||
| (A) | RDA (g) | RDA (%) | RDA (%) |
| Men | 56 | 4 | 27 |
| Women | 46 | 5 | 33 |
| (B) | Protein intake * (g) | Protein intake (%) | Protein intake (%) |
| Men | 100 | 2.5 | 15 |
| Women | 67 | 4 | 22 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Paul, C.; Leser, S.; Oesser, S. Significant Amounts of Functional Collagen Peptides Can Be Incorporated in the Diet While Maintaining Indispensable Amino Acid Balance. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1079. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11051079
Paul C, Leser S, Oesser S. Significant Amounts of Functional Collagen Peptides Can Be Incorporated in the Diet While Maintaining Indispensable Amino Acid Balance. Nutrients. 2019; 11(5):1079. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11051079
Chicago/Turabian StylePaul, Cristiana, Suzane Leser, and Steffen Oesser. 2019. "Significant Amounts of Functional Collagen Peptides Can Be Incorporated in the Diet While Maintaining Indispensable Amino Acid Balance" Nutrients 11, no. 5: 1079. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11051079
APA StylePaul, C., Leser, S., & Oesser, S. (2019). Significant Amounts of Functional Collagen Peptides Can Be Incorporated in the Diet While Maintaining Indispensable Amino Acid Balance. Nutrients, 11(5), 1079. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11051079




