Microbiota and Derived Parameters in Fecal Samples of Infants with Non-IgE Cow’s Milk Protein Allergy under a Restricted Diet
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subjects
2.2. Study Design
2.3. Intestinal Microbial Community Analysis
2.4. Analysis of Short-Chain Fatty Acids (SCFAs)
2.5. Calprotectin Assays
2.6. Transforming Growth Factor-β1 (TGF-β1) Determination
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
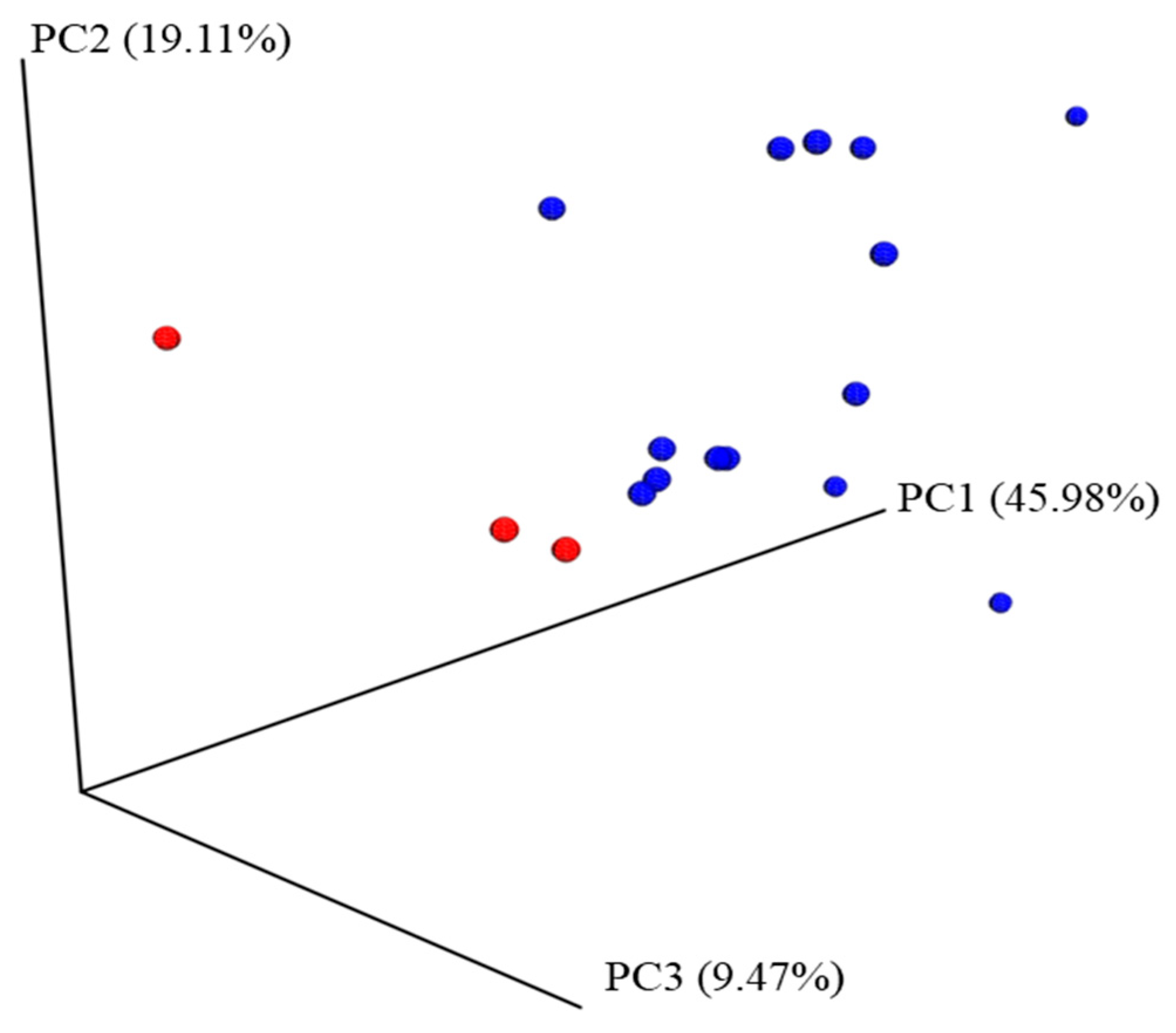
3.1. Microbiota Analysis in NIM-CMPA in Relation to Tolerance and Diet
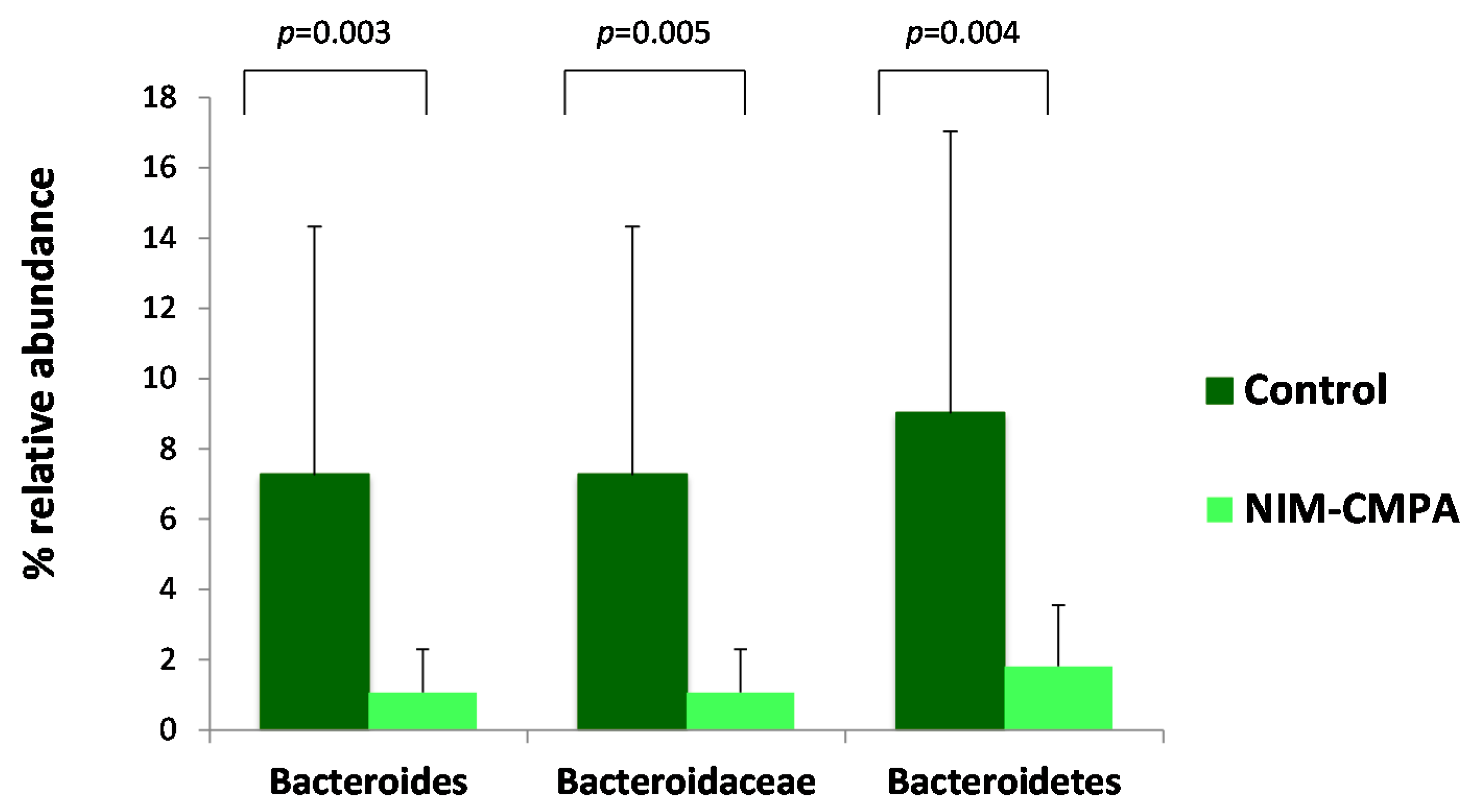
3.2. Microbiota Analysis Comparison between the NIM-CMPA and Control Groups
3.3. Fecal Excreted SCFAs
3.4. Inflammatory Parameters
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nowak-Wegrzyn, A.; Szajewska, H.; Lack, G. Food allergy and the gut. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 14, 241–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venter, C.; Brown, T.; Shah, N.; Fox, A.T. Diagnosis and management of non-IgE-mediated cow’s milk allergy in infancy—A UK primary care practical guide. Clin. Transl. Allergy 2013, 3, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Koletzko, S.; Niggemann, B.; Arato, A.; Dias, J.A.; Heuschkel, R.; Husby, S.; Mearin, M.L.; Papadopoulou, A.; Ruemmele, F.M.; Staiano, A.; et al. Diagnostic approach and management of cow’s-milk protein allergy in infants and children: ESPGHAN GI Committee practical guidelines. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2012, 55, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhatia, J.; Greer, F. American Academy of Pediatrics Committee on Nutrition. Use of soy protein-based formulas in infant feeding. Pediatrics 2008, 121, 1062–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiocchi, A.; Dahda, L.; Dupont, C.; Campoy, C.; Fierro, V.; Nieto, A. Cow’s milk allergy: Towards an update of DRACMA guidelines. World Allergy Organ. J. 2016, 9, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simonyte Sjodin, K.; Vidman, L.; Ryden, P.; West, C.E. Emerging evidence of the role of gut microbiota in the development of allergic diseases. Curr. Opin. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2016, 16, 390–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rachid, R.; Chatila, T.A. The role of the gut microbiota in food allergy. Curr. Opin. Pediatr. 2016, 28, 748–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson-Chagoyan, O.C.; Vieites, J.M.; Maldonado, J.; Edwards, C.; Gil, A. Changes in faecal microbiota of infants with cow’s milk protein allergy—A Spanish prospective case-control 6-month follow-up study. Pediatr. Allergy Immunol. 2010, 21, e394–e400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bunyavanich, S.; Shen, N.; Grishin, A.; Wood, R.; Burks, W.; Dawson, P.; Jones, S.M.; Leung, D.; Sampson, H.; Sicherer, S.; et al. Early-life gut microbiome composition and milk allergy resolution. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2016, 138, 1122–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Candy, D.C.A.; Van Ampting, M.T.J.; Oude Nijhuis, M.M.; Wopereis, H.; Butt, A.M.; Peroni, D.G.; Vandenplas, Y.; Fox, A.T.; Shah, N.; West, C.E.; et al. A synbiotic-containing amino-acid-based formula improves gut microbiota in non-IgE-mediated allergic infants. Pediatr. Res. 2018, 83, 677–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ling, Z.; Li, Z.; Liu, X.; Cheng, Y.; Luo, Y.; Tong, X.; Yuan, L.; Wang, Y.; Sun, J.; Li, L.; et al. Altered fecal microbiota composition associated with food allergy in infants. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 80, 2546–2554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zoetendal, E.G.; Heilig, H.G.; Klaassens, E.S.; Booijink, C.C.; Kleerebezem, M.; Smidt, H.; De Vos, W.M. Isolation of DNA from bacterial samples of the human gastrointestinal tract. Nat. Protoc. 2006, 1, 870–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guadamuro, L.; Delgado, S.; Redruello, B.; Flórez, A.B.; Suárez, A.; Martínez-Camblor, P.; Mayo, B. Equol status and changes in fecal microbiota in menopausal women receiving long-term treatment for menopause symptoms with a soy-isoflavone concentrate. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milani, C.; Hevia, A.; Foroni, E.; Duranti, S.; Turroni, F.; Lugli, G.A.; Sánchez, B.; Martín, R.; Gueimonde, M.; van Sinderen, D.; et al. Assessing the fecal microbiota: An optimized ion torrent 16S rRNA gene-based analysis protocol. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e68739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caporaso, J.G.; Kuczynski, J.; Stombaugh, J.; Bittinger, K.; Bushman, F.D.; Costello, E.K.; Fierer, N.; Gonzalez Peña, A.; Goodrich, J.K.; Gordon, J.I.; et al. QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat. Methods 2010, 7, 335–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Salazar, N.; Gueimonde, M.; Hernandez-Barranco, A.M.; Ruas-Madiedo, P.; de los Reyes-Gavilán, C.G. Exopolysaccharides produced by intestinal Bifidobacterium strains act as fermentable substrates for human intestinal bacteria. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 74, 4737–4745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gómez, M.; Moles, L.; Espinosa-Martos, I.; Bustos, G.; de Vos, W.M.; Fernández, L.; Rodríguez, J.M.; Fuentes, S.; Jiménez, E. Bacteriological and immunological profiling of meconium and fecal samples from preterm infants: A two-year follow-up study. Nutrients 2017, 9, 1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, J.R.; Nagarajan, N.; Pop, M. Statistical methods for detecting differentially abundant features in clinical metagenomic samples. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2009, 5, e1000352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vazquez-Baeza, Y.; Pirrung, M.; Gonzalez, A.; Knight, R. EMPeror: A tool for visualizing high-throughput microbial community data. GigaScience 2013, 2, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hochwallner, H.; Schulmeister, U.; Swoboda, I.; Spitzauer, S.; Valenta, R. Cow’s milk allergy: From allergens to new forms of diagnosis, therapy and prevention. Methods 2014, 66, 22–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milani, C.; Duranti, S.; Bottacini, F.; Casey, E.; Turroni, F.; Mahony, J.; Belzer, C.; Delgado Palacio, S.; Arboleya Montes, S.; Mancabelli, L.; et al. The first microbial colonizers of the human gut: Composition, activities, and health implications of the infant gut microbiota. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2017, 81, e00036-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berni Canani, R.; Nocerino, R.; Terrin, G.; Coruzzo, A.; Cosenza, L.; Leone, L.; Troncone, R. Effect of Lactobacillus GG on tolerance acquisition in infants with cow’s milk allergy: A randomized trial. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2012, 129, 580–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berni Canani, R.; Nocerino, R.; Terrin, G.; Frediani, T.; Lucarelli, S.; Cosenza, L.; Passariello, A.; Leone, L.; Granata, V.; Di Costanzo, M.; et al. Formula selection for management of children with cow’s milk allergy influences the rate of acquisition of tolerance: A prospective multicenter study. J. Pediatr. 2013, 163, 771–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajilic-Stojanovic, M.; de Vos, W.M. The first 1000 cultured species of the human gastrointestinal microbiota. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2014, 38, 996–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Flint, H.J.; Duncan, S.H.; Scott, K.P.; Louis, P. Links between diet, gut microbiota composition and gut metabolism. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2015, 74, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rios-Covian, D.; Ruas-Madiedo, P.; Margolles, A.; Gueimonde, M.; de los Reyes-Gavilán, C.G.; Salazar, N. Intestinal short chain fatty acids and their link with diet and human health. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson-Chagoyan, O.C.; Fallani, M.; Maldonado, J.; Vieites, J.M.; Khanna, S.; Edwards, C.; Doré, J.; Gil, A. Faecal microbiota and short-chain fatty acid levels in faeces from infants with cow’s milk protein allergy. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2011, 156, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, G.D.; Chen, J.; Hoffmann, C.; Bittinger, K.; Chen, Y.-Y.; Keilbaugh, S.A.; Bewtra, M.; Knights, D.; Walters, W.A.; Knight, R.; et al. Linking long-term dietary patterns with gut microbial enterotypes. Science 2011, 334, 105–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- David, L.A.; Maurice, C.F.; Carmody, R.N.; Gootenberg, D.B.; Button, J.E.; Wolfe, B.E.; Ling, A.V.; Devlin, A.S.; Varma, Y.; Fischbach, M.A.; et al. Diet rapidly and reproducibly alters the human gut microbiome. Nature 2014, 505, 559–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Arrieta, M.C.; Stiemsma, L.T.; Amenyogbe, N.; Brown, E.M.; Finlay, B. The intestinal microbiome in early life: Health and disease. Front. Immunol. 2014, 5, 427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azad, M.B.; Konya, T.; Persaud, R.R.; Guttman, D.S.; Chari, R.S.; Field, C.J.; Sears, M.R.; Mandhane, P.J.; Turvey, S.E.; Subbarao, P.; et al. Impact of maternal intrapartum antibiotics, method of birth and breastfeeding on gut microbiota during the first year of life: A prospective cohort study. BJOG 2016, 123, 983–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jakobsson, H.E.; Abrahamsson, T.R.; Jenmalm, M.C.; Harris, K.; Quince, C.; Jernberg, C.; Björkstén, B.; Engstrand, L.; Andersson, A.F. Decreased gut microbiota diversity, delayed Bacteroidetes colonisation and reduced Th1 responses in infants delivered by caesarean section. Gut 2014, 63, 559–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arboleya, S.; Sanchez, B.; Milani, C.; Duranti, S.; Solís, G.; Fernández, N.; de los Reyes-Gavilán, C.; Ventura, M.; Margolles, A.; Gueimonde, M. Intestinal microbiota development in preterm neonates and effect of perinatal antibiotics. J. Pediatr. 2015, 166, 538–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajilic-Stojanovic, M.; Biagi, E.; Heilig, H.G.; Kajander, K.; Kekkonen, R.A.; Tims, S.; de Vos, W.M. Global and deep molecular analysis of microbiota signatures in fecal samples from patients with irritable bowel syndrome. Gastroenterology 2011, 141, 1792–1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caubet, J.C.; Nowak-Wegrzyn, A. Current understanding of the immune mechanisms of food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome. Expert Rev. Clin. Immunol. 2011, 7, 317–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Karlsson, M.R.; Rugtveit, J.; Brandtzaeg, P. Allergen-responsive CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells in children who have outgrown cow’s milk allergy. J. Exp. Med. 2004, 199, 1679–1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, H.L.; Hwang, J.B.; Park, J.J.; Kim, S.G. Expression of transforming growth factor beta1, transforming growth factor type I and II receptors, and TNF-alpha in the mucosa of the small intestine in infants with food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2002, 109, 150–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furusawa, Y.; Obata, Y.; Fukuda, S.; Endo, T.A.; Nakato, G.; Takahashi, D.; Nakanishi, Y.; Uetake, C.; Kato, K.; Kato, T.; et al. Commensal microbe-derived butyrate induces the differentiation of colonic regulatory T cells. Nature 2013, 504, 446–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paparo, L.; di Costanzo, M.; di Scala, C.; Cosenza, L.; Leone, L.; Nocerino, R.; Canani, R.B. The influence of early life nutrition on epigenetic regulatory mechanisms of the immune system. Nutrients 2014, 6, 4706–4719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olafsdottir, E.; Aksnes, L.; Fluge, G.; Berstad, A. Faecal calprotectin levels in infants with infantile colic, healthy infants, children with inflammatory bowel disease, children with recurrent abdominal pain and healthy children. Acta Paediatr. 2002, 91, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beser, O.F.; Sancak, S.; Erkan, T.; Kutlu, T.; Çokuğraş, H.; Çokuğraş, F.Ç. Can fecal calprotectin level be used as a markers of inflammation in the diagnosis and follow-up of cow’s milk protein allergy? Allergy Asthma Immunol. Res. 2014, 6, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vandenplas, Y.; De Greef, E.; Hauser, B. Paradice Study Group. Safety and tolerance of a new extensively hydrolyzed rice protein-based formula in the management of infants with cow’s milk protein allergy. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2014, 173, 1209–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reche, M.; Pascual, C.; Fiandor, A.; Polanco, I.; Rivero-Urgell, M.; Chifre, R.; Johnston, S.; Martín-Esteban, M. The effect of a partially hydrolysed formula based on rice protein in the treatment of infants with cow’s milk protein allergy. Pediatr. Allergy Immunol. 2010, 21, 577–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Terracciano, L.; Bouygue, G.R.; Sarratud, T.; Veglia, F.; Martelli, A.; Fiocchi, A. Impact of dietary regimen on the duration of cow’s milk allergy: A random allocation study. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2010, 40, 637–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Phylum | p Value a | Relative Abundance b | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Non-Tolerant CMPA Infants (n = 3) | Tolerant CMPA Infants (n = 14) | ||
| Actinobacteria | 0.002 | 0.428 ± 0.200 | 21.775 ± 15.731 |
| Family | |||
| Bifidobacteriaceae | 0.002 | 0.087 ± 0.141 | 17.705 ± 15.513 |
| Coriobacteriaceae | 0.009 | 0.266 ± 0.224 | 3.990 ± 4.087 |
| Genus | |||
| Bifidobacterium | 0.002 | 0.087 ± 0.141 | 17.680 ± 15.506 |
| Median (IQR) a | Infants | p Value b | |
|---|---|---|---|
| NIM-CMPA (n = 17) | Control (n = 10) | ||
| BCFAs (µmol/g) | 5.13 (3.08–6.52) | 2.59 (1.94–3.37) | 0.03 |
| Acetic (µmol/g) | 54.88 (48.05–89.63) | 68.61 (50.49–69.96) | 0.90 |
| Propionic (µmol/g) | 16.19 (13.09–21.48) | 15.64 (11.66–24.06) | 0.94 |
| Butyric (µmol/g) | 17.59 (12.74–21.41) | 12.88 (6.14–14.3) | 0.06 |
| TGF-β1 (pg/mL) | 1774.79 (1153.10–3810.88) | 1496.29 (382.23–5820.20) | 0.73 |
| Calprotectin (µg/g) | 47.25 (28.80–106.10) | 68.40 (30.38–76.73) | 1.00 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Díaz, M.; Guadamuro, L.; Espinosa-Martos, I.; Mancabelli, L.; Jiménez, S.; Molinos-Norniella, C.; Pérez-Solis, D.; Milani, C.; Rodríguez, J.M.; Ventura, M.; et al. Microbiota and Derived Parameters in Fecal Samples of Infants with Non-IgE Cow’s Milk Protein Allergy under a Restricted Diet. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1481. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10101481
Díaz M, Guadamuro L, Espinosa-Martos I, Mancabelli L, Jiménez S, Molinos-Norniella C, Pérez-Solis D, Milani C, Rodríguez JM, Ventura M, et al. Microbiota and Derived Parameters in Fecal Samples of Infants with Non-IgE Cow’s Milk Protein Allergy under a Restricted Diet. Nutrients. 2018; 10(10):1481. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10101481
Chicago/Turabian StyleDíaz, María, Lucía Guadamuro, Irene Espinosa-Martos, Leonardo Mancabelli, Santiago Jiménez, Cristina Molinos-Norniella, David Pérez-Solis, Christian Milani, Juan Miguel Rodríguez, Marco Ventura, and et al. 2018. "Microbiota and Derived Parameters in Fecal Samples of Infants with Non-IgE Cow’s Milk Protein Allergy under a Restricted Diet" Nutrients 10, no. 10: 1481. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10101481
APA StyleDíaz, M., Guadamuro, L., Espinosa-Martos, I., Mancabelli, L., Jiménez, S., Molinos-Norniella, C., Pérez-Solis, D., Milani, C., Rodríguez, J. M., Ventura, M., Bousoño, C., Gueimonde, M., Margolles, A., Díaz, J. J., & Delgado, S. (2018). Microbiota and Derived Parameters in Fecal Samples of Infants with Non-IgE Cow’s Milk Protein Allergy under a Restricted Diet. Nutrients, 10(10), 1481. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10101481








