Headache Associated with Coeliac Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Literature Search Strategy
2.2. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
- The study subjects were diagnosed with idiopathic headache and gluten sensitivity or coeliac disease.
- The study subjects were human.
- The study contained original data.
- The study was available as a full-text, English language article, or contained utilisable information in an English language abstract.
- For randomised control trials, a JADAD score [9] of above 3 to ensure good quality and to reduce any potential bias.
2.3. Statistical Analyses
2.4. Compliance with Ethical Guidelines
3. Results
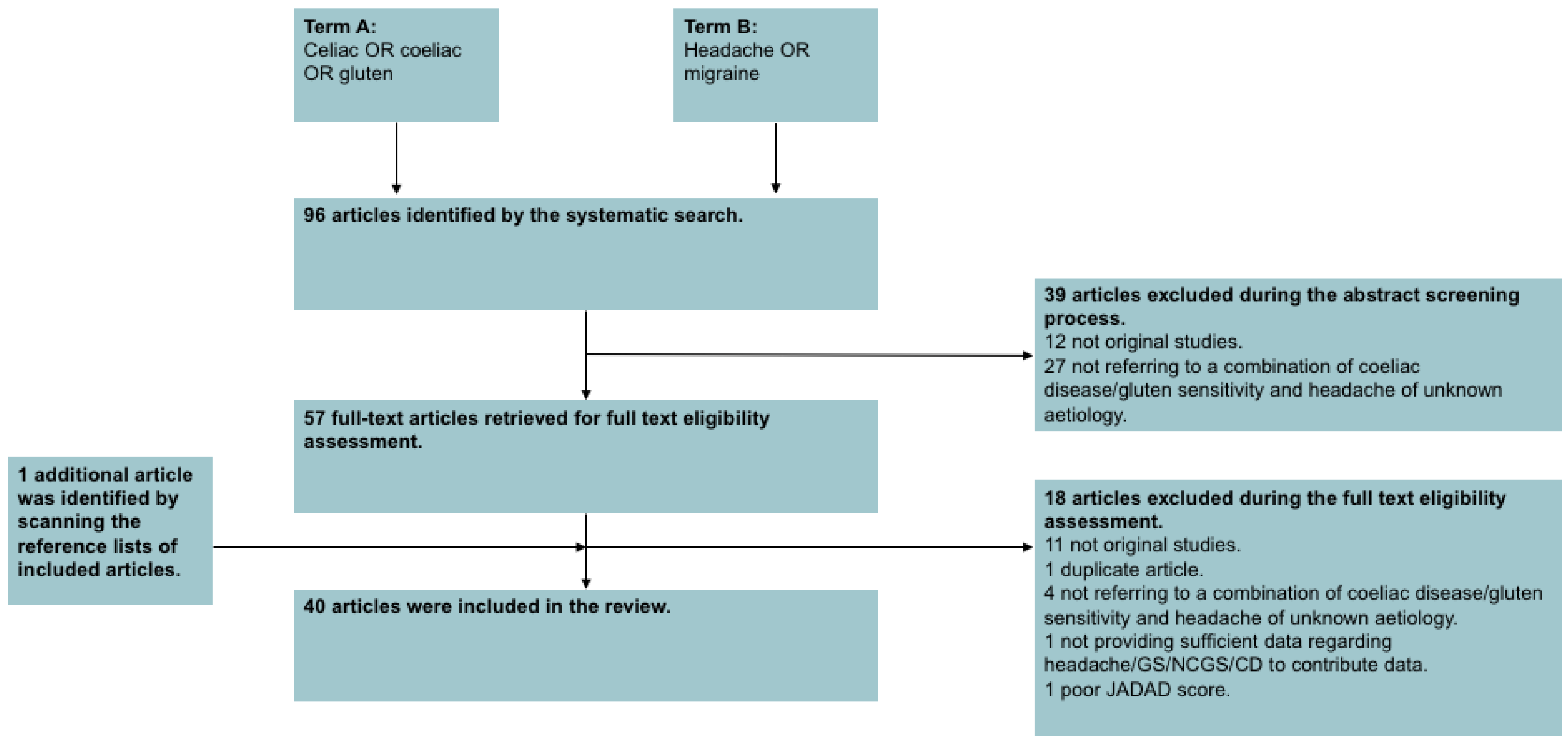
3.1. Selected Studies
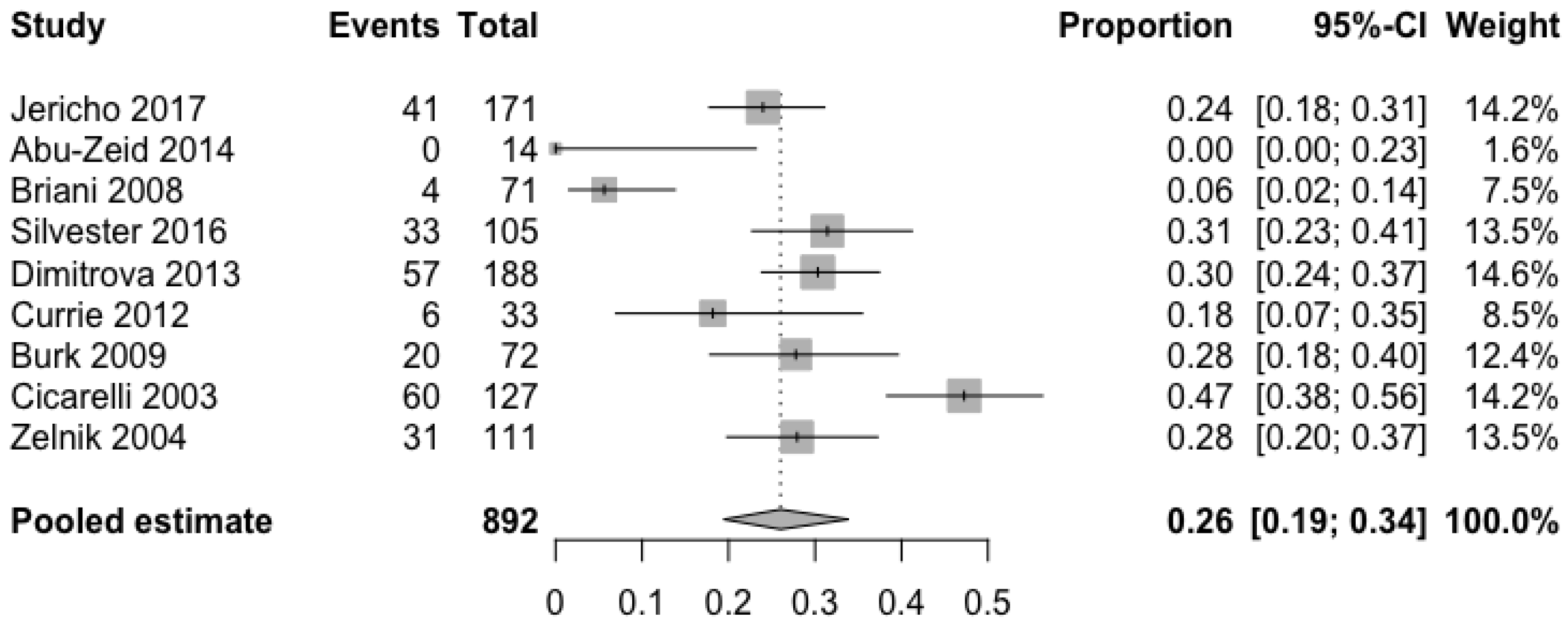
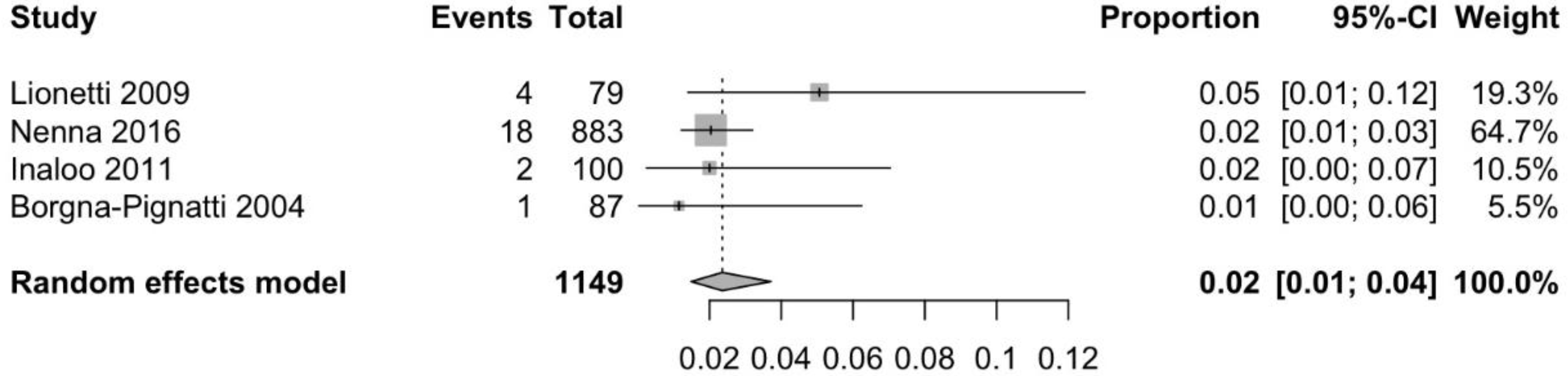
3.2. Prevalence of Headache in Patients with CD
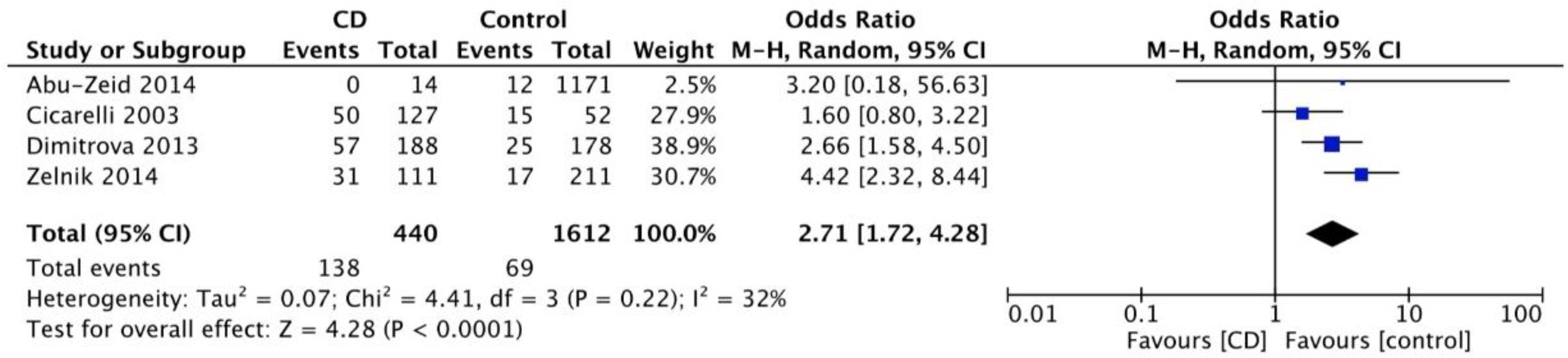
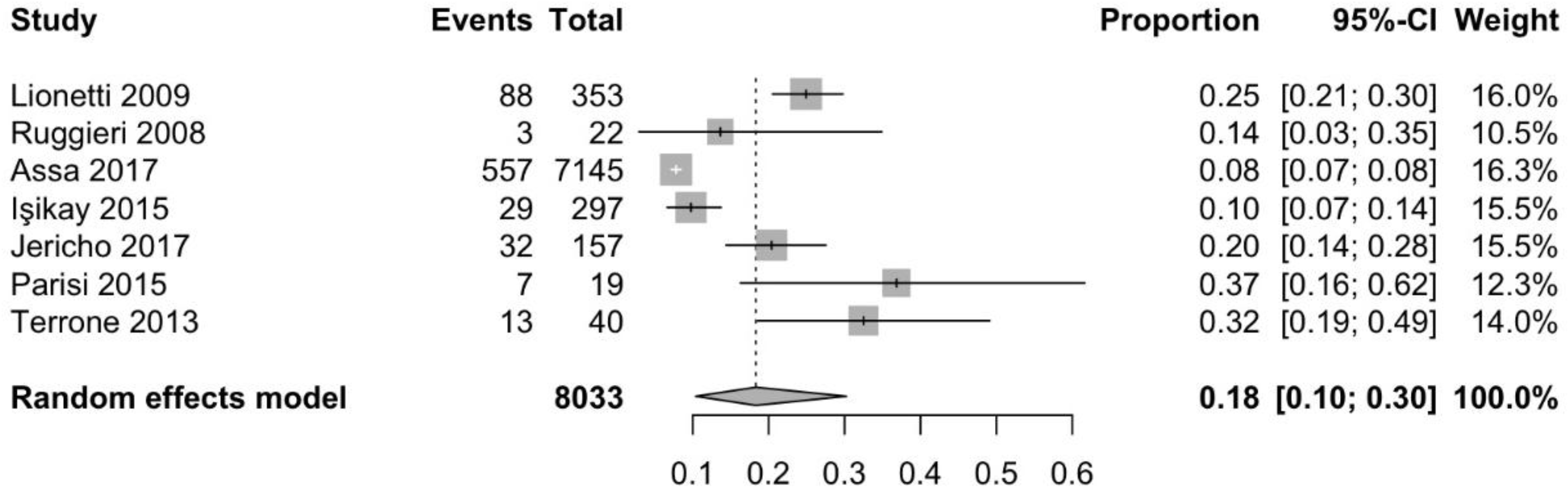
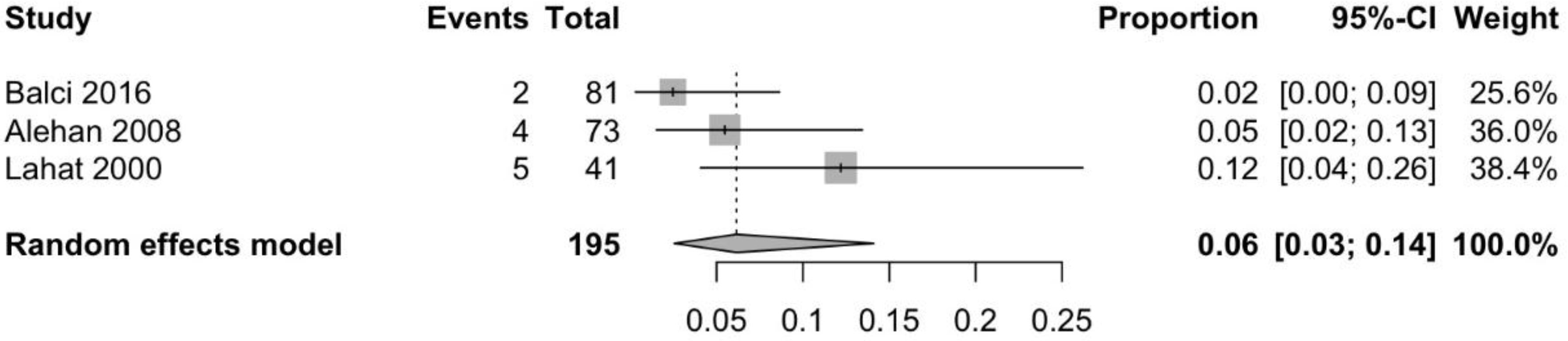
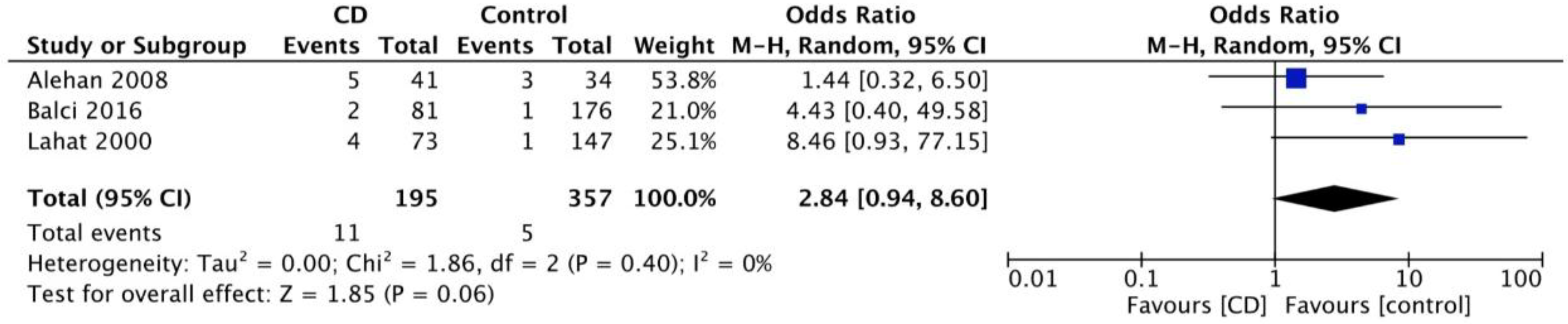
3.3. Prevalence of CD in Patients with Idiopathic Headache
3.4. Imaging Findings
3.4.1. Computed Tomography (CT)
3.4.2. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
3.4.3. Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography (SPECT)
3.4.4. Positron Emission Tomography (PET)
3.5. Effect of Gluten-Free Diet
3.6. Gluten-Related Intracranial Hypertension
3.7. Gluten–Encephalopathy
3.8. NCGS/GS and Headache
4. Conclusions and Future Directions
- There is an increased prevalence of headache amongst patients with CD and an increased prevalence of CD amongst those with idiopathic headache. Such an increased prevalence is evident in both child and adult populations; however, the figures are higher in the latter.
- Headaches that are associated with CD are predominantly migraines. However, many studies that were used in this report tended to report headaches without specifying the exact type (i.e., tension, cluster, migraine, etc.) making the interpretation of the findings more difficult.
- CT calcifications and WMA are frequent in patients with headaches that are related to CD, and therefore patients with such imaging findings in in the context of idiopathic headache require further testing for CD.
- GFD is a very effective treatment for headaches associated with CD and should therefore be offered as soon as possible. This is highly consistent with other neurological GRD, such as the observation that GFD is associated with a significant reduction of pain in patients with gluten neuropathy and an improvement of their quality of life [51,52]. Specialist dietary advise should always be offered, as often patients consume gluten, whilst believe that they are on a strict GFD. Serological testing (i.e., AGA titre) can help in monitoring compliance with diet.
- Further studies of the prevalence of GS in patients with idiopathic headache are needed. Currently, to our knowledge, no such studies in adults exist.
- Although there is some evidence that brain hypoperfusion and perivascular inflammation might play a role in the pathogenesis of GS-related headaches more studies on the likely pathogenetic mechanisms are needed.
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fasano, A.; Catassi, C. Current approaches to diagnosis and treatment of celiac disease: An evolving spectrum. Gastroenterology 2001, 120, 636–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sapone, A.; Bai, J.C.; Ciacci, C.; Dolinsek, J.; Green, P.H.R.; Hadjivassiliou, M.; Kaukinen, K.; Rostami, K.; Sanders, D.S.; Schumann, M.; et al. Spectrum of gluten-related disorders: Consensus on new nomenclature and classification. BMC Med. 2012, 10, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Julian, T.; Hadjivassiliou, M.; Zis, P. Gluten sensitivity and epilepsy: A systematic review. J. Neurol. 2018. Epub ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hadjivassiliou, M.; Grünewald, R.A.; Chattopadhyay, A.K.; Davies-Jones, G.A.; Gibson, A.; Jarratt, J.A.; Kandler, R.H.; Lobo, A.; Powell, T.; Smith, C.M.L. Clinical, radiological, neurophysiological, and neuropathological characteristics of gluten ataxia. Lancet 1998, 352, 1582–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadjivassiliou, M.; Grünewald, R.A.; Kandler, R.H.; Chattopadhyay, A.K.; Jarratt, J.A.; Sanders, D.S.; Sharrack, B.; Wharton, S.B.; Davies-Jones, G.A.B. Neuropathy associated with gluten sensitivity. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2006, 77, 1262–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vinagre-Aragón, A.; Zis, P.; Grunewald, R.A.; Hadjivassiliou, M. Movement Disorders Related to Gluten Sensitivity: A Systematic Review. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hadjivassiliou, M.; Grünewald, R.A.; Lawden, M.; Davies-Jones, G.A.; Powell, T.; Smith, C.M. Headache and CNS white matter abnormalities associated with gluten sensitivity. Neurology 2001, 56, 385–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G.; PRISMA Group. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement. PLoS Med. 2009, 6, e1000097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jadad, A.R.; Moore, R.A.; Carroll, D.; Jenkinson, C.; Reynolds, D.J.; Gavaghan, D.J.; McQuay, H.J. Assessing the quality of reports of randomized clinical trials: Is blinding necessary? Control Clin. Trials 1996, 17, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Team, RC. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- The Cochrane Collaboration. Review Manager; Version 5.3; The Nordic Cochrane Centre: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Lebwohl, B.; Roy, A.; Alaedini, A.; Green, P.H.R.; Ludvigsson, J.F. Risk of Headache-Related Healthcare Visits in Patients With Celiac Disease: A Population-Based Observational Study. Headache 2016, 56, 849–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silvester, J.A.; Graff, L.A.; Rigaux, L.; Walker, J.R.; Duerksen, D.R. Symptomatic suspected gluten exposure is common among patients with coeliac disease on a gluten-free diet. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2016, 44, 612–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Currie, S.; Hadjivassiliou, M.; Clark, M.J.R.; Sanders, D.S.; Wilkinson, I.D.; Griffiths, P.D.; Hoggard, N. Should we be “nervous” about coeliac disease? Brain abnormalities in patients with coeliac disease referred for neurological opinion. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2012, 83, 1216–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bürk, K.; Farecki, M.-L.; Lamprecht, G.; Roth, G.; Decker, P.; Weller, M.; Rammensee, H.-G.; Oertel, W. Neurological symptoms in patients with biopsy proven celiac disease. Mov. Disord. 2009, 24, 2358–2362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Briani, C.; Zara, G.; Alaedini, A.; Grassivaro, F.; Ruggero, S.; Toffanin, E.; Albergoni, M.P.; Luca, M.; Giometto, B.; Ermani, M.; et al. Neurological complications of celiac disease and autoimmune mechanisms: A prospective study. J. Neuroimmunol. 2008, 195, 171–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jericho, H.; Sansotta, N.; Guandalini, S. Extraintestinal Manifestations of Celiac Disease: Effectiveness of the Gluten-Free Diet. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2017, 65, 75–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dimitrova, A.K.; Ungaro, R.C.; Lebwohl, B.; Lewis, S.K.; Tennyson, C.A.; Green, M.W.; Babyatsky, M.W.; Green, P.H. Prevalence of migraine in patients with celiac disease and inflammatory bowel disease. Headache 2013, 53, 344–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cicarelli, G.; Della Rocca, G.; Amboni, M.; Ciacci, C.; Mazzacca, G.; Filla, A.; Barone, P. Clinical and neurological abnormalities in adult celiac disease. Neurol. Sci. 2003, 24, 311–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zelnik, N.; Pacht, A.; Obeid, R.; Lerner, A. Range of neurologic disorders in patients with celiac disease. Pediatrics 2004, 113, 1672–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abu-Zeid, Y.A.; Jasem, W.S.; Lebwohl, B.; Green, P.H.; ElGhazali, G. Seroprevalence of celiac disease among United Arab Emirates healthy adult nationals: A gender disparity. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 15830–15836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruggieri, M.; Incorpora, G.; Polizzi, A.; Parano, E.; Spina, M.; Pavone, P. Low prevalence of neurologic and psychiatric manifestations in children with gluten sensitivity. J. Pediatr. 2008, 152, 244–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Işikay, S.; Kocamaz, H. The neurological face of celiac disease. Arq. Gastroenterol. 2015, 52, 167–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terrone, G.; Parente, I.; Romano, A.; Auricchio, R.; Greco, L.; Del Giudice, E. The Pediatric Symptom Checklist as screening tool for neurological and psychosocial problems in a paediatric cohort of patients with coeliac disease. Acta Paediatr. 2013, 102, e325–e328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parisi, P.; Pietropaoli, N.; Ferretti, A.; Nenna, R.; Mastrogiorgio, G.; Del Pozzo, M.; Principessa, L.; Bonamico, M.; Villa, M.P. Role of the gluten-free diet on neurological-EEG findings and sleep disordered breathing in children with celiac disease. Seizure 2015, 25, 181–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lionetti, E.; Francavilla, R.; Maiuri, L.; Ruggieri, M.; Spina, M.; Pavone, P.; Francavilla, T.; Magistà, A.M.; Pavone, L. Headache in Pediatric Patients With Celiac Disease and Its Prevalence as a Diagnostic Clue. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2009, 49, 202–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Assa, A.; Frenkel-Nir, Y.; Tzur, D.; Katz, L.H.; Shamir, R. Large population study shows that adolescents with celiac disease have an increased risk of multiple autoimmune and nonautoimmune comorbidities. Acta Paediatr. 2017, 106, 967–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diaconu, G.; Burlea, M.; Grigore, I.; Anton, D.T.; Trandafir, L.M. Celiac disease with neurologic manifestations in children. Rev. Med. Chir. Soc. Med. Nat. Iasi. 2013, 117, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Crosato, F.; Senter, S. Cerebral occipital calcifications in celiac disease. Neuropediatrics 1992, 23, 214–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Battistella, P.A.; Mattesi, P.; Casara, G.L.; Carollo, C.; Condini, A.; Allegri, F.; Rigon, F. Bilateral cerebral occipital calcifications and migraine-like headache. Cephalalgia 1987, 7, 125–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serratrice, J.; Disdier, P.; de Roux, C.; Christides, C.; Weiller, P.J. Migraine and coeliac disease. Headache 1998, 38, 627–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mingomataj, E.Ç.; Gjata, E.; Bakiri, A.; Xhixha, F.; Hyso, E.; Ibranji, A. Gliadin allergy manifested with chronic urticaria, headache and amenorrhea. BMJ Case Rep. 2011, 2011, bcr1020114907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- La Mantia, L.; Pollo, B.; Savoiardo, M.; Costa, A.; Eoli, M.; Allegranza, A.; Boiardi, A.; Cestari, C. Meningo-cortical calcifying angiomatosis and celiac disease. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 1998, 100, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karakoç, E.; Erdem, S.; Sökmensüer, C.; Kansu, T. Encephalopathy due to carnitine deficiency in an adult patient with gluten enteropathy. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2006, 108, 794–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Amico, D.; Rigamonti, A.; Spina, L.; Bianchi-Marzoli, S.; Vecchi, M.; Bussone, G. Migraine, celiac disease, and cerebral calcifications: A new case. Headache 2005, 45, 1263–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benjilali, L.; Zahlane, M.; Essaadouni, L. A migraine as initial presentation of celiac disease. Rev. Neurol. 2012, 168, 454–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabrielli, M.; Cremonini, F.; Fiore, G.; Addolorato, G.; Padalino, C.; Candelli, M.; Gasbarrini, A.; Pola, P.; Gasbarrini, A. Association between migraine and Celiac disease: Results from a preliminary case-control and therapeutic study. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2003, 98, 625–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inaloo, S.; Dehghani, S.M.; Farzadi, F.; Haghighat, M.; Imanieh, M.H. A comparative study of celiac disease in children with migraine headache and a normal control group. Turk. J. Gastroenterol. 2011, 22, 32–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borgna-Pignatti, C.; Fiumana, E.; Milani, M.; Calacoci, M.; Soriani, S. Celiac disease in children with migraine. Pediatrics 2004, 114, 1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nenna, R.; Petrarca, L.; Verdecchia, P.; Florio, M.; Pietropaoli, N.; Mastrogiorgio, G.; Bavastrelli, M.; Bonamico, M.; Cucchiara, S. Celiac disease in a large cohort of children and adolescents with recurrent headache: A retrospective study. Dig. Liver Dis. 2016, 48, 495–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alehan, F.; Ozçay, F.; Erol, I.; Canan, O.; Cemil, T. Increased risk for coeliac disease in paediatric patients with migraine. Cephalalgia 2008, 28, 945–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rani, U.; Imdad, A.; Beg, M. Rare Neurological Manifestation of Celiac Disease. Case Rep. Gastroenterol. 2015, 9, 200–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dotan, G.; Goldstein, M.; Stolovitch, C.; Kesler, A. Pediatric Pseudotumor Cerebri Associated With Low Serum Levels of Vitamin A. J. Child. Neurol. 2013, 28, 1370–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rashid, M.; Cranney, A.; Zarkadas, M.; Graham, I.D.; Switzer, C.; Case, S.; Molloy, M.; Warren, R.E.; Burrows, V.; Butzner, J.D. Celiac disease: Evaluation of the diagnosis and dietary compliance in Canadian children. Pediatrics 2005, 116, e754–e759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zarkadas, M.; Cranney, A.; Case, S.; Molloy, M.; Switzer, C.; Graham, I.D.; Butzner, J.D.; Rashid, M.; Warren, R.E.; Burrows, V. The impact of a gluten-free diet on adults with coeliac disease: Results of a national survey. J. Hum. Nutr. Diet. 2006, 19, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faulkner-Hogg, K.B.; Selby, W.S.; Loblay, R.H. Dietary analysis in symptomatic patients with coeliac disease on a gluten-free diet: The role of trace amounts of gluten and non-gluten food intolerances. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 1999, 34, 784–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lahat, E.; Broide, E.; Leshem, M.; Evans, S.; Scapa, E. Prevalence of celiac antibodies in children with neurologic disorders. Pediatr. Neurol. 2000, 22, 393–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balcı, O.; Yılmaz, D.; Sezer, T.; Hızlı, Ş. Is Celiac Disease an Etiological Factor in Children With Migraine? J. Child. Neurol. 2016, 31, 929–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volta, U.; Tovoli, F.; Cicola, R.; Parisi, C.; Fabbri, A.; Piscaglia, M.; Fiorini, E.; Caio, G. Serological tests in gluten sensitivity (nonceliac gluten intolerance). J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2012, 46, 680–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volta, U.; Bardella, M.T.; Calabrò, A.; Troncone, R.; Corazza, G.R.; Study Group for Non-Celiac Gluten Sensitivity. An Italian prospective multicenter survey on patients suspected of having non-celiac gluten sensitivity. BMC Med. 2014, 12, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zis, P.; Sarrigiannis, P.G.; Rao, D.G.; Hadjivassiliou, M. Gluten neuropathy: Prevalence of neuropathic pain and the role of gluten-free diet. J. Neurol. 2018, 265, 2231–2236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zis, P.; Sarrigiannis, P.G.; Rao, D.G.; Hadjivassiliou, M. Quality of Life in Patients with Gluten Neuropathy: A Case-Controlled Study. Nutrients 2018, 10, 662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zis, P.; Rao, D.G.; Sarrigiannis, P.G.; Aeschlimann, P.; Aeschlimann, D.P.; Sanders, D.; Grünewald, R.A.; Hadjivassiliou, M. Transglutaminase 6 antibodies in gluten neuropathy. Dig. Liver Dis. 2017, 49, 1196–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hadjivassiliou, M.; Aeschlimann, P.; Sanders, D.S.; Mäki, M.; Kaukinen, K.; Grünewald, R.A.; Bandmann, O.; Woodroofe, N.; Haddock, G.; Aeschlimann, D.P. Transglutaminase 6 antibodies in the diagnosis of gluten ataxia. Neurology 2013, 80, 1740–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Number of papers | 40 |
| Population (%) | |
| Adult | 18 (45.0) |
| Children | 18 (45.0) |
| Mixed | 4 (10.0) |
| Type of study | |
| Case report | 9 (22.5) |
| Cohort/Case series | 16 (40.0) |
| Case-controlled study | 11 (27.5) |
| Population-based | 2 (5.0) |
| Survey | 2 (5.0) |
| Gluten-related disorder | |
| Coeliac disease | 36 (90.0) |
| Mixed group: CD/GS | 1 (2.5) |
| Mixed group: NCGS/GS | 3 (7.5) |
| Type of headache reported | |
| Migraine | 16 (40.0) |
| All types | 6 (15.0) |
| Not specified | 14 (35.0) |
| Idiopathic intracranial hypertension–related | 2 (5.0) |
| Encephalopathy syndrome | 2 (5.0) |
| Imaging * | |
| MRI | 8 (20.0) |
| CT | 7 (17.5) |
| SPECT | 2 (5.0) |
| No imaging data | 24 (60.0) |
| Year of publication (%) | |
| Until 2000 | 5 (12.5) |
| 2000–2009 | 15 (37.5) |
| 2010–2018 | 20 (50.0) |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zis, P.; Julian, T.; Hadjivassiliou, M. Headache Associated with Coeliac Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1445. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10101445
Zis P, Julian T, Hadjivassiliou M. Headache Associated with Coeliac Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients. 2018; 10(10):1445. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10101445
Chicago/Turabian StyleZis, Panagiotis, Thomas Julian, and Marios Hadjivassiliou. 2018. "Headache Associated with Coeliac Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis" Nutrients 10, no. 10: 1445. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10101445
APA StyleZis, P., Julian, T., & Hadjivassiliou, M. (2018). Headache Associated with Coeliac Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients, 10(10), 1445. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10101445







