Influence of Parental Healthy-Eating Attitudes and Nutritional Knowledge on Nutritional Adequacy and Diet Quality among Preschoolers: The SENDO Project
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Aim, Design, and Setting
2.2. Exposure Assessment
2.3. Outcome Assessment
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
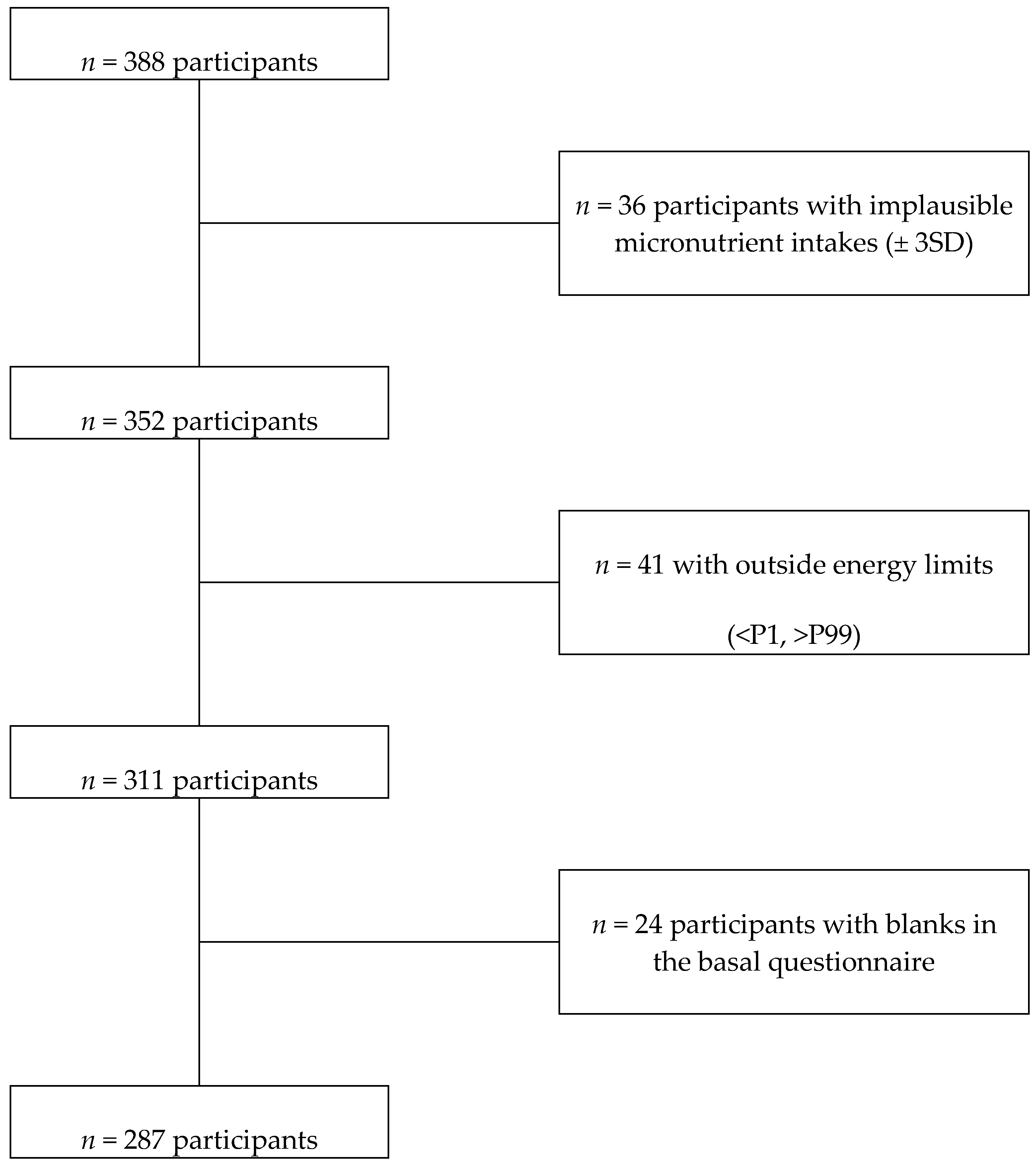
3.1. Recruitment and Baseline Characteristics
3.2. Influence of Parental Nutritional Knowledge and Healthy-Attitudes on Food and Nutrient Intakes
3.3. Influence of Parental Nutritional Knowledge and Healthy-Eating Attitudes on Micronutrient Inadequacy
3.4. Influence of Parental Nutritional Knowledge and Healthy-Eating Attitudes on Mediterranean Adherence.
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Corkins, M.R.; Daniels, S.R.; de Ferranti, S.D.; Golden, N.H.; Kim, J.H.; Magge, S.N.; Schwarzenberg, S.J. Nutrition in children and adolescents. Med. Clin. North Am. 2016, 100, 1217–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Cosmi, V.; Scaglioni, S.; Agostoni, C. Early taste experiences and later food choices. Nutrients 2017, 9, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarnowiecki, D.; Sinn, N.; Petkov, J.; Dollman, J. Parental nutrition knowledge and attitudes as predictors of 5–6-year-old children’s healthy food knowledge. Public Health Nutr. 2012, 15, 1284–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marias, Y.F.; Glasauer, P. Guidelines for Assessing Nutrition-Related Knowledge, Attitudes and Practices; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Roma, Italy, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Manios, Y.; Kourlaba, G.; Kondaki, K.; Grammatikaki, E.; Birbilis, M.; Oikonomou, E.; Roma-Giannikou, E. Diet quality of preschoolers in Greece based on the healthy eating index: The GENESIS study. J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 2009, 109, 616–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beydoun, M.A.; Wang, Y. How do socio-economic status, perceived economic barriers and nutritional benefits affect quality of dietary intake among US adults? Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2008, 62, 303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin-Calvo, N.; Ochoa, M.C.; Marti, A.; Martinez-Gonzalez, M.A. The association between dietary macronutrients intake and obesity among children and adolescents; a case-control study. Nutr. Hosp. 2013, 28, 1515–1522. [Google Scholar]
- Dapcich, V.; Salvador, G.; Ribas, L.; Pérez, C.; Aranceta, J.; Serra, L. Guía de la Alimentación Saludable; Sociedad Española de Nutrición Comunitaria: Barcelona, Spain, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Santiago, S.; Zazpe, I.; Gea, A.; de la Rosa, P.A.; Ruiz-Canela, M.; Martínez-González, M.A. Healthy-eating attitudes and the incidence of cardiovascular disease: The SUN cohort. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2017, 68, 595–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreiras, O. Tablas de Composición de Alimentos: Guía de Prácticas; Pirámide: Madrid, Spain, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Institute of Medicine (IOM). Dietary Reference Intakes: Applications in Dietary Assessment; National Academy Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Serra-Majem, L.; Ribas, L.; Ngo, J.; Ortega, R.M.; Garcia, A.; Perez-Rodrigo, C.; Aranceta, J. Food, youth and the Mediterranean diet in Spain. Development of KIDMED, Mediterranean diet quality index in children and adolescents. Public Health Nutr. 2004, 7, 931–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamo, K.B.; Brett, K.E. Parental perceptions and childhood dietary quality. Matern. Child Health J. 2014, 18, 978–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Variyam, J.N.; Blaylock, J.; Lin, B.-H.; Ralston, K.; Smallwood, D. Mother’s nutrition knowledge and children’s dietary intakes. Am. J. Agric. Econ. 1999, 81, 373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asakura, K.; Todoriki, H.; Sasaki, S. Relationship between nutrition knowledge and dietary intake among primary school children in Japan: Combined effect of children’s and their guardians’ knowledge. J. Epidemiol. 2017, 27, 483–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vereecken, C.; Maes, L. Young children’s dietary habits and associations with the mothers’ nutritional knowledge and attitudes. Appetite 2010, 54, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, J.; Dollman, J.; Petkov, J.; Parletta, N. Associations between parenting styles and nutrition knowledge and 2–5-year-old children’s fruit, vegetable and non-core food consumption. Public Health Nutr. 2013, 16, 1979–1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsaffar, A.A. Validation of a general nutrition knowledge questionnaire in a Turkish student sample. Public Health Nutr. 2012, 15, 2074–2085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parmenter, K.; Wardle, J. Development of a general nutrition knowledge questionnaire for adults. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 1999, 53, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisenberg, M.H.; Lipsky, L.M.; Gee, B.; Liu, A.; Nansel, T.R. Parent healthful eating attitudes and motivation are prospectively associated with dietary quality among youth with type 1 diabetes. Vulnerable Child Youth Stud. 2017, 12, 226–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostanjevec, S.; Jerman, J.; Koch, V. The Influence of nutrition education on the food consumption and nutrition attitude of schoolchildren in Slovenia. US China Educ. Rev. A. Educ Pract. 2012, 2, 953–964. [Google Scholar]
- Tognon, G.; Hebestreit, A.; Lanfer, A.; Moreno, L.A.; Pala, V.; Siani, A.; Tornaritis, M.; De Henauw, S.; Veidebaum, T.; Molnar, D.; et al. Mediterranean diet, overweight and body composition in children from eight European countries: Cross-sectional and prospective results from the IDEFICS study. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2014, 24, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonogeorgos, G.; Panagiotakos, D.B.; Grigoropoulou, D.; Papadimitriou, A.; Anthracopoulos, M.; Nicolaidou, P.; Priftis, K.N. The mediating effect of parents’ educational status on the association between adherence to the Mediterranean diet and childhood obesity: The PANACEA study. Int. J. Public Health. 2013, 58, 401–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grunert, K.G.; Wills, J.; Celemín, L.F.; Lähteenmäki, L.; Scholderer, J.; Storcksdieck genannt Bonsmann, S. Socio-demographic and attitudinal determinants of nutrition knowledge of food shoppers in six European countries. Food Qual. Prefer. 2012, 26, 166–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannoosamy, K.; Pem, D.; Bhagwant, S.; Jeewon, R. Is a nutrition education intervention associated with a higher intake of fruit and vegetables and improved nutritional knowledge among housewives in mauritius? Nutrients 2016, 8, 723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolf, R.L.; Lepore, S.J.; Vandergrift, J.L.; Wetmore-Arkader, L.; McGinty, E.; Pietrzak, G.; Yaroch, A.L. Knowledge, barriers, and stage of change as correlates of fruit and vegetable consumption among urban and mostly immigrant black men. J. Am Diet. Assoc. 2008, 108, 1315–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scaglioni, S.; Salvioni, M.; Galimberti, C. Influence of parental attitudes in the development of children eating behaviour. Br. J. Nutr. 2008, 99 (Suppl.1), S22–S25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slater, B.; Marchioni, D.L.; Fisberg, R.M. Estimating prevalence of inadequate nutrient intake. Rev. Saude Publica 2004, 38, 599–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sobiecki, J.G.; Appleby, P.N.; Bradbury, K.E.; Key, T.J. High compliance with dietary recommendations in a cohort of meat eaters, fish eaters, vegetarians, and vegans: Results from the European prospective investigation into cancer and nutrition-oxford study. Nutr. Res. 2016, 36, 464–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rothman, K.J.; Gallacher, J.E.J.; Hatch, E.E. Why representativeness should be avoided. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2013, 42, 1012–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothman, K.J. Six persistent research misconceptions. J. Gen. Intern. Med. 2014, 29, 1060–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Food Safety Authority. Scientific opinion on principles for deriving and applying dietary reference values. EFSA J. 2010, 8, 1458. [Google Scholar]
- Zaragoza-Jordana, M.; Closa-Monasterolo, R.; Luque, V.; Ferré, N.; Grote, V.; Koletzko, B.; Pawellek, I.; Verduci, E.; ReDionigi, A.; Socha, J.; et al. Micronutrient intake adequacy in children from birth to 8 years. Data from the childhood obesity project. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 37, 630–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
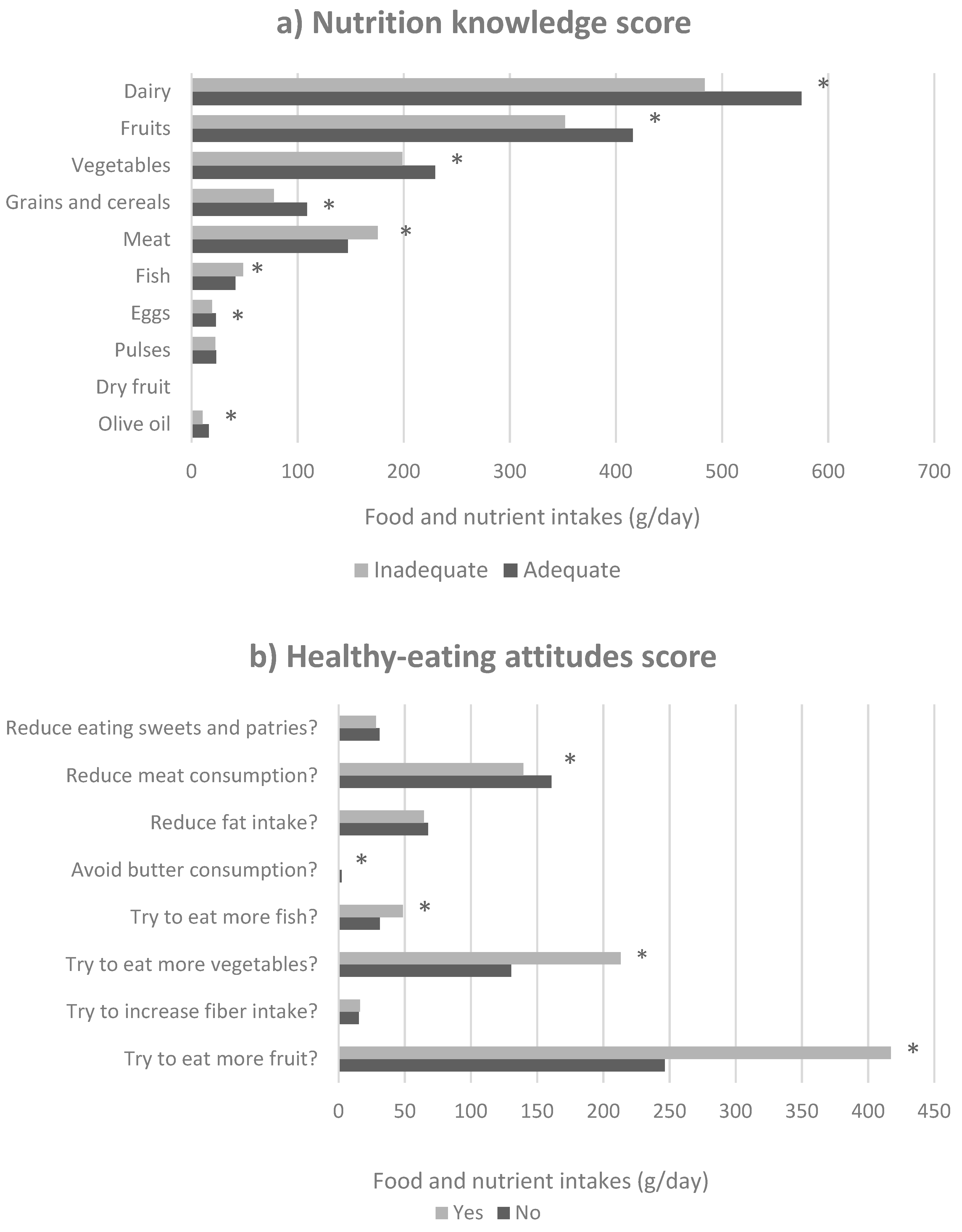
| Nutrition Knowledge Score | Healthy-Eating Attitudes Score | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low | Medium | High | Low | Medium | High | |||
| 0–4 | 5–6 | 7–10 | 0–4 | 5–6 | 7–8 | |||
| Children Characteristics | p value | p value | ||||||
| n (%) | 87 (30.31) | 122 (42.51) | 78 (27.18) | 69 (24.04) | 111 (38.68) | 107 (37.28) | ||
| Age (years) | 7.2 (1.81) | 6.89 (1.69) | 6.56 (1.63) | 0.063 | 6.62 (1.74) | 6.93 (1.67) | 7.03 (1.76) | 0.299 |
| Sex (%) | ||||||||
| Girls | 56.3 | 44.3 | 48.7 | 56.5 | 47.7 | 45.8 | ||
| BMI (kg/m2) | 15.9 (1.7) | 15.8 (1.5) | 15.3 (1.5) | 0.035 | 15.7 (1.4) | 15.5 (1.6) | 15.8 (1.6) | 0.522 |
| Waist /Height ratio | 0.47 (0.05) | 0.48 (0.05) | 0.48 (0.06) | 0.644 | 0.49 (0.05) | 0.47 (0.05) | 0.48 (0.06) | 0.055 |
| Supplement use (%) | 4.65 | 4.13 | 3.9 | 0.970 | 7.25 | 1.82 | 4.76 | 0.201 |
| KIDMED test | 5.86 (1.31) | 5.87 (0.97) | 6.1 (0.95) | 0.258 | 5.74 (1.08) | 5.89 (1.19) | 6.09 (0.95) | 0.093 |
| Physical activity (MET-h/week) | 34.1 (27.8) | 42.9 (31.3) | 37.4 (22.6) | 0.075 | 36.2 (26.1) | 38 (27.2) | 41.2 (30.7) | |
| Leisure activity (%) 1 | 50.6 | 54.1 | 56.4 | 0.748 | 49.3 | 60.4 | 49.5 | 0.195 |
| Eating at home (%) 2 | 71.3 | 77.9 | 85.9 | 0.076 | 73.9 | 77.5 | 81.3 | 0.503 |
| Eating with someone (%) 3 | 79.3 | 86.1 | 80.8 | 0.396 | 79.7 | 82.9 | 84.1 | 0.750 |
| Parental Characteristics | ||||||||
| Age (years) | ||||||||
| Mother | 39.7 (4.5) | 39.2 (3.2) | 39 (3.2) | 0.449 | 38.9 (4.2) | 39.5 (3.6) | 39.3 (3.3) | 0.531 |
| Father | 37.6 (4) | 37.3 (3.2) | 37.1 (3.1) | 0.548 | 36.7 (3.5) | 37.9 (3.6) | 37.2 (3.2) | 0.072 |
| Large family (%) 4 | 35.6 | 31.1 | 28.2 | 0.583 | 0.289 | |||
| Education (%) | ||||||||
| University | 50.6 | 54.9 | 66.7 | 0.098 | 56.5 | 58.6 | 55.1 | 0.877 |
| Do you consider your | ||||||||
| children’s weight as high? (%) | 1.15 | 0.82 | 0 | 0.433 | 0 | 1.8 | 0 | 0.699 |
| Fixed eating schedule (%) | 94.3 | 93.4 | 93.6 | 0.970 | 94.2 | 92.8 | 94.4 | 0.873 |
| Snacking (%) | 6.9 | 7.38 | 7.69 | 0.980 | 8.7 | 7.21 | 6.54 | 0.865 |
| Nutrition Knowledge Score | Healthy-Eating Attitudes Score | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low | Medium | High | Low | Medium | High | |||
| 0–4 | 5–6 | 7–10 | 0–4 | 5–6 | 7–8 | |||
| Food Group | p value | p value | ||||||
| Fruit (g/day) | 368 (190) | 413 (199) | 409 (176) | 0.212 | 364 (174) | 384 (186) | 435 (201) | 0.032 |
| Vegetables (g/day) | 180 (91) | 218 (111) | 220 (97) | 0.013 | 190 (116) | 198 (80) | 229 (110) | 0.022 |
| Pulses (g/day) | 23.5 (15.3) | 23 (11.1) | 22.6 (6.7) | 0.896 | 22.5 (13.1) | 21 (8.3) | 25.5 (13) | 0.014 |
| Daily (g/day) | 503 (218) | 563 (231) | 559 (195) | 0.114 | 540 (223) | 532 (211) | 557 (225) | 0.698 |
| White meat (g/day) | 39.8 (20.9) | 43.6 (19.4) | 40.4 (16.4) | 0.306 | 40.2 (18.1) | 39.4 (17) | 44.8 (21.5) | 0.090 |
| Red meat (g/day) | 111 (43) | 122 (50) | 105 (39) | 0.035 | 123 (48) | 113 (36) | 109 (53) | 0.136 |
| White fish (g/day) | 26.8 (15.1) | 31.6 (16.5) | 33 (14.2) | 0.023 | 26.4 (15.7) | 29.7 (16.3) | 34 (14.3) | 0.005 |
| Blue fish (g/day) | 11.5 (9.3) | 13 (13.5) | 15.2 (13.2) | 0.152 | 9.6 (9.6) | 12.5 (12.6) | 16.1 (13) | 0.002 |
| Olive oil (g/day) | 12.7 (13.1) | 11.5 (11.4) | 13.9 (13.7) | 0.424 | 12.6 (11.4) | 10.4 (11.2) | 14.6 (14.21) | 0.045 |
| Bakery (g/day) | 27.7 (35) | 30.2 (23.2) | 27 (19.8) | 0.652 | 30.2 (38) | 27.6 (21.4) | 28.6 (22.2) | 0.822 |
| Eggs (g/day) | 18 (10) | 22 (14.5) | 25.7 (15.8) | 0.002 | 20.8 (8.1) | 21.5 (15.6) | 22.7 (15.2) | 0.650 |
| Beverage (g/day) | 7.6 (14.81) | 4.6 (8.1) | 3.5 (6.4) | 0.024 | 7.8 (13.3) | 4.2 (7.4) | 4.6 (10.8) | 0.054 |
| Sweets (g/day) | 17.1 (14.2) | 14.8 (9.5) | 13.8 (13.9) | 0.199 | 15.8 (12.1) | 15.2 (11) | 14.9 (13.8) | 0.894 |
| Nutrients | ||||||||
| Energy (kcal/day) | 1700 (409) | 1787 (432) | 1775 (365) | 0.286 | 1753 (395) | 1708 (361) | 1811 (458) | 0.175 |
| HC (% total energy) | 47.8 (6.3) | 46.4 (5.3) | 47.9 (4.9) | 0.109 | 47 (5.7) | 46.6 (5.6) | 48.1 (5.4) | 0.125 |
| Proteins (% total energy) | 19.2 (2.3) | 19.8 (2.6) | 19.1 (1.7) | 0.026 | 19.3 (2.7) | 19.7 (2.5) | 19.2 (1.9) | 0.323 |
| Fat (% total energy) | 33.1 (5.6) | 33.7 (4.4) | 33 (4.6) | 0.533 | 33.7 (4.9) | 33.7 (4.6) | 32.7 (5) | 0.218 |
| Ca (mg/day) | 1102 (344) | 1242 (441) | 1295 (449) | 0.008 | 1184 (380) | 1198 (421) | 1251 (449) | 0.520 |
| Fe (mg/day) | 9.1 (6) | 11.1 (7.5) | 12.6 (7.9) | 0.006 | 11 (6.9) | 10.4 (7.2) | 11.3 (7.8) | 0.680 |
| I (µg/day) | 92 (47) | 111 (53) | 121 (61) | 0.002 | 108 (53) | 104 (53) | 112 (57) | 0.618 |
| Mg (mg/day) | 224 (70) | 263 (95) | 282 (111) | 0.000 | 256 (85) | 246 (88) | 268 (109) | 0.241 |
| Zn (mg/day) | 5.7 (2.4) | 6.9 (3.4) | 7.4 (3.9) | 0.002 | 6.7 (3.1) | 6.5 (3.1) | 6.9 (3.6) | 0.764 |
| Na (mg/day) | 2477 (1095) | 3007 (1361) | 3324 (1310) | 0.000 | 3175 (1298) | 2841 (1321) | 2871 (1296) | 0.207 |
| K (mg/day) | 2401 (1170) | 2907 (1380) | 3177 (1566) | 0.001 | 2798 (1269) | 2686 (1354) | 2992 (1526) | 0.269 |
| P (mg/day) | 1024 (335) | 1224 (447) | 1285 (502) | 0.000 | 1171 (389) | 1150 (436) | 1217 (485) | 0.534 |
| Se (µg/day) | 42.9 (35.4) | 54.4 (43.8) | 63.1 (47.6) | 0.01 | 55.1 (41.8) | 51.2 (42.1) | 54.3 (45.2) | 0.802 |
| Vitamin B1 (mg/day) | 0.8 (0.5) | 1.02 (0.62) | 1.1 (0.7) | 0.004 | 1.00 (0.57) | 0.9 (0.6) | 0.9 (0.6) | 0.929 |
| Vitamin B2 (mg/day) | 1.3 (0.4) | 1.6 (0.6) | 1.66 (0.62) | 0.000 | 1.5 (0.5) | 1.5 (0.6) | 1.6 (0.6) | 0.825 |
| Vitamin B3 (mg/day) | 16.0 (9.7) | 23.6 (12.8) | 27.6 (24.7) | 0.000 | 22.6 (12.9) | 21.9 (11.1) | 22.7 (11.4)) | 0.948 |
| Vitamin B6 (mg/day) | 1.2 (0.7) | 1.5 (0.9) | 1.6 (0.9) | 0.001 | 1.4 (0.8) | 1.4 (0.94) | 1.5 (0.9) | 0.810 |
| Vitamin B9 (µg/day) | 178 (90) | 220 (123) | 237 (123) | 0.002 | 205 (106) | 208 (123) | 221 (115) | 0.573 |
| Vitamin B12 (µg/day) | 2.3 (1.1) | 3.07 (1.61) | 3.4 (1.7) | 0.000 | 2.93 (1.55) | 2.8 (1.6) | 2.9 (1.6) | 0.902 |
| Vitamin C (mg/day) | 79.9 (47.9) | 100.4 (50.1) | 107.3 (52.3) | 0.001 | 89.3 (44.8) | 94.2 (52.8) | 102.4 (52.8) | 0.224 |
| Vitamin A (µg/day) | 465 (272) | 603 (462) | 680 (404) | 0.002 | 583 (427) | 569 (435) | 595 (357) | 0.894 |
| Vitamin D (µg/day) | 1.3 (1.3) | 1.5 (1.4) | 2.15 (1.92) | 0.001 | 1.4 (1.34) | 1.4 (1.4) | 1.95 (1.83) | 0.024 |
| Vitamin E (µg/day) | 14.7 (21) | 16.8 (22.9) | 21.9 (24.8) | 0.121 | 17.6 (22.9) | 15.7 (22) | 19.4 (24.1) | 0.504 |
| Nutrition Knowledge Score | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low | Medium | High | p | ||||
| OR | 95% CI | OR | 95% CI | ||||
| N | 65 | 83 | 47 | ||||
| % intake failing to meet ≥3 EAR | 33.33 | 42.56 | 24.10 | ||||
| Crude | 1 (Ref.) | 0.72 | 0.39, 1.33 | 0.51 | 0.26, 1.00 | 0.051 | |
| Multivariable 1 | 1 (Ref.) | 0.84 | 0.36, 1.98 | 0.70 | 0.28, 1.75 | 0.449 | |
| Multivariable 2 | 1 (Ref.) | 0.80 | 0.34, 1.91 | 0.63 | 0.25, 1.60 | 0.337 | |
| Multivariable 3 | 1 (Ref.) | 1.34 | 0.50, 3.59 | 1.13 | 0.40, 3.23 | 0.961 | |
| Multivariable 4 1 | 1 (Ref.) | 1.45 | 0.54, 3.90 | 1.19 | 0.41, 3.48 | 0.908 | |
| Healthy-Eating Attitudes Score | |||||||
| Low | Medium | High | p | ||||
| OR | 95% CI | OR | 95% CI | ||||
| N | 49 | 77 | 69 | ||||
| % intake failing to meet ≥3 EAR | 25.13 | 39.49 | 35.38 | ||||
| Crude | 1 (Ref.) | 0.92 | 0.48, 1.79 | 0.74 | 0.39, 1.42 | 0.322 | |
| Multivariable 1 | 1 (Ref.) | 0.60 | 0.25, 1.46 | 0.35 | 0.14, 0.88 | 0.026 | |
| Multivariable 2 | 1 (Ref.) | 0.56 | 0.23, 1.38 | 0.34 | 0.14, 0.86 | 0.027 | |
| Multivariable 3 | 1 (Ref.) | 0.63 | 0.23, 1.69 | 0.34 | 0.12, 0.93 | 0.034 | |
| Multivariable 4 2 | 1 (Ref.) | 0.63 | 0.23, 1.72 | 0.34 | 0.12, 0.95 | 0.037 | |
| Nutrition Knowledge Score | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KIDMED | Low | Medium | High | ||||
| β | 95% CI | p | β | 95% CI | p | ||
| Crude | 0 (Ref.) | 0.01 | −0.29, 0.31 | 0.964 | 0.24 | −0.09, 0.57 | 0.154 |
| Multivariable 1 | 0 (Ref.) | 0.02 | −0.28, 0.32 | 0.903 | 0.27 | −0.07, 0.60 | 0.119 |
| Multivariable 2 | 0 (Ref.) | 0.02 | −0.28, 0.32 | 0.897 | 0.28 | −0.06, 0.62 | 0.110 |
| Multivariable 3 | 0 (Ref.) | −0.01 | −0.31, 0.30 | 0.971 | 0.23 | −0.12, 0.57 | 0.195 |
| Multivariable 4 1 | 0 (Ref.) | −0.01 | −0.31, 0.30 | 0.969 | 0.18 | −0.16, 0.53 | 0.293 |
| Healthy-Eating Attitudes Score | |||||||
| KIDMED | Low | Medium | High | ||||
| β | 95% CI | p | β | 95% CI | p | ||
| Crude | 0 (Ref.) | 0.15 | −0.17, 0.48 | 0.355 | 0.35 | 0.03, 0.68 | 0.034 |
| Multivariable 1 | 0 (Ref.) | 0.15 | −0.18, 0.47 | 0.381 | 0.35 | 0.01, 0.68 | 0.041 |
| Multivariable 2 | 0 (Ref.) | 0.15 | −0.18, 0.48 | 0.379 | 0.35 | 0.01, 0.68 | 0.041 |
| Multivariable 3 | 0 (Ref.) | 0.15 | −0.18, 0.48 | 0.369 | 0.36 | 0.03, 0.69 | 0.033 |
| Multivariable 4 2 | 0 (Ref.) | 0.15 | −0.18, 0.48 | 0.361 | 0.34 | 0.01, 0.67 | 0.045 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Romanos-Nanclares, A.; Zazpe, I.; Santiago, S.; Marín, L.; Rico-Campà, A.; Martín-Calvo, N. Influence of Parental Healthy-Eating Attitudes and Nutritional Knowledge on Nutritional Adequacy and Diet Quality among Preschoolers: The SENDO Project. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1875. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10121875
Romanos-Nanclares A, Zazpe I, Santiago S, Marín L, Rico-Campà A, Martín-Calvo N. Influence of Parental Healthy-Eating Attitudes and Nutritional Knowledge on Nutritional Adequacy and Diet Quality among Preschoolers: The SENDO Project. Nutrients. 2018; 10(12):1875. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10121875
Chicago/Turabian StyleRomanos-Nanclares, Andrea, Itziar Zazpe, Susana Santiago, Lucía Marín, Anaïs Rico-Campà, and Nerea Martín-Calvo. 2018. "Influence of Parental Healthy-Eating Attitudes and Nutritional Knowledge on Nutritional Adequacy and Diet Quality among Preschoolers: The SENDO Project" Nutrients 10, no. 12: 1875. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10121875
APA StyleRomanos-Nanclares, A., Zazpe, I., Santiago, S., Marín, L., Rico-Campà, A., & Martín-Calvo, N. (2018). Influence of Parental Healthy-Eating Attitudes and Nutritional Knowledge on Nutritional Adequacy and Diet Quality among Preschoolers: The SENDO Project. Nutrients, 10(12), 1875. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10121875






