Abstract
Lakes are a ubiquitous landscape feature in northern permafrost regions. They have a strong impact on carbon, energy and water fluxes and can be quite responsive to climate change. The monitoring of lake change in northern high latitudes, at a sufficiently accurate spatial and temporal resolution, is crucial for understanding the underlying processes driving lake change. To date, lake change studies in permafrost regions were based on a variety of different sources, image acquisition periods and single snapshots, and localized analysis, which hinders the comparison of different regions. Here, we present a methodology based on machine-learning based classification of robust trends of multi-spectral indices of Landsat data (TM, ETM+, OLI) and object-based lake detection, to analyze and compare the individual, local and regional lake dynamics of four different study sites (Alaska North Slope, Western Alaska, Central Yakutia, Kolyma Lowland) in the northern permafrost zone from 1999 to 2014. Regional patterns of lake area change on the Alaska North Slope (−0.69%), Western Alaska (−2.82%), and Kolyma Lowland (−0.51%) largely include increases due to thermokarst lake expansion, but more dominant lake area losses due to catastrophic lake drainage events. In contrast, Central Yakutia showed a remarkable increase in lake area of 48.48%, likely resulting from warmer and wetter climate conditions over the latter half of the study period. Within all study regions, variability in lake dynamics was associated with differences in permafrost characteristics, landscape position (i.e., upland vs. lowland), and surface geology. With the global availability of Landsat data and a consistent methodology for processing the input data derived from robust trends of multi-spectral indices, we demonstrate a transferability, scalability and consistency of lake change analysis within the northern permafrost region.
Keywords:
lake dynamics; lake change; permafrost region; Landsat; Alaska; Siberia; thermokarst; trend analysis; machine-learning 1. Introduction
More than 25% of the lakes on Earth are located in the northern high latitude region [1]. The distribution of lakes can primarily be explained by prior glaciation histories, the presence of peatlands, and the presence of ice-rich permafrost [2]. Lakes and ponds can occupy more than 20%–40% of the landscape in Arctic lowland regions [3,4]. Grosse et al. [3] estimate that more than half of the lakes found in permafrost regions are likely of thermokarst origin; however, many other lake types in the Arctic are recognized [5,6]. Thus, thermokarst lakes and non-thermokarst lakes are a key component of northern ecosystems and have a strong impact on carbon, energy and water fluxes [7,8,9,10]. Arctic lakes have developed in a highly dynamic environmental setting that is subject to both hydroclimatic and geomorphic changes [11,12]. With respect to thermokarst lakes, they may undergo several generations that include phases of formation, growth, drainage, and reformation [3,13,14,15]. With a rapidly warming Arctic the direction and magnitude of these dynamics and fluxes may change dramatically due to changes in lake hydrology, lake ice characteristics, and permafrost degradation [16,17,18]. Therefore, monitoring of lake-rich Arctic regions at high temporal and spatial resolution as well as across very large regions is crucial for understanding their response to climate change and consequently their feedbacks with various environmental conditions. The dynamics of northern high latitude lakes may also serve as a critical climate change indicator or essential climate variable.
Until recently, global or continental scale water datasets have been too limited in spatial resolution to capture the entire range of lake sizes, such as MODIS-derived products at 250 m resolution [19]. Now, global water body change datasets based on Landsat data have been developed [20,21], but in particular high-latitude regions may not be represented with high accuracies due to snow, ice, persistent cloud cover, sediment suspension or poor data quality. Moreover, these studies mostly focus on overall water body change, not lakes in particular. Due to the sheer number of lakes in the northern high latitude region, ranging in the many millions [4,22,23], and the considerable extent of the northern permafrost region (~23 million km2 [24]), their broad range in size and dynamics makes the monitoring of these locally dominant and important landscape features across the permafrost region a challenging task. Remote sensing, with its capability of establishing calibrated observations over decadal-scale time periods and at sufficiently high spatial resolution (≤30 m), is therefore a key tool to achieve a better insight into permafrost region lake dynamics.
Several local and regional studies focus on the dynamics of selected thermokarst lake regions in the permafrost domain using a variety of spatial and temporal remotely sensed datasets [12,14,25,26,27,28,29,30]. The findings from these studies indicate that regional lake dynamic trends often follow a general pattern. Within the continuous permafrost zone, regional lake area trends were found to be mostly positive or neutral, but lake area loss may exceed lake growth in some regions. Eventually, some lakes ultimately drain, predominantly caused by bank overflow or reaching a drainage gradient [14,15,31]. These processes of lake growth and drainage are typical for thermokarst lakes [3,5]. Some studies find an increase in the number of lakes independent of the regional lake area changes, which may be caused by new thermokarst lake initiation and splitting of larger lakes into multiple remnant lakes [14,26]. Lake area increase has been observed over several regions in North America [16,27,32], and Siberia [26,33,34]. In contrast, lake area loss was found in Western Alaska [14] in Northwestern Canada [12,35], and in the northeastern part of European Russia [36], and Siberia [34,37]. In the discontinuous permafrost zones (<90% permafrost cover), a decrease of lake area has been observed for most regions [26,28,29]. On a local scale, however, large variation of lake area increase, stability, or decrease may occur. Disappearing or shrinking lakes are often caused by increased evaporation and/or the development of connectivity to groundwater following permafrost thaw [29,38,39]. However, the variation in regional net lake change and related hydrological dynamics across different environmental settings depends on a large number of factors affecting hydrological dynamics such as climate, permafrost, geology, topography, and landscape age.
Most prior remote sensing studies focused on lake area changes have been temporally limited, relying on the comparison of imagery from two to three time slices (e.g., [14,25,26,34]). The analyses typically spanned several decades, since the availability of aerial or space-borne imagery at higher temporal frequency in sufficient spatial resolution was not available until recent years. With high spatial resolution images (<5 m) waterbodies can be accurately delineated even to very small sizes (<100 m²; [40,41]). However, due to the limited extent and availability of very high resolution imagery, the studies were usually focused on rather small, image-footprint limited regions [40,41,42,43]. With the focus on single observations so far, the potentially strong intra-annual variation of water-bodies [27,44] cannot be sufficiently accounted for. Moreover, the diversity of data sources and acquisition timing results in limited comparability between different studies. In contrast, moderate or low spatial resolution (≥250 m) remote sensing observations offer temporally high resolution, large area monitoring capabilities, with the drawback that the monitoring of a very large portion of small thermokarst lakes remains impossible at these spatial resolutions.
With the increase of computation capacities and free data availability, the extensive Landsat imagery archive has become increasingly popular for environmental monitoring purposes on local to global scales [21,45,46]. This type of data stream at relatively high spatial and temporal resolutions, with an observation period spanning several decades, allows very detailed observations of the often small-scale but widespread land surface dynamics in permafrost landscapes. Trend analyses based on widely used Landsat multi-spectral indices have been applied for land cover change monitoring to various sites in northwestern Canada [47,48]), the Siberian Lena Delta [49] or even continental scales [50]. With the application of spectral unmixing, sub-pixel lake changes were reliably detected and analyzed [27]. The combination of sub-pixel analysis and its temporal and spatial capabilities makes Landsat a potentially valuable data source for the detection of lake dynamics.
Due to the rapid nature of reported lake and landscape changes occurring in the northern high latitudes, we developed a workflow to analyze Landsat-based trend data with machine-learning classification (MLC) and object-based image analysis (OBIA) for the detection and analysis of lake dynamics in two lake-rich regions in Alaska and two lake rich regions in Siberia spanning a total of 200,000 km². The regions cover different permafrost types (continuous and discontinuous) as well as different eco-zones (coastal lowland tundra to boreal forest), allowing us to test the applicability of our approach over large regions and a wide range of environmental conditions within the permafrost region. Our analysis aims at detecting decadal scale changes in the surface water balance while reducing sensitivity to short-term fluctuations. With the global availability of Landsat data and a consistent methodology for processing the input data derived from robust multi-spectral trends, we here demonstrate a transferable, scalable and consistent lake change analysis within the northern permafrost region.
2. Study Sites
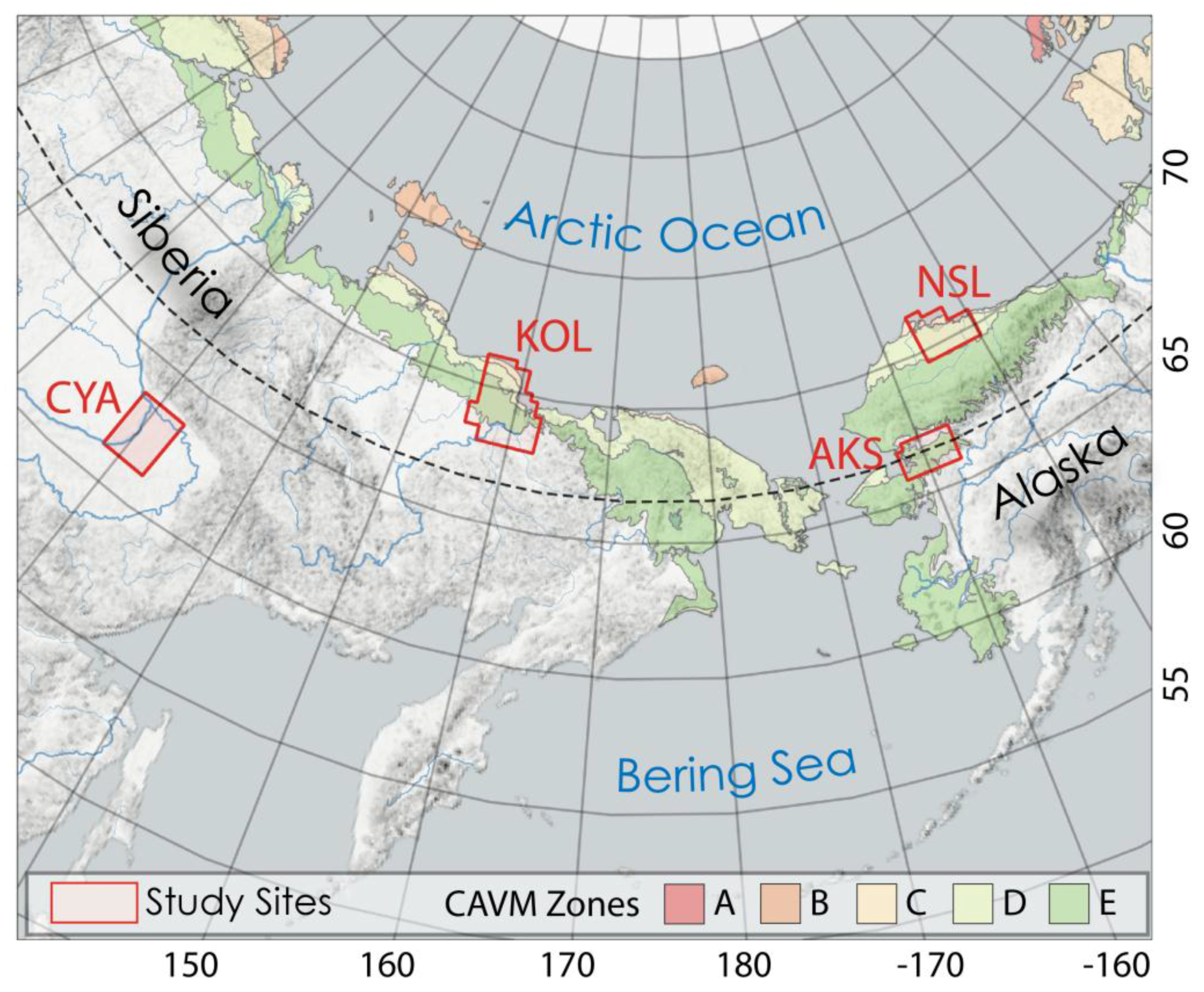
We chose four different study sites (Figure 1) to test our combined MLC and OBIA approach in regions with different environmental properties, including the permafrost type, lake-abundance, eco-zone, and the availability of auxiliary data for comparison and validation. In addition to the environmental conditions, the extent of the study sites was selected to remain within one UTM Zone.
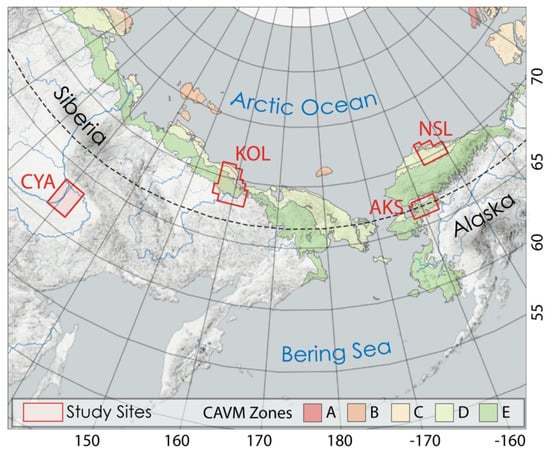
Figure 1.
Overview Map of eastern Siberia and Alaska with study sites and Circum-Arctic Vegetation Map (CAVM) Zones after Walker et al. [51].
In Alaska, the central part of the northern Arctic Coastal Plain and Foothills (North Slope, NSL) and the Kobuk-Selawik Lowlands (AKS) region in Western Alaska were selected. In Siberia, we analyzed the Сentral Yakutian Lena river basin (CYA) as well as the lower Kolyma Lowland region in Northeastern Siberia (KOL). Each region is described in detail below.
2.1. Alaska North Slope (NSL)
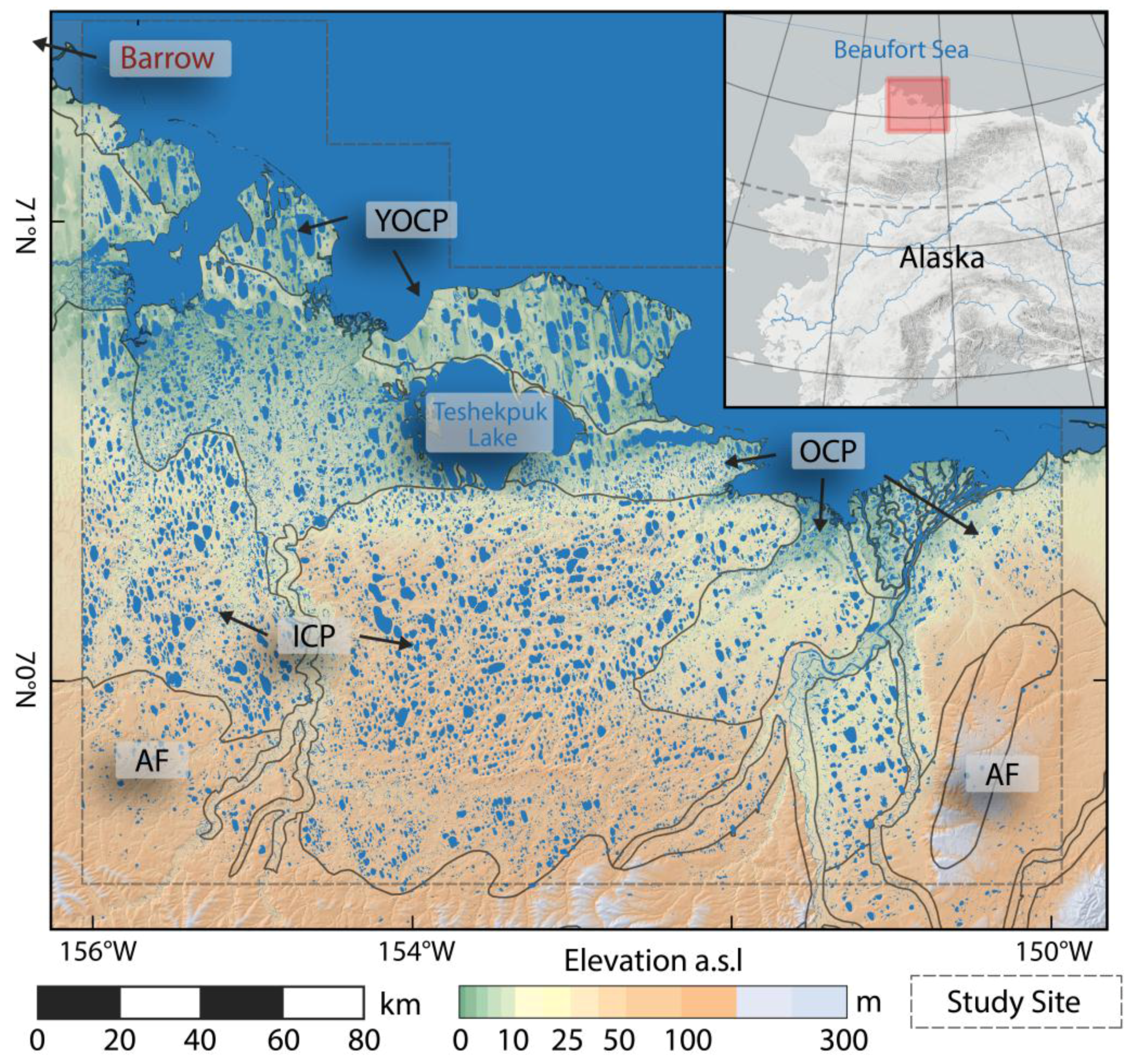
The Alaska North Slope (NSL) study site is located along the northern coast of Alaska north of the Brooks Range and completely within the continuous permafrost that reaches depths of 300 to 600 m [52,53]. For our study, we chose a 31,715 km² study region centered around Teshekpuk Lake. This region is characterized by a very high density of lakes and drained thermokarst lake basins, which cover around 20% and 50 to 65% of the land surface, respectively [15,54]. The area has an arctic continental climate with a mean annual air temperature (MAAT) of −11.2 °C and a mean annual precipitation (MAP) of 115 mm at Barrow [55] (1981–2010).
The study site is separated into several distinct geological zones, Young Outer Coastal Plain (YOCP), Outer Coastal Plain (OCP), Inner Coastal Plains (ICP), and the Arctic Foothills (AF) which are characterized by different thermokarst features [56] (Figure 2). The YOCP and OCP are directly located closer to the Beaufort Sea and are characterized by flat terrain with mostly fine grained ice-rich marine silt (YOCP) or sand (OCP) and numerous shallow lakes, drained thermokarst lake basins, and other lowland thermokarst features [15,16,57]. The ICP in the southern and central part is characterized by undulating terrain with sandy deposits of marine and eolian origin and with a high density of lakes that have shallow margins and deep centers [5,52,58,59]. The AF in the southern margin of our study area are characterized by sloped rolling topography, fine-grained, ice-rich yedoma deposits [60,61] and a low abundance of relatively deep lakes.
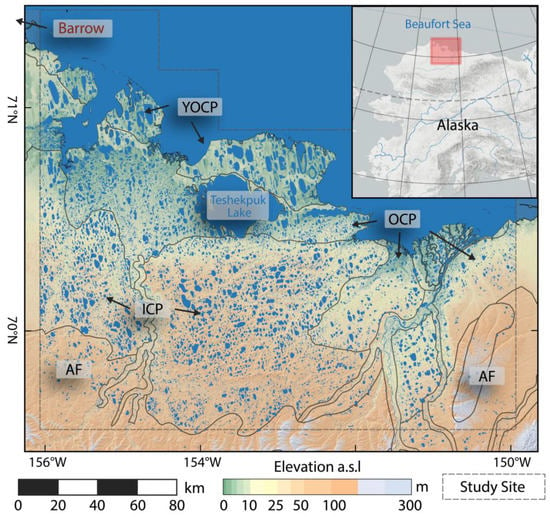
Figure 2.
Overview Map of Alaska North Slope study site (NSL) with generalized geological subzones. YOCP: Younger Outer Coastal Plain; OCP: Outer Coastal Plain; ICP: Inner Coastal Plain; AF: Arctic Foothills.
The land cover generally is dominated by low tundra vegetation of vegetation subzones C, D, and E as well as surface water bodies [51]. In particular along the eastern coastline, economic development affects land cover in the form of hydrocarbon exploration and extraction activities such as construction of roads, pipelines, exploration and extraction pads, pump stations, housing, and other facilities [62].
2.2. Alaska Kobuk-Selawik Lowlands (AKS)
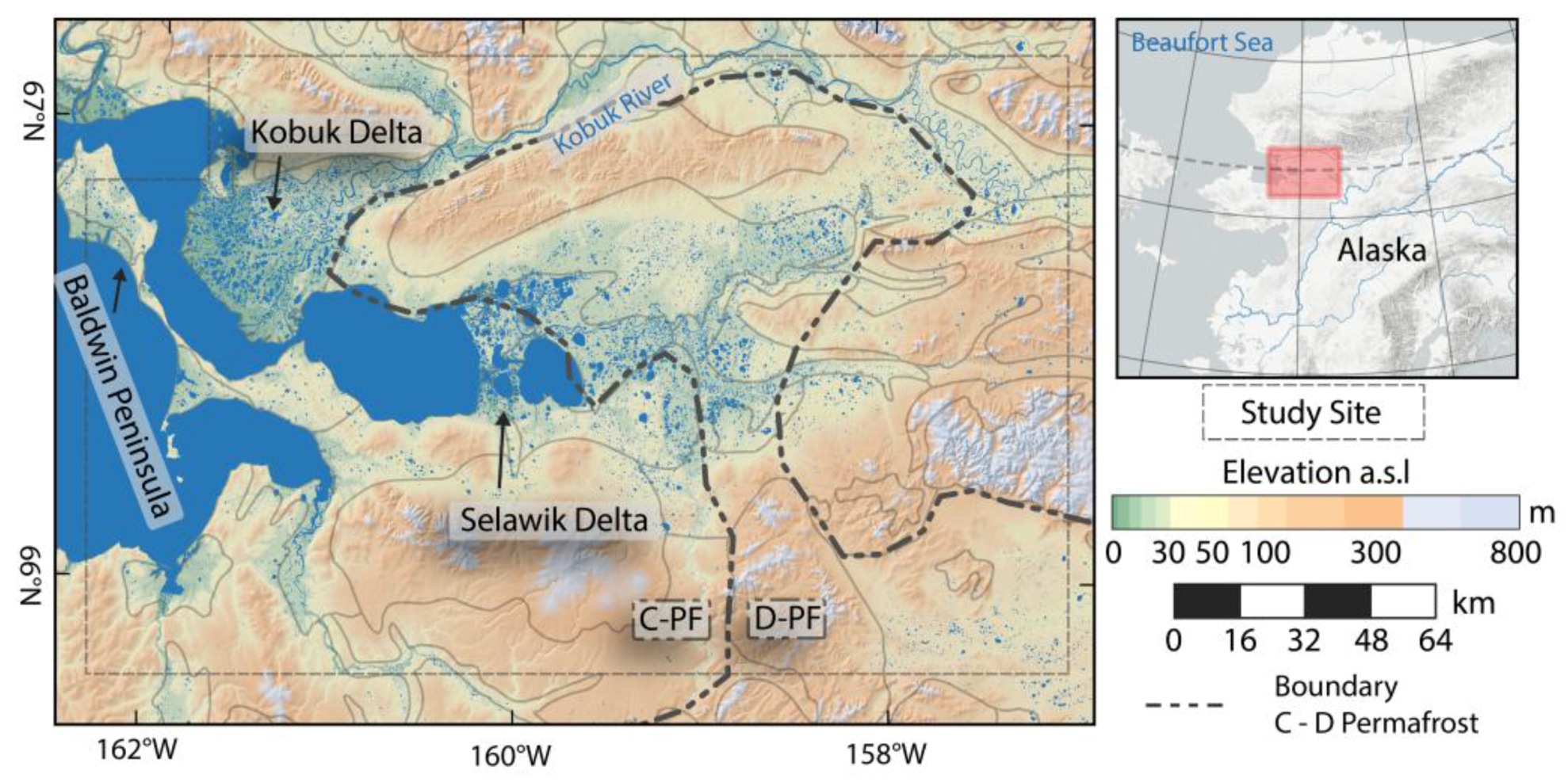
The Alaska Kobuk-Selawik Lowlands (AKS) study site is located in the northwestern coastal region of Alaska bordering the Kotzebue Sound to the west and continuing further east along the Kobuk and Selawik river valleys near the Arctic Circle (Figure 3). The study site has a size of 31,135 km². The region is located at the transition between the continuous and discontinuous permafrost zones [53]. Based on the climate record of Kotzebue, the region has a subarctic continental climate with a MAAT of −5.1 °C and a MAP of 279 mm [55] (1981–2010).
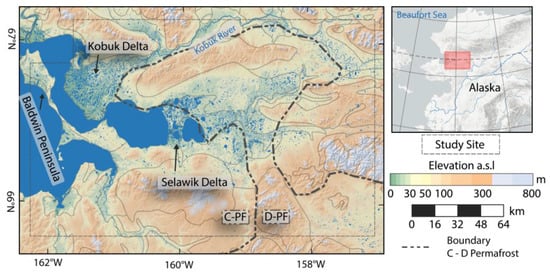
Figure 3.
Overview Map of Alaska Kobuk-Selawik Lowlands study site (AKS) with generalized geological subzone boundaries. C-PF: Continuous permafrost; D-PF: Discontinuous permafrost. Permafrost zonation after Jorgenson et al. [53].
The AKS site contains a large variety of landscape types with river valleys and deltas, alluvial plains, coastal lowlands, and gently rolling uplands [63]. Some regions feature ice-rich permafrost with a high abundance of thermokarst lakes and basins, while other areas are permafrost-free [64]. These lowland features are encompassed by several hill ranges, which are partially located within the study area.
The land cover mostly consists of water bodies. The vegetation in the permafrost transition zone ranges from wetland tundra in the coastal area to the shrub tundra of vegetation subzone E [51] in the river deltas and valleys, to boreal forest in the eastern portion of the study area [65].
2.3. Central Yakutia (CYA)
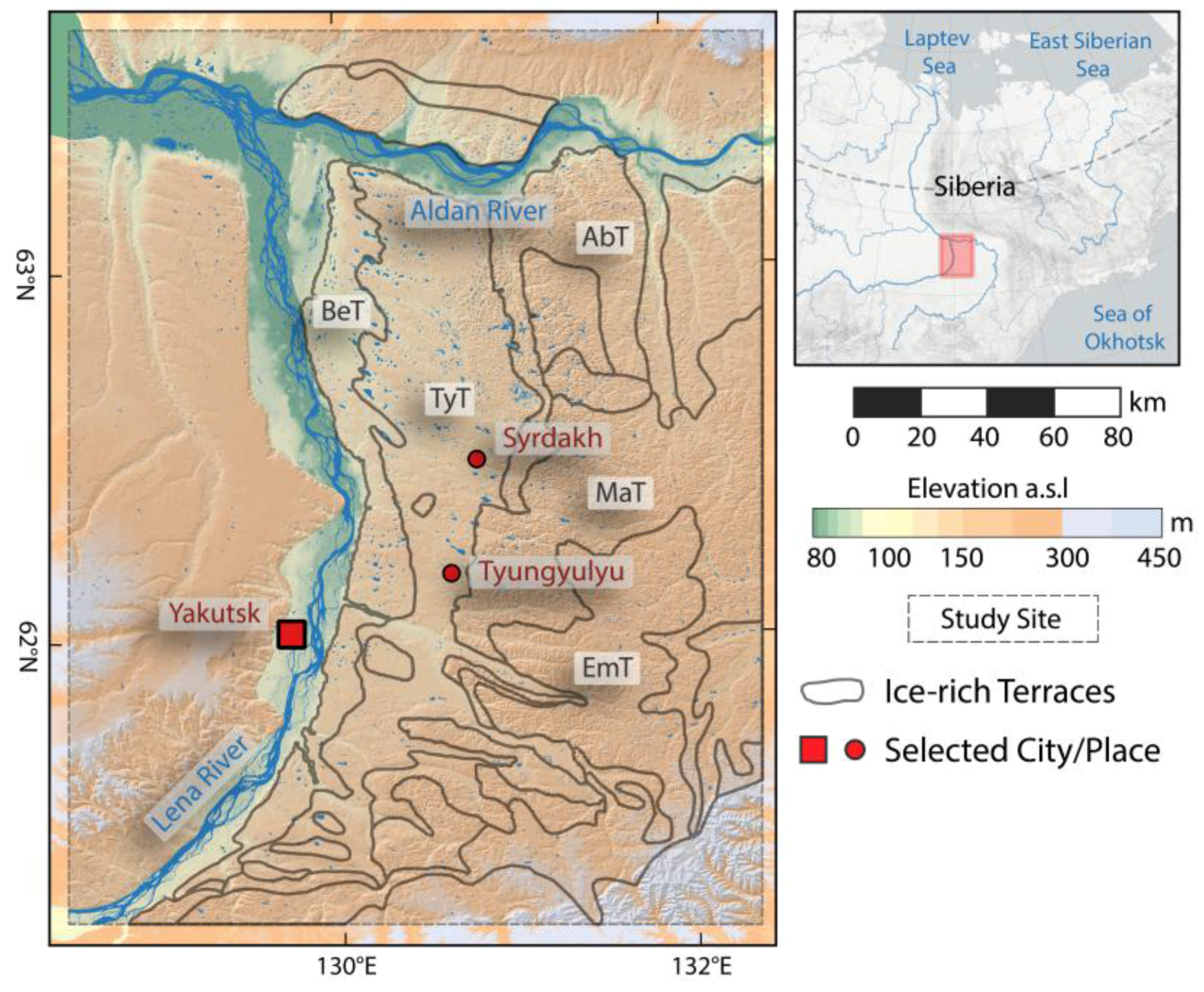
The Central Yakutia (CYA) study site is located in the middle Lena river basin around the city of Yakutsk and encompasses an area of 56,700 km². Central Yakutia belongs to the continuous permafrost zone with permafrost that reaches depths of 450 m [66] and is subject to extreme continental climate conditions. Yakutsk has a MAAT of −9.7 °C (1930–2010) with strong seasonal air temperature differences that can exceed 60 K between very warm summers and extremely cold winters [67]. The MAP is low at 234 mm, but can be subject to strong decadal variation [43]. Large streams, like the Lena or Aldan rivers, have a strong influence on the landscape by shaping large valleys and alluvial plains, which are seasonally flooded during spring ice-break-up [68].
Permafrost in this study area is dominated by ice-rich silty yedoma ice-complex deposits, which are almost completely thawed below thermokarst basins (termed “alas” in this region) and ice-poor sandy floodplains [69]. Within the study site, several distinct terraces with predominantly very ice-rich deposits can be differentiated [43,49] (Figure 4). On these terraces there are abundant thermokarst lakes and alas basins. Over recent decades, there has been an increase in the development of thermokarst lakes [43,70].
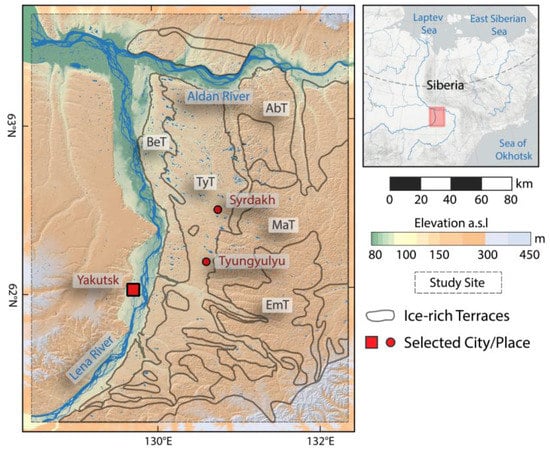
Figure 4.
Overview Map of Central Yakutia study site (CYA) with generalized geological subzones on the eastern banks of the Lena river after Soloviev [69]. BeT: Bestyakhskaya Terrace; TyT: Tyungyulyuyskaja Terrace; AbT: Abalakhskaya Terrace; MaT: Maganskaya Terrace; EmT: Emilskaya Terrace.
Boreal forest with larch, pine, and birch is the dominant land cover within this study site, while grasslands are ubiquitous within alas basins. The region is affected by frequent wildfires during the warm summer months [34,45]. Compared to the other study sites, this region is considerably influenced by land use activities in the form of agriculture, forestry, and infrastructure development for several centuries and in particular over recent decades [71].
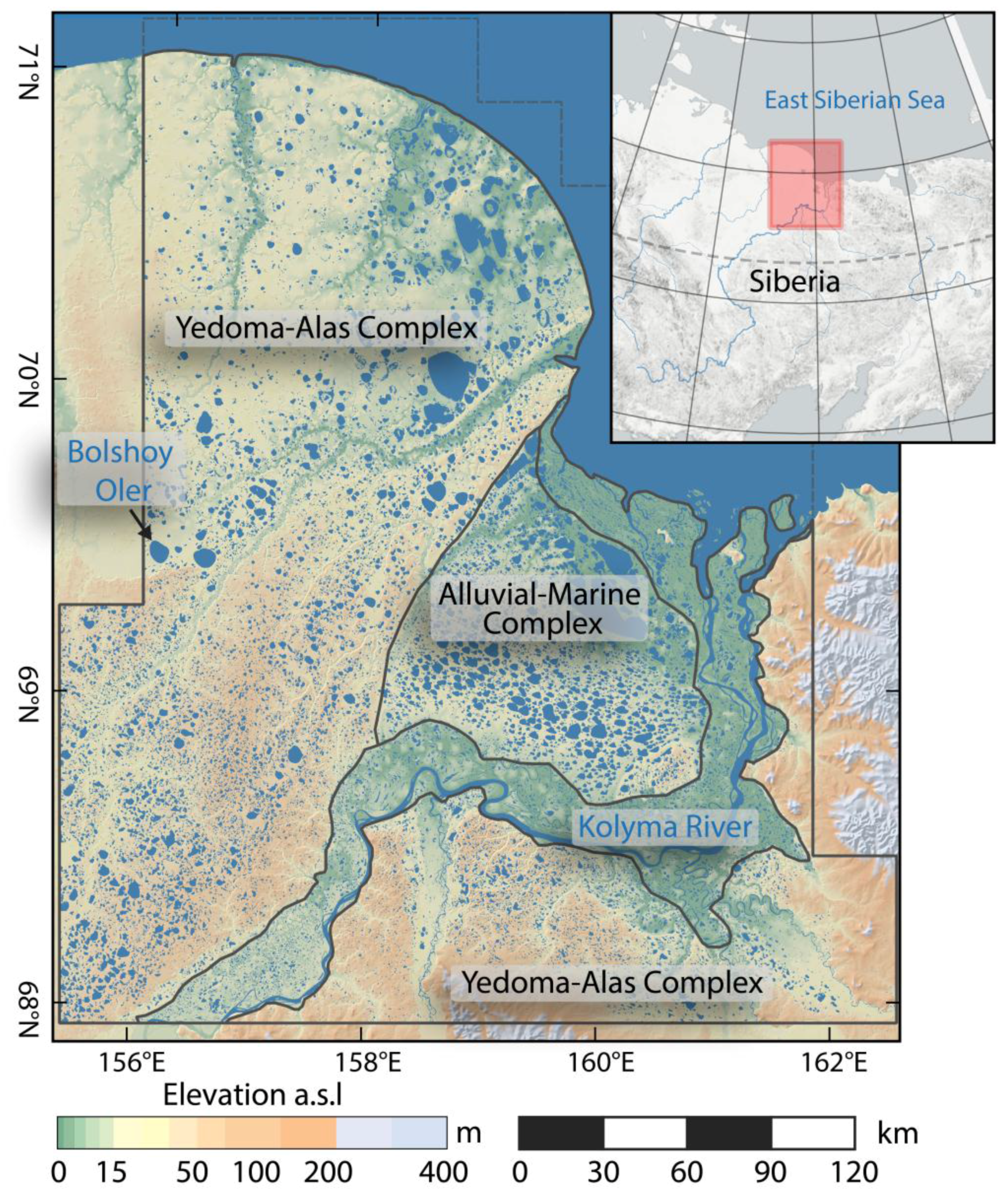
2.4. Kolyma Lowland (KOL)
The Kolyma Lowland study site (KOL) west and northwest of the Kolyma river mouth is completely located within the continuous permafrost zone of northeastern Siberia with depths of 300 to 500 m [72,73], and encompasses an area of 73,339 km². The region has a polar tundra climate with a MAAT of −9.2 °C and MAP of 237 mm at Cherskiy (2009 to 2014).
The region is mostly flat terrain and consists of different geological regions [74] (Figure 5). The western and southern part is dominated by fine-grained and ice-rich late Pleistocene yedoma deposits interspersed with thermokarst basins and river valleys and an abundance of thermokarst lakes and basins (Yedoma-Alas Complex) [75]. Within this zone, the low lying northern coastal regions are dominated by thermokarst basins, which cover 80%–100% of the area, whereas the southern part, north and south of the Kolyma river, has a higher abundance of ice-rich yedoma deposits, covering about 30%–50% of the area [75].
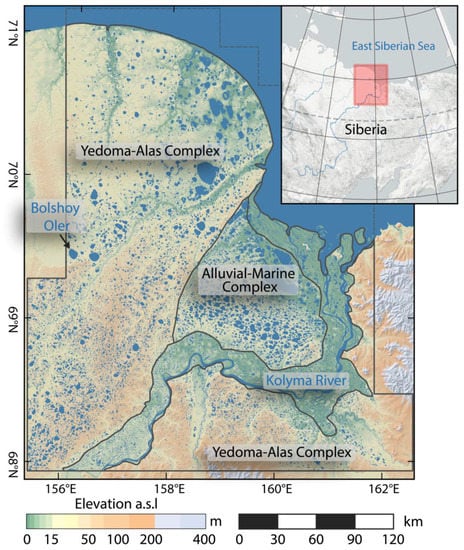
Figure 5.
Overview Map of Kolyma Lowland site (AKS) with generalized geological subzones after Shmelev et al. [74].
West of the Kolyma river mouth, the Alluvial-Marine Complex, composed of sandy deposits [76], forms the landscape and exhibits a high abundance of large oriented lakes. Along its course the Kolyma river forms a wide floodplain and a delta on its outflow into the East Siberian Sea. On its eastern margin, the study site is bordered by hill ranges of up to 700 m. The land cover is dominated by tundra lowlands of vegetation subzones C, D, and E [51]. The southeastern part of the study site, around the town of Cherskiy, is situated in the northern taiga zone.
3. Data and Methods
3.1. Data and Trend Analysis
In this study, we used the entire archive of Landsat data available for our four study regions between 1999 and 2014 filtered to the peak summer months July and August, and a cloud cover of less than 70%. We used only Landsat data from TM, ETM+ and OLI sensors, which have a common spatial resolution (30 m) and (six) overlapping spectral bands: Blue, Green, Red, Near-Infrared (NIR), Shortwave Infrared 1 (SWIR1), and Shortwave Infrared 2 (SWIR2). In order to keep data commonality for all sites, we decided not to include and analyze imagery before 1999. Large parts of Northeastern Siberia and Northwestern Alaska are affected by a very sparse acquisition frequency before 1999.
Data were acquired from United States Geological Survey (USGS) via the EROS Science Processing Architecture (ESPA) ordering system. All scenes were ordered as surface reflectance data and provided with the pre-processed FMask layer [77], which includes pixel quality flag information on cloud, snow, and shadow presence for each scene. The preprocessed scenes were downloaded and processed using an automated processing pipeline consisting of several steps: file extraction; masking of snow/ice, clouds, and shadows; re-projection (where necessary) and sub-setting. The data were structured into subsets of 30 × 30 km and projected into each site’s primary UTM zone.
After data-preprocessing, robust linear trends based on the Theil-Sen regression algorithm [47,78,79,80] were calculated for each pixel and six different multi-spectral indices (MSI): Tasseled Cap Brightness (TCB), Tasseled Cap Greenness (TCG), Tasseled Cap Wetness (TCW), Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI), Normalized Different Water Index (NDWI), and Normalized Different Moisture Index (NDMI). These indices are well established for Landsat and have been widely used in land cover remote sensing applications [47,48,50,81,82,83]. The trend calculation output consists of four trend parameters: slope, intercept, lower confidence interval, and upper confidence interval. Therefore each pixel carries 24 different types of information, i.e., four parameters for each of the six MSI. More detailed information on the processing chain is available in Nitze and Grosse [49].
Since lakes and their areal changes are the main scope of this study, we chose a combined approach of machine-learning classification (MLC) of the pre-calculated spatio-temporal trend information in conjunction with object based image analysis (OBIA).
3.2. Pixel-Based Machine-Learning Classification
We first applied a supervised MLC approach which translates the spectral-temporal signal into semantic information and separates the trend information into four target classes. These include two static classes, stable water (S-W) and stable land (S-L), as well as two dynamic classes, water to land (C-WL) and land to water (C-LW) (cf. Table 1). For the classification process we used a Random Forest (RF) [84] MLC algorithm. This non-parametric method has been established as one of the most accurate and widely used algorithms [85,86,87] for remote sensing and other classification applications because of its robustness, independence of statistical data distributions, and capabilities to work with a wide array of input data types.

Table 1.
Classification scheme with class name, class ID, number of training samples and examples of observed land cover or changes.
3.2.1. Training Sampling
We selected 568 training samples within and in close proximity to our study sites with respect to a variety of surface conditions, such as permafrost type, geological properties, vegetation types, water color and target classes. The extensive choice of ground truth locations, beyond the footprint of our study sites, allows us to account for a wider range of landscape surface conditions.
The ground truth selection process is based on a hybrid of random sampling and stratified manual sampling. As the change regions (classes C-WL and C-LW) cover only a small fraction of the study areas, we manually selected and over-sampled the training data for these classes. A purely random or gridded approach would have led to very small sample sizes of the change classes and was therefore not applicable. As stable land can have a variety of different surface conditions, we increased its sample size to attribute for this variety. The same reasoning was applied for the choice of training areas for lake drainage, which has a wide range of potential spectral and temporal signatures depending on the speed of drainage and post-drainage re-vegetation. In contrast, changes from land to water have a narrower range of appearances and therefore needed a smaller size of training samples. The calculated Landsat trend data as well as high-resolution images and local knowledge of in situ conditions were used for determining suitable locations of the manually selected and determined ground truth locations.
3.2.2. Classification Method Details
Slope, intercept as well as the lower and upper confidence intervals (CI) for each of the six MSI were used as input features for the pixel-based classification process. In addition, the difference between upper and lower CI (confidence interval range) was calculated. Therefore, 30 input variables were used in the MLC (Table 2).

Table 2.
Used input features for the MLC classification process. Each trend metric (n = 5) was calculated for each Multi-spectral index (n = 6) leading to 30 features.
The RF classification model was trained using the 568 training samples (see Table 1) with 200 decision trees. This number of trees has been found to be sufficient for most classification purposes [88]. Two different methods were used for quality assessment of the classification. First, the RF-specific internal quality parameter out-of-bag accuracy (OOB) [84] was used, which provides the classification accuracy through bootstrapped sampling. Second, a 5-fold cross-validation was carried out, based on a stratified randomized sampling of the ground truth data and the overall accuracy and Cohen’s kappa were used as a metrics of the classification quality.
The classification output contains a hard classification output with the four pre-defined classes (Table 1). Furthermore, a confidence layer for each class was calculated, which contains the classification probability of each single class in a range from 0 to 1.
The classification with four defined classes (cf. Table 1, S-W, S-L, C-LW, and C-WL) yielded a perfect separation on the ground truth data of the defined classes. With both evaluation methods, the RF-internal OOB as well as the and the 5-fold cross-validation, all accuracy measures (OOB, overall accuracy, Cohen’s kappa) achieved 100%. This shows a very high separability of pure pixels or endmembers of the four defined classes.
3.3. Object-Based Image Analysis
3.3.1. Lake Object Creation
Based on the hard classification results, lake objects (LO) were defined (Figure 6). Connected pixels of water and both change classes were aggregated into objects, where only 4-point-connected pixels, with neighborhood along pixel edges, were defined as a single LO. Each LO represents either a lake with adjacent change regions, e.g., an expanding or partially draining lake; a lake without any change; or an area which underwent full transition such as a completely drained or newly formed lake.
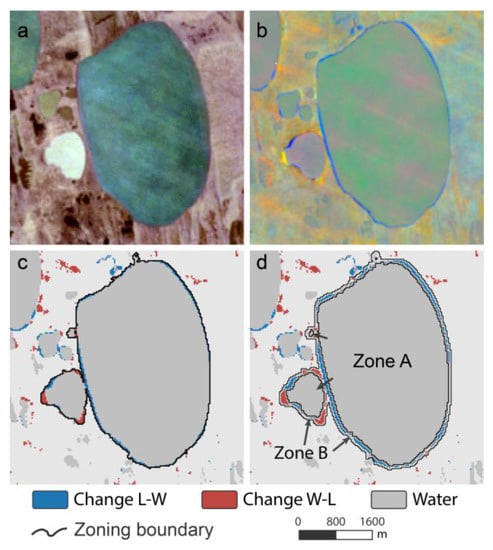
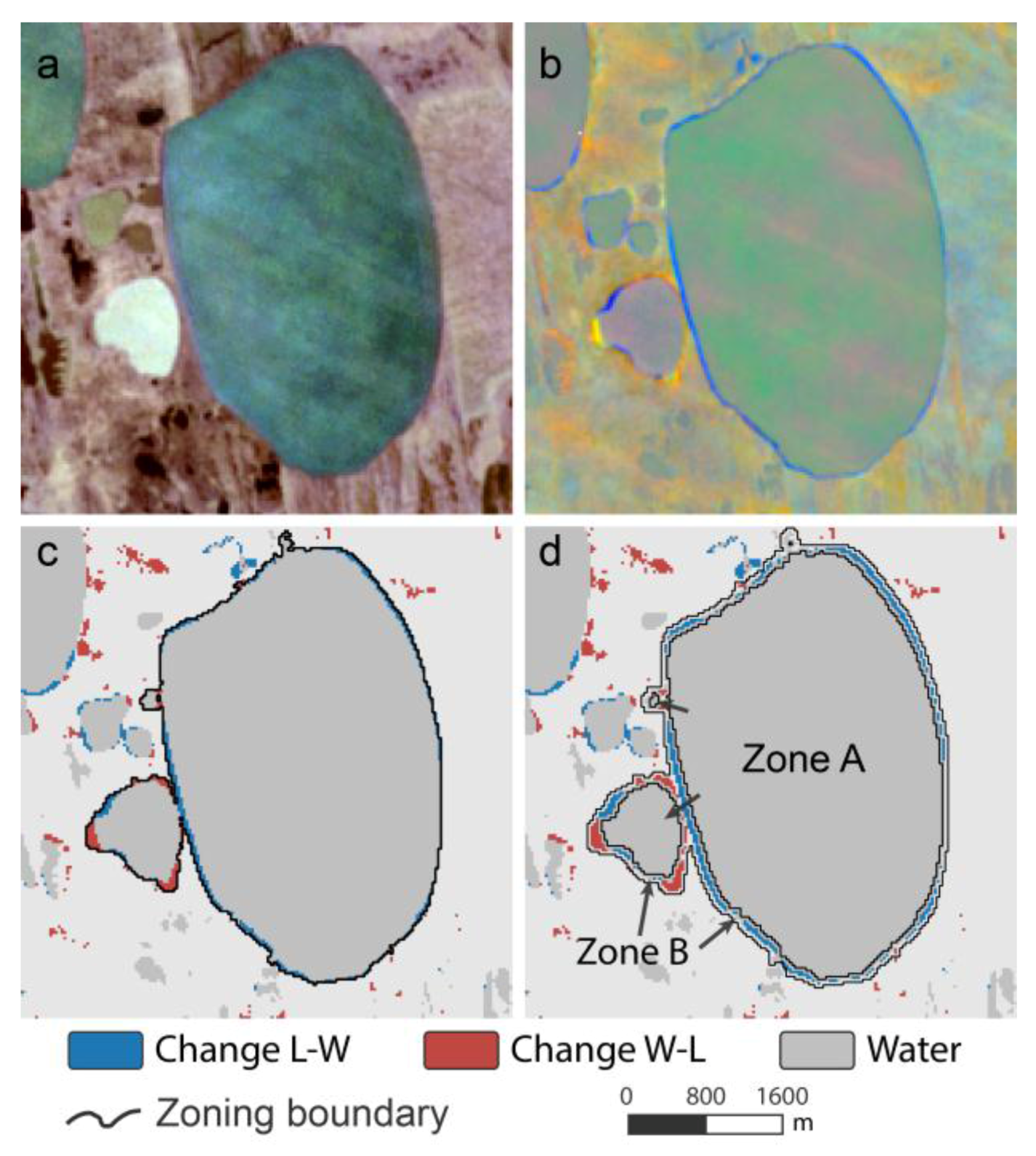
Figure 6.
Example of workflow steps from satellite image to lake zoning on a lake in the Alaska North Slope study site: (a) raw Landsat satellite image (R-G-B); (b) RGB-Visualization of Tasseled Cap Index Trends with R: Brightness, G: Greenness and B: Wetness; (c) classified trend data and lake object delineation; and (d) subdivision into stable (A) and dynamic (B) lake zones.
During the next step, each LO was sub-divided into a static (Zone A) and a dynamic (Zone B) zone (Figure 6). For the static Zone A, we used the hard-classified water mask (class S-W) within each object and applied a morphological erosion to reduce the lake’s radius by 1 pixel to avoid the lake margin, where mixed pixels may occur. This zone represents the non-changing water surface. Zone B represents the dynamic boundary of the lake objects, which is comprised of two different parts. B-1 includes the outside boundary of the stable water zone A with a width of 2 pixels, where thermokarst lake expansion likely occurs on a sub-pixel scale (<30 m). Zone B-2 represents the change region (classes C-WL and C-LW), which is dilated by 1 pixel to capture the transition zone to stable land. Both zones, B-1 and B-2, are merged into a single zone B. Finally, lake objects of less than 1 ha in area were removed.
3.3.2. Lake Change Calculation
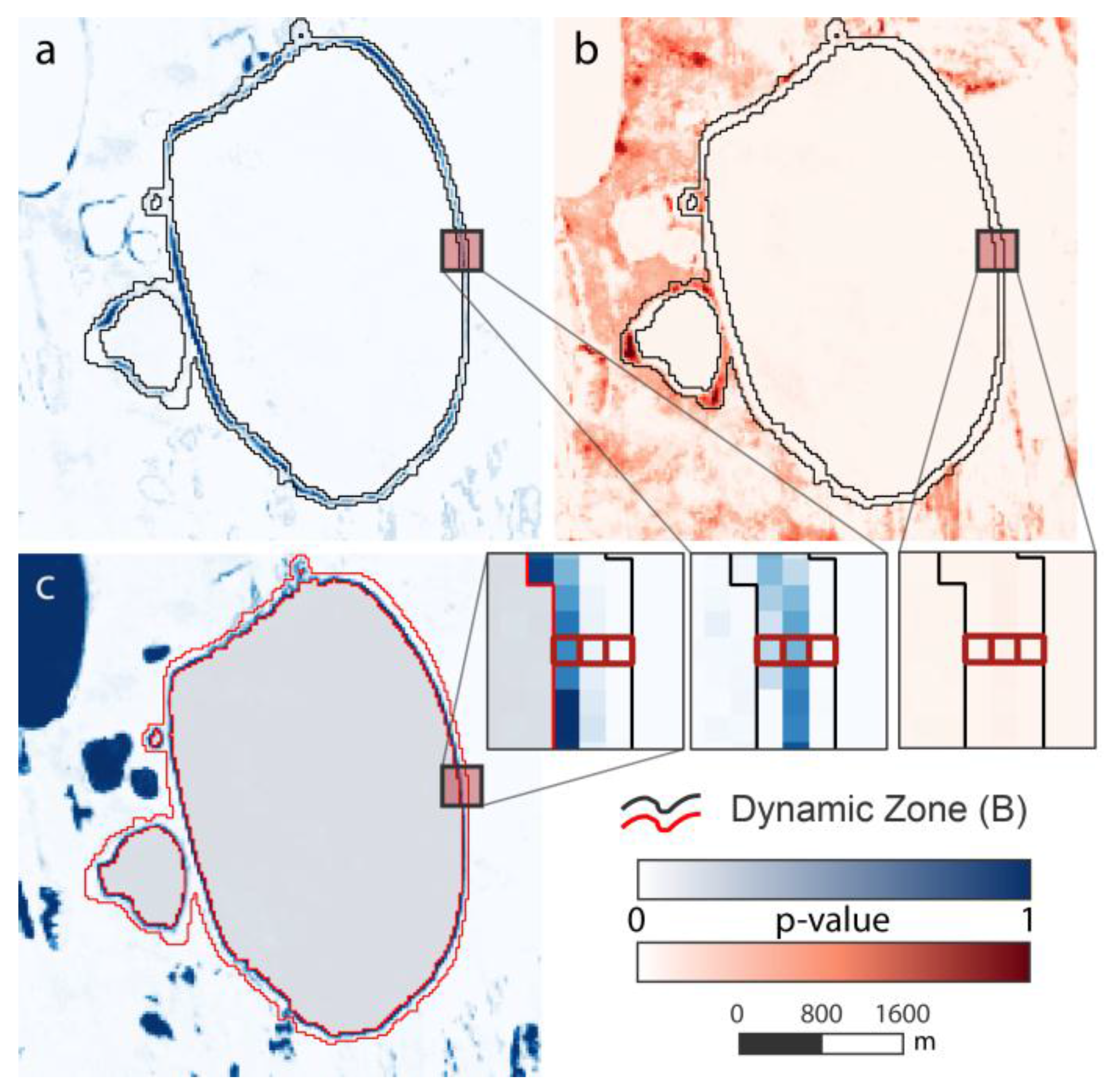
During the final step, we calculated the areal extent of spatial dynamics for each lake object. Each of the two defined zones was treated differently. The stable Zone A was regarded as permanent water and its area was therefore calculated as static surface water over the entire period. For Zone B we chose a more dynamic sub-pixel analysis approach to account for its location on the lake margins and the transition zone. Each class’ area is represented by the classification probability (p-values), which is assumed to be the fraction of each endmember/class and they were tested for plausibility on high-resolution imagery as well as field measurements and observations, which were available for selected locations. These p-values were used as a weighing factor of each class within each pixel of Zone B. A calculation example for the 3-pixel transect through the margin of a large thermokarst lake in the NSL study site is presented in Table 3 and Figure 7. The western pixel has a p-value of 0.705 for stable water representing 70.5% of the 900 m² pixel, hence 634.5 m² are calculated as steady water surface within this pixel. The same applies to each class and pixel. Within this short transect 720 m² of the 2700 m² were subject to a transition from land to water caused by lake shore erosion through thermokarst (cf. Figure A1).

Table 3.
Calculation example for three pixels through the margin of a thermokarst lake.
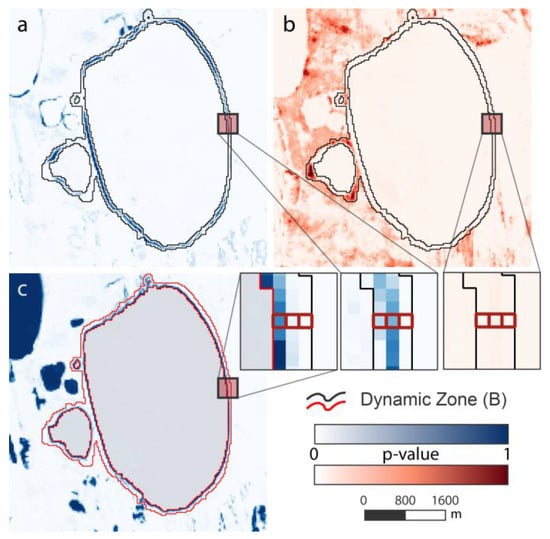
Figure 7.
p-value datasets for the calculation of sub-pixel fractions of lake objects: (a) Change land to water (C-LW); (b) Change water to land (C-WL); and (c) Stable water (S-W). Example pixel locations highlighted.
3.4. Data Quality and Post-Processing
In order to optimize the data quality for the lake change analysis we applied a two-step filtering mechanism to exclude non-lake water bodies, such as rivers or sea areas and their related changes, since these are subject to strong dynamics and would have influence on the lake statistics. In addition, waterbodies intersecting the edge of the study area were removed. Although the defined classes are perfectly separable, other unrelated disturbances, such as burn scars or cast shadows in mountain areas were classified as stable water or one of the change classes in several instances and needed to be addressed in the post-processing.
For the automated removal of these invalid or false positive objects, we classified the water objects based on spatial statistics and shape attributes as well as using topographic information from a pan-Arctic DEM [89] and vegetation information from the Global Forest Change dataset [45] as auxiliary data. Spatial statistics and shape parameters were calculated with the scikit-image python software package for each identified lake. They include shape parameters, such as area, perimeter, orientation, eccentricity, and solidity, as well as spatial statistics of the classified data, DEM data (elevation, slope), and binary forest change dataset information.
We created a spatially stratified training dataset with a binary distinction of manually selected valid and invalid (rivers, cast shadows, and burn scars) lake objects to train a Random Forest machine-learning classifier. The classification model was then applied to each lake object. All lake objects classified as invalid were removed from the analysis. In general, rivers were detected by their particular shape, whereas shadows and fire are predominantly located in sloped terrain during this post-processing procedure. In a second and final filtering step, all objects with a maximum p-value (any class) of less than 0.95 were automatically discarded, which further allowed the removal of remaining false positive lake objects.
3.5. Calculation of Lake Change Statistics
We calculated area specific metrics (water area, water gain, water loss) to map and characterize individual lake specific changes. Regional statistics were then calculated based on the individual lake change metrics (c.f. Table 4). Furthermore, gridded results were calculated for the spatial representation of lake specific water area changes. Each region was subdivided into 3 × 3 km large squares and net lake area changes per pixel within each grid cell were accumulated. Only pixels belonging to detected lakes were included to the calculation.

Table 4.
Regional results of lake analysis.
4. Results
4.1. NSL (Alaska North Slope)
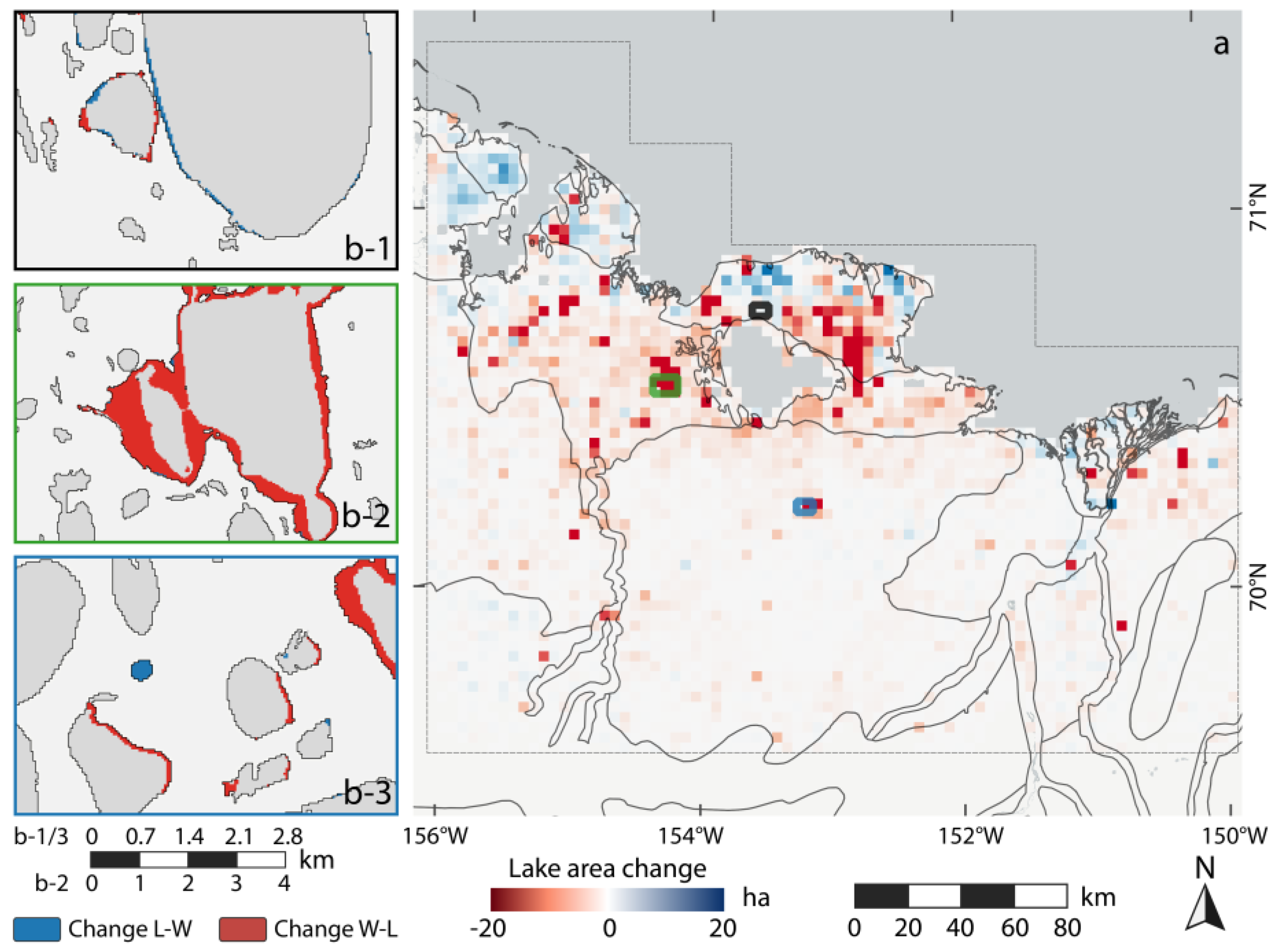
Within the NSL study site, 19,922 lakes were detected (cf. Table 4). During the observation period, the overall lake area changed from 555,478 ha to 551,629 ha, which translates to a net loss of 2806 ha or −0.69%. Lake growth accounted for 3937 ha, while shrinkage resulted in 7786 ha lake area loss. Most lakes remained predominantly stable over the observation period from 1999 to 2014 with 96% of the lakes having a net area change of less than 1 ha. In contrast to the majority of lakes with little or no change, few water bodies accounted for the majority of fluctuations in both directions. Strong relative changes as lake formation or full lake drainage (greater than 300% increase or 75% decrease) occurred infrequently with 4 and 43, respectively.
The largest lakes are typically located in the Younger Outer Coastal Plain (YOCP). A second cluster of large lakes can be found in the Outer and Inner Coastal Plain (OCP, ICP) region. Between the larger lakes, many small lakes and ponds are distributed within the entire study area. The lake area distribution is dominated by a large number of small lakes with a median area of 3.84 ha and a maximum size of 84,732 ha for Teshekpuk Lake. The overall lake density is very high in nearly the entire study site, with only small regions of low limnicity, predominantly in the rolling hills of the Arctic Foothills (AF). Overall, the lake area accounted for 17.5% of the land surface in the NSL study site.
Spatially, the strongest lake dynamics were on the YOCP, where both strong lake growth and shrinkage were detected (Figure 8). Particularly, northeast of Teshekpuk Lake (TL) there was a distinct cluster of lake drainage activity, while lake expansion is dominant north of TL, where the strongest individual lake expansion (+70.2 ha) was measured. The western YOCP is also characterized by widespread lake growth. Based on in-situ observations and overflights (Figure A2), lake change rates were clearly dominated by thermokarst processes, but localized flooding or drying of these very shallow lakes and basins also played an important role for lake water budgets on the YOCP. At Teshekpuk Lake, water area loss, e.g., due to sediment input or drying, outweighed lake growth by 111 ha which translates to 0.14% of the total lake surface.
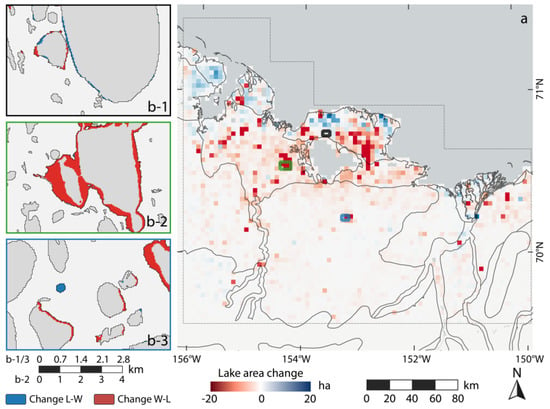
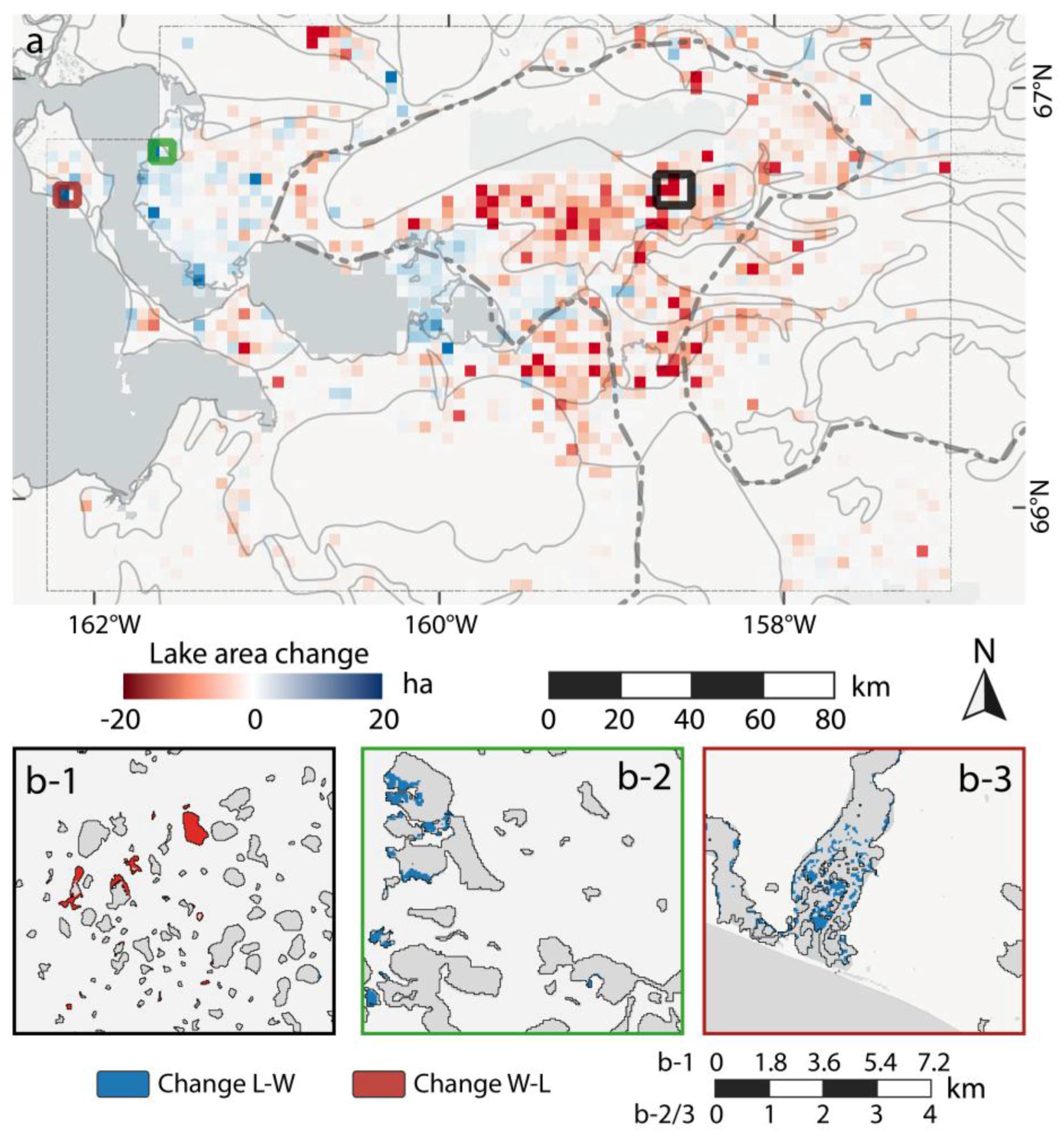
Figure 8.
Regional lake change of NSL study site: (a) gridded spatial net lake change distribution in ha. Gridsize: 3 × 3 km; (b-1) detailed view of thermokarst lake expansion and drainage on the Younger Outer Coastal Plain north of Teshekpuk Lake; (b-2) detailed view of partial lake drainage on the Outer Coastal Plain west of Teshekpuk Lake; and (b-3) detailed view of lake dynamics within Pik Dunes Basin with the formation of a new lake.
The OCP and ICP were dominated by lake stability with fluctuations around zero net change. Apart from the dominating stable pattern, several instances of partial lake drainage were registered on the OCP, e.g., west of Teshekpuk Lake (Figure 8b-2 and Figure A3). In the so-called Pik Dunes basin (Figure 8b-3 and Figure A4), a flat drained lake basin in the ICP region with exposed sand, a more dynamic pattern was observed with fluctuating lake levels inside the basin. In addition, a new lake of around 7 ha area had been naturally dammed up by the formation of large sand dunes at this site.
The AF region, which has a lower lake density, showed a slightly more dynamic pattern, with predominantly growing lakes, but also occasional lake drainage. Within the oil extraction region in the eastern margin of the study site, few occurrences of lake drainages and the construction of artificial water basins were detected.
4.2. AKS (Alaska Kobuk-Selawik Lowlands)
Within the AKS study site, 9771 lakes were detected (cf. Table 4). During the observation period the overall lake area changed from 99,399 ha to 96,592 ha, which translates to a net loss of 2807 ha or 2.82%. Lake growth accounted for 2024 ha, while shrinkage resulted in 4831 ha lake area loss. The majority of lakes remained predominantly stable over the observation period from 1999 to 2014 with 88.8% of the lakes having a net area change of less than 1 ha. However, 16 and 394 lakes were subject to strong expansion (>+300%) or drainage (<−75%), respectively.
The median area of lakes is 3.01 ha and a maximum size of 2430 ha. The large Inland Lake and Selawik Lake, as well as few other lakes within the Kobuk Delta are connected to the open sea and therefore automatically excluded. Generally, the largest lakes are predominantly located within or close to the Kobuk and Selawik deltas. In the inland regions and the Baldwin Peninsula, lake sizes are generally smaller. Overall, the lake area accounts for 3.2% of the land surface in the AKS study site, but can be much higher locally.
This region has a highly heterogeneous pattern of lake area change (Figure 9). Within the Kobuk and Selawik river deltas, we observed mostly lake growth. The largest increase in lake area predominantly took place in the Kobuk Delta close to the deltaic front and in proximity to the river’s main channels with a similar pattern in the Selawik Delta. However, despite the general lake expansion pattern within these sub-regions, several individual lakes were affected by lake area loss.
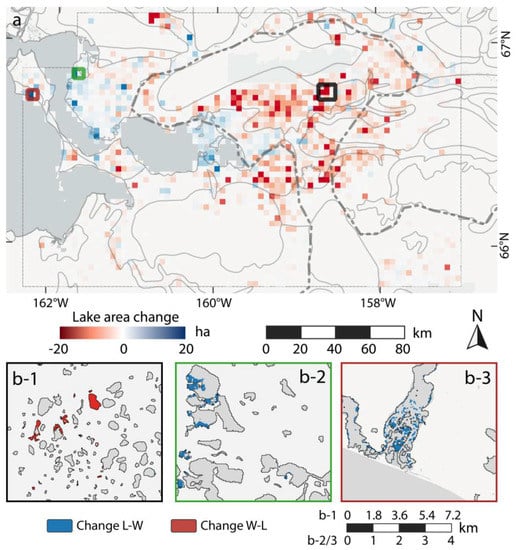
Figure 9.
Regional lake change of AKS study site: (a) gridded spatial net lake change distribution in ha. Gridsize: 3 × 3 km; (b-1) detailed view of catastrophic lake drainage in the northern Selawik valley; (b-2) detailed view of lake area growth in the northern Kobuk river delta; and (b-3) detailed view of flooding on a lagoon on the western Baldwin Peninsula.
In contrast to the deltas, the river valleys exhibit a much more diverse pattern. These regions were characterized by highly dynamic lake change patterns where widespread lake drainage was the dominating change process, though lake expansion occurred frequently in close proximity. Aerial survey flights in summer 2016 confirmed the spatial pattern of high dynamics and hydrological connectivity of this wetland region (see Figure 8b-1 and Figure A5). These dynamics can be observed along the Kobuk and Selawik rivers and its tributaries. Along the northern Selawik valley, many potential small lakes of up to 5 ha were not detected by the lake detection algorithm.
On the Baldwin Peninsula, lake changes of both directions were common, with several drainage events of different intensities and frequent thermokarst lake expansion. The lagoons on the western shore were detected as lakes and were subject to strong wetting, where the northern lagoon was subject to a water area gain of 80.6 ha alone (see Figure 8b-3 and Figure A6).
4.3. CYA (Central Yakutia)
Within the CYA study site, 13,254 lakes were detected (cf. Table 4). During the observation period the overall lake area changed from 93,417 ha to 138,705 ha, which translates to a net gain of 45,288 ha or highly exceptional 48.5%. Lake growth accounted for 50,116 ha, while shrinkage resulted in 4828 ha lake area loss. Barely half of lakes remained predominantly stable over the observation period from 1999 to 2014 with 56.3% of the lakes having a net area change of less than 1 ha. The large lake area increase comes with 1720 lakes, which were subject to a large lake expansion, while 188 were subject to strong water area loss. Among all study regions, the ratio of newly formed or very strongly expanded lakes versus near complete drainage was the opposite in CYA.
The median area of lakes grew from 2.28 ha to 3.56 ha. The largest lake, which is located close to the confluence of the Lena and Aldan rivers nearly tripled in area from 1828 ha to 5008 ha (Figure 10b-2). At the end of the observation period, the limnicity was at 2.4% for the entire study area, up from 1.6% at the beginning of the study period.
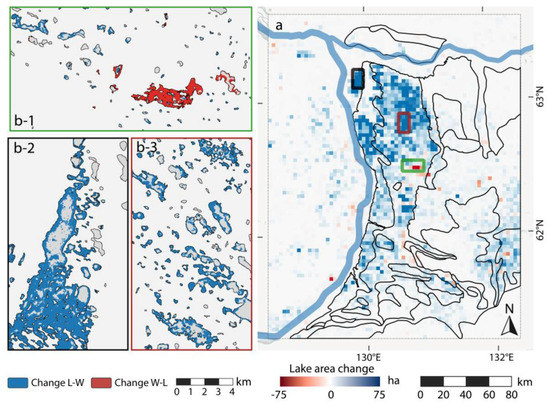
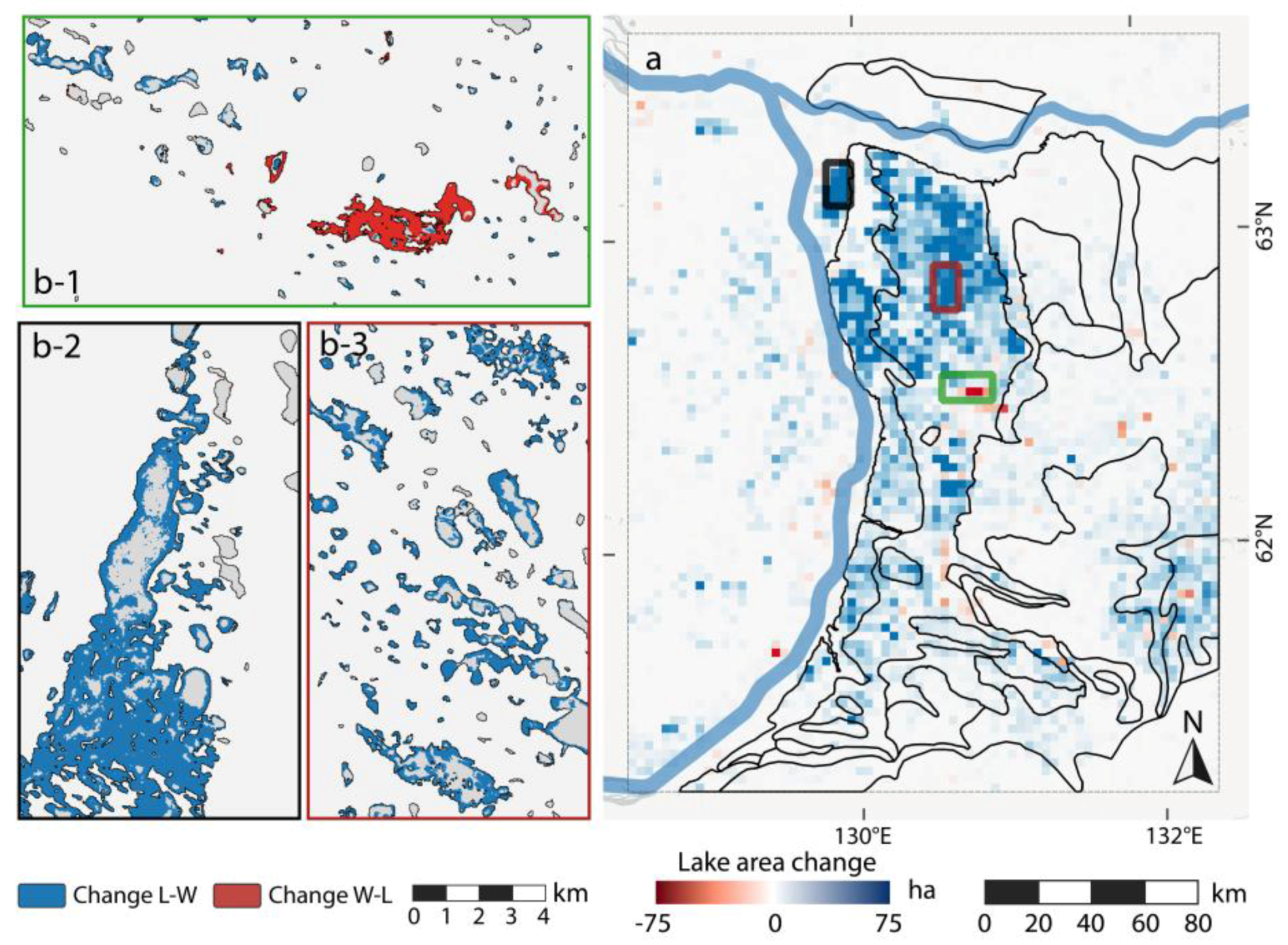
Figure 10.
Regional lake change of CYA study site: (a) gridded spatial net lake change distribution in ha. Gridsize: 3 × 3 km; (b-1) detailed view of lake area loss due agricultural practices; (b-2) detailed view of very strong lake area growth close to the confluence of the Lena and Aldan rivers; and (b-3) detailed view of widespread lake growth on the Tyungyulyuy Terrace.
The proximal eastern terraces of the Lena river (Bestyakhskaya and Tyungyulyunskaya), as well as the southeastern corner of the study area (Abalakhskaya T.) exhibited an extraordinary increase in lake area (Figure 10). In this region, formerly dry [90] or only partially filled thermokarst basins (alas) apparently were re-filled with water during the 16-year observation period. Additionally, thermokarst activity formed new ponds and widened lake basins (Figure 10b-3). Furthermore, numerous large basins were severely affected by the same flooding trend leading to this massive increase in lake area. The northeastern part and southern margin of the CYA study site (Maganskaya T., Abalakhskaya T., Emilskaya T.) were apparently not affected by the exceptional lake growth, which occurred in other parts of the region.
Lake drainage was less widespread than expansion in this part of the study region, but some clusters of lake drainages exist. Most occurrences can be found on the eastern margin of the Tyungyulyunskaya T., in particular within larger alases, for example around the villages Syrdakh and Tyungyulyu, where anthropogenic activity, e.g., through intense water management practices for agriculture in alas basins, likely had a strong influence on the detected lake area (Figure 10b-1). On the lake-poor western bank of the Lena river, lake change was not as drastic as east of the river and rather evenly distributed between growth and shrinkage.
4.4. KOL (Kolyma Lowland)
Within the KOL study site, 38,838 lakes were detected (cf. Table 4). During the observation period, the overall lake area changed from 1,197,263 ha to 1,191,180 ha, which translates to a net loss of 6083 ha or 0.51%. Lake growth accounted for 21,827 ha, while shrinkage resulted in 27,910 ha lake area loss. The majority of lakes remained predominantly stable over the observation period from 1999 to 2014 with 90.2% of the lakes having a net area change of less than 1 ha. In total, 64 lakes were affected by strong lake expansion or formation, whereas 205 lakes were subject to near complete lake drainage. The median area of lakes is 5.59 ha and the largest lake has size of 22,449 ha.
Within this study region, several spatial clusters of noticeable change can be distinguished (Figure 11). The Yedoma-Alas Complex (YAC) is clearly structured into a northern part, where lake expansion and a southern part, where drainage were the dominant lake change processes. The boundary of these zones nearly forms a straight line from northeast to southwest, which coincides with the boundary between the elevated ice-rich yedoma deposits in the south and the low-lying thermokarst basins in the north. Particularly, in the northeastern coastal region, very strong lake expansion rates of up to 1097 ha for one lake were measured (Figure 11b-1). This particular lake exemplifies probably the two main drivers of lake expansion in this region. First, thermokarst caused lake expansion occurs along the shorelines of most lakes in this region. The second driver is the flooding of shallow and low-lying basins along the coast, which might be caused by seawater inundation.
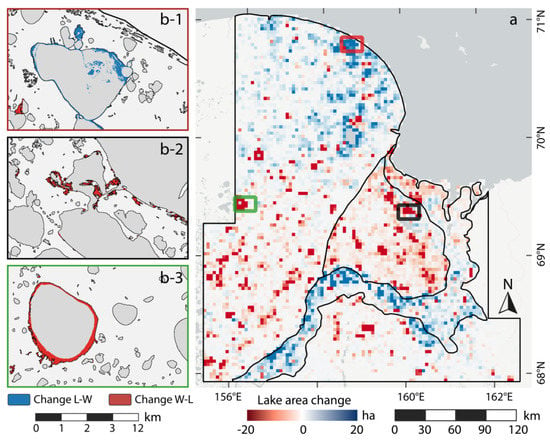
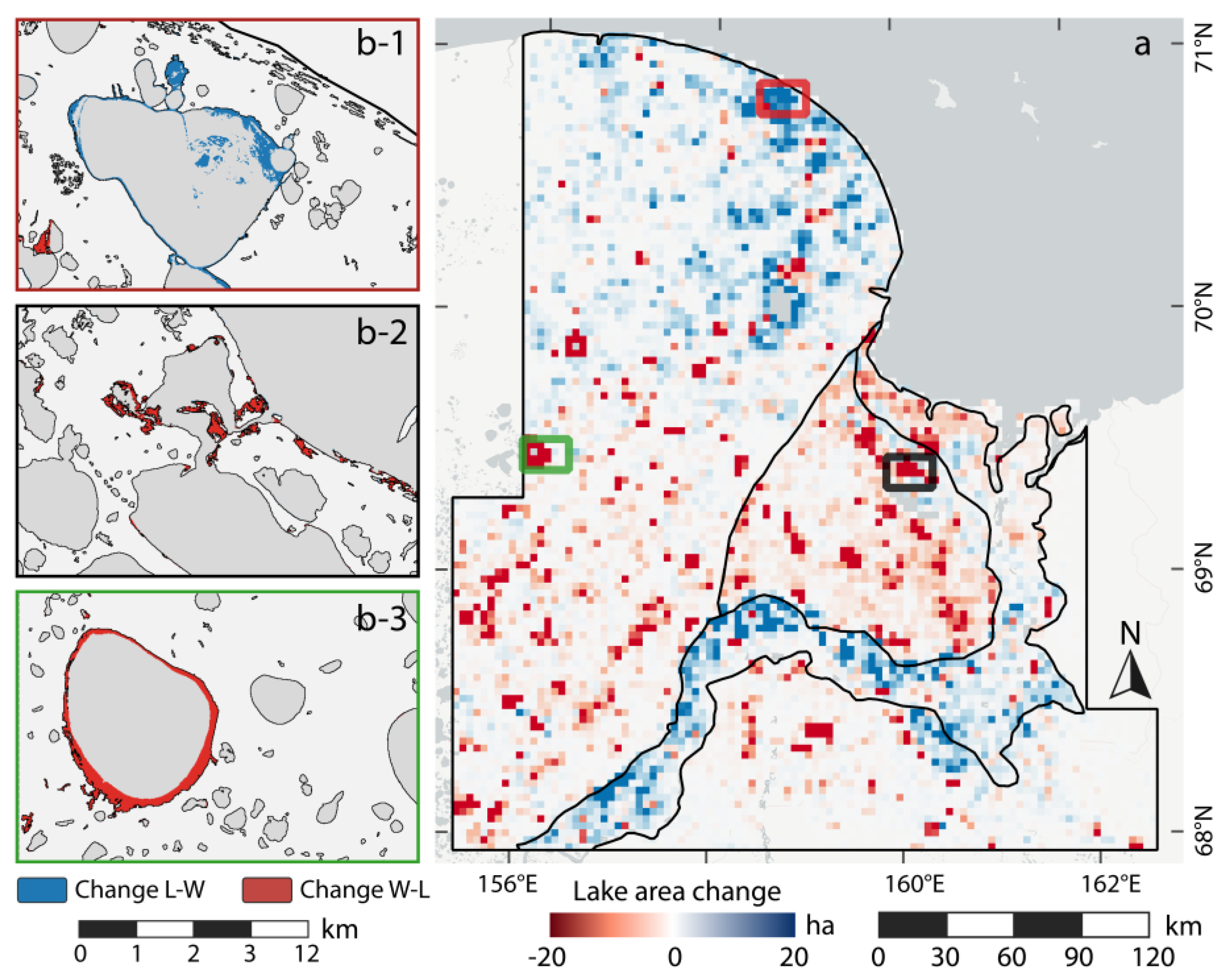
Figure 11.
Regional lake change of KOL study site: (a) gridded spatial net lake change distribution in ha. Gridsize: 3 × 3 km; (b-1) detailed view of lake growth in the coastal region of the Yedoma-Alas Complex; (b-2) detailed view of lake area loss in the Alluvial-Marine Complex; and (b-3) detailed view of lake drainage at Bolshoy Oler lake.
The southern part of the YAC is dominated by lake area loss. Most of the lake area reduction was fueled by the partial drainage of several large lakes, e.g., Bolshoy Oler lake on the western margin of the study region (Figure 11b-3). This particular lake alone lost 752 ha of its water surface. Several other lakes were also affected by lake are loss of more than 100 ha, each. Lake expansion was measured for a large fraction of lakes, but does not outweigh the widespread water area loss.
In the YAC, south of the Kolyma river, lake area loss was more pronounced than lake growth, predominantly caused by the partial drainage of several large lakes. The majority of lakes did not follow a specific spatial pattern and changes in both directions were recorded.
The Alluvial-Marine Complex region west of the Kolyma river mouth showed widespread lake area loss in nearly the entire region. Particularly the northern part, where several large lakes are located, was affected by a strong reduction of lake area (Figure 11b-2). Lake growth was infrequent and only measured for the minority of lakes.
The floodplain of the Kolyma river is dominated by strong dynamics, predominantly as lake expansion. Several individual lakes were affected by drainage of varying degrees. In the river delta, lake drainage and expansion was more evenly distributed with a slight excess of lake area loss.
5. Discussion
5.1. Data Analysis
The combined MLC and OBIA classification into four classes (land, water, and temporal transitions between both) based on the 16-year (1999–2014) Landsat trend data yielded an excellent separation of the input data based on different metrics, such as RF’s internal accuracy estimator (OOB) or five-fold cross-validated classification accuracy and Cohen’s kappa. Area estimates of pure pixels of the defined classes can therefore be considered as highly accurate within the spatial resolution of the data.
However, as thermokarst lakes are characterized by a dynamic, asymmetric behavior with a large number of slowly growing lakes and a low number of quickly draining lakes, and Landsat’s spatial resolution of 30 m, sub-pixel analysis becomes crucial to properly account for the magnitude and direction of changes. Therefore, we included a sub-pixel analysis of changes along the lake margins based on the probability values of the MLC.
The processing step from pixel based classification to lake or lake-change objects worked generally well in most cases. Lakes embedded in tundra, boreal or transitional environments were clearly detected and separated without notable differences between the different eco-zones. However, more dynamic zones without a clear distinction of water and land, e.g., wetlands, are a potential error source for lake change calculations, due to their constantly changing surface conditions, local-scale permafrost landscape features conditions, and its transitional nature between water and non-water, which is a common issue identified in previous studies e.g., [25,34,90,91]. These particular settings usually occurred in coastal or delta regions and river valleys or flat drained lake basins. Such regions might be more susceptible to larger errors than for most other regions. Particularly, the highly dynamic AKS study site was affected by this effect, where many small basins constantly changed their surface water conditions.
Few misclassifications were identified in regions of frequent wildfires, such as boreal taiga or forest tundra regions as wildfires were occasionally classified as change in either direction, due to its strong spectral change over time. The use of global forest cover change information [45] and DEM data [89] helped to detect and mask these regions by automatically discarding false positive classified lake objects. However, as large regions in the tundra-taiga transitional zone are not accounted for in the global forest cover change map, the removal of false positive lake objects due to fire may lack the reliability of boreal regions.
5.2. Comparison of Sites and Prior Studies
Each of the four analyzed regions shows a slightly different behavior in the dynamics of its lakes. The more northerly coastal regions NSL and KOL, have a small decline in lake area with 0.69% and 0.51%, respectively. Lake dynamics are locally varying, and spatial differences, based on several factors, such as geology (types of sediments, ice-content) and geographical setting (e.g., proximity to the coast or rivers) have an influence on the lake dynamics. The western Alaskan site (AKS) is subject to a decrease in lake area by 2.8% and is characterized by frequent dynamics, predominantly as lake drainage. As in the first two regions, clear small-scale local spatial patterns can be distinguished. The Central Yakutian study site (CYA) is characterized by extreme lake expansion of 48.48% between 1999 and 2014, which strongly deviates from the other sites.
The predominantly stable conditions on the Alaska North Slope (NSL) compare well with Jones et al. [59], who found no significant long-term trends of lake area change between 1985 and 2007. Our characterization of mostly stable conditions over most of the North Slope study site confirms Hinkel et al. [31] who found two lake drainage events per year from the mid 1970s to 2001/2002 on a similar sized and largely overlapping part of the North Slope. Considering the same criteria, we observed 2.44 drainage events per year. Arp et al. [16] detected net lake expansion of 3.4% using high-resolution data and 4.1% using Landsat data, between 1979 and 2002 on a small sample of 13 lakes in a more dynamic subset on the YOCP, north of Teshekpuk Lake. For twelve of the same lakes together, we found a zero net change, but strong changes in both directions for individual lakes. The missing lake L195 drained catastrophically in summer 2015 [15] and lost a significant portion of its 80 ha area. Due to the close proximity to the sea, the lake was automatically discarded in our processing, as it was detected as connected to the sea.
In the Kolyma Lowland region, our calculated net lake area decrease of 0.5% reveals a strong discrepancy to Walter et al. [33], who detected a lake area increase of 14.7% along the Kolyma river for a longer time period from 1974 to 2000. The strong difference can be explained by the extent and setting of study areas, as we also found a strong lake area increase within the Kolyma floodplain. Their use of sensors with a different spatial resolution (Landsat MSS to ETM+), may have also had an influence on the results. Considering the discrepancy to the regional statistics, this particular subset is not representative for the entire region, which stresses the spatial variety of lake change processes, particularly within this region. Veremeeva and Gubin [92] found a trend of lake area decrease in the range of 0.9 to 10.7% for a small region in the western Yedoma-Alas Complex from 1973 to 2001. Within this specific region, our results also indicate a strong loss of lake area, largely due to the partial drainage of the around 50 km² large Bolshoy Oler lake. The sharp boundary of lake growth trends and lake shrinkage trends coincided very well with boundary of geomorphology with old low-lying thermokarst basins in the Yedoma-Alas Complex region.
In a comparable Arctic coastal lowland setting, to NSL and KOL, with thick continuous permafrost on the NW Canadian Tuktoyaktuk Peninsula, Olthof et al. [27] found a slight lake area increase of 0.64% over eight years with strong inter-annual fluctuations of up to 4%. Within the same region Plug et al. [32] found substantial lake area fluctuations for large lakes of +14% from 1978 to 1992 and −11% from 1991 to 2001, however with an anomalously low lake area in 2001.
In the western Alaskan study site (AKS), located in the transition zone from continuous to discontinuous permafrost, we observed a net lake area loss of 2.8%. It compares well to Roach et al. [29] who measured a lake area loss of 0.81% per year. Their study site largely covers the area affected by widespread lake drainage and trends of lake change nicely resemble the spatial pattern we found in our study, e.g., lake growth in the Selawik river delta and widespread loss in the northern Selawik river valley. In a more continental site east of the Kobuk Dunes, Necsoiu et al. [42] found an overall decreasing lake area trend from 1978 to 2005 within 22 lakes or ponds. We could detect 14 of these lakes and found a lake area loss of 13.4%, largely fueled by the partial drainage of one lake. Similar trends were detected on the nearby northern Seward Peninsula where Jones et al. [14] found 11% lake area loss where the drainage events of few large lakes were the main drivers for a net lake area loss. Each of the coastal sites showed trends of lake area increase in near-shore areas. To our knowledge this effect has not been described or discussed in other lake change studies. It may be caused by several factors, such as local climatic effects; surface geology, e.g. sediments more prone to erosion; or very flat terrain, which is affected to sea water inundation.
The abundance of disappearing lakes in discontinuous permafrost regions in Central Alaska [28,81] has been linked to increased connectivity to groundwater [38,39]. Permafrost degradation or disappearance along the continuous-discontinuous permafrost interface in the AKS site would be a good explanation for the strong lake drainage trend within this region. Other causes in areas with relative high continentality, such as the central Alaskan Yukon Flats or northwest Canadian Old Crow Flats, include increased evapotranspiration [12,28,35].
However, for the highly continental Central Yakutia site, we calculated a 48.48% increase in lake area for the 1999–2014 period, which is a significant outlier in terms of thermokarst lake dynamics. The same wetting pattern has been described by Boike et al. [34], who used Landsat snapshots and found an increase of around 85% from 2002 to 2009 within the strongest wetting part of the CYA study site. The strongest increase in lake area occurred in 2007 after above-average precipitation in the prior year [44]. Furthermore, this particular region has been subject to very strong rates of lake expansion over the last decades due to several factors, including anthropogenic activity and the change of climatic conditions [43,67]. The recharge of lakes here may be connected to a wetter and warmer climate over the recent decades [34,43,93] and shifting agriculture practices, where meadows and grasslands in alas basins are increasingly managed to produce richer pastures [71]. In addition to the climatic conditions and anthropogenic influence, the local geological conditions seemingly had a strong influence on the lake area changes, where the terraces with ice-rich sediments showed a much more pronounced lake area expansion in comparison to the remaining area.
The comparison of different studies as well as the analysis of local trends highlights the variability of lake dynamics within the northern permafrost region.
The wide variety of spatial scales poses a large challenge for the comparison of different studies and regions, as results may vary strongly even for nearby locations. Furthermore, seasonal or short-term lake area fluctuations, which can exceed long-term trends [27], may mask long-term trends in studies based on the widely applied practice of using snapshots [14,25,26,28,31,33]. The trend analysis of single date lake masks [27,29] can help to suppress short-term fluctuations and produce more reliable and comparable results. In our study we applied the trend analysis at an earlier stage and translated spectral trends to semantic information with MLC, which allowed us to accurately distinguish between zones of stable water or land and changing transition zones around lake margins. With the inclusion of classification probability values, we exploited sub-pixel information to detect permafrost region specific thermokarst lake growth.
Using the trend calculation helps generalize the input data regardless of its location and enables the comparison and upscaling across multiple spatial scales, starting from individual lakes up to very large regional scales. The successful application of the method to different study sites across the permafrost zone proved the transferability and scalability of the highly automated processing method and highlights its strong potential for applying it to the entire permafrost domain to fully characterize lake changes and associated permafrost dynamics.
6. Conclusions
We used a highly automated and hybrid approach based on Landsat TM, ETM+ and OLI data, robust trend analysis, machine-learning classification and object oriented analysis to quantify lake change dynamics for four large study regions in Alaska (North Slope and Kobuk-Selawik Lowlands) and Siberia (Central Yakutia and Kolyma Lowland) encompassing a total area of about 200,000 km². Landsat trend data analysis allowed for the comparison of different study sites over a specific period (1999–2014) and the observation of trends where short-term fluctuations do not affect the long-term change trajectories. In total, around 80,000 individual lakes larger than 1 ha were mapped and analyzed regarding their spatial dynamics over a 16-year period from 1999 to 2014. Regional lake area statistics revealed weak lake area loss for the more northerly Alaska North Slope (−0.69%) and Kolyma Lowland regions (−0.51%), while the lake area in the west Alaskan Kobuk-Selawik Lowlands was subject to a more pronounced area loss (−2.82%). Lake area in Central Yakutia grew considerably by 48.48%. In this latter area, massive recharging of large lakes in alas basins was likely connected to climatic wetting and warming and changes in agricultural practices.
Despite similar regional net change, considerable differences in local dynamics were distinguishable. The lakes in northern Alaska within continuous permafrost exhibited a rather stable and uniform behavior with widespread lake stability and a limited region of pronounced lake dynamics. Lakes in the Kolyma Lowland region showed a low net area change, but were subject to a clear regional zonation of lake growth and drainage. In the warmer west Alaska site, widespread drainage of lakes in inland regions dominated the lake change dynamics. Within this region, where permafrost is transitioning from continuous to discontinuous, the spatial dynamics were locally very diverse and likely affected more strongly by the landscape surface geology and local permafrost conditions.
As lakes and lake dynamics are an important driver of change in the northern permafrost lowlands, these findings will help to better understand the landscape response to a rapidly warming Arctic and degrading permafrost with all its hydrological and biogeochemical consequences. For example, the improved knowledge of large scale lake change dynamics will allow for a better quantification of thermokarst lake-related fluxes of the greenhouse gases methane and carbon dioxide. With the global availability and continuity of Landsat data, the increasing availability of comparable Sentinel-2 data, and the scalability of our method, we envision the expansion of the analysis to a pan-arctic scale.
Supplementary Materials
Supplementary data are available at the PANGAEA data repository [94] (https://doi.org/10.1594/PANGAEA.876553). They include the georeferenced outlines and centroids of detected lakes with major lake area statistics. Furthermore, gridded net lake changes are also made available.
Acknowledgments
I.N. and G.G. were supported by the European Research Council ERC#338335, the Initiative and Networking Fund of the Helmholtz Association (ERC-0013), and the European Space Agency (ESA GlobPermafrost). M.U. was supported by the German Research Foundation (DFG Grant No. UL426/1-1). B.M.J. was supported by the USGS Land Remote Sensing and Land Change Science Programs. C.D.A was supported by a grant from the National Science Foundation (ARC-1417300). Use of trade, product, or firm names is for descriptive purposes only and does not imply endorsement by the U.S. Government. We would like to thank Kimberly Casey and two anonymous reviewers as well as the academic editors whose comments helped to improve this manuscript.
Author Contributions
I.N. wrote the manuscript, designed the framework of this study, developed the data analysis pipeline, and conducted the analysis. G.G. co-developed the framework of this study, significantly revised the manuscript. B.M.J., C.D.A., M.U., and A.V. provided local lake specific data, valuable study site specific knowledge and revised and commented the manuscript. A.F. provided valuable site specific knowledge and commented and revised the manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The founding sponsors had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, and in the decision to publish the results.
Appendix A
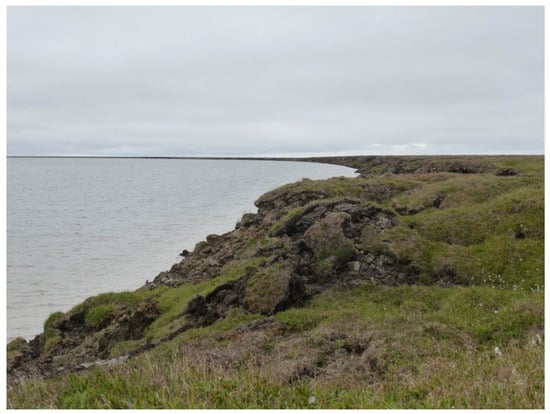

Figure A1.
Photo of example location (Figure 7) with thermokarst lake shore erosion. Looking north. Photo taken on 14 July 2015 by I. Nitze.
Figure A1.
Photo of example location (Figure 7) with thermokarst lake shore erosion. Looking north. Photo taken on 14 July 2015 by I. Nitze.
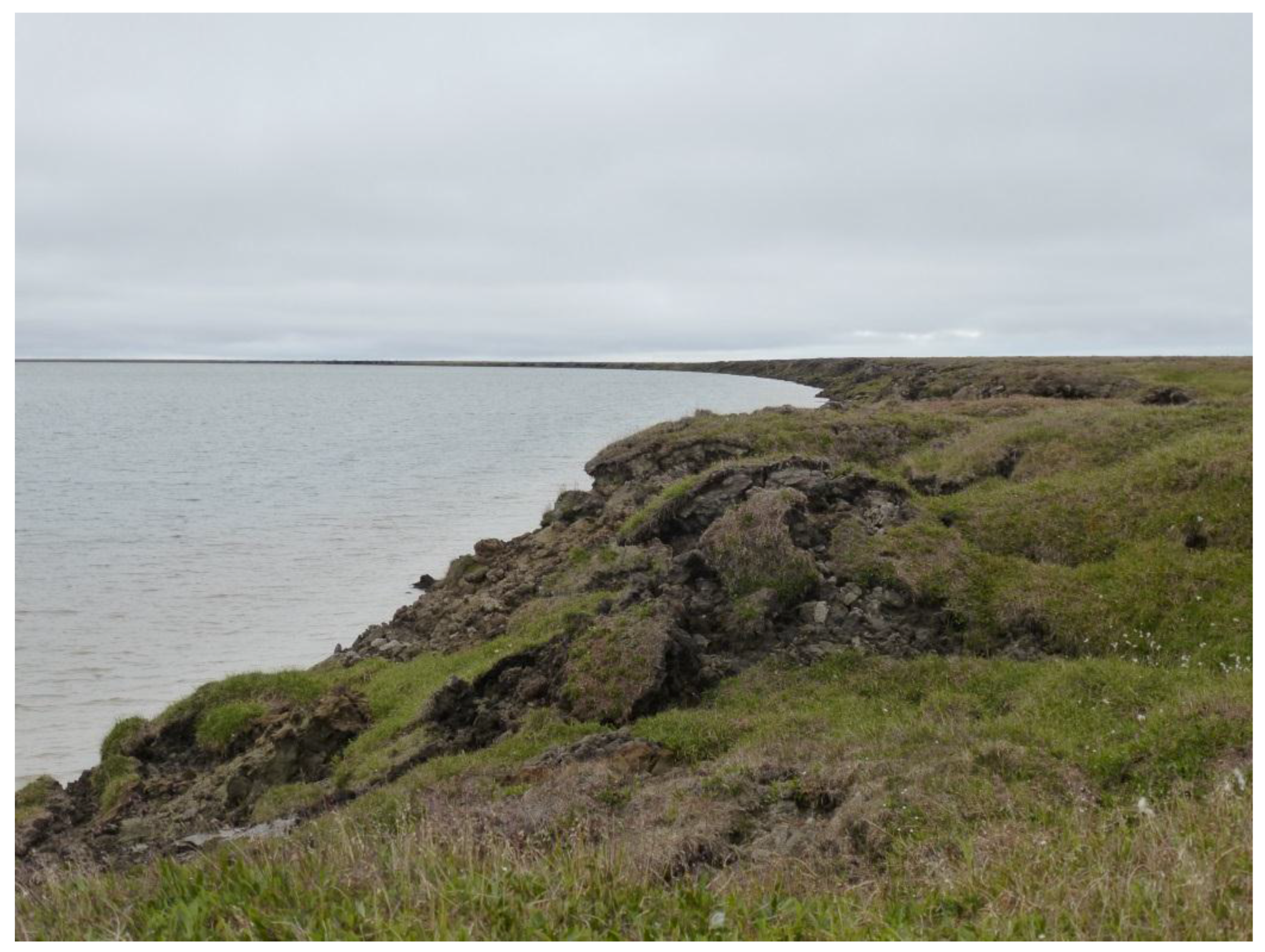
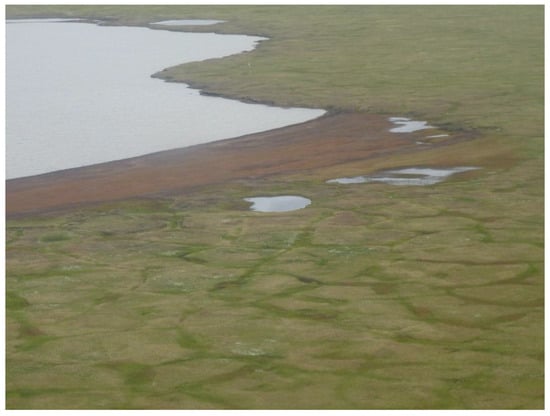


Figure A2.
Oblique aerial photo of partially drained lake on the Alaska North Slope presented in Figure 8b-1. Looking southeast. Photo taken on 15 July 2015 by I. Nitze.
Figure A2.
Oblique aerial photo of partially drained lake on the Alaska North Slope presented in Figure 8b-1. Looking southeast. Photo taken on 15 July 2015 by I. Nitze.
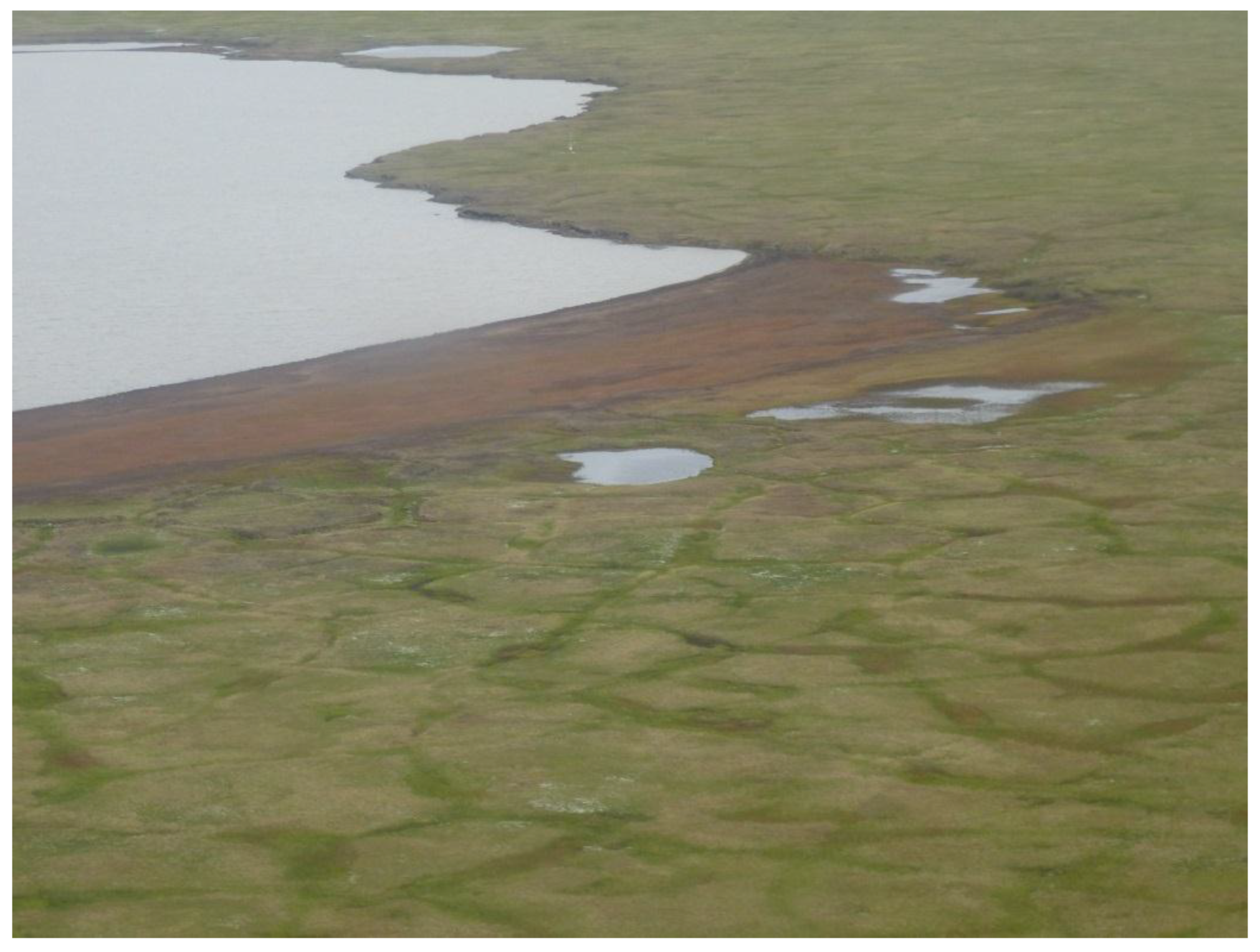
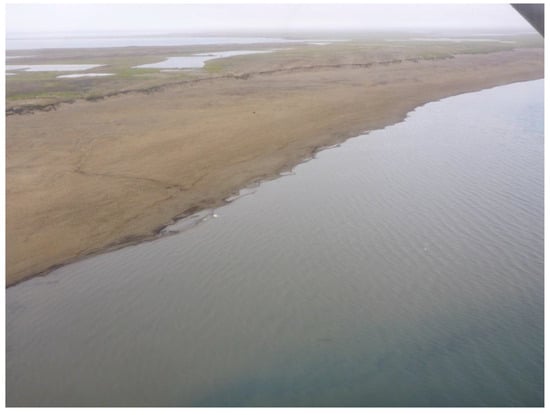


Figure A3.
Oblique aerial photo of partially drained lake on the Alaska North Slope presented in Figure 8b-2. Looking northwest. Photo taken on 19 July 2015 by I. Nitze.
Figure A3.
Oblique aerial photo of partially drained lake on the Alaska North Slope presented in Figure 8b-2. Looking northwest. Photo taken on 19 July 2015 by I. Nitze.
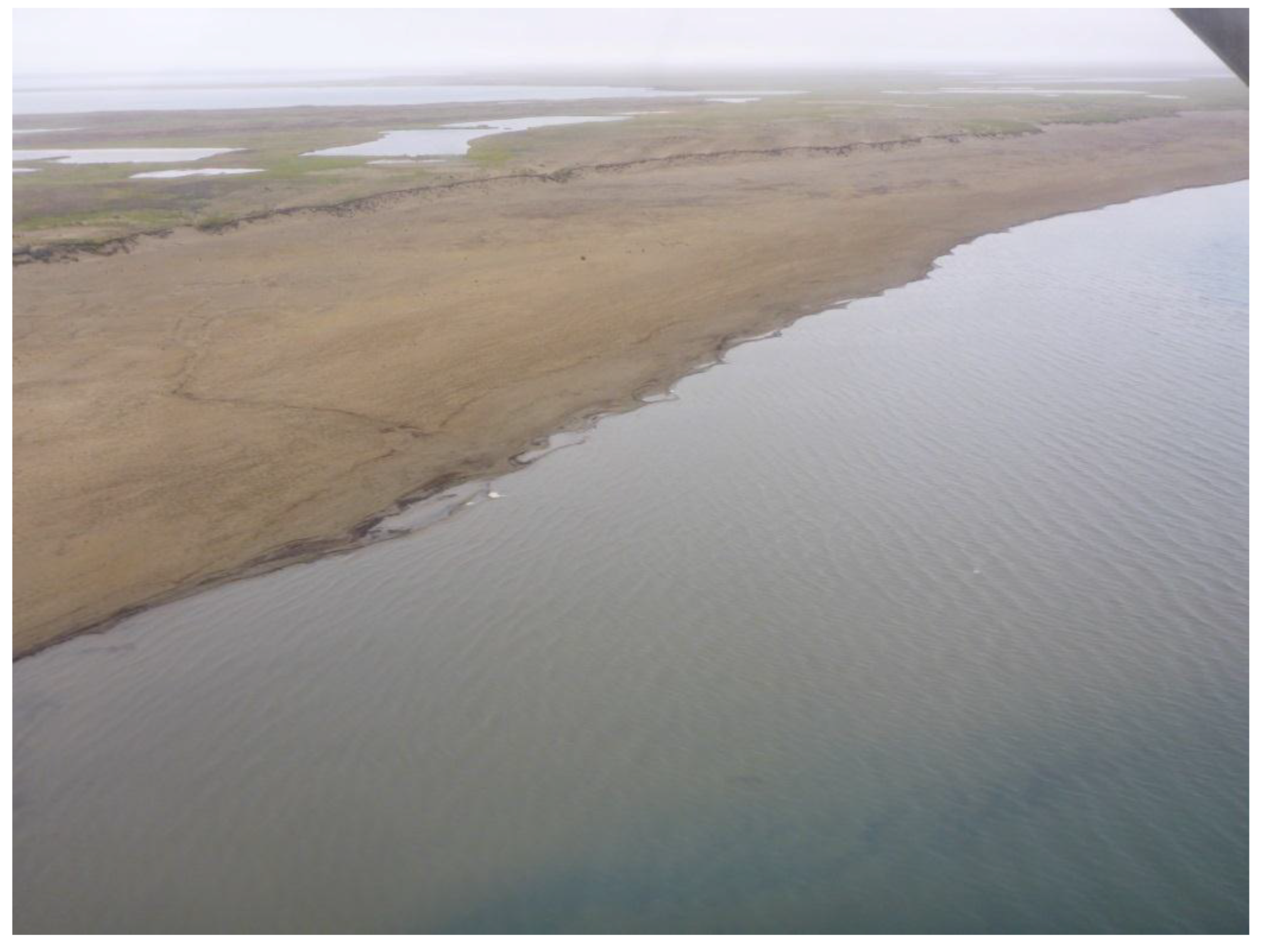
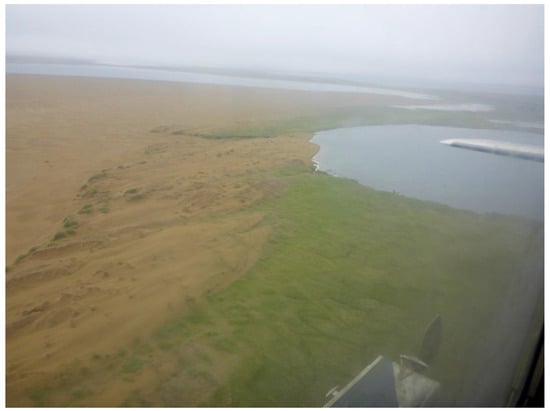


Figure A4.
Oblique aerial photo of refilled, naturally dammed lake on the Alaska North Slope presented in Figure 8b-3. Looking southwest. Photo taken on 19 July 2015 by I. Nitze.
Figure A4.
Oblique aerial photo of refilled, naturally dammed lake on the Alaska North Slope presented in Figure 8b-3. Looking southwest. Photo taken on 19 July 2015 by I. Nitze.
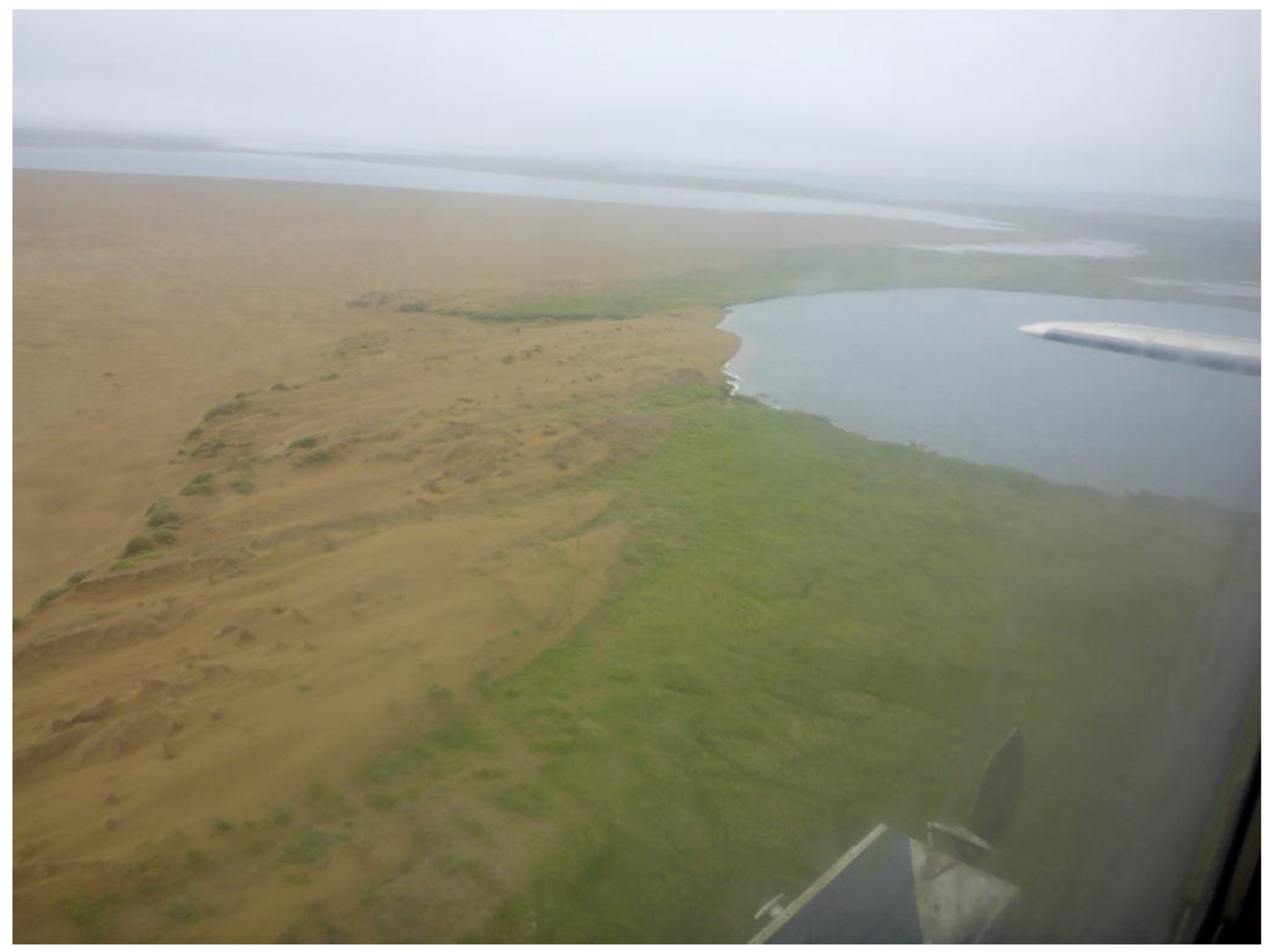
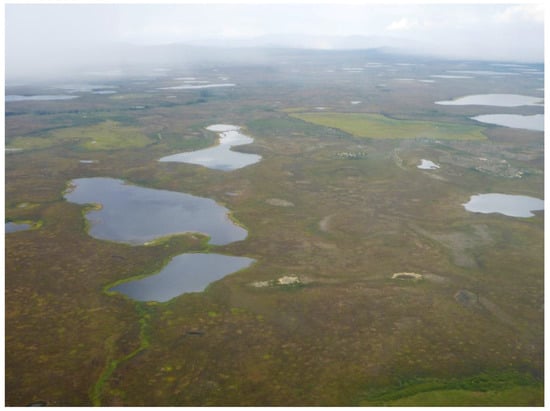


Figure A5.
Oblique aerial photo of drained and filled lakes in Kobuk-Selawik Lowlands in Figure 9b-1. Looking north. Photo taken on 8 August 2016 by J. Lenz.
Figure A5.
Oblique aerial photo of drained and filled lakes in Kobuk-Selawik Lowlands in Figure 9b-1. Looking north. Photo taken on 8 August 2016 by J. Lenz.
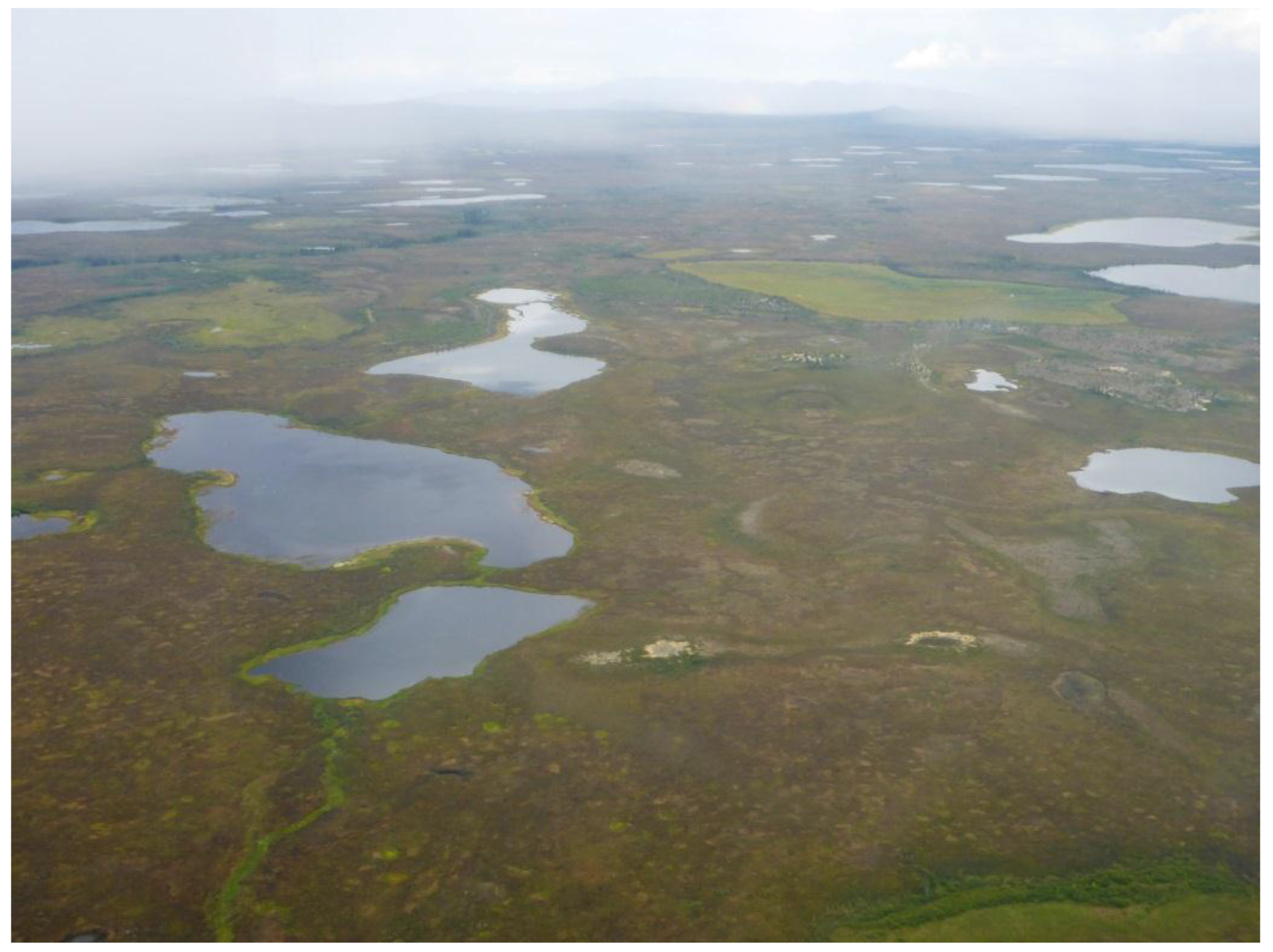
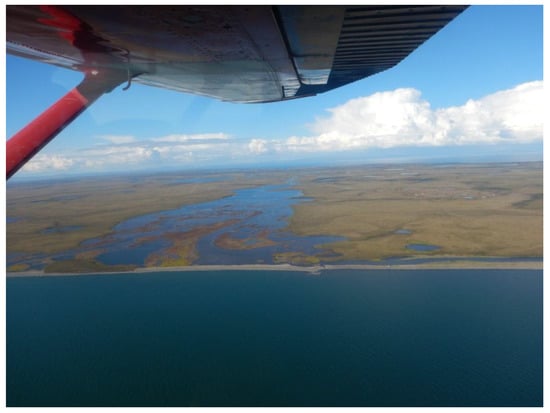


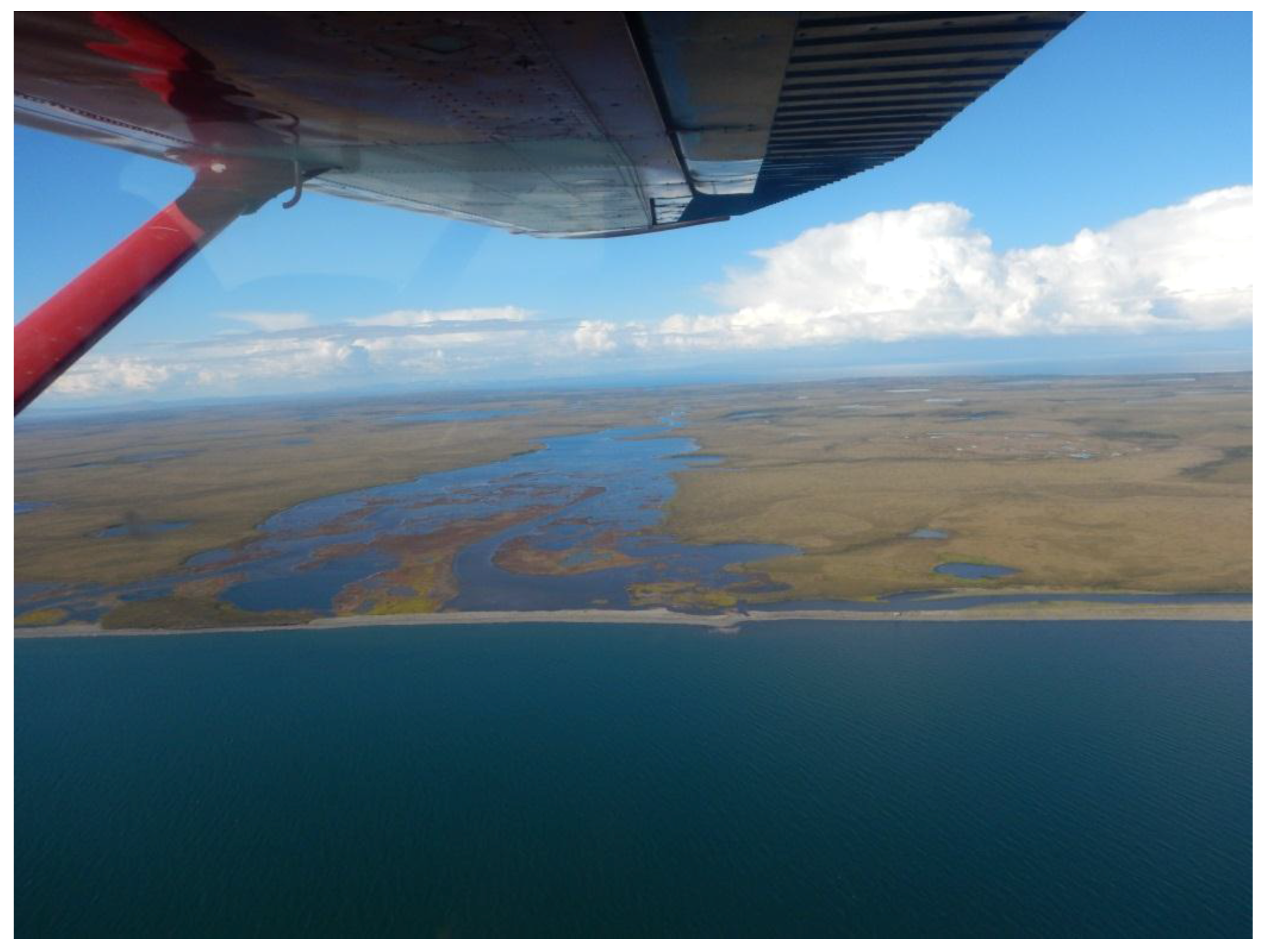
Figure A6.
Oblique aerial photo of wetting lagoon on the western Baldwin Peninsula in Figure 9b-3. Looking northeast. Photo taken on 8 August 2016 by M. Fuchs.
Figure A6.
Oblique aerial photo of wetting lagoon on the western Baldwin Peninsula in Figure 9b-3. Looking northeast. Photo taken on 8 August 2016 by M. Fuchs.

References
- Lehner, B.; Döll, P. Development and validation of a global database of lakes, reservoirs and wetlands. J. Hydrol. 2004, 296, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, L.C.; Sheng, Y.; MacDonald, G.M. A first pan-Arctic assessment of the influence of glaciation, permafrost, topography and peatlands on northern hemisphere lake distribution. Permafr. Periglac. Process. 2007, 18, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grosse, G.; Jones, B.; Arp, C. Thermokarst Lakes, Drainage, and Drained Basins; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Muster, S.; Roth, K.; Langer, M.; Lange, S.; Aleina, F.C.; Bartsch, A.; Morgenstern, A.; Grosse, G.; Jones, B.; Sannel, A.B.K.; et al. PeRL: A Circum-Arctic Permafrost Region Pond and Lake Database. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2017, 9, 317–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorgenson, M.T.; Shur, Y. Evolution of lakes and basins in northern Alaska and discussion of the thaw lake cycle. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2007, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, B.M.; Arp, C.D.; Whitman, M.S.; Nigro, D.; Nitze, I.; Beaver, J.; Gädeke, A.; Zuck, C.; Liljedahl, A.; Daanen, R.; et al. A lake-centric geospatial database to guide research and inform management decisions in an Arctic watershed in northern Alaska experiencing climate and land-use changes. Ambio 2017, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anthony, K.W.; Daanen, R.; Anthony, P.; von Deimling, T.S.; Ping, C.-L.; Chanton, J.P.; Grosse, G. Methane emissions proportional to permafrost carbon thawed in Arctic lakes since the 1950s. Nat. Geosci. 2016, 9, 679–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langer, M.; Westermann, S.; Boike, J.; Kirillin, G.; Grosse, G.; Peng, S.; Krinner, G. Rapid degradation of permafrost underneath waterbodies in tundra landscapes-towards a representation of thermokarst in land surface models. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olefeldt, D.; Goswami, S.; Grosse, G.; Hayes, D.; Hugelius, G.; Kuhry, P.; McGuire, A.D.; Romanovsky, V.E.; Sannel, A.B.K.; Schuur, E.A.G.; et al. Circumpolar distribution and carbon storage of thermokarst landscapes. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boike, J.; Georgi, C.; Kirilin, G.; Muster, S.; Abramova, K.; Fedorova, I.; Chetverova, A.; Grigoriev, M.; Bornemann, N.; Langer, M. Thermal processes of thermokarst lakes in the continuous permafrost zone of northern Siberia--observations and modeling (Lena River Delta, Siberia). Biogeosciences 2015, 12, 5941–5965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arp, C.D.; Jones, B.M.; Schmutz, J.A.; Urban, F.E.; Jorgenson, M.T. Two mechanisms of aquatic and terrestrial habitat change along an Alaskan Arctic coastline. Polar Biol. 2010, 33, 1629–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lantz, T.C.; Turner, K.W. Changes in lake area in response to thermokarst processes and climate in Old Crow Flats, Yukon. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2015, 120, 513–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorgenson, M.T.; Shur, Y.L.; Pullman, E.R. Abrupt increase in permafrost degradation in Arctic Alaska. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, B.M.; Grosse, G.; Arp, C.D.; Jones, M.C.; Anthony, W.A.K.M.; Romanovsky, V.E. Modern thermokarst lake dynamics in the continuous permafrost zone, northern Seward Peninsula, Alaska. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2011, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, B.M.; Arp, C.D. Observing a catastrophic thermokarst lake drainage in northern Alaska. Permafr. Periglac. Process. 2015, 26, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arp, C.D.; Jones, B.M.; Urban, F.E.; Grosse, G. Hydrogeomorphic processes of thermokarst lakes with grounded-ice and floating-ice regimes on the Arctic coastal plain, Alaska. Hydrol. Proce. 2011, 25, 2422–2438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liljedahl, A.K.; Boike, J.; Daanen, R.P.; Fedorov, A.N.; Frost, G.V.; Grosse, G.; Hinzman, L.D.; Iijma, Y.; Jorgenson, J.C.; Matveyeva, N.; et al. Pan-Arctic ice-wedge degradation in warming permafrost and its influence on tundra hydrology. Nat. Geosci. 2016, 9, 312–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindgren, P.R.; Grosse, G.; Romanovsky, V.E.; Farquharson, L.M. Landsat-based lake distribution and changes in western Alaska permafrost regions between 1972 and 2014. Int. Conf. Permafr. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carroll, M.L.; Townshend, J.R.; DiMiceli, C.M.; Noojipady, P.; Sohlberg, R.A. A new global raster water mask at 250 m resolution. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2009, 2, 291–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donchyts, G.; Baart, F.; Winsemius, H.; Gorelick, N.; Kwadijk, J.; van de Giesen, N. Earthś surface water change over the past 30 years. Nat. Climate Chang. 2016, 6, 810–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pekel, J.-F.; Cottam, A.; Gorelick, N.; Belward, A.S. High-resolution mapping of global surface water and its long-term changes. Nature 2016, 540, 418–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paltan, H.; Dash, J.; Edwards, M. A refined mapping of Arctic lakes using Landsat imagery. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2015, 36, 5970–5982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muster, S.; Heim, B.; Abnizova, A.; Boike, J. Water Body Distributions Across Scales: A Remote Sensing Based Comparison of Three Arctic Tundra Wetlands. Remote Sens. 2013, 5, 1498–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Barry, R.G.; Knowles, K.; Heginbottom, J.A.; Brown, J. Statistics and characteristics of permafrost and ground-ice distribution in the Northern Hemisphere. Polar Geogr. 2008, 31, 47–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlsson, J.M.; Lyon, S.W.; Destouni, G. Temporal Behavior of Lake Size-Distribution in a Thawing Permafrost Landscape in Northwestern Siberia. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 621–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, L.C.; Sheng, Y.; MacDonald, G.M.; Hinzman, L.D. Disappearing arctic lakes. Science 2005, 308, 1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olthof, I.; Fraser, R.H.; Schmitt, C. Landsat-based mapping of thermokarst lake dynamics on the Tuktoyaktuk Coastal Plain, Northwest Territories, Canada since 1985. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 168, 194–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riordan, B.; Verbyla, D.; McGuire, A.D. Shrinking ponds in subarctic Alaska based on 1950–2002 remotely sensed images. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2006, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roach, J.K.; Griffith, B.; Verbyla, D. Landscape influences on climate-related lake shrinkage at high latitudes. Global Chang. Biol. 2013, 19, 2276–2284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kravtsova, V.I.; Tarasenko, T.V. The Dynamics of thermokarst lakes under climate change since 1950. Cent. Yakutia Kriosf. Zeml. 2011, 15, 31–42. [Google Scholar]
- Hinkel, K.M.; Jones, B.M.; Eisner, W.R.; Cuomo, C.J.; Beck, R.A.; Frohn, R. Methods to assess natural and anthropogenic thaw lake drainage on the western Arctic coastal plain of northern Alaska. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2007, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plug, L.J.; Walls, C.; Scott, B.M. Tundra lake changes from 1978 to 2001 on the Tuktoyaktuk Peninsula, western Canadian Arctic. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walter, K.M.; Zimov, S.A.; Chanton, J.P.; Verbyla, D.; Chapin, F.S.I.I.I. Methane bubbling from Siberian thaw lakes as a positive feedback to climate warming. Nature 2006, 443, 71–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boike, J.; Grau, T.; Heim, B.; Günther, F.; Langer, M.; Muster, S.; Gouttevin, I.; Lange, S. Satellite-derived changes in the permafrost landscape of central Yakutia, 2000–2011: Wetting, drying, and fires. Global Planet. Chang. 2016, 139, 116–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labrecque, S.; Lacelle, D.; Duguay, C.R.; Lauriol, B.; Hawkings, J. Contemporary (1951–2001) evolution of lakes in the Old Crow Basin, Northern Yukon, Canada: Remote sensing, numerical modeling, and stable isotope analysis. Arctic 2009, 62, 225–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsakov, V.; Marushchak, I. The inter-Year changes of thermokarst lakes on North-East part of European Russia (in Russian). Issled. Zeml. iz Kosm. 2011, 5, 45–57. [Google Scholar]
- Kravtsova, V.; Radionova, T. Variations in size and number of thermokarst lakes in different permafrost regions: Spaceborne evidence. Earth's Cryosphere 2016, 1, 75–81. [Google Scholar]
- Jepsen, S.M.; Voss, C.I.; Walvoord, M.A.; Minsley, B.J.; Rover, J. Linkages between lake shrinkage/expansion and sublacustrine permafrost distribution determined from remote sensing of interior Alaska, USA. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2013, 40, 882–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshikawa, K.; Hinzman, L.D. Shrinking thermokarst ponds and groundwater dynamics in discontinuous permafrost near Council, Alaska. Permafr. Periglac. Process. 2003, 14, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andresen, C.G.; Lougheed, V.L. Disappearing Arctic tundra ponds: Fine-scale analysis of surface hydrology in drained thaw lake basins over a 65 year period (1948--2013). J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2015, 120, 466–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sannel, A.B.K.; Brown, I.A. High-resolution remote sensing identification of thermokarst lake dynamics in a subarctic peat plateau complex. Can. J. Remote Sens. 2010, 36, S26–S40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Necsoiu, M.; Dinwiddie, C.L.; Walter, G.R.; Larsen, A.; Stothoff, S.A. Multi-temporal image analysis of historical aerial photographs and recent satellite imagery reveals evolution of water body surface area and polygonal terrain morphology in Kobuk Valley National Park, Alaska. Environ. Res. Lett. 2013, 8, 025007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulrich, M.; Matthes, H.; Schirrmeister, L.; Schütze, J.; Park, H.; Iijima, Y.; Fedorov, A.N. Differences in behavior and distribution of permafrost-related lakes in Central Yakutia and their response to climatic drivers. Water Res. Res. 2017, 53, 1167–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarasenko, T.V. Interannual variations in the areas of thermokarst lakes in Central Yakutia. Water Res. 2013, 40, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, M.C.; Potapov, P.V.; Moore, R.; Hancher, M.; Turubanova, S.A.; Tyukavina, A.; Thau, D.; Stehman, S.V.; Goetz, S.J.; Loveland, T.R.; et al. High-resolution global maps of 21st-century forest cover change. Science 2013, 342, 850–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wulder, M.A.; White, J.C.; Loveland, T.R.; Woodcock, C.E.; Belward, A.S.; Cohen, W.B.; Fosnight, E.A.; Shaw, J.; Masek, J.G.; Roy, D.P. The global Landsat archive: Status, consolidation, and direction. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 185, 271–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraser, R.H.; Olthof, I.; Kokelj, S.V.; Lantz, T.C.; Lacelle, D.; Brooker, A.; Wolfe, S.; Schwarz, S. Detecting Landscape Changes in High Latitude Environments Using Landsat Trend Analysis: 1. Visualization. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 11533–11557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooker, A.; Fraser, R.H.; Olthof, I.; Kokelj, S.V.; Lacelle, D. Mapping the activity and evolution of retrogressive thaw slumps by tasselled cap trend analysis of a Landsat satellite image stack. Permafr. Periglac. Process. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nitze, I.; Grosse, G. Detection of landscape dynamics in the Arctic Lena Delta with temporally dense Landsat time-series stacks. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 181, 27–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, J.; Masek, J.G. The vegetation greenness trend in Canada and US Alaska from 1984–2012 Landsat data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 176, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, D.A.; Raynolds, M.K.; Daniëls, F.J.A.; Einarsson, E.; Elvebakk, A.; Gould, W.A.; Katenin, A.E.; Kholod, S.S.; Markon, C.J.; Melnikov, E.S.; et al. The circumpolar Arctic vegetation map. J. Veg. Sci. 2005, 16, 267–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinkel, K.M.; Sheng, Y.; Lenters, J.D.; Lyons, E.A.; Beck, R.A.; Eisner, W.R.; Wang, J. Thermokarst Lakes on the Arctic Coastal Plain of Alaska: Geomorphic Controls on Bathymetry. Permafr. Periglac. Process 2012, 23, 218–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorgenson, M.T.; Yoshikawa, K.; Kanevskiy, M.; Shur, Y.; Romanovsky, V.; Marchenko, S.; Grosse, G.; Brown, J.; Jones, B. Permafrost characteristics of Alaska. In Proceedings of the Ninth International Conference on Permafrost, Fairbanks, AK, USA, 29 June–3 July 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Hinkel, K.M.; Frohn, R.C.; Nelson, F.E.; Eisner, W.R.; Beck, R.A. Morphometric and spatial analysis of thaw lakes and drained thaw lake basins in the western Arctic Coastal Plain, Alaska. Permafr. Periglac. Process. 2005, 16, 327–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NOAA. Climate Data Online: 1981–2010 Normals, 2017. Available online: https://www.ncdc.noaa.gov/cdo-web/datatools/normals (accessed on 2 May 2017).
- Farquharson, L.M.; Mann, D.H.; Grosse, G.; Jones, B.M.; Romanovsky, V.E. Spatial distribution of thermokarst terrain in Arctic Alaska. Geomorphology 2016, 273, 116–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenz, J.; Jones, B.M.; Wetterich, S.; Tjallingii, R.; Fritz, M.; Arp, C.D.; Rudaya, N.; Grosse, G. Impacts of shore expansion and catchment characteristics on lacustrine thermokarst records in permafrost lowlands, Alaska Arctic Coastal Plain. Arktos 2016, 2, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sellman, P.V.; Brown, J.; Lewellen, R.I.; McKim, H.; Merry, C. The Classification and Geomor-Phic Implications of Thaw Lakes of the Arctic Coastal Plain, Alaska; U.S. Department of Defense, Department of the Army; Corps of Engineers, Cold Regions Research and Engineering Laboratory: Washington, DC, USA, 1975.
- Jones, B.M.; Arp, C.D.; Hinkel, K.M.; Beck, R.A.; Schmutz, J.A.; Winston, B. Arctic lake physical processes and regimes with implications for winter water availability and management in the National Petroleum Reserve Alaska. Environ. Manag. 2009, 43, 1071–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanevskiy, M.; Shur, Y.; Jorgenson, M.T.; Ping, C.-L.; Michaelson, G.J.; Fortier, D.; Stephani, E.; Dillon, M.; Tumskoy, V. Ground ice in the upper permafrost of the Beaufort Sea coast of Alaska. Cold Reg. Sci. Technol. 2013, 85, 56–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schirrmeister, L.; Froese, D.; Tumskoy, V.; Grosse, G.; Wetterich, S. Yedoma: Late Pleistocene ice-rich syngenetic permafrost of Beringia. In Encyclopedia of Quaternary Science, 2nd ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 542–552. [Google Scholar]
- Raynolds, M.K.; Walker, D.A.; Ambrosius, K.J.; Brown, J.; Everett, K.R.; Kanevskiy, M.; Kofinas, G.P.; Romanovsky, V.E.; Shur, Y.; Webber, P.J. Cumulative geoecological effects of 62 years of infrastructure and climate change in ice-rich permafrost landscapes, Prudhoe Bay Oilfield, Alaska. Global Chang. Biol. 2014, 20, 1211–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larsen, A.S.; O'Donnell, J.A.; Schmidt, J.H.; Kristenson, H.J.; Swanson, D.K. Physical and chemical characteristics of lakes across heterogeneous landscapes in arctic and subarctic Alaska. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cable, W.L.; Romanovsky, V.E.; Jorgenson, M.T. Scaling-up permafrost thermal measurements in western Alaska using an ecotype approach. Cryosphere 2016, 10, 2517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorgenson, M.T.; Roth, J.E.; Miller, P.F.; Macander, M.J.; Duffy, M.S.; Pullman, E.R.; Attanas, L.B.; Wells, A.F.; Talbot, S. An Ecological Land Survey and Landcover Map of the Selawik National Wildlife Refuge; ABR, Inc.: Fairbanks, AK, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Ivanov, M.S. Cryogenic Structure of Quaternary Deposits of the Lena-Aldan-Depression; Nauka: Novosibirsk, Russia, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Fedorov, A.N.; Ivanova, R.N.; Park, H.; Hiyama, T.; Iijima, Y. Recent air temperature changes in the permafrost landscapes of northeastern Eurasia. Polar Sci. 2014, 8, 114–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Kane, D.L.; Hinzman, L.D.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, T.; Ye, H. Siberian Lena River hydrologic regime and recent change. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2002, 107, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soloviev, P.A. Cryolithozone of the Northern Part of the Leno-Amga Interfluve; Publishing House of the USSR Acadamy of Sciences: Moscow, Russia, 1959. [Google Scholar]
- Fedorov, A.N.; Gavriliev, P.P.; Konstantinov, P.Y.; Hiyama, T.; Iijima, Y.; Iwahana, G. Estimating the water balance of a thermokarst lake in the middle of the Lena River basin, eastern Siberia. Ecohydrology 2014, 7, 188–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crate, S.; Ulrich, M.; Habeck, J.; Desyatkin, A.; Desyatkin, R.; Fedorov, A.; Hiyama, T.; Iijima, Y.; Ksenofontov, S.; Mészáros, C.; et al. Permafrost livelihoods: A transdisciplinary analysis of thermokarst-based systems of indigenous land use. Anthropocene 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplina, T. History of permafrost in Northern Yakutia. In History of the Development of Perennial Frozen Deposits in Eurasia; Nauka: Moscow, Russia, 1981; pp. 153–181. [Google Scholar]
- Ershov, E. Geocryology of the USSR; East Siberia and Far East: Moscow, Russia, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Shmelev, D.; Veremeeva, A.; Kraev, G.; Kholodov, A.; Spencer, R.G.M.; Walker, W.S.; Rivkina, E. Estimation and Sensitivity of Carbon Storage in Permafrost of North-Eastern Yakutia. Permafr. Periglac. Process. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veremeeva, A.A.; Glushkova, N.V. Formation of relief in the regions of Ice complex deposits distribution: Remote sensing and GIS studies in the Kolyma lowland tundra. Earth's Cryosphere 2016, 1, 14–24. [Google Scholar]
- Spector, V. Quaternary Deposits of the Coastal Lowland (Khallerchin Tundra); The Cenozoic of East Yakutia, Yakut Branch of the Siberian Department of the USSR Academy of Sciences: Yakutsk, USSR, 1980; pp. 87–97. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Z.; Wang, S.; Woodcock, C.E. Improvement and expansion of the Fmask algorithm: Cloud, cloud shadow, and snow detection for Landsats 4–7, 8, and Sentinel 2 images. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 159, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olthof, I.; Fraser, R.H. Detecting Landscape Changes in High Latitude Environments Using Landsat Trend Analysis: 2. Classification. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 11558–11578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, P.K. Estimates of the regression coefficient based on Kendallś tau. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1968, 63, 1379–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theil, H. A rank-invariant method of linear and polynomial regression analysis. In Henri Theil’s Contributions to Economics and Econometrics; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1992; pp. 345–381. [Google Scholar]
- Rover, J.; Ji, L.; Wylie, B.K.; Tieszen, L.L. Establishing water body areal extent trends in interior Alaska from multi-temporal Landsat data. Remote Sens. Lett. 2012, 3, 595–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raynolds, M.K.; Walker, D.A. Increased wetness confounds Landsat-derived NDVI trends in the central Alaska North Slope region, 1985–2011. Environ. Res. Lett. 2016, 11, 085004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, R.E.; Yang, Z.; Cohen, W.B. Detecting trends in forest disturbance and recovery using yearly Landsat time series: 1. LandTrendr—Temporal segmentation algorithms. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 2897–2910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiman, L. Random Forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nitze, I.; Barrett, B.; Cawkwell, F. Temporal optimisation of image acquisition for land cover classification with Random Forest and MODIS time-series. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2015, 34, 136–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrett, B.; Nitze, I.; Green, S.; Cawkwell, F. Assessment of multi-temporal, multi-sensor radar and ancillary spatial data for grasslands monitoring in Ireland using machine learning approaches. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 152, 109–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belgiu, M.; Drăgut, L. Random forest in remote sensing: A review of applications and future directions. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2016, 114, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nitze, I.; Schulthess, U.; Asche, H. Comparison of machine learning algorithms random forest, artificial neural network and support vector machine to maximum likelihood for supervised crop type classification. In Proceedings of the 4th GEOBIA, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 7–9 May 2012; pp. 7–9. [Google Scholar]
- Santoro, M.; Strozzi, T. Circumpolar digital elevation models >55 N with links to geotiff images. PANGAEA 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desyatkin, R. Soil Formation in Thermokarst Depression—Alases of Cryolithozone; Nauka: Novosibirsk, Russia, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, M.; Rowland, J.C.; Wilson, C.J.; Altmann, G.L.; Brumby, S.P. The importance of natural variability in lake areas on the detection of permafrost degradation: A case study in the Yukon Flats, Alaska. Permafr. Periglac. Process. 2013, 24, 224–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veremeeva, A.; Gubin, S. Modern tundra landscapes of the Kolyma Lowland and their evolution in the Holocene. Permafr. Periglac. Process. 2009, 20, 399–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iijima, Y.; Fedorov, A.N.; Park, H.; Suzuki, K.; Yabuki, H.; Maximov, T.C.; Ohata, T. Abrupt increases in soil temperatures following increased precipitation in a permafrost region, central Lena River basin, Russia. Permafr. Periglac. Process. 2010, 21, 30–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nitze, I.; Grosse, G.; Jones, B.M.; Arp, C.D.; Ulrich, M.; Fedorov, A.; Veremeeva, A. Landsat-based trend analysis of lake dynamics across northern permafrost regions, supplementary material. PANGAEA 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).