Crocin Ameliorates Atopic Dermatitis Symptoms by down Regulation of Th2 Response via Blocking of NF-κB/STAT6 Signaling Pathways in Mice
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Drugs and Reagents
2.2. Animals
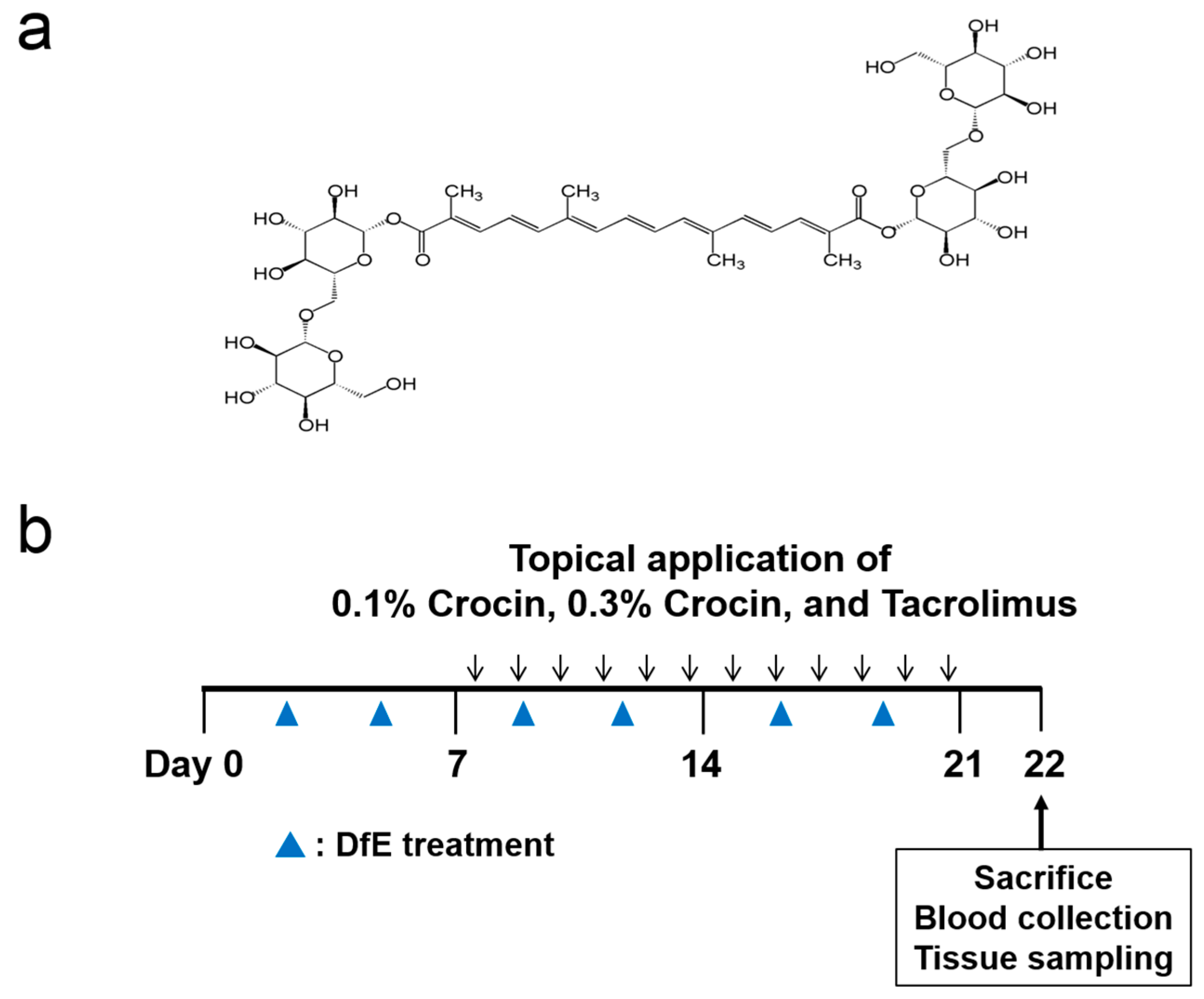
2.3. Induction of AD and Treatment of Drug in Mice
2.4. Evaluation of Ear Thickness and Dermatitis Severity
2.5. Measurement of Serum IgE Levels
2.6. Histopathological Analysis
2.7. Contents of Cytokines and Chemokine in Skin Tissue
2.8. Preparation of Total Cell Lysates and Nuclear Extracts and Western Blotting
2.9. Statistics
3. Results
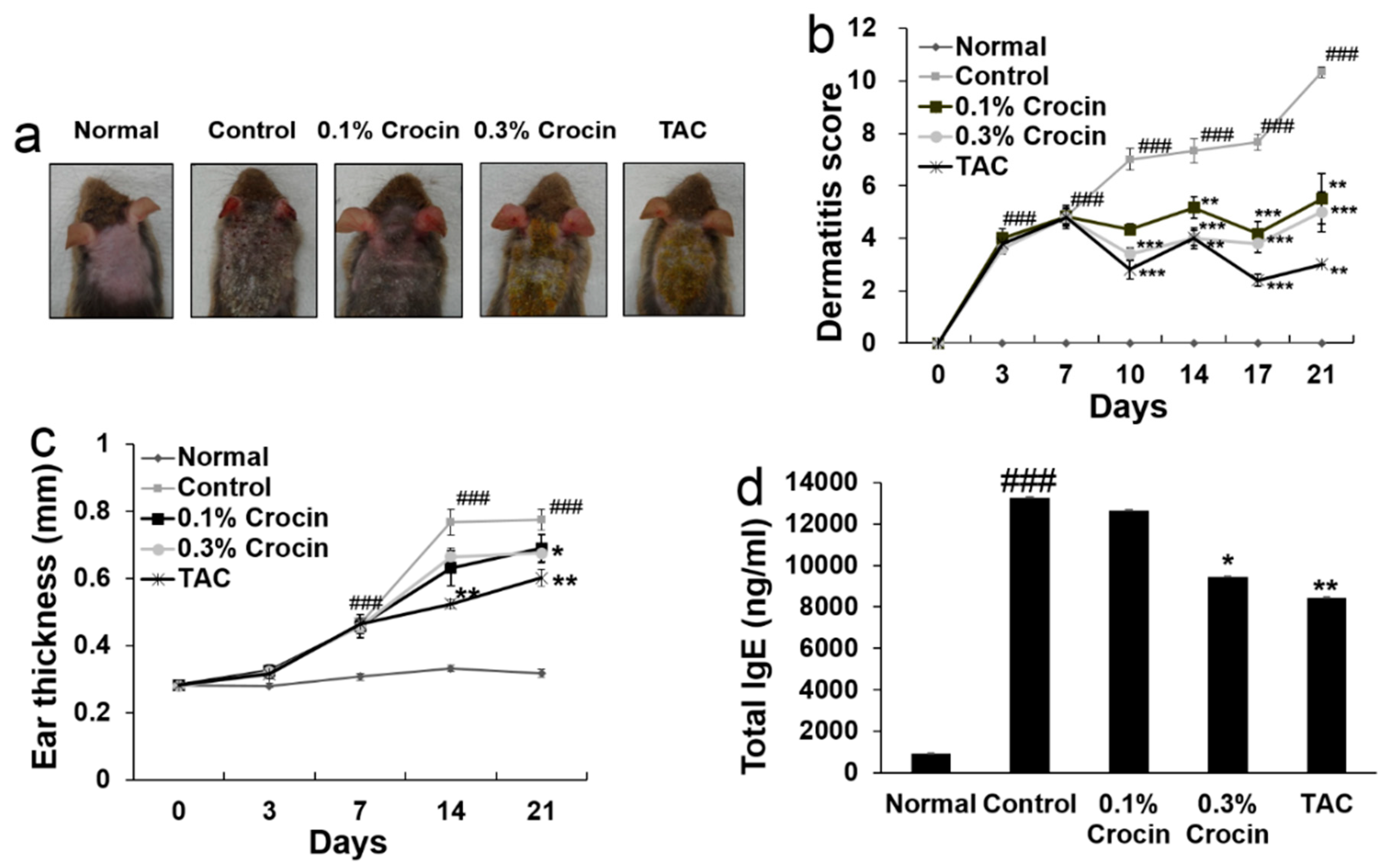
3.1. Effects of Crocin on AD-Induced NC/Nga Mice
3.2. Effect of Crocin on Serum IgE Levels
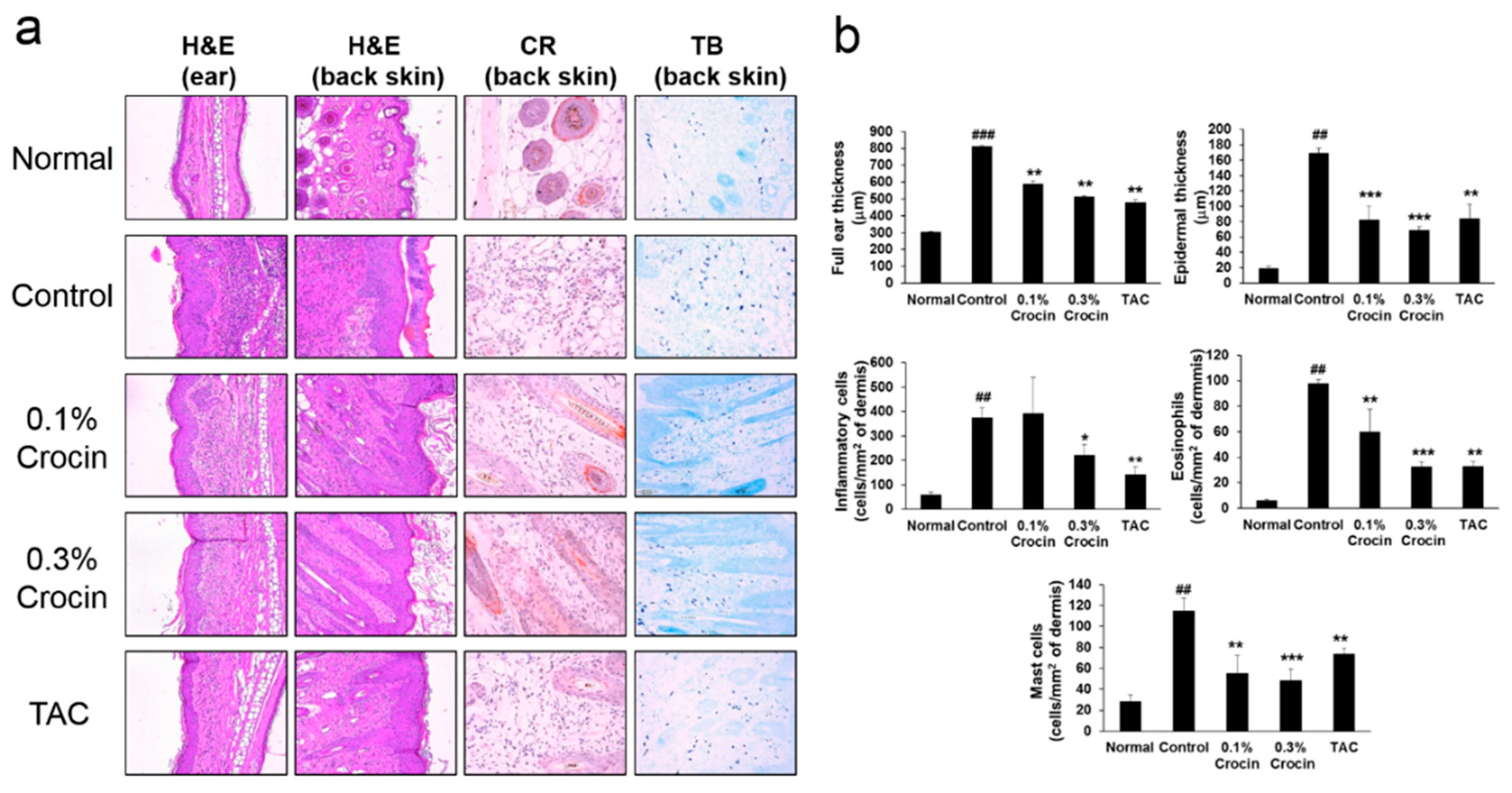
3.3. Effects of Crocin on Histological Features
3.4. Effects of Crocin on Protein Contents of Chemokine and Cytokines in the Dorsal Skin
3.5. Effects of Crocin on Activation of NF-κB and STAT6 in the Back Skin
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brandt, E.B.; Sivaprasad, U. Th2 cytokines and atopic dermatitis. J. Clin. Cell. Immunol. 2011, 2, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nutten, S. Atopic dermatitis: Global epidemiology and risk factors. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 2015, 66, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bantz, S.K.; Zhu, Z.; Zheng, T. The Atopic March: Progression from Atopic Dermatitis to Allergic Rhinitis and Asthma. J. Clin. Cell. Immunol. 2014, 5, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leung, D.Y. New insights into atopic dermatitis: Role of skin barrier and immune dysregulation. Allergol. Int. 2013, 62, 151–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamanaka, K.; Mizutani, H. The role of cytokines/chemokines in the pathogenesis of atopic dermatitis. Curr. Probl. Dermatol. 2011, 41, 80–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- David Boothe, W.; Tarbox, J.A.; Tarbox, M.B. Atopic dermatitis: Pathophysiology. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2017, 1027, 21–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abramovits, M. Atopic dermatitis. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2005, 53, S86–S93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leung, D.Y.; Bieber, T. Atopic dermatitis. Lancet 2003, 361, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boguniewicz, M.; Leung, D.Y. Atopic dermatitis: A disease of altered skin barrier and immune dysregulation. Immunol. Rev. 2011, 242, 233–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hengge, U.R.; Ruzicka, T.; Schwartz, R.A.; Cork, M.J. Adverse effects of topical glucocorticosteroids. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2006, 54, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carr, W.W. Topical calcineurin inhibitors for atopic dermatitis: Review and treatment recommendations. Paediatr. Drugs 2013, 15, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, W.S.; Chae, Y.S.; Kim, D.Y.; Seo, S.W.; Park, H.J.; Bae, G.S.; Kim, T.H.; Oh, H.J.; Yun, K.J.; Park, R.K.; et al. Gardenia jasminoides protects against cerulein-induced acute pancreatitis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2008, 14, 6188–6194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sung, Y.Y.; Lee, A.Y.; Kim, H.K. The Gardenia jasminoides extract and its constituent, geniposide, elicit anti-allergic effects on atopic dermatitis by inhibiting histamine in vitro and in vivo. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2014, 156, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Lei, H.T.; Cao, L.; Mi, Y.N.; Li, S.; Cao, Y.X. Crocin alleviates coronary atherosclerosis via inhibiting lipid synthesis and inducing M2 macrophage polarization. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2017, 55, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, Y.; Wang, J.; Yu, H.; Zhang, X.; Miao, C. Anti-asthma potential of crocin and its effect on MAPK signaling pathway in a murine model of allergic airway disease. Immunopharmacol. Immunotoxicol. 2015, 37, 236–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yosri, H.; Elkashef, W.F.; Said, E.; Gameil, N.M. Crocin modulates IL-4/IL-13 signaling and ameliorates experimentally induced allergic airway asthma in a murine model. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2017, 50, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.H.; Lee, K.Y.; Park, B.; Yoon, J. Suppression of Th2 chemokines by crocin via blocking of ERK-MAPK/NF-κB/STAT1 signaling pathways in TNF-α/IFN-γ-stimulated human epidermal keratinocytes. Exp. Dermatol. 2015, 24, 634–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuoka, H.; Maki, N.; Yoshida, S.; Arai, M.; Wang, J.; Oikawa, Y.; Ikeda, T.; Hirota, N.; Nakagawa, H.; Ishii, A. A mouse model of the atopic eczema/dermatitis syndrome by repeated application of a crude extract of house-dust mite Dermatophagoides farinae. Allergy 2003, 58, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sung, Y.Y.; Lee, A.Y.; Kim, H.K. Forsythia suspensa fruit extracts and the constituent matairesinol confer anti-allergic effects in an allergic dermatitis mouse model. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2016, 187, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, M.; Haruna, T.; Yasui, K.; Takahashi, H.; Iduhara, M.; Takaki, S.; Deguchi, M.; Arimura, A. A novel atopic dermatitis model induced by topical application with Dermatophagoides farinae extract in NC/Nga mice. Allergol. Int. 2007, 56, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiba, T.; Takeuchi, S.; Esaki, H.; Yamamura, K.; Kurihara, Y.; Moroi, Y.; Furue, M. Topical application of PPARα (but not β/δ or γ) suppresses atopic dermatitis in NC/Nga mice. Allergy 2012, 67, 936–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, C.H.; Park, C.D.; Lee, A.Y. Administration of poly(I:C) improved Dermatophagoides farinae-induced atopic dermatitis-like skin lesions in NC/Nga mice by the regulation of Th1/Th2 balance. Vaccine 2012, 30, 2405–2410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, C.G.; Kang, M.; Lee, Y.H.; Min, W.G.; Kim, Y.H.; Kang, S.J.; Song, C.H.; Park, S.J.; Park, J.H.; Han, C.H.; et al. Bathing effects of various seawaters on allergic (atopic) dermatitis-like skin lesions induced by 2,4-dinitrochlorobenzene in hairless mice. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2015, 2015, 179185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.H.; Park, S.J.; Lee, Y.J.; Lee, J.E.; Song, C.H.; Choi, S.H.; Ku, S.K.; Kang, S.J. Inhibition of UVB-induced skin damage by exopolymers from Aureobasidium pullulans SM-2001 in hairless mice. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2015, 116, 73–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grewe, M.; Bruijnzeel-Koomen, C.A.; Schopf, E.; Thepen, T.; Langeveld-Wildschut, A.G.; Ruzicka, T.; Krutmann, J. A role for Th1 and Th2 cells in the immuno- pathogenesis of atopic dermatitis. Immunol. Today 1998, 19, 359–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, C.W.; Ahn, K.S.; Rho, N.K.; Park, Y.D.; Lee, D.Y.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, E.S.; Yang, J.M. Differential in vivo cytokine mRNA expression in lesional skin of intrinsic vs. extrinsic atopic dermatitis patients using semiquantitative RT-PCR. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2003, 33, 1717–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, T.; Fujita, H.; Saeki, H.; Mitsui, H.; Sugaya, N.; Tada, Y.; Kakinuma, T.; Torii, H.; Nakamura, K.; Asahina, A.; et al. Thymus and activation-regulated chemokine (TARC/CCL17) produced by mouse epidermal Langerhans cells is upregulated by TNF-alpha and IL-4 and downregulated by IFN-gamma. Cytokine 2003, 23, 126–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeki, H.; Tamaki, K. Thymus and activation regulated chemokine (TARC)/CCL17 and skin diseases. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2006, 43, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kakinuma, T.; Nakamura, K.; Wakugawa, M.; Mitsui, H.; Tada, Y.; Saeki, H.; Torii, H.; Asahina, A.; Onai, N.; Matsushima, K.; et al. Thymus and activation-regulated chemokine in atopic dermatitis: Serum thymus and activation-regulated chemokine level is closely related with disease activity. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2001, 107, 535–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kataoka, Y. Thymus and activation-regulated chemokine as a clinical biomarker in atopic dermatitis. J. Dermatol. 2014, 41, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Barnes, P.J.; Karin, M. Nuclear factor-kappaB: A pivotal transcription factor in chronic inflammatory diseases. N. Engl. J. Med. 1997, 336, 1066–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, J.W.; Lee, K.S.; Kim, C.W. Curcumin attenuates the expression of IL-1beta, IL-6, and TNF-alpha as well as cyclin E in TNF-alpha-treated HaCaT cells; NF-kappaB and MAPKs as potential upstream targets. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2007, 19, 469–474. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kwon, D.J.; Bae, Y.S.; Ju, S.M.; Goh, A.R.; Youn, G.S.; Choi, S.Y.; Park, J. Casuarinin suppresses TARC/CCL17 and MDC/CCL22 production via blockade of NF-κB and STAT1 activation in HaCaT cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2012, 417, 1254–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yagi, R.; Nagai, H.; Iigo, Y.; Akimoto, T.; Arai, T.; Kubo, M. Development of atopic dermatitis-like skin lesions in STAT6-deficient NC/Nga mice. J. Immunol. 2002, 168, 2020–2027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Normal | Control | 0.1% Crocin | 0.3% Crocin | TAC | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TARC (pg/mg) | 4.78 ± 0.64 | 8.22 ± 0.80 # | 9.61 ± 1.70 | 2.10 ± 0.35 * | 2.79 ± 0.86 ** |
| IL-4 (pg/mg) | 2.00 ± 0.64 | 4.77 ± 0.65 # | 1.62 ± 0.40 ** | 0.98 ± 0.05 ** | 1.96 ± 0.45 * |
| IL-5 (pg/mg) | 2.35 ± 0.41 | 3.88 ± 0.46 | 2.78 ± 0.22 | 3.11 ± 0.33 | 4.40 ± 0.66 |
| IL-13 (pg/mg) | 2.24 ± 0.47 | 5.81 ± 1.52 # | 1.55 ± 0.17 * | 1.00 ± 0.13 * | 2.02 ± 0.14 * |
| IFN-γ (pg/mg) | 11.57 ± 1.94 | 4.88 ± 0.39 # | 5.34 ± 0.85 | 5.43 ± 0.51 | 6.36 ± 0.34 * |
| IL-12 (pg/mg) | 1.45 ± 0.26 | 0.49 ± 0.09 # | 0.97 ± 0.25 | 0.76 ± 0.10 | 0.91 ± 0.09 * |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sung, Y.-Y.; Kim, H.K. Crocin Ameliorates Atopic Dermatitis Symptoms by down Regulation of Th2 Response via Blocking of NF-κB/STAT6 Signaling Pathways in Mice. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1625. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10111625
Sung Y-Y, Kim HK. Crocin Ameliorates Atopic Dermatitis Symptoms by down Regulation of Th2 Response via Blocking of NF-κB/STAT6 Signaling Pathways in Mice. Nutrients. 2018; 10(11):1625. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10111625
Chicago/Turabian StyleSung, Yoon-Young, and Ho Kyoung Kim. 2018. "Crocin Ameliorates Atopic Dermatitis Symptoms by down Regulation of Th2 Response via Blocking of NF-κB/STAT6 Signaling Pathways in Mice" Nutrients 10, no. 11: 1625. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10111625
APA StyleSung, Y.-Y., & Kim, H. K. (2018). Crocin Ameliorates Atopic Dermatitis Symptoms by down Regulation of Th2 Response via Blocking of NF-κB/STAT6 Signaling Pathways in Mice. Nutrients, 10(11), 1625. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10111625





