In Vivo Effects of Einkorn Wheat (Triticum monococcum) Bread on the Intestinal Microbiota, Metabolome, and on the Glycemic and Insulinemic Response in the Pig Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Breads
2.2. Animals and Study Design
2.3. Sampling and Blood Analysis
2.4. Microbial DNA Extraction, Illumina MiSeq Sequencing and Data Processing
2.5. Metabolomics
2.6. Statistics
2.7. Data Availability
3. Results
3.1. Postprandial Glycemic and Insulinemic Response
3.2. Complete Blood Count (CBC), Fecal Score and Body Weight
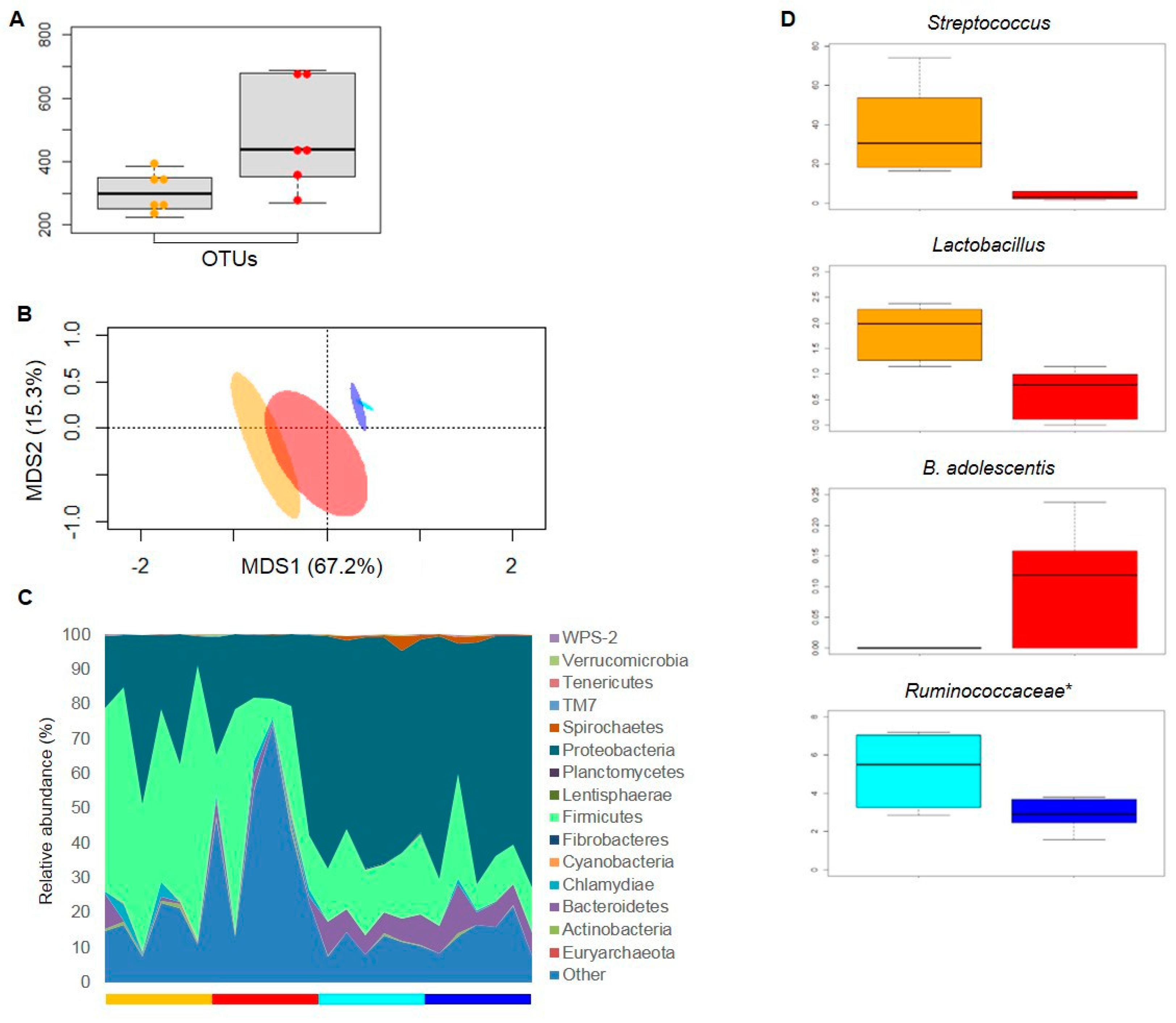
3.3. Gut Microbiota Response to Nutritional Intervention
3.4. Mucosa-Associated Microbiota from Ileal and Colonic Compartments
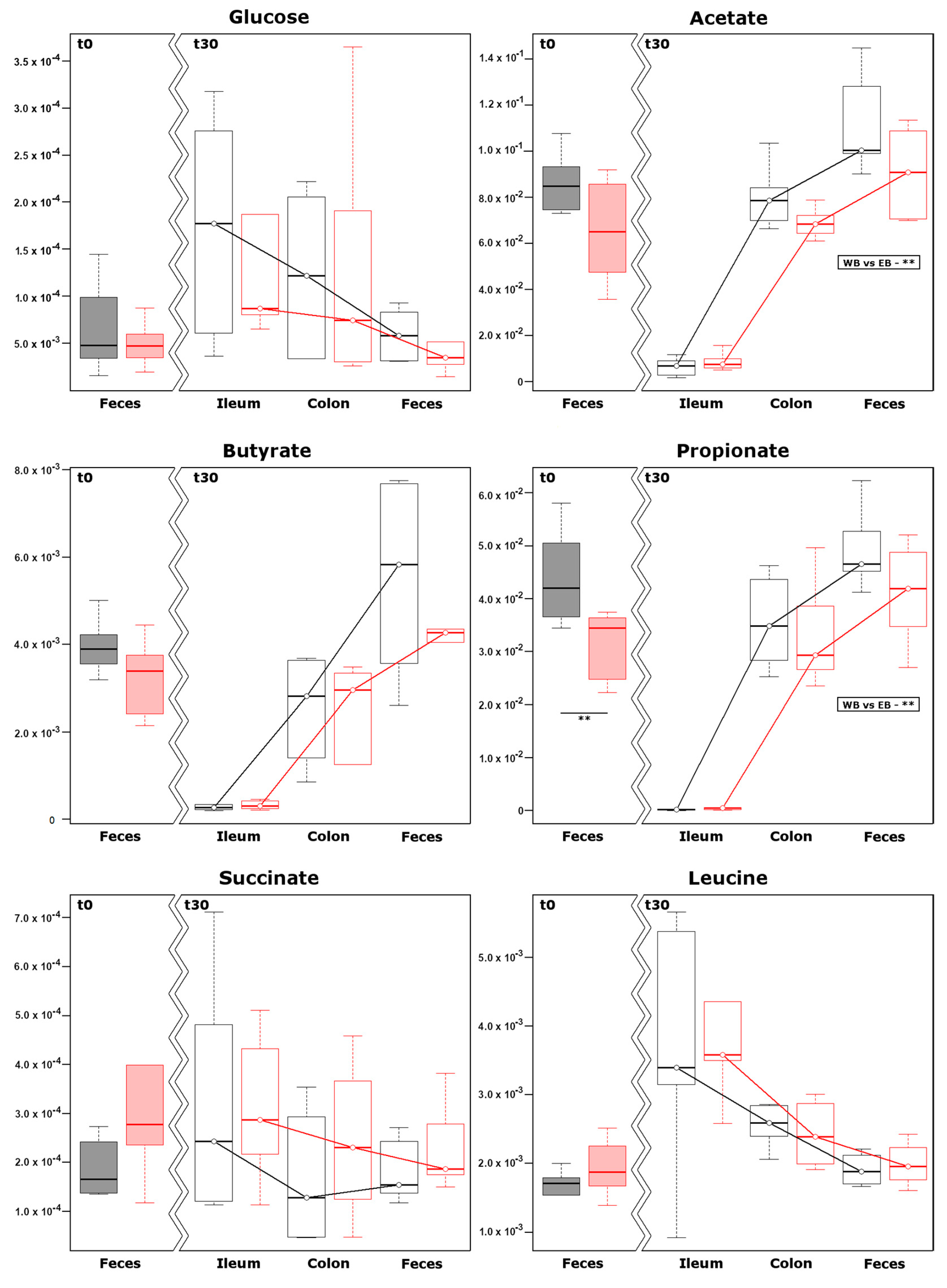
3.5. Metabolomics on Water Soluble Fraction
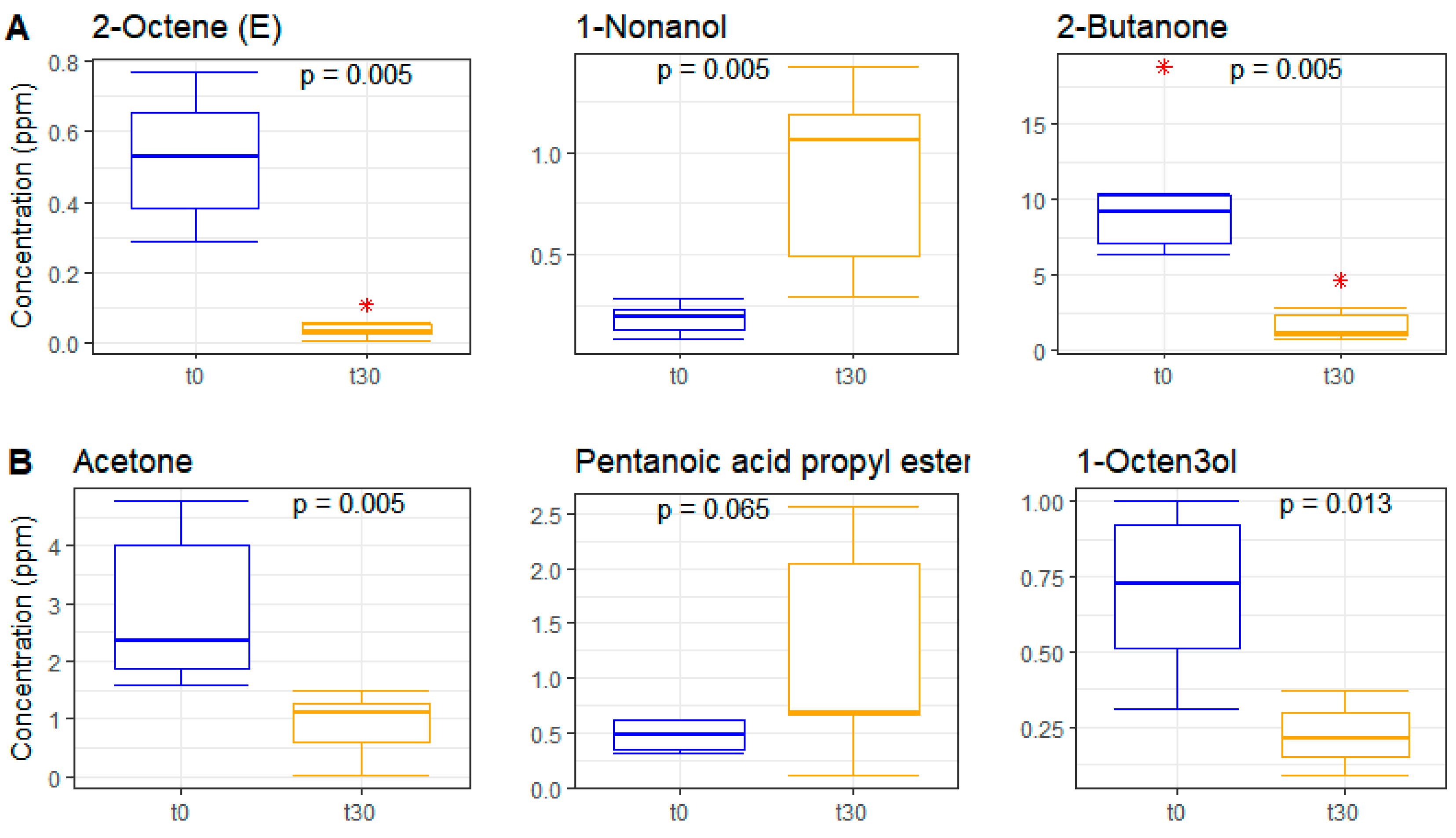
3.6. Metabolomics on Volatile Fraction
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dinu, M.; Whittaker, A.; Pagliai, G.; Benedettelli, S.; Sofi, F. Ancient wheat species and human health: Biochemical and clinical implications. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2018, 52, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hidalgo, A.; Brandolini, A. Nutritional properties of einkorn wheat (Triticum monococcum L.). J. Sci. Food Agric. 2014, 94, 601–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molberg, Ø.; Uhlen, A.K.; Jensen, T.; Flæte, N.S.; Fleckenstein, B.; Arentz-Hansen, H.; Raki, M.; Lundin, K.E.A.; Sollid, L.M. Mapping of gluten T-cell epitopes in the bread wheat ancestors: Implications for celiac disease. Gastroenterology 2005, 128, 393–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antognoni, F.; Mandrioli, R.; Bordoni, A.; Di Nunzio, M.; Viadel, B.; Gallego, E.; Villalba, M.P.; Tomás-Cobos, L.; Taneyo Saa, D.L.; Gianotti, A. Integrated evaluation of the potential health benefits of einkorn-based breads. Nutrients 2017, 9, 1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turroni, S.; Brigidi, P.; Cavalli, A.; Candela, M. Microbiota-host transgenomic metabolism, bioactive molecules from the inside. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 61, 47–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bordoni, A.; Danesi, F.; Di Nunzio, M.; Taccari, A.; Valli, V. Ancient wheat and health: A legend or the reality? A review on KAMUT khorasan wheat. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2017, 68, 278–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thorup, A.C.; Gregersen, S.; Jeppesen, P.B. Ancient wheat diet delays diabetes development in a type 2 diabetes animal model. Rev. Diabet. Stud. 2014, 11, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bo, S.; Seletto, M.; Choc, A.; Ponzo, V.; Lezo, A.; Demagistris, A.; Evangelista, A.; Ciccone, G.; Bertolino, M.; Cassader, M.; et al. The acute impact of the intake of four types of bread on satiety and blood concentrations of glucose, insulin, free fatty acids, triglyceride and acylated ghrelin. A randomized controlled cross-over trial. Food Res. Int. 2017, 92, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graham, H.; Åman, P. The pig as a model in dietary fibre digestion studies. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 1987, 22, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kararli, T.T. Comparison of the gastrointestinal anatomy, physiology, and biochemistry of humans and commonly used laboratory animals. Biopharm. Drug Dispos. 1995, 16, 351–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leulier, F.; MacNeil, L.T.; Lee, W.J.; Rawls, J.F.; Cani, P.D.; Schwarzer, M.; Zhao, L.; Simpson, S.J. Integrative physiology: At the crossroads of nutrition, microbiota, animal physiology, and human health. Cell Metab. 2017, 25, 522–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bryszewska, M.A.; Laghi, L.; Zannoni, A.; Gianotti, A.; Barone, F.; Taneyo Saa, D.L.; Bacci, M.L.; Ventrella, D.; Forni, M. Bioavailability of microencapsulated iron from fortified bread assessed using piglet model. Nutrients 2017, 9, 272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venn, B.J.; Green, T.J. Glycemic index and glycemic load: Measurement issues and their effect on diet–disease relationships. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2007, 61, S122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De La Fuente-Arrillaga, C.; Martinez-Gonzalez, M.A.; Zazpe, I.; Vazquez-Ruiz, Z.; Benito-Corchon, S.; Bes-Rastrollo, M. Glycemic load, glycemic index, bread and incidence of overweight/obesity in a Mediterranean cohort: The SUN project. BMC Public Health 2014, 14, 1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Z.; Morrison, M. Improved extraction of PCR-quality community DNA from digesta and fecal samples. Biotechniques 2004, 36, 808–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biagi, E.; Franceschi, C.; Rampelli, S.; Severgnini, M.; Ostan, R.; Turroni, S.; Consolandi, C.; Quercia, S.; Scurti, M.; Monti, D.; et al. Gut microbiota and extreme longevity. Curr. Biol. 2016, 26, 1480–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masella, A.P.; Bartram, A.K.; Truszkowski, J.M.; Brown, D.G.; Neufeld, J.D. PANDAseq: Paired-end assembler for illumina sequences. BMC Bioinform. 2012, 13, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caporaso, J.G.; Kuczynski, J.; Stombaugh, J.; Bittinger, K.; Bushman, F.D.; Costello, E.K.; Fierer, N.; Pẽa, A.G.; Goodrich, J.K.; Gordon, J.I.; et al. QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat. Methods 2010, 7, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, R.C. Search and clustering orders of magnitude faster than BLAST. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 2460–2461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ventrella, D.; Laghi, L.; Barone, F.; Elmi, A.; Romagnoli, N.; Bacci, M.L. Age-related 1H NMR characterization of Cerebrospinal fluid in newborn and young healthy piglets. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0157623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbara, G.; Scaioli, E.; Barbaro, M.R.; Biagi, E.; Laghi, L.; Cremon, C.; Marasco, G.; Colecchia, A.; Picone, G.; Salfi, N.; et al. Gut microbiota, metabolome and immune signatures in patients with uncomplicated diverticular disease. Gut 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dieterle, F.; Ross, A.; Schlotterbeck, G.; Senn, H. Probabilistic quotient normalization as robust method to account for dilution of complex biological mixtures. Application in 1H NMR metabonomics. Anal. Chem. 2006, 78, 4281–4290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taneyo Saa, D.; Turroni, S.; Serrazanetti, D.I.; Rampelli, S.; Maccaferri, S.; Candela, M.; Severgnini, M.; Simonetti, E.; Brigidi, P.; Gianotti, A. Impact of Kamut® Khorasan on gut microbiota and metabolome in healthy volunteers. Food Res. Int. 2014, 63, 227–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohart, F.; Gautier, B.; Singh, A.; Lê Cao, K.A. mixOmics: An R package for ‘omics feature selection and multiple data integration. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2017, 13, e1005752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enot, D.P.; Lin, W.; Beckmann, M.; Parker, D.; Overy, D.P.; Draper, J. Preprocessing, classification modeling and feature selection using flow injection electrospray mass spectrometry metabolite fingerprint data. Nat. Protoc. 2008, 3, 446–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conover, W.J. Practical Nonparametric Statistics, 3rd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: London, UK, 1980; ISBN 0471028673r0471084573. [Google Scholar]
- Hubert, M.; Rousseeuw, P.J.; Vanden Branden, K. ROBPCA: A new approach to robust principal component analysis. Technometrics 2005, 47, 64–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ventrella, D.; Dondi, F.; Barone, F.; Serafini, F.; Elmi, A.; Giunti, M.; Romagnoli, N.; Forni, M.; Bacci, M.L. The biomedical piglet: Establishing reference intervals for haematology and clinical chemistry parameters of two age groups with and without iron supplementation. BMC Vet. Res. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Layman, D.K. Symposium: Dairy product components and weight regulation the role of leucine in weight loss diets and glucose homeostasis 1,2. J. Nutr. 2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mithieux, G. A novel function of intestinal gluconeogenesis: Central signaling in glucose and energy homeostasis. Nutrition 2009, 25, 881–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ulven, T. Short-chain free fatty acid receptors FFA2/GPR43 and FFA3/GPR41 as new potential therapeutic targets. Front. Endocrinol. 2012, 3, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Psichas, A.; Reimann, F.; Gribble, F.M. Gut chemosensing mechanisms. J. Clin. Investig. 2015, 125, 908–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Vadder, F.; Kovatcheva-Datchary, P.; Zitoun, C.; Duchampt, A.; Bäckhed, F.; Mithieux, G. Microbiota-produced succinate improves glucose homeostasis via intestinal gluconeogenesis. Cell Metab. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nuttall, F.Q.; Mooradian, A.D.; Gannon, M.C.; Billington, C.J.; Krezowski, P. Effect of protein ingestion on the glucose and insulin response to a standardized oral glucose load. Diabetes Care 1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Aal, E.S.M.; Hucl, P. Amino acid composition and in vitro protein digestibility of selected ancient wheats and their end products. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2002, 15, 737–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidalgo, A.; Brandolini, A.; Ratti, S. Influence of genetic and environmental factors on selected nutritional traits of Triticum monococcu. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 6342–6348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosén, L.A.H.; Östman, E.M.; Shewry, P.R.; Ward, J.L.; Andersson, A.A.M.; Piironen, V.; Lampi, A.M.; Rakszegi, M.; Bedö, Z.; Björck, I.M.E. Postprandial glycemia, insulinemia, and satiety responses in healthy subjects after whole grain rye bread made from different rye varieties. 1. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bervoets, L.; Mewis, A.; Massa, G. The shape of the plasma glucose curve during an oral glucose tolerance test as an indicator of beta cell function and insulin sensitivity in end-pubertal obese girls. Horm. Metab. Res. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, H.M.; Xu, P.; Libman, I.M.; Becker, D.J.; Marks, J.B.; Skyler, J.S.; Palmer, J.P.; Sosenko, J.M. The shape of the glucose concentration curve during an oral glucose tolerance test predicts risk for type 1 diabetes. Diabetologia 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manell, E.; Hedenqvist, P.; Svensson, A.; Jensen-Waern, M. Establishment of a refined oral glucose tolerance test in pigs, and assessment of insulin, glucagon and glucagon-like peptide-1 responses. PLoS ONE 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carr, J. Garth Pig Stockmanship Standards; 5M Enterprises Limited: Sheffield, UK, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Suiryanrayna, M.V.A.N.; Ramana, J.V. A review of the effects of dietary organic acids fed to swine. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2015, 6, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Respondek, F.; Goachet, A.G.; Julliand, V. Effects of dietary short-chain fructooligosaccharides on the intestinal microflora of horses subjected to a sudden change in diet. J. Anim. Sci. 2008, 86, 316–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konikoff, T.; Gophna, U. Oscillospira: A central, enigmatic component of the human gut microbiota. Trends Microbiol. 2016, 24, 523–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- David, L.A.; Maurice, C.F.; Carmody, R.N.; Gootenberg, D.B.; Button, J.E.; Wolfe, B.E.; Ling, A.V.; Devlin, A.S.; Varma, Y.; Fischbach, M.A.; et al. Diet rapidly and reproducibly alters the human gut microbiome. Nature 2014, 505, 559–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez-Siles, M.; Duncan, S.H.; Garcia-Gil, L.J.; Martinez-Medina, M. Faecalibacterium prausnitzii: From microbiology to diagnostics and prognostics. ISME J. 2017, 11, 841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenq, R.R.; Taur, Y.; Devlin, S.M.; Ponce, D.M.; Goldberg, J.D.; Ahr, K.F.; Littmann, E.R.; Ling, L.; Gobourne, A.C.; Miller, L.C.; et al. Intestinal blautia is associated with reduced death from graft-versus-host disease. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.L.; Kuang, X.Z.; Shi, X.S.; Yuan, X.Z.; Guo, R.B. Paludibacter jiangxiensis sp. nov., a strictly anaerobic, propionate-producing bacterium isolated from rice paddy field. Arch. Microbiol. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.; Fang, S.; Huang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Ke, S.; Yang, H.; Li, Z.; Gao, J.; Chen, C.; Huang, L. Evaluating the contribution of gut microbiota to the variation of porcine fatness with the cecum and fecal samples. Front. Microbiol. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holman, D.B.; Brunelle, B.W.; Trachsel, J.; Allen, H.K. Meta-analysis to define a core microbiota in the swine gut. mSystems 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ormerod, K.L.; Wood, D.L.A.; Lachner, N.; Gellatly, S.L.; Daly, J.N.; Parsons, J.D.; Dal’Molin, C.G.O.; Palfreyman, R.W.; Nielsen, L.K.; Cooper, M.A.; et al. Genomic characterization of the uncultured Bacteroidales family S24-7 inhabiting the guts of homeothermic animals. Microbiome 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, C.; Wang, B.; Kaliannan, K.; Wang, X.; Lang, H.; Hui, S.; Huang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, M.; Chen, M.; et al. Gut microbiota mediates the protective effects of dietary capsaicin against chronic low-grade inflammation and associated obesity induced by high-fat diet. MBio 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonnenburg, E.D.; Sonnenburg, J.L. Starving our microbial self: The deleterious consequences of a diet deficient in microbiota-accessible carbohydrates. Cell Metab. 2014, 20, 779–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Louis, P.; Flint, H.J. Formation of propionate and butyrate by the human colonic microbiota. Environ. Microbiol. 2017, 19, 29–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reichardt, N.; Duncan, S.H.; Young, P.; Belenguer, A.; McWilliam Leitch, C.; Scott, K.P.; Flint, H.J.; Louis, P. Phylogenetic distribution of three pathways for propionate production within the human gut microbiota. ISME J. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beaumont, M.; Neyrinck, A.M.; Olivares, M.; Rodriguez, J.; de Rocca Serra, A.; Roumain, M.; Bindels, L.B.; Cani, P.D.; Evenepoel, P.; Muccioli, G.G.; et al. The gut microbiota metabolite indole alleviates liver inflammation in mice. FASEB J. 2018, fj.201800544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cani, P.D. Gut microbiota and pregnancy, a matter of inner life. Br. J. Nutr. 2009, 101, 1579–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vernocchi, P.; Del Chierico, F.; Putignani, L. Gut microbiota profiling: Metabolomics based approach to unravel compounds affecting human health. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vhile, S.G.; Kjos, N.P.; Sørum, H.; Øverland, M. Feeding Jerusalem artichoke reduced skatole level and changed intestinal microbiota in the gut of entire male pigs. Animal 2012, 6, 807–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yokoyama, M.T.; Carlson, J.R.; Holdeman, L.V. Isolation and characteristics of a skatole-producing Lactobacillus sp. from the bovine rumen. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1977, 34, 837–842. [Google Scholar]
- Vitali, B.; Ndagijimana, M.; Cruciani, F.; Carnevali, P.; Candela, M.; Guerzoni, M.E.; Brigidi, P. Impact of a synbiotic food on the gut microbial ecology and metabolic profiles. BMC Microbiol. 2010, 10, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Barone, F.; Laghi, L.; Gianotti, A.; Ventrella, D.; Taneyo Saa, D.L.; Bordoni, A.; Forni, M.; Brigidi, P.; Bacci, M.L.; Turroni, S. In Vivo Effects of Einkorn Wheat (Triticum monococcum) Bread on the Intestinal Microbiota, Metabolome, and on the Glycemic and Insulinemic Response in the Pig Model. Nutrients 2019, 11, 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11010016
Barone F, Laghi L, Gianotti A, Ventrella D, Taneyo Saa DL, Bordoni A, Forni M, Brigidi P, Bacci ML, Turroni S. In Vivo Effects of Einkorn Wheat (Triticum monococcum) Bread on the Intestinal Microbiota, Metabolome, and on the Glycemic and Insulinemic Response in the Pig Model. Nutrients. 2019; 11(1):16. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11010016
Chicago/Turabian StyleBarone, Francesca, Luca Laghi, Andrea Gianotti, Domenico Ventrella, Danielle Laure Taneyo Saa, Alessandra Bordoni, Monica Forni, Patrizia Brigidi, Maria Laura Bacci, and Silvia Turroni. 2019. "In Vivo Effects of Einkorn Wheat (Triticum monococcum) Bread on the Intestinal Microbiota, Metabolome, and on the Glycemic and Insulinemic Response in the Pig Model" Nutrients 11, no. 1: 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11010016
APA StyleBarone, F., Laghi, L., Gianotti, A., Ventrella, D., Taneyo Saa, D. L., Bordoni, A., Forni, M., Brigidi, P., Bacci, M. L., & Turroni, S. (2019). In Vivo Effects of Einkorn Wheat (Triticum monococcum) Bread on the Intestinal Microbiota, Metabolome, and on the Glycemic and Insulinemic Response in the Pig Model. Nutrients, 11(1), 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11010016









