An Improved Local Gradient Method for Sea Surface Wind Direction Retrieval from SAR Imagery
Abstract
:1. Introduction
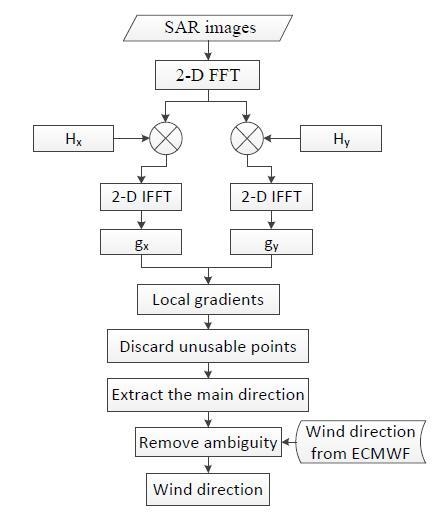
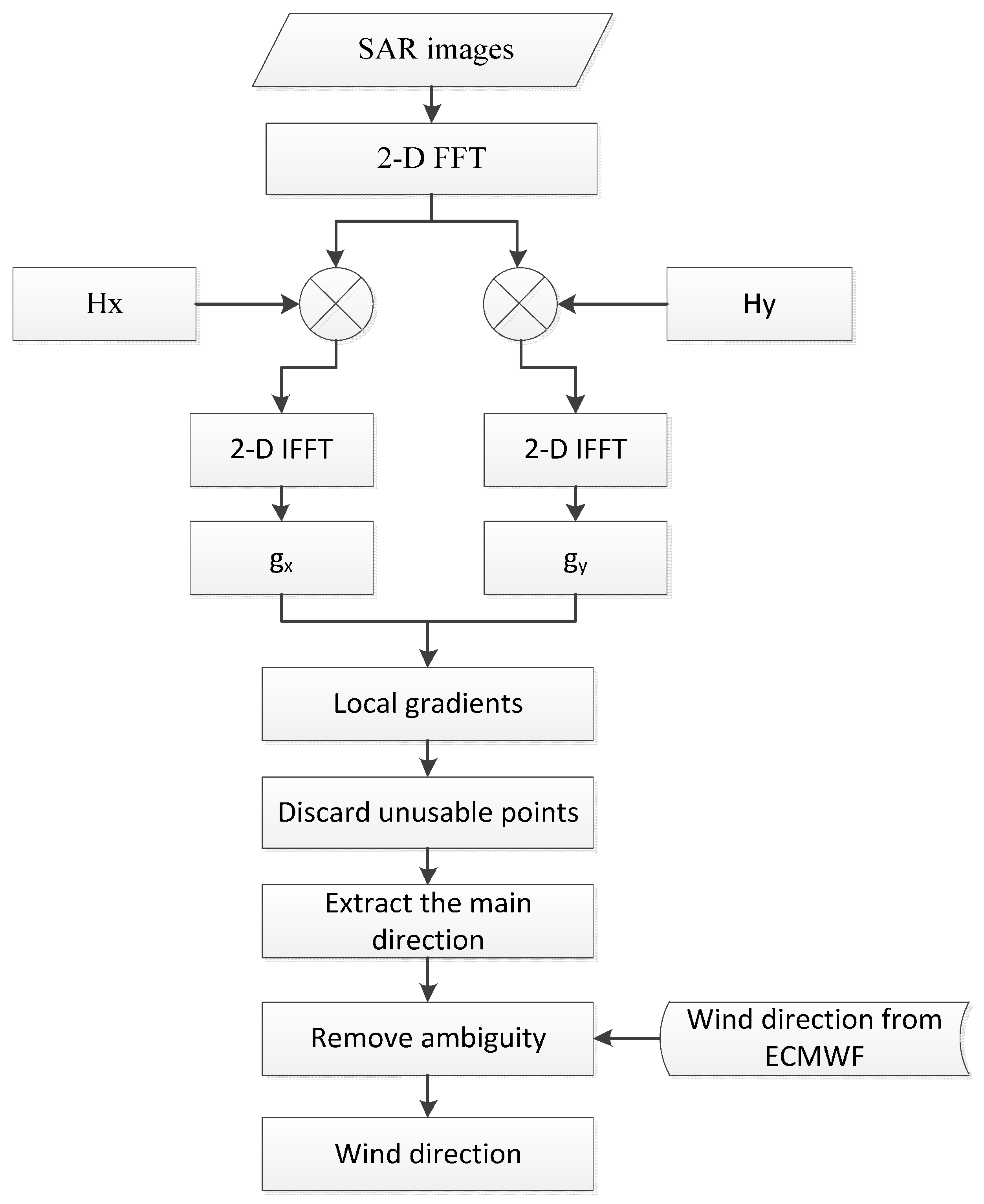
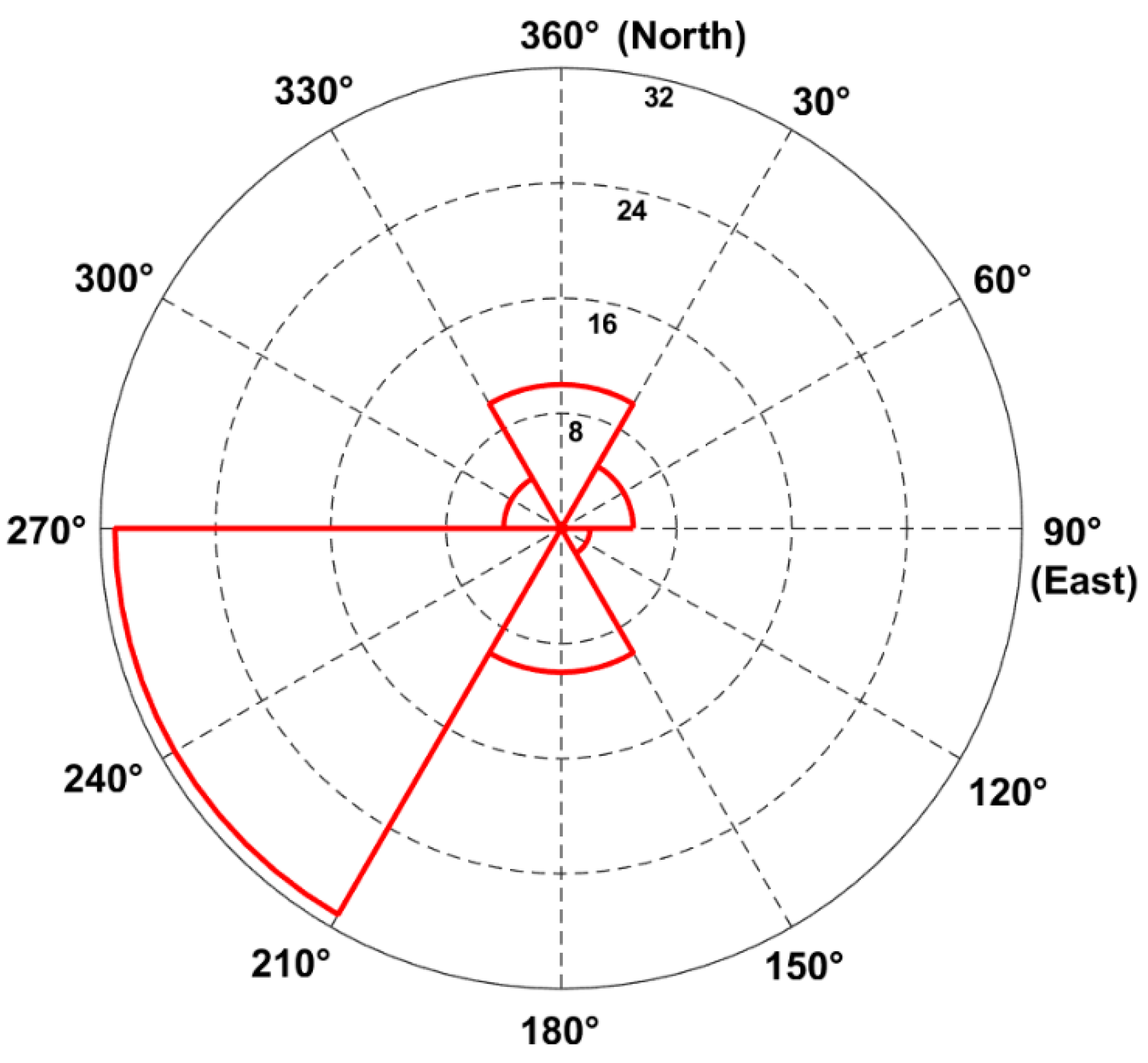
2. Improved Local Gradients Method
3. Data Sets
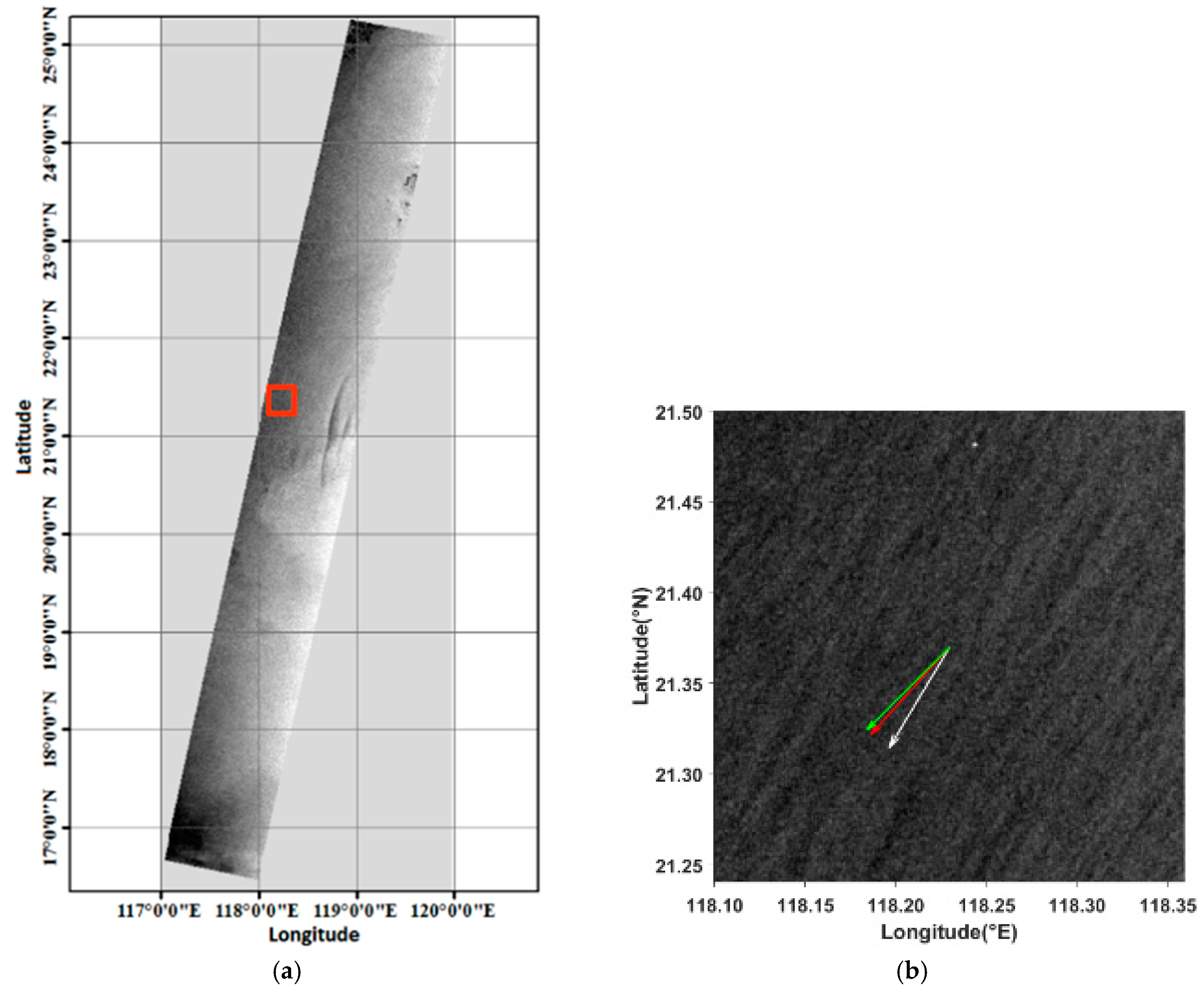
3.1. SAR Data
3.2. ECMWF Data
3.3. CCMP Data
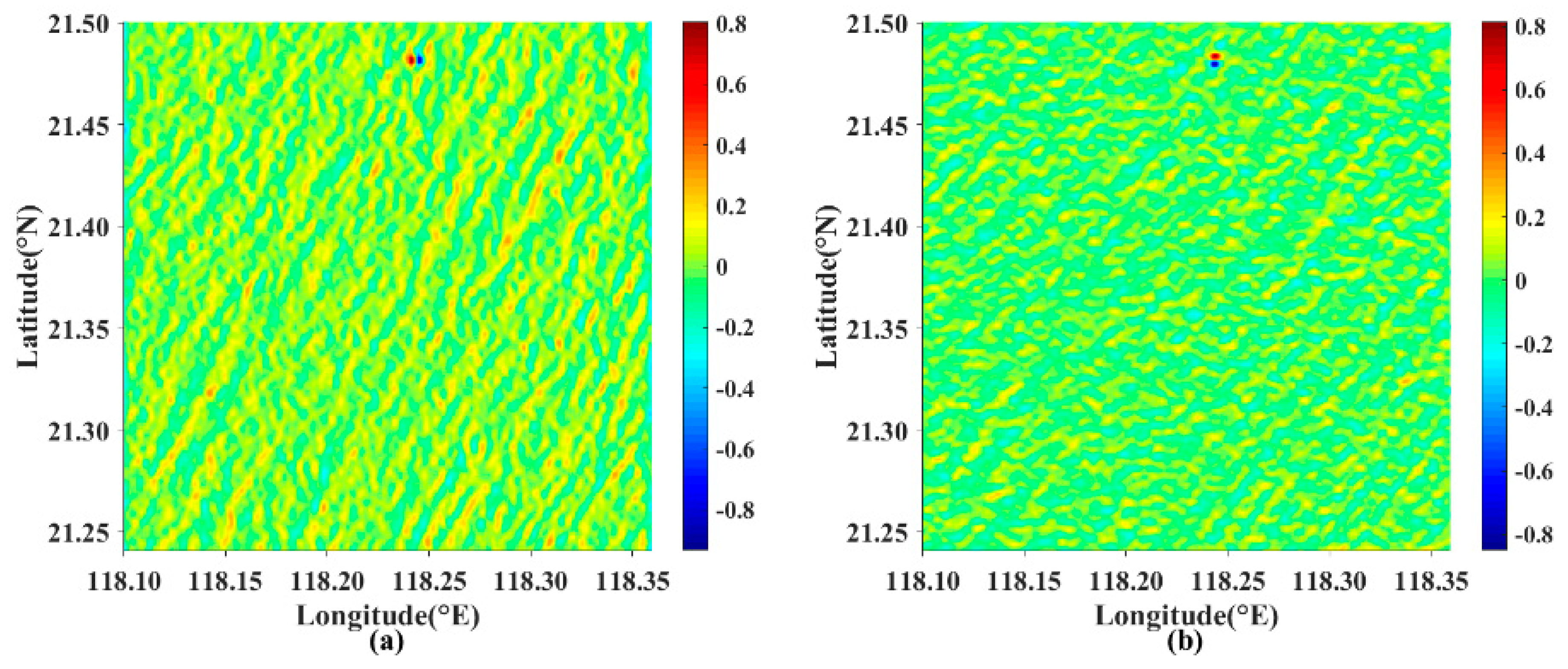
4. Results and Discussion
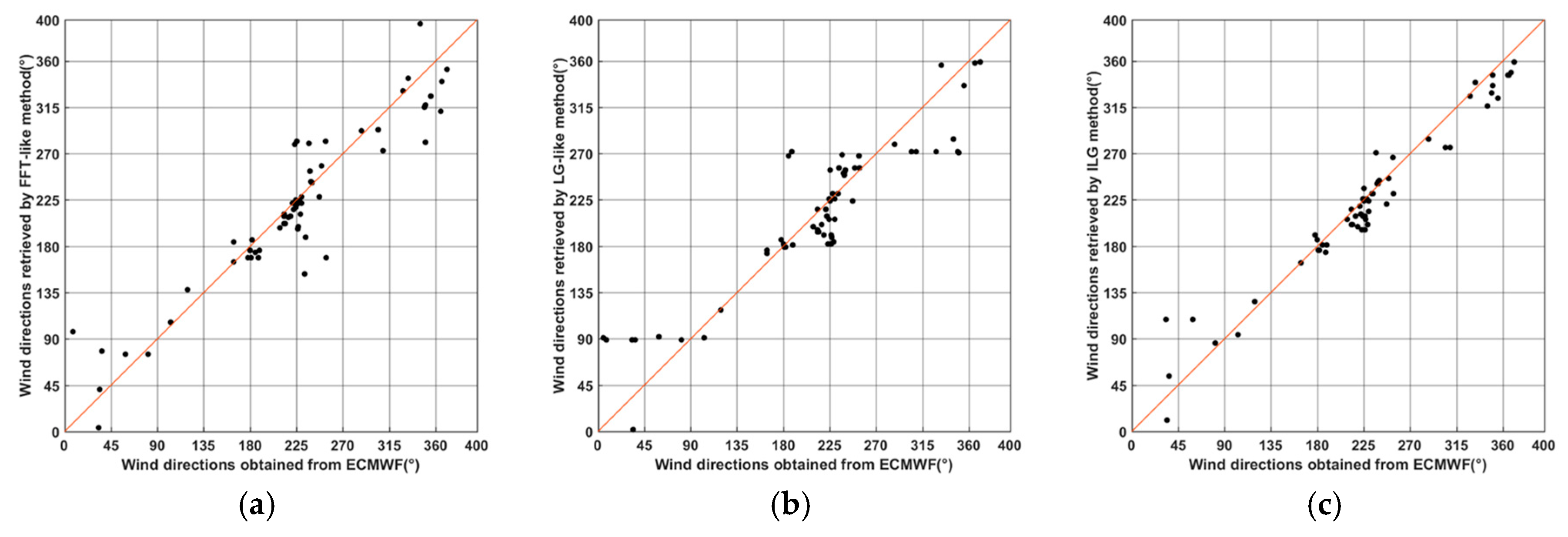
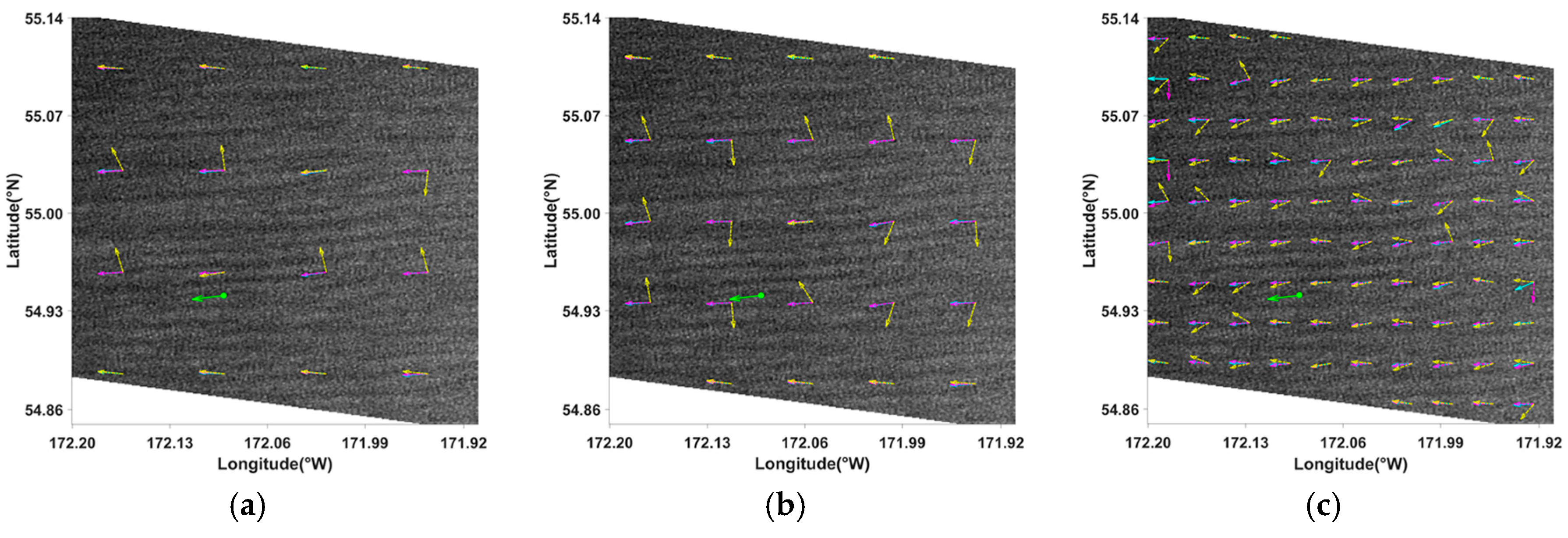
4.1. Comparison with ECMWF
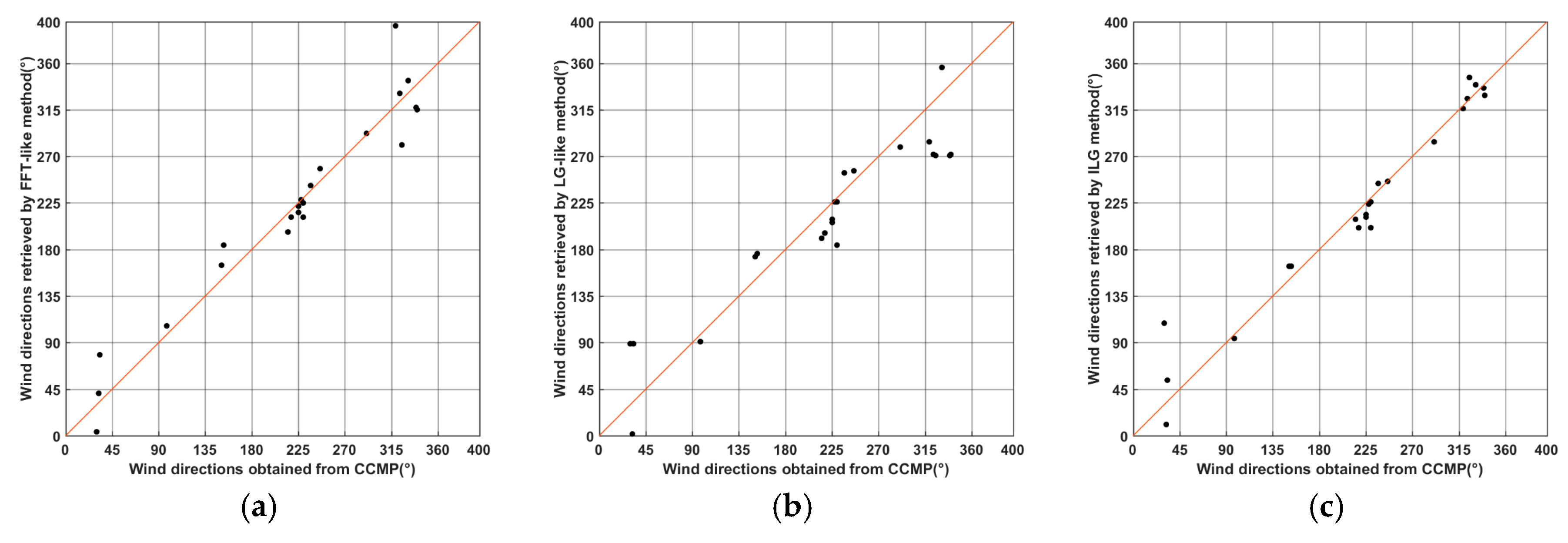
4.2. Comparison with CCMP
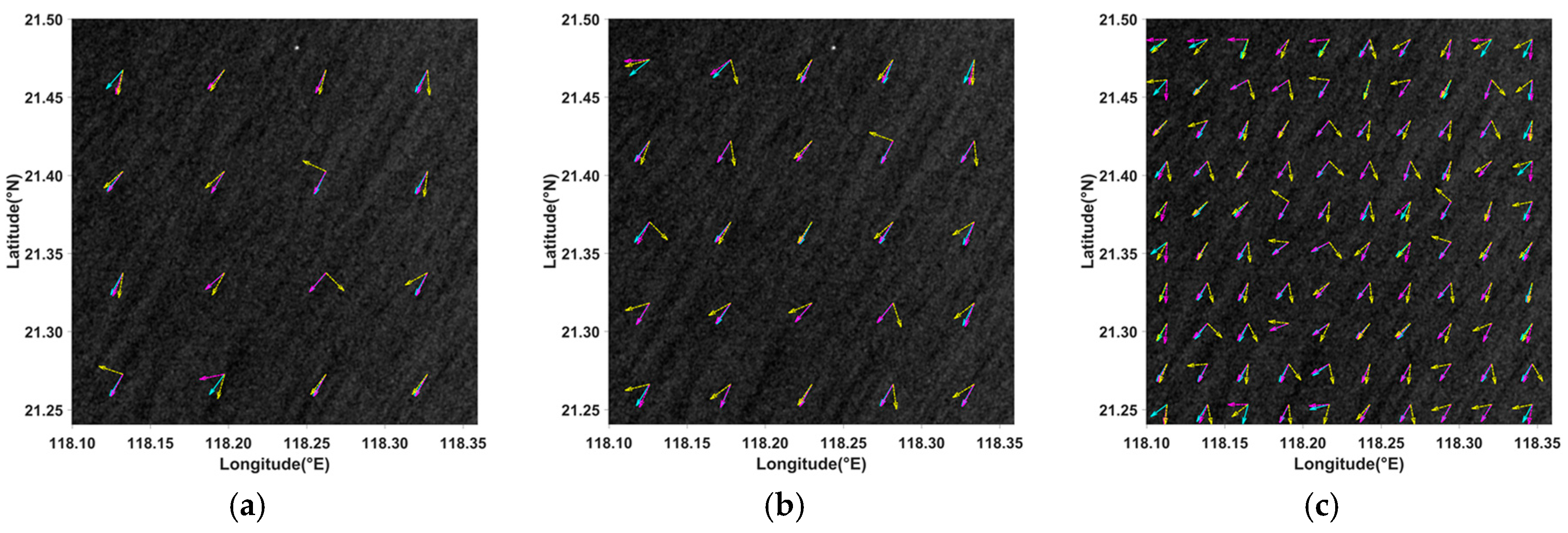
4.3. Discussion
5. Sensitivities to Different Noise
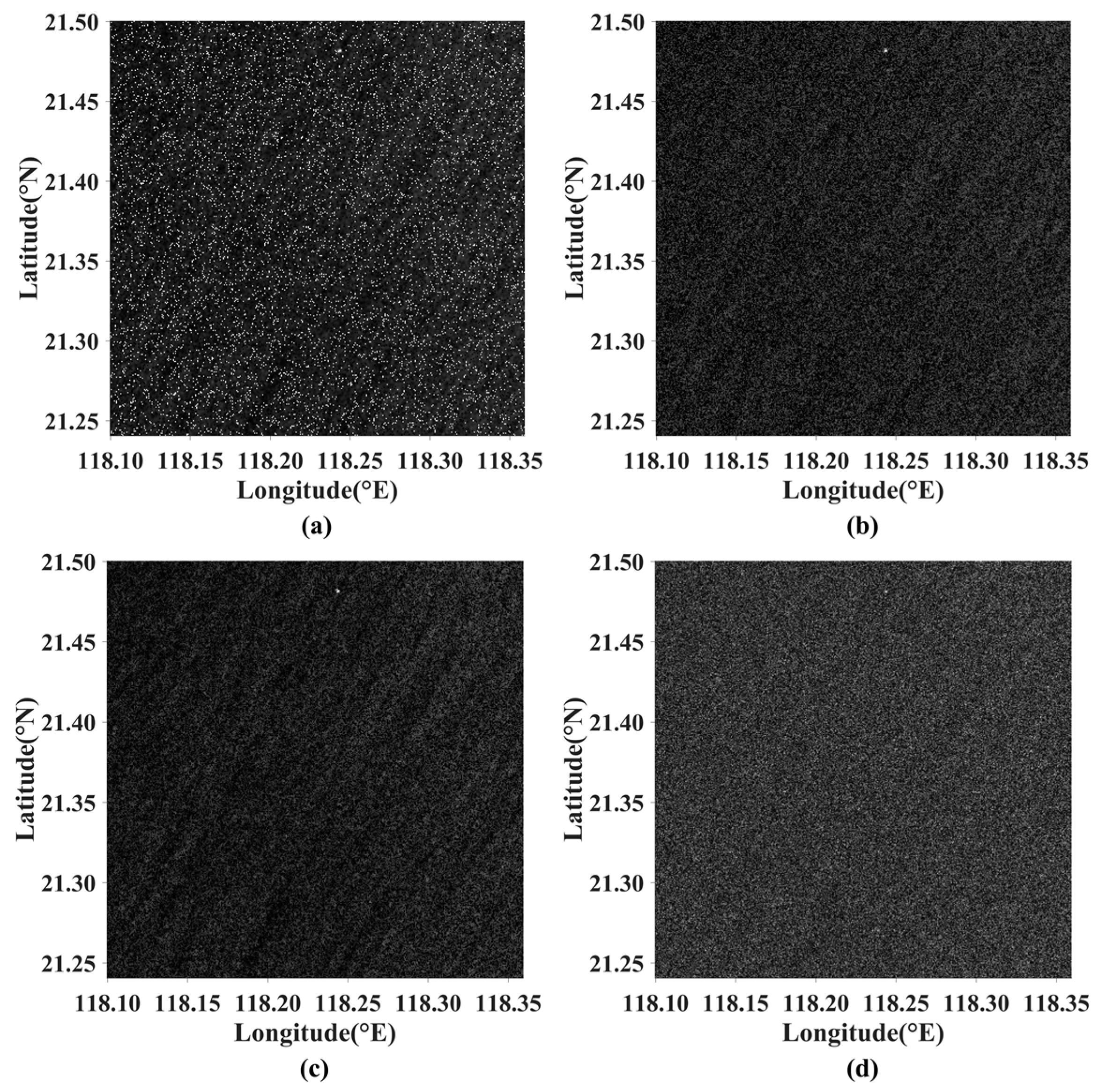
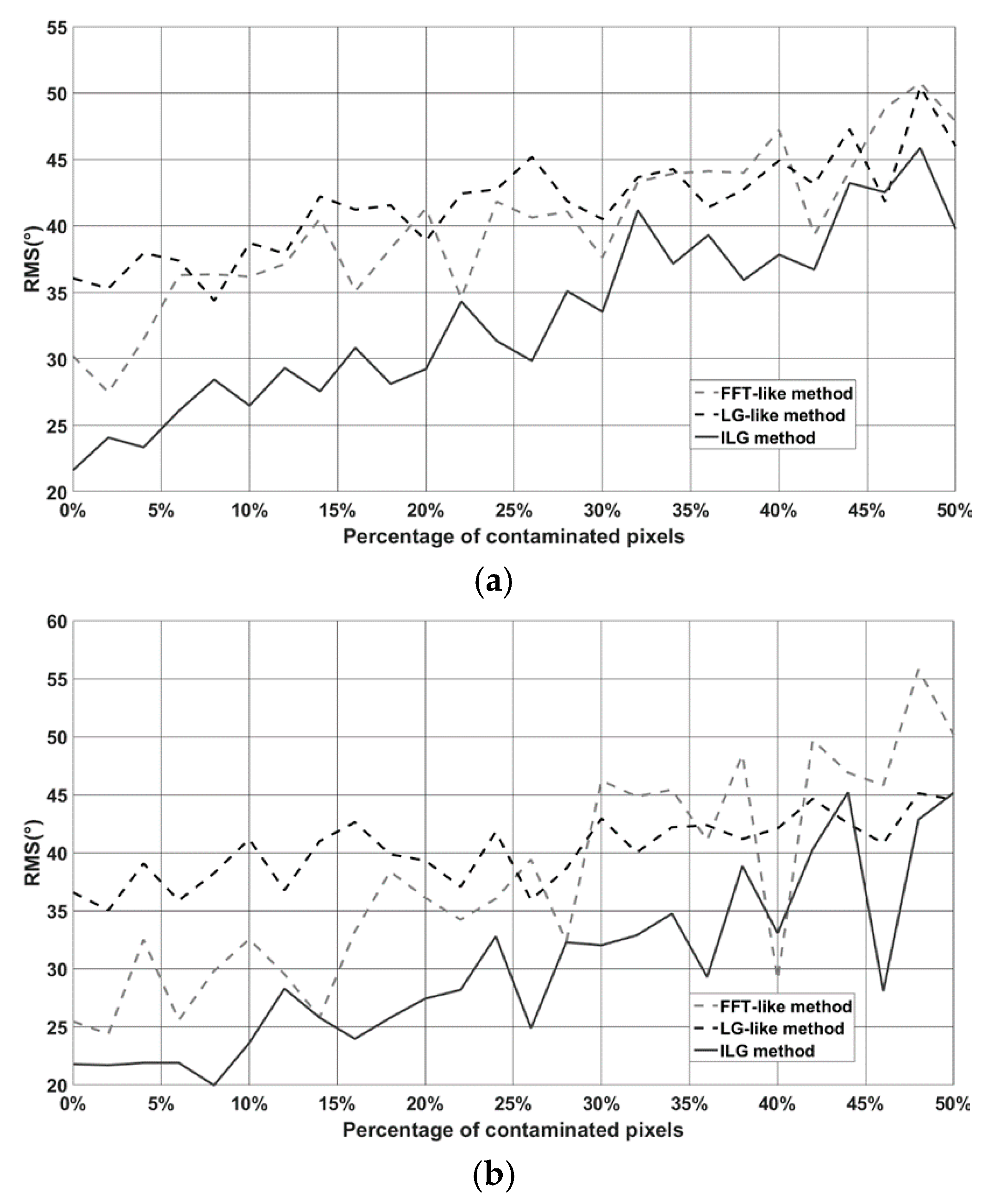
5.1. Salt-and-Pepper Noise
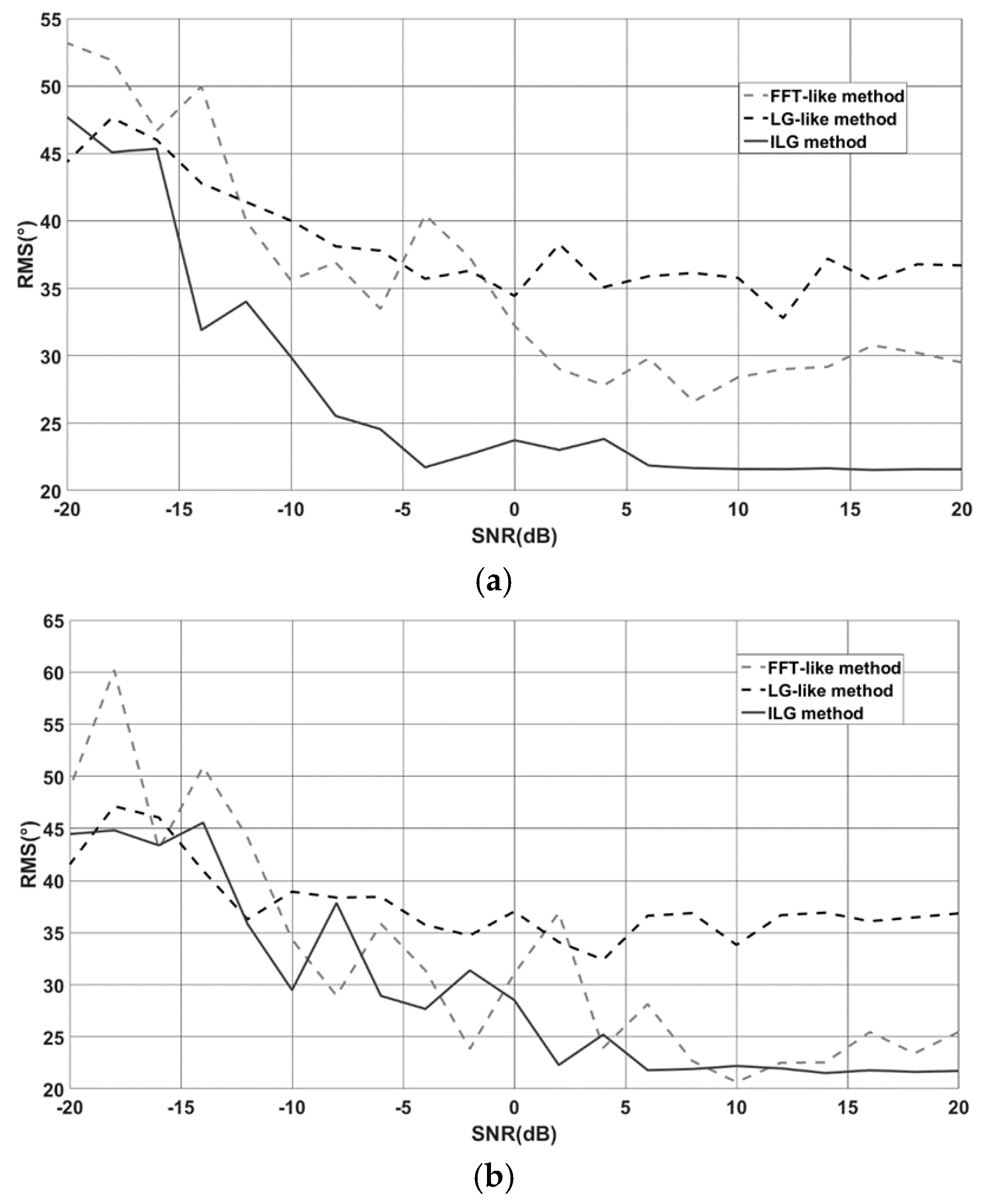
5.2. Additive Noise
5.3. Multiplicative Noise
6. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Friedman, K.S.; Sikora, T.D.; Pichel, W.G.; Clementecolón, P.; Hufford, G. Using spaceborne synthetic aperture radar to improve marine surface analyses. Weather Forecast. 2010, 16, 270–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Ahn, J.M.; Sienkiewicz, J.M.; Chang, P.S. Operational impact of QuikSCAT winds at the NOAA ocean prediction center. Weather Forecast. 2006, 21, 523–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christiansen, M.B.; Koch, W.; Horstmann, J.; Hasager, C.B.; Nielsen, M. Wind resource assessment from C-band SAR. Remote Sens. Environ. 2006, 105, 68–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, R.; Zhu, R.; Badger, M.; Hasager, C.B.; Xing, X.; Jiang, Y. Offshore wind resources assessment from multiple satellite data and WRF modeling over south China sea. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 467–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavaleri, L.; Alves, J.H.; Ardhuin, F.; Babanin, A.; Banner, M.; Belibassakis, K.; Benoit, M.; Donelan, M.; Groeneweg, J.; Herbers, T.H.C. Wave modeling—The state of the art. Prog. Oceanogr. 2007, 74, 603–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, P.P.; Mcwilliams, J.C. Dynamics of winds and currents coupled to surface waves. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 2009, 42, 19–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Li, X.; Wei, Y.; Tang, Z.; Cheng, Y.; Pichel, W.G. Satellite observations and modeling of oil spill trajectories in the Bohai sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2013, 71, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Y.; Liu, B.; Li, X.; Nunziata, F. Monitoring of oil spill trajectories with Cosmo-SkyMed X-band SAR images and model simulation. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2014, 7, 2895–2901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atlas, R.; Hoffman, R.N.; Ardizzone, J.; Leidner, S.M.; Jusem, J.C.; Smith, D.K.; Gombos, D. A cross-calibrated, multiplatform ocean surface wind velocity product for meteorological and oceanographic applications. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2011, 92, 157–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salonen, K.; Niemelä, S.; Fortelius, C. Application of radar wind observations for low-level NWP wind forecast validation. J. Appl. Meteorol. 2011, 50, 1362–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Li, X.; Zheng, Q.; Gu, X.F. Comparison of ocean-surface winds retrieved from QuikSCAT scatterometer and Radarsat-1 SAR in offshore waters of the US west coast. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2011, 8, 163–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wentz, F.J. Measurement of oceanic wind vector using satellite microwave radiometers. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1992, 30, 960–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naderi, F.M.; Freilich, M.H.; Long, D. Spaceborne radar measurement of wind velocity over the ocean—An overview of the NSCAT scatterometer system. Proc. IEEE 1991, 79, 850–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerling, T.W. Structure of the surface wind field from the Seasat SAR. J. Geophys. Res. 1986, 91, 2308–2320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastenbroek, K. High-resolution wind fields from ERS SAR. Earth Obs. Quart. 1998, 59, 20–22. [Google Scholar]
- Horstmann, J.; Koch, W. Ocean wind field retrieval using Envisat ASAR data. In Proceedings of the Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Toulouse, France, 21–25 July 2003; pp. 3102–3104. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, B.; Perrie, W.; He, Y. Wind speed retrieval from Radarsat-2 quad-polarization images using a new polarization ratio model. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2011, 116, 1318–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X. The first Sentinel-1 SAR image of a typhoon. Acta Ocean. Sin. 2015, 34, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.S.; Park, K.A.; Li, X.; Hong, S. SAR-derived wind fields at the coastal region in the East/Japan sea and relation to coastal upwelling. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2014, 35, 3947–3965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuan, Z.; Yang, X.F.; Li, Z.W.; Yang, Y.; Bi, H.B.; Sheng, M.; Li, X.F. Estimation of tropical cyclone parameters and wind fields from SAR images. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2013, 56, 1977–1987. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Zhang, J.A.; Yang, X.; Pichel, W.G.; Demaria, M.; Long, D.; Li, Z. Tropical cyclone morphology from spaceborne synthetic aperture radar. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2013, 94, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Pichel, W.G.; He, M.; Wu, S.Y. Observation of hurricane-generated ocean swell refraction at the Gulf Stream north wall with the Radarsat-1 synthetic aperture radar. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2002, 40, 2131–2142. [Google Scholar]
- Friedman, K.S.; Li, X. Monitoring hurricanes over the ocean with wide swath SAR. Johns Hopkins Apl Tech. Dig. 2000, 21, 80–85. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Zheng, W.; Pichel, W.G.; Zou, C.Z.; Clemente-Colón, P. Coastal katabatic winds imaged by SAR. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34, 300–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zheng, W.; Yang, X.; Zhang, J.A.; Pichel, W.G.; Li, Z. Coexistence of atmospheric gravity waves and boundary layer rolls observed by SAR. J. Atmos. Sci. 2013, 70, 3448–3459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Li, Z.; Yang, X.; Pichel William, G.; Yu, Y.; Zheng, Q.; Li, X. Atmospheric frontal gravity waves observed in satellite SAR images of the Bohai sea and Huanghai sea. Acta Ocean. Sin. 2010, 29, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Dong, C.; Clemente-Colón, P.; Pichel, W.G.; Friedman, K.S. Synthetic aperture radar observation of the sea surface imprints of upstream atmospheric solitons generated by flow impeded by an island. J. Geophys. Res. 2004, 109, 235–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chunchuzov, I.; Vachon, P.W.; Li, X. Analysis and modeling of atmospheric gravity waves observed in Radarsat SAR images. Remote Sens. Environ. 2000, 74, 343–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zheng, W.; Zou, C.Z.; Pichel, W.G. A SAR observation and numerical study on ocean surface imprints of atmospheric vortex streets. Sensors 2008, 8, 3321–3334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Clemente-Colón, P.; Pichel, W.G.; Vachon, P.W. Atmospheric vortex streets on a Radarsat SAR image. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2000, 27, 1655–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yang, X.; Zheng, W.; Zhang, J.A. Synergistic use of satellite observations and numerical weather model to study atmospheric occluded fronts. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2015, 53, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouche, A.; Collard, F.; Chapron, B.; Dagestad, K.; Guitton, G.; Johannessen, J.A.; Kerbaol, V.; Hansen, M.W. On the use of Doppler shift for sea surface wind retrieval from SAR. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2012, 50, 2901–2909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wackerman, C.C.; Pichel, W.G.; Clemente-Colon, P. Automated estimation of wind vectors from SAR. In Proceedings of the 12th Annual Conference on Satellite Meteorology at the 83rd Annual Meteorological Association Meeting, Long Beach, CA, USA, 9–13 February 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Koch, W. Directional analysis of SAR images aiming at wind direction. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2004, 42, 702–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Perrie, W.; Li, X.; Zhang, J.A. A hurricane morphology and sea surface wind vector estimation model based on C-band cross-polarization SAR imagery. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2017, 55, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Perrie, W.; Vachon, P.W.; Li, X.; Pichel, W.G.; Guo, J.; He, Y. Ocean vector winds retrieval from C-band fully polarimetric SAR measurements. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2012, 50, 4252–4261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Yang, X.; Li, X.; Zhang, B. A systematic comparison of the effect of polarization ratio models on sea surface wind retrieval from C-band synthetic aperture radar. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2013, 6, 1100–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wackerman, C.; Shuchman, R.; Fetterer, F. Estimation of wind speed and wind direction from ERS-1 imagery. In Proceedings of the Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Pasadena, CA, USA, 8–12 August 1994; pp. 1222–1224. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.S.; Huang, W.G.; Zhou, C.B.; Bin, F.U.; Shi, A.Q.; Li, D.L. Coastal ocean surface wind retrieval from SAR imagery. J. Remote Sens. 2001, 5, 13–16. [Google Scholar]
- Ulaby, F.T.; Moore, R.K.; Fung, A.K. Microwave Remote Sensing: Active and Passive, Volume 2—Radar Remote Sensing and Surface Scattering and Emission Theory; Addison-Wesley: Boston, MA, USA, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, M. Wind retrieval over the ocean using advanced synthetic aperture radar. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Geoinformatics, Shanghai, China, 24–26 June 2011; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Dee, D.P.; Uppala, S.M.; Simmons, A.J.; Berrisford, P.; Poli, P.; Kobayashi, S.; Andrae, U.; Balmaseda, M.A.; Balsamo, G.; Bauer, P. The ERA-interim reanalysis: Configuration and performance of the data assimilation system. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2011, 137, 553–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| FFT-Like Method | LG-Like Method | ILG Method | |
|---|---|---|---|
| RMS(°) | 30.22 | 36.10 | 21.57 |
| R | 0.9344 | 0.9314 | 0.9765 |
| p-value | 1.38 × 10−28 | 4.30 × 10−25 | 1.03 × 10−41 |
| FFT-Like Method | LG-Like Method | ILG Method | |
|---|---|---|---|
| RMS(°) | 25.41 | 36.65 | 21.61 |
| R | 0.9659 | 0.9413 | 0.9771 |
| p-value | 3.29 × 10−13 | 6.92 × 10−11 | 6.55 × 10−15 |
| FFT-Like Method | LG-Like Method | ILG Method | |
|---|---|---|---|
| ECMWF | 46.73° | 45.29° | 37.06° |
| CCMP | 46.39° | 42.14° | 37.19° |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, L.; Zheng, G.; Li, X.; Yang, J.; Ren, L.; Chen, P.; Zhang, H.; Lou, X. An Improved Local Gradient Method for Sea Surface Wind Direction Retrieval from SAR Imagery. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 671. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9070671
Zhou L, Zheng G, Li X, Yang J, Ren L, Chen P, Zhang H, Lou X. An Improved Local Gradient Method for Sea Surface Wind Direction Retrieval from SAR Imagery. Remote Sensing. 2017; 9(7):671. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9070671
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Lizhang, Gang Zheng, Xiaofeng Li, Jingsong Yang, Lin Ren, Peng Chen, Huaguo Zhang, and Xiulin Lou. 2017. "An Improved Local Gradient Method for Sea Surface Wind Direction Retrieval from SAR Imagery" Remote Sensing 9, no. 7: 671. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9070671
APA StyleZhou, L., Zheng, G., Li, X., Yang, J., Ren, L., Chen, P., Zhang, H., & Lou, X. (2017). An Improved Local Gradient Method for Sea Surface Wind Direction Retrieval from SAR Imagery. Remote Sensing, 9(7), 671. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9070671