Dietary Determinants of Metabolic Syndrome Parameters Differ by Gender in College Students
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Collection and Analysis Methods
2.2. Anthropometrics
2.3. Diet Records
2.4. Blood Sample Collection and Testing
2.5. Statistical Analyses
2.5.1. Decision Trees
2.5.2. Linear Regression Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Demographics and Prevalence of MetS
3.2. My Plate Food Group Consumption and Physical Activity
3.3. Metabolic Syndrome Parameters Decision Trees
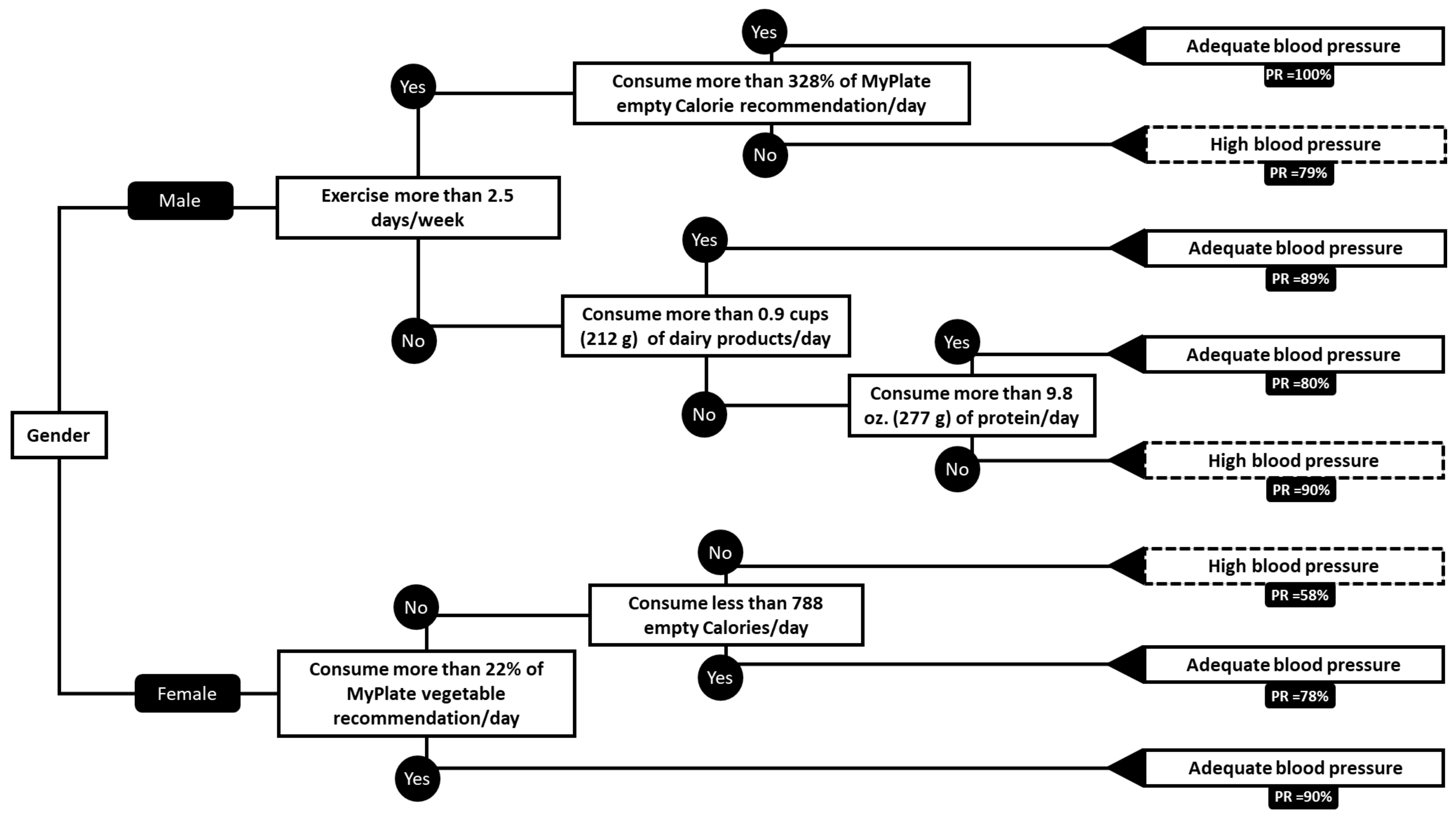
3.3.1. Blood Pressure
Results in Male Blood Pressure
Results in Female Blood Pressure
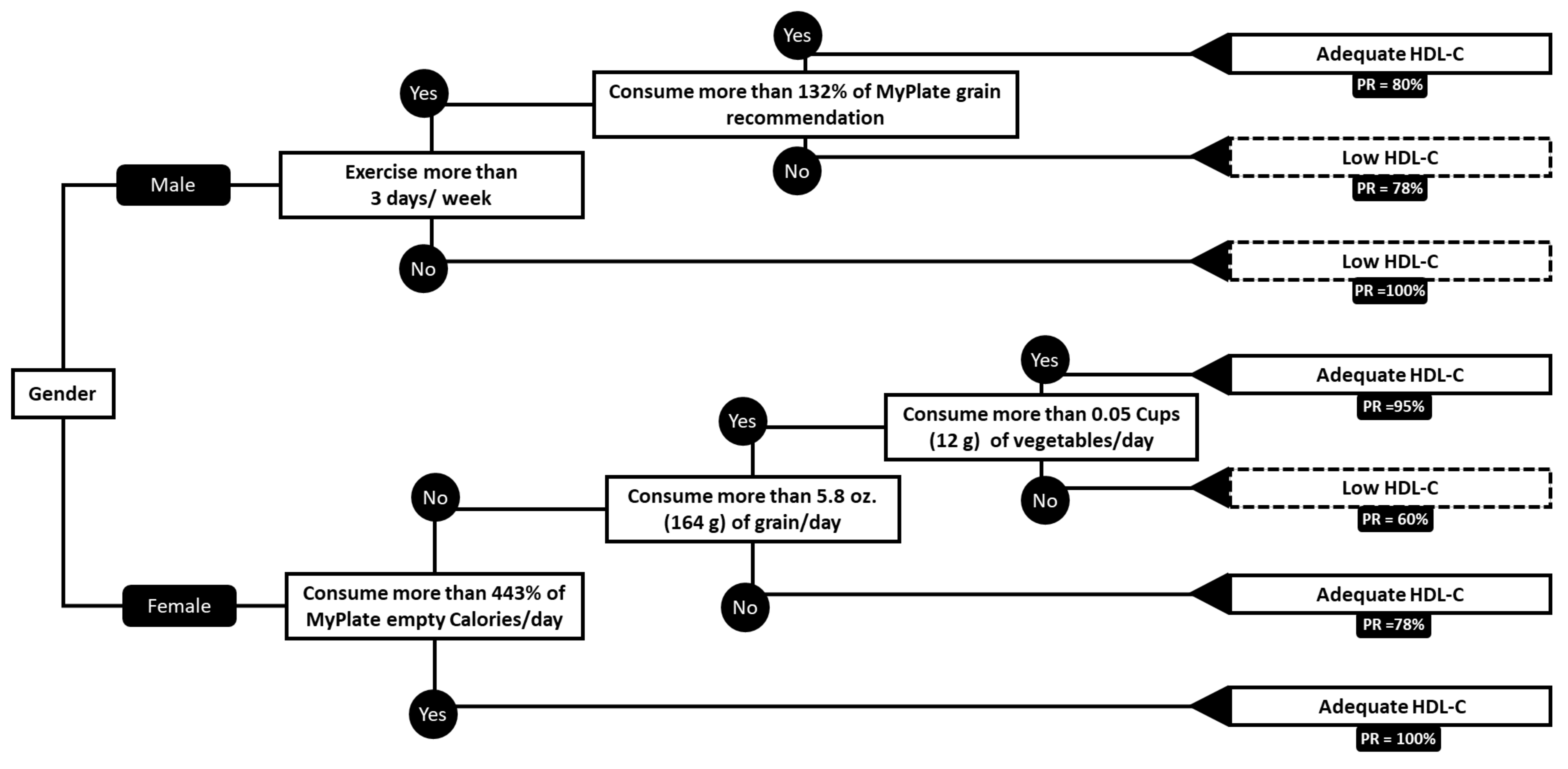
3.3.2. HDL-Cholesterol
Results in Male HDL-C
Results in Female HDL-C
3.4. Regression Analysis
3.4.1. Waist Circumference in Males
3.4.2. Diastolic Blood Pressure in Males
3.5. Prediction and Modeling of Other MetS Parameters
4. Discussion
4.1. Decision Trees
4.1.1. Male Blood Pressure
Exercise
Dairy
Protein
Empty Calories
4.1.2. Female Blood Pressure
Vegetables
Empty Calories
4.1.3. Male HDL-Cholesterol
Exercise
Grains
4.1.4. Female HDL-Cholesterol
Empty Calories
Grains
Vegetables
4.2. Regression Analysis
4.2.1. Male Waist Circumference
4.2.2. Male Diastolic Blood Pressure
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jacobson, T.A.; Ito, M.K.; Maki, K.C.; Orringer, C.E.; Bays, H.E.; Jones, P.H.; McKenney, J.M.; Grundy, S.M.; Gill, E.A.; Wild, R.A.; et al. National Lipid Association recommendations for patient-centered management of dyslipidemia: Part 1—Executive summary. J. Clin. Lipidol. 2014, 8, 473–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, J.X. Metabolic Syndrome Prevalence by Race/Ethnicity and Sex in the United States, National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 1988–2012. Prev. Chronic Dis. 2017, 14, E24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swarup, S.; Zeltser, R. Metabolic Syndrome. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Metabolic Syndrome | National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI). Available online: https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health-topics/metabolic-syndrome. (accessed on 2 July 2019).
- Heart Disease Facts & Statistics | cdc.gov. 9 October 2018. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/heartdisease/facts.htm (accessed on 3 July 2019).
- Stroke Statistics | Internet Stroke Center. Available online: http://www.strokecenter.org/patients/about-stroke/stroke-statistics/ (accessed on 2 July 2019).
- CDC. CDC Press Releases. 1 January 2016. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/media/releases/2017/p0718-diabetes-report.html. (accessed on 2 July 2019).
- About Us. Choose MyPlate. 4 November 2015. Available online: https://www.choosemyplate.gov/about-us (accessed on 4 July 2019).
- MyPlate Plan, Choose MyPlate. 3 April 2015. Available online: https://www.choosemyplate.gov/MyPlatePlan. (accessed on 7 July 2019).
- Empty Calories: Do They Add up? Obesity Action Coalition. Available online: https://www.obesityaction.org/community/article-library/empty-calories-do-they-add-up/. (accessed on 4 July 2019).
- Quinlan, J.J.; Lee, L.; Mangroo, A.; Vierow, K. Evaluation of MyPlate as a Dietary Learning Tool among Young Adults. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2012, 112, A85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wardle, J.; Haase, A.M.; Steptoe, A.; Nillapun, M.; Jonwutiwes, K.; Bellisle, F. Gender differences in food choice: The contribution of health beliefs and dieting. Ann. Behav. Med. 2004, 27, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asarian, L.; Geary, N. Sex differences in the physiology of eating. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2013, 305, R1215–R1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manippa, V.; Padulo, C.; van der Laan, L.N.; Brancucci, A. Gender Differences in Food Choice: Effects of Superior Temporal Sulcus Stimulation. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Factors That Influence Our Food Choices: (EUFIC). Available online: https://www.eufic.org/en/healthy-living/article/the-determinants-of-food-choice (accessed on 8 July 2019).
- Berbesque, J.C.; Marlowe, F.W. Sex Differences in Food Preferences of Hadza Hunter-Gatherers. Evol. Psychol. 2009, 7, 147470490900700400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, A.M.; Loughead, J.; Bakizada, Z.M.; Hopkins, C.M.; Geliebter, A.; Gur, R.C.; Wadden, T.A. Sex/Gender Differences in Neural Correlates of Food Stimuli: A Systematic Review of Functional Neuroimaging Studies. Obes. Rev. 2017, 18, 687–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davy, S.R.; Benes, B.A.; Driskell, J.A. Sex differences in dieting trends, eating habits, and nutrition beliefs of a group of midwestern college students. J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 2006, 106, 1673–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Killgore, W.D.S.; Yurgelun-Todd, D.A. Sex differences in cerebral responses to images of high versus low-calorie food. Neuroreport 2010, 21, 354–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klump, K.L.; Racine, S.; Hildebrandt, B.; Sisk, C.L. Sex differences in binge eating patterns in male and female adult rats. Int. J. Eat. Disord. 2013, 46, 729–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowen, D.J. Taste and food preference changes across the course of pregnancy. Appetite 1992, 3, 233–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- About Metabolic Syndrome. Available online: https://www.heart.org/en/health-topics/metabolic-syndrome/about-metabolic-syndrome (accessed on 24 June 2019).
- Choose MyPlate. 3 April 2015. Available online: https://www.choosemyplate.gov/ (accessed on 7 July 2019).
- Saneei, P.; Salehi-Abargouei, A.; Esmaillzadeh, A.; Azadbakht, L. Influence of Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension (DASH) diet on blood pressure: A systematic review and meta-analysis on randomized controlled trials. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2014, 24, 1253–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiferaw, B.; Verrill, L.; Booth, H.; Zansky, S.M.; Norton, D.M.; Crim, S.; Henao, O.L. Sex-based differences in food consumption: Foodborne Diseases Active Surveillance Network (FoodNet) Population Survey, 2006–2007. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2012, 54, S453–S457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Everett, B.; Zajacova, A. Gender Differences in Hypertension and Hypertension Awareness among Young Adults. Biodemography Soc. Biol. 2015, 61, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariano, I.M.; Domingos, D.C.; Ribeiro, A.L.; Peçanha, T.; Simões, H.G.; Puga, G.M. Sex and exercise-mode differences in post-exercise blood pressure and heart rate variability responses during a workday. Mot. Rev. De Educ. Física 2019, 25, e101930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brito, A.D.; Brasileiro-Santos, M.D.S.; de Oliveira, C.V.C.; da Nóbrega, T.K.S.; Forjaz, C.L.D.; Santos, A.D. High-Intensity Resistance Exercise Promotes Postexercise Hypotension Greater than Moderate Intensity and Affects Cardiac Autonomic Responses in Women Who Are Hypertensive. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2015, 29, 3486–3493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokkinos, P.F.; Fernhall, B. Physical activity and high density lipoprotein cholesterol levels: What is the relationship? Sports Med. 1999, 28, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McArdle, W.D.; Katch, F.I.; Katch, V.L. Essentials of Exercise Physiology, 5th ed.; Lippincott Williams and Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2016; p. 924. [Google Scholar]
- American College of Sports Medicine Position Stand. Exercise and Hypertension.-PubMed-NCBI. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15076798 (accessed on 30 September 2019).
- Physical Activity and the Prevention of Hypertension. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3901083/ (accessed on 30 September 2019).
- Associations between Dairy Intake and Metabolic Risk Parameters in a Health. EBSCOhost. Available online: https://web-b-ebscohost-com.hal.weber.edu/ehost/detail/detail?vid=4&sid=a13a7ffc-a0de-45b3-a638-dec374f0fae8%40pdc-v-sessmgr03&bdata=JnNpdGU9ZWhvc3QtbGl2ZQ%3d%3d#AN=99368217&db=asn (accessed on 30 September 2019).
- Dairy Consumption is Inversely Associated with the Prevalence of the Metabolic Syndrome in Tehranian Adults.-PubMed-NCBI. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16155263 (accessed on 30 September 2019).
- Blood Pressure and Nutrient Intake in the United States.-PubMed-NCBI. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/6729459 (accessed on 30 September 2019).
- Plasma Osmolality -An Overview | ScienceDirect Topics. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/medicine-and-dentistry/plasma-osmolality (accessed on 4 October 2019).
- Dietary Protein and Amino Acids Intake and its Relationship with Blood Pres: EBSCOhost. Available online: https://web-b-ebscohost-com.hal.weber.edu/ehost/detail/detail?vid=7&sid=8cfde8ae-e126-4b6c-8414-78ef53c65d82%40pdc-v-sessmgr02&bdata=JnNpdGU9ZWhvc3QtbGl2ZQ%3d%3d#AN=108935787&db=asn (accessed on 30 September 2019).
- Proteins and Amino Acids: Effects on the Sympathetic Nervous System and Blood Pressure Regulation. PubMed-NCBI. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/2875780 (accessed on 30 September 2019).
- Dietary Protein and Blood Pressure: A Systematic Review. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2920332/#pone.0012102-Anderson2 (accessed on 30 September 2019).
- Dietary Protein Intake and Blood Pressure: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials.-PubMed-NCBI. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23035142 (accessed on 30 September 2019).
- Swain, D.P.; Franklin, B.A. Comparison of Cardioprotective Benefits of Vigorous Versus Moderate Intensity Aerobic Exercise. Am. J. Cardiol. 2006, 97, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marrugat, J.; Elosua, R.; Covas, M.-I.; Molina, L.; Rubiés-Prat, J. Amount and intensity of physical activity, physical fitness, and serum lipids in men. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1996, 143, 562–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, F.B.; Sigal, R.J.; Rich-Edwards, J.W.; Colditz, G.A.; Solomon, C.G.; Willett, W.C.; Speizer, F.E.; Manson, J.E. Walking compared with vigorous physical activity and risk of type 2 diabetes in women: A prospective study. J. Am. Med Assoc. 1999, 282, 1433–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, J.; Wylie-Rosett, J.; Cohen, H.W.; Kaplan, R.C.; Alderman, M.H. Exercise, body mass index, caloric intake, and cardiovascular mortality. Am. J. Prev. Med. 2003, 25, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Effects of Oral Potassium on Blood Pressure. Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Clinical Trials.-PubMed-NCBI. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9168293 (accessed on 29 September 2019).
- Effects of Fruit and Vegetable Consumption on Plasma Antioxidant Concentrat: EBSCOhost. Available online: https://web-b-ebscohost-com.hal.weber.edu/ehost/pdfviewer/pdfviewer?vid=7&sid=489cec4c-706e-43b3-9093-dbc9d26d81e4%40pdc-v-sessmgr03 (accessed on 29 September 2019).
- A Clinical Trial of the Effects of Dietary Patterns on Blood Pressure | NEJM. Available online: https://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJM199704173361601 (accessed on 29 September 2019).
- Ascorbic Acid Status and Subsequent Diastolic and Systolic Blood Pressure.-PubMed-NCBI. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11230282 (accessed on 29 September 2019).
- Abbasy, M.A. The Diuretic Action of Vitamin C. Biochem. J. 1937, 31, 339–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Big Doses of Vitamin C May Lower Blood Pressure. 18 April 2012. Available online: https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/news/media/releases/big_doses_of_vitamin_c_may_lower_blood_pressure (accessed on 4 October 2019).
- Endogenous Nitric Oxide Synthase Inhibitor: A Novel Marker of Atherosclerosis.-PubMed-NCBI. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10069780 (accessed on 29 September 2019).
- Nitric Oxide and Atherosclerosis: An Update.-PubMed-NCBI. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16684613 (accessed on 29 September 2019).
- Association between Usual Sodium and Potassium Intake and Blood Pressure an: EBSCOhost. Available online: https://web-b-ebscohost-com.hal.weber.edu/ehost/detail/detail?vid=40&sid=489cec4c-706e-43b3-9093-dbc9d26d81e4%40pdc-v-sessmgr03&bdata=JnNpdGU9ZWhvc3QtbGl2ZQ%3d%3d#AN=94477799&db=asn. (accessed on 29 September 2019).
- Adrogué, H.J. Sodium and Potassium in the Pathogenesis of Hypertension. N. Engl. J. Med. 2007, 356, 1966–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wells, J.R. Medium-intensity rhythmic exercise and high-intensity resistance exercise reduces fasting plasma cholesterol/HDL Ratio. Proc. Physiol. Soc. 2013, 37, 719P–720P. [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein, M.S.; Constanza, M.C.; James, R.W.; Morris, M.A.; Cambien, F.; Raoux, S.; Morabia, A. No Physical Activity × CETP 1b.-629 Interaction Effects on Lipid Profile. Med Sci Sports Exerc 2003, 35, 1124–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crawford, P.; Paden, S.L. What is the dietary treatment for low HDL cholesterol? J. Fam. Pract. 2006, 55, 1076–1078. [Google Scholar]
- Lichtenstein, A.H.; Appel, L.J.; Brands, M.; Carnethon, M.; Daniels, S.; Franch, H.A.; Franklin, B.; Kris-Etherton, P.; Harris, W.S.; Howard, B.; et al. Diet and lifestyle recommendations revision 2006: A scientific statement from the American Heart Association Nutrition Committee. Circulation 2006, 114, 82–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Relationship between Carbohydrate Quality and the Prevalence of Metab: EBSCOhost. Available online: https://web-b-ebscohost-com.hal.weber.edu/ehost/detail/detail?vid=18&sid=8cfde8ae-e126-4b6c-8414-78ef53c65d82%40pdc-v-sessmgr02&bdata=JnNpdGU9ZWhvc3QtbGl2ZQ%3d%3d#AN=128598001&db=asn. (accessed on 30 September 2019).
- DiMarco, D.M.; Missimer, A.; Murillo, A.G.; Lemos, B.S.; Malysheva, O.V.; Caudill, M.A.; Blesso, C.N.; Fernandez, M.L. Intake of up to 3 Eggs/Day Increases HDL Cholesterol and Plasma Choline While Plasma Trimethylamine-N-oxide is Unchanged in a Healthy Population. Lipids 2017, 52, 255–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drouin-Chartier, J.P.; Côté, J.A.; Labonté, M.È.; Brassard, D.; Tessier-Grenier, M.; Desroches, S.; Couture, P.; Lamarche, B. Comprehensive Review of the Impact of Dairy Foods and Dairy Fat on Cardiometabolic Risk. Adv. Nutr. 2016, 7, 1041–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Sonoda, S.; Liu, H. Unprocessed red meat intakes are associated with increased inflammation, triglycerides and HDL cholesterol in past smokers. Nutr. Diet. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jenkins, D.; Wolever, T.; Rao, A.V.; Hegele, R.A.; Mitchell, S.J.; Ransom, T.; Boctor, D.L.; Spadafora, P.J.; Jenkins, A.L.; Mehling, C.; et al. Effect on Blood Lipids of Very High Intakes of Fiber in Diets Low in Saturated Fat and Cholesterol. N. Engl. J. Med. 1993, 329, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beneficial Effect of Higher Dietary Fiber Intake on Plasma HDL-C and TC/HDL-C Ratio among Chinese Rural-to-Urban Migrant Workers. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4454936/ (accessed on 30 September 2019).
- Obesity Education Initiative Electronic Textbook--Treatment Guidelines. Available online: https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health-pro/guidelines/current/obesity-guidelines/e_textbook/txgd/4142.htm (accessed on 14 October 2019).
- Physical Activity.Obesity Prevention Source. 21 October 2012. Available online: https://www.hsph.harvard.edu/obesity-prevention-source/obesity-causes/physical-activity-and-obesity/ (accessed on 14 October 2019).
- Staiano, A.E.; Reeder, B.A.; Elliott, S.; Joffres, M.R.; Pahwa, P.; Kirkland, S.A.; Paradis, G.; Katzmarzyk, P.T. Physical activity level, waist circumference, and mortality. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 2012, 37, 1008–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
| Gender | WC | HDL–C | TG | BP | BG | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Range (cm) | Prev % | Range (mg/dL) | Prev % | Range (mg/dL) | Prev % | Range (mmHg) | Prev % | Range (mg/dL) | Prev % | |
| Male | 62–144 | 13.1 | 15–111 | 50.3 | 45–577 | 20.9 | 71/44–155/106 | 54.3 | 69–119 | 12.4 |
| Female | 60–181 | 19.4 | 15–149 | 43.4 | 45–613 | 14.2 | 88/45–150/111 | 37.9 | 67–214 | 7.7 |
| Variable | Overall | With MetS | Without MetS | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M | F | M | F | M | F | |
| Age (years) | 23 ± 1.4 | 25 ± 0.7 | 24 ± 7.1 | 30 ± 0 | 23 ± 1.4 | 24 ± 0.1 |
| WC (cm) | 86.3 ± 14.5 | 79.8 ± 0.7 | 100.3 ± 11.3 | 103.2 ± 12.0 | 82.6 ± 16.6 | 76.1 ± 0.1 |
| HDL-C (mg/dL) | 41.0 ± 6.3 | 53.1 ± 2.1 | 33.2 ± 36.7 | 41.4 ± 2.8 | 43.1 ± 6.3 | 55.1 ± 2.2 |
| TG (mg/dL) | 111.6 ± 52.3 | 104.3 ± 17.6 | 207.6 ± 241.8 | 182.1 ± 42.4 | 85.1 ± 52.3 | 90.9 ± 17.7 |
| BP (mmHg) | 128/81 ± 7.1/8.5 | 113/79 ± 10.2/2.8 | 138/89 ± 4.9/6.7 | 124/89 ± 6.0/12.7 | 125/79 ± 4.5/8.4 | 111/77 ± 10.3/2.8 |
| BG (mg/dL) | 91.9 ± 2.8 | 89.0 ± 10.6 | 96 ± 0 | 100 ± 33.2 | 91 ± 2.8 | 87 ± 10.6 |
| Gender | Fruit | Vegetables | Grain | Protein | Dairy | Empty Calories | Exercise | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cups | % Goal | Cups | % Goal | Ounces | % Rec | Ounces | % Goal | Ounces | % Goal | Calories | % Goal | Days/Week | |
| Male | 1.0 ± 0.1 | 47 | 0.8 ± 0.1 | 25 | 6.8 ± 0.3 | 79 | 11.7 ± 0.5 | 129 | 1.9 ± 0.1 | 64 | 764.2 ± 89.6 | 179 | 3.4 ± 0.09 |
| Female | 1.2 ± 0.2 | 50 | 1.1 ± 0.1 | 42 | 5.6 ± 0.1 | 77 | 6.0 ± 0.2 | 105 | 1.6 ± 0.1 | 53 | 653.2 ± 38.3 | 223 | 3.0 ± 0.05 |
| Variable | Regression Coefficient | Standard Error | t-Value | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Constant | 15.8 | 14.8 | 1.9 | 0.28 |
| DBP (mm/Hg) | 0.6 | 0.1 | 4.6 | <0.001 |
| TG (mg/dL) | 0.04 | 0.01 | 3.9 | <0.001 |
| Glucose (mg/dL) | 0.3 | 0.12 | 2.4 | 0.01 |
| Exercise (days/week) | −2.1 | 0.8 | −2.4 | 0.02 |
| Empty Calories (%) | −0.02 | 0.008 | −2.6 | 0.009 |
| Variable | Regression Coefficient | Standard Error | t-Value | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Constant | 44.7 | 4.53 | 9.9 | <0.001 |
| WC (cm) | 0.4 | 0.05 | 7.6 | <0.001 |
| TG (mg/dL) | 0.04 | 0.01 | 2.4 | 0.02 |
| Vegetables (%) | −0.05 | 0.02 | −2.3 | 0.02 |
| Dairy (%) | −0.02 | 0.01 | −2.1 | 0.04 |
| Protein (%) | 0.005 | 0.002 | 2.3 | 0.02 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Saltzgiver, S.; Nielson, A.; Costello, H.; Baker, A.; Chan, J.; Aguilar, D. Dietary Determinants of Metabolic Syndrome Parameters Differ by Gender in College Students. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2892. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11122892
Saltzgiver S, Nielson A, Costello H, Baker A, Chan J, Aguilar D. Dietary Determinants of Metabolic Syndrome Parameters Differ by Gender in College Students. Nutrients. 2019; 11(12):2892. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11122892
Chicago/Turabian StyleSaltzgiver, Sara, Alexander Nielson, Heidi Costello, Adam Baker, Julian Chan, and David Aguilar. 2019. "Dietary Determinants of Metabolic Syndrome Parameters Differ by Gender in College Students" Nutrients 11, no. 12: 2892. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11122892
APA StyleSaltzgiver, S., Nielson, A., Costello, H., Baker, A., Chan, J., & Aguilar, D. (2019). Dietary Determinants of Metabolic Syndrome Parameters Differ by Gender in College Students. Nutrients, 11(12), 2892. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11122892




