Effects of Periodic Fasting on Fatty Liver Index—A Prospective Observational Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Subjects
2.3. Study Interventions
2.4. Outcome Measures
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics of Study Participants
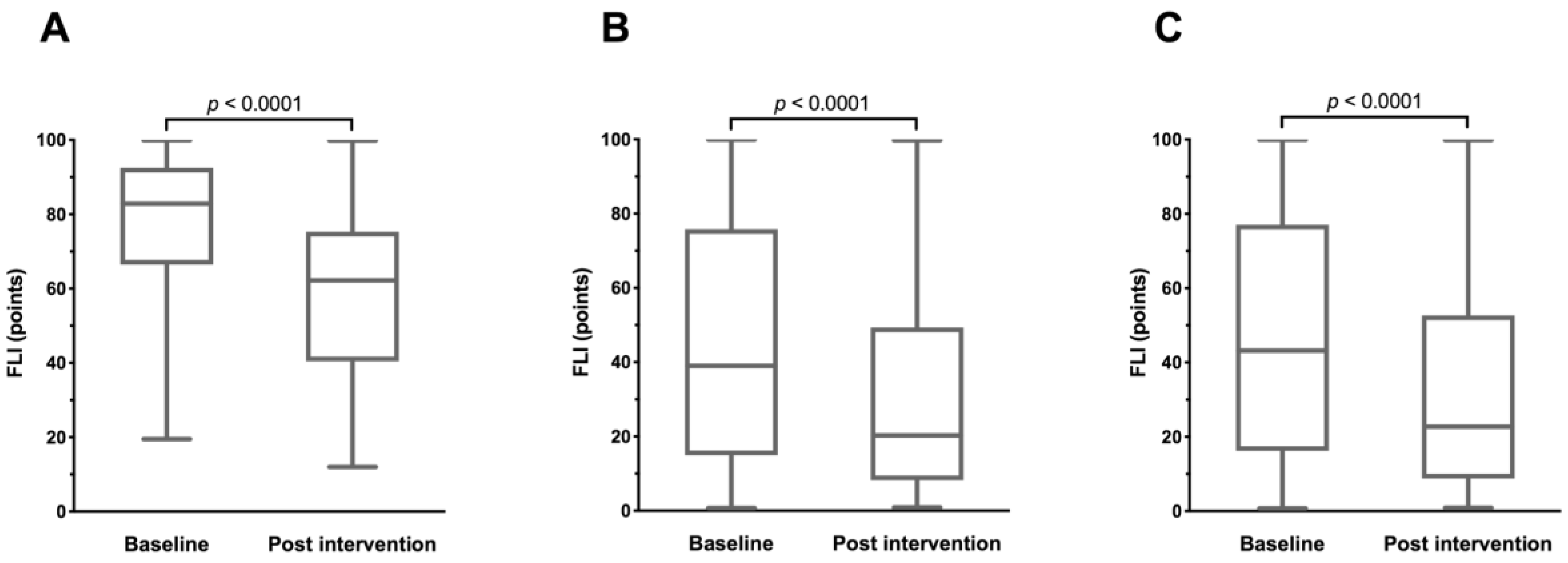
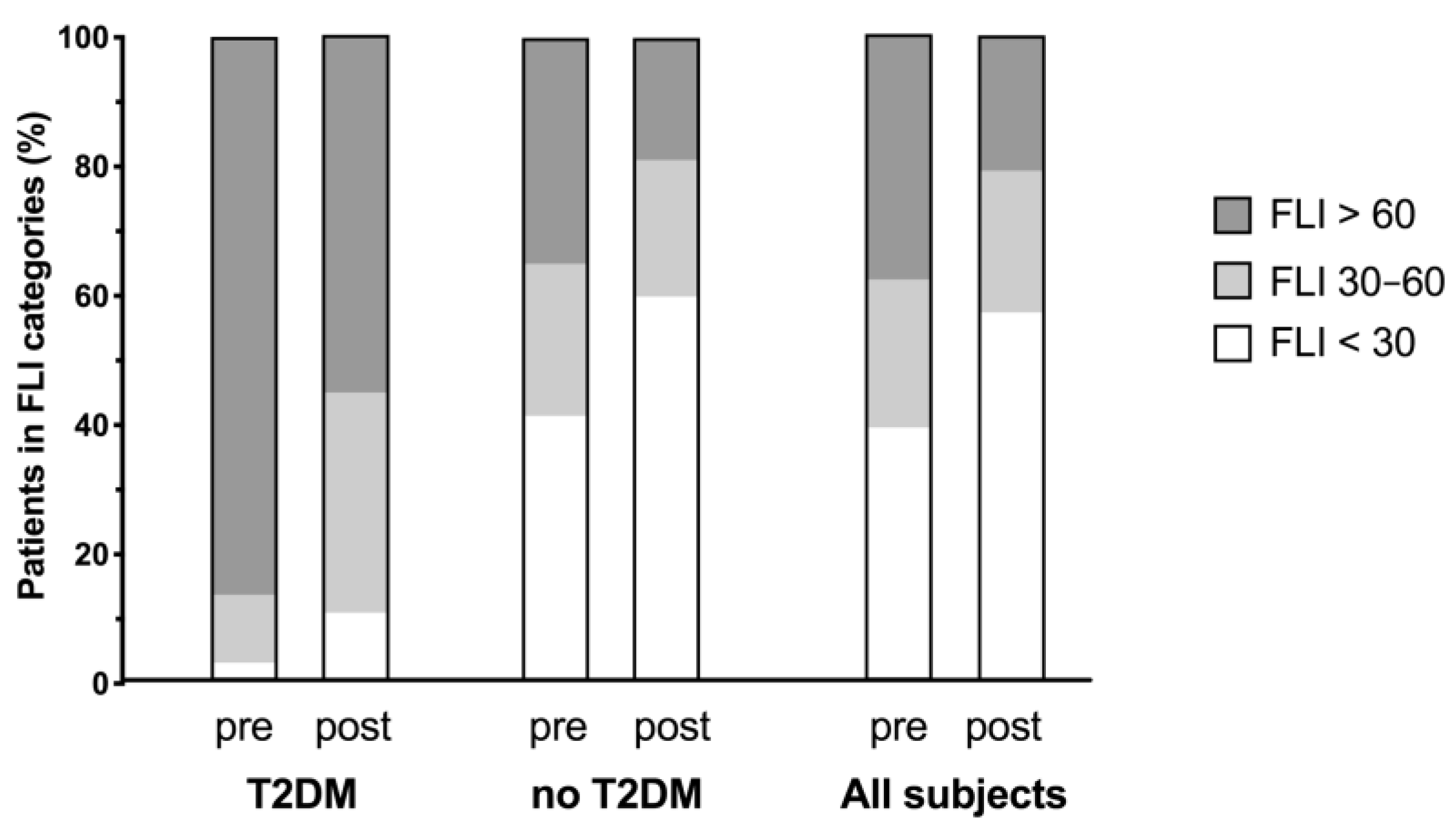
3.2. Changes in FLI
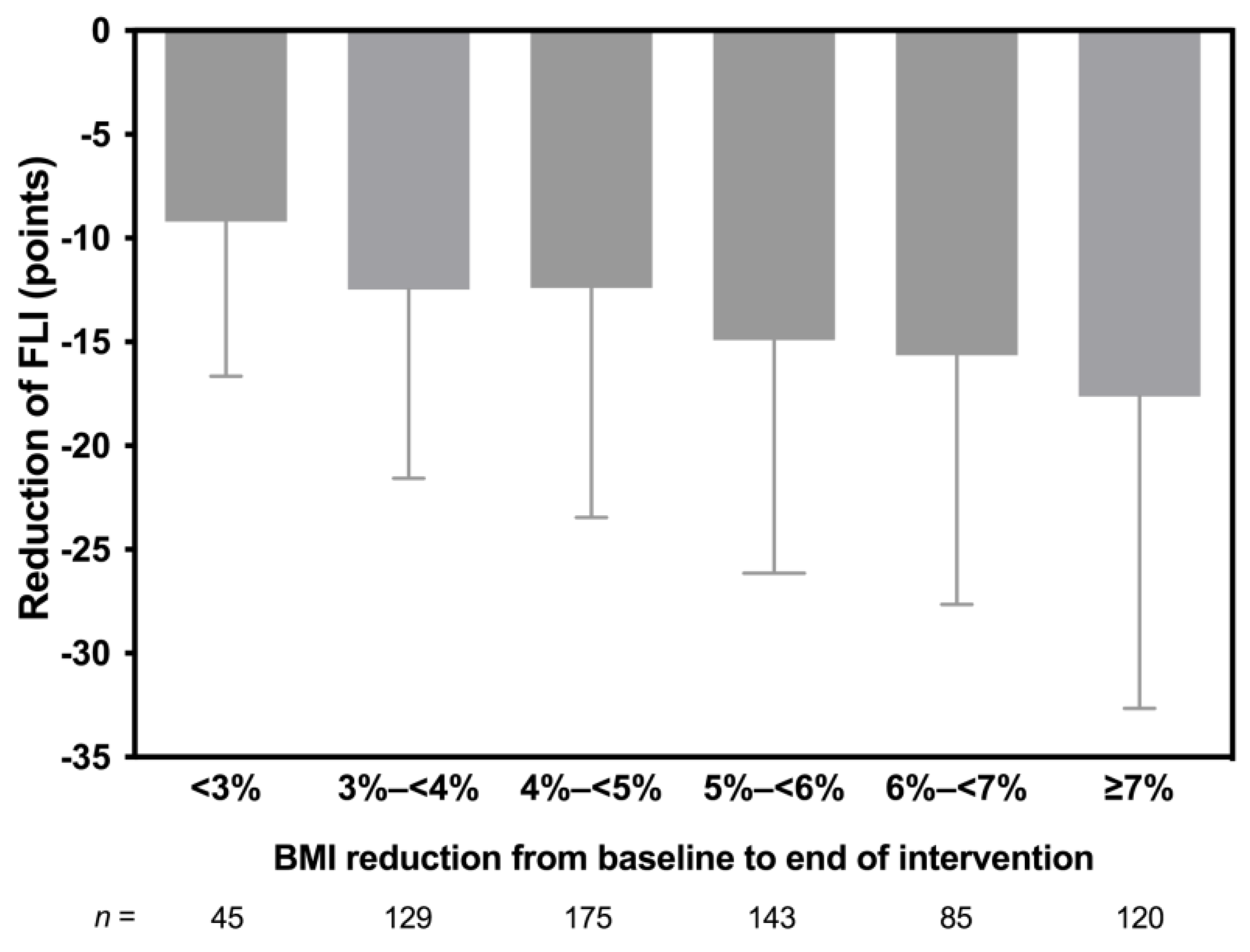
3.3. Changes in Anthropometric and Metabolic Parameters
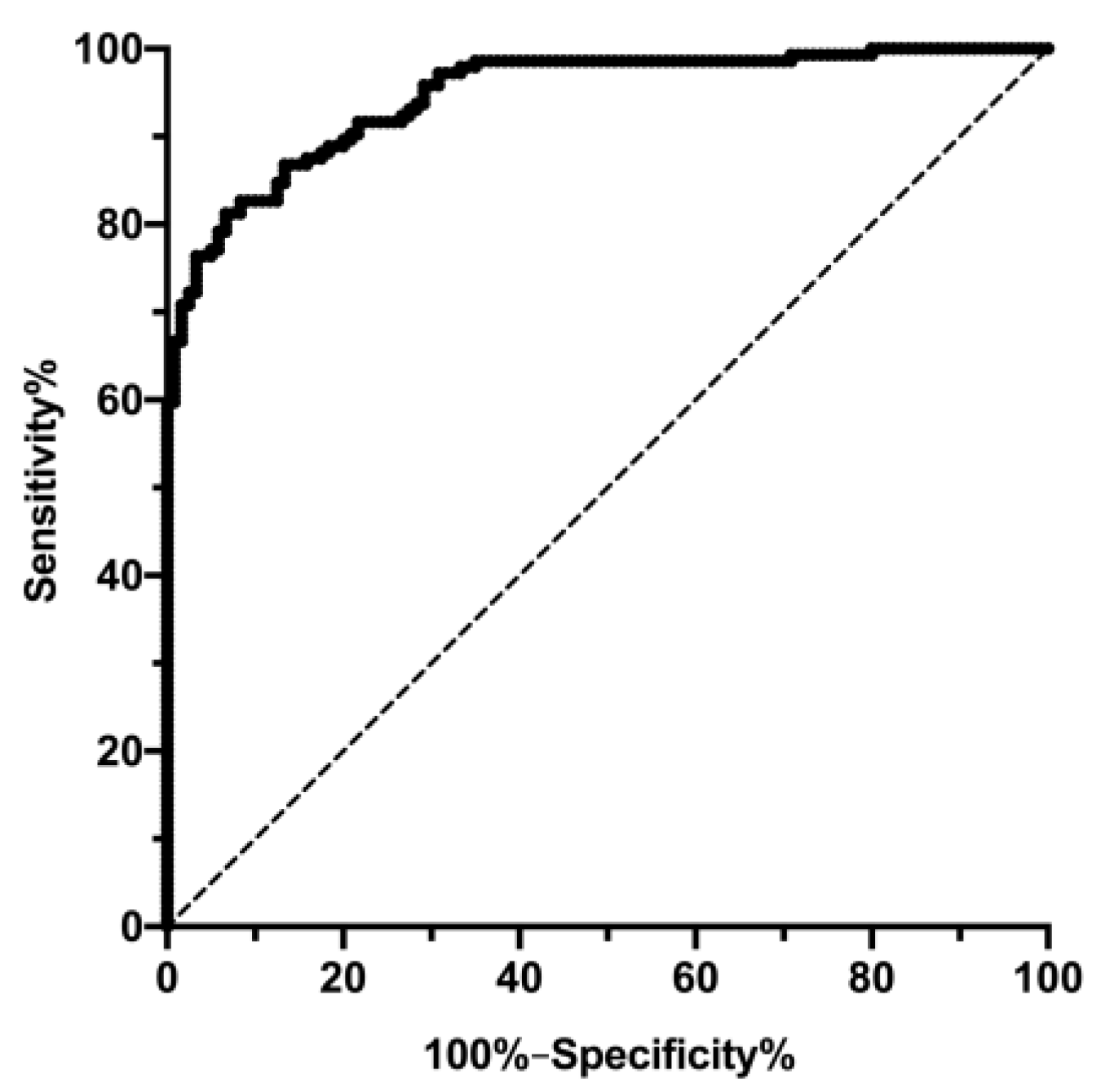
3.4. Correlations Analyses
3.5. Safety
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Glen, J.; Floros, L.; Day, C.; Pryke, R.; Grp, G.D. Non–alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD): Summary of NICE guidance. BMJ Brit. Med. J. 2016, 354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Younossi, Z.M.; Koenig, A.B.; Abdelatif, D.; Fazel, Y.; Henry, L.; Wymer, M. Global Epidemiology of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease-Meta-Analytic Assessment of Prevalence, Incidence, and Outcomes. Hepatology 2016, 64, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vernon, G.; Baranova, A.; Younossi, Z.M. Systematic review: The epidemiology and natural history of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis in adults. Aliment. Pharm. Ther. 2011, 34, 274–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, V.W.; Wong, G.L.; Choi, P.C.; Chan, A.W.; Li, M.K.; Chan, H.Y.; Chim, A.M.; Yu, J.; Sung, J.J.; Chan, H.L. Disease progression of non–alcoholic fatty liver disease: A prospective study with paired liver biopsies at 3 years. Gut 2010, 59, 969–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calzadilla Bertot, L.; Adams, L.A. The Natural Course of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballestri, S.; Zona, S.; Targher, G.; Romagnoli, D.; Baldelli, E.; Nascimbeni, F.; Roverato, A.; Guaraldi, G.; Lonardo, A. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease is associated with an almost twofold increased risk of incident type 2 diabetes and metabolic syndrome. Evidence from a systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 31, 936–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kantartzis, K.; Machann, J.; Schick, F.; Fritsche, A.; Haring, H.U.; Stefan, N. The impact of liver fat vs. visceral fat in determining categories of prediabetes. Diabetologia 2010, 53, 882–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souto, K.P.; Meinhardt, N.G.; Ramos, M.J.; Ulbrich–Kulkzynski, J.M.; Stein, A.T.; Damin, D.C. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in patients with different baseline glucose status undergoing bariatric surgery: Analysis of intraoperative liver biopsies and literature review. Surg. Obes. Relat. Dis. 2018, 14, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shulman, G.I. Ectopic Fat in Insulin Resistance, Dyslipidemia, and Cardiometabolic Disease REPLY. New Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 2237–2238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrera, F.; George, J. The Role of Diet and Nutritional Intervention for the Management of Patients with NAFLD. Clin. Liver Dis. 2014, 18, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelmalek, M.F.; Suzuki, A.; Guy, C.; Unalp–Arida, A.; Colvin, R.; Johnson, R.J.; Diehl, A.M.; Clini, N.S. Increased Fructose Consumption Is Associated with Fibrosis Severity in Patients with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Hepatology 2010, 51, 1961–1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kahl, S.; Strassburger, K.; Nowotny, B.; Livingstone, R.; Kluppelholz, B.; Kessel, K.; Hwang, J.H.; Giani, G.; Hoffmann, B.; Pacini, G.; et al. Comparison of liver fat indices for the diagnosis of hepatic steatosis and insulin resistance. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e94059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bedogni, G.; Bellentani, S.; Miglioli, L.; Masutti, F.; Passalacqua, M.; Castiglione, A.; Tiribelli, C. The Fatty Liver Index: A simple and accurate predictor of hepatic steatosis in the general population. BMC Gastroenterol. 2006, 6, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lonardo, A.; Nascimbeni, F.; Targher, G.; Bernardi, M.; Bonino, F.; Bugianesi, E.; Casini, A.; Gastaldelli, A.; Marchesini, G.; Marra, F.; et al. AISF position paper on nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD): Updates and future directions. Digest. Liver Dis. 2017, 49, 471–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, V.W.; Wong, G.L.; Chan, R.S.; Shu, S.S.; Cheung, B.H.; Li, L.S.; Chim, A.M.; Chan, C.K.; Leung, J.K.; Chu, W.C.; et al. Beneficial effects of lifestyle intervention in non-obese patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Hepatol. 2018, 69, 1349–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benedict, M.; Zhang, X. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: An expanded review. World J. Hepatol. 2017, 9, 715–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Promrat, K.; Kleiner, D.E.; Niemeier, H.M.; Jackvony, E.; Kearns, M.; Wands, J.R.; Fava, J.L.; Wing, R.R. Randomized controlled trial testing the effects of weight loss on nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Hepatology 2010, 51, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilar–Gomez, E.; Martinez–Perez, Y.; Calzadilla–Bertot, L.; Torres–Gonzalez, A.; Gra–Oramas, B.; Gonzalez–Fabian, L.; Friedman, S.L.; Diago, M.; Romero–Gomez, M. Weight Loss Through Lifestyle Modification Significantly Reduces Features of Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis. Gastroenterology 2015, 149, 367–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotman, Y.; Sanyal, A.J. Current and upcoming pharmacotherapy for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Gut 2017, 66, 180–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalasani, N.; Younossi, Z.; Lavine, J.E.; Diehl, A.M.; Brunt, E.M.; Cusi, K.; Charlton, M.; Sanyal, A.J. The diagnosis and management of non–alcoholic fatty liver disease: Practice guideline by the American Gastroenterological Association, American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases, and American College of Gastroenterology. Gastroenterology 2012, 142, 1592–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuomilehto, J.; Lindstrom, J.; Eriksson, J.G.; Valle, T.T.; Hamalainen, H.; Ilanne–Parikka, P.; Keinanen–Kiukaanniemi, S.; Laakso, M.; Louheranta, A.; Rastas, M.; et al. Prevention of type 2 diabetes mellitus by changes in lifestyle among subjects with impaired glucose tolerance. N. Engl. J. Med. 2001, 344, 1343–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardona–Morrell, M.; Rychetnik, L.; Morrell, S.L.; Espinel, P.T.; Bauman, A. Reduction of diabetes risk in routine clinical practice: Are physical activity and nutrition interventions feasible and are the outcomes from reference trials replicable? A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Public Health 2010, 10, 653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michalsen, A.; Li, C. Fasting therapy for treating and preventing disease—Current state of evidence. Forsch Komplementmed 2013, 20, 444–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michalsen, A.; Hoffmann, B.; Moebus, S.; Backer, M.; Langhorst, J.; Dobos, G.J. Incorporation of fasting therapy in an integrative medicine ward: Evaluation of outcome, safety, and effects on lifestyle adherence in a large prospective cohort study. J. Altern. Complement. Med. 2005, 11, 601–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, E.L.; Hollingsworth, K.G.; Aribisala, B.S.; Chen, M.J.; Mathers, J.C.; Taylor, R. Reversal of type 2 diabetes: Normalisation of beta cell function in association with decreased pancreas and liver triacylglycerol. Diabetologia 2011, 54, 2506–2514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumeier, C.; Kaiser, D.; Heeren, J.; Scheja, L.; John, C.; Weise, C.; Eravci, M.; Lagerpusch, M.; Schulze, G.; Joost, H.G.; et al. Caloric restriction and intermittent fasting alter hepatic lipid droplet proteome and diacylglycerol species and prevent diabetes in NZO mice. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2015, 1851, 566–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wilhelmi de Toledo, F.; Grundler, F.; Bergouignan, A.; Drinda, S.; Michalsen, A. Safety, health improvement and well–being during a 4 to 21–day fasting period in an observational study including 1422 subjects. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0209353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilhelmi de Toledo, F.; Buchinger, A.; Burggrabe, H.; Holz, G.; Kuhn, C.; Lischka, E.; Lischka, N.; Lutzner, H.; May, W.; Ritzmann–Widderich, M.; et al. Fasting therapy—An expert panel update of the 2002 consensus guidelines. Forsch Komplementmed 2013, 20, 434–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Dayyat, H.M.; Rayyan, Y.M.; Tayyem, R.F. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and associated dietary and lifestyle risk factors. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. 2018, 12, 569–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunkley, A.J.; Bodicoat, D.H.; Greaves, C.J.; Russell, C.; Yates, T.; Davies, M.J.; Khunti, K. Diabetes prevention in the real world: Effectiveness of pragmatic lifestyle interventions for the prevention of type 2 diabetes and of the impact of adherence to guideline recommendations: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetes Care 2014, 37, 922–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Sadraie, B.; Steckhan, N.; Kessler, C.; Stange, R.; Jeitler, M.; Michalsen, A. Effects of A One-Week Fasting Therapy in Patients with Type-2 Diabetes Mellitus and Metabolic Syndrome—A Randomized Controlled Explorative Study. Exp. Clin. Endocrinol. Diabetes 2017, 125, 618–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerndt, P.R.; Naughton, J.L.; Driscoll, C.E.; Loxterkamp, D.A. Fasting: The history, pathophysiology and complications. West. J. Med. 1982, 137, 379–399. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Peng, L.; Wang, J.; Li, F. Weight reduction for non–alcoholic fatty liver disease. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Browning, J.D.; Baker, J.A.; Rogers, T.; Davis, J.; Satapati, S.; Burgess, S.C. Short–term weight loss and hepatic triglyceride reduction: Evidence of a metabolic advantage with dietary carbohydrate restriction. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2011, 93, 1048–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabbous, Z.; Bashir, M.; Elzouki, A.N.; Ahmed, M.S.; Farouk, S.; Hassanien, M.; Malik, R.A.; Abou Samra, A.B.; Elhadd, T.; Group, P.S. Differential effects of gender and patient background diversity on the changes in metabolic and biophysical profiles in people with type-2 diabetes from different ethnicities who fast during Ramadan (H1439): A prospective study from Qatar. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2019, 152, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cahill, G.F., Jr. Fuel metabolism in starvation. Annu Rev. Nutr 2006, 26, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puchalska, P.; Crawford, P.A. Multi-dimensional Roles of Ketone Bodies in Fuel Metabolism, Signaling, and Therapeutics. Cell Metab. 2017, 25, 262–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mannisto, V.T.; Simonen, M.; Hyysalo, J.; Soininen, P.; Kangas, A.J.; Kaminska, D.; Matte, A.K.; Venesmaa, S.; Kakela, P.; Karja, V.; et al. Ketone body production is differentially altered in steatosis and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis in obese humans. Liver Int. 2015, 35, 1853–1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degirolamo, C.; Sabba, C.; Moschetta, A. Therapeutic potential of the endocrine fibroblast growth factors FGF19, FGF21 and FGF23. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2016, 15, 51–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, R.; Al–Mrabeh, A.; Zhyzhneuskaya, S.; Peters, C.; Barnes, A.C.; Aribisala, B.S.; Hollingsworth, K.G.; Mathers, J.C.; Sattar, N.; Lean, M.E.J. Remission of Human Type 2 Diabetes Requires Decrease in Liver and Pancreas Fat Content but Is Dependent upon Capacity for β Cell Recovery. Cell Metab. 2018, 28, 547–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, M.A.; Cruz, J.F.; Macena, L.B.; de Santana, D.S.; Oliveira, C.C.; Lima, S.O.; Franca, A.V. Association of the Nonalcoholic Hepatic Steatosis and Its Degrees with the Values of Liver Enzymes and Homeostasis Model Assessment—Insulin Resistance Index. Gastroenterol. Res. 2015, 8, 260–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van den Berg, E.H.; Amini, M.; Schreuder, T.C.; Dullaart, R.P.; Faber, K.N.; Alizadeh, B.Z.; Blokzijl, H. Prevalence and determinants of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in lifelines: A large Dutch population cohort. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0171502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mameli, C.; Krakauer, N.Y.; Krakauer, J.C.; Bosetti, A.; Ferrari, C.M.; Moiana, N.; Schneider, L.; Borsani, B.; Genoni, T.; Zuccotti, G. The association between a body shape index and cardiovascular risk in overweight and obese children and adolescents. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0190426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lean, M.E.; Leslie, W.S.; Barnes, A.C.; Brosnahan, N.; Thom, G.; McCombie, L.; Peters, C.; Zhyzhneuskaya, S.; Al–Mrabeh, A.; Hollingsworth, K.G.; et al. Primary care–led weight management for remission of type 2 diabetes (DiRECT): An open–label, cluster–randomised trial. Lancet 2018, 391, 541–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| T2DM | No Diabetes | All | p Value T2DM vs. No Diabetes | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | 38 | 659 | 697 | |
| Female, n (%) | 11 (28.9) | 429 (65.1) | 440 (63.1) | |
| Age, years | 60.92 ± 9.74 | 54.23 ± 13.46 | 54.60 ± 13.36 | 0.0021 |
| BMI, kg/m2 | 31.79 ± 5.15 | 27.98 ± 5.25 | 28.19 ± 5.31 | <0.0001 |
| BMI categories <25 kg/m2, n (%) ≥25 kg/m2, n (%) | 1 (2.6) 37 (97.4) | 206 (79.5) 453 (20.5) | 207 (29.7) 490 (60.3) | <0.0001 |
| Height, cm | 173.21 ± 0.10 | 169.23 ± 0.09 | 169.45 ± 0.09 | 0.0162 |
| Weight, kg | 95.45 ± 17.78 | 80.46 ± 17.89 | 81.28 ± 18.19 | <0.0001 |
| Waist, cm | 107.13 ± 11.32 | 92.06 ± 15.21 | 92.88 ± 15.40 | <0.0001 |
| Glucose, mmoL/L | 8.10 ± 2.40 | 5.19 ± 0.72 | 5.35 ± 1.11 | <0.0001 |
| HbA1c, mmoL/moL | 55.2 ± 15.0 | 35.28 ± 3.94 | 36.37 ± 6.86 | <0.0001 |
| GGT, µkat/L | 0.75 ± 0.95 | 0.47 ± 0.53 | 0.48 ± 0.57 | 0.0003 |
| GOT, µkat/L | 0.46 ± 0.20 | 0.40 ± 0.21 | 0.41 ± 0.21 | 0.0550 |
| GPT, µkat/L | 0.63 ± 0.38 | 0.49 ± 0.35 | 0.50 ± 0.35 | 0.0006 |
| AP, µkat/L | 1.06 ± 0.31 | 1.09 ± 0.30 | 1.09 ± 0.30 | 0.5164 |
| Cholesterol, mmoL/L | 4.83 ± 1.18 | 5.60 ± 1.18 | 5.56 ± 1.19 | 0.0002 |
| TG, mmoL/L | 2.09 ± 0.95 | 1.52 ± 0.77 | 1.55 ± 0.80 | <0.0001 |
| HDL, mmoL/L | 1.17 ± 0.34 | 1.57 ± 0.47 | 1.55 ± 0.48 | <0.0001 |
| LDL, mmoL/L | 3.01 ± 1.02 | 3.49 ± 1.07 | 3.46 ± 1.08 | 0.0083 |
| FLI, points | 78.36 ± 16.97 | 44.92 ± 31.57 | 46.75 ± 31.86 | <0.0001 |
| FLI category <30 points ≥30–<60 points ≥60 points | 1 4 33 | 272 156 231 | 273 160 264 | <0.0001 |
| T2DM (n = 38) | No Diabetes (n = 659) | All (n = 697) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean ± SD | p Value | Mean ± SD | p Value | Mean ± SD | p Value | p Value T2DM vs. No Diabetes | |
| Weight, kg | −5.29 ± 2.56 | <0.0001 | −4.31 ± 2.41 | <0.0001 | −4.37 ± 2.42 | <0.0001 | 0.0045 |
| BMI, kg/m2 | −1.75 ± 0.85 | <0.0001 | −1.50 ± 0.81 | <0.0001 | −1.51 ± 0.82 | <0.0001 | 0.0213 |
| Waist, cm | −6.32 ± 3.37 | <0.0001 | −5.34 ± 3.27 | <0.0001 | −5.39 ± 3.28 | <0.0001 | 0.0433 |
| FLI, points | −19.15 ± 11.00 | <0.0001 | −13.73 ± 11.65 | <0.0001 | −14.02 ± 11.67 | <0.0001 | 0.0020 |
| Glucose, mmoL/L | −2.69 ± 2.56 | <0.0001 | −0.60 ± 1.24 | <0.0001 | −0.72 ± 1.42 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 |
| HbA1c, mmoL/moL | −4.43 ± 6.65 | <0.0001 | −1.60 ± 2.91 | <0.0001 | −1.76 ± 3.28 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 |
| GGT, µkat/L | −0.18 ± 0.37 | <0.0001 | −0.12 ± 0.27 | <0.0001 | −0.12 ± 0.28 | <0.0001 | 0.0694 |
| GOT, µkat/L | 0.29 ± 0.30 | <0.0001 | 0.20 ± 0.28 | <0.0001 | 0.21 ± 0.29 | <0.0001 | 0.0613 |
| GPT, µkat/L | 0.34 ± 0.45 | <0.0001 | 0.18 ± 0.34 | <0.0001 | 0.18 ± 0.35 | <0.0001 | 0.0147 |
| AP, µkat/L | −0.03 ± 0.19 | 0.3297 | −0.04 ± 0.14 | <0.0001 | −0.04 ± 0.15 | <0.0001 | 0.9886 |
| Cholesterol, mmoL/L | −0.44 ± 1.05 | 0.0136 | −0.66 ± 0.78 | <0.0001 | −0.64 ± 0.79 | <0.0001 | 0.1858 |
| TG, mmoL/L | −0.78 ± 0.96 | <0.0001 | −0.43 ± 0.69 | <0.0001 | −0.44 ± 0.71 | <0.0001 | 0.0057 |
| HDL, mmoL/L | −0.07 ± 0.27 | 0.0905 | −0.24 ± 0.26 | <0.0001 | −0.23 ± 0.27 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 |
| LDL, mmoL/L | −0.20 ± 1.03 | 0.2327 | −0.31 ± 0.79 | <0.0001 | −0.30 ± 0.81 | <0.0001 | 0.6141 |
| T2DM (n = 38) | No Diabetes (n = 659) | All (n = 697) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| r | p Value | r | p Value | r | p Value | |
| FLI vs. Fasting days | −0.42 | 0.0091 | −0.18 | <0.0001 | −0.20 | <0.0001 |
| FLI vs. BMI | 0.32 | 0.0474 | 0.27 | <0.0001 | −0.14 | 0.0001 |
| FLI vs. WC | 0.39 | 0.0165 | 0.28 | <0.0001 | 0.29 | <0.0001 |
| FLI vs. GGT | 0.22 | 0.1907 | 0.48 | <0.0001 | 0.47 | <0.0001 |
| FLI vs. GOT | 0.18 | 0.2716 | −0.10 | 0.0102 | −0.10 | 0.0120 |
| FLI vs. GPT | 0.18 | 0.2802 | −0.02 | 0.6154 | −0.02 | 0.5673 |
| FLI vs. AP | 0.35 | 0.0322 | 0.17 | <0.0001 | 0.18 | <0.0001 |
| FLI vs. Cholesterol | 0.33 | 0.0451 | 0.30 | <0.0001 | 0.29 | <0.0001 |
| FLI vs. TG | 0.23 | 0.1576 | 0.63 | <0.0001 | 0.62 | <0.0001 |
| FLI vs. fG | 0.03 | 0.8563 | 0.07 | 0.0942 | −0.02 | 0.6890 |
| FLI vs. HbA1C | 0.14 | 0.4096 | 0.04 | 0.3186 | 0.06 | 0.0891 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Drinda, S.; Grundler, F.; Neumann, T.; Lehmann, T.; Steckhan, N.; Michalsen, A.; Wilhelmi de Toledo, F. Effects of Periodic Fasting on Fatty Liver Index—A Prospective Observational Study. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2601. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11112601
Drinda S, Grundler F, Neumann T, Lehmann T, Steckhan N, Michalsen A, Wilhelmi de Toledo F. Effects of Periodic Fasting on Fatty Liver Index—A Prospective Observational Study. Nutrients. 2019; 11(11):2601. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11112601
Chicago/Turabian StyleDrinda, Stefan, Franziska Grundler, Thomas Neumann, Thomas Lehmann, Nico Steckhan, Andreas Michalsen, and Francoise Wilhelmi de Toledo. 2019. "Effects of Periodic Fasting on Fatty Liver Index—A Prospective Observational Study" Nutrients 11, no. 11: 2601. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11112601
APA StyleDrinda, S., Grundler, F., Neumann, T., Lehmann, T., Steckhan, N., Michalsen, A., & Wilhelmi de Toledo, F. (2019). Effects of Periodic Fasting on Fatty Liver Index—A Prospective Observational Study. Nutrients, 11(11), 2601. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11112601





