Estimation of FAPAR over Croplands Using MISR Data and the Earth Observation Land Data Assimilation System (EO-LDAS)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials
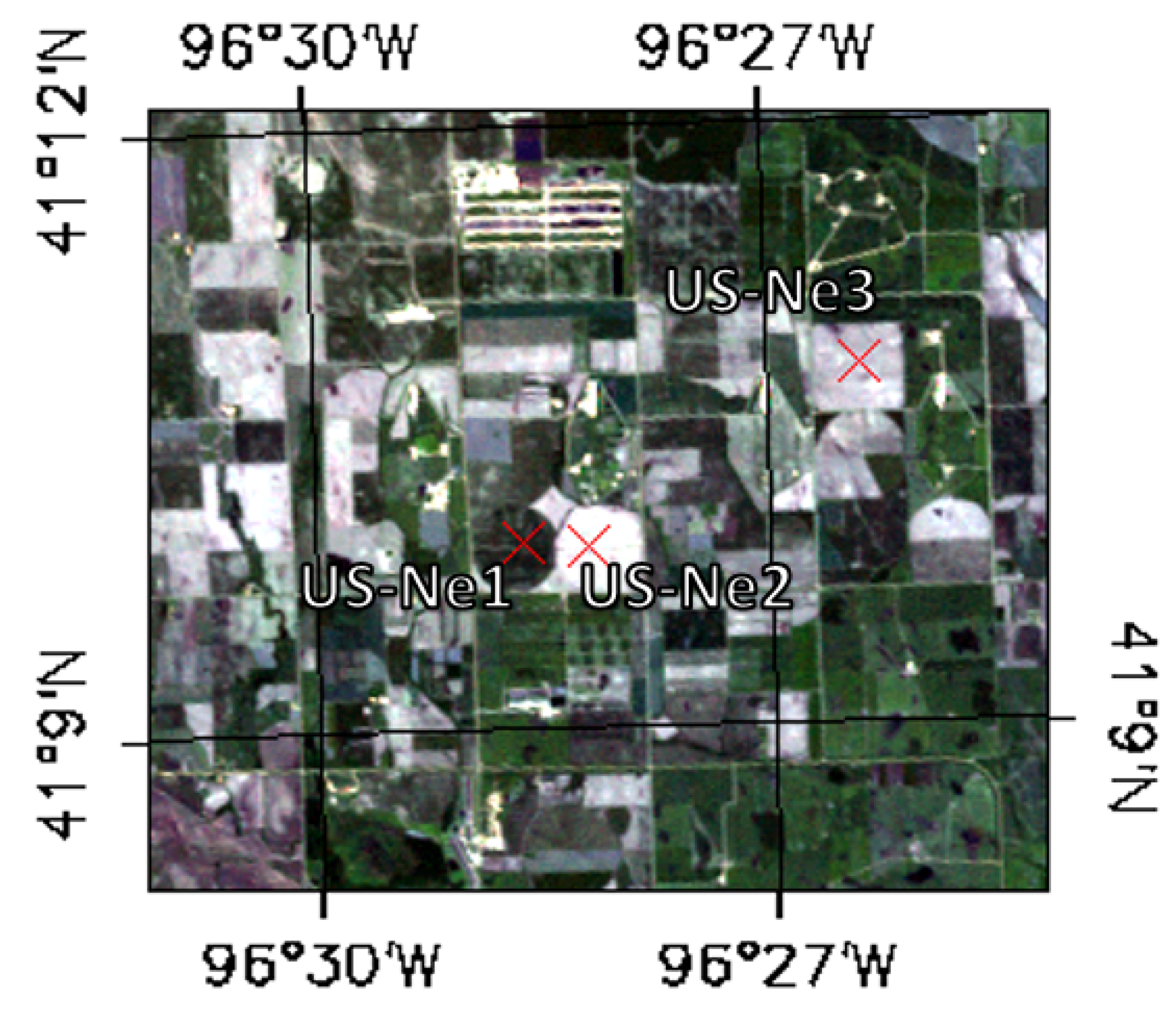
2.1. Test Site Description and Ground-Based Data Collection
2.2. Remote Sensing Data and Products
2.2.1. MISR Observations
2.2.2. The JRC-TIP MISR Product
2.2.3. The JRC MERIS FAPAR Product
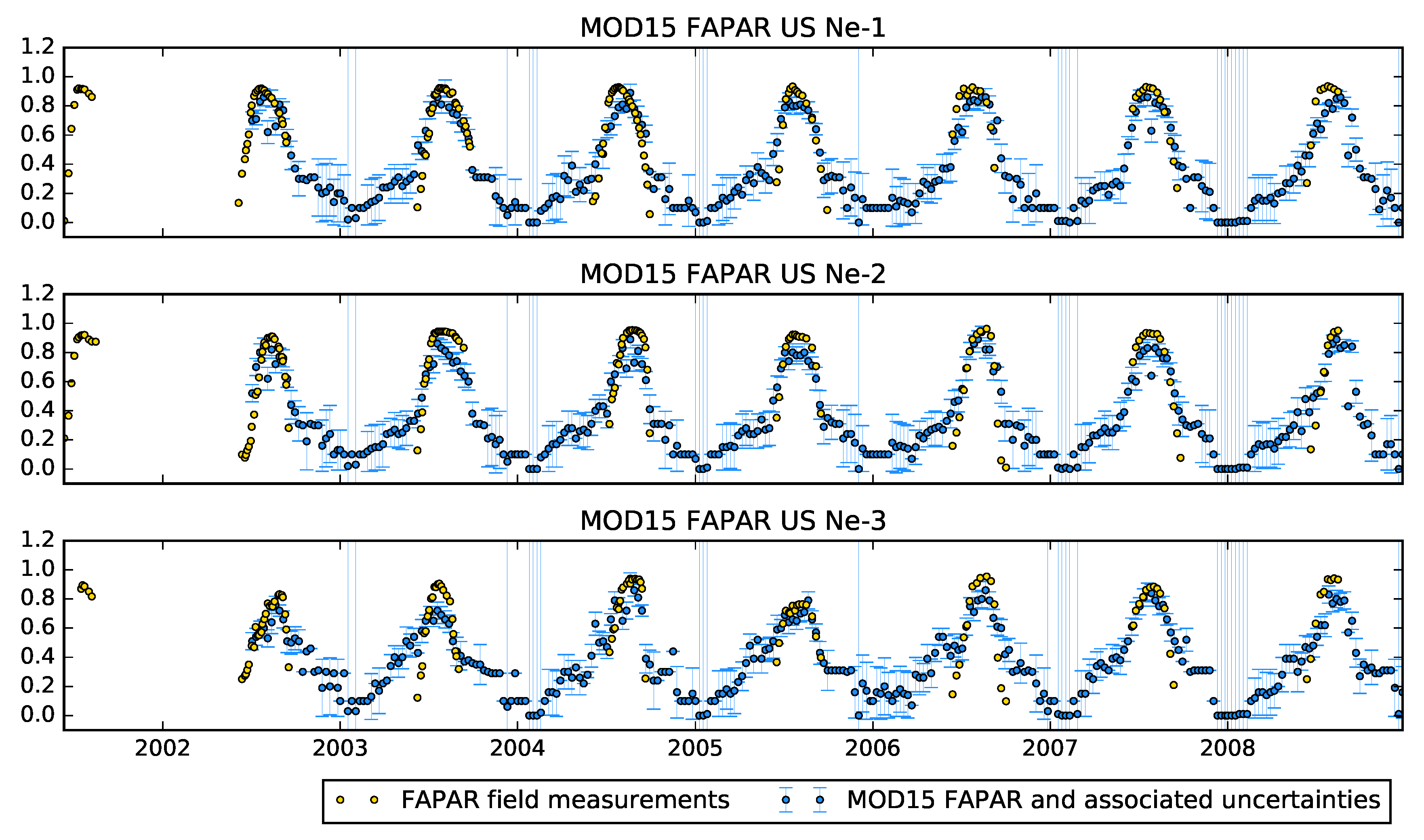
2.2.4. The MODIS FAPAR Product
3. Methods
3.1. The EO-LDAS Approach
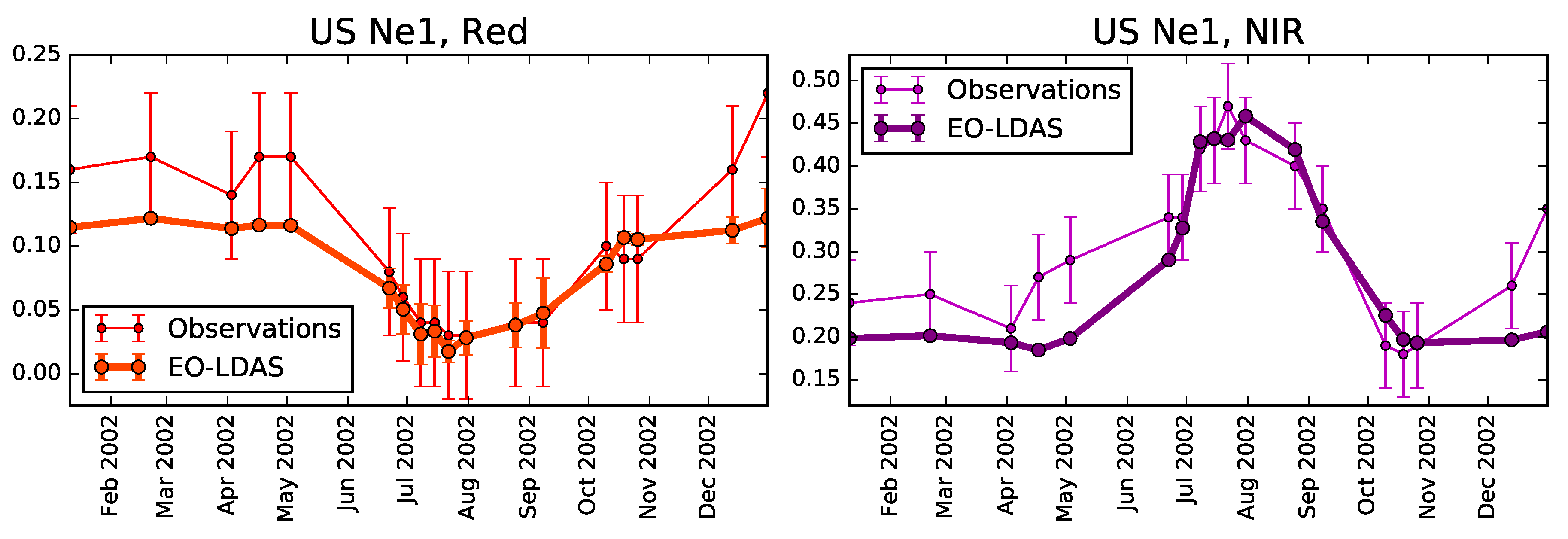
3.2. Fit to Observations
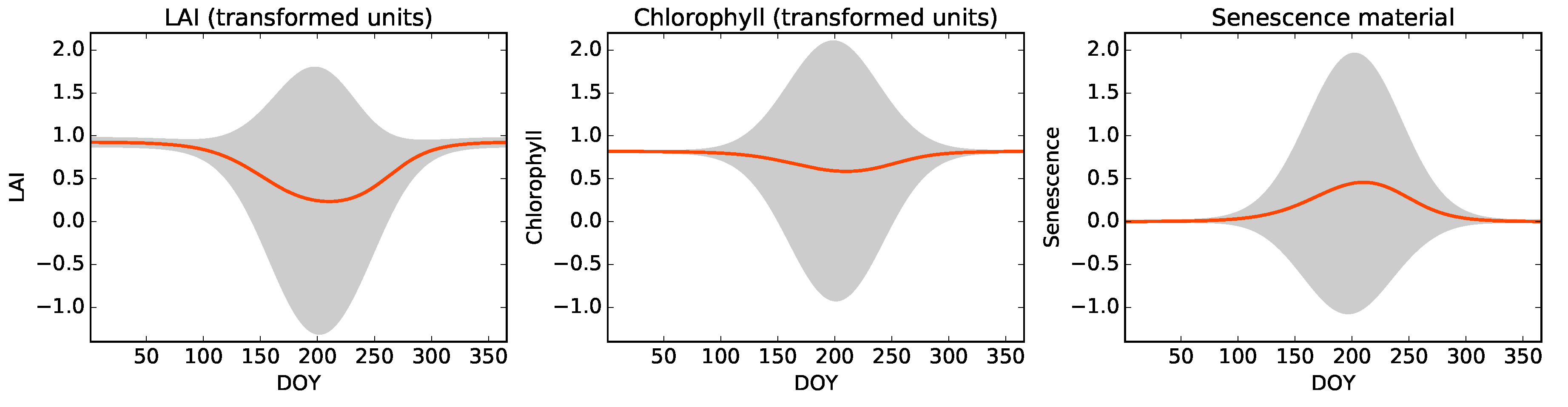
3.3. The Prior
3.4. Temporal Regularisation
3.5. Gaussian Process Emulators
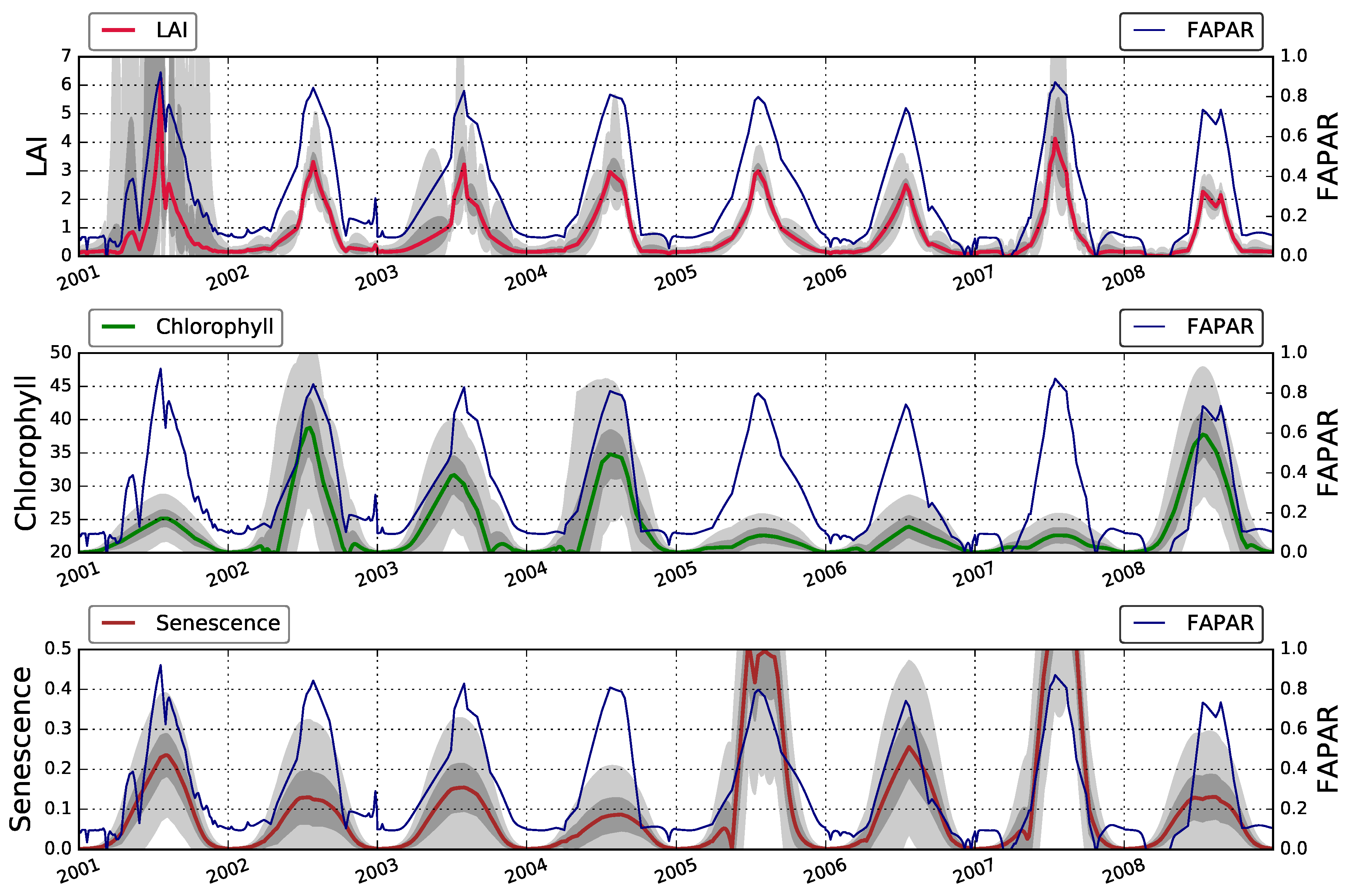
3.6. FAPAR
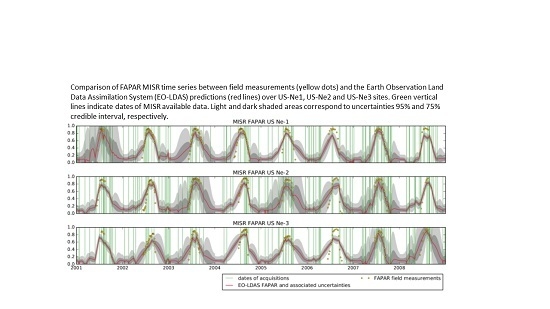
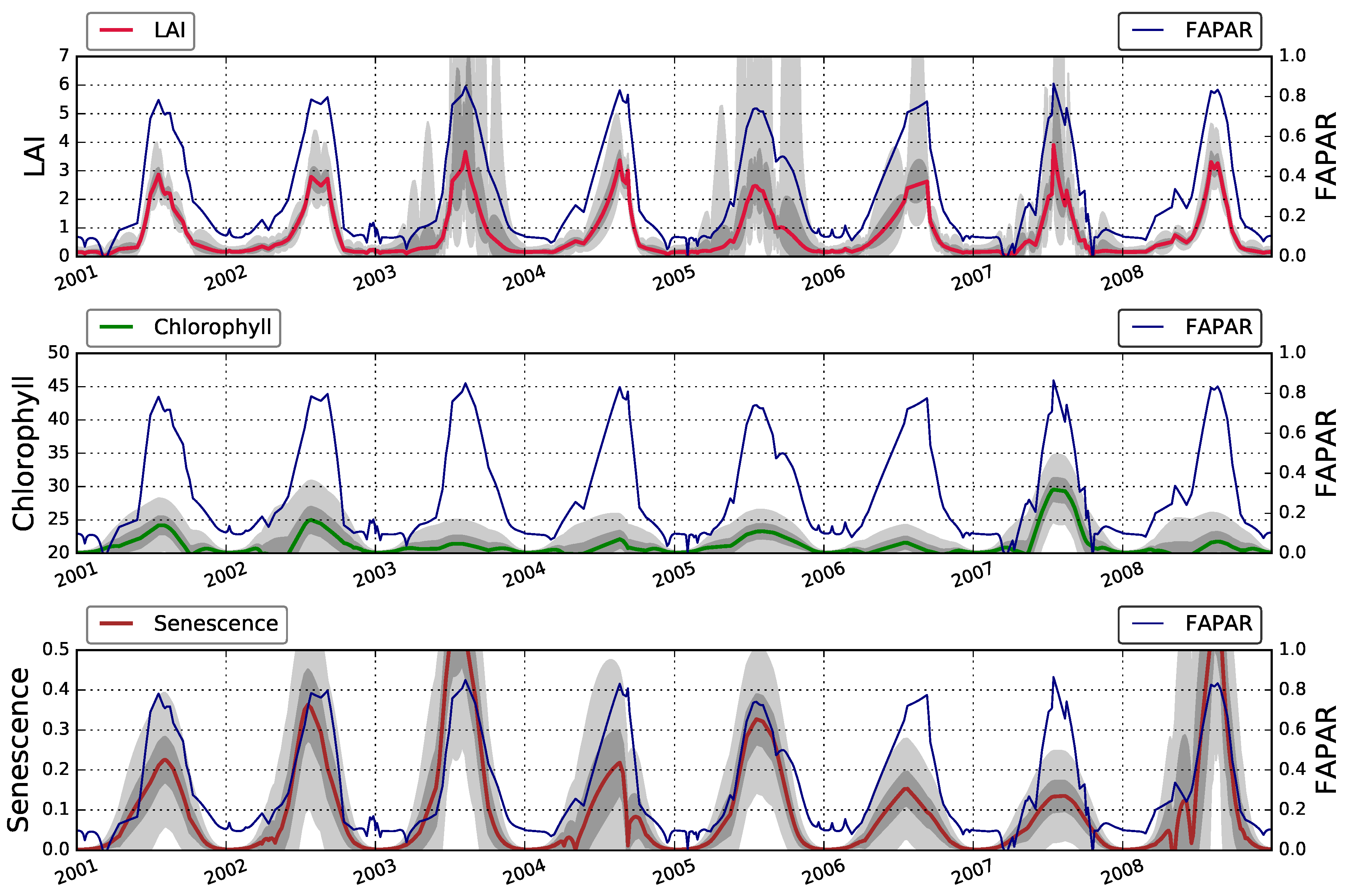
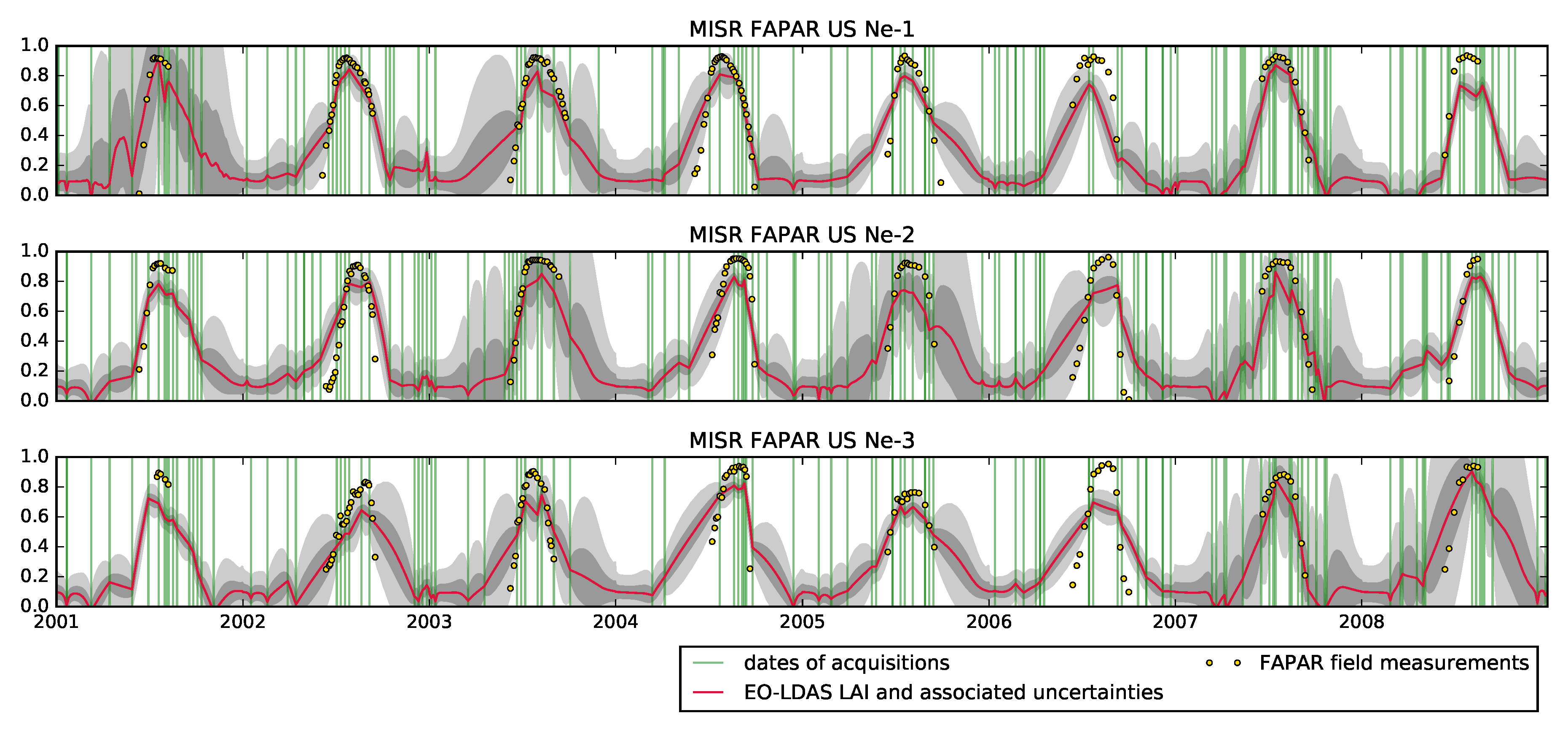
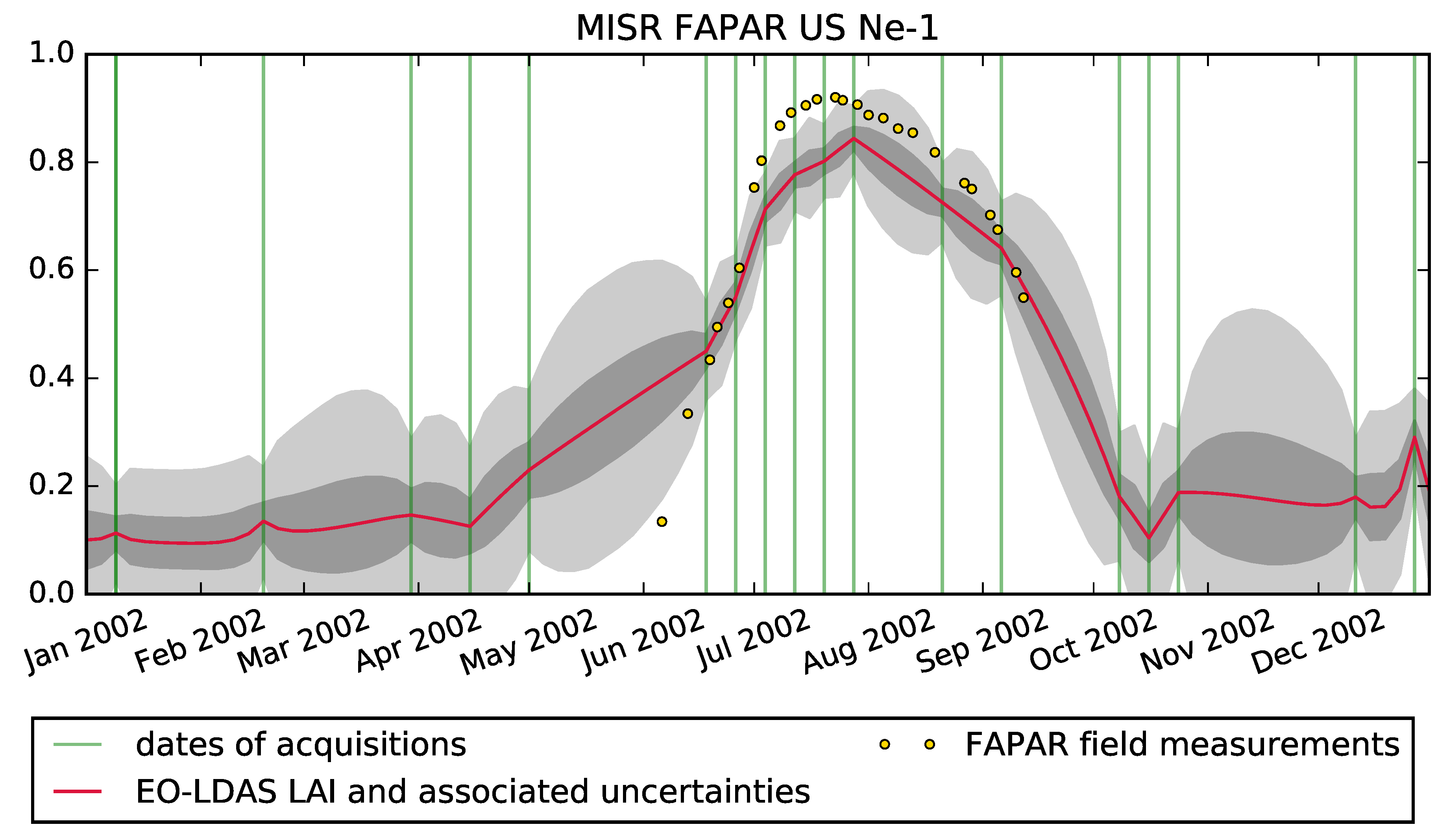
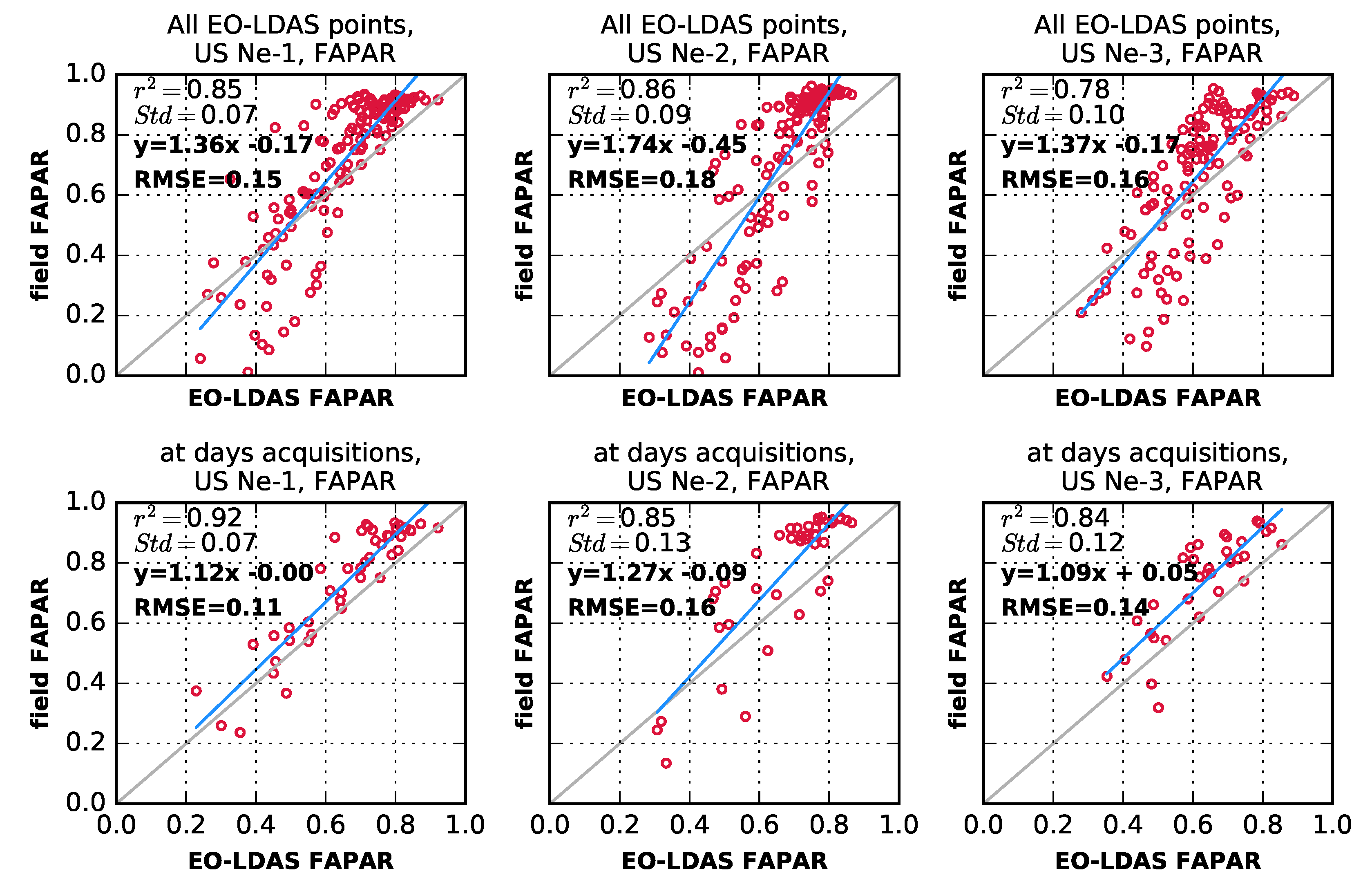
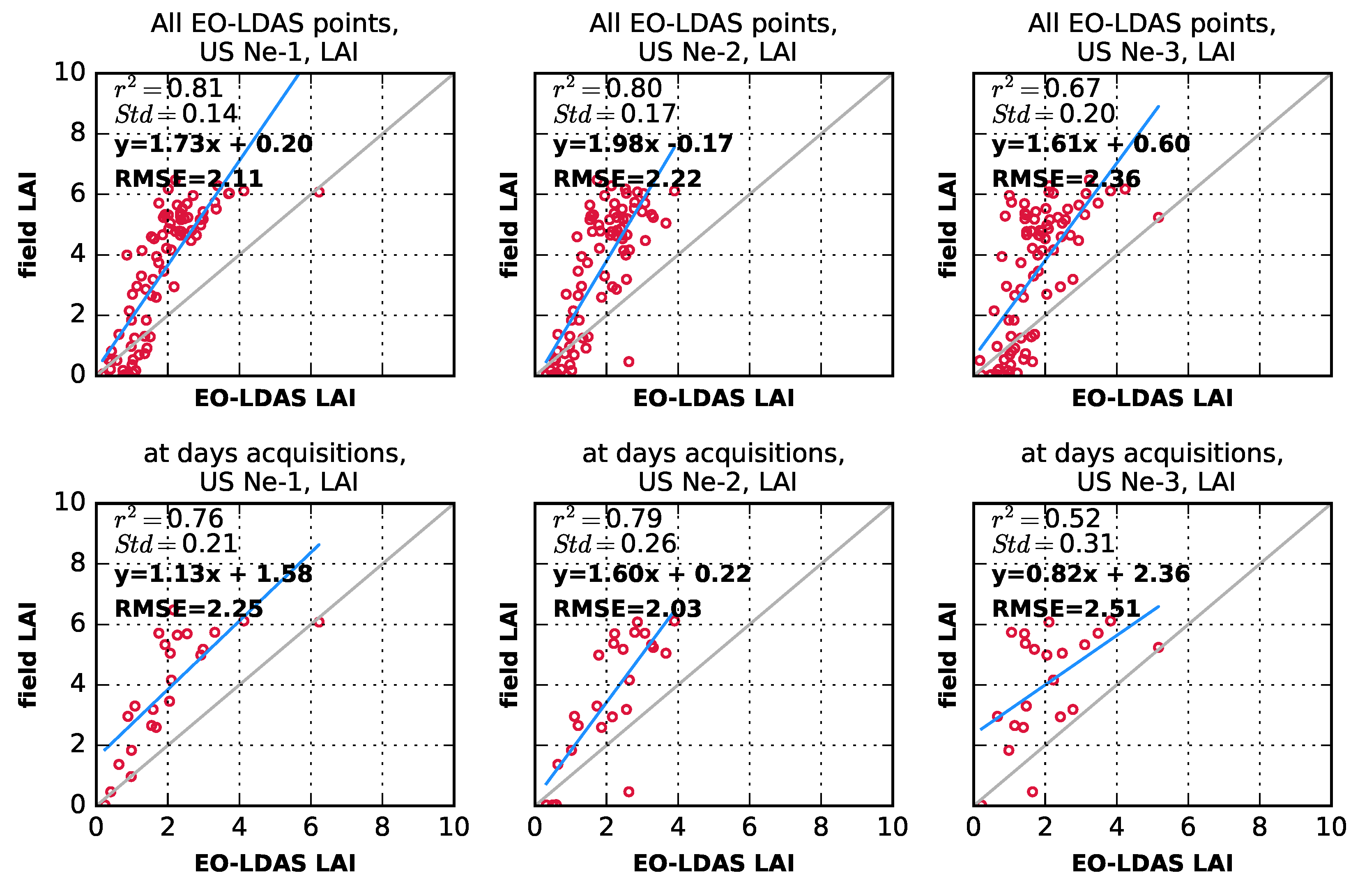
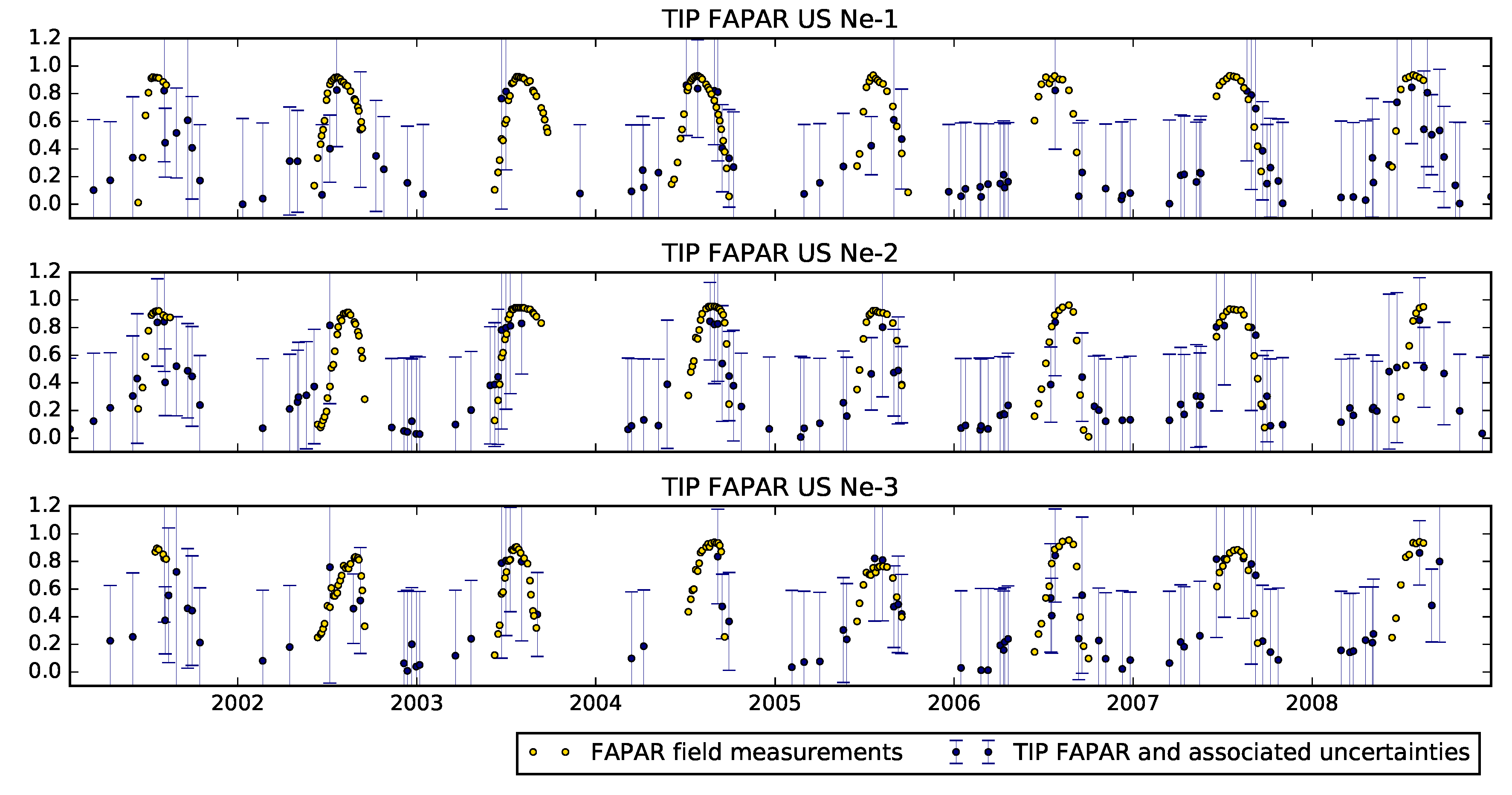
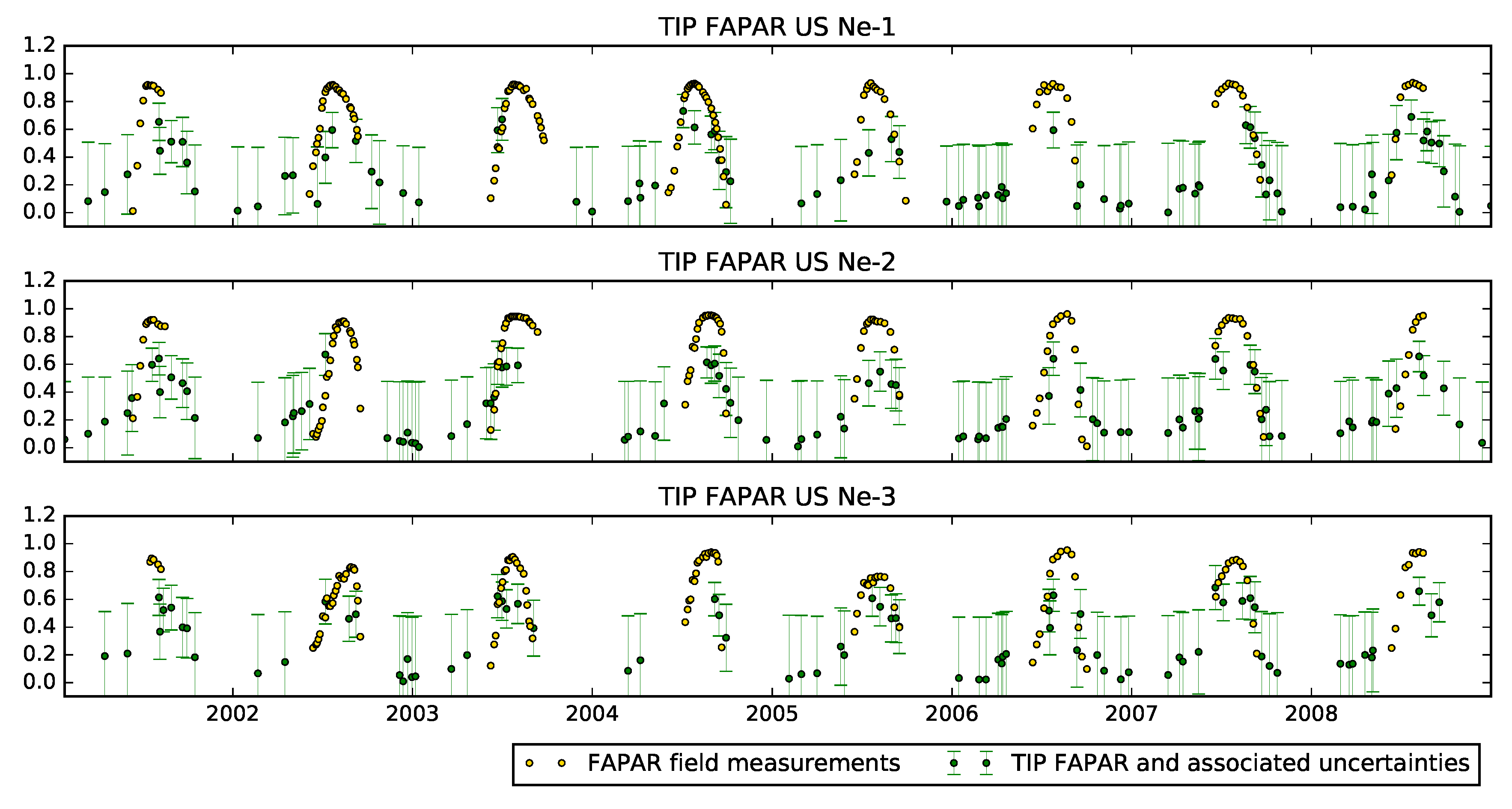
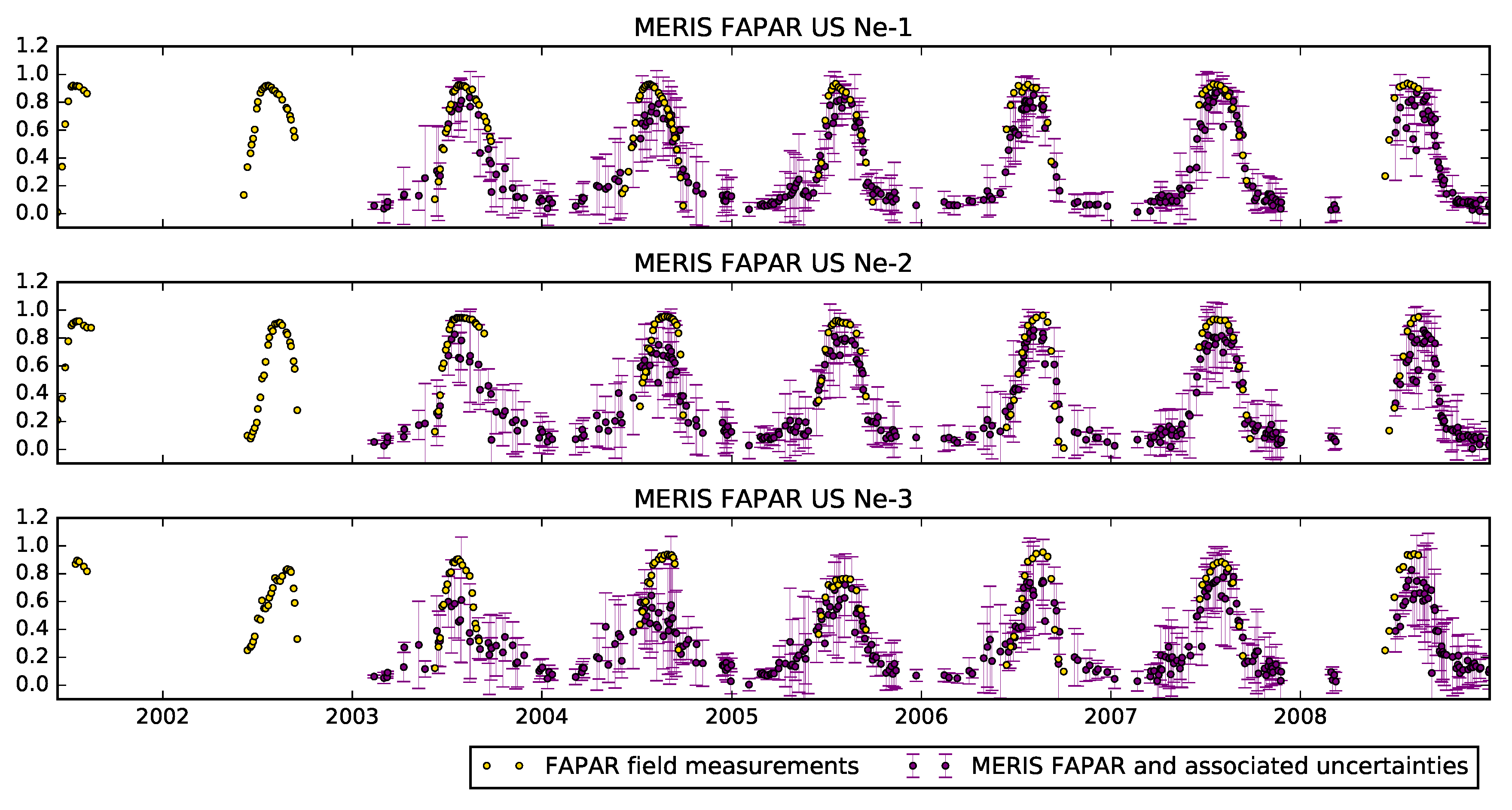
4. Results
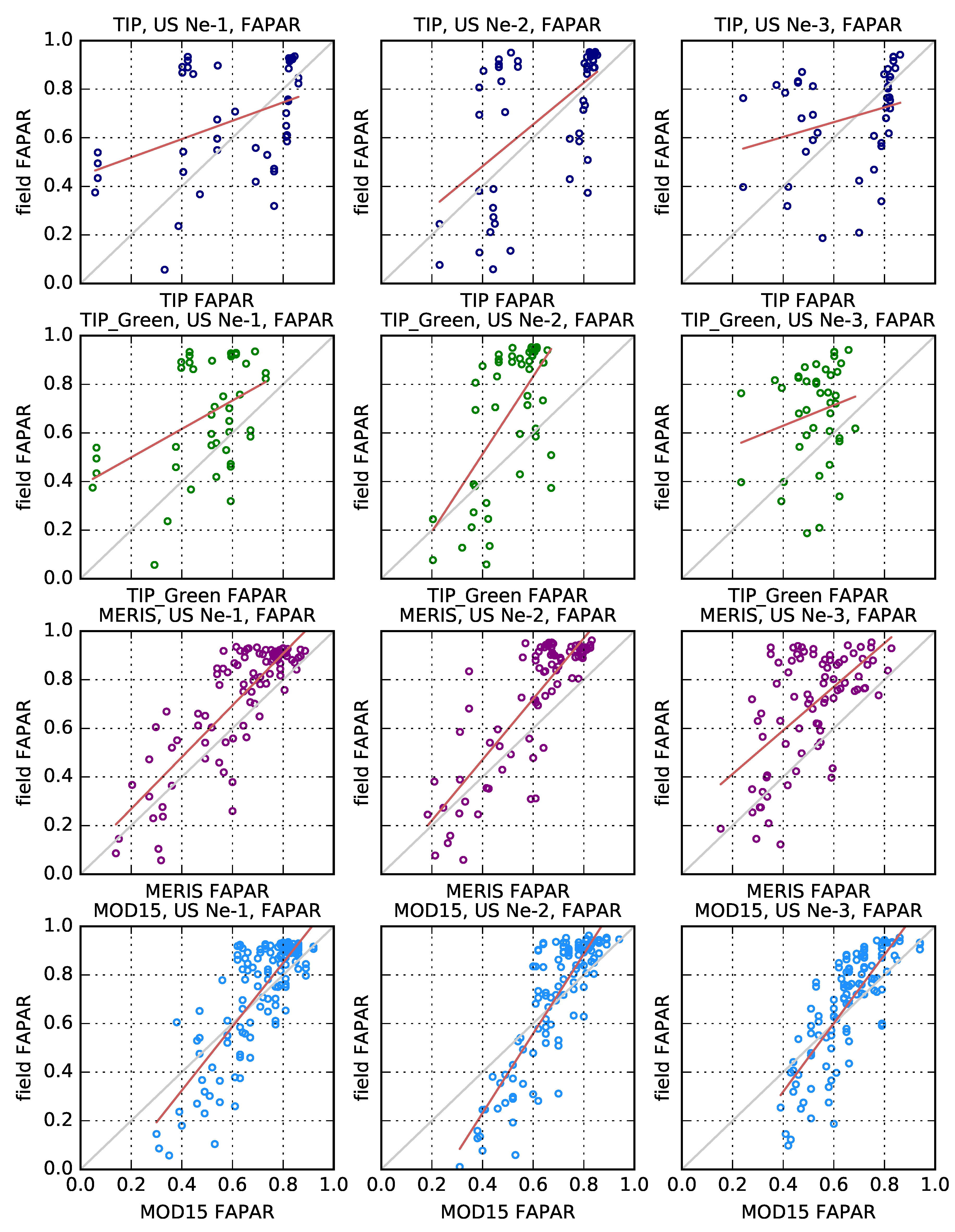
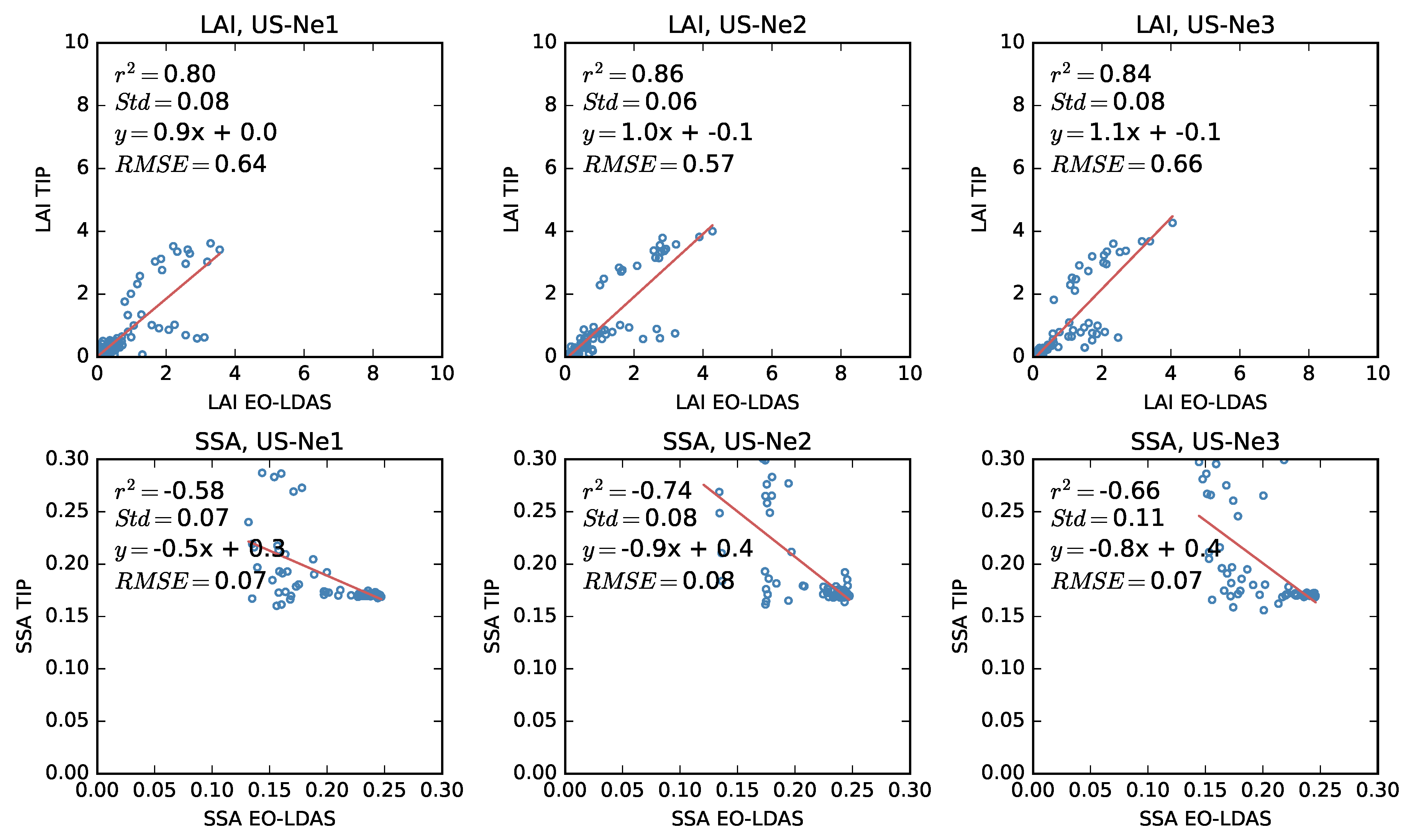
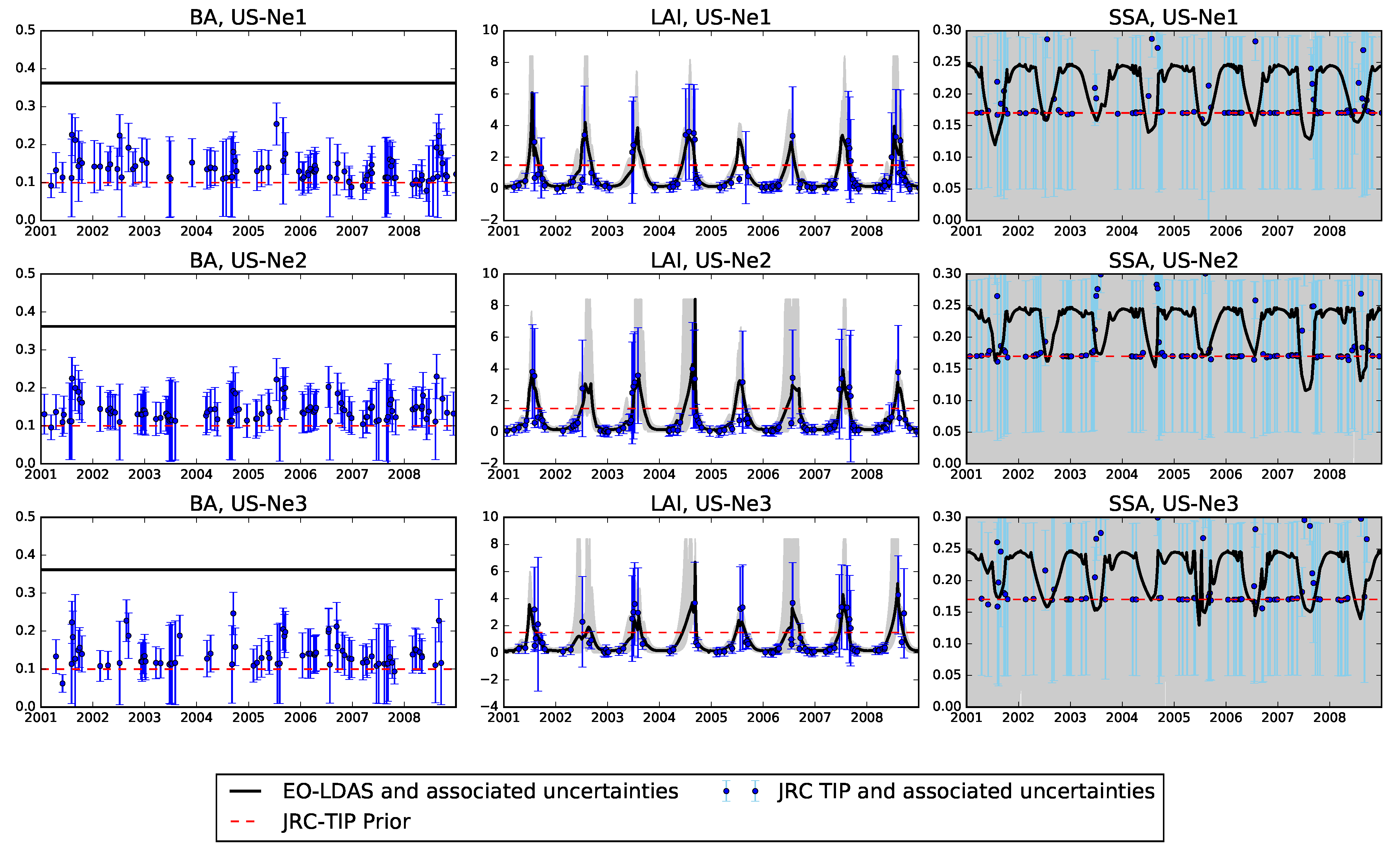
4.1. The JRC-TIP Results
4.2. The JRC MERIS Product
4.3. The MODIS FAPAR/LAI Product
5. Discussion
6. Concluding Remarks
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Global Terrestrial Observing System (GTOS). Terrestrial Essential Climate Variables for Climate Change Assessment, Mitigation and Adaptation; Technical Report; Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO): Rome, Italy, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Gower, S.T.; Kucharik, C.J.; Norman, J.M. Direct and Indirect Estimation of Leaf Area Index, fAPAR, and Net Primary Production of Terrestrial Ecosystems. Remote Sens. Environ. 1999, 70, 29–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gobron, N.; Pinty, B.; Mélin, F.; Taberner, M.; Verstraete, M.M.; Belward, A.; Lavergne, T.; Widlowski, J. The state of vegetation in Europe following the 2003 drought. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2005, 26, 2013–2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senna, M.; Costa, M.; Shimabukuro, Y. Fraction of photosynthetically active radiation absorbed by Amazon tropical forest: A comparison of field measurements, modeling, and remote sensing. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2005, 110, G01008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verstraete, M.M.; Gobron, N.; Aussedat, O.; Robustelli, M.; Pinty, B.; Widlowski, J.L.; Taberner, M. An automatic procedure to identify key vegetation phenology events using the JRC-FAPAR products. Adv. Space Res. 2008, 41, 1773–1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coops, N.; Wulder, M.; Duro, D.; Han, T.; Berry, S. The development of a Canadian dynamic habitat index using multi-temporal satellite estimates of canopy light absorbance. Ecol. Indic. 2008, 8, 754–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaminski, T.; Rayner, P.J.; Voßbeck, M.; Scholze, M.; Koffi, E. Observing the continental-scale carbon balance: Assessment of sampling complementarity and redundancy in a terrestrial assimilation system by means of quantitative network design. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2012, 12, 7867–7879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loew, A.; van Bodegom, P.M.; Widlowski, J.L.; Otto, J.; Quaife, T.; Pinty, B.; Raddatz, T. Do we (need to) care about canopy radiation schemes in DGVMs? Caveats and potential impacts. Biogeosciences 2014, 11, 1873–1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, M.; Baret, F.; Garrigues, S.; Lacaze, R. LAI and fAPAR CYCLOPES global products derived from VEGETATION. Part 2: Validation and comparison with MODIS collection 4 products. Remote Sens. Environ. 2007, 110, 317–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Román, M.O.; Schaaf, C.B.; Lewis, P.; Gao, F.; Anderson, G.P.; Privette, J.L.; Strahler, A.H.; Woodcock, C.E.; Barnsley, M. Assessing the coupling between surface albedo derived from MODIS and the fraction of diffuse skylight over spatially-characterized landscapes. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 738–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Odorico, P.; Gonsamo, A.; Pinty, B.; Gobron, N.; Coops, N.; Mendez, E.; Schaepman, M.E. Intercomparison of fraction of absorbed photosynthetically active radiation products derived from satellite data over Europe. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 142, 141–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Global Climate Observing System (GCOS). The Second Report on the Adequacy of the Global Observing Systems for Climate in Support of the UNFCCC. Available online: https://www.wmo.int/pages/prog/gcos/Publications/gcos-822AR.pdf (accessed on 26 June 2017).
- Kimes, D.; Knyazikhin, Y.; Privette, J.; Abuelgasim, A.; Gao, F. Inversion methods for physically based models. Remote Sens. Rev. 2000, 18, 381–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadamard, J. Sur les problèmes aux dérivées partielles et leur signification physique. Princet. Univ. Bull. 1902, 13, 49–52. [Google Scholar]
- Combal, B.; Baret, F.; Weiss, M.; Trubuil, A.; Mace, D.; Pragnere, A.; Myneni, R.; Knyazikhin, Y.; Wang, L. Retrieval of canopy biophysical variables from bidirectional reflectance using prior information to solve the ill-posed inverse problem. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 84, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, P.; Gómez-Dans, J.; Kaminski, T.; Settle, J.; Quaife, T.; Gobron, N.; Styles, J.; Berger, M. An Earth Observation Land Data Assimilation System (EO-LDAS). Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 120, 219–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinty, B.; Jung, M.; Kaminski, T.; Lavergne, T.; Mund, M.; Plummer, S.; Thomas, E.; Widlowski, J.L. Evaluation of the JRC-TIP 0.01° products over a mid-latitude deciduous forest site. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 3567–3581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaminski, T.; Mathieu, P.P. Reviews and syntheses: Flying the satellite into your model: On the role of observation operators in constraining models of the Earth system and the carbon cycle. Biogeosciences 2017, 14, 2343–2357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaminski, T.; Pinty, B.; Voßbeck, M.; Lopatka, M.; Gobron, N.; Robustelli, M. Consistent retrieval of land surface radiation products from EO, including traceable uncertainty estimates. Biogeosciences 2017, 14, 2527–2541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, P.; Gomez-Dans, J.; Kaminski, T.; Settle, J.; Quaife, T.; Gobron, N.; Styles, J.; Berger, M. Data assimilation of Sentinel-2 observations: Preliminary results from EO-LDAS and outlook. In Proceedings of the First Sentinel-2 Preparatory Symposium, Frascati, Italy, 23–27 April 2012; Volume ESA SP-707. [Google Scholar]
- Gómez-Dans, J.L.; Lewis, P.E.; Disney, M. Efficient Emulation of Radiative Transfer Codes Using Gaussian Processes and Application to Land Surface Parameter Inferences. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 119. [Google Scholar]
- Gitelson, A.A.; Peng, Y.; Huemmrich, K.F. Relationship between fraction of radiation absorbed by photosynthesizing maize and soybean canopies and NDVI from remotely sensed data taken at close range and from MODIS 250 m resolution data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 147, 108–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myneni, R.; Knyazikhin, Y.; Park, T. MCD15A2H MODIS/Terra+Aqua Leaf Area Index/FPAR 8-day L4 Global 500 m SIN Grid V006. NASA EOSDIS Land Processes DAAC, 2015. Available online: https://doi.org/10.5067/MODIS/MCD15A2H.006 (acccessed on 26 June 2017).
- Pinty, B.; Widlowski, J.L.; Gobron, N.; Verstraete, M.M.; Diner, D.J.; Member, A. Uniqueness of Multiangular Measurements—Part I: An Indicator of Subpixel Surface Heterogeneity From MISR. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2002, 40, 1560–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deschamps, P.Y.; Breon, F.M.; Leroy, M.; Podaire, A.; Bricaud, A.; Buriez, J.C.; Seze, G. The POLDER mission: Instrument characteristics and scientific objectives. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1994, 32, 598–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SLSTR Instrument. Available online: https://sentinel.esa.int/web/sentinel/technical-guides/sentinel-3-slstr/instrument/description (accessed on 20 June 2017).
- Diner, D.J.; Beckert, J.C.; Reilly, T.H.; Bruegge, C.J.; Conel, J.E.; Kahn, R.A.; Martonchik, J.V.; Ackerman, T.P.; Davies, R.; Gerstl, S.A.W.; et al. Multi-angle Imaging SpectroRadiometer (MISR) instrument description and experiment overview. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1998, 36, 1072–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knyazikhin, Y.; Martonchik, J.V.; Myneni, R.B.; Diner, D.J.; Running, S.W. Synergistic algorithm for estimating vegetation canopy leaf area index and fraction of absorbed photosynthetically active radiation from MODIS and MISR data. J. Geophys. Res. 1998, 103, 32257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gobron, N.; Pinty, B.; Verstraete, M.M.; Martonchik, J.V.; Knyazikhin, Y.; Diner, D.J. Potential of multiangular spectral measurements to characterize land surfaces: Conceptual approach and exploratory application. J. Geophys. Res. 2000, 105, 17539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widlowski, J.L.; Pinty, B.; Gobron, N.; Verstraete, M.M.; Diner, D.J.; Davis, A.B. Canopy structure parameters derived from multi-angular remote sensing data for terrestrial carbon studies. Clim. Chang. 2004, 67, 403–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurent, V.C.; Verhoef, W.; Clevers, J.G.; Schaepman, M.E. Inversion of a coupled canopy-atmosphere model using multi-angular top-of-atmosphere radiance data: A forest case study. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 2603–2612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinty, B.; Lavergne, T.; Voßbeck, M.; Kaminski, T.; Aussedat, O.; Giering, R.; Gobron, N.; Taberner, M.; Verstraete, M.M.; Widlowski, J.L. Retrieving surface parameters for climate models from Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS)-Multiangle Imaging Spectroradiometer (MISR) albedo products. J. Geophys. Res. 2007, 112, D10116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verstraete, M.M.; Member, S.; Hunt, L.A.; Scholes, R.J.; Clerici, M.; Pinty, B.; Nelson, D.L. Generating 275-m Resolution Land Surface Products From the Multi-Angle Imaging SpectroRadiometer Data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2012, 50, 3980–3990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinty, B.; Lavergne, T.; Dickinson, R.E.; Widlowski, J.L.; Gobron, N.; Verstraete, M.M. Simplifying the Interaction of Land Surfaces with Radiation for Relating Remote Sensing Products to Climate Models. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2006, 111, D02116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinty, B.; Clerici, M.; Andredakis, I.; Kaminski, T.; Taberner, M.; Verstraete, M.M.; Gobron, N.; Plummer, S.; Widlowski, J.L. Exploiting the MODIS albedos with the Two-stream Inversion Package (JRC-TIP): 2. Fractions of transmitted and absorbed fluxes in the vegetation and soil layers. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2011, 116, D09106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viña, A.; Gitelson, A.A. New developments in the remote estimation of the fraction of absorbed photosynthetically active radiation in crops. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2005, 32, L17403. [Google Scholar]
- MISR Web Site. Available online: http://www-misr.jpl.nasa.gov/ (accessed on 27 January 2017).
- Giering, R.; Kaminski, T. Recipes for adjoint code construction. ACM Trans. Math. Softw. 1998, 24, 437–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gobron, N.; Pinty, B.; Verstraete, M.; Widlowski, J.L. Advanced vegetation indices optimized for up-coming sensors: Design, performance, and applications. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2000, 38, 2489–2505. [Google Scholar]
- Gobron, N.; Pinty, B.; Verstraete, M.; Govaerts, Y. The MERIS Global Vegetation Index (MGVI): Description and preliminary application. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1999, 20, 1917–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gobron, N.; Pinty, B.; Aussedat, O.; Taberner, M.; Faber, O.; Mélin, F.; Lavergne, T.; Robustelli, M.; Snoeij, P. Uncertainty estimates for the FAPAR operational products derived from MERIS—Impact of top-of-atmosphere radiance uncertainties and validation with field data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 1871–1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gobron, N. Uncertainties assessment for MERIS/OLCI FAPAR. In Proceedings of the 2015 ESA Sentinel-3 for Science Workshop, Venice, Italy, 2–5 June 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, W.; Tan, B.; Huang, D.; Rautiainen, M.; Shabanov, N.V.; Wang, Y.; Privette, J.L.; Huemmrich, K.F.; Fensholt, R.; Sandholt, I.; et al. MODIS leaf area index products: From validation to algorithm improvement. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2006, 44, 1885–1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zupanski, D. A general weak constraint applicable to operational 4DVAR data assimilation systems. Mon. Weather Rev. 1997, 125, 2274–2292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Dans, J. The eoldas_ng Python Library. Available online: http://github.com/jgomezdans/eoldas_ng (accessed on 19 March 2017).
- Verhoef, W.; Bach, H. Coupled soil—Leaf-canopy and atmosphere radiative transfer modeling to simulate hyperspectral multi-angular surface reflectance and TOA radiance data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2007, 109, 166–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quaife, T.; Lewis, P. Temporal Constraints on Linear BRDF Model Parameters. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2010, 48, 2445–2450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez-Dans, J.L.; Lewis, P. EOLDAS Users’ Documentation. Available online: http://jgomezdans.github.io/eoldasrelease/EOLDASUsersGuide.pdf (accessed on 26 June 2017).
- Atzberger, C.; Richter, K. Spatially constrained inversion of radiative transfer models for improved LAI mapping from future Sentinel-2 imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 120, 208–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atzberger, C. Object-based retrieval of biophysical canopy variables using artificial neural nets and radiative transfer models. Remote Sens. Environ. 2004, 93, 53–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yang, C.; Li, X. Regularizing kernel-based BRDF model inversion method for ill-posed land surface parameter retrieval using smoothness constraint. J. Geophys. Res. 2008, 113, D13101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurent, V.C.; Verhoef, W.; Damm, A.; Schaepman, M.E.; Clevers, J.G. A Bayesian object-based approach for estimating vegetation biophysical and biochemical variables from APEX at-sensor radiance data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 139, 6–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chernetskiy, M.; Gomez-Dans, J.; Lewis, P. Validation of the Earth Observation Land Data Assimilation System by the field data of ESA SPARC field campaign. In Proceedings of the 2013 ESA Living Planet Symposium, Edinburgh, UK, 9–13 September 2013; Volume ESA SP-722, pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Mousivand, A.; Menenti, M.; Gorte, B.; Verhoef, W. Multi-temporal, multi-sensor retrieval of terrestrial vegetation properties from spectral–directional radiometric data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 158, 311–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quaife, T.; Lewis, P.; De Kauwe, M.; Williams, M.; Law, B.; Disney, M.; Bowyer, P. Assimilating canopy reflectance data into an ecosystem model with an Ensemble Kalman Filter. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 1347–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thacker, W.C. The role of the Hessian matrix in fitting models to measurements. Geophys. Res. 1989, 94, 6177–6196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, M.; Baret, F.; Myneni, R.; Pragnère, A.; Knyazikhin, Y. Investigation of a model inversion technique to estimate canopy biophysical variables from spectral and directional reflectance data. Agronomie 2000, 20, 3–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gobron, N.; Pinty, B.; Verstraete, M.M.; Govaerts, Y. A semidiscrete model for the scattering of light by vegetation. J. Geophys. Res. 1997, 102, 9431–9446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacquemoud, S.; Baret, F. PROSPECT: A model of leaf optical properties spectra. Remote Sens. Environ. 1990, 34, 75–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, J. On the information content of soil reflectance spectra. Remote Sens. Environ. 1990, 33, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, P.S.A.; Atzberger, C.; Høgda, K.A.; Johansen, B.; Skidmore, A.K. Improved monitoring of vegetation dynamics at very high latitudes: A new method using MODIS NDVI. Remote Sens. Environ. 2006, 100, 321–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shunlin, L.; Zhiqiang, X. Global Land Surface Products: Leaf Area Index Product Data Collection (1985–2010). 2012. Available online: http://glcf.umd.edu/data/lai/ (accessed on 26 June 2017).
- Zarco-Tejada, P.J.; Rueda, C.; Ustin, S. Water content estimation in vegetation with MODIS reflectance data and model inversion methods. Remote Sens. Environ. 2003, 85, 109–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verrelst, J.; Camps-Valls, G.; Muñoz-Marí, J.; Rivera, J.P.; Veroustraete, F.; Clevers, J.G.; Moreno, J. Optical remote sensing and the retrieval of terrestrial vegetation bio-geophysical properties—A review. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2015, 108, 273–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camps-Valls, G.; Verrelst, J.; Munoz-Mari, J.; Laparra, V.; Mateo-Jimenez, F.; Gomez-Dans, J. A Survey on Gaussian Processes for Earth-Observation Data Analysis: A Comprehensive Investigation. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Mag. 2016, 4, 58–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Dans, J.; Lewis, P. gp_emulator: A Python Library for Emulating Radiative Transfer Codes. 2016. Available online: http://jgomezdans.github.io/gp_emulator/ (accessed on 26 June 2017).
- Earth System Research Laboratory: Solar Calculation Details. Available online: http://www.esrl.noaa.gov/gmd/grad/solcalc/calcdetails.html (accessed on 30 January 2017).
- Weiss, M.; Baret, F.; Smith, G.J.; Jonckheere, I.; Coppin, P. Review of methods for in situ leaf area index (LAI) determination Part II. Estimation of LAI, errors and sampling. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2004, 121, 37–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gobron, N.; Pinty, B.; Verstraete, M.M. Theoretical limits to the estimation of the leaf area index on the basis of visible and near-infrared remote sensing data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1997, 35, 1438–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Disney, M.; Muller, J.P.; Kharbouche, S.; Kaminski, T. A New Global fAPAR and LAI Dataset Derived from Optimal Albedo Estimates: Comparison with MODIS Products. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez-Dans, J.; Lewis, P.; Disney, M.; Roy, D.; Quaife, T.; Wooster, M. Edge-Preserving Data Assimilation for Fire Monitoring Using Optical Data. Available online: https://ftp.space.dtu.dk/pub/Ioana/papers/s252gome.pdf (accessed on 26 June 2017).
- Walthall, C.L.; Norman, J.M.; Welles, J.M.; Campbell, G.; Blad, B.L. Simple equation to approximate the bidirectional reflectance from vegetative canopies and bare soil surfaces. Appl. Opt. 1985, 24, 383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hapke, B. Bidirectional reflectance spectroscopy: 1. Theory. J. Geophys. Res. 1981, 86, 3039–3054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.; Townshend, J.R. A modified hapke model for soil bidirectional reflectance. Remote Sens. Environ. 1996, 55, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S. Numerical experiments on the spatial scaling of land surface albedo and leaf area index. Remote Sens. Rev. 2000, 19, 225–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfeifer, M.; Disney, M.; Quaife, T.; Marchant, R. Terrestrial ecosystems from space: A review of earth observation products for macroecology applications. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2012, 21, 603–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kira, O.; Nguy-Robertson, A.L.; Arkebauer, T.J.; Linker, R.; Gitelson, A.A. Toward Generic Models for Green LAI Estimation in Maize and Soybean: Satellite Observations. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguy-Robertson, A.L.; Gitelson, A.A. Algorithms for estimating green leaf area index in C3 and C4 crops for MODIS, Landsat TM/ETM+, MERIS, Sentinel MSI/OLCI, and Venμs sensors. Remote Sens. Lett. 2015, 6, 360–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morisette, J.T.; Baret, F.; Privette, J.L.; Myneni, R.B.; Nickeson, J.E.; Garrigues, S.; Shabanov, N.V.; Weiss, M.; Fernandes, R.A.; Leblanc, S.G.; et al. Validation of global moderate-resolution LAI products: A framework proposed within the CEOS land product validation subgroup. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2006, 44, 1804–1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baret, F.; Weiss, M.; Allard, D.; Garrigue, S.; Leroy, M.; Jeanjean, H.; Fernandes, R.; Myneni, R.; Privette, J.; Morisette, J.; et al. VALERI: A network of sites and a methodology for the validation of medium spatial resolution land satellite products. Remote Sens. Environ. 2005, 76, 36–39. [Google Scholar]
- Garrigues, S.; Lacaze, R.; Baret, F.; Morisette, J.T.; Weiss, M.; Nickeson, J.E.; Fernandes, R.; Plummer, S.; Shabanov, N.V.; Myneni, R.B.; et al. Validation and intercomparison of global Leaf Area Index products derived from remote sensing data. J. Geophys. Res. 2008, 113, G02028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Povey, A.C.; Grainger, R.G. Known and unknown unknowns: uncertainty estimation in satellite remote sensing. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2015, 8, 4699–4718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinnington, E.M.; Casella, E.; Dance, S.L.; Lawless, A.S.; Morison, J.I.L.; Nichols, N.K.; Wilkinson, M.; Quaife, T.L. Investigating the role of prior and observation error correlations in improving a model forecast of forest carbon balance using Four-dimensional Variational data assimilation. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2016, 228–229, 299–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| S | A | mS | mA | wP | mP | b (log) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LAI | 175 | 245 | 0.04 | 0.05 | 0.15 | 4.22 | 200 | 30 | 0.25 |
| Leaf chlorophyll content | 175 | 245 | 0.04 | 0.05 | 1 | 90 | 200 | 40 | 0.05 |
| Proportion of senescence material | 175 | 245 | 0.04 | 0.05 | 0.001 | 0.7 | 200 | 70 | 0.05 |
| Name | Symbol | Units | Default or Prior Value | Lower Limit | Upper Limit | Prior STD (Transf. Units) | Transform |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Leaf Area | () | Dynamic | 0.02 | 8.4 | Dynamic | ||
| Index (LAI) | |||||||
| Canopy height | () | 1 | 0.05 | 10 | 1 | - | |
| Leaf radius | () | 0.1 | 0.01 | 0.1 | 1 | - | |
| Chlorophyll a,b | () | Dynamic | 20 | 51 | Dynamic | ||
| Proportion of | na | Dynamic | 0.001 | 1 | Dynamic | - | |
| senescent material | |||||||
| Leaf water | () | 0.0001 | 0.00002 | 0.092 | 1 | ||
| Dry matter | () | 0.00005 | 0.00001 | 0.012 | 1 | ||
| Leaf layers | N | na | 1.9 | 1 | 5 | 1 | - |
| Soil PC1 | na | 1.22 | 0.5 | 2 | 1 | - | |
| Soil PC2 | na | 1.32 | -1 | 1.5 | 1 | - | |
| Leaf angle | na | Spherical | - | ||||
| distribution | (Uniform) |
| Stat. Param | EO-LDAS All | EO-LDAS Obs. | TIP | TIP Gr. | MERIS | MCD15 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.85 | 0.92 | 0.41 | 0.45 | 0.83 | 0.80 | |
| 0.07 | 0.07 | 0.13 | 0.18 | 0.08 | 0.09 | |
| 1.36 | 1.12 | 0.38 | 0.58 | 1.06 | 1.31 | |
| −0.17 | −0.00 | 0.44 | 0.38 | 0.06 | −0.20 | |
| 0.15 | 0.11 | 0.26 | 0.28 | 0.16 | 0.14 |
| Stat. Param | EO-LDAS All | EO-LDAS Obs. | TIP | TIP Gr. | MERIS | MCD15 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.86 | 0.85 | 0.59 | 0.64 | 0.83 | 0.86 | |
| 0.09 | 0.13 | 0.17 | 0.27 | 0.09 | 0.09 | |
| 1.74 | 1.27 | 0.86 | 1.60 | 1.25 | 1.64 | |
| −0.45 | −0.09 | 0.14 | −0.13 | −0.03 | −0.42 | |
| 0.18 | 0.16 | 0.24 | 0.29 | 0.19 | 0.16 |
| Stat. Param | EO-LDAS All | EO-LDAS Obs. | TIP | TIP Gr. | MERIS | MCD15 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.78 | 0.84 | 0.28 | 0.21 | 0.59 | 0.80 | |
| 0.10 | 0.12 | 0.17 | 0.31 | 0.14 | 0.10 | |
| 1.37 | 1.09 | 0.30 | 0.42 | 0.90 | 1.41 | |
| −0.17 | 0.05 | 0.48 | 0.46 | 0.23 | −0.24 | |
| 0.16 | 0.14 | 0.23 | 0.26 | 0.26 | 0.14 |
| Field | MISR | MODIS | MERIS |
|---|---|---|---|
| US-Ne1 | |||
| US-Ne2 | |||
| US-Ne3 | |||
| Years | 2001–2008 | 2001–2008 | 2003–2008 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chernetskiy, M.; Gómez-Dans, J.; Gobron, N.; Morgan, O.; Lewis, P.; Truckenbrodt, S.; Schmullius, C. Estimation of FAPAR over Croplands Using MISR Data and the Earth Observation Land Data Assimilation System (EO-LDAS). Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 656. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9070656
Chernetskiy M, Gómez-Dans J, Gobron N, Morgan O, Lewis P, Truckenbrodt S, Schmullius C. Estimation of FAPAR over Croplands Using MISR Data and the Earth Observation Land Data Assimilation System (EO-LDAS). Remote Sensing. 2017; 9(7):656. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9070656
Chicago/Turabian StyleChernetskiy, Maxim, Jose Gómez-Dans, Nadine Gobron, Olivier Morgan, Philip Lewis, Sina Truckenbrodt, and Christiane Schmullius. 2017. "Estimation of FAPAR over Croplands Using MISR Data and the Earth Observation Land Data Assimilation System (EO-LDAS)" Remote Sensing 9, no. 7: 656. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9070656
APA StyleChernetskiy, M., Gómez-Dans, J., Gobron, N., Morgan, O., Lewis, P., Truckenbrodt, S., & Schmullius, C. (2017). Estimation of FAPAR over Croplands Using MISR Data and the Earth Observation Land Data Assimilation System (EO-LDAS). Remote Sensing, 9(7), 656. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9070656