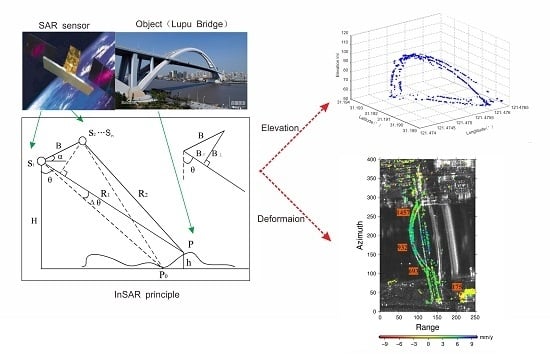
Elevation Extraction and Deformation Monitoring by Multitemporal InSAR of Lupu Bridge in Shanghai
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Research Area, Data and Methods
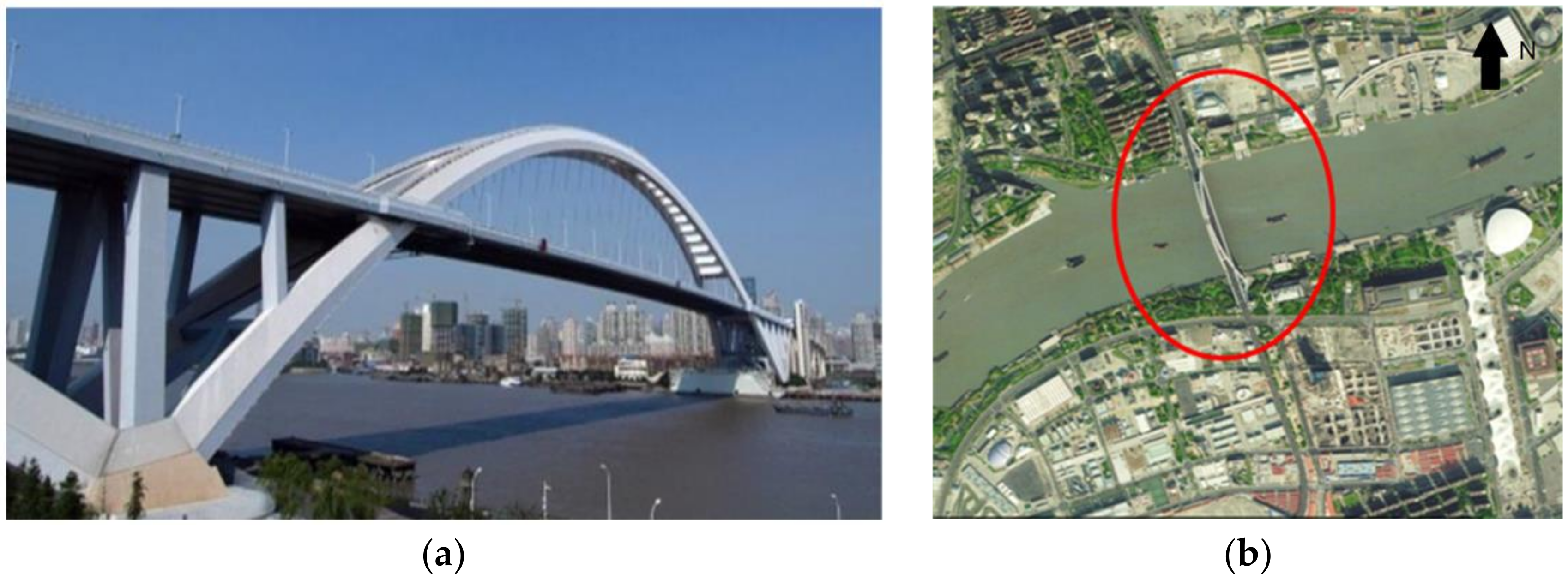
2.1. Research Area and Data
2.2. Data Processing Chain
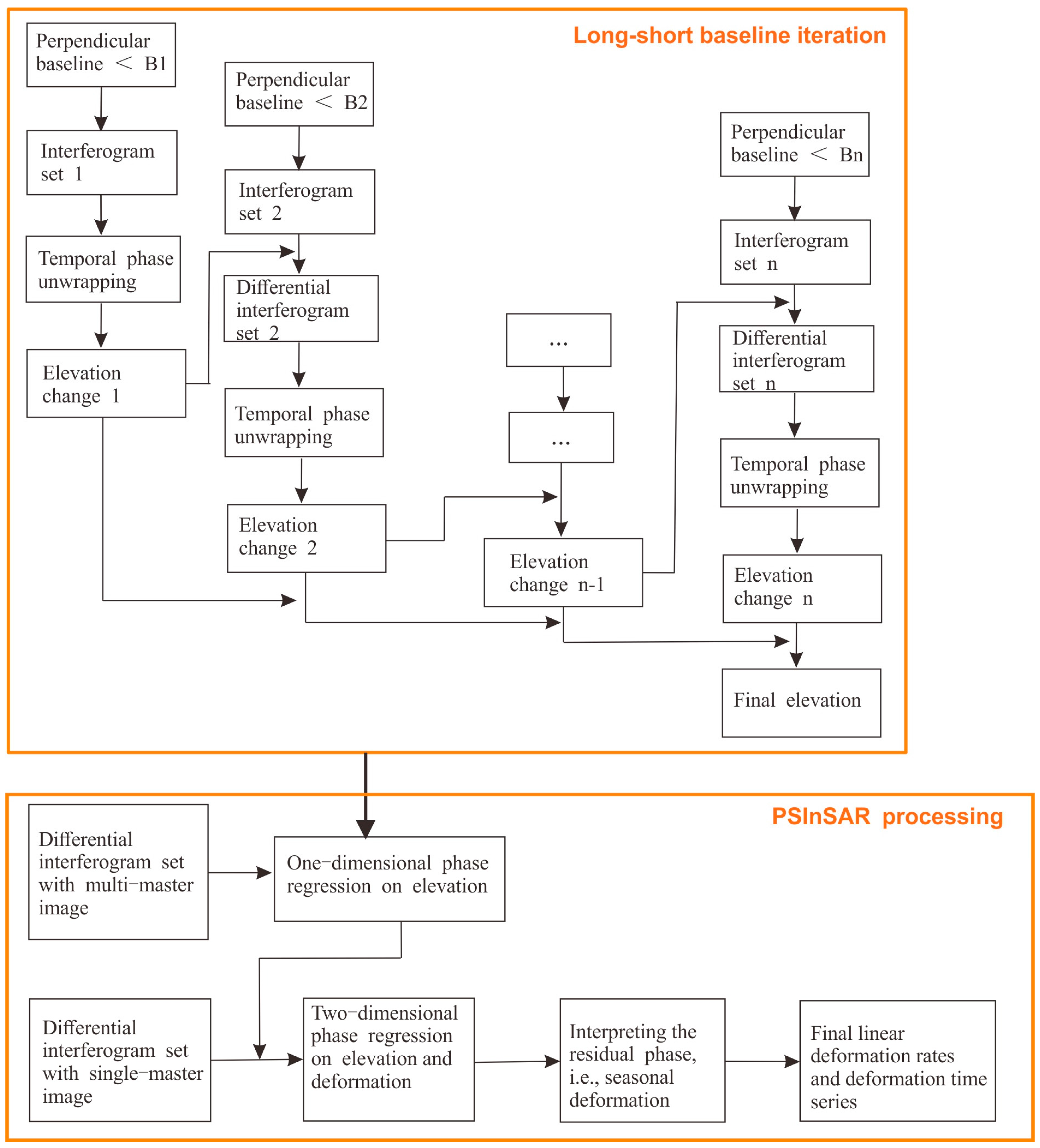
2.2.1. Long–Short Baseline Iteration PSInSAR Method
2.2.2. The LLL Lattice Reduction Algorithm
2.2.3. LLL Lattice Reduction Algorithm Used for PSInSAR
3. Results and Discussion
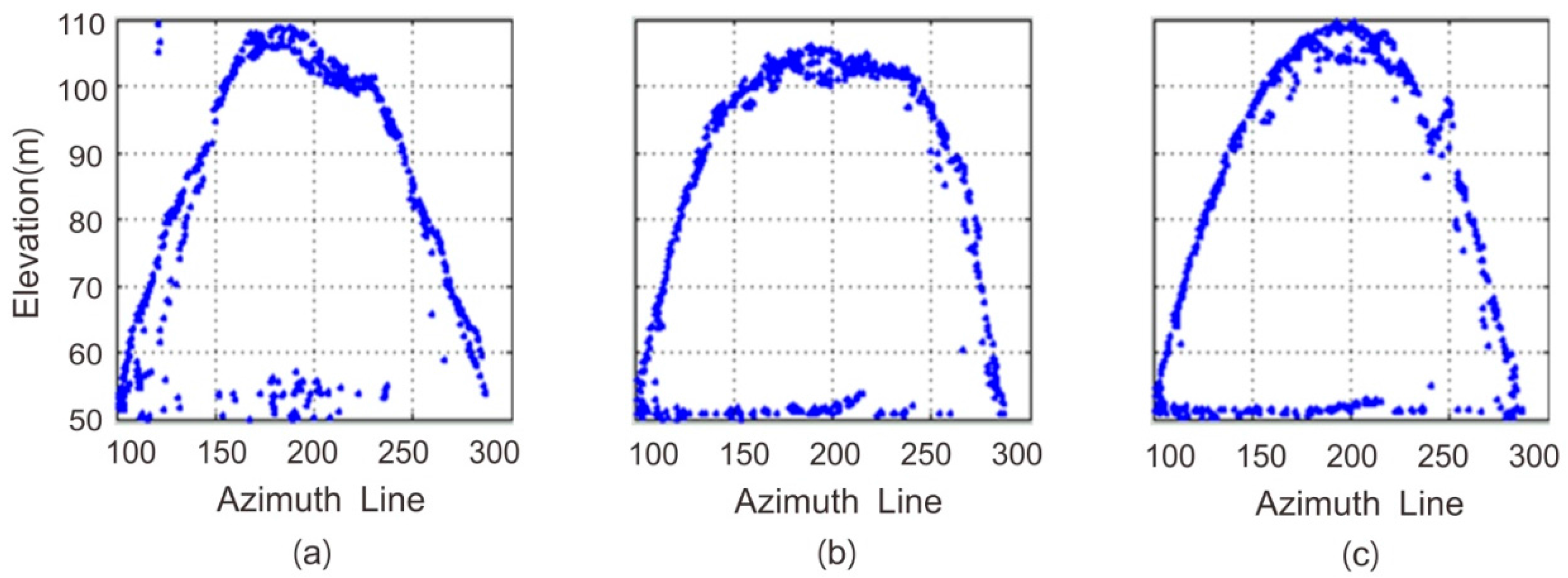
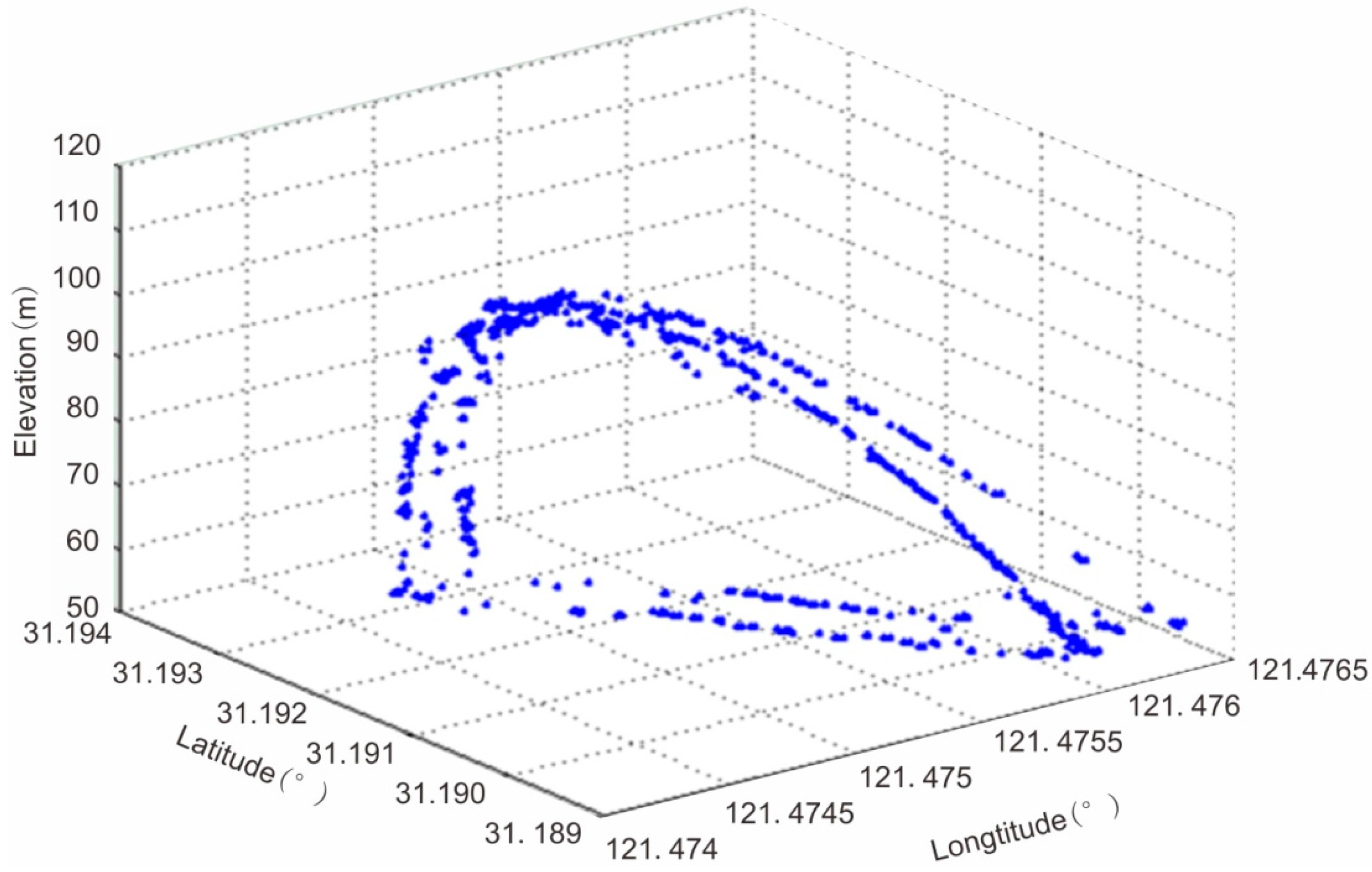
3.1. Bridge Elevation Extraction
3.2. Bridge Deformation Extraction
4. Conclusions and Outlook
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ferretti, A.; Prati, C.; Rocca, F. Permanent scatterers in SAR interferometry. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2001, 39, 8–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kampes, B.M. Radar Interferometry: Persistent Scatterer Technique; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Gernhardt, S.; Bamler, R. Deformation monitoring of single buildings using meter-resolution SAR data in PSI. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2012, 73, 68–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.X. Very High Resolution Tomographic SAR Inversion for Urban Infrastructure Monitoring—A Sparse and Nonlinear Tour. Ph.D. Thesis, University of München, München, Germany, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Adam, N.; Gonzalez, F.R.; Parizzi, A.; Brcic, R. Wide area persistent scatterer interferometry: Current developments, algorithms and examples. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGRASS), Melbourne, Australia, 21–26 July 2013; pp. 1857–1860. [Google Scholar]
- Gernhardt, S. High Precision 3D Localization and Motion Analysis of Persistent Scatterers Using Meter-Resolution Radar Satellite Data. Ph.D. Thesis, University of München, München, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, X.X.; Shahzad, M. Facade reconstruction using multiview spaceborne TomoSAR point clouds. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 52, 3541–3552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakon, M.; Perissin, D.; Lazecky, M.; Papco, J. Infrastructure nonlinear deformation monitoring via satellite radar interferometry. In Proceedings of the Conference on Enterprise Information Systems (ICEIS), Lisbon, Portugal, 27–30 April 2014; pp. 294–300. [Google Scholar]
- Lazecky, M.; Perissin, D.; Bakon, M.; Sousa, J.J.M.; Hlavacova, I.; Real, N. Potential of satellite InSAR techniques for monitoring of bridge deformations. Presented at the Joint Urban Remote Sensing Event, Lausanne, Switzerland, 1 April 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein, R.M.; Zebker, H.A.; Werner, C.L. Satellite radar interferometry: Two-dimensional phase unwrapping. Radio Sci. 1988, 23, 713–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flynn, T.J. Consistent 2-D phase unwrapping guided by a quality map. In Proceedings of the 1996 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGRASS), Piscataway, NE, USA, 31 May 1996; pp. 2057–2059. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, W.; Cumming, I. A region-growing algorithm for InSAR phase unwrapping. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1999, 37, 124–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carballo, G.F.; Fieguth, P.W. Probabilistic cost functions for network flow phase unwrapping. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2000, 38, 2192–2201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.W. Statistical-Cost Network-Flow Approaches to Two-Dimensional Phase Unwrapping for Radar Interferometry. Ph.D. Thesis, Stanford University, Stanford, CA, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Hooper, A.; Zebker, H.A. Phase unwrapping in three dimensions with application to InSAR time series. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 2007, 24, 2737–2747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herráez, M.A.; Burton, D.R.; Lalor, M.J.; Gdeisat, M.A. Fast two-dimensional phase-unwrapping algorithm based on sorting by reliability following a noncontinuous path. Appl. Opt. 2002, 41, 7437–7444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bioucas-Dias, J.M.; Valadao, G. Phase unwrapping via graph cuts. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2007, 16, 698–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Zhu, D.Y. A residue-pairing algorithm for InSAR phase unwrapping. Prog. Electromagn. Res. 2009, 95, 341–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenstra, A.K.; Lenstra, H.W.; Lovász, L. Factoring polynomials with rational coefficients. Math. Ann. 1982, 261, 515–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fincke, U.; Pohst, M. On reduction algorithms in non-linear integer mathematical programming. In Proceedings of the Operation Research, Mannheim, Germany, 21–23 September 1983; pp. 289–295. [Google Scholar]
- Lagarias, J.C. Knapsack Public Key Cryptosystems and Diophantine Approximation; Springer US: New York, NY, USA, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Coppersmith, D. Small solutions to polynomial equations and low exponent vulnerabilities. J. Cryptol. 1997, 10, 223–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaltofen, E.; Yui, N. Explicit Construction of the Hilbert Class Fields of Imaginary Quadratic Fields by Integer Lattice Reduction; Springer US: New York, NY, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.N.; Yu, X.W.; Zhang, X.H. GNSS ambiguity resolution using the lattice theory. Acta Geod. Cartogr. Sin. 2012, 41, 636–645. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, L.F. Monitoring Ground Deformation in Urban Major Project Area with High-Resolution Persistent Scatterer SAR Interferometry. Ph.D. Thesis, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Robertson, A.E. Multi-Baseline Interferometric SAR for Iterative Height Estimation. Master’s Thesis, Brigham Young University, Provo, UT, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Thompson, D.G.; Robertson, A.E.; Arnold, D.V.; Long, D.G. Multi-baseline interferometric SAR for iterative height estimation. In Proceedings of the 1999 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGRASS), Hamburg, Germany, 28 June–2 July 1999; pp. 251–253. [Google Scholar]
- Pieraccini, M.; Luzi, G.; Atzeni, C. Terrain mapping by ground-based interferometric radar. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2001, 39, 2176–2181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Academician Lin Yuanpei Tells the History of Shanghai Bridges. Available online: http://tieba.baidu.com/p/1108985575 (accessed on 14 June 2011).
- Reale, D.; Fornaro, G.; Pauciullo, A. Extension of 4-D SAR imaging to the monitoring of thermally dilating scatterers. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2013, 51, 5296–5306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fornaro, G.; Reale, D.; Verde, S. Bridge thermal dilation monitoring with millimeter sensitivity via multidimensional SAR imaging. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2013, 10, 677–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monserrat, O.; Crosetto, M.; Cuevas, M.; Crippa, B. The thermal expansion component of persistent scatterer interferometry observations. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2011, 8, 864–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goel, K.; Gonzalez, F.R.; Adam, N.; Duro, J.; Gaset, M. Thermal dilation monitoring of complex urban infrastructure using high resolution SAR data. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGRASS), Quebec, QC, Canada, 13–18 July 2014; pp. 954–957. [Google Scholar]
- Cuevas, M.; Monserrat, O.; Crosetto, M.; Crippa, B. A new product from persistent scatterer interferometry: The thermal dilation maps. In Proceedings of the 2011 Joint Urban Remote Sensing Event (JURSE), Munich, Germany, 11–13 April 2011; pp. 285–288. [Google Scholar]
- Montazeri, S.; Zhu, X.X.; Eineder, M.; Bamler, R. Three-Dimensional Deformation Monitoring of Urban Infrastructure by Tomographic SAR Using Multitrack TerraSAR-X Data Stacks. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2016, 54, 6868–6878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazecky, M.; Hlavacova, I.; Bakon, M.; Sousa, J.J.; Perissin, D.; Patricio, G. Bridge Displacements Monitoring Using Space-Borne X-Band SAR Interferometry. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2017, 10, 205–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

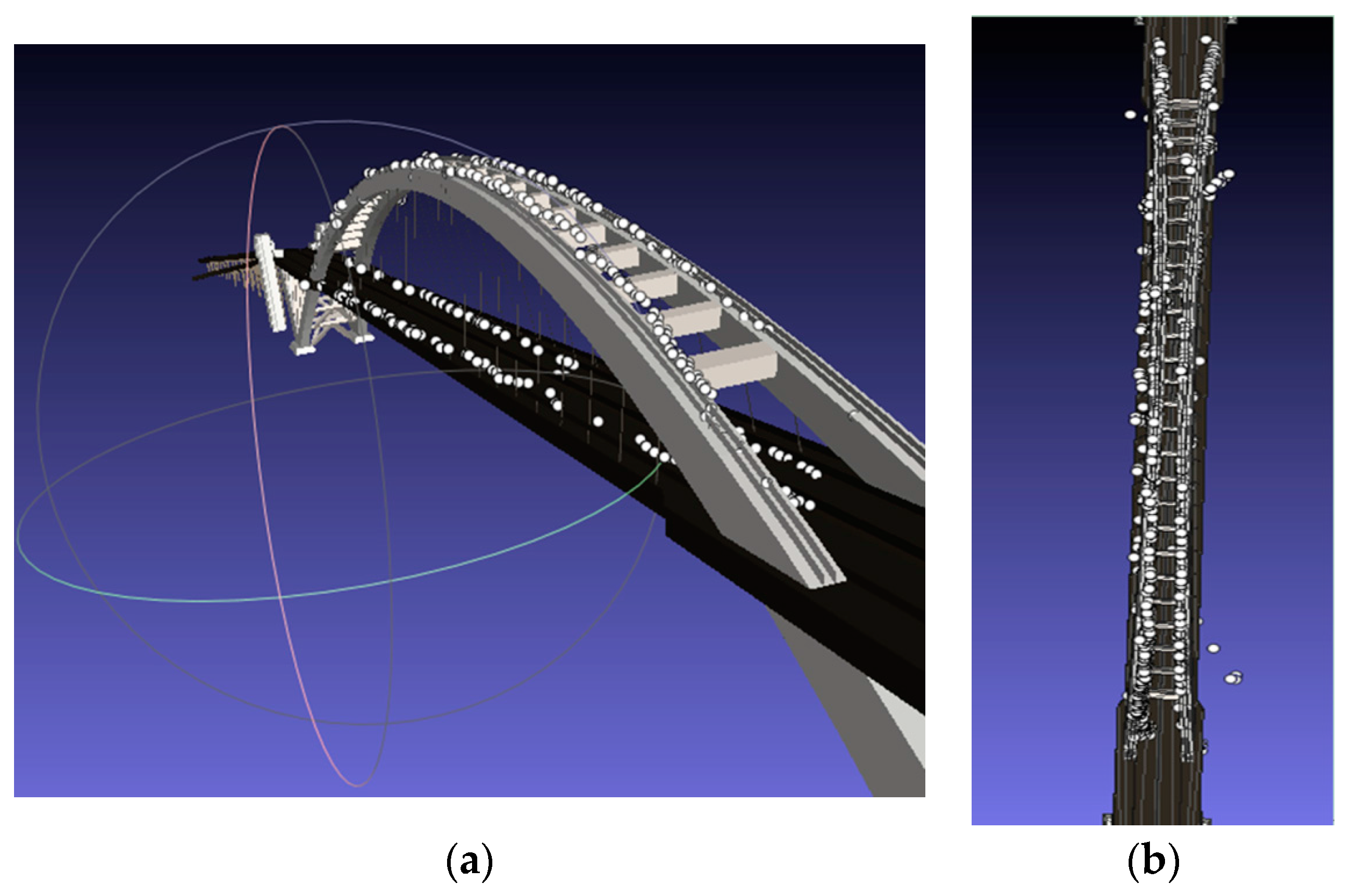
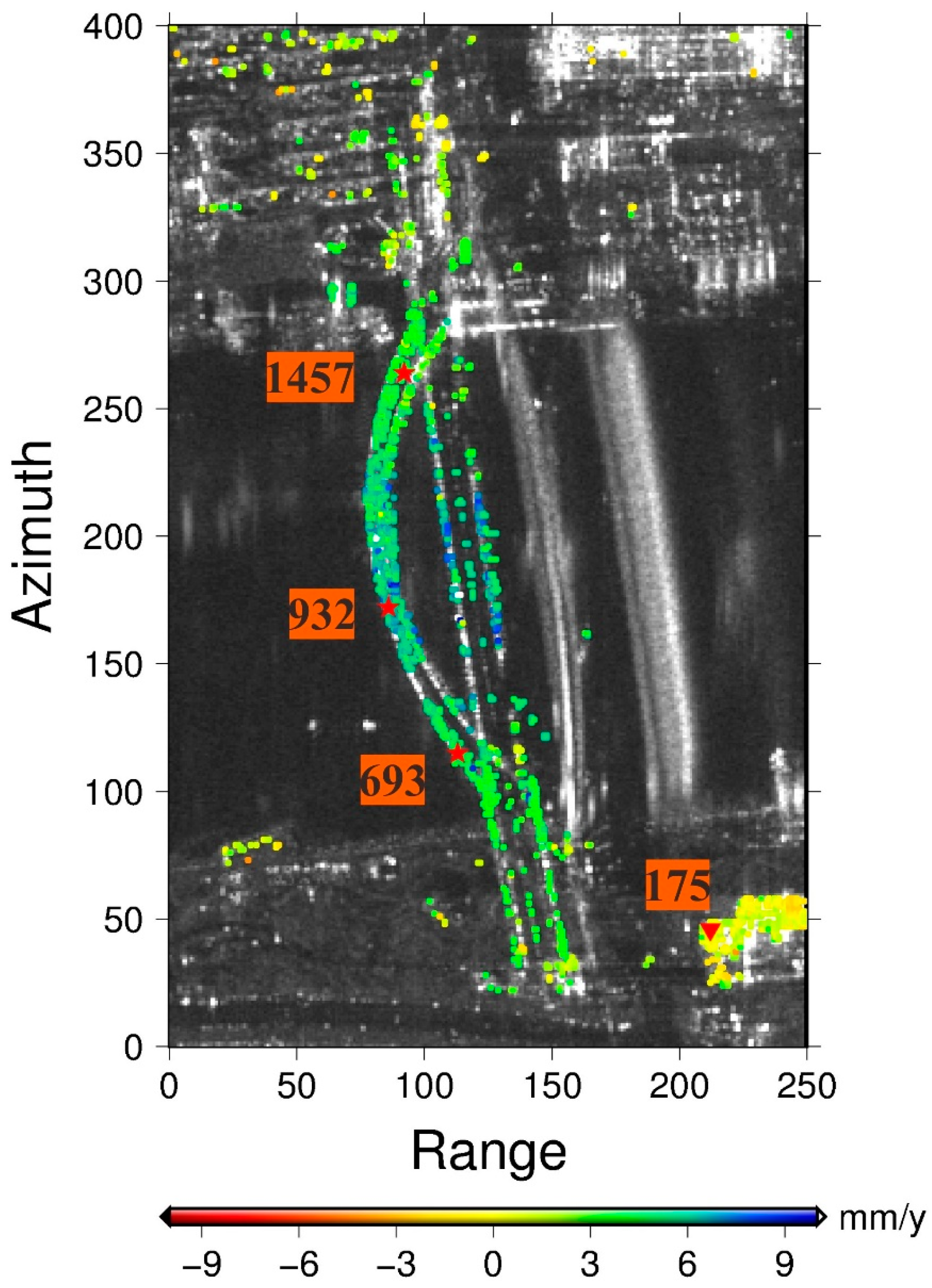
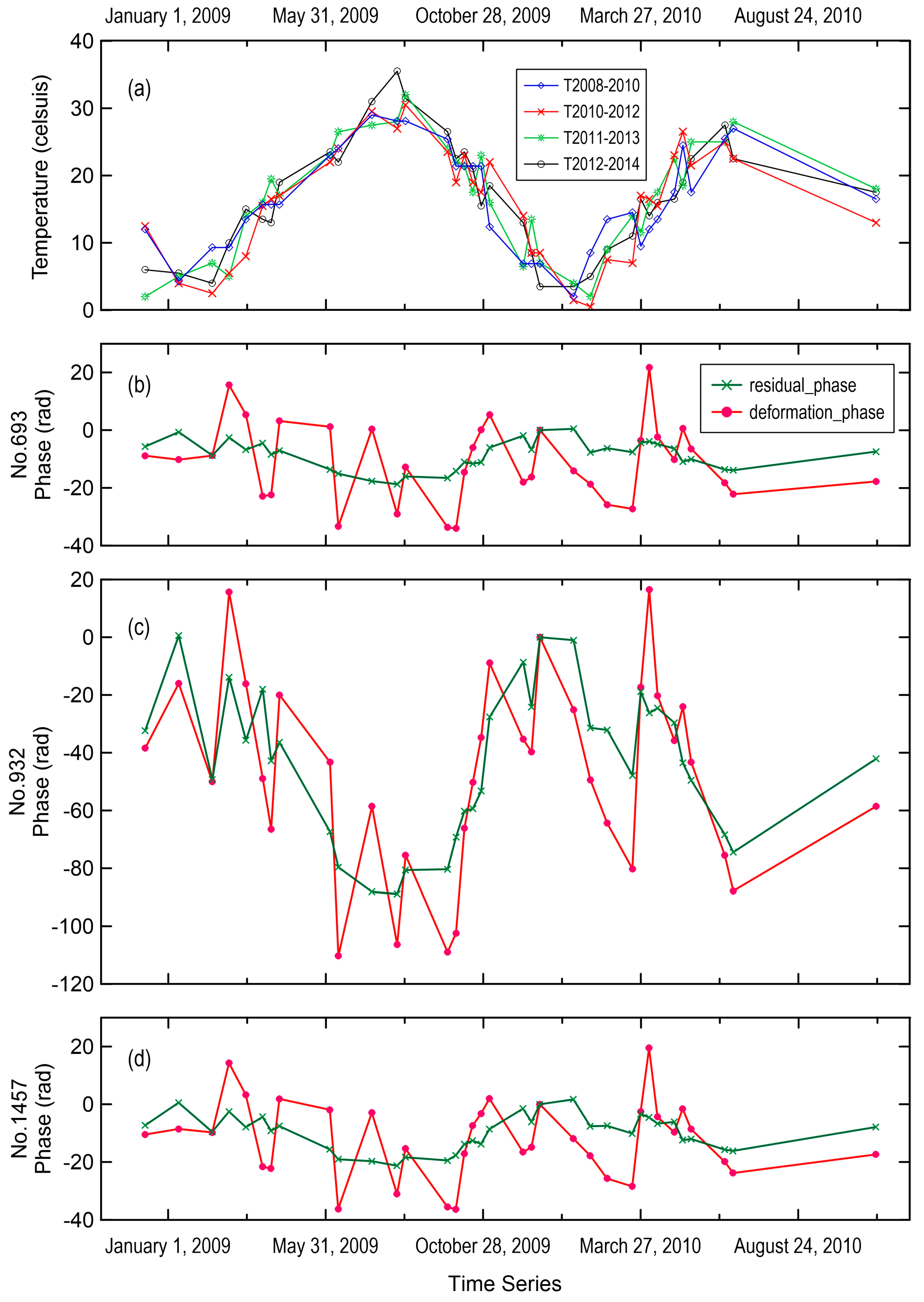
| Time Range | Number of Scenes | Azimuth Lines | Range Columns | Incident Angle (°) | Heading (°) | Azimuth Resolution (m) | Range Resolution (m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 December 2008–6 November 2010 | 35 | 400 | 250 | 40 | −10.34 | 2.25 | 1.25 |
| Iteration Round | Temporal Baseline (Day) | Perpendicular Baseline (m) | Number of Interferometric Pairs | Number of Arcs Used in the Net | Elevation Ambiguity (m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | <65 | <50 | 8 | 1320 | 150.0 |
| 2 | <65 | <200 | 38 | 1271 | 37.6 |
| 3 | <65 | <360 | 58 | 1395 | 20.9 |
| 4 | <65 | <600 | 77 | 1233 | 12.5 |
| 5 | <65 | <1000 | 119 | 1237 | 7.5 |
| Iteration 1 | Iteration 3 | Iteration 5 | Official Model | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Maximum arch elevation (m) | 109.1 | 106.0 | 109.6 | 109.35 |
| Minimum deck elevation (m) | 41.1 | 47.3 | 50.1 | |
| Maximum deck elevation (m) | 59.1 | 54.2 | 53.2 | |
| Mean deck elevation (m) | 53.60 |
| PS Point Number | Location | Correlation Coefficient (Residual Unwrapped Phase vs. Temperature) | Correlation Coefficient (Unwrapped Deformation Phase vs. Temperature) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 693 | Southern end of arch | −0.9225 | −0.2526 |
| 932 | Center | −0.9163 | −0.6460 |
| 1457 | Northern end of arch | −0.9240 | −0.3421 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, J.; Wu, J.; Ding, X.; Wang, M. Elevation Extraction and Deformation Monitoring by Multitemporal InSAR of Lupu Bridge in Shanghai. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 897. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9090897
Zhao J, Wu J, Ding X, Wang M. Elevation Extraction and Deformation Monitoring by Multitemporal InSAR of Lupu Bridge in Shanghai. Remote Sensing. 2017; 9(9):897. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9090897
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Jingwen, Jicang Wu, Xiaoli Ding, and Mingzhou Wang. 2017. "Elevation Extraction and Deformation Monitoring by Multitemporal InSAR of Lupu Bridge in Shanghai" Remote Sensing 9, no. 9: 897. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9090897
APA StyleZhao, J., Wu, J., Ding, X., & Wang, M. (2017). Elevation Extraction and Deformation Monitoring by Multitemporal InSAR of Lupu Bridge in Shanghai. Remote Sensing, 9(9), 897. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9090897