Impact of Maternal Nutrition and Perinatal Factors on Breast Milk Composition after Premature Delivery
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
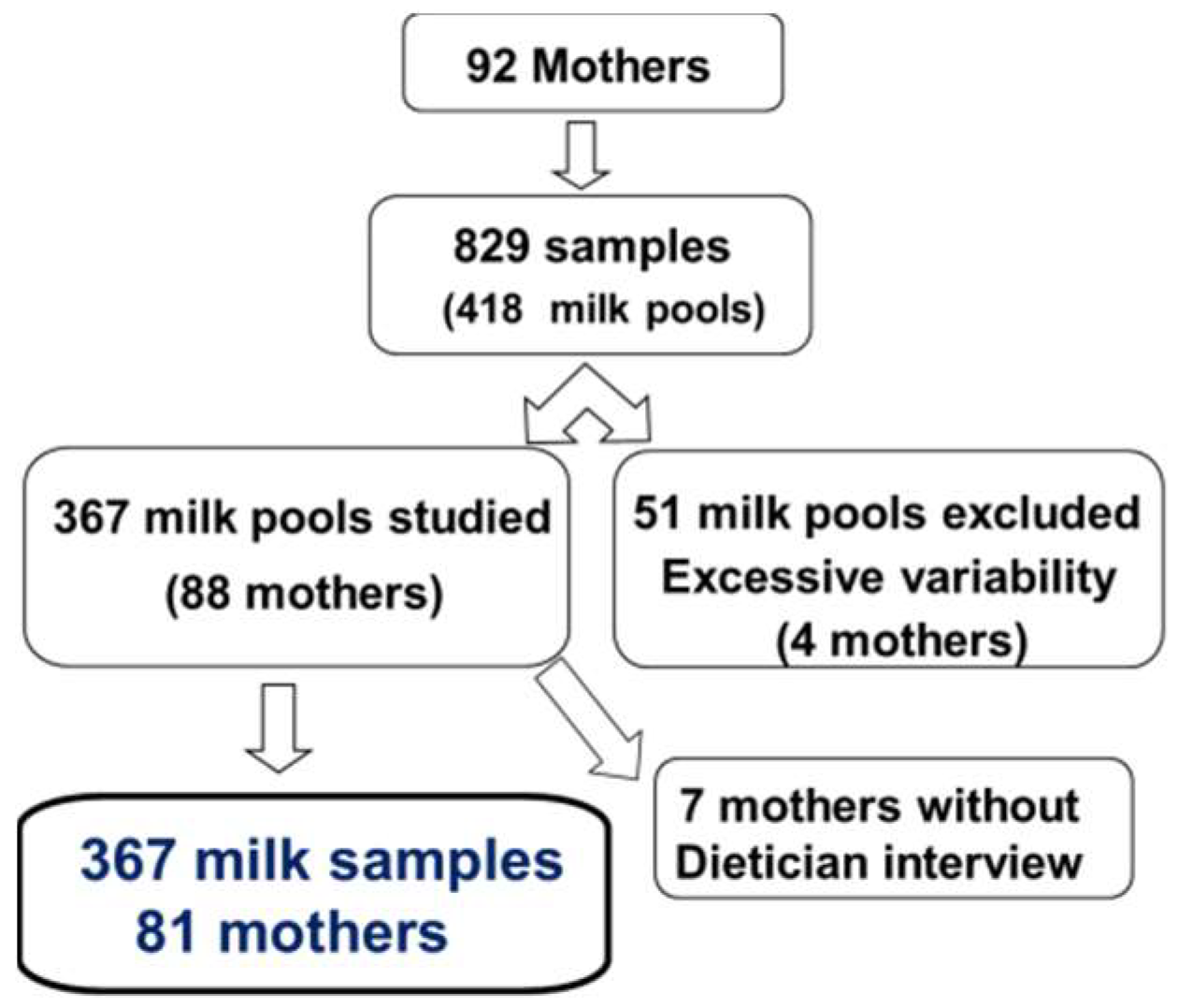
3.1. Description of the Studied Population
3.2. Maternal Nutritional Intake and Milk Composition
3.3. Perinatal Factors’ Effect on Milk Composition
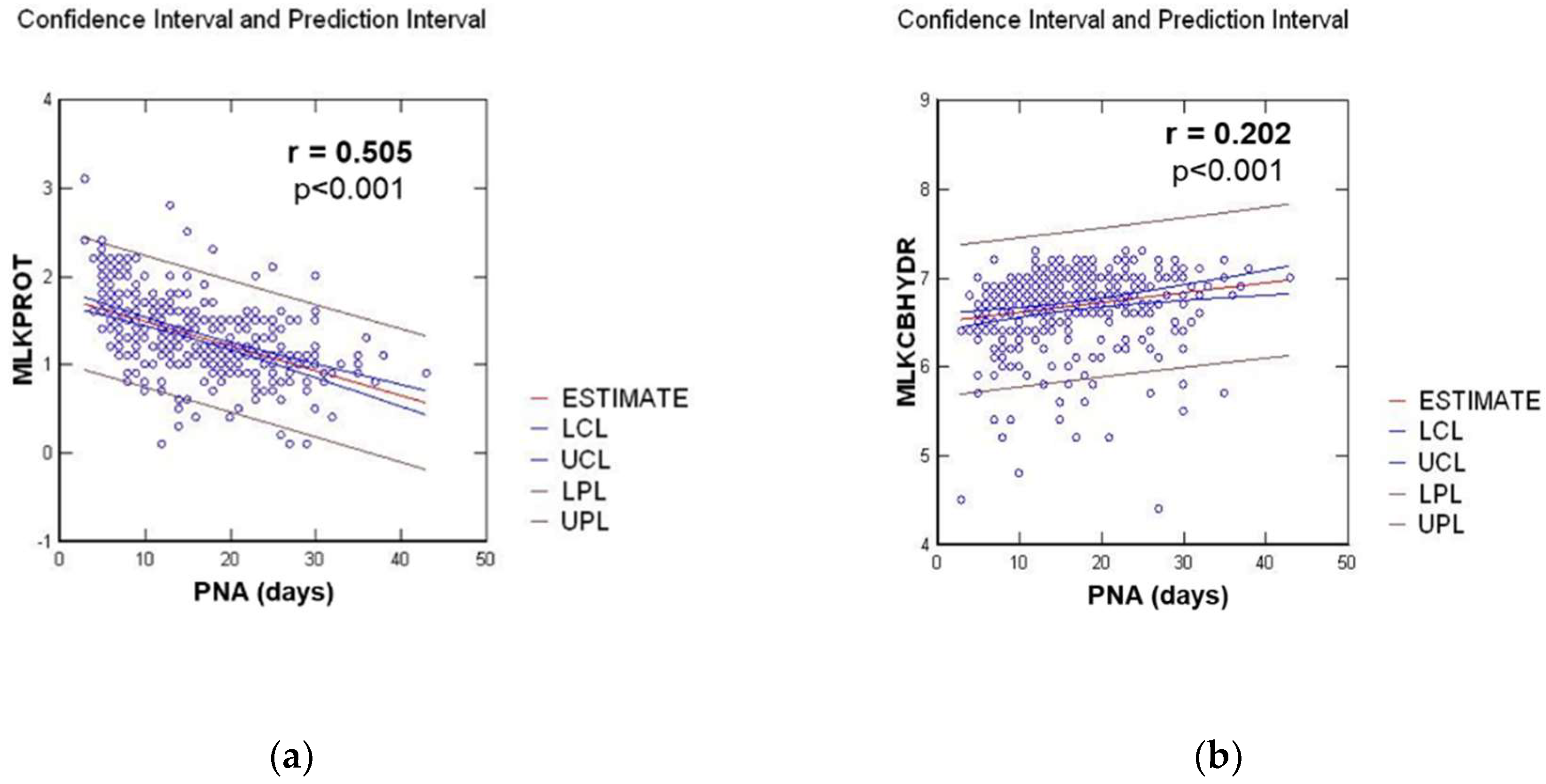
3.3.1. Postnatal Age Effect on Milk Composition
3.3.2. Perinatal Factors’ Impact on Milk Composition in Bivariate Analysis
3.3.3. Stepwise Multivariate Regression Analysis of Factors Associated with Milk Composition in Bivariate Analysis
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Agostoni, C.; Buonocore, G.; Carnielli, V.; De Curtis, M.; Darmaun, D.; Decsi, T.; Domellöf, M.; Embleton, N.; Fusch, C.; Genzel-Boroviczeny, O.; et al. Enteral Nutrient Supply for Preterm Infants: Commentary from the European Society of Paediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition Committee on Nutrition. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2010, 50, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, C.R.; Brown, Y.F.; Ehrenkranz, R.A.; O’Shea, T.M.; Allred, E.N.; Belfort, M.B.; McCormick, M.C.; Leviton, A. Nutritional Practices and Growth Velocity in the First Month of Life in Extremely Premature Infants. Pediatrics 2009, 124, 649–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McLeod, G.; Sherriff, J.; Nathan, E.; E Hartmann, P.; Simmer, K. Four-week nutritional audit of preterm infants born < 33 weeks gestation. J. Paediatr. Child Health 2013, 49, E332–E339. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mahajan, S.; Chawla, D.; Kaur, J.; Jain, S. Macronutrients in breastmilk of mothers of preterm infants. Indian Pediatr. 2017, 54, 635–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Embleton, N.E.; Pang, N.; Cooke, R.J. Postnatal Malnutrition and Growth Retardation: An Inevitable Consequence of Current Recommendations in Preterm Infants? Pediatrics 2001, 107, 270–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooke, R.J.; Ainsworth, S.B.; Fenton, A.C. Postnatal growth retardation: A universal problem in preterm infants. Arch. Dis. Child.-Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2004, 89, 428–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bzikowska-Jura, A.; Czerwonogrodzka-Senczyna, A.; Olędzka, G.; Szostak-Węgierek, D.; Weker, H.; Wesołowska, A. Maternal Nutrition and Body Composition During Breastfeeding: Association with Human Milk Composition. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malý, J.; Burianova, I.; Vitkova, V.; Ticha, E.; Navratilova, M.; Cermáková, E. Preterm human milk macronutrient concentration is independent of gestational age at birth. Arch. Dis. Child. Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2018, 104, F50–F56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buffin, R.; Decullier, E.; Loys, C.-M.; Hays, S.; Studzinsky, F.; Jourdes, E.; Picaud, J.-C.; De Halleux, V.; Rigo, J. Assessment of human milk composition using mid-infrared analyzers requires calibration adjustment. Am. J. Perinatol. 2017, 37, 552–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Xu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Sun, Y. Studies of the relation between the nutritional status of lactating mothers and milk composition as well as the milk intake and growth of their infants in Beijing. Pt. 4. The protein and amino acid content of breast milk. Ying Yang Xue Bao 1989, 11, 227–332. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mazurier, E.; Rigourd, V.; Perez, P.; Buffin, R.; Couedelo, L.; Vaysse, C.; Belcadi, W.; Sitta, R.; Nacka, F.; Lamireau, D.; et al. Effects of Maternal Supplementation with Omega-3 Precursors on Human Milk Composition. J. Hum. Lact. 2017, 33, 319–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hebel, P.; Francou, A.; Van Egroo, L.D.; Rougé, C.; Mares, P. Consommation alimentaire et apports nutritionnels chez les femmes allaitantes, en France. Cah. Nutr. Diét. 2018, 25, 303. [Google Scholar]
- Underwood, M.A. Human Milk for the Premature Infant. Pediatr. Clin. N. Am. 2013, 60, 189–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charpak, N.; Ruiz, J.; M Med Sci on behalf of the KMC Team. M Med Sci on behalf of the KMC Team. Breast milk composition in a cohort of pre-term infants’ mothers followed in an ambulatory programme in Colombia. Acta Paediatr. 2007, 96, 1755–1759. [Google Scholar]
- Bauer, J.; Gerss, J. Longitudinal analysis of macronutrients and minerals in human milk produced by mothers of preterm infants. Clin. Nutr. 2011, 30, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoneyama, K.; Goto, I.; Nagata, H. Relationship between volume and concentrations of various components of breast milk in early and 2-6 months lactation. Nihon Koshu Eisei Zasshi 1994, 41, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rochow, N.; Fusch, G.; Choi, A.; Chessell, L.; Elliott, L.; McDonald, K.; Kuiper, E.; Purcha, M.; Turner, S.; Chan, E.; et al. Target Fortification of Breast Milk with Fat, Protein, and Carbohydrates for Preterm Infants. J. Pediatr. 2013, 163, 1001–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bachour, P.; Yafawi, R.; Jaber, F.; Choueiri, E.; Abdel-Razzak, Z. Effects of Smoking, Mother’s Age, Body Mass Index, and Parity Number on Lipid, Protein, and Secretory Immunoglobulin A Concentrations of Human Milk. Breastfeed. Med. 2012, 7, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gidrewicz, D.A.; Fenton, T.R. A systematic review and meta-analysis of the nutrient content of preterm and term breast milk. BMC Pediatr. 2014, 14, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Nutrients Intake | Milk Calories | Milk Proteins | Milk Lipids | Milk Carbohydrates |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Log Energy | 0.110 * | 0.094 | 0.106 * | 0.034 |
| Protein | 0.01 | 0.03 | 0.01 | 0.04 |
| Fat | 0.03 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 0.03 |
| Carbohydrates | 0.131 ** | 0.109 * | 0.127 * | 0.035 |
| Week | 1 (n = 52) | 2 (n = 125) | 3 (n = 91) | 4 (n = 68) | 5 (n = 31) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Protein | 1.78 ± 0.39 * | 1.40 ± 0.40 * | 1.26 ± 0.34 * | 1.08 ± 0.36 * | 1.05 ± 0.40 |
| Lipids | 3.23 ± 0.80 | 3.58 ± 0.98 | 3.59 ± 0.97 | 3.41 ± 0.96 | 3.40 ± 1.06 |
| CHO | 6.50 ± 0.43 * | 6.66 ± 0.38 * | 6.70 ± 0.46 * | 6.81 ± 0.44 * | 6.75 ± 0.44 |
| Milk Content (Mean, g/100 mL) | Smoking | Antenatal Steroids | Birth Weight (Linear Regression: r) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yes | No | Yes | No | ||
| Lipids | 3.10 | 3.59 * | 3.6 * | 3.1 | 0.082 |
| Carbohydrates | 6.57 | 6.71 * | 6.7 | 6.6 | −0.259 * |
| Protein | 1.34 | 1.33 | 1.3 | 1.2 | −0.318 * |
| Calories | 62.8 | 67.8 * | 67.6 * | 61.9 | −0.106 |
| Milk Content | Postnatal Age | Carbohydrate Intake | Smoking | No Steroids | Weight Gain |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lipids (r2 = 0.087) | NS | 1.279 * | −0.557 * | NS | NS |
| Carbohydrates (r2 = 0.071) | 0.012 * | NS | −0.167 * | NS | NS |
| Protein (r2 = 0.299) | −0.028 * | 0.449 * | NS | −0.066 * | NS |
| Calories (r2 = 0.101) | NS | 14.053 * | −5.901 * | NS | NS |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hascoët, J.-M.; Chauvin, M.; Pierret, C.; Skweres, S.; Van Egroo, L.-D.; Rougé, C.; Franck, P. Impact of Maternal Nutrition and Perinatal Factors on Breast Milk Composition after Premature Delivery. Nutrients 2019, 11, 366. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11020366
Hascoët J-M, Chauvin M, Pierret C, Skweres S, Van Egroo L-D, Rougé C, Franck P. Impact of Maternal Nutrition and Perinatal Factors on Breast Milk Composition after Premature Delivery. Nutrients. 2019; 11(2):366. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11020366
Chicago/Turabian StyleHascoët, Jean-Michel, Martine Chauvin, Christine Pierret, Sébastien Skweres, Louis-Dominique Van Egroo, Carole Rougé, and Patricia Franck. 2019. "Impact of Maternal Nutrition and Perinatal Factors on Breast Milk Composition after Premature Delivery" Nutrients 11, no. 2: 366. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11020366
APA StyleHascoët, J.-M., Chauvin, M., Pierret, C., Skweres, S., Van Egroo, L.-D., Rougé, C., & Franck, P. (2019). Impact of Maternal Nutrition and Perinatal Factors on Breast Milk Composition after Premature Delivery. Nutrients, 11(2), 366. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11020366





