Investigating the Influence of Variable Freshwater Ice Types on Passive and Active Microwave Observations
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Study Area
3. Data and Methods
3.1. Snow and Ice Cover Data
3.2. Airborne Radiometer Data
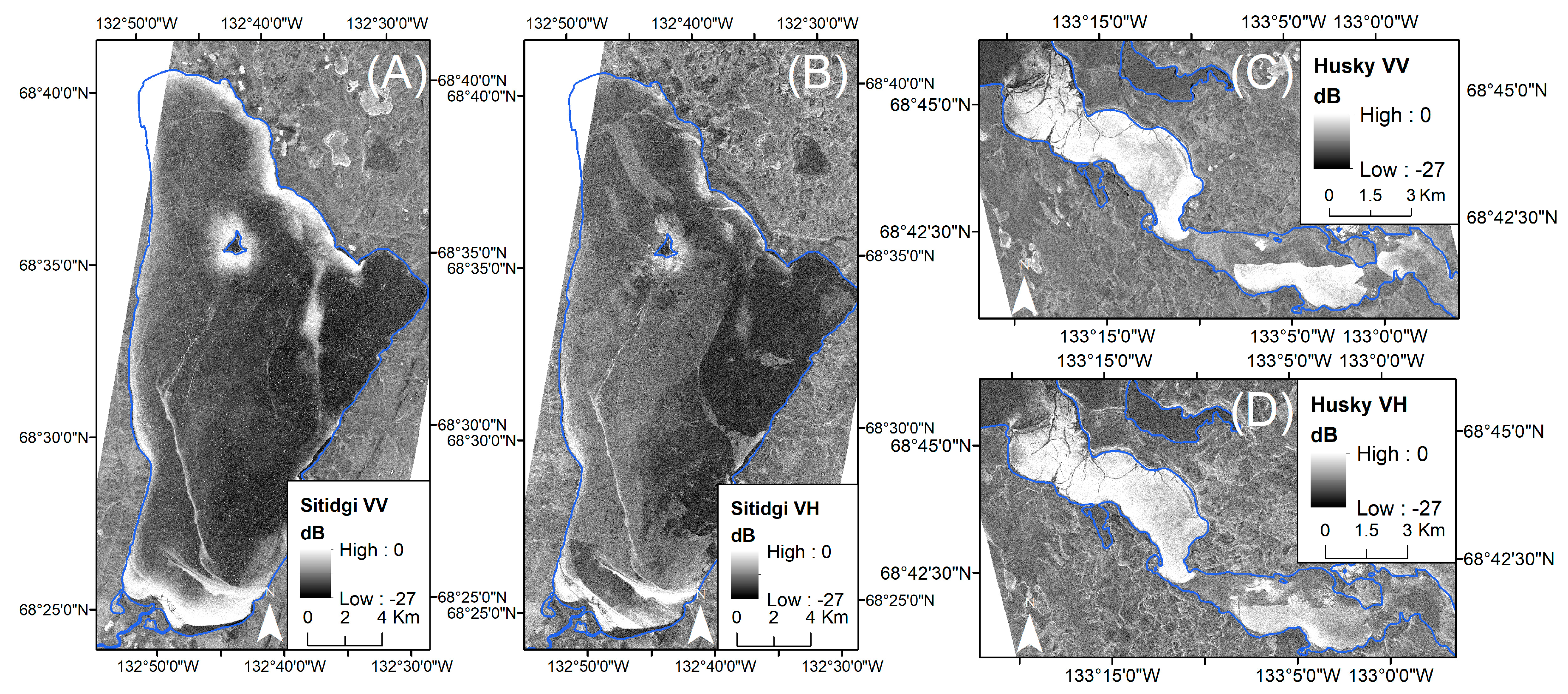
3.3. Spaceborne Active Microwave Data
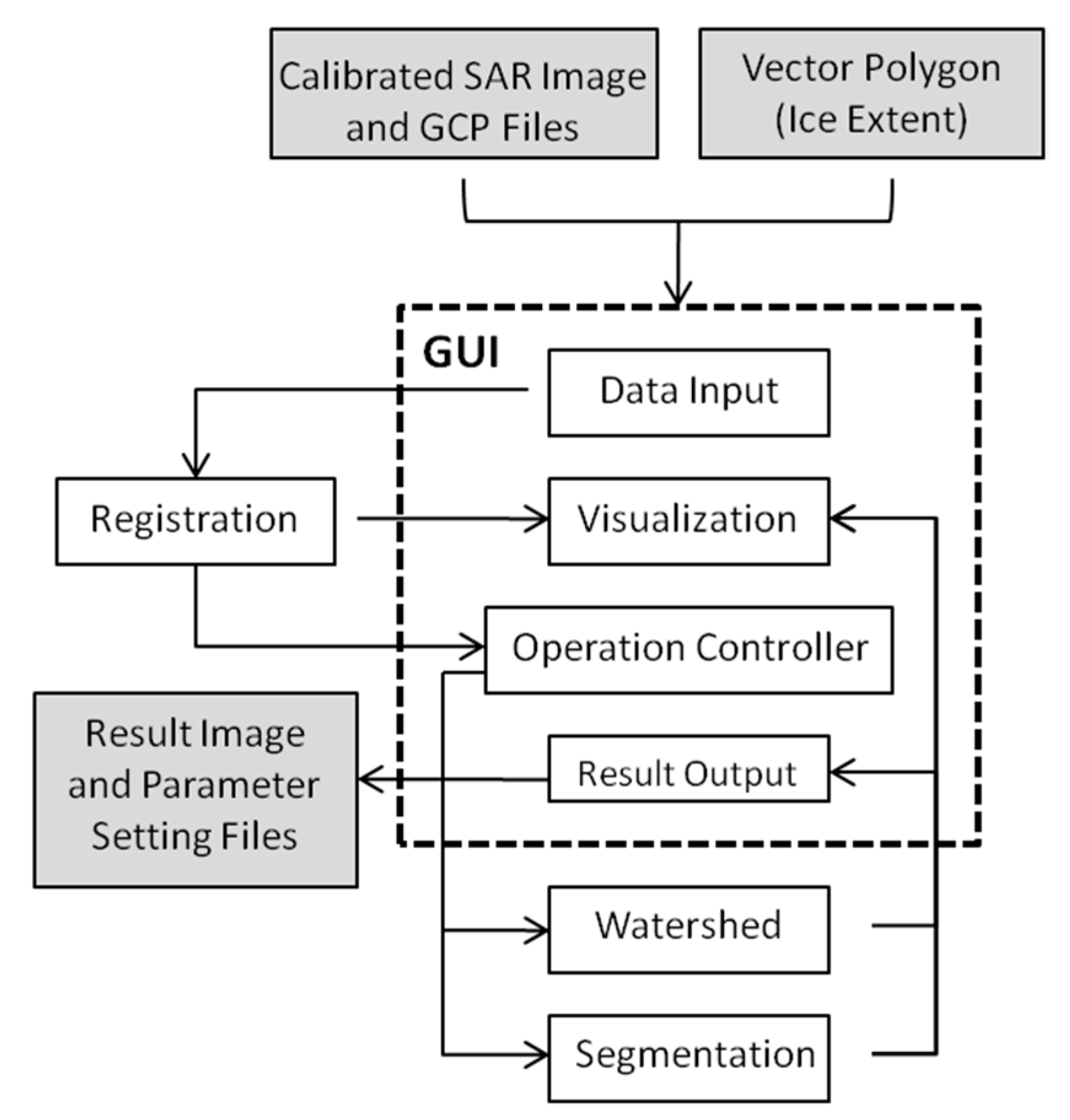
3.4. Model Description: MAGIC
4. Results
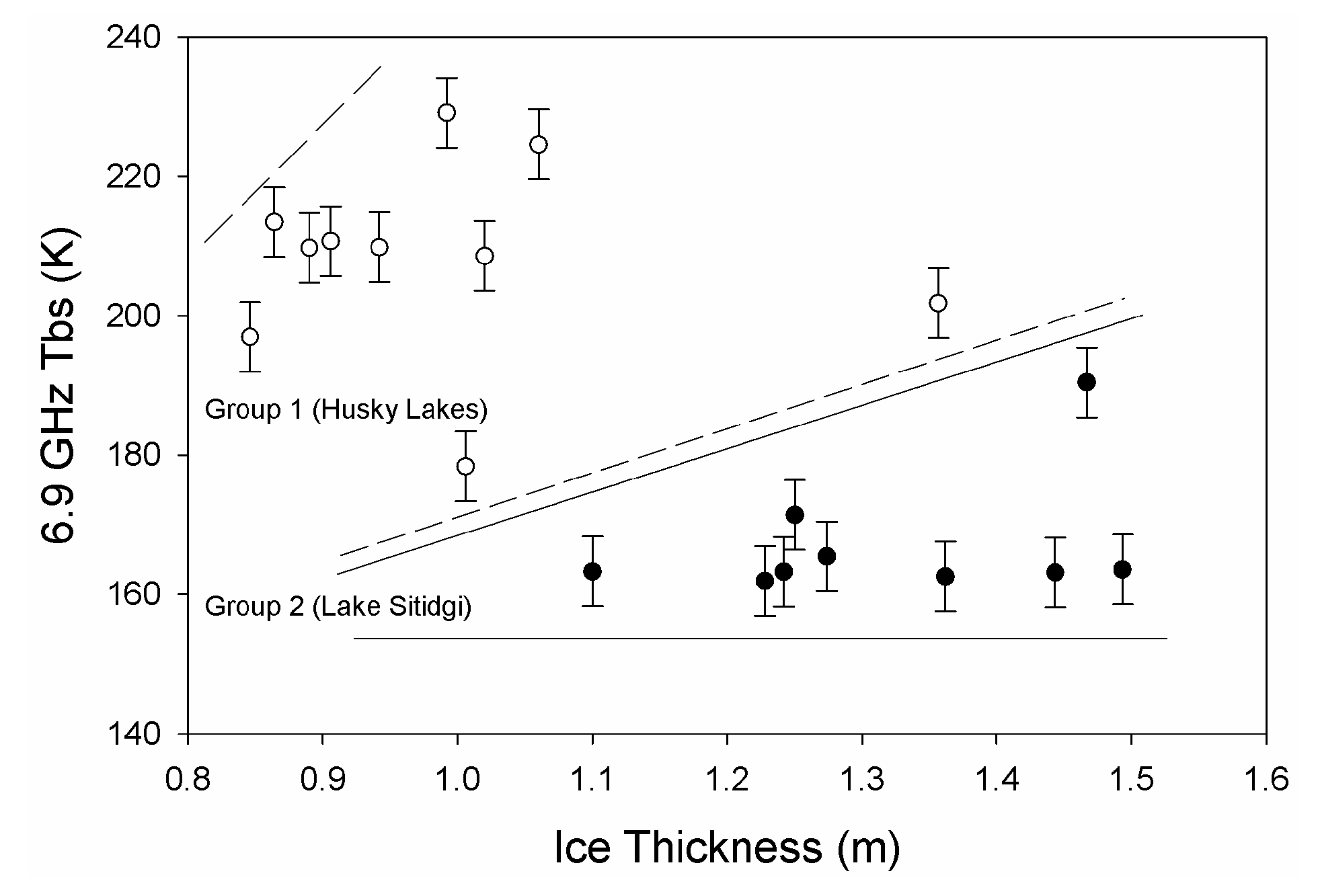
4.1. Brackish/Freshwater Class Delineation From Passive Microwave Tb
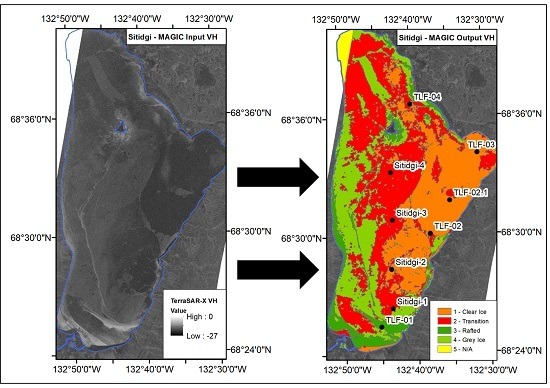
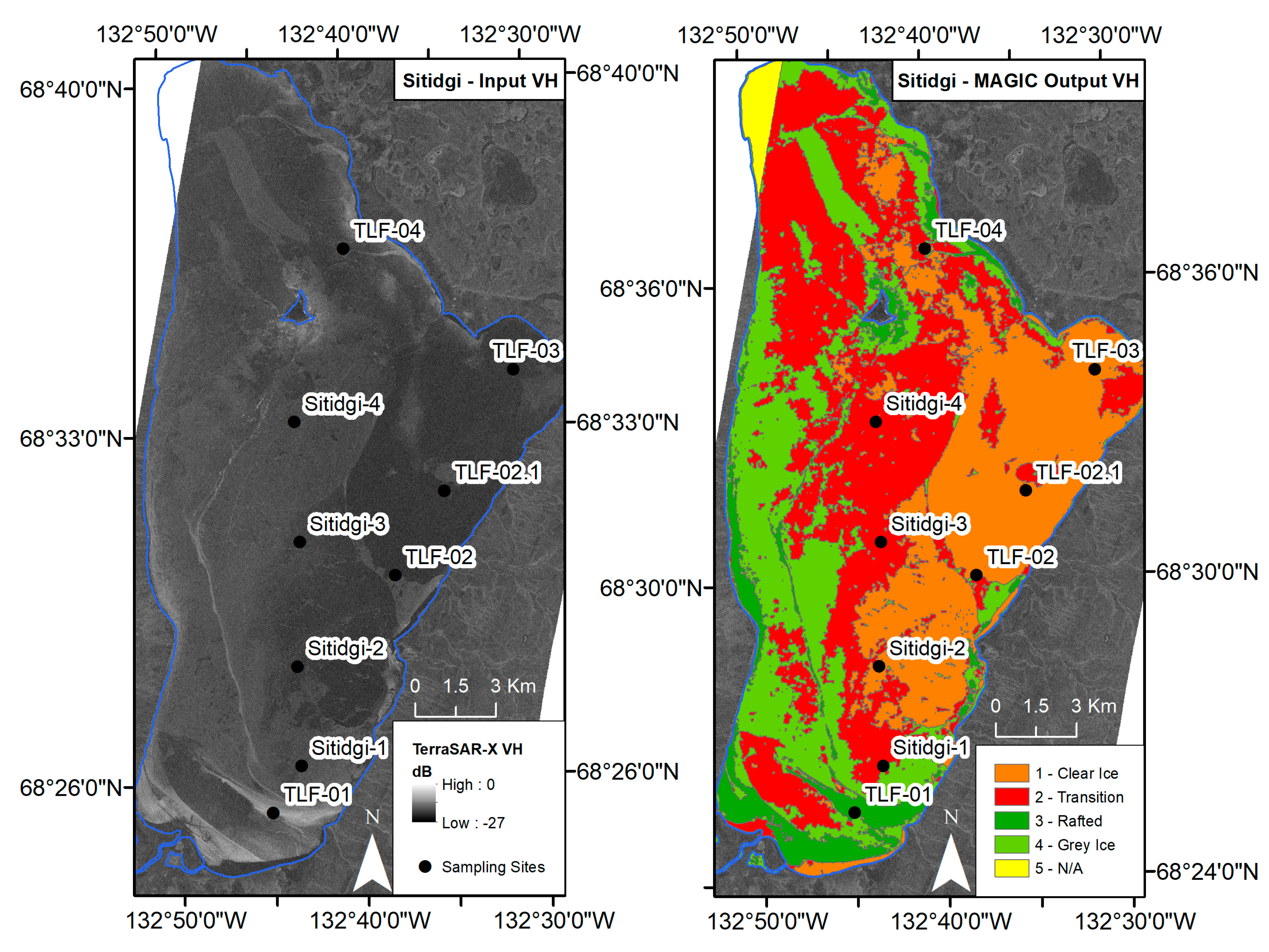
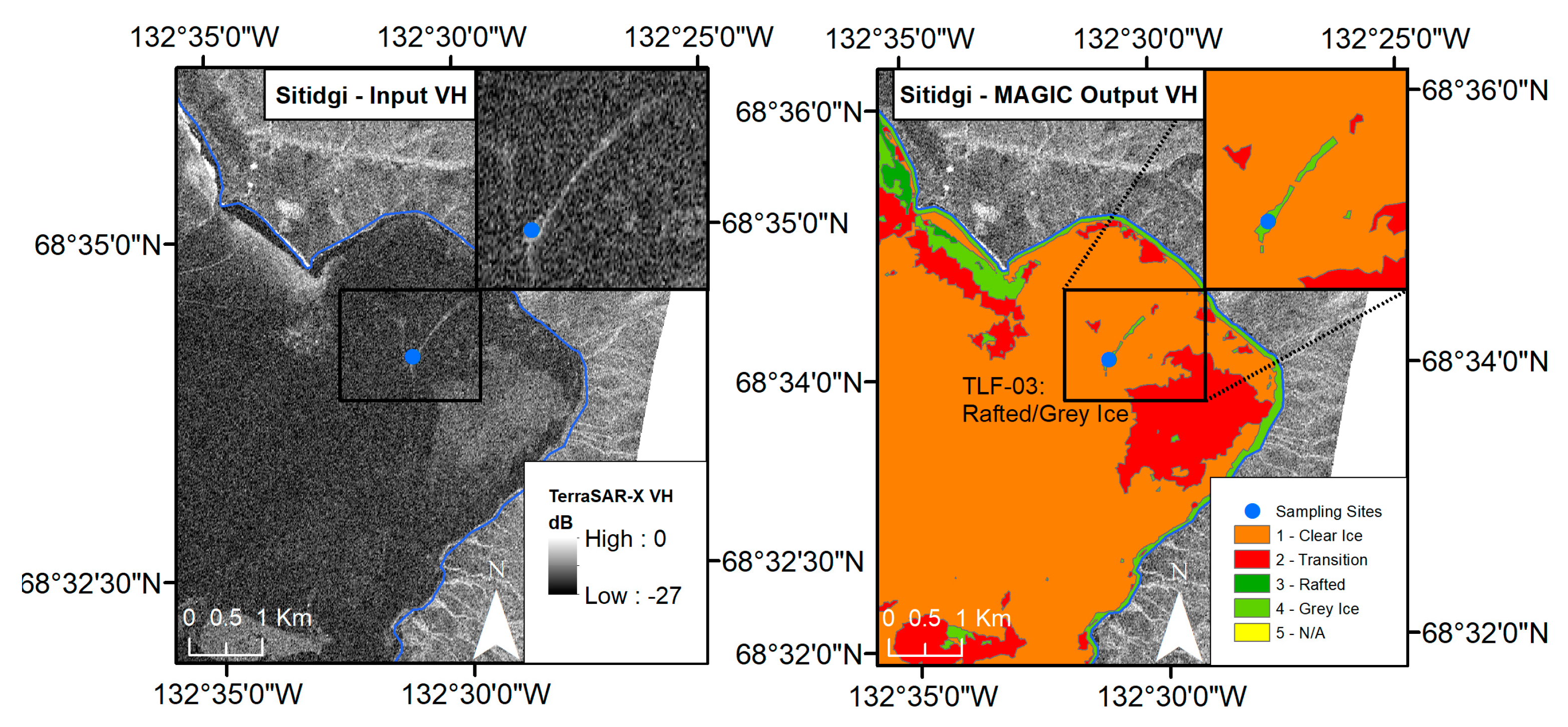
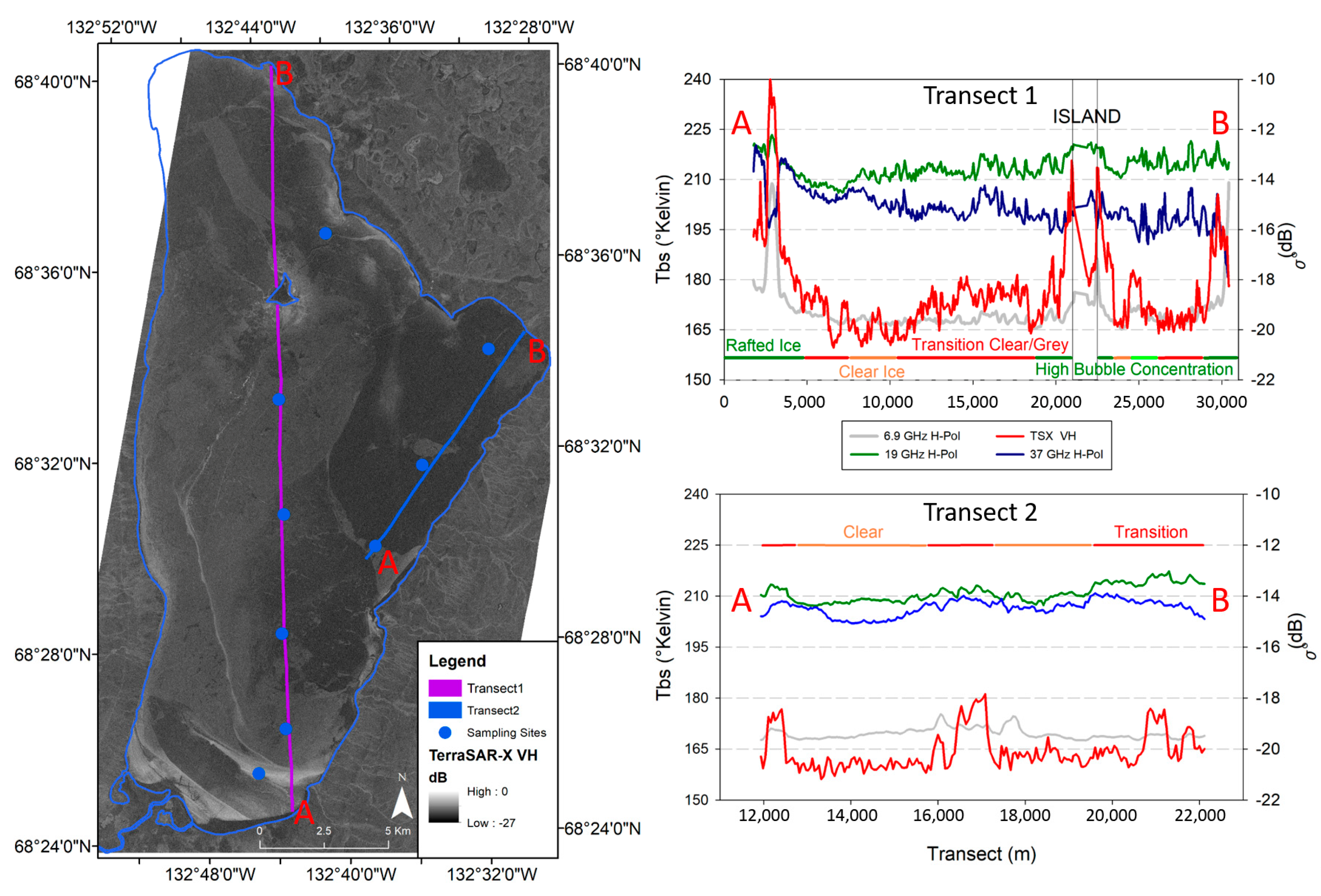
4.2. MAGIC Segmentation—Sitidgi Lake
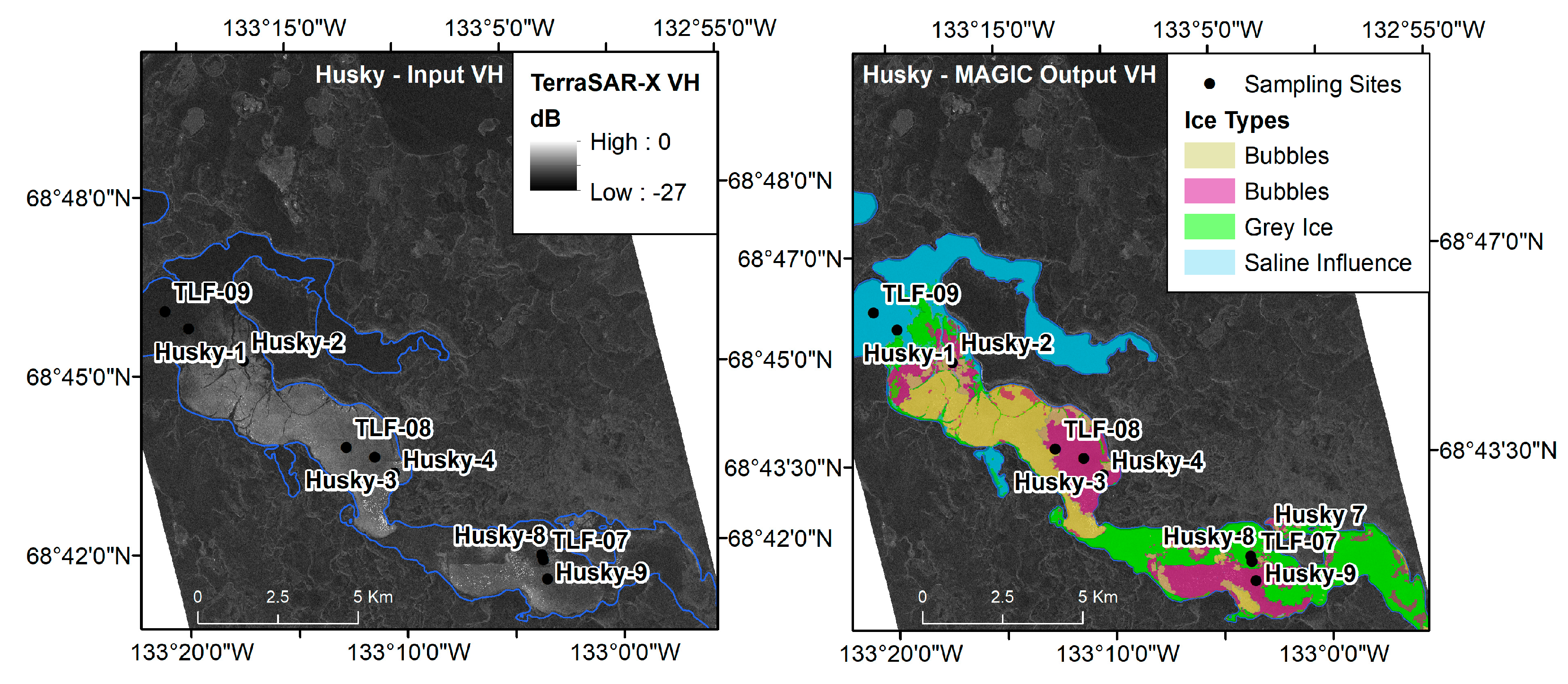
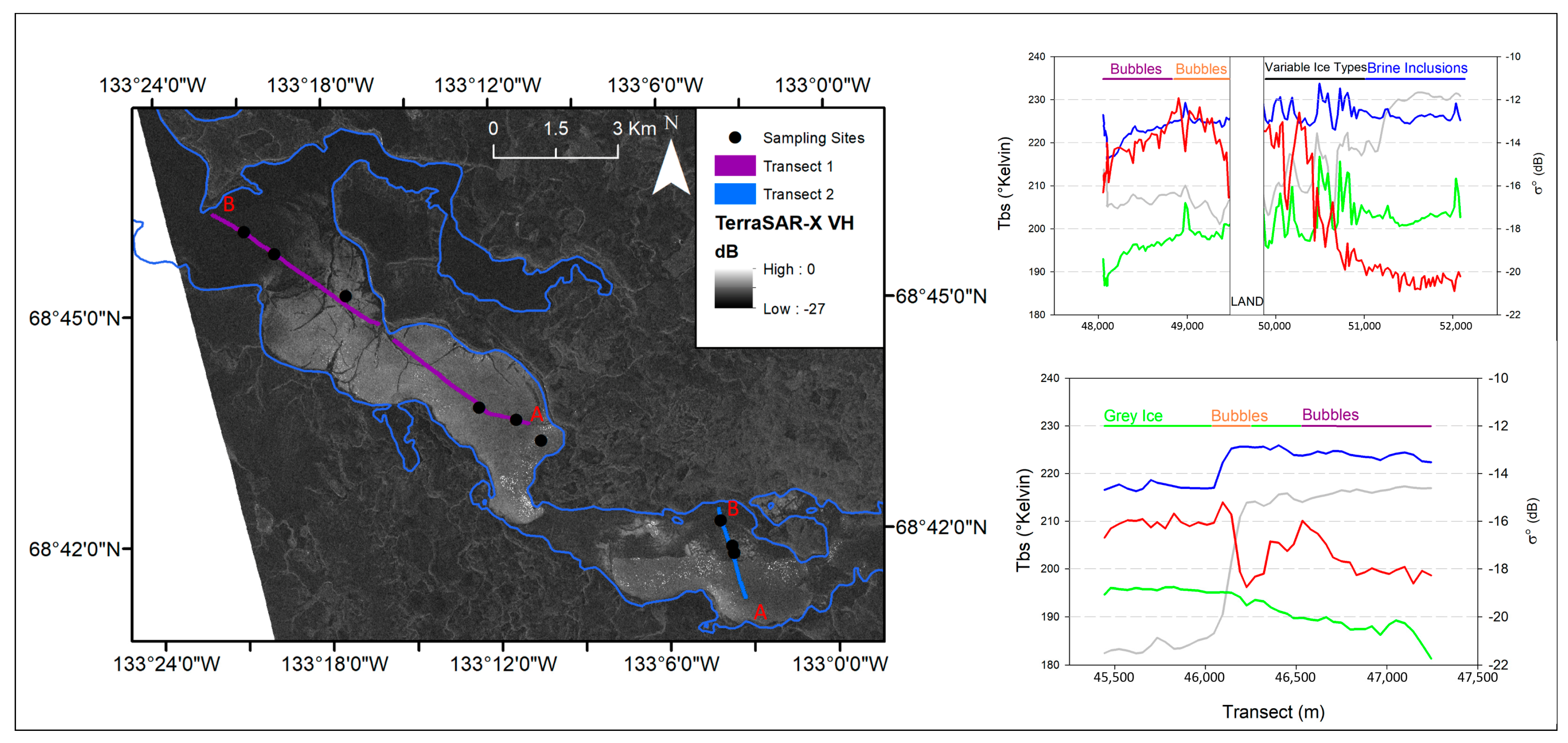
4.3. MAGIC Segmentation—Husky Lakes
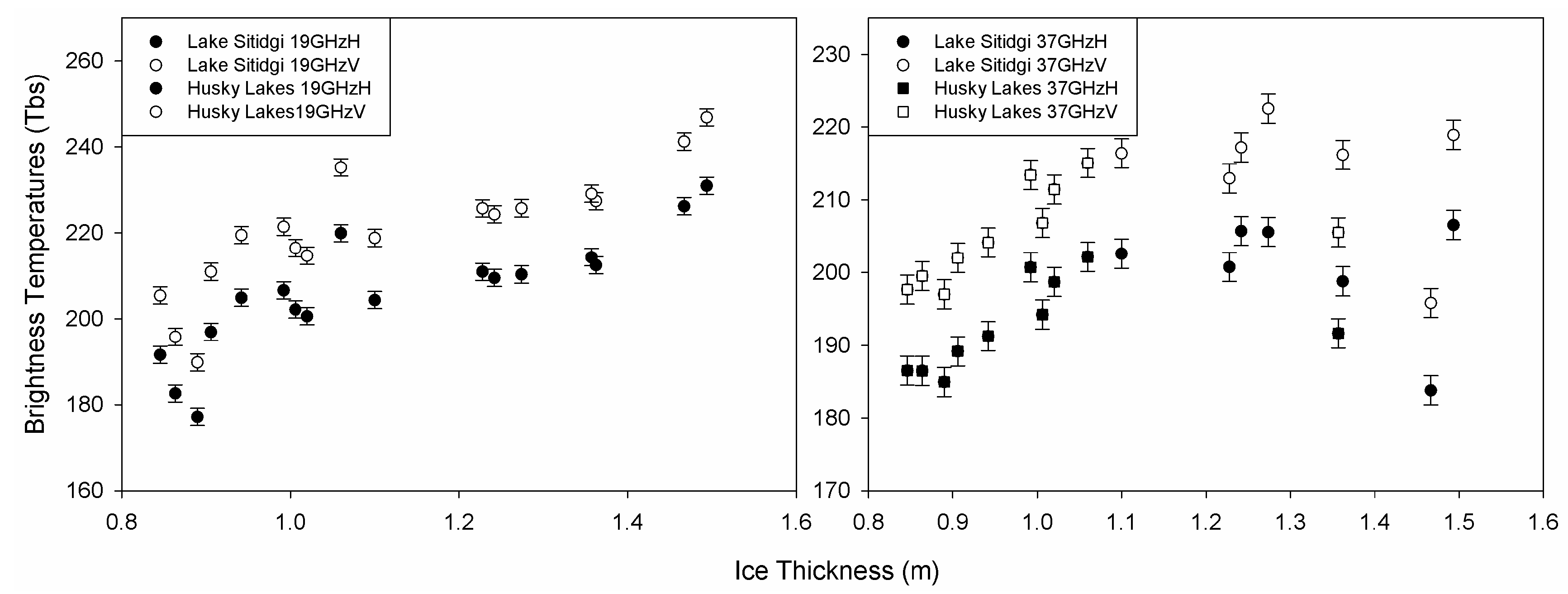
5. Active/Passive Microwave Relationships
5.1. Sitidgi Lake—Active/Passive Transects
5.2. Husky Lakes—Active/Passive Transects
6. Discussion
7. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brown, R.; Walker, A.E.; Goodison, B. Seasonal snow cover monitoring in Canada: An assessment of Canadian contributions for global climate modeling. In Proceedings of the 57th Eastern Snow Conference, Syracuse, NY, USA, 17–19 May 2000; pp. 131–141. [Google Scholar]
- Adams, R.M.; Houston, L.L.; Weiher, R.F. The Value of Snow and Snow Information Services; Technical Report; DG1330-03-SE-1097; NOAA’s National Operational Hydrological Remote Sensing Center: Chanhassen, NH, USA, 2004.
- Hirose, T.; Kapfer, M.; Bennett, J.; Cott, P.; Manson, G.; Solomon, S. Bottomfast Ice Mapping and the Measurement of Ice Thickness on tundra Lakes Using C-Band Synthetic Aperture Radar Remote Sensing. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2008, 44, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, S.; Glatzmaier, G.; Roads, J.O. Snow Hydrology. In Climate Change and Energy Policy; Rosen, L., Glasser, R., Eds.; American Institute of Physics: New York, NY, USA, 1992; pp. 149–154. [Google Scholar]
- Kelly, R.E.; Chang, T.; Tsang, L.; Foster, J.L. A prototype AMSR-E global snow area and snow depth algorithm. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2003, 41, 230–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prowse, T.D.; Bonsal, B.R.; Duguay, C.R.; Lacroix, M.P. River-ice break-up/freeze-up: A review of climatic drivers, historical trends and future predictions. Ann. Glaciol. 2007, 46, 443–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, L.C.; Duguay, C.R. The response and role of ice cover in lake-climate interactions. Prog. Phys. Geogr. 2010, 34, 671–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serreze, M.C.; Francis, J.A. The Arctic amplification debate. Clim. Chang. 2006, 76, 241–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derksen, C.; Walker, A.; Goodison, B. A comparison of 18 winter seasons of in situ and passive microwave-derived snow water equivalent estimates in Western Canada. Remote Sens. Environ. 2003, 88, 271–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, A.; Foster, J.; Hall, D.K. Nimbus-7 SMMR derived global snow cover parameters. Ann. Glaciol. 1987, 9, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, T.Y. Passive microwave snow research in the Canadian high Arctic. Can. J. Remote Sens. 1996, 22, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goita, K.; Walker, A.E.; Goodison, B.E. Algorithm development for the estimation of snow water equivalent in the boreal forest using passive microwave data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2003, 24, 1097–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derksen, C.; Walker, A.; Goodison, B. Evaluation of passive microwave snow water equivalent retrievals across the boreal forest/tundra transition of western Canada. Remote Sens. Environ. 2005, 96, 315–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surdyk, S. Using microwave brightness temperature to detect short-term surface air temperature changes in Antarctica: An analytical approach. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 80, 256–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mätzler, C. Applications of SMOS over terrestrial ice and snow. In Proceedings of the Third SMOS Workshop, DLR, Oberpfaffenhofen, Germany, 10–12 December 2001; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Derksen, C.; Toose, P.; Rees, A.; Wang, L.; English, M.; Walker, A.; Sturm, M. Development of a tundra-specific snow water equivalent retrieval algorithm for satellite passive microwave data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 1699–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulliainen, J. Mapping of snow water equivalent and snow depth in boreal and sub-arctic zones by assimilating space-borne microwave radiometer data and ground-based observations. Remote Sens. Environ. 2006, 101, 257–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemmetyinen, J.; Pulliainen, J.; Rees, A.; Kontu, A.; Qui, Y.; Derksen, C. Multiple-layer adaptation of HUT snow emission model: Comparison with experimental data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2010, 48, 2781–2794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunn, G.E.; Duguay, C.R.; Derksen, C.; Lemmetyinen, J.; Toose, P. Evaluation of the HUT modified snow emission model over lake ice using airborne passive microwave measurements. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 233–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swift, C.T.; Jones, W.L.; Harrington, R.F.; Fedors, J.C.; Couch, R.H. Microwave radar and radiometric remote sensing measurements of lake ice. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1980, 7, 243–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, D.K.; Foster, J.L.; Chang, A.T.C.; Rango, A. Freshwater ice thickness observations using passive microwave sensors. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1981, GE-19, 189–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, A.T.C.; Foster, J.L.; Hall, D.K.; Goodison, B.E.; Walker, A.E.; Metcalfe, J.R.; Harby, A. Snow parameters derived from microwave measurements during the BOREAS winter field campaign. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1997, 102, 29663–29671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, K.K.; Duguay, C.R.; Howell, S.E.L.; Derksen, C.P.; Kelly, R.E.J. Sensitivity of AMSR-E brightness temperatures to the seasonal evolution of lake ice thickness. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2010, 7, 751–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, K.K.; Duguay, C.R.; Howell, S.E.L. Estimating ice phenology on large northern lakes from AMSR-E: Algorithm development and application to Great Bear Lake and Great Slave Lake, Canada. Cryosphere 2012, 6, 235–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duguay, C.; Green, J.; Derksen, C.; English, M.; Rees, A.; Sturm, M.; Walker, A. Preliminary assessment of the impact of lakes on passive microwave snow retrieval algorithms in the Arctic. In Proceedings of the 62nd Eastern Snow Conference Proceedings, Waterloo, ON, Canada, 7–10 June 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Derksen, C.; Silis, A.; Sturm, M.; Holmgren, J.; Liston, G.E.; Huntington, H.; Solie, D. Northwest Territories and Nunavut snow characteristics from a subarctic traverse: Implications for passive microwave remote sensing. J. Hydrometeorol. 2009, 10, 448–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weeks, W.F.; Sellmann, P.V.; Campbell, W.J. Interesting features of radar imagery of ice-covered North Slope lakes. J. Glaciol. 1977, 18, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duguay, C.R.; Pultz, T.; Lafleur, P.M.; Drai, D. RADARSAT backscatter characteristics of ice growing on shallow sub-Arctic lakes, Churchill, Manitoba, Canada. Hydrol. Process. 2002, 16, 1631–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weeks, W.F.; Gow, A.J.; Schertler, R.J. Ground-Truth Observations of Ice-Covered North Slope Lakes Imaged by Radar; Research Report 81‒19; Cold Regions Research and Engineering Laboratory: Hanover, NH, USA, 1981; p. 24. Available online: www.dtic.mil/get-tr-doc/pdf?AD=ADA108342v (accessed on 1 December 2017).
- Jeffries, M.O.; Morris, K.; Weeks, W.F.; Wakabayashi, H. Structural and stratigraphic features and ERS-1 synthetic aperture radar backscatter characteristics of ice growing on shallow lakes in NW Alaska, winter 1991–1992. J. Geophys. Res. 1994, 99, 22459–22472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duguay, C.R.; Lafleur, P.M. Determining depth and ice thickness of shallow sub-Arctic lakes using space-borne optical and SAR data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2003, 24, 475–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nolan, M.; Liston, G.; Prokein, P.; Brigham-Grette, J.; Sharpton, V.L.; Huntzinger, R. Analysis of lake ice dynamics and morphology on Lake El’gygytgyn, NE Siberia, using synthetic aperture radar (SAR) and Landsat. J. Geophys. Res. 2002, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leconte, R.S.D.; Gauthier, Y.; Yankielun, N.; Bérubé, F.; Bernier, M. A controlled experiment to retrieve freshwater ice characteristics from an FM-CW radar system. Cold Reg. Sci. Technol. 2009, 55, 212–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clausi, D.A.; Qin, K.; Chowdhury, M.S.; Yu, P.; Maillard, P. MAGIC: MAp-Guided Ice Classification. Can. J. Remote Sens. 2010, 36, S13–S25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsh, P.; Pomeroy, J.; Pohl, S.; Quinton, W.; Onclin, C.; Russell, M.; Neumann, N.; Pietroniro, A.; Davison, B.; McCartney, S. Snowmelt processes and runoff at the arctic treeline: Ten years of MAGS research. In Cold Region Atmospheric and Hydrologic Studies; Woo, M., Ed.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2008; pp. 97–123. [Google Scholar]
- Harwood, L.A.; Sparling, P. Lake trout distribution and salinity: An assessment of the relative abundance and distribution of lake trout throughout Husky Lakes, 2001–2004. In Proceedings of the Second North American Lake Trout Symposium 2005, Yellowknife, Northwest Territories, Canada, 16‒19 August 2005; Mills, K.H., Dyck, M., Hardwood, L.A., Eds.; Fisheries Oceans Canada: Winnipeg, MB, Canada, 2008; pp. 226–229. [Google Scholar]
- Sturm, M.; Liston, G.E. The snow cover on lakes of the Arctic Coastal Plain of Alaska, U.S.A. J. Glaciol. 2003, 49, 370–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derksen, C.; Toose, P.; Lemmetyinen, J.; Pulliainen, J.; Langlois, A.; Rutter, N.; Fuller, M.C. Evaluation of passive microwave brightness temperature simulations and snow water equivalent retrievals through a winter season. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 117, 236–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallikainen, M.; Winebrenner, D.P. The Physical Basis for Sea Ice Remote Sensing. In Microwave Remote Sensing of Sea Ice; Carsey, F., Ed.; American Geophysical Union: Washington, DC, USA, 1992; Volume 68, pp. 29–46. [Google Scholar]
- Vincent, L.; Soille, P. Watersheds in digital spaces: An efficient algorithm based on immersion simulations. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 1991, 13, 583–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.; Clausi, D.A. SAR sea-ice image analysis based on iterative region growing using semantics. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2005, 45, 3919–3931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.; Clausi, D.A. IGRS: Image segmentation using edge penalties and region growing. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. 2008, 30, 2126–2139. [Google Scholar]
- Hewison, T.J.; English, S.J. Airborne retrievals of snow and ice surface emissivity at millimeter wavelengths. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1999, 37, 1871–1879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eppler, D.T.; Anderson, M.R.; Cavalieri, D.J.; Comiso, J.; Farmer, L.D.; Garrity, C.; Gloersen, P.; Grenfell, T.C.; Hallikainen, M.; Lohanick, A.W.; et al. Passive microwave signatures of sea ice. In Microwave Remote Sensing of Sea Ice; Carsey, F., Ed.; American Geophysical Union: Washington, DC, USA, 1992; Volume 68, pp. 47–71. [Google Scholar]
- Melloh, R.A.; Eppler, D.T.; Farmer, L.D.; Gatto, L.W.; Chacho, E.F. Interpretation of Passive Microwave Imagery of Surface Snow and Ice, Harding Lake, Alaska; CRREL Report 91-11; Cold Regions Research and Engineering Laboratory: Hanover, NH, USA, 1991; p. 36. [Google Scholar]
- Atwood, D.K.; Gunn, G.E.; Rossi, C.; Duguay, C.R.; Sarabandi, K. Microwave backscatter form Arctic lake ice and polarimetric implications. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2015, 53, 5972–5982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Atwood, D.K.; Sarabandi, K. Scattering phenomenology of arctic lake ice. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Beijing, China, 10–15 July 2016; pp. 3668–3671. [Google Scholar]
- Onstott, R.G. SAR and scatterometer signatures of sea ice. In Microwave Remote Sensing of Sea Ice; Carsey, F., Ed.; American Geophysical Union: Washington, DC, USA, 1992; Volume 68, pp. 73–104. [Google Scholar]
- Perrin, C.J. Fish Species Distribution and Associated Water Chemistry Attributes in the Husky Lake and Sitidgi Lake System, NT; Limnotek Research and Development Inc.: Vancouver, BC, Canada, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Rees, A.; Lemmetyinen, J.; Derksen, C.; Pulliainen, J.; English, M. Observed and modelled effects of ice lens formation on passive microwave brightness temperatures over snow covered tundra. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 116–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Fresh Water | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Site | Date Observed | Air Temp (°C) | Avg Snow Depth (cm) | Avg SWE (mm) | Avg Density (g/cm3) | Avg Grain Size (mm) | AvgIce Thickness (m) | Dominant Ice Type |
| Sitidgi-1 | 8 April 2008 | −15.0 | 29 | 105 | 0.355 | 2.3 | 1.27 | Grey Surface |
| Sitidgi-2 | 8 April 2008 | −15.0 | 30 | 93 | 0.310 | 2.3 | 1.24 | Grey Surface/Clear |
| Sitidgi-3 | 8 April 2008 | −15.0 | 27 | 77 | 0.281 | 2.3 | 1.23 | Clear Ice |
| Sitidgi-4 | 8 April 2008 | −15.0 | 35 | 100 | 0.284 | 2.3 | 1.10 | Grey Surface |
| TLF-01 | 6 April 2008 | −7.1 | 35 | 105 | 0.298 | 1.5 | 1.47 | Rough/Rafted Surface |
| TLF-02 | 6 April 2008 | −7.1 | 25 | 85 | 0.335 | 1.3 | 1.49 | Clear Ice |
| TLF-02.1 | 6 April 2008 | −15.0 | 27 | 87 | 0.314 | 2.3 | 1.36 | Clear Ice |
| TLF-03 | 6 April 2008 | −15 | 32 | 111 | 0.337 | 1.76 | 1.24 | Rough/Rafted/Grey Surface |
| TLF-04 | 6 April 2008 | −15 | 23 | 68 | 0.300 | N/A | 1.44 | Clear Ice |
| Brackish Water | ||||||||
| Husky-1 | 12 April 2008 | −11 | 30 | 79 | 0.252 | 1.5 | 1.06 | Clear Ice |
| Husky-2 | 12 April 2008 | −11 | 37 | 103 | 0.271 | 2.4 | 1.02 | Clear Ice |
| Husky-3 | 12 April 2008 | −11 | 40 | 117 | 0.286 | 3.2 | 0.89 | Clear Ice |
| Husky-4 | 12 April 2008 | −11 | 36 | 84 | 0.232 | 2.7 | 0.85 | Clear Ice |
| Husky-7 | 12 April 2008 | −11 | 36 | 80 | 0.225 | 3.1 | 0.86 | Clear with Bubbles |
| Husky-8 | 12 April 2008 | −11 | 36 | 91 | 0.247 | 2.5 | 0.91 | Grey Surface |
| Husky-9 | 12 April 2008 | −11 | 31 | 82 | 0.257 | 2.5 | 1.01 | Clear Ice |
| TLF-07 | 6 April 2008 | −7.1 | 31 | 90 | 0.283 | 2.4 | 0.94 | Grey Surface |
| TLF-08 | 6 April 2008 | −7.1 | 25 | 84 | 0.315 | 2.4 | 1.36 | Clear Ice |
| TLF-09 | 6 April 2008 | −7.1 | 31 | 95 | 0.311 | 2.4 | 0.99 | Clear Ice |
| Chang [10] | MSC [9] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RMSE | MBE | RMSE | MBE | |
| Sitidgi | 68.37 | −23.97 | 82.41 | −73.15 |
| Husky | 75.07 | −56.39 | 94.40 | −88.98 |
| TLF02.1 | TLF 02 | Sitidgi 2 | TLF-03 | Sitidgi 1 | Sitidgi 3 | Sitidgi 4 | TLF-04 | TLF 01 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TLF02.1 | 1 | 0.88 (3155) | 0.39 (2984) | 0.00 (6139) | 0.00 (1280) | 0.00 (1007) | 0.00 (710) | 0.00 (7377) | 0.00 (0.00) |
| TLF 02 | 0.88 (3155) | 1 | 0.55 (2927) | 0.00 (5860) | 0.00 (1188) | 0.00 (913) | 0.00 (614) | 0.00 (7070) | 0.00 (0.00) |
| Sitidgi 2 | 0.39 (2984) | 0.55 (2927) | 1 | 0.00 (6446) | 0.00 (1371) | 0.00 (1002) | 0.00 (633) | 0.00 (7920) | 0.00 (0.00) |
| TLF-03 | 0.00 (6139) | 0.00 (5860) | 0.00 (6446) | 1 | 0.57 (12277) | 0.06 (10913) | 0.00 (10088) | 0.00 (39859) | 0.00 (0.00) |
| Sitidgi 1 | 0.00 (1280) | 0.00 (1188) | 0.00 (1371) | 0.57 (12277) | 1 | 0.01 (2472) | 0.00 (2150) | 0.00 (10417) | 0.00 (0.00) |
| Sitidgi 3 | 0.00 (1007) | 0.00 (913) | 0.00 (1002) | 0.06 (10913) | 0.01 (2472) | 1 | 0.53 (3015) | 0.00 (39859) | 0.00 (0.00) |
| Sitidgi 4 | 0.00 (710) | 0.00 (614) | 0.00 (633) | 0.00 (10088) | 0.00 (2150) | 0.53 (3015) | 1 | 0.00 (6223) | 0.00 (0.00) |
| TLF-04 | 0.00 (7377) | 0.00 (7070) | 0.00 (7920) | 0.00 (39859) | 0.00 (10417) | 0.00 (39859) | 0.00 (6223) | 1 | 0.00 (0.00) |
| TLF 01 | 0.00 (0.00) | 0.00 (0.00) | 0.00 (0.00) | 0.00 (0.00) | 0.00 (0.00) | 0.00 (0.00) | 0.00 (0.00) | 0.00 (0.00) | 1 |
| Frequency (GHz) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6.9 V | 6.9 H | 19 V | 19 H | |
| Sitidgi Transect 1 (n = 468) | 0.61 * | 0.64 * | 0.28 * | 0.46 * |
| Sitidgi Transect 2 (n = 131) | 0.23 * | 0.32 * | 0.01 * | 0.63 * |
| 6.9 GHz V | 6.9 GHz H | 19 GHz V | 19 GHz H | X-band | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clear Ice | Quartile (25%) | 199.51 | 167.47 | 236.46 | 209.44 | −20.46 |
| Median | 200.58 | 168.81 | 238.59 | 211.38 | −20.10 | |
| Quartile (75%) | 201.87 | 170.43 | 240.29 | 213.72 | −19.66 | |
| Transition Clear/Grey | Quartile (25%) | 199.29 | 167.60 | 235.00 | 211.00 | −19.39 |
| Median | 200.23 | 168.85 | 236.90 | 212.79 | −18.92 | |
| Quartile (75%) | 201.14 | 170.33 | 238.84 | 214.97 | −18.49 | |
| Grey Ice | Quartile (25%) | 200.22 | 169.32 | 235.64 | 212.30 | −18.53 |
| Median | 201.68 | 171.49 | 238.67 | 214.36 | −17.93 | |
| Quartile (75%) | 203.95 | 174.90 | 241.14 | 217.54 | −17.06 | |
| Rough/Rafted Ice | Quartile (25%) | 202.16 | 171.39 | 237.85 | 214.13 | −16.94 |
| Median | 204.14 | 174.80 | 239.95 | 216.76 | −15.85 | |
| Quartile (75%) | 210.21 | 182.51 | 241.76 | 219.30 | −14.07 |
| Frequency (GHz) | 6.9 V | 6.9 H | 19 V | 19 H |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Husky Transect 1 (n = 157) | −0.56 * | −0.73 * | −0.56 * | −0.56 * |
| Husky Transect 2 (n = 41) | −0.84 * | −0.82 * | −0.54 * | −0.34 * |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gunn, G.E.; Duguay, C.R.; Derksen, C.; Clausi, D.A.; Toose, P. Investigating the Influence of Variable Freshwater Ice Types on Passive and Active Microwave Observations. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 1242. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9121242
Gunn GE, Duguay CR, Derksen C, Clausi DA, Toose P. Investigating the Influence of Variable Freshwater Ice Types on Passive and Active Microwave Observations. Remote Sensing. 2017; 9(12):1242. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9121242
Chicago/Turabian StyleGunn, Grant E., Claude R. Duguay, Chris Derksen, David A. Clausi, and Peter Toose. 2017. "Investigating the Influence of Variable Freshwater Ice Types on Passive and Active Microwave Observations" Remote Sensing 9, no. 12: 1242. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9121242
APA StyleGunn, G. E., Duguay, C. R., Derksen, C., Clausi, D. A., & Toose, P. (2017). Investigating the Influence of Variable Freshwater Ice Types on Passive and Active Microwave Observations. Remote Sensing, 9(12), 1242. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9121242