Sleep Apnea and Sleep Habits: Relationships with Metabolic Syndrome
Abstract
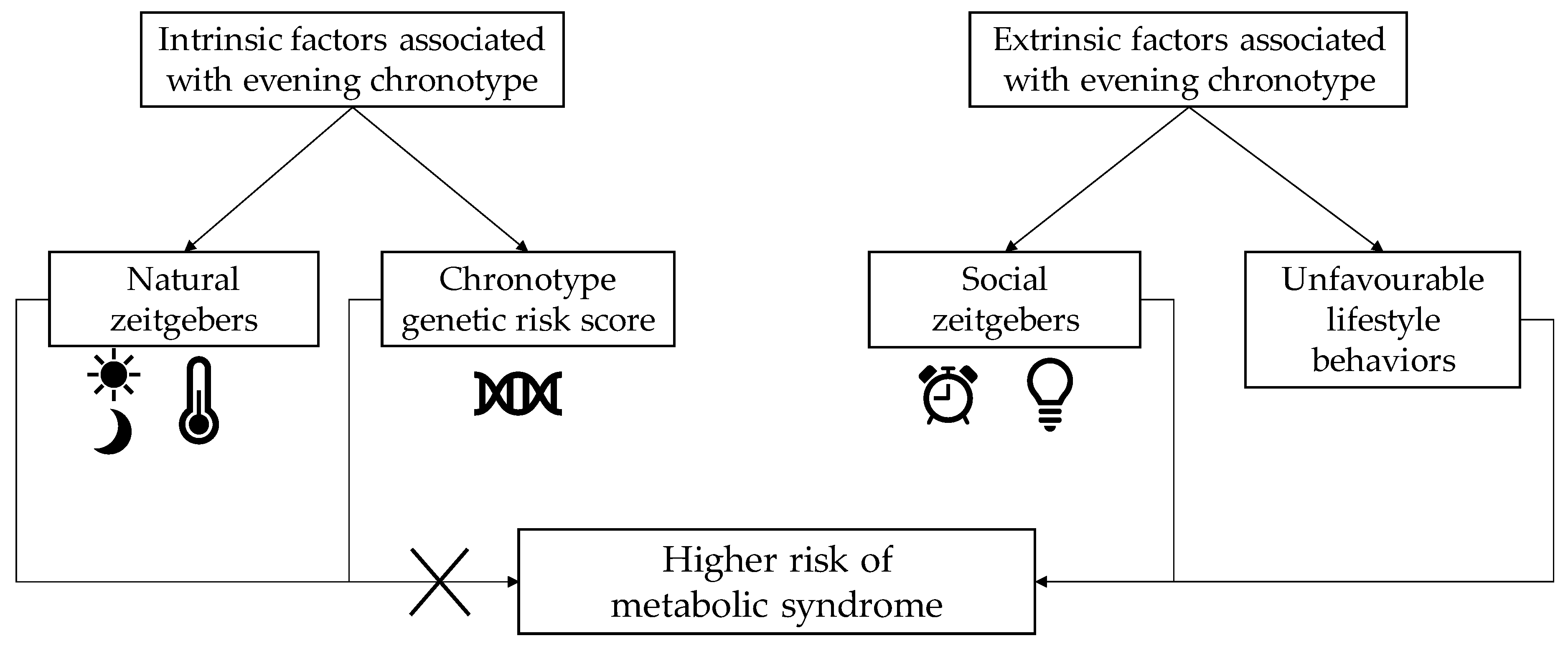
1. Introduction
2. Sleep Habits and Metabolic Syndrome
2.1. Definitions
2.2. Epidemiological Evidence Related to Metabolic Syndrome
2.3. Mechanisms of Action
3. Obstructive Sleep Apnea and Metabolic Syndrome
3.1. Definition
3.2. Epidemiological Evidence Relating OSAS to Metabolic Syndrome
3.3. Mechanism of Action
4. Sleep as a Component of a Comprehensive Lifestyle Intervention
4.1. First Steps of Chronotherapy as a Lifestyle Intervention
4.2. Effect of OSAS Treatment
5. Conclusions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alberti, K.G.; Eckel, R.H.; Grundy, S.M.; Zimmet, P.Z.; Cleeman, J.I.; Donato, K.A.; Fruchart, J.C.; James, W.P.; Loria, C.M.; Smith, S.C., Jr. Harmonizing the Metabolic Syndrome: A Joint Interim Statement of the International Diabetes Federation Task Force on Epidemiology and Prevention; National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute; American Heart Association; World Heart Federation; International Atherosclerosis Society; and International Association for the Study of Obesity. Circulation 2009, 120, 1640–1645. [Google Scholar]
- Sperling, L.S.; Mechanick, J.I.; Neeland, I.J.; Herrick, C.J.; Despres, J.P.; Ndumele, C.E.; Vijayaraghavan, K.; Handelsman, Y.; Puckrein, G.A.; Araneta, M.R.; et al. The CardioMetabolic Health Alliance: Working Toward a New Care Model for the Metabolic Syndrome. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2015, 66, 1050–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Despres, J.P.; Lemieux, I. Abdominal Obesity and Metabolic Syndrome. Nature 2006, 444, 881–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neeland, I.J.; Poirier, P.; Despres, J.P. Cardiovascular and Metabolic Heterogeneity of Obesity: Clinical Challenges and Implications for Management. Circulation 2018, 137, 1391–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levy, P.; Kohler, M.; McNicholas, W.T.; Barb, F.; Mcevoy, R.D.; Somers, V.K.; Lavie, L.; Pepin, J.L. Obstructive Sleep Apnoea Syndrome. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2015, 1, 15015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larcher, S.; Benhamou, P.Y.; Pepin, J.L.; Borel, A.L. Sleep Habits and Diabetes. Diabetes Metab. 2015, 41, 263–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larcher, S.; Gauchez, A.S.; Lablanche, S.; Pepin, J.L.; Benhamou, P.Y.; Borel, A.L. Impact of Sleep Behavior on Glycemic Control in Type 1 Diabetes: The Role of Social Jetlag. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2016, 175, 411–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baehr, E.K.; Revelle, W.; Eastman, C.I. Individual Differences in the Phase and Amplitude of the Human Circadian Temperature Rhythm: With an Emphasis on Morningness-Eveningness. J. Sleep Res. 2000, 9, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roenneberg, T.; Kuehnle, T.; Juda, M.; Kantermann, T.; Allebrandt, K.; Gordijn, M.; Merrow, M. Epidemiology of the Human Circadian Clock. Sleep Med. Rev. 2007, 11, 429–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roenneberg, T.; Wirz-Justice, A.; Merrow, M. Life between Clocks: Daily Temporal Patterns of Human Chronotypes. J. Biol. Rhythm. 2003, 18, 80–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horne, J.A.; Ostberg, O. A Self-Assessment Questionnaire to Determine Morningness-Eveningness in Human Circadian Rhythms. Int. J. Chronobiol. 1976, 4, 97–110. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Roenneberg, T.; Allebrandt, K.V.; Merrow, M.; Vetter, C. Social Jetlag and Obesity. Curr. Biol. 2012, 22, 939–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knutson, K.L.; Van Cauter, E.; Rathouz, P.J.; DeLeire, T.; Lauderdale, D.S. Trends in the Prevalence of Short Sleepers in the USA: 1975–2006. Sleep 2010, 33, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cappuccio, F.P.; Taggart, F.M.; Kandala, N.B.; Currie, A.; Peile, E.; Stranges, S.; Miller, M.A. Meta-Analysis of Short Sleep Duration and Obesity in Children and Adults. Sleep 2008, 31, 619–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, M.A.; Kruisbrink, M.; Wallace, J.; Ji, C.; Cappuccio, F.P. Sleep Duration and Incidence of Obesity in Infants, Children, and Adolescents: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Prospective Studies. Sleep 2018, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magee, L.; Hale, L. Longitudinal Associations between Sleep Duration and Subsequent Weight Gain: A Systematic Review. Sleep Med. Rev. 2012, 16, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, B.; He, D.; Zhang, M.; Xue, J.; Zhou, D. Short Sleep Duration Predicts Risk of Metabolic Syndrome: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Sleep Med. Rev. 2014, 18, 293–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulido-Arjona, L.; Correa-Bautista, J.E.; Agostinis-Sobrinho, C.; Mota, J.; Santos, R.; Correa-Rodriguez, M.; Garcia-Hermoso, A.; Ramirez-Velez, R. Role of Sleep Duration and Sleep-Related Problems in the Metabolic Syndrome Among Children and Adolescents. Ital. J. Pediatr. 2018, 44, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas-De La Cruz, L.; Martin-Espinosa, N.; Cavero-Redondo, I.; Gonzalez-Garcia, A.; Diez-Fernandez, A.; Martinez-Vizcaino, V.; Notario-Pacheco, B. Sleep Patterns and Cardiometabolic Risk in Schoolchildren from Cuenca, Spain. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0191637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, H.B.; Tam, T.; Zee, B.C.; Chung, R.Y.; Su, X.; Jin, L.; Chan, T.C.; Chang, L.Y.; Yeoh, E.K.; Lao, X.Q. Short Sleep Duration Increases Metabolic Impact in Healthy Adults: A Population-Based Cohort Study. Sleep 2017, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.Y.; Yadav, D.; Ahn, S.V.; Koh, S.B.; Park, J.T.; Yoon, J.; Yoo, B.S.; Lee, S.H. A Prospective Study of Total Sleep Duration and Incident Metabolic Syndrome: The ARIRANG Study. Sleep Med. 2015, 16, 1511–1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Q.; Liu, X.; Zhou, W.; Wang, X.; Wu, S. Changes in sleep Duration and Risk of Metabolic Syndrome: The Kailuan Prospective Study. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 36861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez-Mendoza, J.; He, F.; LaGrotte, C.; Vgontzas, A.N.; Liao, D.; Bixler, E.O. Impact of the Metabolic Syndrome on Mortality is Modified by Objective Short Sleep Duration. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2017, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hege, A.; Lemke, M.K.; Apostolopoulos, Y.; Sonmez, S. Occupational Health Disparities among U.S. long-Haul Truck Drivers: The Influence of Work Organization and Sleep on Cardiovascular and Metabolic Disease Risk. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0207322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Itani, O.; Kaneita, Y.; Tokiya, M.; Jike, M.; Murata, A.; Nakagome, S.; Otsuka, Y.; Ohida, T. Short Sleep Duration, Shift Work, and Actual Days Taken off Work are Predictive Life-Style Risk Factors for New-Onset Metabolic Syndrome: A Seven-Year Cohort Study of 40,000 Male Workers. Sleep Med. 2017, 39, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maukonen, M.; Kanerva, N.; Partonen, T.; Mannisto, S. Chronotype and Energy Intake Timing in Relation to Changes in Anthropometrics: A 7-Year Follow-Up Study in Adults. Chronobiol. Int. 2019, 36, 27–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xiong, Y.; Dong, J.; Guo, T.; Tang, X.; Zhao, Y. Caffeinated Drinks Intake, Late Chronotype, and Increased Body Mass Index among Medical Students in Chongqing, China: A Multiple Mediation Model. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Lozano, T.; Vidal, J.; De Hollanda, A.; Canteras, M.; Garaulet, M.; Izquierdo-Pulido, M. Evening Chronotype Associates with Obesity in Severely Obese Subjects: Interaction with CLOCK 3111T/C. Int. J. Obes. 2016, 40, 1550–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malone, S.K.; Zemel, B.; Compher, C.; Souders, M.; Chittams, J.; Thompson, A.L.; Pack, A.; Lipman, T.H. Social Jet Lag, Chronotype and Body Mass Index in 14–17-Year-Old Adolescents. Chronobiol. Int. 2016, 33, 1255–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.H.; Yun, C.H.; Ahn, J.H.; Suh, S.; Cho, H.J.; Lee, S.K.; Yoo, H.J.; Seo, J.A.; Kim, S.G.; Choi, K.M.; et al. Evening Chronotype is Associated with Metabolic Disorders and Body Composition in Middle-Aged Adults. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 100, 1494–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vera, B.; Dashti, H.S.; Gomez-Abellan, P.; Hernandez-Martinez, A.M.; Esteban, A.; Scheer, F.; Saxena, R.; Garaulet, M. Modifiable Lifestyle Behaviors, but not a Genetic Risk Score, Associate with Metabolic Syndrome in Evening Chronotypes. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McMahon, D.M.; Burch, J.B.; Youngstedt, S.D.; Wirth, M.D.; Hardin, J.W.; Hurley, T.G.; Blair, S.N.; Hand, G.A.; Shook, R.P.; Drenowatz, C.; et al. Relationships between Chronotype, Social Jetlag, Sleep, Obesity and Blood Pressure in Healthy Young Adults. Chronobiol. Int. 2019, 36, 493–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marinac, C.R.; Quante, M.; Mariani, S.; Weng, J.; Redline, S.; Cespedes Feliciano, E.M.; Hipp, J.A.; Wang, D.; Kaplan, E.R.; James, P.; et al. Associations between Timing of Meals, Physical Activity, Light Exposure, and Sleep With Body Mass Index in Free-Living Adults. J. Phys. Act. Health 2019, 16, 214–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yetish, G.; Kaplan, H.; Gurven, M.; Wood, B.; Pontzer, H.; Manger, P.R.; Wilson, C.; McGregor, R.; Siegel, J.M. Natural Sleep and its Seasonal Variations in Three Pre-Industrial Societies. Curr. Biol. 2015, 25, 2862–2868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Minguez, J.; Ordonana, J.R.; Sanchez-Romera, J.F.; Madrid, J.A.; Garaulet, M. Circadian System Heritability as Assessed by Wrist Temperature: A Twin Study. Chronobiol. Int. 2015, 32, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lane, J.M.; Vlasac, I.; Anderson, S.G.; Kyle, S.D.; Dixon, W.G.; Bechtold, D.A.; Gill, S.; Little, M.A.; Luik, A.; Loudon, A.; et al. Genome-Wide Association Analysis Identifies Novel Loci for Chronotype in 100,420 Individuals from the UK Biobank. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 10889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, S.E.; Tyrrell, J.; Wood, A.R.; Beaumont, R.N.; Ruth, K.S.; Tuke, M.A.; Yaghootkar, H.; Hu, Y.; Teder-Laving, M.; Hayward, C.; et al. Genome-Wide Association Analyses in 128,266 Individuals Identifies New Morningness and Sleep Duration Loci. PLoS Genet. 2016, 12, e1006125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Shmygelska, A.; Tran, D.; Eriksson, N.; Tung, J.Y.; Hinds, D.A. GWAS of 89,283 Individuals Identifies Genetic Variants Associated with Self-Reporting of being a Morning Person. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 10448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goel, N. Genetic Markers of Sleep and Sleepiness. Sleep Med. Clin. 2017, 12, 289–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrero-Vargas, N.N.; Espitia-Bautista, E.; Buijs, R.M.; Escobar, C. Shift-Work: Is Time of Eating Determining Metabolic Health? Evidence from Animal Models. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2018, 77, 199–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maukonen, M.; Kanerva, N.; Partonen, T.; Kronholm, E.; Tapanainen, H.; Kontto, J.; Mannisto, S. Chronotype Differences in Timing of Energy and Macronutrient Intakes: A Population-Based Study in Adults. Obesity 2017, 25, 608–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, Q.; Garaulet, M.; Scheer, F. Meal Timing and Obesity: Interactions with Macronutrient Intake and Chronotype. Int. J. Obes. 2019, 43, 1701–1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reutrakul, S.; Hood, M.M.; Crowley, S.J.; Morgan, M.K.; Teodori, M.; Knutson, K.L. The Relationship between Breakfast Skipping, Chronotype, and Glycemic Control in Type 2 Diabetes. Chronobiol. Int. 2014, 31, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kandeger, A.; Selvi, Y.; Tanyer, D.K. The Effects of Individual Circadian Rhythm Differences on Insomnia, Impulsivity, and Food Addiction. Eat. Weight Disord. 2019, 24, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maukonen, M.; Kanerva, N.; Partonen, T.; Kronholm, E.; Konttinen, H.; Wennman, H.; Mannisto, S. The Associations between Chronotype, a Healthy Diet and Obesity. Chronobiol. Int. 2016, 33, 972–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mota, M.C.; Waterhouse, J.; De-Souza, D.A.; Rossato, L.T.; Silva, C.M.; Araujo, M.B.; Tufik, S.; De Mello, M.T.; Crispim, C.A. Association between Chronotype, Food Intake and Physical Activity in Medical Residents. Chronobiol. Int. 2016, 33, 730–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patterson, F.; Malone, S.K.; Lozano, A.; Grandner, M.A.; Hanlon, A.L. Smoking, Screen-Based Sedentary Behavior, and Diet Associated with Habitual Sleep Duration and Chronotype: Data from the UK Biobank. Ann. Behav. Med. 2016, 50, 715–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wennman, H.; Kronholm, E.; Partonen, T.; Peltonen, M.; Vasankari, T.; Borodulin, K. Evening Typology and Morning Tiredness Associates with Low Leisure Time Physical Activity and High Sitting. Chronobiol. Int. 2015, 32, 1090–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olds, T.S.; Maher, C.A.; Matricciani, L. Sleep Duration or Bedtime? Exploring the Relationship between Sleep Habits and Weight Status and Activity Patterns. Sleep 2011, 34, 1299–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dashti, H.S.; Redline, S.; Saxena, R. Polygenic Risk Score Identifies Associations between Sleep Duration and Diseases Determined from an Electronic Medical Record Biobank. Sleep 2019, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corella, D.; Asensio, E.M.; Coltell, O.; Sorli, J.V.; Estruch, R.; Martinez-Gonzalez, M.A.; Salas-Salvado, J.; Castaner, O.; Aros, F.; Lapetra, J.; et al. CLOCK Gene Variation is Associated with Incidence of Type-2 Diabetes and Cardiovascular Diseases in Type-2 Diabetic Subjects: Dietary Modulation in the PREDIMED Randomized Trial. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2016, 15, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dashti, H.S.; Follis, J.L.; Smith, C.E.; Tanaka, T.; Garaulet, M.; Gottlieb, D.J.; Hruby, A.; Jacques, P.F.; Kiefte-De Jong, J.C.; Lamon-Fava, S.; et al. Gene-Environment Interactions of Circadian-Related Genes for Cardiometabolic Traits. Diabetes Care 2015, 38, 1456–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balachandran, J.S.; Patel, S.R. In the Clinic. Obstructive Sleep Apnea. Ann. Intern. Med. 2014, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tregear, S.; Reston, J.; Schoelles, K.; Phillips, B. Obstructive Sleep Apnea and Risk of Motor Vehicle Crash: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2009, 5, 573–581. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mulgrew, A.T.; Nasvadi, G.; Butt, A.; Cheema, R.; Fox, N.; Fleetham, J.A.; Ryan, C.F.; Cooper, P.; Ayas, N.T. Risk and Severity of Motor Vehicle Crashes in Patients with Obstructive Sleep Apnoea/Hypopnoea. Thorax 2008, 63, 536–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazza, S.; Pepin, J.L.; Naegele, B.; Rauch, E.; Deschaux, C.; Ficheux, P.; Levy, P. Driving Ability in Sleep Apnoea Patients before and after CPAP Treatment: Evaluation on a Road Safety Platform. Eur. Respir. J. 2006, 28, 1020–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drager, L.F.; Togeiro, S.M.; Polotsky, V.Y.; Lorenzi-Filho, G. Obstructive Sleep Apnea: A Cardiometabolic Risk in Obesity and the Metabolic Syndrome. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2013, 62, 569–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Resta, O.; Foschino-Barbaro, M.P.; Legari, G.; Talamo, S.; Bonfitto, P.; Palumbo, A.; Minenna, A.; Giorgino, R.; De Pergola, G. Sleep-Related Breathing Disorders, Loud Snoring and Excessive Daytime Sleepiness in Obese Subjects. Int. J. Obes. Relat. Metab. Disord. 2001, 25, 669–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pepin, J.L.; Borel, A.L.; Tamisier, R.; Baguet, J.P.; Levy, P.; Dauvilliers, Y. Hypertension and Sleep: Overview of a Tight Relationship. Sleep Med. Rev. 2014, 18, 509–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borel, A.L.; Monneret, D.; Tamisier, R.; Baguet, J.P.; Faure, P.; Levy, P.; Halimi, S.; Pepin, J.L. The Severity of Nocturnal Hypoxia but not Abdominal Adiposity is Associated with Insulin Resistance in non-Obese Men with Sleep Apnea. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e71000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borel, A.L.; Tamisier, R.; Bohme, P.; Priou, P.; Avignon, A.; Benhamou, P.Y.; Hanaire, H.; Pepin, J.L.; Kessler, L.; Valensi, P.; et al. Obstructive Sleep Apnoea Syndrome in Patients Living with Diabetes: Which Patients should be Screened? Diabetes Metab. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, Y.; Xu, H.; Wang, Y.; Yi, H.; Guan, J.; Yin, S. Obstructive Sleep Apnea Predicts Risk of Metabolic Syndrome Independently of Obesity: A Meta-Analysis. Arch. Med. Sci. 2016, 12, 1077–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirotsu, C.; Haba-Rubio, J.; Togeiro, S.M.; Marques-Vidal, P.; Drager, L.F.; Vollenweider, P.; Waeber, G.; Bittencourt, L.; Tufik, S.; Heinzer, R. Obstructive Sleep Apnoea as a Risk Factor for Incident Metabolic Syndrome: A Joined Episono and HypnoLaus Prospective Cohorts Study. Eur. Respir. J. 2018, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fletcher, E.C. Sympathetic over Activity in the Etiology of Hypertension of Obstructive Sleep Apnea. Sleep 2003, 26, 15–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somers, V.K.; Dyken, M.E.; Clary, M.P.; Abboud, F.M. Sympathetic Neural Mechanisms in Obstructive Sleep Apnea. J. Clin. Investig. 1995, 96, 1897–1904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, S.; Mc Nicholas, W.T. Intermittent Hypoxia and Activation of Inflammatory Molecular Pathways in OSAS. Arch. Physiol. Biochem. 2008, 114, 261–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, S.; Taylor, C.T.; Mc Nicholas, W.T. Selective Activation of Inflammatory Pathways by Intermittent Hypoxia in Obstructive Sleep Apnea Syndrome. Circulation 2005, 112, 2660–2667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, S.; Taylor, C.T.; Mc Nicholas, W.T. Systemic Inflammation: A Key Factor in the Pathogenesis of Cardiovascular Complications in Obstructive Sleep Apnoea Syndrome? Thorax 2009, 64, 631–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnaud, C.; Beguin, P.C.; Lantuejoul, S.; Pepin, J.L.; Guillermet, C.; Pelli, G.; Burger, F.; Buatois, V.; Ribuot, C.; Baguet, J.P.; et al. The Inflammatory Preatherosclerotic Remodeling Induced by Intermittent Hypoxia is Attenuated by RANTES/CCL5 inhibition. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care. Med. 2011, 184, 724–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jelic, S.; Padeletti, M.; Kawut, S.M.; Higgins, C.; Canfield, S.M.; Onat, D.; Colombo, P.C.; Basner, R.C.; Factor, P.; LeJemtel, T.H. Inflammation, Oxidative Stress, and Repair Capacity of the Vascular Endothelium in Obstructive Sleep Apnea. Circulation 2008, 117, 2270–2278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.S.; Kim, J.W.; Osborne, O.; Oh, D.Y.; Sasik, R.; Schenk, S.; Chen, A.; Chung, H.; Murphy, A.; Watkins, S.M.; et al. Increased Adipocyte O2 Consumption Triggers HIF-1alpha, Causing Inflammation and Insulin Resistance in Obesity. Cell 2014, 157, 1339–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poulain, L.; Thomas, A.; Rieusset, J.; Casteilla, L.; Levy, P.; Arnaud, C.; Dematteis, M. Visceral white Fat Remodelling Contributes to Intermittent Hypoxia-Induced Atherogenesis. Eur. Respir. J. 2014, 43, 513–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leproult, R.; Copinschi, G.; Buxton, O.; Van Cauter, E. Sleep Loss Results in an Elevation of Cortisol Levels the next Evening. Sleep 1997, 20, 865–870. [Google Scholar]
- Vgontzas, A.N.; Pejovic, S.; Zoumakis, E.; Lin, H.M.; Bentley, C.M.; Bixler, E.O.; Sarrigiannidis, A.; Basta, M.; Chrousos, G.P. Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Adrenal Axis Activity in Obese Men with and without Sleep Apnea: Effects of Continuous Positive Airway Pressure Therapy. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2007, 92, 4199–4207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bratel, T.; Wennlund, A.; Carlstrom, K. Pituitary Reactivity, Androgens and Catecholamines in Obstructive Sleep Apnoea. Effects of Continuous Positive Airway Pressure Treatment (CPAP). Respir. Med. 1999, 93, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leproult, R.; Van Cauter, E. Role of Sleep and Sleep Loss in Hormonal Release and Metabolism. Endocr. Dev. 2010, 17, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hotamisligil, G.S. Inflammation and Metabolic Disorders. Nature 2006, 444, 860–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Barnes, G.T.; Yang, Q.; Tan, G.; Yang, D.; Chou, C.J.; Sole, J.; Nichols, A.; Ross, J.S.; Tartaglia, L.A.; et al. Chronic Inflammation in Fat Plays a Crucial Role in the Development of Obesity-Related Insulin Resistance. J. Clin. Investig. 2003, 112, 1821–1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vgontzas, A.N.; Zoumakis, E.; Lin, H.M.; Bixler, E.O.; Trakada, G.; Chrousos, G.P. Marked Decrease in Sleepiness in Patients with Sleep Apnea by Etanercept, a Tumor Necrosis Factor-Alpha Antagonist. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2004, 89, 4409–4413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, P.; Turek, F.W. Timing of Meals: When is as Critical as what and how much. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2017, 312, E369–E380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandin, C.; Scheer, F.A.; Luque, A.J.; Avila-Gandia, V.; Zamora, S.; Madrid, J.A.; Gomez-Abellan, P.; Garaulet, M. Meal Timing Affects Glucose Tolerance, Substrate Oxidation and Circadian-Related Variables: A Randomized, Crossover Trial. Int. J. Obes. 2015, 39, 828–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gill, S.; Panda, S. A Smartphone App Reveals Erratic Diurnal Eating Patterns in Humans that Can Be Modulated for Health Benefits. Cell Metab. 2015, 22, 789–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henst, R.H.P.; Pienaar, P.R.; Roden, L.C.; Rae, D.E. The Effects of Sleep Extension on Cardiometabolic Risk Factors: A Systematic Review. J. Sleep Res. 2019, e12865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Khatib, H.K.; Hall, W.L.; Creedon, A.; Ooi, E.; Masri, T.; McGowan, L.; Harding, S.V.; Darzi, J.; Pot, G.K. Sleep Extension is a Feasible Lifestyle Intervention in Free-Living Adults who are Habitually Short Sleepers: A Potential Strategy for Decreasing Intake of Free Sugars? A Randomized Controlled Pilot Study. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 107, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tasali, E.; Chapotot, F.; Wroblewski, K.; Schoeller, D. The Effects of Extended Bedtimes on Sleep Duration and Food Desire in Overweight Young Adults: A Home-Based Intervention. Appetite 2014, 80, 220–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- So-Ngern, A.; Chirakalwasan, N.; Saetung, S.; Chanprasertyothin, S.; Thakkinstian, A.; Reutrakul, S. Effects of Two-Week Sleep Extension on Glucose Metabolism in Chronically Sleep-Deprived Individuals. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2019, 15, 711–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.Y.; Ho, K.H.; Chen, H.C.; Chien, M.Y. Exercise Training Improves Sleep Quality in Middle-Aged and Older Adults with Sleep Problems: A Systematic Review. J. Physiother. 2012, 58, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, A.N.; Mann, J.I.; Williams, S.; Venn, B.J. Advice to Walk after Meals is more Effective for Lowering Postprandial Glycaemia in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus than Advice that does not Specify Timing: A Randomised Crossover Study. Diabetologia 2016, 59, 2572–2578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borror, A.; Zieff, G.; Battaglini, C.; Stoner, L. The Effects of Postprandial Exercise on Glucose Control in Individuals with Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review. Sports Med. 2018, 48, 1479–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, C.E.; Issa, F.G.; Berthon-Jones, M.; Eves, L. Reversal of Obstructive Sleep Apnoea by Continuous Positive Airway Pressure Applied Through the Nares. Lancet 1981, 1, 862–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDaid, C.; Griffin, S.; Weatherly, H.; Duree, K.; Van Der Burgt, M.; Van Hout, S.; Akers, J.; Davies, R.J.; Sculpher, M.; Westwood, M. Continuous Positive Airway Pressure Devices for the Treatment of Obstructive Sleep Apnoea-Hypopnoea Syndrome: A Systematic Review and Economic Analysis. Health Technol. Assess. 2009, 13, iii–iv, xi–xiv, 1–119, 143–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peppard, P.E.; Young, T.; Palta, M.; Dempsey, J.; Skatrud, J. Longitudinal Study of Moderate Weight Change and Sleep-Disordered Breathing. JAMA 2000, 284, 3015–3021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drager, L.F.; Brunoni, A.R.; Jenner, R.; Lorenzi-Filho, G.; Bensenor, I.M.; Lotufom, P.A. Effects of CPAP on Body Weight in Patients with Obstructive Sleep Apnoea: A Meta-Analysis of Randomised Trials. Thorax 2015, 70, 258–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoyos, C.M.; Killick, R.; Yee, B.J.; Phillips, C.L.; Grunstein, R.R.; Liu, P.Y. Cardiometabolic Changes after Continuous Positive Airway Pressure for Obstructive Sleep Apnoea: A Randomised Sham-Controlled Study. Thorax 2012, 67, 1081–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furlan, S.F.; Braz, C.V.; Lorenzi-Filho, G.; Drager, L.F. Management of Hypertension in Obstructive Sleep Apnea. Curr. Cardiol. Rep. 2015, 17, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Cao, Q.; Guo, Z.; Dai, Q. Continuous Positive Airway Pressure in Patients With Obstructive Sleep Apnea and Resistant Hypertension: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. J. Clin. Hypertens. 2016, 18, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Liu, Z.; Yang, H.; Luo, Q. Effects of Continuous Positive Airway Pressure on Glycemic Control and Insulin Resistance in Patients with Obstructive Sleep Apnea: A Meta-Analysis. Sleep Breath. 2013, 17, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinstock, T.G.; Wang, X.; Rueschman, M.; Ismail-Beigi, F.; Aylor, J.; Babineau, D.C.; Mehra, R.; Redline, S. A Controlled Trial of CPAP Therapy on Metabolic Control in Individuals with Impaired Glucose Tolerance and Sleep Apnea. Sleep 2012, 35, 617–625B. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coughlin, S.R.; Mawdsley, L.; Mugarza, J.A.; Wilding, J.P.; Calverley, P.M. Cardiovascular and Metabolic Effects of CPAP in Obese Males with OSA. Eur. Respir. J. 2007, 29, 720–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craig, S.E.; Kohler, M.; Nicoll, D.; Bratton, D.J.; Nunn, A.; Davies, R.; Stradling, J. Continuous Positive Airway Pressure Improves Sleepiness but not Calculated Vascular Risk in Patients with Minimally Symptomatic Obstructive Sleep Apnoea: The MOSAIC Randomised Controlled Trial. Thorax 2012, 67, 1090–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Zhou, Z.; McEvoy, R.D.; Anderson, C.S.; Rodgers, A.; Perkovic, V.; Neal, B. Association of Positive Airway Pressure with Cardiovascular Events and Death in Adults With Sleep Apnea: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. JAMA 2017, 318, 156–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borel, A.L.; Leblanc, X.; Almeras, N.; Tremblay, A.; Bergeron, J.; Poirier, P.; Despres, J.P.; Series, F. Sleep Apnoea Attenuates the Effects of a Lifestyle Intervention Programme in Men with Visceral Obesity. Thorax 2012, 67, 735–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chirinos, J.A.; Gurubhagavatula, I.; Teff, K.; Rader, D.J.; Wadden, T.A.; Townsend, R.; Foster, G.D.; Maislin, G.; Saif, H.; Broderick, P.; et al. CPAP, Weight Loss, or Both for Obstructive Sleep Apnea. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 370, 2265–2275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

© 2019 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Borel, A.-L. Sleep Apnea and Sleep Habits: Relationships with Metabolic Syndrome. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2628. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11112628
Borel A-L. Sleep Apnea and Sleep Habits: Relationships with Metabolic Syndrome. Nutrients. 2019; 11(11):2628. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11112628
Chicago/Turabian StyleBorel, Anne-Laure. 2019. "Sleep Apnea and Sleep Habits: Relationships with Metabolic Syndrome" Nutrients 11, no. 11: 2628. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11112628
APA StyleBorel, A.-L. (2019). Sleep Apnea and Sleep Habits: Relationships with Metabolic Syndrome. Nutrients, 11(11), 2628. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11112628




