Relevance of Leptin and Other Adipokines in Obesity-Associated Cardiovascular Risk
Abstract
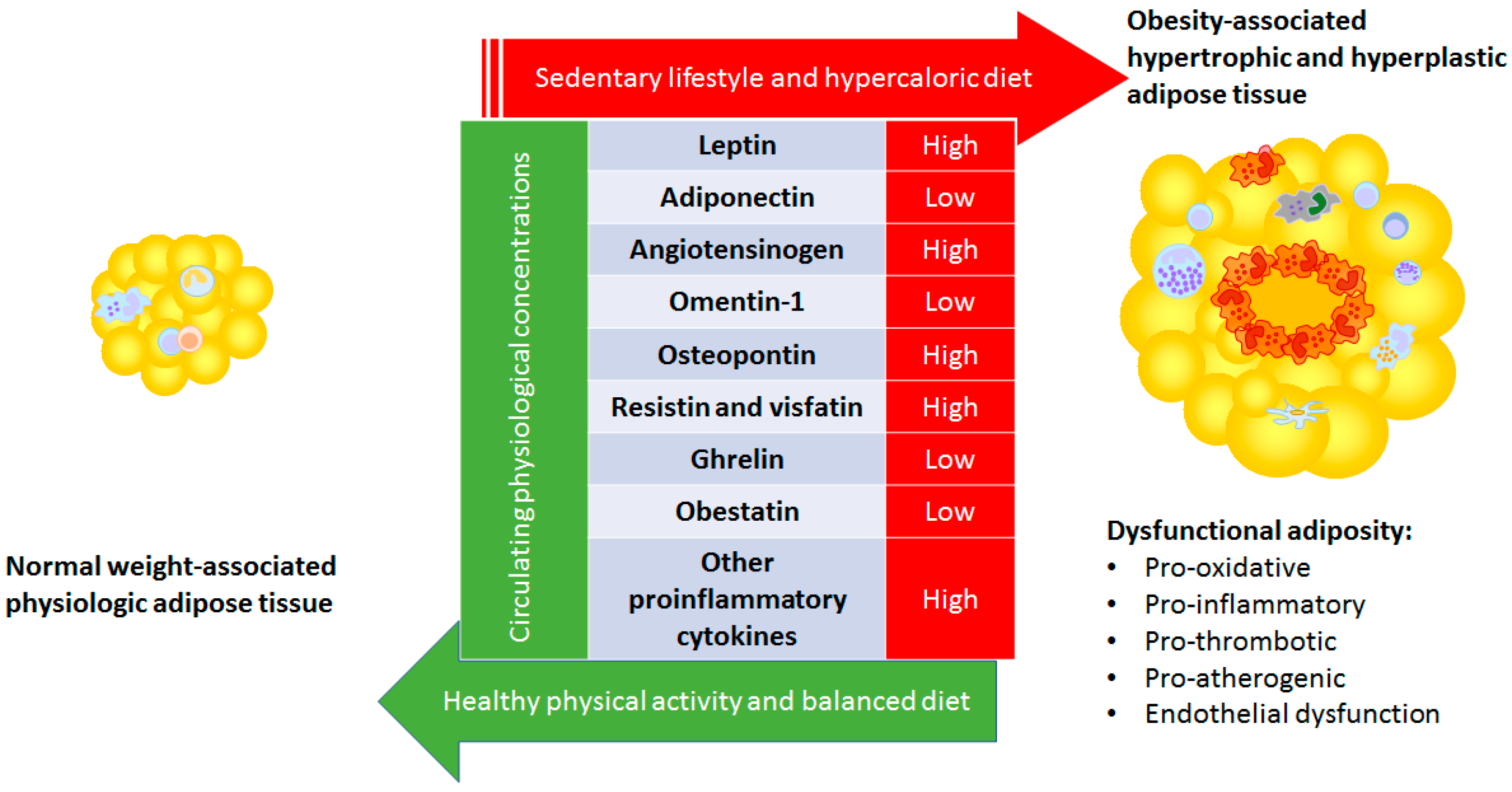
1. Introduction
2. Adipose Tissue Physiology
3. Specific Adipokines
3.1. Leptin
3.2. Adiponectin
3.3. Angiotensinogen
3.4. Omentin-1
3.5. Osteopontin
3.6. RESISTIN and VISFATIN
3.7. Ghrelin
3.8. Obestatin
3.9. Other Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines
4. Conclusions
5. Review Criteria
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- The GBD 2015 Obesity Collaborators. Health Effects of Overweight and Obesity in 195 Countries over 25 Years. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 13–27. Available online: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28604169 (accessed on 11 July 2017). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- NCD Risk Factor Collaboration. Worldwide Trends in Body-Mass Index, Underweight, Overweight, and Obesity From 1975 to 2016: A Pooled Analysis of 2416 Population-Based Measurement Studies in 128·9 Million Children, Adolescents, and Adults. Lancet (Lond. Engl.) 2017, 390, 2627–2642. Available online: https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0140673617321293 (accessed on 8 November 2018). [CrossRef]
- Fruhbeck, G.; Toplak, H.; Woodward, E.; Yumuk, V.; Maislos, M.; Oppert, J.M. Executive Committee of the European Association for the Study of Obesity Obesity: The gateway to ill Health-An EASO Position Statement on a Rising Public Health, Clinical and Scientific Challenge in Europe. Obes. Facts 2013, 6, 117–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ARoberto, C.; Swinburn, B.; Hawkes, C.; Huang, T.T.K.; ACosta, S.; Ashe, M.; Zwicker, L.; Cawley, J.H.; Brownell, K.D. Patchy Progress on Obesity Prevention: Emerging Examples, Entrenched Barriers, and New Thinking. Lancet 2015, 385, 2400–2409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catalan, V.; Gomez-Ambrosi, J.; Rodriguez, A.; Fruhbeck, G. Adipose Tissue Immunity and Cancer. Front Physiol. 2013, 4, 275. Available online: http://journal.frontiersin.org/article/10.3389/fphys.2013.00275/abstract (accessed on 17 July 2019). [CrossRef]
- Gomez-Ambrosi, J.; Catalan, V.; Rodriguez, A.; Andrada, P.; Ramirez, B.; Ibanez, P.; Vila, N.; Romero, S.; Margall, M.A.; Gil, M.J.; et al. Increased Cardiometabolic Risk Factors and Inflammation in Adipose Tissue in Obese Subjects Classified as Metabolically Healthy. Diabetes Care 2014, 37, 2813–2821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fruhbeck, G.; Kiortsis, D.N.; Catalan, V. Precision medicine: Diagnosis and Management of Obesity. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2017, 6, 164–166. Available online: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28919063 (accessed on 5 February 2018). [CrossRef]
- Alamuddin, N.; Bakizada, Z.; Wadden, T.A. Management of Obesity. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 4295–4305. Available online: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26868660 (accessed on 19 November 2018). [CrossRef]
- Eckel, R.H.; Krauss, R.M. American Heart Association Call to Action: Obesity as a Major Risk Factor for Coronary Heart Disease. Circulation 1998, 97, 2099–2100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogers, R.P.; Bemelmans, W.J.E.; Hoogenveen, R.T.; Boshuizen, H.C.; Woodward, M.; Knekt, P.; Van Dan, R.M.; Hu, F.B.; Visscher, T.L.S.; Menotti, A.; et al. Association of Overweight with Increased Risk of Coronary Heart Disease Partly Independent of Blood Pressure and Cholesterol Levels: A Meta-Analysis of 21 Cohort Studies Including more than 300 000 persons. Arch. Intern. Med. 2007, 167, 1720–1728. Available online: http://archinte.jamanetwork.com/article.aspx?doi=10.1001/archinte.167.16.1720 (accessed on 6 November 2018). [CrossRef]
- Ahima, R.S.; Lazar, M.A. Physiology. The Health Risk of Obesity--Better Metrics Imperative. Science 2013, 341, 856–858. Available online: http://www.sciencemag.org/cgi/doi/10.1126/science.1241244 (accessed on 12 November 2018). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stefan, N.; Haring, H.U.; Schulze, M.B. Metabolically Healthy Obesity: The Low-Hanging Fruit in Obesity Treatment? Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2018, 6, 249–258. Available online: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28919065 (accessed on 1 October 2019). [CrossRef]
- Vecchie, A.; Dallegri, F.; Carbone, F.; Bonaventura, A.; Liberale, L.; Portincasa, P.; Frühbeck, G.; Montecucco, F. Obesity Phenotypes and their Paradoxical Association with Cardiovascular Diseases. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2018, 48, 6–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez, A.; Ezquerro, S.; Mendez-Gimenez, L.; Becerril, S.; Fruhbeck, G.; Fruhbeck, G. Revisiting the Adipocyte: A Model for Integration of Cytokine Signaling in the Regulation of Energy Metabolism. Am. J. Physiol. Metab. 2015, 309, E691–E714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fruhbeck, G.; Gomez-Ambrosi, J. Control of Body Weight: A Physiologic and Transgenic Perspective. Diabetologia 2003, 46, 143–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tchernof, A.; Despres, J.P. Pathophysiology of Human Visceral Obesity: An Update. Physiol. Rev. 2013, 93, 359–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusuf, S.; Hawken, S.; Ounpuu, S.; Steven, H.; Rumboldt, Z.; Ounpuu, S.; Bautista, L.; Franzosi, M.G.; Commerford, P.; Tanomsup, S.; et al. Obesity and the Risk of Myocardial Infarction in 27,000 Participants From 52 Countries: A Case-Control Study. Lancet (Lond. Engl.) 2005, 366, 1640–1649. Available online: http://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0140673605676635 (accessed on 7 November 2018). [CrossRef]
- Oikonomou, E.K.; Antoniades, C. The Role of Adipose Tissue in Cardiovascular Health and Disease. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2018, 16, 83–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fruhbeck, G. Leptin-Induced Lipolysis Opposes the Tonic Inhibition of Endogenous Adenosine in white Adipocytes. FASEB J. 2001, 15, 333–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fruhbeck, G.; Gomez-Ambrosi, J. Modulation of the Leptin-Induced white Adipose Tissue Lipolysis by Nitric Oxide. Cell. Signal. 2001, 13, 827–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaborit, B.; Venteclef, N.; Ancel, P.; Gariboldi, V.; Pelloux, V.; Leprince, P.; Amour, J.; Hatem, S.N.; Jouve, E.; Dutour, A.; et al. Human Epicardial Adipose Tissue has a Specific Transcriptomic Signature Depending on its Anatomical Peri-Atrial, Peri-Ventricular, or Peri-Coronary Location. Cardiovasc. Res. 2015, 108, 62–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spalding, K.L.; Arner, E.; Westermark, P.O.; Bernard, S.; Buchholz, B.A.; Bergmann, O.; Blomqvist, L.; Hoffstedt, J.; Naslund, E.; Britton, T.; et al. Dynamics of Fat Cell Turnover in Humans. Nature 2008, 453, 783–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fruhbeck, G. Overview of Adipose Tissue and its Role in Obesity and Metabolic Disorders. Methods Mol. Biol. 2008, 456, 1–22. Available online: http://link.springer.com/10.1007/978-1-59745-245-8_1 (accessed on 7 November 2018). [PubMed]
- Fruhbeck, G.; Mendez-Gimenez, L.; Fernandez-Formoso, J.A.; Fernandez, S.; Rodriguez, A. Regulation of Adipocyte Lipolysis. Nutr. Res. Rev. 2014, 27, 63–93. Available online: http://www.journals.cambridge.org/abstract_S095442241400002X (accessed on 7 November 2018). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, H.; Gerhold, K.; Mayers, J.R.; Wiest, M.M.; Watkins, S.M.; Hotamisligil, G.S.; Watkins, S.M. Identification of a Lipokine, a Lipid Hormone Linking Adipose Tissue to Systemic Metabolism. Cell 2008, 134, 933–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mozaffarian, D.; Cao, H.; King, I.B.; Lemaitre, R.N.; Song, X.; Siscovick, D.S.; Hotamisligil, G.S. Trans-Palmitoleic Acid, Metabolic Risk Factors, and New-Onset Diabetes in U.S. Adults. Ann. Intern. Med. 2010, 153, 790. Available online: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21173413 (accessed on 1 October 2019). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stefan, N.; Kantartzis, K.; Celebi, N.; Staiger, H.; Machann, J.; Schick, F.; HAring, H.U.; Cegan, A.; Fritsche, A.; Schleicher, E.; et al. Circulating Palmitoleate Strongly and Independently Predicts Insulin Sensitivity in Humans. Diabetes Care 2010, 33, 405–407. Available online: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19889804 (accessed on 1 October 2019). [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, A.; Becerril, S.; Ezquerro, S.; Mendez-Gimenez, L.; Fruhbeck, G. Cross-Talk between Adipokines and Myokines in Fat Browning. Acta Physiol. 2017, 219, 362–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margaritis, M.; Antonopoulos, A.S.; Digby, J.; Lee, R.; Reilly, S.; Coutinho, P.; Shirodaria, C.; Sayeed, R.; Petrou, M.; De Silva, R.; et al. Interactions Between Vascular Wall and Perivascular Adipose Tissue Reveal Novel Roles for Adiponectin in the Regulation of Endothelial Nitric Oxide Synthase Function in Human Vessels. Circulation 2013, 127, 2209–2221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, A.L.; Polhemus, D.J.; Bhushan, S.; Otsuka, H.; Kondo, K.; Nicholson, C.K.; Bradley, J.M.; Islam, K.N.; Calvert, J.W.; Tao, Y.-X.; et al. Hydrogen Sulfide Cytoprotective Signaling is Endothelial Nitric Oxide Synthase-Nitric Oxide Dependent. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 3182–3187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.C.; Chang, H.H.; Chiang, C.L.; Liu, C.H.; Yeh, J.I.; Chen, M.F.; Chen, P.Y.; Kuo, J.S.; Lee, T.J. Role of Perivascular Adipose Tissue–Derived Methyl Palmitate in Vascular Tone Regulation and Pathogenesis of Hypertension. Circulation 2011, 124, 1160–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, N.; Li, H. The Role of Perivascular Adipose Tissue in Obesity-Induced Vascular Dysfunction. Br. J. Pharm. 2017, 174, 3425–3442. Available online: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27761903 (accessed on 9 November 2018). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, L.; Xiong, W.; Zhao, X.; Fan, Y.; Guo, Y.; Garcia-Barrio, M.; Zhang, J.; Jiang, Z.; Lin, J.D.; Chen, Y.E. Bmal1 in Perivascular Adipose Tissue Regulates Resting-Phase Blood Pressure Through Transcriptional Regulation of Angiotensinogen. Circulation 2018, 138, 67–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreno, M.U.; San Jose, G.; Pejenaute, A.; Landecho, M.F.; Diez, J.; Beloqui, O.; Zalba, G.; Zalba, G. Association of Phagocytic NADPH Oxidase Activity with Hypertensive Heart Disease: A Role for Cardiotrophin-1? Hypertension 2014, 63, 468–474. Available online: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24324051 (accessed on 17 October 2016). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antonopoulos, A.S.; Margaritis, M.; Coutinho, P.; Shirodaria, C.; Psarros, C.; Herdman, L.; Krasopoulos, G.; Channon, K.M.; Casadei, B.; Tousoulis, D.; et al. Adiponectin as a Link Between Type 2 Diabetes and Vascular NADPH Oxidase Activity in the Human Arterial Wall: The Regulatory Role of Perivascular Adipose Tissue. Diabetologia 2015, 64, 2207–2219. Available online: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25552596 (accessed on 9 November 2018). [CrossRef]
- Fortuno, A.; Bidegain, J.; Baltanas, A.; Moreno, M.U.; Montero, L.; Landecho, M.F.; Beloqui, O.; Diez, J.; Zalba, G. Is Leptin Involved in Phagocytic NADPH Oxidase Overactivity in Obesity? Potential clinical implications. J. Hypertens. 2010, 28, 1944–1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortuno, A.; Bidegain, J.; San Jose, G.; Robador, P.A.; Landecho, M.F.; Beloqui, O.; DIez, J.; Zalba, G. Insulin Resistance Determines Phagocytic Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide Phosphate Oxidase Overactivation in Metabolic Syndrome Patients. J. Hypertens. 2009, 27, 1420–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beloqui, O.; Moreno, M.U.; San Jose, G.; Pejenaute, A.; Cortes, A.; Landecho, M.F.; Zalba, G.; Fortuno, A.; Diez, J.; Landecho, M.F.; et al. Increased Phagocytic NADPH Oxidase Activity Associates with Coronary Artery Calcification in Asymptomatic Men. Free Radic. Res. 2017, 51, 389–396. Available online: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28427294 (accessed on 8 November 2018). [CrossRef]
- Fruhbeck, G.; Catalan, V.; Rodriguez, A.; Gomez-Ambrosi, J. Adiponectin-Leptin Ratio: A Promising Index to Estimate Adipose Tissue Dysfunction. Relation with Obesity-Associated Cardiometabolic Risk. Adipocyte 2018, 7, 57–62. Available online: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29205099 (accessed on 9 November 2018). [CrossRef]
- Fruhbeck, G.; Catalan, V.; Rodriguez, A.; Ramirez, B.; Becerril, S.; Portincasa, P.; Gomez-Ambrosi, J. Normalization of Adiponectin Concentrations by Leptin Replacement in ob/ob Mice is Accompanied by Reductions in Systemic Oxidative Stress and Inflammation. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 2752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.J.; Wu, C.S.; Lin, H.; Lee, I.T.; Wu, C.M.; Tseng, J.J.; Chou, M.M.; Sheu, W.H.H. Visfatin-Induced Expression of Inflammatory Mediators in Human Endothelial Cells through the NF-Κb pathway. Int. J. Obes. 2009, 33, 465–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oikonomou, E.K.; Antoniades, C.; Oikonomou, D.E.K.; Antoniades, D.C. Immunometabolic Regulation of Vascular Redox State: The Role of Adipose Tissue. Antioxid. Redox. Signal. 2018, 29, 313–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Unamuno, X.; Gomez-Ambrosi, J.; Rodriguez, A.; Becerril, S.; Fruhbeck, G.; Catalan, V.; Berrecil, S. Adipokine Dysregulation and Adipose Tissue Inflammation in Human Obesity. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2018, 48, e12997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sawaki, D.; Czibik, G.; Pini, M.; Ternacle, J.; Suffee, N.; Mercedes, R.; Marcelin, G.; Surenaud, M.; Marcos, E.; Gual, P.; et al. Visceral Adipose Tissue Drives Cardiac Aging Through Modulation of Fibroblast Senescence by Osteopontin Production. Circulation 2018, 138, 809–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muruzabal, F.J.; Fruhbeck, G.; Gomez-Ambrosi, J.; Archanco, M.; Burrell, M. Immunocytochemical Detection of Leptin in Non-Mammalian Vertebrate Stomach. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2002, 128, 149–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, A.; Gomez-Ambrosi, J.; Catalan, V.; Fortuno, A.; Fruhbeck, G. Leptin Inhibits the Proliferation of Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells Induced by Angiotensin II through Nitric Oxide-Dependent Mechanisms. Mediat. Inflamm. 2010, 2010, 105489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez-Ambrosi, J.; Salvador, J.; A Paramo, J.; Orbe, J.; De Irala, J.; Diez-Caballero, A.; Gil, M.J.; Cienfuegos, A.; Fruhbeck, G. Involvement of Leptin in the Association between Percentage of Body Fat and Cardiovascular Risk Factors. Clin. Biochem. 2002, 35, 315–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweeney, G. Cardiovascular Effects of Leptin. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2010, 7, 22–29. Available online: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19949425 (accessed on 9 November 2018). [CrossRef]
- Wallace, A.M.; McMahon, A.D.; Packard, C.J.; Kelly, A.; Shepherd, J.; Gaw, A.; Sattar, N. Plasma Leptin and the Risk of Cardiovascular Disease in the West of Scotland Coronary Prevention Study (WOSCOPS). Circulation 2001, 104, 3052–3056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, S.S.; Blaha, M.J.; Muse, E.D.; Qasim, A.N.; Reilly, M.P.; Blumenthal, R.S.; Allison, M.A.; Hughes, A.M.J.; McClelland, R.L.; Criqui, M.H.; et al. Leptin and Incident Cardiovascular Disease: The Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis (MESA). Atherosclerosis 2015, 239, 67–72. Available online: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25574859 (accessed on 9 May 2019). [CrossRef]
- Dirksen, C.; Jørgensen, N.B.; Bojsen-Moller, K.N.; Jacobsen, S.H.; Hansen, D.L.; Worm, D.; Holst, J.J.; Madsbad, S. Mechanisms of Improved Glycaemic Control after Roux-En-Y Gastric bypass. Diabetologia 2012, 55, 1890–1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, T.D.; Davidson, L.E.; Litwin, S.E.; Kim, J.; Kolotkin, R.L.; Nanjee, M.N.; Hopkins, P.N.; Brinton, M.D.; Eliot, A.; Ibele, M.D.; et al. Weight and Metabolic Outcomes 12 Years after Gastric Bypass. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 1143–1155. Available online: http://www.nejm.org/doi/10.1056/NEJMoa1700459 (accessed on 12 July 2019). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huypens, P.R. Leptin and Adiponectin Regulate Compensatory Beta Cell Growth in Accordance to Overweight. Med. Hypotheses 2007, 68, 1134–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamauchi, T.; Kadowaki, T. Adiponectin Receptor as a Key Player in Healthy Longevity and Obesity-Related Diseases. Cell Metab. 2013, 17, 185–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.J.; Cheng, Y.J.; Gu, W.J.; Aung, L.H.H. Adiponectin is Associated with Increased Mortality in Patients with Already Established Cardiovascular Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Metabolism 2014, 63, 1157–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vega, G.L.; Grundy, S.M. Metabolic Risk Susceptibility in Men Is Partially Related to Adiponectin/Leptin Ratio. J. Obes. 2013, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, F.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, Y.; Geng, D.; Liu, J. Adiponectin Downregulates Hyperglycemia and Reduces Pancreatic Islet Apoptosis After Roux-En-Y Gastric Bypass Surgery. Obes. Surg. 2011, 21, 768–773. Available online: http://link.springer.com/10.1007/s11695-011-0357-6 (accessed on 4 November 2016). [CrossRef]
- Fruhbeck, G. The Adipose Tissue as a Source of Vasoactive Factors. Curr. Med. Chem. Cardiovasc. Hematol. Agents 2004, 2, 197–208. Available online: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15320786 (accessed on 13 November 2018). [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Cassis, L.A.; Kooi, C.W.V.; Daugherty, A. Structure and Functions of Angiotensinogen. Hypertens. Res. 2016, 39, 492–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlsson, C.; Lindell, K.; Ottosson, M.; Sjostrom, L.; Carlsson, B.; Carlsson, L.M. Human Adipose Tissue Expresses Angiotensinogen and Enzymes Required for its Conversion to Angiotensin II. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1998, 83, 3925–3929. Available online: https://academic.oup.com/jcem/article-lookup/doi/10.1210/jcem.83.11.5276 (accessed on 9 November 2018). [CrossRef]
- Crespo, T.S.; Andrade, J.M.O.; Paraiso, A.F.; De Farias Lelis, D.; Chagas, P.V.F.; Jorge, A.S.B.; Santos, S.H.S.; Sena, A.L.; Batista, A.M.; Paula, D.; et al. Effects of Sleeve Gastrectomy on the Metabolic Profile and on the Expression of Renin-Angiotensin System in Adipose Tissue of Obese Rats. Protein Pept. Lett. 2017, 24, 861–868. Available online: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28758596 (accessed on 15 July 2019). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, W.; Ye, D.D. The Potential of Adipokines as Biomarkers and Therapeutic Agents for Vascular Complications in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2019, 48, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreno-Navarrete, J.M.; Catalan, V.; Ortega, F.; Gomez-Ambrosi, J.; Ricart, W.; Fruhbeck, G.; Fernandez-Real, J.M. Circulating Omentin Concentration Increases after Weight Loss. Nutr. Metab. 2010, 7, 27. Available online: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20380714 (accessed on 15 July 2019). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shibata, R.; Ouchi, N.; Kikuchi, R.; Takahashi, R.; Takeshita, K.; Kataoka, Y.; Ohashi, K.; Ikeda, N.; Kihara, S.; Murohara, T. Circulating Omentin is Associated with Coronary Artery Disease in Men. Atheroscler 2011, 219, 811–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Souza Batista, C.M.; Yang, R.Z.; Lee, M.J.; Lee, M.J.; Glynn, N.M.; Yu, D.Z.; Pray, J.; Fried, S.K.; Patil, J.; Patil, S.; et al. Omentin Plasma Levels and Gene Expression Are Decreased in Obesity. Diabetes 2007, 56, 1655–1661. Available online: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17329619 (accessed on 9 November 2018). [CrossRef]
- Narumi, T.; Watanabe, T.; Kadowaki, S.; Kinoshita, D.; Yokoyama, M.; Honda, Y.; Otaki, Y.; Nishiyama, S.; Takahashi, H.; Arimoto, T.; et al. Impact of Serum Omentin-1 Levels on Cardiac Prognosis in Patients with Heart Failure. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2014, 13, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapointe, M.; Poirier, P.; Martin, J.; Bastien, M.; Auclair, A.; Cianflone, K. Omentin Changes Following Bariatric Surgery and Predictive Links with Biomarkers for Risk of Cardiovascular Disease. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2014, 13, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Cruz, L.A.; Gil, M.J.; Cienfuegos, J.A.; Gomez-Ambrosi, J.; Catalan, V.; Diez-Caballero, A.; Garcia-Foncillas, J.; Salvador, J.; Mato, J.M.; Fruhbeck, G. Gene Expression Profile of Omental Adipose Tissue in Human Obesity. FASEB J. 2004, 18, 215–217. [Google Scholar]
- Scatena, M.; Liaw, L.; Giachelli, C.M. Osteopontin: A Multifunctional Molecule Regulating Chronic Inflammation and Vascular Disease. Arter. Thromb Vasc. Biol. 2007, 27, 2302–2309. Available online: https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/10.1161/ATVBAHA.107.144824 (accessed on 9 November 2018). [CrossRef]
- Kiefer, F.W.; Zeyda, M.; Todoric, J.; Huber, J.; Geyeregger, R.; Weichhart, T.; Aszmann, O.; Ludvik, B.; Silberhumer, G.R.; Prager, G.; et al. Osteopontin Expression in Human and Murine Obesity: Extensive Local Up-Regulation in Adipose Tissue but Minimal Systemic Alterations. Endocrinology 2008, 149, 1350–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahles, F.; Findeisen, H.M.; Bruemmer, D. Osteopontin: A Novel Regulator at the Cross Roads of Inflammation, obesity and diabetes. Mol. Metab. 2014, 3, 384–393. Available online: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24944898 (accessed on 15 July 2019). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashkar, S.; Weber, G.F.; Panoutsakopoulou, V.; Sanchirico, M.E.; Jansson, M.; Zawaideh, S.; Rittling, S.R.; Denhardt, D.T.; Glimcher, M.J.; Cantor, H. Eta-1 (Osteopontin): An Early Component of Type-1 (Cell-Mediated) Immunity. Science 2000, 287, 860–864. Available online: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10657301 (accessed on 9 November 2018). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denhardt, D.T.; Noda, M.; Oregan, A.W.; Pavlin, D.; Berman, J.S. Osteopontin as a Means to Cope with Environmental Insults: Regulation of Inflammation, Tissue Remodeling, and Cell Survival. J. Clin. Investig. 2001, 107, 1055–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Içer, M.A.; Gezmen-Karadag, M. The Multiple Functions and Mechanisms of Osteopontin. Clin. Biochem. 2018, 59, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefan, N.; Haring, H.U.; Cusi, K. Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Causes, Diagnosis, Cardiometabolic Consequences, and Treatment Strategies. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2019, 7, 313–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, B.; Gonzalez, A.; Lindner, D.; Westermann, D.; Ravassa, S.; Beaumont, J.; Larman, M.; Gallego, A.; Brugnolaro, C.; Querejeta, R.; et al. Osteopontin-Mediated Myocardial Fibrosis in Heart Failure: A Role for Lysyl Oxidase? Cardiovasc. Res. 2013, 99, 111–120. Available online: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23619422 (accessed on 9 November 2018). [CrossRef]
- Carbone, F.; Montecucco, F. Novel Cardiovascular Risk Biomarkers in Carotid Atherogenesis. Biomark. Med. 2018, 12, 1065–1067. Available online: https://www.futuremedicine.com/doi/10.2217/bmm-2018-0198 (accessed on 15 November 2018). [CrossRef]
- Lancha, A.; Moncada, R.; Valenti, V.; Rodriguez, A.; Catalan, V.; Becerril, S.; Ramirez, B.; Mendez-Gimenez, L.; Fruhbeck, G.; Gomez-Ambrosi, J. Effect of Sleeve Gastrectomy on Osteopontin Circulating Levels and Expression in Adipose Tissue and Liver in Rats. Obes. Surg. 2014, 24, 1702–1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.K.; Kwak, M.K.; Kim, H.J.; Ahima, R.S. Linking Resistin, Inflammation, and Cardiometabolic Diseases. Korean J. Intern. Med. 2017, 32, 239–247. Available online: http://kjim.org/journal/view.php?doi=10.3904/kjim.2016.229 (accessed on 12 July 2019). [CrossRef]
- Fontana, A.; Spadaro, S.; Copetti, M.; Spoto, B.; Salvemini, L.; Pizzini, P.; Frittitta, L.; Mallamaci, F.; Pellegrini, F.; Trischitta, V.; et al. Association between Resistin Levels and All-Cause and Cardiovascular Mortality: A New Study and a Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0120419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doulamis, I.P.; Konstantopoulos, P.; Tzani, A.; Antoranz, A.; Minia, A.; Daskalopoulou, A.; Menenakos, E.; Perrea, L.; Alexopulos, L.; Charalampopoulos, A.; et al. Visceral white Adipose Tissue and Serum Proteomic Alternations in Metabolically Healthy Obese Patients Undergoing Bariatric Surgery. Cytokine 2019, 115, 76–83. Available online: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30472106 (accessed on 15 July 2019). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arica, P.C.; Aydin, S.; Zengin, U.; Kocael, A.; Orhan, A.; Zengin, K.; Uzun, H.; Taskin, M.; Gelisgen, R. The Effects on Obesity Related Peptides of Laparoscopic Gastric Band Applications in Morbidly Obese Patients. J. Investig. Surg. 2018, 31, 89–95. Available online: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28635510 (accessed on 15 July 2019). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hung, W.C.; Yu, T.H.; Hsu, C.C.; Lu, L.F.; Chung, F.M.; Tsai, I.T.; Wang, C.P.; Lee, Y.J.; Houng, J.Y.; Lu, Y.C. Plasma Visfatin Levels are Associated with Major Adverse Cardiovascular Events in Patients with Acute ST-Elevation Myocardial Infarction. Clin. Investig. Med. 2015, 38, E100–E109. Available online: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26026637 (accessed on 9 November 2018). [CrossRef]
- Dahl, T.B.; Yndestad, A.; Skjelland, M. Increased Expression of Visfatin in Macrophages of Human Unstable Carotid and Coronary Atherosclerosis. Circulation 2007, 115, 972–980. Available online: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17283255 (accessed on 15 July 2019). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isgaard, J.; Granata, R. Ghrelin in Cardiovascular Disease and Atherogenesis. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2011, 340, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gauna, C.; Delhanty, P.J.D.; Hofland, L.J.; Janssen, J.A.M.J.L.; Broglio, F.; Ross, R.J.M.; Ghigo, E.; Van Der Lely, A.J. Ghrelin Stimulates, Whereas Des-Octanoyl Ghrelin Inhibits, Glucose Output by Primary Hepatocytes. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2005, 90, 1055–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokudome, T.; Kishimoto, I.; Miyazato, M.; Kangawa, K. Ghrelin and the Cardiovascular System. Front Horm. Res. 2014, 43, 125–133. [Google Scholar]
- Ezquerro, S.; Fruhbeck, G.; Rodriguez, A. Ghrelin and Autophagy. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2017, 20, 402–408. Available online: https://insights.ovid.com/pubmed?pmid=28590260 (accessed on 12 July 2019). [CrossRef]
- Nagaya, N.; Kojima, M.; Uematsu, M.; Yamagishi, M.; Hosoda, H.; Oya, H.; Hayashi, Y.; Kangawa, K. Hemodynamic and Hormonal Effects of Human Ghrelin in Healthy Volunteers. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2001, 280, R1483–R1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagaya, N.; Uematsu, M.; Kojima, M.; Ikeda, Y.; Yoshihara, F.; Shimizu, W.; Hosoda, H.; Hirota, Y.; Ishida, H.; Mori, H.; et al. Chronic Administration of Ghrelin Improves Left Ventricular Dysfunction and Attenuates Development of Cardiac Cachexia in Rats with Heart Failure. Circulation 2001, 104, 1430–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagaya, N.; Moriya, J.; Yasumura, Y.; Uematsu, M.; Ono, F.; Shimizu, W.; Ueno, K.; Kitakaze, M.; Miyatake, K.; Kangawa, K. Effects of Ghrelin Administration on Left Ventricular Function, Exercise Capacity, and Muscle Wasting in Patients With Chronic Heart Failure. Circulation 2004, 110, 3674–3679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezquerro, S.; Mendez-Gimenez, L.; Becerril, S.; Moncada, R.; Valenti, V.; Catalan, V.; Gomez-Ambrosi, J.; Fruhbeck, G.; Rodriguez, A. Acylated and Desacyl Ghrelin are Associated with Hepatic Lipogenesis, β-Oxidation and Autophagy: Role in NAFLD Amelioration after Sleeve Gastrectomy in Obese Rats. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 39942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, L.; Ren, Y.; Liu, X.; Li, W.G.; Yang, J.; Geng, B.; Weintraub, N.L.; Tang, C. Protective Effects of Ghrelin on Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury in the Isolated Rat Heart. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2004, 43, 165–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwenke, D.O.; Tokudome, T.; Kishimoto, I.; Horio, T.; Shirai, M.; Cragg, P.A.; Kangawa, K. Early Ghrelin Treatment after Myocardial Infarction Prevents an Increase in Cardiac Sympathetic Tone and Reduces Mortality. Endocrinology 2008, 149, 5172–5176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, Y.; Tokudome, T.; Otani, K.; Kishimoto, I.; Nakanishi, M.; Hosoda, H.; Kangawa, K.; Miyazato, M.; Hosoda, H.; Nakanishi, M.; et al. Ghrelin Prevents Incidence of Malignant Arrhythmia after Acute Myocardial Infarction through Vagal Afferent Nerves. Endocrinology 2012, 153, 3426–3434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soeki, T.; Kishimoto, I.; Schwenke, D.O.; Tokudome, T.; Horio, T.; Yoshida, M.; Hosoda, H.; Kangawa, K. Ghrelin Suppresses Cardiac Sympathetic Activity and Prevents Early Left Ventricular Remodeling in Rats with Myocardial Infarction. Am. J. Physiol. Circ. Physiol. 2008, 294, H426–H432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowan, E.; Burch, K.J.; Green, B.D.; Grieve, D.J. Obestatin as a Key Regulator of Metabolism and Cardiovascular Function with Emerging Therapeutic Potential for Diabetes. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2016, 173, 2165–2181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agnew, A.J.; Robinson, E.; McVicar, C.M.; Harvey, A.P.; Ali, I.H.E.; Lindsay, J.; McDonald, D.M.; Green, B.D.; Grieve, D.J. The Gastrointestinal Peptide Obestatin Induces Vascular Relaxation Via Specific Activation of Endothelium-Dependent NO Signalling. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2012, 166, 327–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kellokoski, E.; Kunnari, A.; Jokela, M.; Makela, S.; Kesaniemi, Y.A.; Horkko, S. Ghrelin and Obestatin Modulate Early Atherogenic Processes on Cells: Enhancement of Monocyte Adhesion and Oxidized Low-Density Lipoprotein Binding. Metabolism 2009, 58, 1572–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alloatti, G.; Arnoletti, E.; Bassino, E.; Penna, C.; Perrelli, M.G.; Ghe, C.; Muccioli, G. Obestatin Affords Cardioprotection to the Ischemic-Reperfused Isolated Rat Heart and Inhibits Apoptosis in Cultures of Similarly Stressed Cardiomyocytes. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2010, 299, H470–H481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catalan, V.; Gomez-Ambrosi, J.; Rodriguez, A.; Ramirez, B.; Valenti, V.; Moncada, R.; Fruhbeck, G.; Landecho, F.M.; Silva, C.; Salvador, J.; et al. Increased IL-32 Levels in Obesity Promote Adipose Tissue Inflammation and Extracellular Matrix Remodeling. Effect Weight Loss. Diabetes 2016, 65, 3636–3648. Available online: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27630206 (accessed on 17 October 2016). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomez-Ambrosi, J.; Salvador, J.; Rotellar, F.; Silva, C.; Catalan, V.; Rodriguez, A.M.; Gil, J.; Fruhbeck, G. Increased Serum Amyloid A Concentrations in Morbid Obesity Decrease after Gastric Bypass. Obes. Surg. 2006, 16, 262–269. Available online: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16545156 (accessed on 15 November 2018). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catalan, V.; Gomez-Ambrosi, J.; Rodriguez, A.; Silva, C.; Rotellar, F.; Gil, M.J.; Fruhbeck, G.; Salvador, J. Expression of Caveolin-1 in Human Adipose Tissue is Upregulated in Obesity and Obesity-Associated Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Related to Inflammation. Clin. Endocrinol. 2008, 68, 213–219. Available online: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17803693 (accessed on 13 November 2018). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallego-Escuredo, J.M.; Gomez-Ambrosi, J.; Catalan, V.; Domingo, P.; Giralt, M.; Frühbeck, G.; Villarroya, F. Opposite Alterations in FGF21 and FGF19 Levels and Disturbed Expression of the Receptor Machinery for Endocrine FGFs in Obese Patients. Int. J. Obes. 2015, 39, 121–129. Available online: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24813368 (accessed on 13 November 2018). [CrossRef]
- Victoria, C.J.; GOmez-Ambrosi, A.; Rodriguez, B.; Ramirez, F.; Rotellar, V.; Valenti, C.; Silva, M.J.; Gil, J.; Manuel, F.R.; Javier, S.; et al. Increased Levels of Calprotectin in Obesity are Related to Macrophage Content: Impact on Inflammation and Effect of Weight Loss. Mol. Med. 2011, 17, 1157–1167. Available online: http://www.molmed.org/content/pdfstore/11_144_Catalan.pdf (accessed on 13 November 2018).
- Boa, B.C.S.; Yudkin, J.S.; Van Hinsbergh, V.W.M.; Bouskela, E.; Eringa, E.C. Exercise Effects on Perivascular Adipose Tissue: Endocrine and Paracrine Determinants of Vascular Function. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2017, 174, 3466–3481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardo, M.; Crujeiras, A.B.; Amil, M.; Aguera, Z.; Jimenez-Murcia, S.; Banos, R.; Botella, C.; De La Torre, R.; Estivill, X.; Fagundo, A.B.; et al. Association of Irisin with Fat Mass, Resting Energy Expenditure, and Daily Activity in Conditions of Extreme Body Mass Index. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2014, 2014, 857270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Landecho, M.F.; Tuero, C.; Valentí, V.; Bilbao, I.; de la Higuera, M.; Frühbeck, G. Relevance of Leptin and Other Adipokines in Obesity-Associated Cardiovascular Risk. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2664. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11112664
Landecho MF, Tuero C, Valentí V, Bilbao I, de la Higuera M, Frühbeck G. Relevance of Leptin and Other Adipokines in Obesity-Associated Cardiovascular Risk. Nutrients. 2019; 11(11):2664. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11112664
Chicago/Turabian StyleLandecho, Manuel F., Carlota Tuero, Víctor Valentí, Idoia Bilbao, Magdalena de la Higuera, and Gema Frühbeck. 2019. "Relevance of Leptin and Other Adipokines in Obesity-Associated Cardiovascular Risk" Nutrients 11, no. 11: 2664. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11112664
APA StyleLandecho, M. F., Tuero, C., Valentí, V., Bilbao, I., de la Higuera, M., & Frühbeck, G. (2019). Relevance of Leptin and Other Adipokines in Obesity-Associated Cardiovascular Risk. Nutrients, 11(11), 2664. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11112664




