Ironing out the Details: Untangling Dietary Iron and Genetic Background in Diabetes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Diet and Diabetes: A Need for Dietary Perspective
3. Dietary Iron: Too Much of A Good Thing?
4. Adipose Tissue: At the Intersection of Iron and Insulin Sensitivity
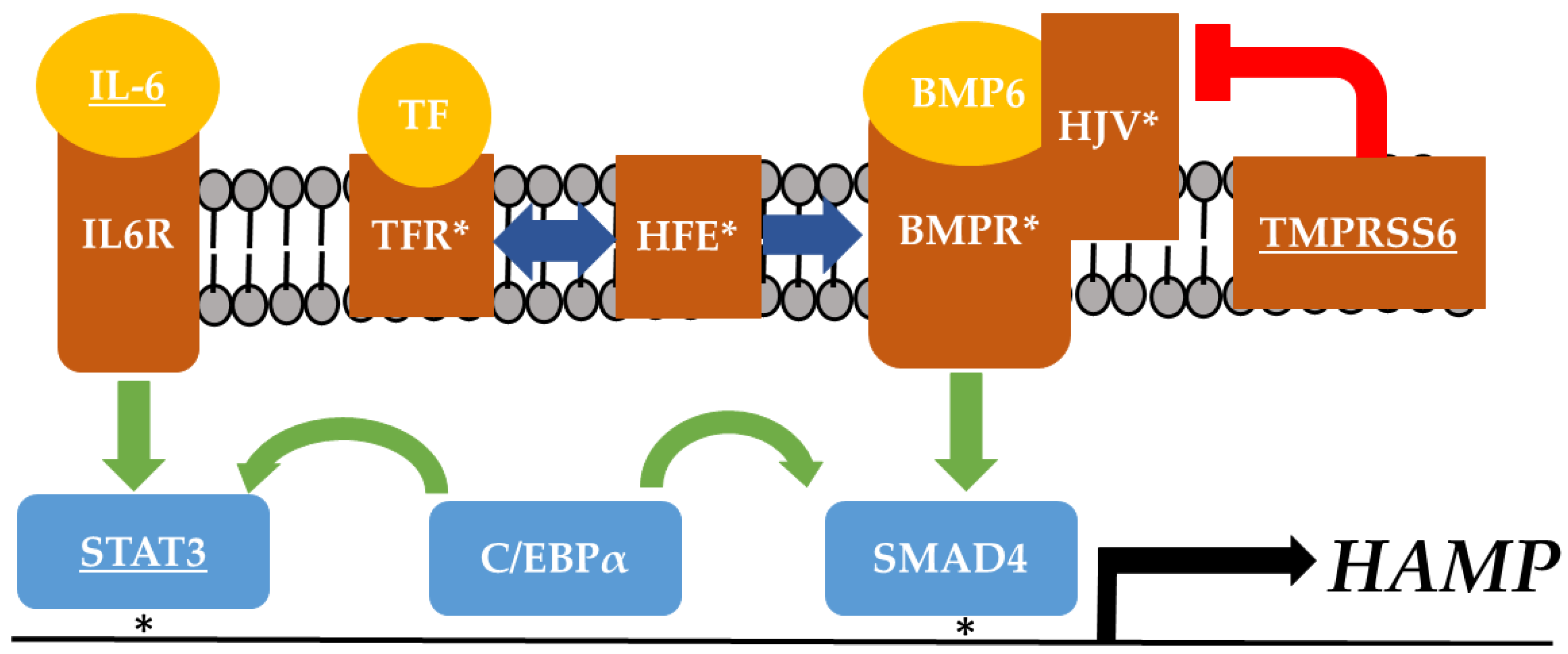
5. Hepcidin: A Potential Link between Dietary Iron, Adipose Tissue, and Insulin Resistance
6. Concluding Remarks
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Franks, P.W.; Pearson, E.; Florez, J.C. Gene-environment and gene-treatment interactions in type 2 diabetes: Progress, pitfalls, and prospects. Diabetes Care 2013, 36, 1413–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Irigoyen, M.; Davidson, L.L.; Carriero, D.; Seaman, C. Randomized, placebo-controlled trial of iron supplementation in infants with low hemoglobin levels fed iron-fortified formula. Pediatrics 1991, 88, 320–326. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fleming, D.J.; Jacques, P.F.; Tucker, K.L.; Massaro, J.M.; D’Agostino, S.; Wilson, P.W.F.; Wood, R.J. Iron status of the free-living, elderly Framingham heart study cohort: An iron-replete population with a high prevalence of elevated iron stores. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2001, 73, 638–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haffner, S.M.; Lehto, S.; Rönnemaa, T.; Pyörälä, K.; Laakso, M. Mortality from coronary heart disease in subjects with type 2 diabetes and in nondiabetic subjects with and without prior myocardial infarction. N. Engl. J. Med. 1998, 339, 229–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saxena, R.; Elbers, C.C.; Guo, Y.; Peter, I.; Gaunt, T.R.; Mega, J.L.; Lanktree, M.B.; Tare, A.; Castillo, B.A.; Li, Y.R.; et al. Large-scale gene-centric meta-analysis across 39 studies identifies type 2 diabetes loci. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2012, 90, 410–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hindorff, L.A.; Sethupathy, P.; Junkins, H.A.; Ramos, E.M.; Mehta, J.P.; Collins, F.S.; Manolio, T.A. Potential etiologic and functional implications of genome-wide association loci for human diseases and traits. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 9362–9367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Voight, B.F.; Scott, L.J.; Steinthorsdottir, V.; Morris, A.P.; Dina, C.; Welch, R.P.; Zeggini, E.; Huth, C.; Aulchenko, Y.S.; Thorleifsso, G.; et al. Twelve type 2 diabetes susceptibility loci identified through large-scale association analysis. Nat. Genet. 2010, 42, 579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dupuis, J.; Langenberg, C.; Prokopenko, I.; Saxena, R.; Soranzo, N.; Jackson, A.U.; Wheeler, E.; Glazer, N.L.; Bouatia-Naji, N.; Gloyn, A.I.; et al. New genetic loci implicated in fasting glucose homeostasis and their impact on type 2 diabetes risk. Nat. Genet. 2010, 42, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Poulsen, P.; Kyvik, K.O.; Vaag, A.; Beck-Nielsen, H. Heritability of type II (non-insulin-dependent) diabetes mellitus and abnormal glucose tolerance—A population-based twin study. Diabetologia 1999, 42, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehtovirta, M.; Pietiläinen, K.H.; Levälahti, E.; Heikkilä, K.; Groop, L.; Silventoinen, K.; Koskenvuo, M.; Kaprio, J. Evidence that BMI and type 2 diabetes share only a minor fraction of genetic variance: A follow-up study of 23,585 monozygotic and dizygotic twins from the Finnish twin cohort study. Diabetologia 2010, 53, 1314–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luan, J.; Browne, P.O.; Harding, A.H.; Halsall, D.J.; O’Rahilly, S.; Chatterjee, V.K.; Wareham, N.J. Evidence for gene-nutrient interaction at the PPARγ locus. Diabetes 2001, 50, 686–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanoni, S.; Nettleton, J.A.; Hivert, M.F.; Ye, Z.; Van Rooij, F.J.; Shungin, D.; Gustafsson, S. Total zinc intake may modify the glucose-raising effect of a zinc transporter (SLC30A8) variant: A 14-cohort meta-analysis. Diabetes 2011, 60, 2407–2416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lawson, H.A.; Zayed, M.; Wayhart, J.P.; Fabbrini, E.; Love-Gregory, L.; Klein, S.; Semenkovich, C.F. Physiologic and genetic evidence links hemopexin to triglycerides in mice and humans. Int. J. Obes. 2017, 41, 631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawson, H.A. Animal models of metabolic syndrome. In Animal Models for the Study of Human Disease, 1st ed.; Conn, P.M., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Przybyszewska, J.; Zekanowska, E. The role of hepcidin, ferroportin, HCP1, and DMT1 protein in iron absorption in the human digestive tract. Prz. Gastroenterol. 2014, 9, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayle, K.M.; Le, A.M.; Kamei, D.T. The intracellular trafficking pathway of transferrin. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gen. Subj. 2012, 1820, 264–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, W.; Knovich, M.A.; Coffman, L.G.; Torti, F.M.; Torti, S.V. Serum ferritin: Past, present and future. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2010, 1800, 760–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ganz, T.; Nemeth, E. Hepcidin and iron homeostasis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Mol. Cell. Res. 2012, 1823, 1434–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoltzfus, R.J. Iron deficiency: Global prevalence and consequences. Food Nutr. Bull. 2003, 24, S99–S103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Von Haehling, S.; Jankowska, E.A.; van Veldhuisen, D.J.; Ponikowski, P.; Anker, S.D. Iron deficiency and cardiovascular disease. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2015, 12, 659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urrechaga, E. Influence of iron deficiency on Hb A1c levels in type 2 diabetic patients. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. 2018, 12, 1051–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mora, J.O. Iron supplementation: Overcoming technical and practical barriers. J. Nutr. 2002, 132, 853S–855S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nutrient Data Laboratory. USDA Table of Nutrient Retention Factors, Release 5; National Academic Press: Beltsville, MD, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Jehn, M.L.; Guallar, E.; Clark, J.M.; Couper, D.; Duncan, B.B.; Ballantyne, C.M.; Hoogeveen, R.C.; Harris, Z.L.; Pankow, J.S. A prospective study of plasma ferritin level and incident diabetes: The Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) Study. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2007, 165, 1047–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Scholl, T.O.; Stein, T.P. Association of elevated serum ferritin levels and the risk of gestational diabetes mellitus in pregnant women: The Camden study. Diabetes Care 2006, 29, 1077–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jehn, M.; Clark, J.M.; Guallar, E. Serum ferritin and risk of the metabolic syndrome in U.S. adults. Diabetes Care 2004, 27, 2422–2428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheu, W.H.H.; Chen, Y.T.; Lee, W.J.; Wang, C.W.; Lin, L.Y. A relationship between serum ferritin and the insulin resistance syndrome is present in non-diabetic women but not in non-diabetic men. Clin. Endocrinol. (Oxf.) 2003, 58, 380–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, Y.; He, L.; Chen, Y.; Fang, Y.; Yao, Y. Association between serum ferritin levels and metabolic syndrome: An updated meta-analysis. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2015, 8, 13317. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Padwal, M.K.; Murshid, M.; Nirmale, P.; Melinkeri, R.R. Association of serum ferritin levels with metabolic syndrome and insulin resistance. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2015, 9, BC11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández-Real, J.M.; Peñarroja, G.; Castro, A.; García-Bragado, F.; Hernández-Aguado, I.; Ricart, W. Blood letting in high-ferritin type 2 diabetes: Effects on insulin sensitivity and beta-cell function. Diabetes 2002, 25, 2249–2255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kell, D.B.; Pretorius, E. Serum ferritin is an important inflammatory disease marker, as it is mainly a leakage product from damaged cells. Metallomics 2014, 6, 748–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Muñoz-Bravo, C.; Gutiérrez-Bedmar, M.; Gómez-Aracena, J.; García-Rodríguez, A.; Navajas, J.F.-C. Iron: Protector or risk factor for cardiovascular disease? Still controversial. Nutrients 2013, 5, 2384–2404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nemeth, E.; Tuttle, M.S.; Powelson, J.; Vaughn, M.D.; Donovan, A.; Ward, D.M.V.; Ganz, T.; Kaplan, J. Hepcidin regulates cellular iron efflux by binding to ferroportin and inducing its internalization. Science 2004, 306, 2090–2093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dymock, I.W.; Cassar, J.; Pyke, D.A.; Oakley, W.G.; Williams, R. Observations on the pathogenesis, complications and treatment of diabetes in 115 cases of haemochromatosis. Am. J. Med. 1972, 52, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, Y.; Nakanishi, K.; Hiraga, T.; Okubo, M.; Murase, T.; Kosaka, K.; Miyakoshi, S.; Mutoh, Y.; Kobayashi, T. Recovery of pancreatic β-cell function in hemochromatosis: Combined treatment with recombinant human erythropoietin and phlebotomy. Am. J. Med. Sci. 1997, 314, 401–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooksey, R.C.; Jouihan, H.A.; Ajioka, R.S.; Hazel, M.W.; Jones, D.L.; Kushner, J.P.; McClain, D.A. Oxidative stress, beta-cell apoptosis, and decreased insulin secretory capacity in mouse models of hemochromatosis. Endocrinology 2004, 145, 5305–5312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dongiovanni, P.; Ruscica, M.; Rametta, R.; Recalcati, S.; Steffani, L.; Gatti, S.; Girelli, D.; Cairo, G.; Magni, P.; Fargion, S.; et al. Dietary iron overload induces visceral adipose tissue insulin resistance. Am. J. Pathol. 2013, 182, 2254–2263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.S.; Koh, I.U.; Lee, H.J.; Kim, W.H.; Song, J. Effects of excess dietary iron and fat on glucose and lipid metabolism. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2013, 24, 1634–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooksey, R.C.; Jones, D.; Gabrielsen, S.; Huang, J.; Simcox, J.A.; Luo, B.; Soesanto, Y.; Rienhoff, H.; Abel, E.D.; McClain, D.A. Dietary iron restriction or iron chelation protects from diabetes and loss of beta-cell function in the obese (ob/ob lep−/−) mouse. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2010, 298, E1236–E1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Sweeney, G. Adiponectin action in skeletal muscle. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 28, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orr, J.S.; Kennedy, A.; Anderson-Baucum, E.K.; Webb, C.D.; Fordahl, S.C.; Erikson, K.M.; Zhang, Y.; Etzerodt, A.; Moestrup, S.K.; Hasty, A.H. Obesity alters adipose tissue macrophage iron content and tissue iron distribution. Diabetes 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabrielsen, J.S.; Gao, Y.; Simcox, J.A.; Huang, J.; Thorup, D.; Jones, D.; Cooksey, R.C.; Gabrielsen, D.; Adams, T.D.; Hunt, S.C.; et al. Adipocyte iron regulates adiponectin and insulin sensitivity. J. Clin. Investig. 2012, 122, 3529–3540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ku, B.J.; Kim, S.Y.; Lee, T.Y.; Park, K.S. Serum ferritin is inversely correlated with serum adiponectin level: Population-based cross-sectional study. Dis. Markers 2009, 27, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paz-Filho, G.; Mastronardi, C.; Wong, M.L.; Licinio, J. Leptin therapy, insulin sensitivity, and glucose homeostasis. Indian J. Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 16, S549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Li, Z.; Scott Gabrielsen, J.; Simcox, J.A.; Lee, S.H.; Jones, D.; Cooksey, B.; Stoddard, G.; Cefalu, W.T.; McClain, D.A. Adipocyte iron regulates leptin and food intake. J. Clin. Investig. 2015, 125, 3681–3691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Barnes, K.; Miner, J. Role of resistin in insulin sensitivity in rodents and humans. Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 2009, 10, 96–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fleming, R.E.; Sly, W.S. Hepcidin: A putative iron-regulatory hormone relevant to hereditary hemochromatosis and the anemia of chronic disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 8160–8162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Suárez-Ortegón, M.F.; Moreno, M.; Arbeláez, A.; Xifra, G.; Mosquera, M.; Moreno-Navarrete, J.M.; Aguilar-de Plata, C.; Esteve, E.; Ricart, W.; Fernández-Real, J.M. Circulating hepcidin in type 2 diabetes: A multivariate analysis and double blind evaluation of metformin effects. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2015, 59, 2460–2470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aregbesola, A.; Voutilainen, S.; Virtanen, J.K.; Aregbesola, A.; Tuomainen, T.-P. Serum hepcidin concentrations and type 2 diabetes. World J. Diabetes 2015, 6, 978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez-Real, J.M.; Equitani, F.; Moreno, J.M.; Manco, M.; Ortega, F.; Ricart, W. Study of circulating prohepcidin in association with insulin sensitivity and changing iron stores. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2009, 94, 982–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, X.; Zhou, D.; An, P.; Wu, Q.; Wang, H.; Wu, A.; Mu, M.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, H.; et al. Associations between serum hepcidin, ferritin and Hb concentrations and type 2 diabetes risks in a Han Chinese population. Br. J. Nutr. 2013, 110, 2180–2185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Poli, M.; Asperti, M.; Ruzzenenti, P.; Regoni, M.; Arosio, P. Hepcidin antagonists for potential treatments of disorders with hepcidin excess. Front. Pharmacol. 2014, 5, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hereditary Hemochromatosis, Genetics Home Reference. Available online: https://ghr.nlm.nih.gov/condition/hereditary-hemochromatosis (accessed on 14 July 2018).
- Gan, W.; Guan, Y.; Wu, Q.; An, P.; Zhu, J.; Lu, L.; Jing, L.; Yu, Y.; Ruan, S.; Xie, D.; et al. Association of TMPRSS6 polymorphisms with ferritin, hemoglobin, and type 2 diabetes risk in a Chinese Han population. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2012, 95, 626–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Courselaud, B.; Pigeon, C.; Inoue, Y.; Inoue, J.; Gonzalez, F.J.; Leroyer, P.; Gilot, D.; Boudjema, K.; Guguen-Guillouzo, C.; Brissot, P.; et al. C/EBPalpha regulates hepatic transcription of hepcidin, an antimicrobial peptide and regulator of iron metabolism. Cross-talk between C/EBP pathway and iron metabolism. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 41163–41170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Li, H.; Jiang, X.; Shi, W.; Shen, Z.; Li, M. Hepcidin is directly regulated by insulin and plays an important role in iron overload in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Diabetes 2014, 63, 1506–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Guenno, G.; Chanséaume, E.; Ruivard, M.; Morio, B.; Mazur, A. Study of iron metabolism disturbances in an animal model of insulin resistance. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2007, 77, 363–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayele, H.K.; Srai, S.K.S. Regulatory variation in hepcidin expression as a heritable quantitative trait. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2009, 384, 22–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Island, M.L.; Jouanolle, A.M.; Mosser, A.; Deugnier, Y.; David, V.; Brissot, P.; Loréal, O. A new mutation in the hepcidin promoter impairs its BMP response and contributes to a severe phenotype in HFE related hemochromatosis. Haematologica 2009, 94, 720–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Andreani, M.; Radio, F.C.; Testi, M.; De Bernardo, C.; Troiano, M.; Majore, S.; Bertucci, P.; Polchi, P.; Rosati, R.; Grammatico, P. Association of hepcidin promoter c.-582 A> G variant and iron overload in thalassemia major. Haematologica 2009, 94, 1293–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porto, G.; Roetto, A.; Daraio, F.; Pinto, J.P.; Almeida, S.; Bacelar, C.; Nemeth, E.; Ganz, T.; Camaschella, C. A Portuguese patient homozygous for the −25G>A mutation of the HAMP promoter shows evidence of steady-state transcription but fails to up-regulate hepcidin levels by iron. Blood 2005, 106, 2922–2923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Miranda, M.A.; Lawson, H.A. Ironing out the Details: Untangling Dietary Iron and Genetic Background in Diabetes. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1437. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10101437
Miranda MA, Lawson HA. Ironing out the Details: Untangling Dietary Iron and Genetic Background in Diabetes. Nutrients. 2018; 10(10):1437. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10101437
Chicago/Turabian StyleMiranda, Mario A., and Heather A. Lawson. 2018. "Ironing out the Details: Untangling Dietary Iron and Genetic Background in Diabetes" Nutrients 10, no. 10: 1437. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10101437
APA StyleMiranda, M. A., & Lawson, H. A. (2018). Ironing out the Details: Untangling Dietary Iron and Genetic Background in Diabetes. Nutrients, 10(10), 1437. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10101437



