Cyano-B12 or Whey Powder with Endogenous Hydroxo-B12 for Supplementation in B12 Deficient Lactovegetarians
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
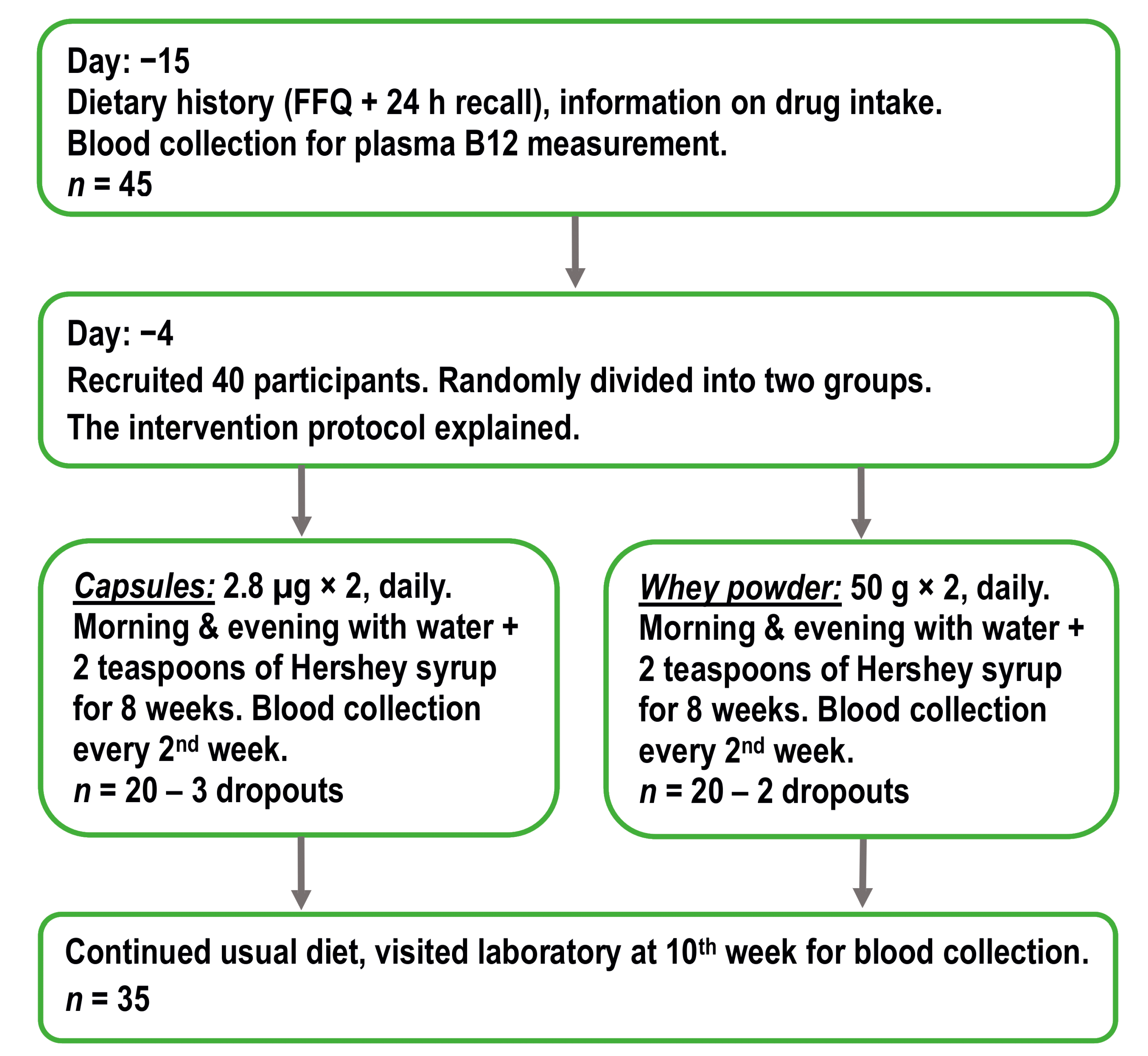
2.1. Study Design and Supplementation Products
2.2. Participants
2.3. Blood Sampling and Biochemical Methods
2.4. Combined Analysis of Markers
2.5. Statistical Procedures and Software
2.6. Correction for Baselines, Data Approximation, and Fitting Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of Participants
3.2. Median Biomarker Values after Four and Eight Weeks of Treatment with Capsules or Whey Powder
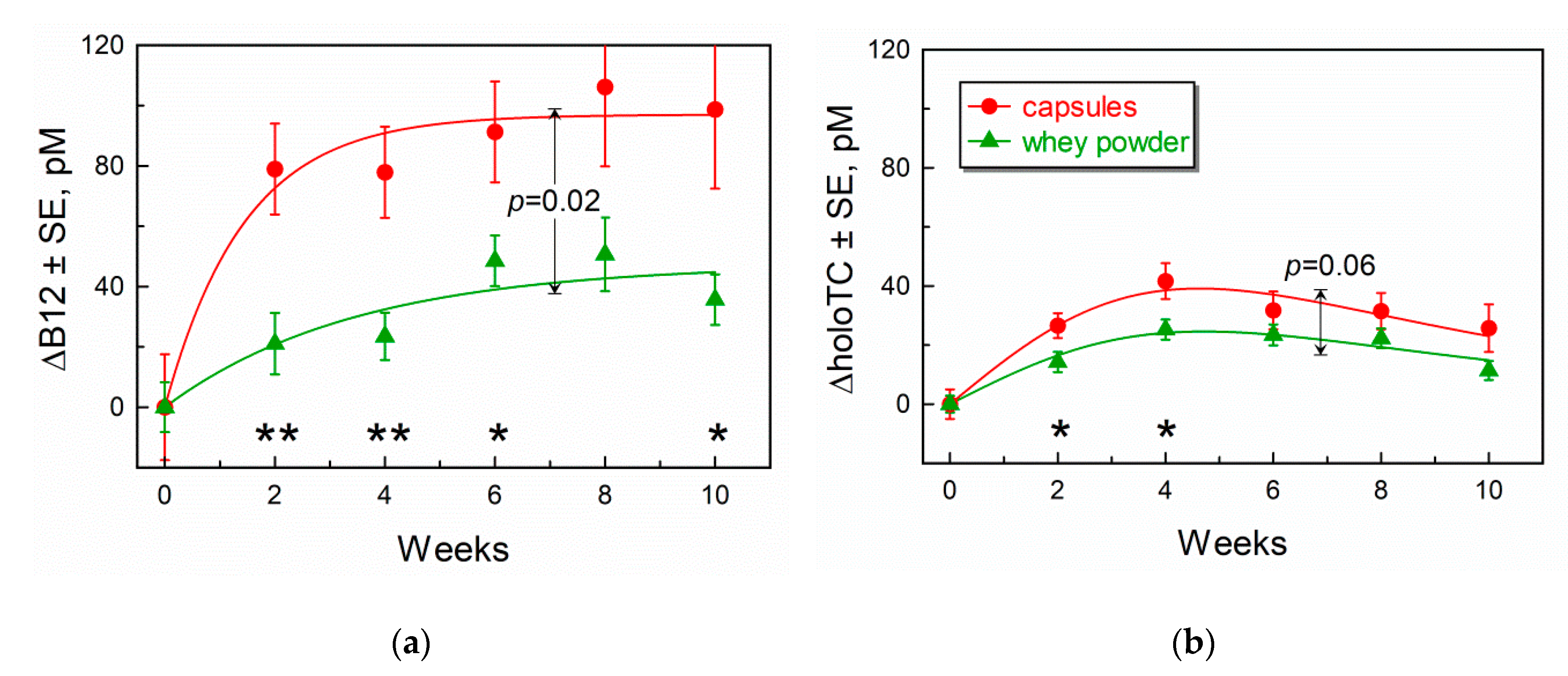
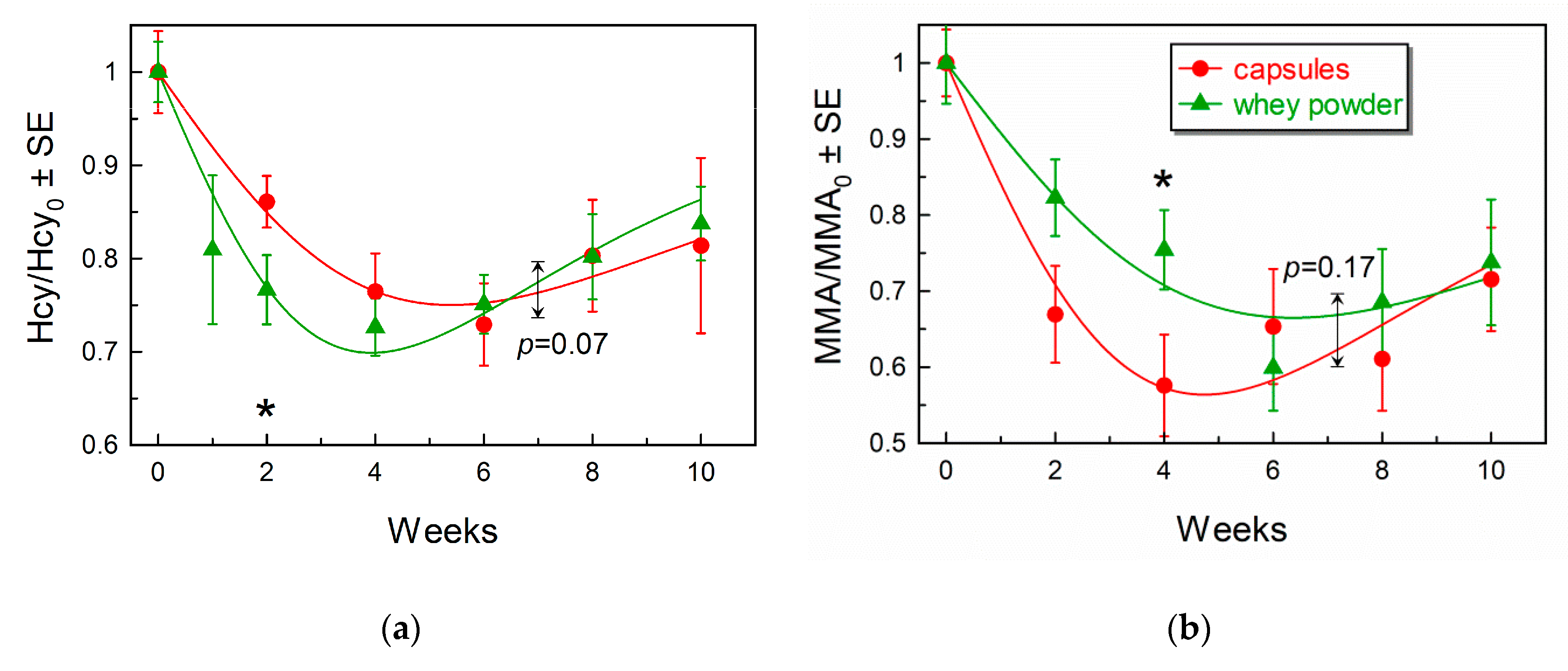
3.3. Comparison of Marker Response Curves Following Treatment with Capsules or Whey Powder
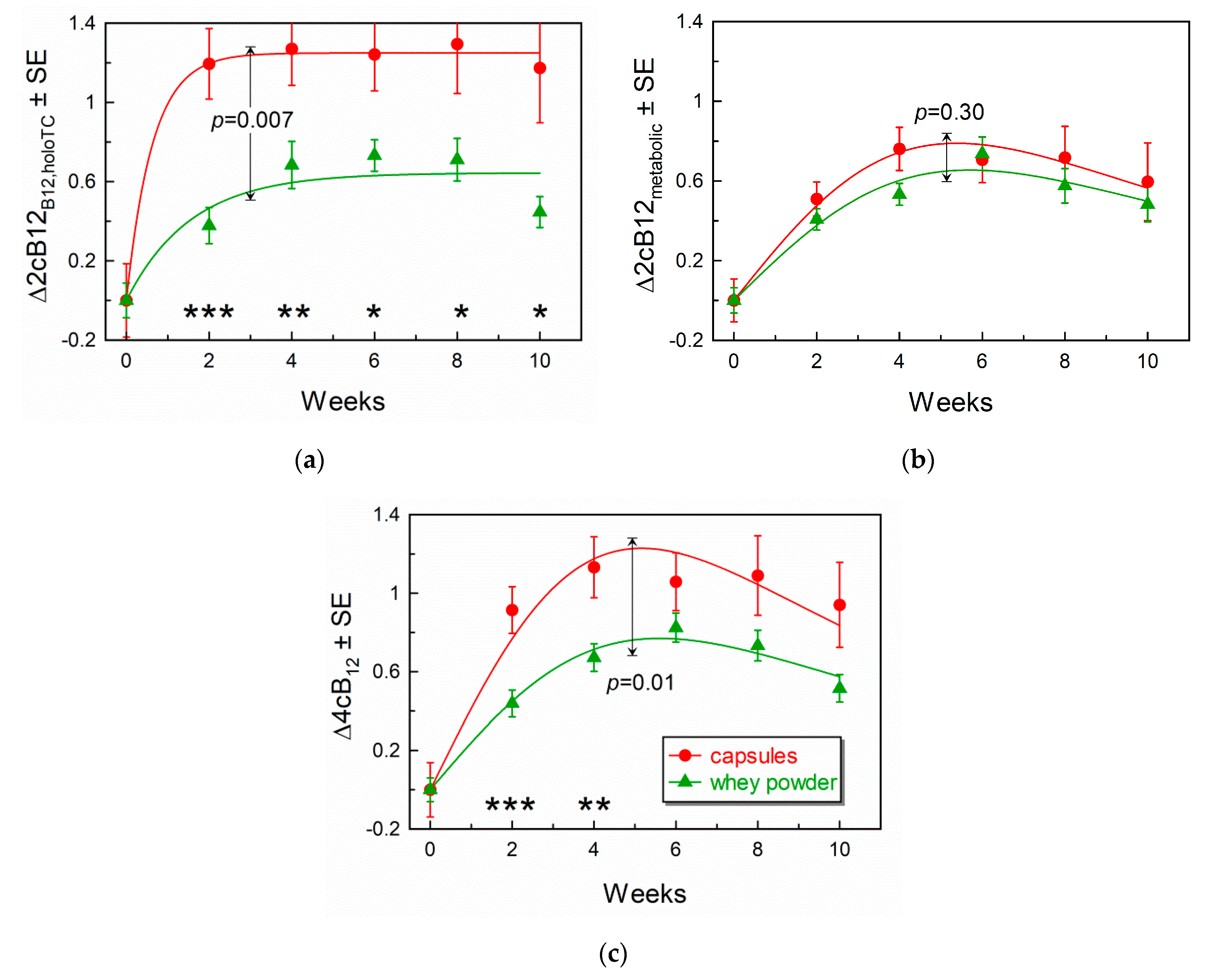
3.4. Comparison of Response Curves for the Combined Indicators of B12-Status
3.5. Forms of B12 Present on TC and HC
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Green, R.; Allen, L.H.; Bjørke-Monsen, A.L.; Brito, A.; Guéant, J.L.; Miller, J.W.; Molloy, A.M.; Nexo, E.; Stabler, S.; Toh, B.H.; et al. Vitamin B12 deficiency. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2017, 3, 17040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, L.H.; Miller, J.W.; de Groot, L.; Rosenberg, I.H.; Smith, A.D.; Refsum, H.; Raiten, D.J. Biomarkers of Nutrition for Development (BOND): Vitamin B-12 Review. J. Nutr. 2018, 148, 1995S–2027S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, L.H. How common is vitamin B-12 deficiency. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2009, 89, 693S–696S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davey, G.K.; Spencer, E.A.; Appleby, P.N.; Allen, N.E.; Knox, K.H.; Key, T.J. EPIC-Oxford: Lifestyle characteristics and nutrient intakes in a cohort of 33 883 meat-eaters and 31 546 non meat-eaters in the UK. Public Health Nutr. 2003, 6, 259–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, D.R.; Specker, B.L.; Ho, M.L.; Norman, E.J. Vitamin B12 status in a macrobiotic community. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1991, 53, 524–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ralapanawa, D.M.; Jayawickreme, K.P.; Ekanayake, E.M.; Jayalath, W.A. B12 deficiency with neurological manifestations in the absence of anaemia. BMC Res. Notes 2015, 8, 458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naik, S.; Bhide, V.; Babhulkar, A.; Mahalle, N.; Parab, S.; Thakre, R.; Kulkarni, M. Daily milk intake improves vitamin B-12 status in young vegetarian Indians: An intervention trial. Nutr. J. 2013, 12, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahalle, N.; Bhide, V.; Greibe, E.; Heegaard, C.W.; Nexo, E.; Fedosov, S.N.; Naik, S. Comparative Bioavailability of Synthetic B12 and Dietary Vitamin B12 Present in Cow and Buffalo Milk: A Prospective Study in Lactovegetarian Indians. Nutrients 2019, 11, 304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogiatzoglou, A.; Smith, A.D.; Nurk, E.; Berstad, P.; Drevon, C.A.; Ueland, P.M.; Vollset, S.E.; Tell, G.S.; Refsum, H. Dietary sources of vitamin B12 and their association with plasma vitamin B12 concentrations in the general population: The Hordaland Homocysteine Study. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2009, 89, 1078–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brouwer-Brolsma, E.M.; Dhonukshe-Rutten, R.A.; van Wijngaarden, J.P.; Zwaluw, N.L.; Velde, N.; de Groot, L.C. Dietary sources of vitamin B-12 and their association with vitamin B-12 status markers in healthy older adults in the B-PROOF study. Nutrients 2015, 7, 7781–7797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matte, J.J.; Guay, F.; Girard, C.L. Bioavailability of vitamin B12 in cow’s milk. Br. J. Nutr. 2012, 107, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedosov, S.N.; Nexo, E.; Heegaard, C.W. Binding aquacobalamin to bovine casein and its peptides via coordination to histidine residues. Int. Dairy J. 2017, 76, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedosov, S.N.; Nexo, E.; Heegaard, C.W. Vitamin B12 and its binding proteins in milk from cow and buffalo in relation to bioavailability of B12. J. Dairy Sci. 2019, 102, 4891–4905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kornerup, L.S.; Juul, C.B.; Fedosov, S.N.; Heegaard, C.W.; Greibe, E.; Nexo, E. Absorption and retention of free and milk protein-bound cyano- and hydroxocobalamins. An experimental study in rats. Biochimie 2016, 126, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kornerup, L.S.; Fedosov, S.N.; Juul, C.B.; Heegaard, C.W.; Greibe, E.; Nexo, E. Tissue distribution of oral vitamin B12 influenced by vitamin B12 status and B12 form. An experimental study in rats. Eur. J. Nutr. 2018, 57, 1459–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greibe, E.; Kornerup, L.; Juul, C.; Fedosov, S.; Heegaard, C.; Nexo, E. The tissue profile of metabolically active coenzyme forms of vitamin B12 differs in B12-depleted rats treated with hydroxo-B12 and cyano-B12. Br. J. Nutr. 2018, 120, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhillon, V.S.; Zabaras, D.; Almond, T.; Cavuoto, P.; James-Martin, G.; Fenech, M. Whey protein isolate improves vitamin B(12) and folate status in elderly Australians with subclinical deficiency of vitamin B(12). Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2017, 61, 1600915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greibe, E.; Mahalle, N.; Bhide, V.; Heegaard, C.W.; Naik, S.; Nexo, E. Increase in circulating holotranscobalamin or hydroxocobalamin in healthy adults with low and normal cobalamin satus. Eur. J. Nutr. 2018, 57, 2847–2855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Haemoglobin Concentrations for the Diagnosis of Anaemia and Assessment of Severity. Vitamin and Mineral Nutrition Information System; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Hardlei, T.F.; Nexo, E. A new principle for measurement of cobalamin and corrinoids, used for studies of cobalamin analogs on serum haptocorrin. Clin. Chem. 2009, 55, 1002–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardlei, T.F.; Mørkbak, A.L.; Bor, M.V.; Bailey, L.B.; Hvas, A.M.; Nexo, E. Assessment of vitamin B(12) absorption based on the accumulation of orally administered cyanocobalamin on transcobalamin. Clin. Chem. 2010, 56, 432–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedosov, S.N.; Britto, A.; Miller, J.W.; Green, R.; Allen, L.H. Combined indicator of vitamin B12 status: Modification for missing biomarkers and folate status and recommendations for revised cut–points. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2015, 53, 1215–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gimsing, P. Determination of cobalamins in biological material: I. Improvement in the unequal recovery of cobalamins by preincubation with cadmium acetate. Anal. Biochem. 1983, 129, 288–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gimsing, P.; Nexo, E.; Hippe, E. Determination of cobalamins in biological material: II. The cobalamins in human plasma and erythrocytes after desalting on nonpolar adsorbent material, and separation by one-dimensional thin-layer chromatography. Anal. Biochem. 1983, 129, 296–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greibe, E.; Mahalle, N.; Bhide, V.; Fedosov, S.; Heegaard, C.W.; Naik, S.; Nexo, E. Effect of 8-week oral supplementation with 3-µg cyano-B12 or hydroxo-B12 in a vitamin B12-deficient population. Eur. J. Nutr. 2019, 58, 261–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morkbak, A.L.; Poulsen, S.S.; Nexo, E. Haptocorrin in humans. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2007, 45, 1751–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedosov, S.N. Physiological and molecular aspects of cobalamin transport. In Water Soluble Vitamins; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlnds, 2012; pp. 347–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutti, E.; Ruetz, M.; Birn, H.; Kräutler, B.; Nexo, E. 4-ethylphenyl-cobalamin impairs tissue uptake of vitamin B12 and causes vitamin B12 deficiency in mice. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e75312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Marker | Reference Interval * | Capsules (CN-B12) Median (min/max) n = 17 (15 Female) | Whey Powder (HO-B12) Median (Min/Max) n = 18 (8 Female) | Mann-Whitney p-Values |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| P, total vitamin B12 (pmol/L) | 148–630 | 106 (61/185) | 114 (71/184) | 0.10 |
| P, creatinine µmol/L | 52–110 | 67 (52–110) | 69 (55–102) | 0.56 |
| P, holotranscobalamin (pmol/L) | 35–150 | 19 (4/40) | 23 (8/99) | 0.17 |
| P, total homocysteine (µmol/L) | 5.0–15.0 | 19 (9/52) | 17 (9/49) | 0.73 |
| P, methylmalonic acid (µmol/L) | 0.1–0.28 | 0.81 (0.28/2.46) | 0.91 (0.30/2.34) | 0.69 |
| S, folate (nmol/L) | 4.54–38.6 | 13.5 (11.1/16.0) | 13.0 (10.6/16.3) | 0.78 |
| combined index (4cB12) | −0.5–1.5 | −1.87 (−3.01/−0.37) | −1.67 (−2.36/−0.33) | 0.30 |
| B, Hemoglobin (g/L) Mild anemia | M 130–180 F 120–150 | 128 (116/137) 1 M, 1 F | 132 (122–142) 1 M, 2 F | 0.67 |
| B, red blood cell, mean corpuscular volume (fL) | 80–96 | 82.5 (80/91.6) | 81.6 (81.5/92) | 0.58 |
| Plasma Markers | Capsules (CN-B12) Median | Whey POWDER (HO-B12) Median | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 Weeks n = 17 | 4 Weeks n = 17 | 8 Weeks n = 13 | Baseline n = 18 | 4 Weeks n = 18 | 8 Weeks n = 18 | |
| Total B12 pmol/L 0 vs. 4 and 8 weeks, p 1 | 106 | 172 | 182 | 114 | 134 | 158 |
| – | 0.00003 | 0.00007 | – | 0.004 | 0.001 | |
| HoloTC (pmol/L) 0 vs. 4 and 8 weeks p 1 | 19 | 59 | 53 | 23 | 49 | 48 |
| – | 0.00003 | 0.00001 | – | 0.000008 | 0.000007 | |
| Total Hcy (µmol/L) 0 vs. 4 and 8 weeks p 1 | 18.9 | 13.3 | 15.5 | 16.8 | 13.0 | 13.6 |
| – | 0.0009 | 0.005 | – | 0.0002 | 0.001 | |
| MMA (µmol/L) 0 vs. 4 and 8 weeks p 1 | 0.81 | 0.38 | 0.46 | 0.91 | 0.62 | 0.50 |
| – | 0.0006 | 0.004 | – | 0.003 | 0.001 | |
| 4cB12 0 vs. 4 and 8 weeks p 1 | −1.87 | −0.42 | −0.63 | −1.67 | −0.96 | −0.91 |
| – | 0.00003 | 0.00006 | – | 0.0003 | 0.0005 | |
| 2cB12B12,holoTC 0 vs. 4 and 8 weeks p 1 | −1.36 | +0.08 | −0.07 | −0.92 | −0.28 | −0.24 |
| – | 0.00003 | 0.00002 | – | 0.0003 | 0.00005 | |
| 2cB12metabolites 0 vs. 4 and 8 weeks p 1 | −1.76 | −0.92 | −1.22 | −1.94 | −1.31 | −1.33 |
| – | 0.005 | 0.0001 | – | 0.000008 | 0.00004 | |
| Vitamin Form | Capsules (CN-B12) | Whey Powder (HO-B12) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bound to TC 1, pmol/L, (%) | Bound to HC 1, pmol/L, (%) | Bound to TC 1, pmol/L, (%) | Bound to HC 1, pmol/L, (%) | |
| Week 8 | ||||
| HO-B12 | 24 (9) | 81 (30) | 63 (26) | 134 (55) |
| CN-B12 | 44 (16) | 122 (45) | 16 (7) | 30 (12) |
| total | 68 (25) | 203 (75) | 79 (33) | 164 (67) |
| Week 10 | ||||
| HO-B12 | 26 (12) | 112 (52) | 53 (26) | 114 (57) |
| CN-B12 | 6.4 (3) | 69 (32) | 12 (6) | 22 (11) |
| total | 32 (15) | 181 (84) | 65 (32) | 136 (68) |
| Dose and Time | Total Plasma ΔB12 2, pmol/L, mean ± SE | ΔcB12metabolic 2 mean ± SE | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN-B12 | HO-B12 | CN-B12 | HO-B12 | |
| 2 × 0.76 µg/day 1 four weeks [8] | +30 ± 7 | +29 ± 15 | +0.37 ± 0.08 | +0.29 ± 0.11 |
| p = 0.95 | p = 0.55 | |||
| 3 µg/day eight weeks [25] | +55 ± 6 | +37 ± 8 | +0.33 ± 0.61 | +0.22 ± 0.11 |
| p = 0.07 | p = 0.86 | |||
| 2 × 2.8 µg/day eight weeks (present study) | +97 ± 20 | +47 ± 13 | +0.70 ± 0.13 | +0.59 ± 0.08 |
| p = 0.04 | p = 0.48 | |||
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Naik, S.; Mahalle, N.; Greibe, E.; Ostenfeld, M.S.; Heegaard, C.W.; Nexo, E.; Fedosov, S.N. Cyano-B12 or Whey Powder with Endogenous Hydroxo-B12 for Supplementation in B12 Deficient Lactovegetarians. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2382. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11102382
Naik S, Mahalle N, Greibe E, Ostenfeld MS, Heegaard CW, Nexo E, Fedosov SN. Cyano-B12 or Whey Powder with Endogenous Hydroxo-B12 for Supplementation in B12 Deficient Lactovegetarians. Nutrients. 2019; 11(10):2382. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11102382
Chicago/Turabian StyleNaik, Sadanand, Namita Mahalle, Eva Greibe, Marie S. Ostenfeld, Christian W. Heegaard, Ebba Nexo, and Sergey N. Fedosov. 2019. "Cyano-B12 or Whey Powder with Endogenous Hydroxo-B12 for Supplementation in B12 Deficient Lactovegetarians" Nutrients 11, no. 10: 2382. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11102382
APA StyleNaik, S., Mahalle, N., Greibe, E., Ostenfeld, M. S., Heegaard, C. W., Nexo, E., & Fedosov, S. N. (2019). Cyano-B12 or Whey Powder with Endogenous Hydroxo-B12 for Supplementation in B12 Deficient Lactovegetarians. Nutrients, 11(10), 2382. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11102382





