Momordica charantia Ethanol Extract Attenuates H2O2-Induced Cell Death by Its Antioxidant and Anti-Apoptotic Properties in Human Neuroblastoma SK-N-MC Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of 70% Ethanol Extract of Momordica Charantia (MCEE)
2.2. Cell Culture and Treatment
2.3. Cell Viability and Cytotoxicity
2.4. Hoechst 33342 Staining
2.5. Annexin V-FITC and PI Double-Staining Assay
2.6. Measurement of Intracellular ROS
2.7. Measurement of Superoxide Dismutase (SOD), Reduced Glutathione (GSH), and Malondialdehyde (MDA)
2.8. Measurement of Mitochondrial Membrane Potential (MMP, ΔΨm)
2.9. Total RNA Extraction and Quantitative Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction
2.10. Western Blot Analysis
2.11. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
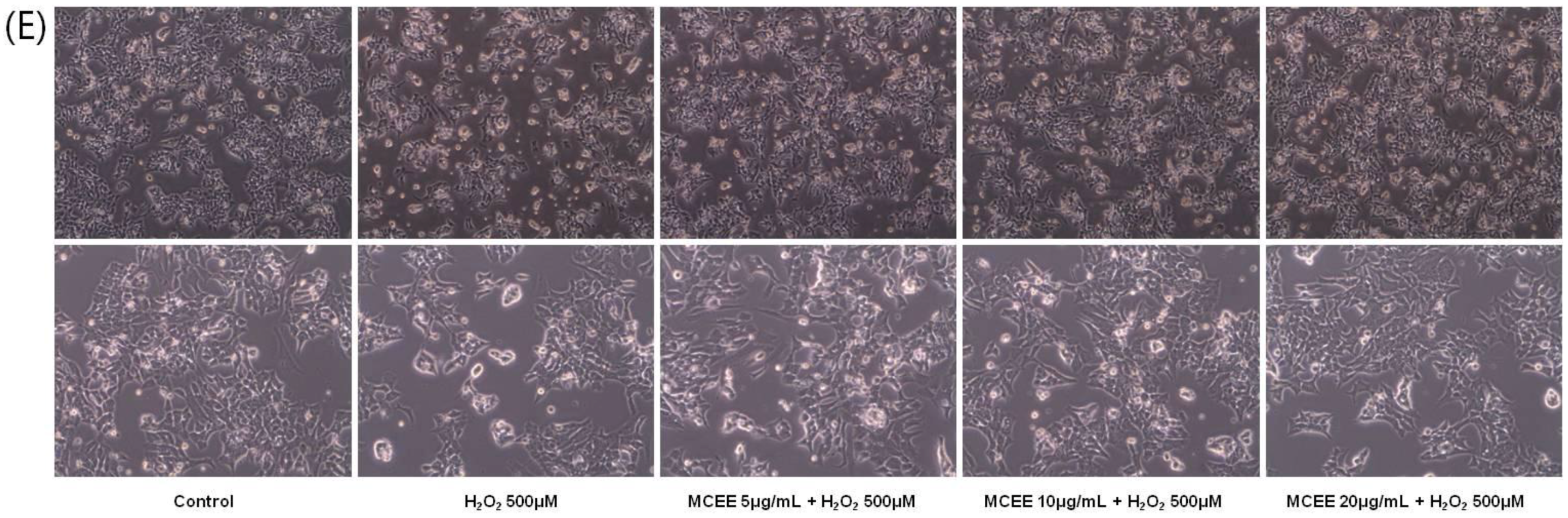
3.1. Effect of the MCEE on H2O2-Induced Cytotoxicity in SK-N-MC Cells
3.2. MCEE Decreased Intracellular ROS Produced by H2O2
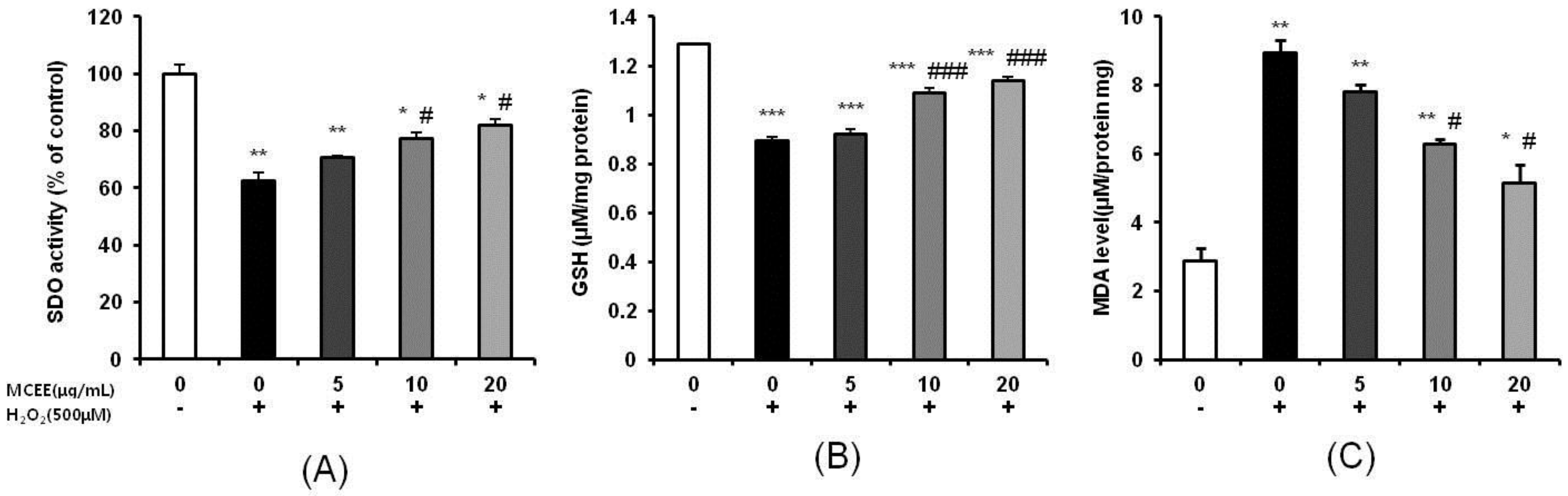
3.3. Effect of MCEE on Antioxidant Properties
3.4. MCEE Reduced H2O2-Induced Apoptotic Cell Death
3.5. MCEE Ameliorates H2O2-Induced Mitochondrial Membrane Potential (MMP, Δψm)
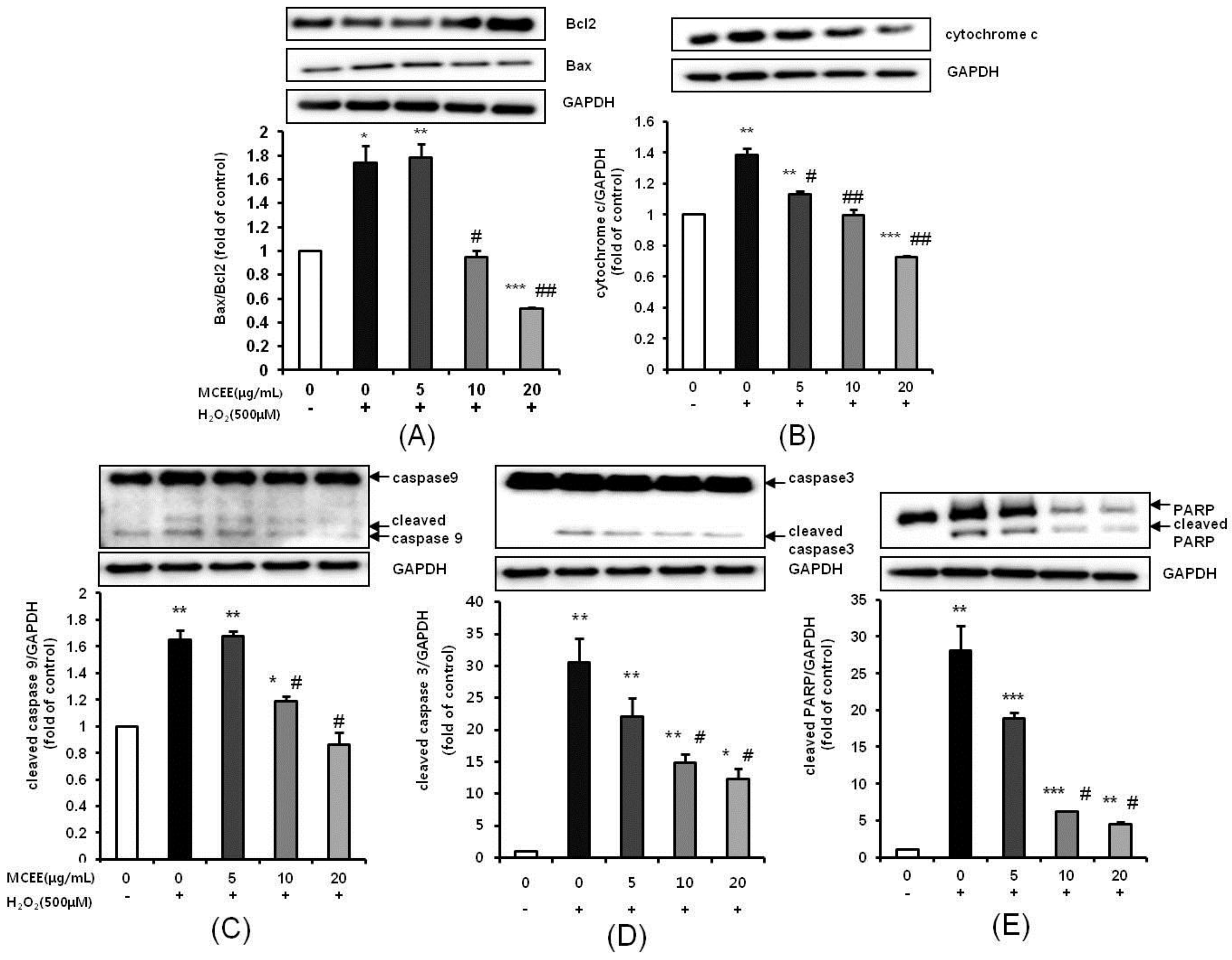
3.6. MCEE Modulated the Expression of Apoptosis-Related Proteins Expression Induced by H2O2
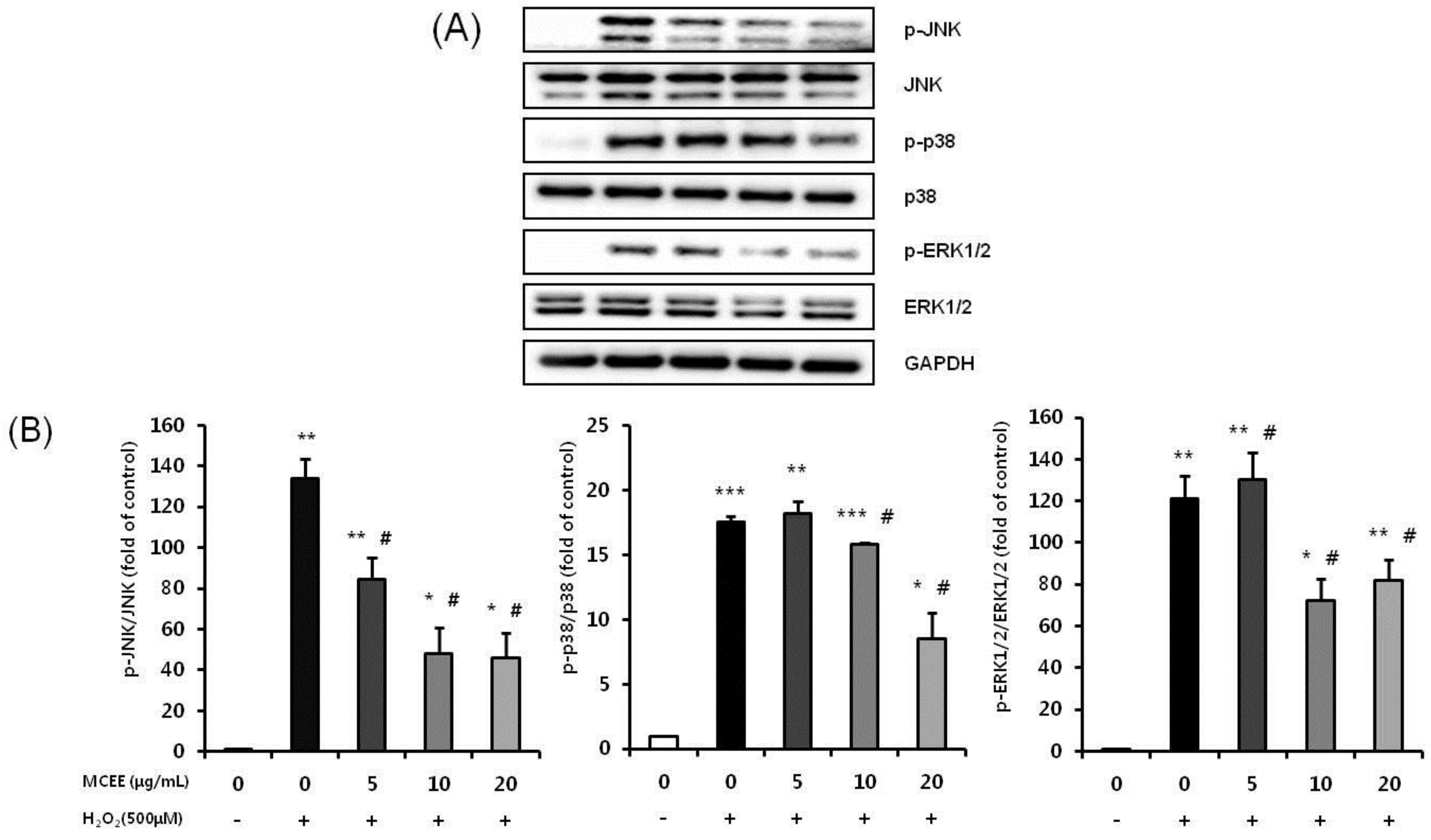
3.7. MCEE Attenuates the H2O2-Induced Activation of the JNK, p38, and ERK1/2 MAPK Signaling Pathway
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lee, K.H.; Lee, S.-J.; Lee, H.J.; Choi, G.E.; Jung, Y.H.; Kim, D.I.; Gabr, A.A.; Ryu, J.M.; Han, H.J. Amyloid β1-42 (Aβ1-42) induces the CDK2-mediated phosphorylation of Tau through the activation of the mTORC1 signaling pathway while promoting neuronal cell death. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2017, 10, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kich, D.M.; Bitencourt, S.; Alves, C.; Silva, J.; Pinteus, S.; Pedrosa, R.; Laufer, S.; de Souza, C.F.V.; Goettert, M.I. Neuromodulatory effects of Calyptranthes grandifolia extracts against 6-hydroxydopamine-induced neurotoxicity in SH-SY5Y cells. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2016, 84, 382–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaafaru, M.S.; Abd Karim, N.A.; Enas, M.E.; Rollin, P.; Mazzon, E.; Abdull Razis, A.F. Protective effect of glucosinolates hydrolytic products in neurodegenerative diseases (NDDs). Nutrients 2018, 10, 580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liguori, I.; Russo, G.; Curcio, F.; Bulli, G.; Aran, L.; Della-Morte, D.; Gargiulo, G.; Testa, G.; Cacciatore, F.; Bonaduce, D. Oxidative stress, aging, and diseases. Clin Interv. Aging 2018, 13, 757–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gay, N.H.; Phopin, K.; Suwanjang, W.; Songtawee, N.; Ruankham, W.; Wongchitrat, P.; Prachayasittikul, S.; Prachayasittikul, V. Neuroprotective effects of phenolic and carboxylic acids on oxidative stress-induced toxicity in human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells. Neurochem. Res. 2018, 43, 619–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Ma, F.; Hu, M.; Ma, C.W.; Xiao, L.; Zhang, J.; Xiang, Y.; Huang, Z. Polysaccharides from medicinal herbs as potential therapeutics for aging and age-related neurodegeneration. Rejuvenation Res. 2014, 17, 201–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solanki, I.; Parihar, P.; Parihar, M.S. Neurodegenerative diseases: From available treatments to prospective herbal therapy. Neurochem. Int. 2016, 95, 100–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venkatesh Gobi, V.; Rajasankar, S.; Ramkumar, M.; Dhanalakshmi, C.; Manivasagam, T.; Justin Thenmozhi, A.; Essa, M.M.; Chidambaram, R. Agaricus blazei extract attenuates rotenone-induced apoptosis through its mitochondrial protective and antioxidant properties in SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells. Nutr. Neurosci. 2018, 21, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Metaxakis, A.; Ploumi, C.; Tavernarakis, N. Autophagy in age-associated neurodegeneration. Cells 2018, 7, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, D.J.; Cho, S.; Seo, J.Y.; Lee, H.B.; Park, Y.I. Neuroprotective effects of the Phellinus linteus ethyl acetate extract against H2O2-induced apoptotic cell death of SK-N.-MC cells. Nutr. Res. 2016, 36, 31–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, X.; Sui, S.; Huang, J.; Bai, J.P.; Ren, T.S.; Zhao, Q.C. Neuroprotective effects of Arctium lappa L. roots against glutamate-induced oxidative stress by inhibiting phosphorylation of p38, JNK and ERK 1/2 MAPKs in PC12 cells. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2014, 38, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, D.J.; Kim, S.-L.; Choi, J.W.; Park, Y.I. Neuroprotective effects of corn silk maysin via inhibition of H2O2-induced apoptotic cell death in SK-N.-MC cells. Life Sci. 2014, 109, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, X.; Gao, L.; An, L.; Jiang, X.; Bai, J.; Huang, J.; Meng, W.; Zhao, Q. Pretreatment of MQA, a caffeoylquinic acid derivative compound, protects against H2O2-induced oxidative stress in SH-SY5Y cells. Neurol. Res. 2016, 38, 1079–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuliani, S.; Mustofa; Partadiredja, G. The neuroprotective effects of an ethanolic turmeric (Curcuma longa L.) extract against trimethyltin-induced oxidative stress in rats. Nutr. Neurosci. 2018, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, H.R.; Lee, H.; Park, H.; Jeon, J.W.; Cho, W.-K.; Ma, J.Y. Neuroprotective effects of Liriope platyphylla extract against hydrogen peroxide-induced cytotoxicity in human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2015, 15, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nataraj, J.; Manivasagam, T.; Justin Thenmozhi, A.; Essa, M.M. Neuroprotective effect of asiatic acid on rotenone-induced mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress-mediated apoptosis in differentiated SH-SYS5Y cells. Nutr. Neurosci. 2017, 20, 351–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramachandra Shobha, C.; Prashant, V.; Akila, P.; Chandini, R.; Nataraj Suma, M.; Basavanagowdappa, H. Fifty percent ethanolic extract of momordica charantia inhibits adipogenesis and promotes Adipolysis in 3T3-L1 pre-adipocyte cells. Rep. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2017, 6, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Perveen, H.; Dash, M.; Khatun, S.; Maity, M.; Islam, S.S.; Chattopadhyay, S. Electrozymographic evaluation of the attenuation of arsenic induced degradation of hepatic SOD, catalase in an in vitro assay system by pectic polysaccharides of Momordica charantia in combination with curcumin. Biochem. Biophys. Rep. 2017, 11, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, S.; Shen, M.; Zhang, F.; Xie, J. Recent advances in Momordica charantia: Functional components and biological activities. Int J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dia, V.P.; Krishnan, H.B. BG-4, a novel anticancer peptide from bitter gourd (Momordica charantia), promotes apoptosis in human colon cancer cells. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 33532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, L.-Y.; Chiu, C.-F.; Chu, P.-C.; Lin, W.-Y.; Chiu, S.-J.; Weng, J.-R. A triterpenoid from wild bitter gourd inhibits breast cancer cells. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 22419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dandawate, P.R.; Subramaniam, D.; Padhye, S.B.; Anant, S. Bitter melon: A panacea for inflammation and cancer. Chin. J. Nat. Med. 2016, 14, 81–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shodehinde, S.A.; Adefegha, S.A.; Oboh, G.; Oyeleye, S.I.; Olasehinde, T.A.; Nwanna, E.E.; Adedayo, B.C.; Boligon, A.A. Phenolic composition and evaluation of methanol and aqueous extracts of bitter gourd (Momordica charantia L) leaves on Angiotensin-I-Converting enzyme and some pro-oxidant-induced lipid peroxidation in vitro. J. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2016, 21, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, Y.; Tang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, R.; Wei, Z.; Tang, X.; Zhang, M. Protective effect of Momordica charantia water extract against liver injury in restraint-stressed mice and the underlying mechanism. Food Nutr. Res. 2017, 61, 1348864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fachinan, R.; Fagninou, A.; Nekoua, M.P.; Amoussa, A.M.; Adjagba, M.; Lagnika, L.; Lalèyè, A.; Moutairou, K.; Yessoufou, A. Evidence of immunosuppressive and Th2 immune polarizing effects of antidiabetic momordica charantia fruit juice. Biomed. Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 9478048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harinantenaina, L.; Tanaka, M.; Takaoka, S.; Oda, M.; Mogami, O.; Uchida, M.; Asakawa, Y. Momordica charantia constituents and antidiabetic screening of the isolated major compounds. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2006, 54, 1017–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahamad, J.; Amin, S.; Mir, S.R. Momordica charantia Linn. (Cucurbitaceae): Review on phytochemistry and pharmacology. Res. J. Phytochem. 2017, 11, 53–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Zhang, H.; Ye, J. Traditional chinese medicine in treatment of metabolic syndrome. Endocr. Metab. Immune Disord. Drug Targets 2008, 8, 99–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandes, N.P.; Lagishetty, C.V.; Panda, V.S.; Naik, S.R. An experimental evaluation of the antidiabetic and antilipidemic properties of a standardized Momordica charantia fruit extract. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2007, 7, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.J.; Ryu, J.M.; Jung, Y.H.; Lee, S.-J.; Kim, J.Y.; Lee, S.H.; Hwang, I.K.; Seong, J.K.; Han, H.J. High glucose upregulates BACE1-mediated Aβ production through ROS-dependent HIF-1α and LXRα/ABCA1-regulated lipid raft reorganization in SK-N.-MC cells. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 36746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, X.-W.; Bai, J.-P.; Zhang, Q.; Hu, X.-L.; Tian, X.; Zhu, J.; Liu, J.; Meng, W.-H.; Zhao, Q.-C. Caffeoylquinic Acid Derivatives Protect SH-SY5Y Neuroblastoma Cells from Hydrogen Peroxide-Induced Injury Through Modulating Oxidative Status. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2017, 37, 499–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, X.; Guo, L.-P.; Hu, X.-L.; Huang, J.; Fan, Y.-H.; Ren, T.-S.; Zhao, Q.-C. Protective Effects of Arctium lappa L. roots against hydrogen peroxide-induced cell injury and potential mechanisms in SH-SY5Y cell. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2015, 35, 335–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.; Chin, Y.-W.; Cho, J. Protection of cultured cortical neurons by luteolin against oxidative damage through inhibition of apoptosis and induction of heme oxygenase-1. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2017, 40, 256–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, L.; Xia, X.; Xiang, X.; Huang, F.; Zhang, Z. Protective effects of canolol against hydrogen peroxide-induced oxidative stress in AGS cells. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 42826–42832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, Y.; Cheong, Y.-K.; Kim, N.-H.; Chung, H.-T.; Kang, D.G.; Pae, H.-O. Mitogen-activated protein kinases and reactive oxygen species: How can ROS activate MAPK pathways? J. Signal Transduct. 2011, 2011, 792639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Cao, J.; Ma, X.; Wang, X.; Chen, Q.; Yan, S.; Zhao, N.; Geng, Z.; Wang, Z. Neuroprotection by polynitrogen manganese complexes: Regulation of reactive oxygen species-related pathways. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 20853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joshi, A.; Soni, P.; Malviya, S.; Kharia, A. Memory enhancing activity of Momordica charantia by scopolamine induced amnesia in rats. Int J. Compr. Adv. Pharm. 2017, 2, 11–18. [Google Scholar]
- Malik, Z.A.; Singh, M.; Sharma, P.L. Neuroprotective effect of Momordica charantia in global cerebral ischemia and reperfusion induced neuronal damage in diabetic mice. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2011, 133, 729–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, A.Y.; Choi, J.M.; Lee, M.H.; Lee, J.; Lee, S.; Cho, E.J. Protective effects of perilla oil and alpha linolenic acid on SH-SY5Y neuronal cell death induced by hydrogen peroxide. Nutr. Res. Pract. 2018, 12, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, M.J.; Lee, S.; Park, Y.I.; Lee, J.; Kwon, K.H. Neuroprotective effects of phytosterols and flavonoids from Cirsium setidens and Aster scaber in human brain neuroblastoma SK-N.-SH cells. Life Sci. 2016, 148, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Chen, B.; Du, M.; Song, J.; Cheng, X.; Wang, X.; Mao, X. Casein Glycomacropeptide hydrolysates exert cytoprotective effect against cellular oxidative stress by up-regulating HO-1 expression in HepG2 cells. Nutrients 2017, 9, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shan, B.; Xie, J.H.; Zhu, J.H.; Peng, Y. Ethanol modified supercritical carbon dioxide extraction of flavonoids from Momordica charantia L. and its antioxidant activity. Food Bioprod. Process. 2012, 90, 579–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, S.P.; Stathopoulos, C.; Parks, S.; Roach, P. An optimised aqueous extract of phenolic compounds from bitter melon with high antioxidant capacity. Antioxidants 2014, 3, 814–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kenny, O.; Smyth, T.J.; Hewage, C.M.; Brunton, N.P. Antioxidant properties and quantitative UPLC-MS analysis of phenolic compounds from extracts of fenugreek (Trigonella foenum-graecum) seeds and bitter melon (Momordica charantia) fruit. Food Chem. 2013, 141, 4295–4302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raish, M. Momordica charantia, polysaccharides ameliorate oxidative stress, hyperlipidemia, inflammation, and apoptosis during myocardial infarction by inhibiting the NF-κB signaling pathway. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 97, 544–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Song, K.; Huh, E.; Oh, M.S.; Kim, Y.S. Neuroprotection against 6-OHDA toxicity in PC12 cells and mice through the Nrf2 pathway by a sesquiterpenoid from Tussilago farfara. Redox Biol. 2018, 18, 6–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magesh, S.; Chen, Y.; Hu, L. Small Molecule Modulators of Keap1-Nrf2-ARE pathway as Potential Preventive and Therapeutic Agents. Med. Res. Rev. 2012, 32, 687–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.-Z.; Li, J.-N.; Zhang, Y.-Q.; Cao, Z.-Y.; Liu, Z.-Z.; Wang, S.-Q.; Liao, L.-M.; Du, J. Fuzheng Qingjie recipe induces apoptosis in HepG2 cells via P38 MAPK activation and the mitochondria-dependent apoptotic pathway. Mol. Med. Rep. 2014, 9, 2381–2387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camilleri, A.; Zarb, C.; Caruana, M.; Ostermeier, U.; Ghio, S.; Högen, T.; Schmidt, F.; Giese, A.; Vassallo, N. Mitochondrial membrane permeabilisation by amyloid aggregates and protection by polyphenols. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1828, 2532–2543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandoval-Acuña, C.; Ferreira, J.; Speisky, H. Polyphenols and mitochondria: An update on their increasingly emerging ROS-scavenging independent actions. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2014, 559, 75–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; E, Q.; Zuo, J.; Tao, Y.; Liu, W. Protective effect of Cordyceps polysaccharide on hydrogen peroxide-induced mitochondrial dysfunction in HL-7702 cells. Mol. Med. Rep. 2013, 7, 747–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, J.; Sun, F.; Li, Y.; Zhou, X.; Duan, Z.; Duan, F.; Zhao, L.; Chen, H.; Qi, S.; Shen, J. Momordica charantia polysaccharides could protect against cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury through inhibiting oxidative stress mediated c-Jun N-terminal kinase 3 signaling pathway. Neuropharmacology 2015, 91, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, J.; Chang, Q.; Wang, X.; Son, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, G.; Luo, J.; Bi, Y.; Chen, F.; Shi, X. Reactive oxygen species-activated Akt/ASK1/p38 signaling pathway in nickel compound-induced apoptosis in BEAS 2B cells. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2010, 23, 568–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, E.K.; Choi, E.-J. Pathological roles of MAPK signaling pathways in human diseases. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2010, 1802, 396–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.M.; Chung, M.J.; Ha, T.J.; Choi, H.N.; Jang, S.J.; Kim, S.O.; Chun, M.H.; Do, S.I.; Choo, Y.K.; Park, Y.I. Neuroprotective effects of black soybean anthocyanins via inactivation of ASK1-JNK/p38 pathways and mobilization of cellular sialic acids. Life Sci. 2012, 90, 874–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, H.-R.; Hu, L.-S.; Li, G.-Y. SH-SY5Y human neuroblastoma cell line: In vitro cell model of dopaminergic neurons in Parkinson’s disease. Chin. Med. J. 2010, 123, 1086–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, K.B.; Lee, S.; Kang, I.; Kim, J.-H. Momordica charantia Ethanol Extract Attenuates H2O2-Induced Cell Death by Its Antioxidant and Anti-Apoptotic Properties in Human Neuroblastoma SK-N-MC Cells. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1368. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10101368
Kim KB, Lee S, Kang I, Kim J-H. Momordica charantia Ethanol Extract Attenuates H2O2-Induced Cell Death by Its Antioxidant and Anti-Apoptotic Properties in Human Neuroblastoma SK-N-MC Cells. Nutrients. 2018; 10(10):1368. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10101368
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Kkot Byeol, SeonAh Lee, Inhae Kang, and Jung-Hee Kim. 2018. "Momordica charantia Ethanol Extract Attenuates H2O2-Induced Cell Death by Its Antioxidant and Anti-Apoptotic Properties in Human Neuroblastoma SK-N-MC Cells" Nutrients 10, no. 10: 1368. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10101368
APA StyleKim, K. B., Lee, S., Kang, I., & Kim, J.-H. (2018). Momordica charantia Ethanol Extract Attenuates H2O2-Induced Cell Death by Its Antioxidant and Anti-Apoptotic Properties in Human Neuroblastoma SK-N-MC Cells. Nutrients, 10(10), 1368. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10101368




