Characteristics of Effective Interventions Promoting Healthy Eating for Pre-Schoolers in Childcare Settings: An Umbrella Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
Objectives
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Search Strategy and Eligibility Criteria
2.2. Assessment of Methodological Quality and Data Extraction
3. Results
3.1. Study Selection Process
3.2. Description of Reviews
3.3. Findings of the Reviews
3.3.1. Effectiveness
Dietary Intake
Weight Status
Multi-Level Interventions
Parental Involvement and Engagement
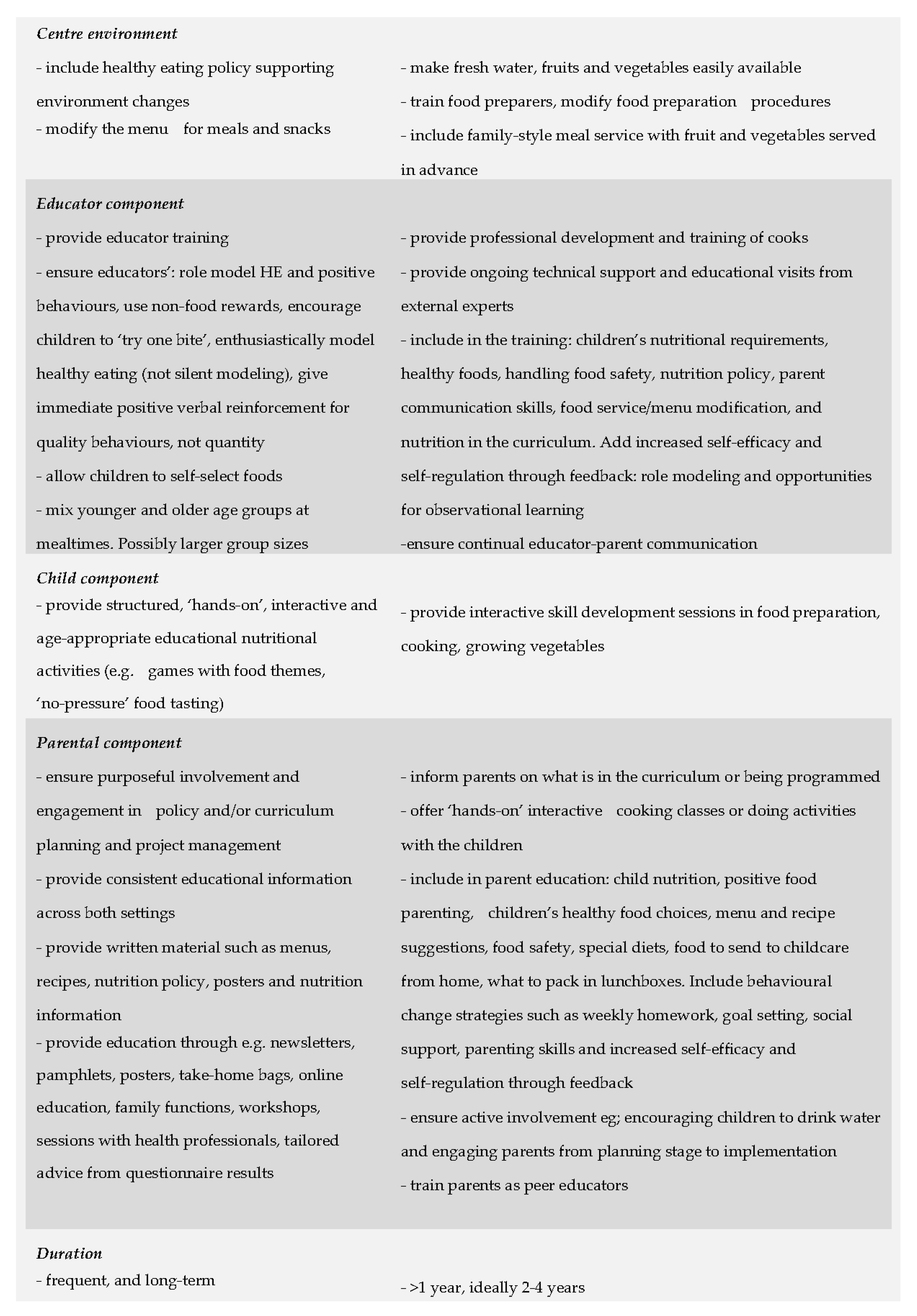
3.4. Characteristics of Successful Interventions
3.4.1. Delivery of Interventions
3.4.2. Behavioural Change Theories
3.4.3. Characteristics of Interventions Involving Educators
3.4.4. Characteristics of Interventions Directly Involving Children
3.4.5. Characteristics of Interventions Involving Parents
3.5. Review Recommendations
4. Discussion
4.1. Implications for Practice and Policy
4.2. Evidence Gap
4.3. Limitations of the Studies
4.4. Limitations and Strengths of the Umbrella Review
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Birch, L.L.; Anzman, S.L. Learning to Eat in an Obesogenic Environment: A Developmental Systems Perspective on Childhood Obesity. Child Dev. Perspect. 2010, 4, 138–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lien, N.; Lytle, L.A.; Klepp, K.I. Stability in consumption of fruit, vegetables, and sugary foods in a cohort from age 14 to age 21. Prev. Med. 2001, 33, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mikkila, V.; Rasanen, L.; Raitakari, O.T.; Pietinen, P.; Viikari, J. Consistent dietary patterns identified from childhood to adulthood: The cardiovascular risk in Young Finns Study. Br. J. Nutr. 2005, 93, 923–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, M.; Fleming, T.; Robinson, M.; Thomson, B.; Graetz, N.; Margono, C.; Mullany, E.C.; Biryukov, S.; Abbafati, C.; Abera, S.F.; et al. Global, regional, and national prevalence of overweight and obesity in children and adults during 1980–2013: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. Lancet 2014, 384, 766–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.M.; Pilli, S.; Gebremariam, A.; Keirns, C.C.; Davis, M.M.; Vijan, S.; Freed, G.L.; Herman, W.H.; Gurney, J.G. Getting heavier, younger: Trajectories of obesity over the life course. Int. J. Obes. 2010, 34, 614–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayes, A.; Chevalier, A.; D’Souza, M.; Baur, L.; Wen, L.M.; Simpson, J. Early childhood obesity: Association with healthcare expenditure in Australia. Obesity 2016, 24, 1752–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russell-Mayhew, S.; McVey, G.; Bardick, A.; Ireland, A. Mental health, wellness, and childhood overweight/obesity. J. Obes. 2012, 2012, 281801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Angelantonio, E.; Bhupathiraju, S.N.; Wormser, D.; Gao, P.; Kaptoge, S.; de Gonzalez, A.B.; Cairns, B.J.; Huxley, R.; Jackson, C.L.; Joshy, G.; et al. Body-mass index and all-cause mortality: Individual-participant-data meta-analysis of 239 prospective studies in four continents. Lancet 2016, 388, 776–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gortmaker, S.L.P.; Taveras, E.M. Who Becomes Obese during Childhood—Clues to Prevention. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 370, 475–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabin, M.A.; Kiess, W. Childhood obesity: Current and novel approaches. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 29, 327–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verschuuren, M.F.N.; Greenwell, F.; Raj, T.; Stein, C.; World Health Organisation. The European Health Report 2015—Targets and Beyond—Reaching New Frontiers in Evidence; WHO Regional Office for Europe: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. Report of the Commission on Ending Childhood Obesity; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Cauchi, D.; Glonti, K.; Petticrew, M.; Knai, C. Environmental components of childhood obesity prevention interventions: An overview of systematic reviews. Obes. Rev. 2016, 17, 1116–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waters, E.; de Silva-Sanigorski, A.; Hall, B.J.; Brown, T.; Campbell, K.J.; Gao, Y.; Armstrong, R.; Prosser, L.; Summerbell, C.D. Interventions for preventing obesity in children. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2011, CD001871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corcoran, L.; Steinley, K. Early Childhood Program Participation, From the National Household Education Surveys Program of 2016 (NCES 2017-101); National Center for Education Statistics, Institute of Education Sciences, U.S. Department of Education: Washington, DC, USA, 2017.
- Australian Bureau Statistics (ABS). 4402.0—Childhood Education and Care, Australia, June 2014; Australian Bureau Statistics: Canberra, Australia, 2014.
- Organisation for Economic Co-Operation and Development (OECD). PF4.1: Typology of Childcare and Early Education Services; Social Policy Division—Directorate of Employment LaSA, Ed.; OECD: Paris, France, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Sinha, M. Spotlight on Canadians: Results from the General Social Survey–Child Care in Canada; Social and Aboriginal Statistical Division: Ottawa, ON, Canada, 2014.
- Organisation for Economic Co-Operation and Development (OECD). PF3.2: Enrolment in Childcare and Pre-School; Social Policy Division—Directorate of Employment LaSA, Ed.; OECD: Paris, France, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Mikkelsen, B.E. Images of foodscapes: Introduction to foodscape studies and their application in the study of healthy eating out-of-home environments. Perspect. Public Health 2011, 131, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birch, L.L.; Doub, A.E. Learning to eat: Birth to age 2 y. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2014, 99, 723S–728S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peters, J.; Parletta, N.; Campbell, K.; Lynch, J. Parental influences on the diets of 2- to 5-year-old children: Systematic review of qualitative research. J. Early Child. Res. 2014, 12, 3–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larson, N.; Ward, D.S.; Neelon, S.B.; Story, M. What role can child-care settings play in obesity prevention? A review of the evidence and call for research efforts. J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 2011, 111, 1343–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazarello Paes, V.; Ong, K.K.; Lakshman, R. Factors influencing obesogenic dietary intake in young children (0–6 years): Systematic review of qualitative evidence. BMJ Open 2015, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steenbock, B.; Pischke, C.R.; Schonbach, J.; Pottgen, S.; Brand, T. The effectiveness of primary prevention interventions promoting physical activity and healthy eating in preschool children: A review of reviews. Bundesgesundheitsblatt Gesundheitsforschung Gesundheitsschutz 2015, 58, 609–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cliff, D.P.; Hesketh, K.D.; Vella, S.A.; Hinkley, T.; Tsiros, M.D.; Ridgers, N.D.; Carver, A.; Veitch, J.; Parrish, A.M.; Hardy, L.L.; et al. Objectively measured sedentary behaviour and health and development in children and adolescents: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Obes. Rev. 2016, 17, 330–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Zhang, S.; Huang, Y.; Chen, K. Sleep duration and obesity in children: A systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies. J. Paediatr. Child Health 2017, 53, 378–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gori, D.; Guaraldi, F.; Cinocca, S.; Moser, G.; Rucci, P.; Fantini, M.P. Effectiveness of educational and lifestyle interventions to prevent paediatric obesity: Systematic review and meta-analyses of randomized and non-randomized controlled trials. Obes. Sci. Pract. 2017, 3, 235–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osei-Assibey, G.; Dick, S.; Macdiarmid, J.; Semple, S.; Reilly, J.J.; Ellaway, A.; Cowie, H.; McNeill, G. The influence of the food environment on overweight and obesity in young children: A systematic review. BMJ Open 2012, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erinosho, T.O.; Hales, D.P.; McWilliams, C.P.; Emunah, J.; Ward, D.S. Nutrition policies at child-care centers and impact on role modeling of healthy eating behaviors of caregivers. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2012, 112, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bastian, H.; Glasziou, P.; Chalmers, I. Seventy-five trials and eleven systematic reviews a day: How will we ever keep up? PLoS Med. 2010, 7, e1000326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartling, L.; Chisholm, A.; Thomson, D.; Dryden, D.M. A descriptive analysis of overviews of reviews published between 2000 and 2011. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e49667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aromataris, E.; Fernandez, R.; Godfrey, C.; Holly, C.; Kahlil, H.; Tungpunkom, P. Summarizing systematic reviews:methodological development, conduct and reporting of an Umbrella review approach. Int. J. Evid. Based Healthc. 2015, 13, 132–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onishi, A.; Furukawa, T.A. State-of-the-Art Reporting. In Umbrella Reviews: Evidence Synthesis with Overviews of Reviews and Meta-Epidemiologic Studies; Biondi-Zoccai, G., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 189–202. [Google Scholar]
- Ballard, M.; Montgomery, P. Risk of bias in overviews of reviews: A scoping review of methodological guidance and four-item checklist. Res. Synth. Methods 2017, 8, 92–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pollock, A.; Campbell, P.; Brunton, G.; Hunt, H.; Estcourt, L. Selecting and implementing overview methods: Implications from five exemplar overviews. Syst. Rev. 2017, 6, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Organisation for Economic Co-Operation and Development (OECD). Country Classification; OECD: Paris, France, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Hesketh, K.D.; Campbell, K.J. Interventions to prevent obesity in 0–5 year olds: An updated systematic review of the literature. Obesity 2010, 18 (Suppl. 1), S27–S35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nixon, C.A.; Moore, H.J.; Douthwaite, W.; Gibson, E.L.; Vogele, C.; Kreichauf, S.; Wildgruber, A.; Manios, Y.; Summerbell, C.D. ToyBox-Study Group. Identifying effective behavioural models and behaviour change strategies underpinning preschool- and school-based obesity prevention interventions aimed at 4–6-year-olds: A systematic review. Obes. Rev. 2012, 13, 106–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johanna Briggs Institute. Joanna Briggs Institute Reviewers’ Manual: 2014 edition/Supplement. In Johanna Briggs Institute Reviewers Manual 2014 Methodology for JBI Umbrella Reviews; Johanna Briggs Institute: Adelaide, Australia, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Campbell, K.J.; Hesketh, K.D. Strategies which aim to positively impact on weight, physical activity, diet and sedentary behaviours in children from zero to five years. A systematic review of the literature. Obes. Rev. 2007, 8, 327–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Connelly, J.B. Evaluating complex public health interventions: Theory, methods and scope of realist enquiry. J. Eval. Clin. Pract. 2007, 13, 935–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Onise, K.; Lynch, J.W.; Sawyer, M.G.; McDermott, R.A. Can preschool improve child health outcomes? A systematic review. Soc. Sci. Med. 2010, 70, 1423–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pearson, N.; Biddle, S.J. Sedentary behavior and dietary intake in children, adolescents, and adults. A systematic review. Am. J. Prev. Med. 2011, 41, 178–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bond, M.; Wyatt, K.; Lloyd, J.; Taylor, R. Systematic review of the effectiveness of weight management schemes for the under fives. Obes. Rev. 2011, 12, 242–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hendrie, G.A.; Brindal, E.; Corsini, N.; Gardner, C.; Baird, D.; Golley, R.K. Combined Home and School Obesity Prevention Interventions for Children: What Behavior Change Strategies and Intervention Characteristics Are Associated With Effectiveness? Health Educ. Behav. 2012, 39, 159–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monasta, L.; Batty, G.D.; Macaluso, A.; Ronfani, L.; Lutje, V.; Bavcar, A.; van Lenthe, F.J.; Brug, J.; Cattaneo, A. Interventions for the prevention of overweight and obesity in preschool children: A systematic review of randomized controlled trials. Obes. Rev. 2011, 12, e107–e118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Summerbell, C.D.; Moore, H.J.; Vögele, C.; Kreichauf, S.; Wildgruber, A.; Manios, Y.; Douthwaite, W.; Nixon, C.A.; Gibson, E.L. ToyBox-Study Group. Evidence-based recommendations for the development of obesity prevention programs targeted at preschool children. Obes. Rev. 2012, 13, 129–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swyden, K.; Sisson, S.B.; Lora, K.; Castle, S.; Copeland, K.A. Association of childcare arrangement with overweight and obesity in preschool-aged children: A narrative review of literature. Int. J. Obes. 2017, 41, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ward, S.; Belanger, M.; Donovan, D.; Horsman, A.; Carrier, N. Correlates, determinants, and effectiveness of childcare educators’ practices and behaviours on preschoolers’ physical activity and eating behaviours: A systematic review protocol. Syst. Rev. 2015, 4, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolfenden, L.; Wyse, R.J.; Britton, B.I.; Campbell, K.J.; Hodder, R.K.; Stacey, F.G.; McElduff, P.; James, E.L. Interventions for increasing fruit and vegetable consumption in children aged 5 years and under. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2012, 11, CD008552. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ling, J.; Robbins, L.B.; Wen, F. Interventions to prevent and manage overweight or obesity in preschool children: A systematic review. Int. J. Nurs. Stud. 2016, 53, 270–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, H.; Skouteris, H.; Edwards, S.; Rutherford, L. Obesity prevention interventions in early childhood education and care settings with parental involvement: A systematic review. Early Child Dev. Care 2014, 185, 1283–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sisson, S.B.; Krampe, M.; Anundson, K.; Castle, S. Obesity prevention and obesogenic behavior interventions in child care: A systematic review. Prevent. Med. 2016, 87, 57–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ward, D.S.; Welker, E.; Choate, A.; Henderson, K.E.; Lott, M.; Tovar, A.; Wilson, A.; Sallis, J.F. Strength of obesity prevention interventions in early care and education settings: A systematic review. Prev. Med. 2016, 95, S37–S52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.E.; Emerson, J.S.; Levine, R.S.; Kihlberg, C.J.; Hull, P.C. Childhood Obesity Prevention Interventions in Childcare Settings: Systematic Review of Randomized and Nonrandomized Controlled Trials. Am. J. Health Promot. 2014, 28, e92–e103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bell, L.K.; Golley, R.K. Interventions for improving young children's dietary intake through early childhood settings: A systematic review. Int. J. Child Health Nutr. 2015, 4, 14–32. [Google Scholar]
- Mikkelsen, M.V.; Husby, S.; Skov, L.R.; Perez-Cueto, F.J. A systematic review of types of healthy eating interventions in preschools. Nutr. J. 2014, 13, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ward, S.; Bélanger, M.; Donovan, D.; Carrier, N. Systematic review of the relationship between childcare educators’ practices and preschoolers’ physical activity and eating behaviours. Obes. Rev. 2015, 16, 1055–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ward, S.A.; Bélanger, M.F.; Donovan, D.; Carrier, N. Relationship between eating behaviors and physical activity of preschoolers and their peers: A systematic review. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2016, 13, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolfenden, L.; Jones, J.; Williams, C.M.; Finch, M.; Wyse, R.J.; Kingsland, M.; Tzelepis, F.; Wiggers, J.; Williams, A.J.; Seward, K.; et al. Strategies to improve the implementation of healthy eating, physical activity and obesity prevention policies, practices or programmes within childcare services. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2016, 10, CD011779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, C.; Ye, D.; Li, Y.; Huang, Y.; Li, L.; Gao, Y.; Wang, S. Evaluation of a kindergarten-based nutrition education intervention for pre-school children in China. Public Health Nutr. 2010, 13, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Başkale, H.; Bahar, Z. Outcomes of nutrition knowledge and healthy food choices in 5- to 6-year-old children who received a nutrition intervention based on Piaget's theory. J. Spec. Pediatr. Nurs. 2011, 16, 263–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Céspedes, J.; Briceño, G.; Farkouh, M.E.; Vedanthan, R.; Baxter, J.; Leal, M.; Boffetta, P.; Woodward, M.; Hunn, M.; Dennis, R.; et al. Targeting Preschool Children to Promote Cardiovascular Health: Cluster Randomized Trial. Am. J. Med. 2013, 126, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guyatt, G.H.; Mills, E.J.; Elbourne, D. In the Era of Systematic Reviews, Does the Size of an Individual Trial Still Matter? (The PLoS Medicine Debate). PLoS Med. 2008, 5, e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bleich, S.N.; Segal, J.; Wu, Y.; Wilson, R.; Wang, Y. Systematic review of community-based childhood obesity prevention studies. Pediatrics 2013, 132, e201–e210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerra, P.H.; da Silveira, J.A.; Salvador, E.P. Physical activity and nutrition education at the school environment aimed at preventing childhood obesity: Evidence from systematic reviews. J. Pediatr. 2016, 92, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Safron, M.; Cislak, A.; Gaspar, T.; Luszczynska, A. Effects of School-based Interventions Targeting Obesity-Related Behaviors and Body Weight Change: A Systematic Umbrella Review. Behav. Med. 2011, 37, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biddle, S.J.H.; Atkin, A.J.; Cavill, N.; Foster, C. Correlates of physical activity in youth: A review of quantitative systematic reviews. Int. Rev. Sport Exerc. Psychol. 2011, 4, 25–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brand, T.; Pischke, C.R.; Steenbock, B.; Schoenbach, J.; Poettgen, S.; Samkange-Zeeb, F.; Zeeb, H. What works in community-based interventions promoting physical activity and healthy eating? A review of reviews. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2014, 11, 5866–5888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bandura, A. Health Promotion by Social Cognitive Means. Health Educ. Behav. 2004, 31, 143–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sallis, J.; Fisher, E.; Owen, N. Ecological Models of Health Behaviour. In Health Behavior and Health Education: Theory, Research, and Practice, 4th ed.; Editors: Glanz, K., Rimer, B.K., Viswanath, K., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2008; pp. 465–485. [Google Scholar]
- McPherson, K.K.P.; Butland, B.; Jebb, S.; Thomas, S.; Mardell, J.; Parry, V. Tackling Obesities: Future Choices-Project Report, 2nd ed.; Government Office of Science: London, UK, 2007.
- Natale, R.A.; Messiah, S.E.; Asfour, L.; Uhlhorn, S.B.; Delamater, A.; Arheart, K.L. Role modeling as an early childhood obesity prevention strategy: Effect of parents and teachers on preschool children’s healthy lifestyle habits. J. Dev. Behav. Pediatr. JDBP 2014, 35, 378–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lynch, M.; Batal, M. Factors Influencing Childcare Providers’ Food and Mealtime Decisions: An Ecological Approach. Child Care Pract. 2011, 17, 185–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, C.; Määttä, S.; Lehto, R.; Roos, G.; Roos, E. Influencing factors of children’s fruit, vegetable and sugar-enriched food intake in a Finnish preschool setting—Preschool personnel’s perceptions. Appetite 2016, 103, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otten, J.J.; Hirsch, T.; Lim, C. Factors Influencing the Food Purchases of Early Care and Education Providers. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2017, 117, 725–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerritsen, S. Nutrition education for early childhood managers, teachers and nursery cooks: A prerequisite for effective obesity prevention. Public Health 2016, 140, 56–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laws, R.; Campbell, K.J.; van der Pligt, P.; Russell, G.; Ball, K.; Lynch, J.; Crawford, D.; Taylor, R.; Askew, D.; Denney-Wilson, E. The impact of interventions to prevent obesity or improve obesity related behaviours in children (0–5 years) from socioeconomically disadvantaged and/or indigenous families: A systematic review. BMC Public Health 2014, 14, 779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fitzgibbon, M.L.; Stolley, M.R.; Schiffer, L.; Kong, A.; Braunschweig, C.L.; Gomez-Perez, S.L.; Odoms-Young, A.; Van Horn, L.; Christoffel, K.K.; Dyer, A.R. Family-based hip-hop to health: Outcome results. Obesity 2013, 21, 274–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fitzgibbon, M.L.; Stolley, M.R.; Schiffer, L.; Van Horn, L.; KauferChristoffel, K.; Dyer, A. Two-year follow-up results for Hip-Hop to Health Jr.: A randomized controlled trial for overweight prevention in preschool minority children. J. Pediatr. 2005, 146, 618–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fitzgibbon, M.L.; Stolley, M.R.; Schiffer, L.; Van Horn, L.; KauferChristoffel, K.; Dyer, A. Hip-Hop to Health Jr. for Latino preschool children. Obesity 2006, 14, 1616–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fitzgibbon, M.L.; Stolley, M.R.; Schiffer, L.A.; Braunschweig, C.L.; Gomez, S.L.; Van Horn, L.; Dyer, A.R. Hip-Hop to Health Jr. Obesity Prevention Effectiveness Trial: Postintervention results. Obesity 2011, 19, 994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, A.; Buscemi, J.; Stolley, M.R.; Schiffer, L.A.; Kim, Y.; Braunschweig, C.L.; Gomez-Perez, S.L.; Blumstein, L.B.; Van Horn, L.; Dyer, A.R.; et al. Hip-Hop to Health Jr. Randomized Effectiveness Trial: 1-Year Follow-up Results: 1-Year Follow-up Results. Am. J. Prev. Med. 2016, 50, 136–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, C.L.; Bollella, M.C.; Strobino, B.A.; Spark, A.; Nicklas, T.A.; Tolosi, L.B.; Pittman, B.P. “Healthy-Start”: Outcome of an Intervention to Promote a Heart Healthy Diet in Preschool Children. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2002, 21, 62–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, C.L.; Strobino, B.A.; Bollella, M.; Brotanek, J. Cardiovascular Risk Reduction in Preschool Children: The “Healthy Start” Project. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2004, 23, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayer, O.; Von Kries, R.; Strauss, A.; Mitschek, C.; Toschke, A.M.; Hose, A.; Koletzko, B.V. Short- and mid-term effects of a setting based prevention program to reduce obesity risk factors in children: A cluster-randomized trial. Clin. Nutr. 2009, 28, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bell, A.C.; Davies, L.; Finch, M.; Wolfenden, L.; Francis, J.L.; Sutherland, R.; Wiggers, J. An implementation intervention to encourage healthy eating in centre-based child-care services: Impact of the Good for Kids Good for Life programme. Public Health Nutr. 2015, 18, 1610–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Bock, F.; Breitenstein, L.; Fischer, J.E. Positive impact of a pre-school-based nutritional intervention on children’s fruit and vegetable intake: Results of a cluster-randomized trial. Public Health Nutr. 2012, 15, 466–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Coen, V.; De Bourdeaudhuij, I.; Vereecken, C.; Verbestel, V.; Haerens, L.; Huybrechts, I.; Van Lippevelde, W.; Maes, L. Effects of a 2-year healthy eating and physical activity intervention for 3–6-year-olds in communities of high and low socio-economic status: The POP (Prevention of Overweight among Pre-school and school children) project. Public Health Nutr. 2012, 15, 1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peñalvo, J.; Santos-Beneit, G.; Sotos-Prieto, M.; Martínez, R.; Rodríguez, C.; Franco, M.; López-Romero, P.; Pocock, S.; Redondo, J.; Fuster, V. A cluster randomized trial to evaluate the efficacy of a school-based behavioral intervention for health promotion among children aged 3 to 5. BMC Public Health 2013, 13, 656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puder, J.J.; Marques-Vidal, P.; Schindler, C.; Zahner, L.; Niederer, I.; Bürgi, F.; Ebenegger, V.; Nydegger, A.; Kriemler, S. Effect of multidimensional lifestyle intervention on fitness and adiposity in predominantly migrant preschool children (Ballabeina): Cluster randomised controlled trial. BMJ 2011, 343, d6195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zask, A.; Adams, J.K.; Brooks, L.O.; Hughes, D.F. Tooty Fruity Vegie: An obesity prevention intervention evaluation in Australian preschools. Health Promot. J. Aust. 2012, 23, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milat, A.; Newson, R.; King, L.; Rissel, C.; Wolfenden, L.; Bauman, A.; Redman, S.; Giffin, M. A guide to scaling up population health interventions. Public Health Res. Pract. 2016, 26, e2611604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Reilly, S.L. Translational research: The ingredients are only the start of the recipe for better dietetic practice. Nutr. Diet. 2016, 73, 307–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollingworth, W.; Hawkins, J.; Lawlor, D.A.; Brown, M.; Marsh, T.; Kipping, R.R. Economic evaluation of lifestyle interventions to treat overweight or obesity in children. Int. J. Obes. 2012, 36, 559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- John, J.; Wolfenstetter, S.B.; Wenig, C.M. An economic perspective on childhood obesity: Recent findings on cost of illness and cost effectiveness of interventions. Nutrition 2012, 28, 829–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moher, D.; Pham, B.; Jones, A.; Cook, D.J.; Jadad, A.R.; Moher, M.; Tugwell, P.; Klassen, T.P. Does quality of reports of randomised trials affect estimates of intervention efficacy reported in meta-analyses? Lancet 1998, 352, 609–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onwuegbuzie, A.J.; Leech, N.L. On Becoming a Pragmatic Researcher: The Importance of Combining Quantitative and Qualitative Research Methodologies. Int. J. Soc. Res. Methodol. 2005, 8, 375–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Author/Date | Objectives Examined | Number of Primary Studies Included in Each Review/Total Number of Diet-Related Studies. Participant Characteristics | Study Design | Key Findings of the Review | Overall Recommendations of the Review |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bell and Golley 2015 | Effectiveness of nutrition promotion interventions on children’s dietary intake. | 24/25 Children 0–5 years, providers and staff or parents of children, formal childcare | Prospective studies with or without a comparison group, outcomes measured at baseline and post intervention 4 RCT, 1 cross-over cluster-RCT, 8 CCT, 10 cohort, 1 cross-over, 1 cross-over quasi-experimental | ECS interventions can achieve changes in children’s dietary intake and associated social-environmental determinants. DI; Significant effect on children’s dietary intake (8/11). Significant improvements in centres nutrition environment (6) including policy (2), nutrition best practices (3), nutritional quality of centres’ menus (3), parental food provision (4), child knowledge/attitudes/preferences (2), and staff knowledge/attitudes/behaviours (2). | ECS are potential settings for effective nutrition health promotion Environmental interventions can achieve dietary improvements Evaluate effect of nutrition environment changes on children’s dietary intake Utilise age-appropriate behaviour change theory |
| Hesketh and Campbell 2010 | Effectiveness of interventions to prevent obesity, promote healthy eating and/or physical activity or reduce sedentary behaviours. | 3/9 Children 2–5 years, preschool/formal childcare | Experimental studies 2 cluster-RCT, 1 CCT | Achieved success in modifying outcomes of interest. AN: Significantly lower BMI increases at 1 and 2 years follow up in one study. Two studies significant decrease in serum cholesterol but no change to height-weight ratio. DI: Significant decrease in saturated fat and total fat in snacks, and corresponding reduction in intake in two studies | Add parental component. Build knowledge and skills of educators and parents Consider SBT-based strategies Build on existing research activities Need cost-effective studies |
| Ling, Robbins et al., 2016 | Effects of prevention and management interventions on overweight/obesity. | 13/16 Children 2–5 years, formal childcare | Intervention studies with a sample > 30 centres 13 cluster-RCT | Studies which combined diet with PA, had a significant effect on measures of BMI (6/13). Findings supported teaching preschool children with interactive education and their families with interactive education and behavioural therapy. Lack of parental involvement may account for limited success in all studies. | Build knowledge and skill capability of educators with education, and health-promoting component for educators. Build HE capacity of both parents and children. Offer parents interactive education and nutrition-related behavioural therapy. Use age-appropriate interactive, hands-on experiences with children |
| Mikkelsen, Husby et al., 2014 | Effectiveness of different strategies influencing children’s food choice at an early age. | 26 studies Children 3–6 years, preschools/formal childcare | Intervention studies with baseline and follow-up measurements 11 RCT, 9 quasi RCT, 1 cross-over, 2 pre-post test design, 3 cluster-RCT | Comprehensive interventions more likely to succeed in behaviour change, especially when targeting children of low-income families. Multi-component programs which included education, changes to the centre environment, policy and involvement of parents were most effective. DI: Significant increase in fruit and vegetable intake and in nutrition knowledge in relevant studies. AN: No significant effect | More comprehensive interventions likely to be more successful i.e., multi-component and multi-level Target disadvantaged groups Add longer follow-up Focus on implementation drivers and barriers to increase understanding of what makes an intervention work |
| Morris, Skouteris et al., 2014 | How have parents been incorporated into ECEC childhood obesity interventions and to what extent, if any does their involvement impact the outcomes of the intervention? | 12/15 Parents of children in preschools/formal childcare | Experimental studies 2 RCT, 6 cluster-RCT, 3 quasi-experimental, 1 prospective cohort | AN: Positive and significant weight changes in some studies (6/12). No changes in anthropometry in all studies despite change in parental and child knowledge and attitudes and child unhealthy-diet behaviours. DI: Secondary outcome relating to healthy eating seen in most studies. | Build capacity of educators and parentsIncrease educators’ role in parental engagement Include collaborative parental involvement, including in curricula Future research on collaborative parental involvement and effects |
| Nixon, Moore et al., 2012 | Identify effective behavioural models and behaviour change strategies, underpinning preschool and school-based interventions aimed at preventing obesity. | 4/9 Children 4–6 years, pre-schools/formal childcare | Intervention studies with before and after measures in the same children plus follow-up of 6 months or longer 1 RCT, 3 cluster-RCT | Interventions that combined high levels of parental involvement, interactive learning plus targeted dietary change with long-term follow-up were most effective. DI: significant favourable changes in dietary behaviours (4/4). AN; significant favourable changes in intervention group (2/2). | Include BCS Build children’s (and parents) perceived competency to make dietary changes with education and modelling positive behaviours Change centre-environment and measure impact Ensure evidence-base driven by users involvement |
| Sisson, Krampe et al., 2016 | Effectiveness and description of interventions that target obesogenic behaviours in child care centres. | 45/71 Children 3–5 years, childcare settings | Experimental studies 22 RCT, 19 quasi-experimental or pre-post design, 3 natural experiments | DI: Most studies achieved a significant effect in at least one nutrition outcome (87% desired effect). | Multi-level (child, environment), multi-component Focus on childcare environment including technical support and training Include parental involvement Include BCS e.g., SEM, SCT Focus future research on RCT underpinned with BCT with emphasis on parental involvement Measure environmental effects on child’s dietary intake |
| Ward, Welker et al., 2016 | Identify the most promising obesity prevention intervention characteristics associated with successful behavioural and/or anthropometric outcomes. | 18/47 Children 2–6 years, early care and education centres | All study designs with pre- and post-evaluation using objective or validated measures 4 RCT, 4 cluster-RCT, 3 randomised cross-over trial, 6 pre-post design, 1 quasi-experimental trial | Tentative evidence that multi-component and multi-level ECS interventions with parental engagement are most likely to be effective. AN: Healthy eating and parental involvement correlated with favourable anthropometric outcomes. DI: Most studies showed at least one positive dietary effect. No correlations found between HE intervention strength (calculated by authors using own system) and HE outcomes, with or without parental engagement. | Comprehensive, multi-level Stronger interventions with parental engagement and environmental and policy components Research already-effective interventions Explore whether comprehensiveness is negatively associated with feasibility and fidelity if educator led |
| Ward, Bélanger et al., 2015 | Identify if childcare educators’ practices are associated with pre-schoolers’ physical activity and eating behaviours. Assess the effectiveness of interventions that control educators’ practices or behaviours | 5/15 Pre-schoolers, educators, childcare facilities | All types of quantitative studies, excluding multi-component interventions or studies focusing on more than educators. 1 cross-over RCT, 2 quasi-experimental, 2 pre-post design | Educators may play a positive role in promoting healthy eating behaviours in children. DI: Significant, positive changes in dietary intake, particularly fruit and vegetables. Increased intake and acceptance of new or healthy food/snacks (5/5). | Educators have a crucial role in promoting HE behaviours in children Involve peers as change agents for positive eating Reassess interventions in today’s changed environment, use diverse populations, use objective or validated measurements |
| Ward, Bélanger et al., 2016 | Effectiveness of the relationship between pre-schoolers’ eating behaviours and physical activity, and those of their peers. | 7/13 Children 2–5 years, childcare centres | All types of quantitative studies 1 RCT, 3 pre-post design, 3 non-RCT | All nutrition interventions reported peers may influence eating behaviours. Social influences particularly modelling was a strong determinant of individual’s food intake. Moderated by number of peers, age, gender, perceived personality of role models. DI: Significant increase in targeted foods (7/7). | Use peers as agents for positive eating behaviours |
| Wolfenden, Jones et al., 2016 | Effectiveness of strategies improving the implementation of policies, practices or programmes by childcare services that promote child healthy eating, physical activity and/or obesity prevention. | 8/10 Children up to 5–6 years, centre-based childcare | Any study with a parallel control group that compared any strategy to improve the implementation of a healthy eating policy, practice or programme to no intervention, ‘usual’ practice or an alternative strategy and Included baseline. 1 RCT, 3 cluster-RCT, 2 quasi-experimental trial, 1 randomised CCT, 1randomised parallel-group trial | No intervention improved the implementation of all policies and practices targeted by the implementation strategies relative to a comparison group. Most reported at least one favourable change to policies or practices (7/8). DI: Significant positive changes in types of foods provided and foods selected. Consumed significantly less energy, fat, saturated fat compared to control in one study. AN: Significant reduction in centre-level child adiposity compared to control in one study. No significant intervention effect in one study following menu changes. | Include institutional changes: policy, health promotion, education, staff training, curriculum Assess cost-effectiveness Use comprehensive theoretical frameworks to identify implementation barriers Further determine barriers to implementation with formative research |
| Zhou, Emerson et al., 2014 | Efficacy of childhood obesity interventions in childcare settings on outcomes of dietary intake, physical activity, and adiposity. | 13/15 Children up to 5–6 years, preschool/ formal childcare | Any interventions with controlled study design 12 RCT-Cluster, 1 cluster controlled | Interventions variably effective in improving adiposity and dietary behaviours | Include institutional changes: policies, age-appropriate health promoting education curricula, educators’ training Include cost-effectiveness studies Research improving nutrition environments and target diverse populations Use consistent outcome measures, validated or objective measurements Add sufficient follow-up time |
| Research Recommendations | Author | Practice Recommendations | Author |
|---|---|---|---|
| Future research should build upon existing activities | [38,55] | ECS have potential as settings for effective nutrition promotion | [38,53,54,57,58,61] |
| Include cost-effectiveness | [38,56,61] | Underpin intervention design with effective social behavioural change theory (e.g., Social Ecological Model, Social Cognitive Theory) | [38,39,52,53,54,57,58] |
| Be driven by user involvement (educators, parents) and children’s views | [39,52,58] | Target intervention strategies at environmental-level and individual-level determinants. Successful outcomes are more likely with a multi-component, multi-level approach | [39,54,55,56,58,59] |
| Measure children’s dietary changes as well as environmental impact | [39,54,57] | Involve and engage parents in intervention strategies. Changes are more likely with high levels of parental engagement | [38,39,52,53,54,55] |
| Include formative research to (1) determine barriers to strategy implementation (2) identify implementation drivers and barriers to increase understanding of how interventions work | [56,58,61] | Build the capacity of educators, who also have a role in inviting parental participation | [38,52,53,56,59] |
| Have longer follow-up to allow for behavioural changes to have an impact and to measure longer-term outcomes | [39,56,58] | Build the capacity of parents and of children with educational, hands-on experiences | [39,52,53,54] |
| Include more high-quality RCT with larger sample sizes using validated measurements and tools. | [54,56,59,60] | Involve peers (children) as change agents for positive eating behaviours | [59,60] |
| Explore whether collaborative parental engagement effects change | [54,55] | Include institutional changes; policies, age-appropriate education curricula, educators’ training | [56,61] |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Matwiejczyk, L.; Mehta, K.; Scott, J.; Tonkin, E.; Coveney, J. Characteristics of Effective Interventions Promoting Healthy Eating for Pre-Schoolers in Childcare Settings: An Umbrella Review. Nutrients 2018, 10, 293. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10030293
Matwiejczyk L, Mehta K, Scott J, Tonkin E, Coveney J. Characteristics of Effective Interventions Promoting Healthy Eating for Pre-Schoolers in Childcare Settings: An Umbrella Review. Nutrients. 2018; 10(3):293. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10030293
Chicago/Turabian StyleMatwiejczyk, Louisa, Kaye Mehta, Jane Scott, Emma Tonkin, and John Coveney. 2018. "Characteristics of Effective Interventions Promoting Healthy Eating for Pre-Schoolers in Childcare Settings: An Umbrella Review" Nutrients 10, no. 3: 293. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10030293
APA StyleMatwiejczyk, L., Mehta, K., Scott, J., Tonkin, E., & Coveney, J. (2018). Characteristics of Effective Interventions Promoting Healthy Eating for Pre-Schoolers in Childcare Settings: An Umbrella Review. Nutrients, 10(3), 293. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10030293






