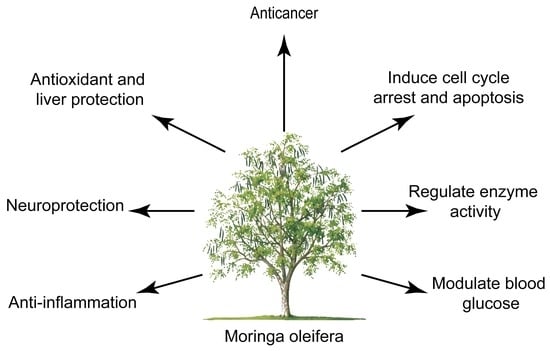
Nutraceutical or Pharmacological Potential of Moringa oleifera Lam.
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Antimicrobial Activity
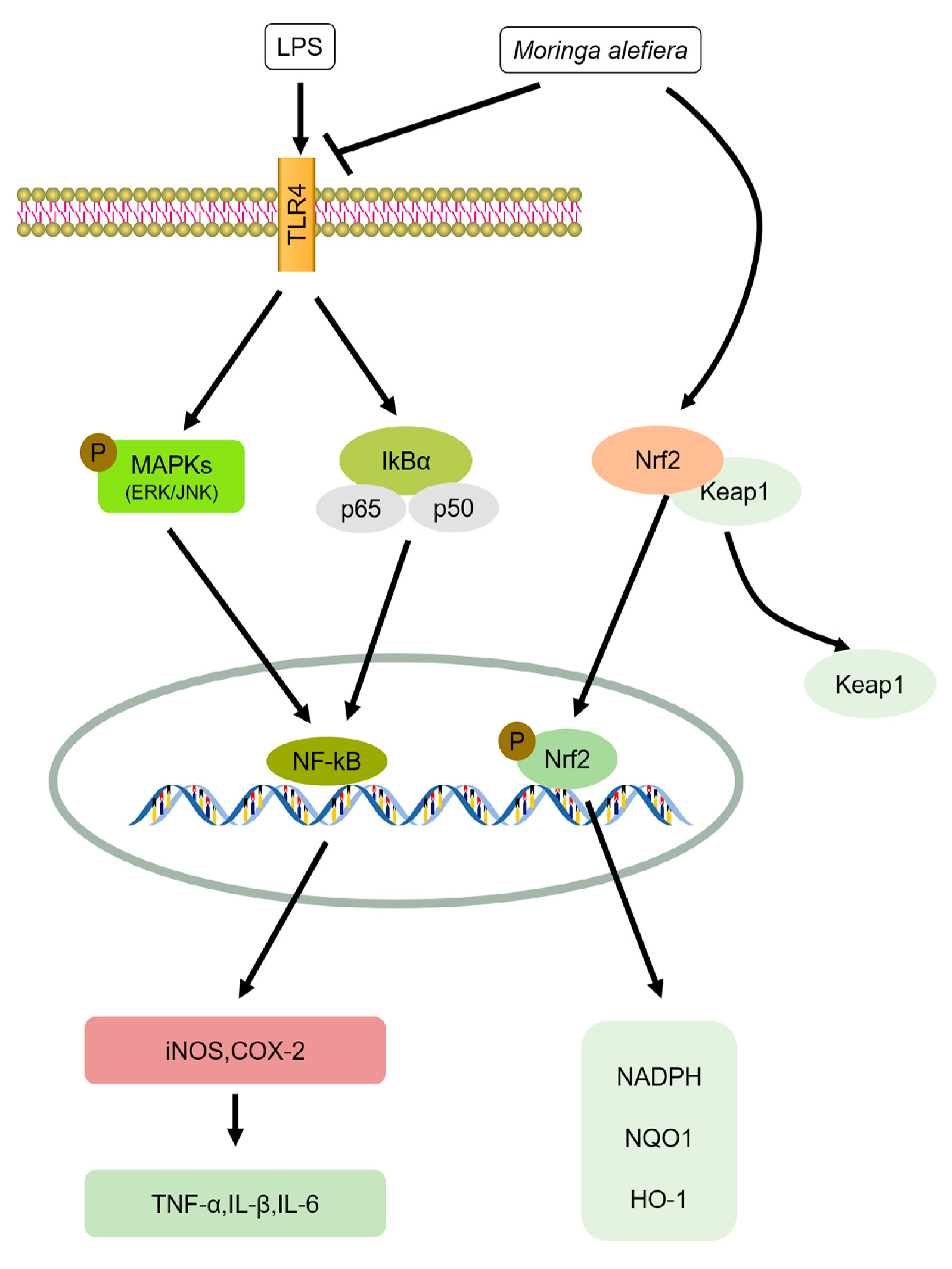
3. Anti-Inflammation
4. Antioxidant and Hepatoprotective Effects
5. Neuroprotective Effect
6. Anticancer Property of M. oleifera
6.1. Regulation of Cell Proliferation
6.2. Cell Cycle Arrest and Apoptosis
6.3. Synergistic Effect on Chemotherapeutic Drugs
6.4. Regulating Enzyme Activity
7. Modulation of Blood Glucose
8. Future Perspectives
9. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Anwar, F.; Latif, S.; Ashraf, M.; Gilani, A.H. Moringa oleifera: A food plant with multiple medicinal uses. Phytother. Res. 2007, 21, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahmood, K.T.; Mugal, T.; Haq, I.U. Moringa oleifera: A natural gift—A review. J. Pharm. Sci. Res. 2010, 2, 775–781. [Google Scholar]
- Abdull, R.A.; Ibrahim, M.D.; Kntayya, S.B. Health benefits of Moringa oleifera. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. APJCP 2014, 15, 8571–8576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Posmontier, B. The medicinal qualities of Moringa oleifera. Holist. Nurs. Pract. 2011, 25, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banji, O.J.; Banji, D.; Kavitha, R. Immunomodulatory effects of alcbholic and hydroalcoholic extracts of Moringa olifera Lam. leaves. Indian J. Exp. Biol. 2012, 50, 270–276. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chumark, P.; Khunawat, P.; Sanvarinda, Y.; Phornchirasilp, S.; Morales, N.P.; Phivthong-Ngam, L.; Ratanachamnong, P.; Srisawat, S.; Pongrapeeporn, K.U. The in vitro and ex vivo antioxidant properties, hypolipidaemic and antiatherosclerotic activities of water extract of Moringa oleifera Lam. leaves. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2008, 116, 439–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elgamily, H.; Moussa, A.; Elboraey, A.; El-Sayed, H.; Al-Moghazy, M.; Abdalla, A. Microbiological assessment of Moringa oleifera extracts and its incorporation in novel dental remedies against some oral pathogens. Open Access Maced. J. Med. Sci. 2016, 4, 585–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehta, K.; Balaraman, R.; Amin, A.H.; Bafna, P.A.; Gulati, O.D. Effect of fruits of Moringa oleifera on the lipid profile of normal and hypercholesterolaemic rabbits. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2003, 86, 191–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moura, M.C.; Napoleao, T.H.; Coriolano, M.C.; Paiva, P.M.; Figueiredo, R.C.; Coelho, L.C. Water-soluble Moringa oleifera lectin interferes with growth, survival and cell permeability of corrosive and pathogenic bacteria. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2015, 119, 666–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikkon, F.; Saud, Z.A.; Rahman, M.H.; Haque, M.E. In vitro antimicrobial activity of the compound isolated from chloroform extract of Moringa oleifera Lam. Pakistan J. Biol. Sci. 2003, 6, 1888–1890. [Google Scholar]
- Peixoto, J.R.; Silva, G.C.; Costa, R.A.; de Sousa, F.J.; Vieira, G.H.; Filho, A.A.; Dos, F.V.R. In vitro antibacterial effect of aqueous and ethanolic Moringa leaf extracts. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Med. 2011, 4, 201–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruckmani, K.; Kavimani, S.; Anandan, R.; Jaykar, B. Effect of Moringa oleifera Lam. on paracetamol induced hepatoxicity. Indian J. Pharm. Sci. 1998, 60, 33–35. [Google Scholar]
- Ariel, A.; Serhan, C.N. Resolvins and protectins in the termination program of acute inflammation. Trends Immunol. 2007, 28, 176–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhatelia, K.; Singh, K.; Singh, R. TLRs: Linking inflammation and breast cancer. Cell Signal. 2014, 26, 2350–2357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aggarwal, B.B. Nuclear factor-kappaB: The enemy within. Cancer Cell 2004, 6, 203–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kou, X.; Qi, S.; Dai, W.; Luo, L.; Yin, Z. Arctigenin inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced iNOS expression in RAW264.7 cells through suppressing JAK-STAT signal pathway. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2011, 11, 1095–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kooltheat, N.; Sranujit, R.P.; Chumark, P.; Potup, P.; Laytragoon-Lewin, N.; Usuwanthim, K. An ethyl acetate fraction of Moringa oleifera Lam. inhibits human macrophage cytokine production induced by cigarette smoke. Nutrients 2014, 6, 697–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minaiyan, M.; Asghari, G.; Taheri, D.; Saeidi, M.; Nasr-Esfahani, S. Anti-inflammatory effect of Moringa oleifera Lam. seeds on acetic acid-induced acute colitis in rats. Avicenna J. Phytomed. 2014, 4, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Arulselvan, P.; Tan, W.S.; Gothai, S.; Muniandy, K.; Fakurazi, S.; Esa, N.M.; Alarfaj, A.A.; Kumar, S.S. Anti-inflammatory potential of ethyl acetate fraction of Moringa oleifera in downregulating the NF-kappaB signaling pathway in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated macrophages. Molecules 2016, 21, 1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fard, M.T.; Arulselvan, P.; Karthivashan, G.; Adam, S.K.; Fakurazi, S. Bioactive extract from Moringa oleifera inhibits the pro-inflammatory mediators in lipopolysaccharide stimulated macrophages. Pharmacogn. Mag. 2015, 11, S556–S563. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Park, E.J.; Cheenpracha, S.; Chang, L.C.; Kondratyuk, T.P.; Pezzuto, J.M. Inhibition of lipopolysaccharide-induced cyclooxygenase-2 and inducible nitric oxide synthase expression by 4-[(2’-O-acetyl-alpha-l-rhamnosyloxy)benzyl]isothiocyanate from Moringa oleifera. Nutr. Cancer 2011, 63, 971–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaja-Chimedza, A.; Graf, B.L.; Simmler, C.; Kim, Y.; Kuhn, P.; Pauli, G.F.; Raskin, I. Biochemical characterization and anti-inflammatory properties of an isothiocyanate-enriched moringa (Moringa oleifera) seed extract. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0182658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maurya, S.K.; Singh, A.K. Clinical efficacy of Moringa oleifera Lam. stems bark in urinary tract infections. Int. Sch. Res. Notices 2014, 2014, 906843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niedzwiecki, A.; Roomi, M.W.; Kalinovsky, T.; Rath, M. Anticancer efficacy of polyphenols and their combinations. Nutrients 2016, 8, 552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thapa, A.; Carroll, N.J. Dietary modulation of oxidative stress in Alzheimer’s disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.F.; Wang, X.L.; Yang, X.Q.; Chen, N. Autophagy-associated targeting pathways of natural products during cancer treatment. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. APJCP 2014, 15, 10557–10563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atawodi, S.E.; Atawodi, J.C.; Idakwo, G.A.; Pfundstein, B.; Haubner, R.; Wurtele, G.; Bartsch, H.; Owen, R.W. Evaluation of the polyphenol content and antioxidant properties of methanol extracts of the leaves, stem, and root barks of Moringa oleifera Lam. J. Med. Food 2010, 13, 710–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verma, A.R.; Vijayakumar, M.; Mathela, C.S.; Rao, C.V. In vitro and in vivo antioxidant properties of different fractions of Moringa oleifera leaves. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2009, 47, 2196–2201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sreelatha, S.; Padma, P.R. Antioxidant activity and total phenolic content of Moringa oleifera leaves in two stages of maturity. Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. 2009, 64, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinha, M.; Das, D.K.; Bhattacharjee, S.; Majumdar, S.; Dey, S. Leaf extract of Moringa oleifera prevents ionizing radiation-induced oxidative stress in mice. J. Med. Food 2011, 14, 1167–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinha, M.; Das, D.K.; Datta, S.; Ghosh, S.; Dey, S. Amelioration of ionizing radiation induced lipid peroxidation in mouse liver by Moringa oleifera Lam. leaf extract. Indian J. Exp. Biol. 2012, 50, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Uma, N.J.; Fakurazi, S.; Hairuszah, I. Moringa oleifera enhances liver antioxidant status via elevation of antioxidant enzymes activity and counteracts paracetamol-induced hepatotoxicity. Malays. J. Nutr. 2010, 16, 293–307. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fakurazi, S.; Hairuszah, I.; Nanthini, U. Moringa oleifera Lam. prevents acetaminophen induced liver injury through restoration of glutathione level. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2008, 46, 2611–2615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharifudin, S.A.; Fakurazi, S.; Hidayat, M.T.; Hairuszah, I.; Moklas, M.A.; Arulselvan, P. Therapeutic potential of Moringa oleifera extracts against acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity in rats. Pharm. Biol. 2013, 51, 279–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, D.; Arya, P.V.; Aggarwal, V.P.; Gupta, R.S. Evaluation of antioxidant and hepatoprotective activities of Moringa oleifera Lam. leaves in carbon tetrachloride-intoxicated rats. Antioxidants (Basel) 2014, 3, 569–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pari, L.; Kumar, N.A. Hepatoprotective activity of Moringa oleifera on antitubercular drug-induced liver damage in rats. J. Med. Food 2002, 5, 171–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, N.; Sikder, K.; Ghosh, S.; Fromenty, B.; Dey, S. Moringa oleifera Lam. leaf extract prevents early liver injury and restores antioxidant status in mice fed with high-fat diet. Indian J. Exp. Biol. 2012, 50, 404–412. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Prince, M.; Bryce, R.; Albanese, E.; Wimo, A.; Ribeiro, W.; Ferri, C.P. The global prevalence of dementia: A systematic review and metaanalysis. Alzheimer’s Dement. J. Alzheimer’s Assoc. 2013, 9, 63–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kou, X.; Li, J.; Bian, J.; Yang, Y.; Yang, X.; Fan, J.; Jia, S.; Chen, N. Ampelopsin attenuates 6-OHDA-induced neurotoxicity by regulating GSK-3β/NRF2/ARE signaling. J. Funct. Food 2015, 19, 765–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, X.; Liu, X.; Chen, X.; Li, J.; Yang, X.; Fan, J.; Yang, Y.; Chen, N. Ampelopsin attenuates brain aging of D-gal-induced rats through miR-34a-mediated SIRT1/mTOR signal pathway. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 74484–74495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finkel, T.; Holbrook, N.J. Oxidants, oxidative stress and the biology of ageing. Nature 2000, 408, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kou, X.; Chen, N. Resveratrol as a natural autophagy regulator for prevention and treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Nutrients 2017, 9, 927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganguly, R.; Guha, D. Alteration of brain monoamines & EEG wave pattern in rat model of Alzheimer's disease & protection by Moringa oleifera. Indian J. Med. Res. 2008, 128, 744–751. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Giacoppo, S.; Rajan, T.S.; De Nicola, G.R.; Iori, R.; Rollin, P.; Bramanti, P.; Mazzon, E. The isothiocyanate isolated from Moringa oleifera shows potent anti-inflammatory activity in the treatment of murine subacute Parkinson’s disease. Rejuvenat. Res. 2017, 20, 50–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hannan, M.A.; Kang, J.Y.; Mohibbullah, M.; Hong, Y.K.; Lee, H.; Choi, J.S.; Choi, I.S.; Moon, I.S. Moringa oleifera with promising neuronal survival and neurite outgrowth promoting potentials. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2014, 152, 142–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sutalangka, C.; Wattanathorn, J.; Muchimapura, S.; Thukham-mee, W. Moringa oleifera mitigates memory impairment and neurodegeneration in animal model of age-related dementia. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2013, 2013, 695936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ekong, M.B.; Ekpo, M.M.; Akpanyung, E.O.; Nwaokonko, D.U. Neuroprotective effect of Moringa oleifera leaf extract on aluminium-induced temporal cortical degeneration. Metab. Brain Dis. 2017, 32, 1437–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, G.; Invally, M.; Sanzagiri, R.; Buttar, H.S. Evaluation of the antidepressant activity of Moringa oleifera alone and in combination with fluoxetine. J. Ayurveda Integr. Med. 2015, 6, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegel, R.; Naishadham, D.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics for Hispanics/Latinos, 2012. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2012, 62, 283–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boggs, D.A.; Palmer, J.R.; Wise, L.A.; Spiegelman, D.; Stampfer, M.J.; Adams-Campbell, L.L.; Rosenberg, L. Fruit and vegetable intake in relation to risk of breast cancer in the Black Women's Health Study. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2010, 172, 1268–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fowke, J.H.; Chung, F.L.; Jin, F.; Qi, D.; Cai, Q.; Conaway, C.; Cheng, J.R.; Shu, X.O.; Gao, Y.T.; Zheng, W. Urinary isothiocyanate levels, brassica, and human breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2003, 63, 3980–3986. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Al-Asmari, A.K.; Albalawi, S.M.; Athar, M.T.; Khan, A.Q.; Al-Shahrani, H.; Islam, M. Moringa oleifera as an anti-cancer agent against breast and colorectal cancer cell lines. PloS ONE 2015, 10, e0135814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berkovich, L.; Earon, G.; Ron, I.; Rimmon, A.; Vexler, A.; Lev-Ari, S. Moringa oleifera aqueous leaf extract down-regulates nuclear factor-kappaB and increases cytotoxic effect of chemotherapy in pancreatic cancer cells. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2013, 13, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fahey, J.W.; Zalcmann, A.T.; Talalay, P. The chemical diversity and distribution of glucosinolates and isothiocyanates among plants. Phytochemistry 2001, 56, 5–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, D.; Srivastava, S.K.; Lew, K.L.; Zeng, Y.; Hershberger, P.; Johnson, C.S.; Trump, D.L.; Singh, S.V. Allyl isothiocyanate, a constituent of cruciferous vegetables, inhibits proliferation of human prostate cancer cells by causing G2/M arrest and inducing apoptosis. Carcinogenesis 2003, 24, 891–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, N.; Budhraja, A.; Cheng, S.; Liu, E.H.; Chen, J.; Yang, Z.; Chen, D.; Zhang, Z.; Shi, X. Phenethyl isothiocyanate exhibits antileukemic activity in vitro and in vivo by inactivation of Akt and activation of JNK pathways. Cell Death Dis. 2011, 2, e140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karim, N.A.; Ibrahim, M.D.; Kntayya, S.B.; Rukayadi, Y.; Hamid, H.A.; Razis, A.F. Moringa oleifera Lam: Targeting chemoprevention. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. APJCP 2016, 17, 3675–3686. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sreelatha, S.; Jeyachitra, A.; Padma, P.R. Antiproliferation and induction of apoptosis by Moringa oleifera leaf extract on human cancer cells. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2011, 49, 1270–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waterman, C.; Cheng, D.M.; Rojas-Silva, P.; Poulev, A.; Dreifus, J.; Lila, M.A.; Raskin, I. Stable, water extractable isothiocyanates from Moringa oleifera leaves attenuate inflammation in vitro. Phytochemistry 2014, 103, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, I.L. Soluble extract from Moringa oleifera leaves with a new anticancer activity. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e95492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guon, T.E.; Chung, H.S. Moringa oleifera fruit induce apoptosis via reactive oxygen species-dependent activation of mitogen-activated protein kinases in human melanoma A2058 cells. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 14, 1703–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leelawat, S.; Leelawat, K. Molecular mechanisms of cholangiocarcinoma cell inhibition by medicinal plants. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 13, 961–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.; Yu, B.; Rasul, A.; Al, S.A.; Yi, F.; Yang, H.; Ma, T. Jaceosidin induces apoptosis in U87 glioblastoma cells through G2/M phase arrest. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2012, 2012, 703034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.; Zheng, B.; Yi, F.; Rasul, A.; Gu, Z.; Li, T.; Gao, H.; Qazi, J.I.; Yang, H.; Ma, T. Pseudolaric Acid B induces caspase-dependent and caspase-independent apoptosis in u87 glioblastoma cells. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2012, 2012, 957568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kou, X.; Fan, J.; Chen, N. Potential molecular targets of ampelopsin in prevention and treatment of cancers. Anti-Cancer Agents Med. Chem. 2017, 17, 1610–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jafarain, A.; Asghari, G.; Ghassami, E. Evaluation of cytotoxicity of Moringa oleifera Lam. callus and leaf extracts on Hela cells. Adv. Biomed. Res. 2014, 3, 194. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Singh, R.P.; Padmavathi, B.; Rao, A.R. Modulatory influence of Adhatoda vesica (Justicia adhatoda) leaf extract on the enzymes of xenobiotic metabolism, antioxidant status and lipid peroxidation in mice. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2000, 213, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, V.; Paliwal, R.; Janmeda, P.; Sharma, S. Chemopreventive efficacy of Moringa oleifera pods against 7, 12-dimethylbenz[a]anthracene induced hepatic carcinogenesis in mice. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. APJCP 2012, 13, 2563–2569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bharali, R.; Tabassum, J.; Azad, M.R. Chemomodulatory effect of Moringa oleifera Lam. on hepatic carcinogen metabolising enzymes, antioxidant parameters and skin papillomagenesis in mice. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. APJCP 2003, 4, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sharma, V.; Paliwal, R. Potential chemoprevention of 7,12-dimethylbenz[a]anthracene induced renal carcinogenesis by Moringa oleifera pods and its isolated saponin. Indian J. Clin. Biochem. 2014, 29, 202–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grover, J.K.; Yadav, S.; Vats, V. Medicinal plants of India with anti-diabetic potential. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2002, 81, 81–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kar, A.; Choudhary, B.K.; Bandyopadhyay, N.G. Comparative evaluation of hypoglycaemic activity of some Indian medicinal plants in alloxan diabetic rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2003, 84, 105–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mbikay, M. Therapeutic potential of Moringa oleifera leaves in chronic hyperglycemia and dyslipidemia: A review. Front. Pharmacol. 2012, 3, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omabe, M.; Nwudele, C.; Omabe, K.N.; Okorocha, A.E. Anion gap toxicity in alloxan induced type 2 diabetic rats treated with antidiabetic noncytotoxic bioactive compounds of ethanolic extract of Moringa oleifera. J. Toxicol. 2014, 2014, 406242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuorkey, M.J. Effects of Moringa oleifera aqueous leaf extract in alloxan induced diabetic mice. Interv. Med. Appl. Sci. 2016, 8, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ndong, M.; Uehara, M.; Katsumata, S.; Suzuki, K. Effects of oral administration of Moringa oleifera Lam. on glucose tolerance in goto-kakizaki and wistar rats. J. Clin. Biochem. Nutr. 2007, 40, 229–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omodanisi, E.I.; Aboua, Y.G.; Oguntibeju, O.O. Assessment of the anti-hyperglycaemic, anti-inflammatory and antioxidant activities of the methanol extract of Moringa oleifera in diabetes-induced nephrotoxic male wistar rats. Molecules 2017, 22, 439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Malki, A.L.; El, R.H. The antidiabetic effect of low doses of Moringa oleifera Lam. seeds on streptozotocin induced diabetes and diabetic nephropathy in male rats. Biomed. Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 381040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, N.; Karantza-Wadsworth, V. Role and regulation of autophagy in cancer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2009, 1793, 1516–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, S.V.; White, E. Tumor suppression by autophagy through the management of metabolic stress. Autophagy 2008, 4, 563–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orvedahl, A.; Levine, B. Eating the enemy within: Autophagy in infectious diseases. Cell Death Differ. 2009, 16, 57–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saitoh, T.; Fujita, N.; Jang, M.H.; Uematsu, S.; Yang, B.G.; Satoh, T.; Omori, H.; Noda, T.; Yamamoto, N.; Komatsu, M.; et al. Loss of the autophagy protein Atg16L1 enhances endotoxin-induced IL-1beta production. Nature 2008, 456, 264–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yen, W.L.; Klionsky, D.J. How to live long and prosper: Autophagy, mitochondria, and aging. Physiology (Bethesda) 2008, 23, 248–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Arencibia, M.; Hochfeld, W.E.; Toh, P.P.; Rubinsztein, D.C. Autophagy, a guardian against neurodegeneration. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2010, 21, 691–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kou, X.; Li, B.; Olayanju, J.B.; Drake, J.M.; Chen, N. Nutraceutical or Pharmacological Potential of Moringa oleifera Lam. Nutrients 2018, 10, 343. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10030343
Kou X, Li B, Olayanju JB, Drake JM, Chen N. Nutraceutical or Pharmacological Potential of Moringa oleifera Lam. Nutrients. 2018; 10(3):343. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10030343
Chicago/Turabian StyleKou, Xianjuan, Biao Li, Julia B. Olayanju, Justin M. Drake, and Ning Chen. 2018. "Nutraceutical or Pharmacological Potential of Moringa oleifera Lam." Nutrients 10, no. 3: 343. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10030343
APA StyleKou, X., Li, B., Olayanju, J. B., Drake, J. M., & Chen, N. (2018). Nutraceutical or Pharmacological Potential of Moringa oleifera Lam. Nutrients, 10(3), 343. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10030343