Abstract
Multi-temporal Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar (MT-InSAR) technique has proven to be a powerful tool for the monitoring of time-series ground deformations along the line-of-sight (LOS) direction. However, the one-dimensional (1-D) measurements cannot provide comprehensive information for interpreting the related geo-hazards. Recently, a novel method has been proposed to map the three-dimensional (3-D) deformation associated with underground fluid flows based on single-track InSAR LOS measurements and the deformation modeling associated with the Green’s function. In this study, the method is extended in temporal domain by exploiting the MT-InSAR measurements, and applied for the first time to investigate the 3-D time series deformation over Sebei gas field in Qinghai, Northwest China with 37 Sentinel-1 images acquired during October 2014–July 2017. The estimated 3-D time series deformations provide a more complete view of ongoing deformation processes as compared to the 1-D time series deformations or the 3-D deformation velocities, which is of great importance for assessing the possible geohazards. In addition, the extended method allows for the retrieval of time series of fluid volume changes due to the gas extraction in the Sebei field, which agrees well with those from the PetroChina Qinghai Oilfield Company Yearbooks (PQOCYs). This provides a new way to study the variations of subsurface fluids at unprecedented resolution.
1. Introduction
Intensive exploitation of underground fluid (e.g., underground water, petroleum, natural gas and geothermal) induces pressure changes of underground reservoir [1,2,3,4,5,6], further causing ground deformations, especially horizontal inhomogeneous deformations, which affect the safety of the surface or subsurface facilities. Therefore, the dynamic temporal and spatial distribution of three-dimensional (3-D) deformations is vital to determine the most severely damaged areas, to mitigate (or even eliminate) the causes of ground deformations [7], to provide information for the interpretation of deformation mechanism and to predict deformation evolution resulting from future underground fluid withdrawal.
Multi-Temporal Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar (MT-InSAR) techniques, such as Persistent Scatterer (PS) [8,9] or Small Baseline Subset (SBAS) [10,11], have been well-developed to monitor time-series ground deformations by compensating for the inherent deficiencies (e.g., decorrelation noises [12] and atmospheric artifacts [13]) of traditional differential InSAR (D-InSAR). MT-InSAR has been successfully and extensively used in monitoring the deformations induced by exploitation of underground fluids, such as groundwater [7,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21], oil [22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31], natural gas [14,30,32,33,34,35,36,37], and geothermal [38,39,40,41,42,43,44,45], because of its low cost, wide spatial coverage, high measurement precision, and fine spatial resolution. However, MT-InSAR can capture only one-dimensional (1-D) time-series deformation that includes the sum of projections on the line-of-sight (LOS) direction of actual 3-D time series ground deformations. Therefore, the MT-InSAR measurements cannot provide complete information for detecting potential disasters related to such deformations [46].
Several methods have been proposed to extract 2-D/3-D time-series deformations from SAR measurements. Generally, these methods can be divided into four categories. (i) Integrating of InSAR and Offset-Tracking: Raucoules et al. [47] obtained time-variable 3-D ground displacements fields in the La Valette landslide by combining the ascending and descending Offset-Tracking [48,49,50] and InSAR measurements. The temporal discrepancy between the different acquired times of SAR images from ascending and descending tracks is ignored by interpolating the displacement rates according to the images acquired epochs. Sigleton et al. [51] estimated the 2-D information of the time series displacements caused by the landslide of the Three Gorges region (China) with the same combinational technology. (ii) Integrating of InSAR and Multi-Aperture InSAR (MAI): He et al. [52] employed the MAI [53] and InSAR measurements from single track to obtain 2-D time-series deformation fields induced by the exploitation of open-pit mine. However, the Offset-Tracking or MAI techniques can only be applied in areas with great displacements, indicating that the aforementioned methods cannot monitor the slow developing 3-D deformations. (iii) Integrating of InSAR and GPS: Samsonov et al. [54] derived the 3-D surface motion maps of southern California from InSAR and sparse GPS measurements based on the random field theory. Guglielmino et al. [55] proposed a method, the SISTEM (Simultaneous and Integrated Strain Tensor Estimation from geodetic and satellite deformation Measurements), to estimate 3-D displacements by integrating GPS and InSAR measurements based upon the elastic theory. These methods can be extended to produce 3-D time-series estimations using the MT-InSAR measurements. Vollrath et al. [56] decomposed InSAR time-series deformation into 3-D with the assistance of GPS data in the case of low strain rates with the SISTEM. Obviously, this method is dependent on the number and distribution of the GPS sites, which are always limited by the high deployment and operational cost [50]. (iv) Neglecting of N–S (North–South) deformation: Ozawa and Ueda [57] estimated U–D (Up–Down) and E–W (East–West) time-series deformations in Miyake-jima by neglecting the contribution of N–S displacements on InSAR LOS measurements [58], and employed a smooth constraint of temporal displacement change to settle the problem of temporal discrepancy. Similarly, Hu et al. [59] estimated U–D and E–W time-series deformations in Southern California under the assumption of zero contribution of N–S displacements on InSAR LOS measurements, and Kalman filter is employed to fill the temporal gaps among multi-sensors and multi-tracks. Obviously, this method has the capability to estimate the slow-moving time-series 2-D (i.e., U–D and E–W) displacements, but is incompetent to expose the time-series of full 3-D deformations.
According to the above analysis, it can be concluded that the main reasons hampering the generating of 3-D time series deformations are the temporal discrepancy between different sensors/tracks and the insensitiveness of InSAR to the N–S displacements. Recently, Hu et al. [46] proposed a novel InSAR-based method to retrieve the full 3-D deformation induced by underground fluid flows. In the method, the relationship between the ground deformations and the subsurface fluids volume changes, which is based on a Green’s function, is exploited to compensate for the N–S insensitiveness of InSAR. In addition, since the InSAR LOS measurements from single track are sufficient in the method, temporal discrepancy between the measurements from different sensors/tracks can be avoided. This provides a great potential for resolving 3-D time series deformations induced by underground fluid flows with InSAR. In this study, the method is extended to the temporal domain by the 1-D time series deformation measurements from weight least square (WLS) InSAR algorithm [40], and applied for the first time to investigate the 3-D time series deformation over the Sebei gas field in Qinghai, China, with 37 Sentinel-1 images acquired during October 2014–July 2017. Subsequently, by extending the method in [46] to the temporal series, we obtain the full 3-D time-series displacements associated with the dynamic underground gas volume changes for the first time. Meanwhile, the time series of the gas volume changes within the Sebei field are generated as the by-product of the InSAR measurements.
2. Study Area and Data Coverage
As the largest biogas accumulation field and one of the four largest gas fields in China, the Sebei gas field is located in the Three-lake Depression region of the eastern margin of the Qaidam Basin in Qinghai Province, Northwest China (see Figure 1). The terrain of the area of interest is relatively flat with an average elevation of 2750 m (see Figure 1a). From 1980 to 2016, the mean annual precipitation of Sebei gas field is 292.35 mm, while the annual evaporation reaches 3300 mm (raw precipitation data are accessible at [60]). The Sebei gas field is a Quaternary unconsolidated sandstone gas reservoir, where seal rocks are superposed on a syndepositional anticline [61]. The gas field is shallow buried and has high abundance, thin and multi-layer, large spans, long gas wells, complicated gas and water distribution, poor diagenesis, and inter-layer heterogeneity [62]. Its lithofacies is characterized by siltstone, dirt or argillaceous siltstone, and minor fine sandstone [63]. As a biogas reservoir, the Sebei gas field has several distinct geological features. Firstly, the depositional environments are mainly shore and shallow-lacustrine facies or almost-littoral and shallow-marine facies, with sandstones and mudstones. Secondly, the reservoir composes of multiple interbedded thin-layered and mudstone beds. The formation interfaces define the upper and lower surface of the interblended (sandstone/mudstone) layers. Therefore, the multi-layers is essential subsurface feature of the Sebei gas reservoir. Specifically, this gas field contains more than 60 gas layers, of which thickness of less than 3 m, 3~5 m and greater than 5 m accounts for 71% to 79%, 17% to 22% and 3% to 7%, respectively. However, there are no obvious boundaries among the gas layers and even one layer has different depths and thicknesses. Thus, the Sebei gas reservoir can be regarded as a unique source within a homogeneous elastic half-space. According to the field investigation, the mean permeability, mean porosity, reservoir pressure and reservoir temperature are m2, 29.6%, 7.1–17.6 MPa and 305.7–331 K, respectively. Using this method requires the thicknesses from the upper surface to the lower surface of the fluid flows and depths from ground surface to the upper surface of the fluid flows. For simplicity, we assumed there is a single layer in the Sebei gas field and employed the mean thickness of 102 m and depth of 1072 m within the three major gas fields [64,65,66,67,68,69,70,71].
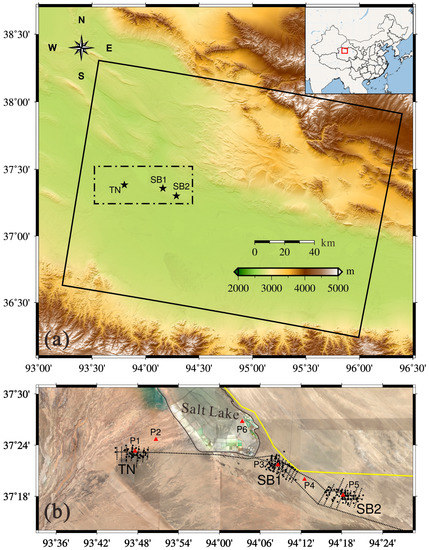
Figure 1.
(a) Study area and data coverage. Top right inset shows the approximate location of the study area in China. The black line outlines the coverage of Sentinel-1 data used in this study. The area of interest is outlined by the black dashed box. The black stars indicate the three primary gas fields, i.e., SB1, SB2 and TN. (b) Optical image of the area of interest. The yellow line, dashed black lines and solid black dots represent the locations of the China National Highway 315 (G315), gas pipelines and gas production wells, respectively. The region outlined by the solid black line is a Salt Lake. P1, P2, P3, P4, P5 and P6 are points used for 3-D time series deformation analysis shown in a later section.
Sebei gas field consists mainly of three major gas fields termed by Sebei No. 1 (SB1), Sebei No. 2 (SB2) and Tainan (TN), respectively. According to the PetroChina Qinghai Oilfield Company Yearbooks (PQOCY) of 2008–2009 [65], the gas storage capacity of the three primary gas fields occupies 95.5% of the total gas storage in Sebei gas field. Gas field SB1 was found by the Qinghai Petroleum Exploration Bureau in 1964. However, the gas field exploitation was abandoned temporarily since the primary mission was finding oil at that time. The gas reservoirs of Sebei gas fields were preliminarily investigated in 1974, and the gas field SB2 was found the next year. Nevertheless, the preliminarily investigative work was suspended again when the Gasikule oil field was found. Sebei gas field was in the exploration evaluation phase until the late 1980s, during which the gas field TN was discovered. SB1, SB2 and TN gas fields began pilot production in 1995, 1998 and 2005, respectively. On 31 August 1996, the completion of the first long-distance gas transmission pipeline (Sebei gas field to Golmud) within eastern Qaidam Basin signified the real meaningful exploitation of Sebei gas field. In 2003, 1.34 billion m3 of gas was produced from the Sebei gas field, followed by steady growth. According to China News Agency, as reported on 23 January 2015, Sebei gas field has produced total 50 billion m3 of gas, which has induced gigantic surface deformation in the gas field.
In this study, 37 Sentinel-1 Single Look Complex (SLC) descending images, spanning from 3 November 2014 to 2 July 2017, were acquired to monitor the gas-extraction-induced 3-D time series deformations and the corresponding gas volume changes. The spatial coverage of the Sentinel-1 data can be observed in Figure 1. These images were acquired via the C-band (i.e., ~5.6 cm wavelength and ~5.4 GHz) Active Microwave Instrument (AMI) onboard ESA’s Sentinel-1 satellite with the average altitude of ~715 km, along the sun-synchronous polar orbits. The images cover about ~28,800 km2 (~180 km by ~160 km) with the slant range pixel spacing of 2.3 m and the azimuth range pixel spacing of 13.4 m. LOS has the mean incidence angle of 39.2° and the ground track of satellite is tilted ~9.6° with respect to the N–S direction. In addition, the Digital Elevation Model (DEM) from Shuttle Radar Topography Mission (SRTM) [72] with ~30 m spatial resolution is acquired to separate the phase contribution of the topography in the interferograms [73]. Moreover, the precise satellite orbit data for Sentinel-1 images is employed to guarantee the accuracy of satellite’s positions and to reduce the interferogram baselines estimation error.
3. Methodology
3.1. SAR Data Pre-Processing
In total, 37 SAR images spanning nearly three years were processed. Orbit state vectors for the 37 SLC scenes were first improved by using the recalculated orbital data, which is publicly accessible via the URL [74]. Subsequently, the scene stack was co-registered to a single master image acquired on 9 March 2016, resulting in a co-registration accuracy of less than 0.01 pixel for all slaves in both the range and azimuth directions. It should be noted that the co-registration accuracy 0.01 pixel is got between master and slave images, while that among the overlaps of bursts in same Sentinel-1 image is generally less than 0.001 pixel in this study. As shown in Figure 1b, a subset of full scene frame was then selected to cover the area of interest by cropping the co-registered scenes, reducing the processing area size to 30,000 pixels in range and 3200 pixels in azimuth, which corresponds to ~3100 km2 area on the ground. Multi-looking factors (i.e., 20 in the range and 4 in the azimuth directions) were employed to decrease the radar speckle noise and enhance the phase signal quality, but decrease the image resolution to ~80 m.
3.2. WLS InSAR Processing Implementation
Considering the fact that the acquired images are adequate and the baselines are generally less than 100 m, we choose 80 days and 70 m as the thresholds of temporal and perpendicular baselines, respectively. Sixty-four interferograms are generated from the co-registered 37 SAR images (see Figure 2).
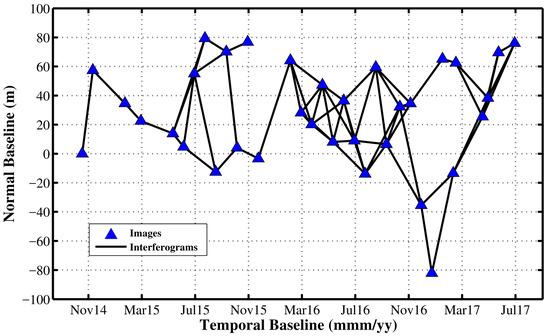
Figure 2.
Spatial-temporal baselines of the selected InSAR pairs. Blue triangles and black lines represent the SAR images and small-baseline interferograms, respectively.
Two-pass D-InSAR was employed to process the 64 interferograms. The ~30 m resolution SRTM DEM was utilized to remove the topographic phase in the interferograms. Subsequently, the differential interferograms was filtered by using improved Goldstein filter [75], and was unwrapped by using the minimum-cost flow algorithm [76]. To ensure the accuracy of the unwrapping phase, we mask out the low coherence part with a threshold of 0.35. The reference point is selected in the stable area, far away from the area of interest. Following that, a polynomial model was applied to mitigate the orbit errors. Finally, the WLS InSAR algorithm was employed to retrieve the LOS time-series deformation measurements [40]. Since the study area is relatively flat and far away from the coastline, and the climate is quite dry, the atmospheric artifacts basically are absent in the interferograms [77,78], and thus were ignored in the WLS InSAR processing.
3.3. 3-D Deformations and Volume Changes Inversion
Given the fact that the volume changes of subsurface fluids could induce the corresponding ground deformations, we assume the volumetric source component within the SB1, SB2 and TN systems based on the elastic half-space theory. This means a relationship between the underground fluids volume changes and the 3-D surface deformations [1,40,79,80]:
where are the 3-D deformations of point at surface, and indicates the E–W, N–S, and U–D components, respectively. and represent the fluid volume and volume change rate of a block within a source volume . is the Green’s function written as:
where is the distance between the point and the block ; and is the Poisson’s ratio (classical value of 0.25 is used in this study).
To simplify the model, is divided into blocks. Equation (1) can be written as:
where (with ) are the misfit errors of Equation (3) at point .
Considering the estimated LOS ground deformation is actually the combined contribution of E–W, N–S, and U–D deformations, the relationship between LOS measurement and 3-D deformations can be bridged as:
with
where is the LOS measurement. are the E–W, N–S, and U–D projection coefficients of LOS measurement at point ; presents the observation errors in the LOS measurement; and and are the radar azimuth angle and incidence angle of point , respectively
Combining Equations (3) and (4), and forming them to matrix notation, we get the joint model:
where is the observation matrix consisting of real observations from LOS measurements and virtual observations; is the corresponding residual matrix; is the 4M * (3M + N) design matrix; and is the (3M + N) * 1 pending parameters.
with
It is obvious that we can retrieve the 3-D deformation and the volume changes included in simultaneously by solving the Equation (5) with Least Square (LS) algorithm if . Although Equation (5) is over determined, it may be unstable because of ill-conditions [81,82]. To ensure the stability of LS inversion, a fit smoothness constraint should be involved in the model. This is an ideally but reasonable assumption since the expected compaction of the reservoir is spatially continuous. A matrix that estimates the spatial derivative of the fractional volume change can be added as the smoothness matrix, with a smoothness factor controlling the level of the fitness [40]. The final time-series 3-D deformations and dynamic gas volume changes will be obtained via performing the original method on the LOS measurements of each epoch.
4. Results
The estimated LOS time-series deformations are presented in Figure 3. All the subplots show the accumulative deformation with respect to the reference date (i.e., 3 November 2014). Most of the region maintain good coherence except a small part of the study area located in the west of the area of interest. The estimated LOS time-series deformations show that Sebei gas fields have experienced noticeable ground deformation. As expected, main deformations concentrate on the three primary gas fields (i.e., TN, SB1 and SB2), and the deformation increases dramatically. The maximum deformation during the study period reached −181.1 mm. In addition to the apparent deformation areas in the three major gas fields, the region of Salt Lake has also experienced noticeable deformation.
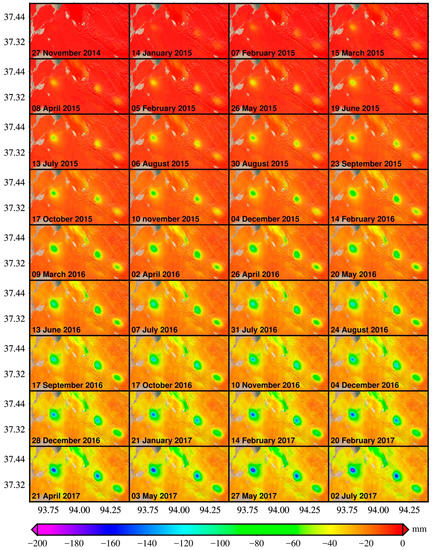
Figure 3.
The dynamic LOS deformations map with respect to 3 November 2014. The acquisition time of corresponding SAR images is stated in the lower-left corner of each subplot (the same in the other figures).
The LOS time-series deformations are further used to estimate the 3-D time series deformations and the corresponding subsurface gas volume changes. The mean displacement velocity map and the time-series deformation maps along the E–W direction are presented in Figure 4a and Figure 5, respectively. It can be found that the E–W accumulated deformation keeps on increasing, and several significant displacement patterns are obvious at the three fundamental gas fields (SB1, SB2 and TN), with the highest westward and eastward displacements up to 62.7 mm and 59.3 mm, respectively. Besides the primary gas fields, a highly deformed area has also been observed near the Salt Lake named East Tai Ji Nai Er.
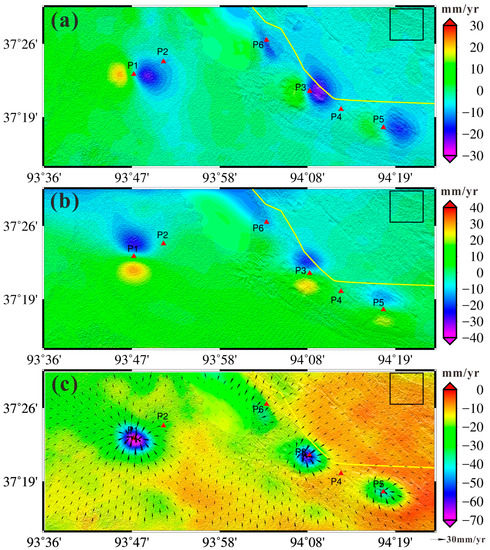
Figure 4.
(a) The East–West (E–W) mean displacement velocity map; (b) the North–South (N–S) mean displacement velocity map; and (c) the 3-D mean displacement velocity map, where the color and arrow indicate the Up–Down (U–D) and horizontal mean displacement velocities, respectively. The yellow solid line marks the China National Highway 315 (G315), red dots represent the selected points for time series analysis and black box is the selected region for the quantitative assessment in the Discussion.
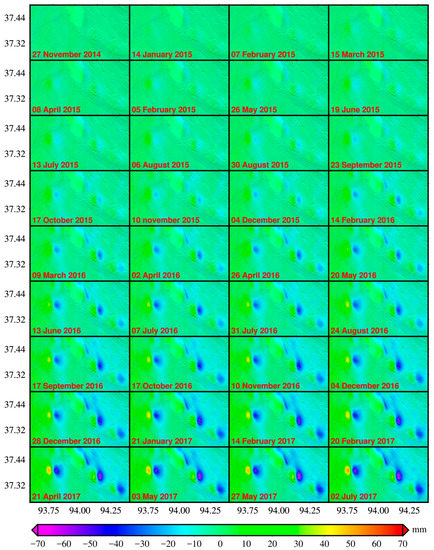
Figure 5.
The E–W time-series accumulated deformation map.
Figure 4b shows the North–South (N–S) mean displacement velocity map, with the peak mean displacement rate of 31.3 mm/year northward and 25.6 mm/year southward observed in TN gas field, respectively. The N–S time-series deformations accumulated map is shown in Figure 6, from which we can learn about that the study area had experienced increasingly obvious N–S displacements with the maximum northward and southward accumulation up to 78.1 mm and 68.0 mm in TN gas field, respectively. As shown in Figure 4b and Figure 6, significant N–S displacement patterns have been identified at the three gas fields of Sebei.
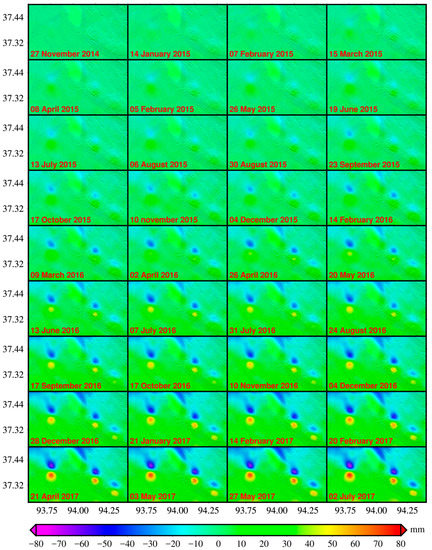
Figure 6.
The N–S time-series accumulated deformation map.
The 3-D mean displacement rate map is shown in Figure 4c, where the color and the arrow indicate the vertical and horizontal components, respectively. We can observe that the significant 3-D displacement regions appear mainly in gas production areas, with the peak mean subsidence rate of 73.4 mm/year identified at TN gas field. Figure 7 shows the Up–Down (U–D) time-series accumulated deformations, with a maximum subsidence of 195.4 mm observed at TN gas field within less than three years. In addition, it is found that the U–D deformation is much greater than the E–W and N–S ones.
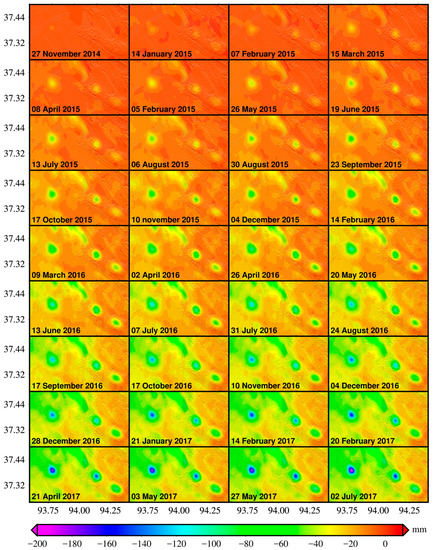
Figure 7.
The U–D time-series accumulated deformation map.
Six points, i.e., P1–P6 in Figure 1b, are selected to further describe the evolution processes of the 3-D time-series deformations. Figure 8a–f shows the detailed information of 3-D time series surface deformations of the selected points P1–P6, respectively.
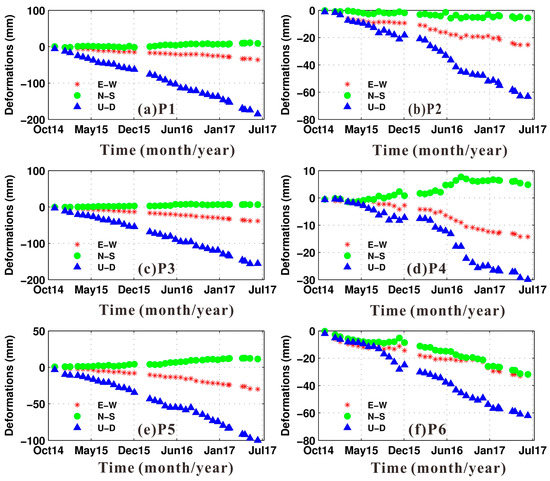
Figure 8.
3-D time-series accumulated deformations for the selected points. (a–f) represent for points P1–P6, respectively. Stars, cycles and triangles mark for the E–W, N–S and U–D temporal deformations, respectively.
P1, P3 and P5 are situated near the centers of the TN, SB1 and SB2 gas fields, respectively, and experience serious deformation, mainly caused by intensive gas production. It can be found that the deformations of these points is dominated by the U–D components. Most ground subsidence occurs in P1. This is expected, since the gas production of TN is more than those of SB1 and SB2 [66,67,68,69,70].
P2 is located on the edge of the TN gas fields, and has experienced obvious nonlinear deformations. P4, located between SB1 and SB2 gas fields, is suffering noticeable deformations. Faint seasonal displacements can be observed in the 3-D time-series displacements of P2 and P4, manifesting that the influence of seasonal factors such as rainfall and temperature on the deformations of Sebei gas field cannot be ignored. P6, located in the Salt Lake, is suffering apparent deformations in all the three directions, as a result of the Salt Lake production activities.
Figure 9 shows the estimated mean gas volume change rates (GVCR) of the underground gas reservoir in Sebei fields, with the peak mean GVCR of , and identified at TN, SB1 and SB3 gas fields, respectively. It should be noted that the GVCR is dimensionless, which equals the ratio of the gas volume change to the corresponding volume of underground gas reservoir unit. Figure 10 shows the time-series cumulated gas volume changes over the study area. Gas volume change mainly concentrated in areas with obvious deformations, such as the three huge funnels in TN, SB1 and SB2, with the maximum accumulated GVCR of . The total effective GVCR induced by the gas production activities in the study area is −0.9, after subtracting the part caused by the Salt Lake production activities from the total GVCR. This is equivalent to underground volume change of .
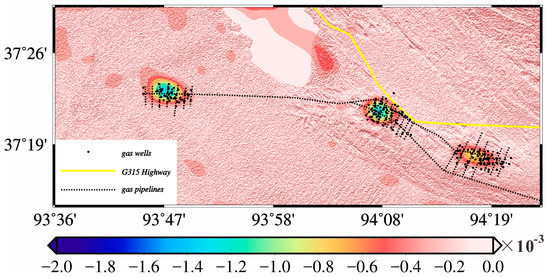
Figure 9.
The mean gas volume change rate map. The yellow solid line, black dashed lines and black dots represent the locations of the China National Highway 315 (G315), gas pipelines and gas production wells, respectively.
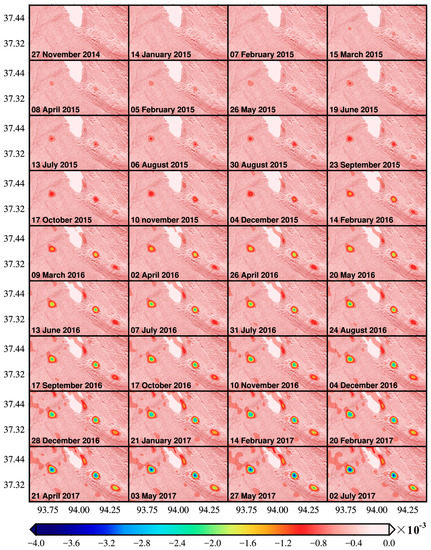
Figure 10.
The time-series accumulated GVCR map.
5. Discussion
Previous studies in Sebei gas fields indicate that gas exploitation will lead to the compression of the Quaternary deposit and ground sinking [61,63,83]. However, these studies seldom consider the quantitative ground subsidence induced by the gas production. In addition, the field data in this region are unavailable to us, so it is impracticable to conduct an effective external validation for the estimated 3-D time series displacements. In this study, the accuracies of the estimated 3-D time-series displacements mainly depend on the accuracies of the InSAR-derived time-series LOS deformations and the misfit of the joint model. Since the study area is relatively flat and dry, the contamination of the InSAR inherent errors (e.g., elevation residual and atmospheric artifacts) can be very small for the time-series LOS deformations. With respect to the misfit of the joint model, it is always ideal to model the reality, but the elastic half-space theory is quite applicable for the Sebei gas field which the surrounding earth medium is basically homogeneous without faults. To provide a quantitative assessment, we chose a 100 × 100 pixels region (see Figure 4 for the location) that is far away from the mainly deformation areas. By assuming the 3-D deformations are zero in the selected region, the standard deviations are 5.0, 2.7 and 1.6 mm/year for the E–W, N–S and U–D time series displacements, respectively.
Since there is no available prior information about the gas reservoir to constrain the model, a smoothness constraint has been introduced into the model to suppress the possible ill-conditions in the inversion. A smoothness factor of 20 is employed in this case, which is determined from extensive experiments based on an examination of the data misfit. The determined smoothness factor is expected to adjust the weights between the InSAR-measured displacements and the pseudo displacements provided by the modeling. In addition, we found that the smoothness factor has considerable influence on the derived gas volume change but has little impact on the derived 3-D displacements.
It is obvious that 3-D time-series deformations extracted by the proposed method can reveal more information about the actual land displacements than the single LOS time series deformations. The estimated E–W, N–S and U–D time-series displacements demonstrate clear evolution patterns of three orthogonal directions. Inhomogeneous deformations caused by gas exploitation in Sebei gas fields would be great threatens to the safe operation of the gas pipelines and wells. According to the PQOCYs, some gas wells of the study region were completely destroyed, and some gas wells in S1 were damaged to various degrees. Besides, leakage occurred in some gas pipelines. These damages can be ascribed to the nonlinear behaviors of the 3-D time-series deformations, indicating that some specific control measures should be implemented timely to mitigate the adverse effects associated with the 3-D time-series deformations caused by gas exploitation.
Besides the obvious destruction of wells and pipelines, the potential threaten of the 3-D time series displacements to the G315 Highway should be taken seriously. G315 Highway, as the “lifeline” connecting Xinjiang and Qinghai Provinces, plays a vital role in the development of western China. However, as shown in Figure 4, G315 Highway situates across the main deformation areas. It is illustrated in Figure 11 that the 3-D time-series of accumulated deformations along the G315 Highway. Since the G315 Highway is located on the northwest of the TN, SB1 and SB2 gas fields, it can be found at a distance of about 22 km from the beginning of the G315 Highway that the horizontal deformation of the G315 Highway is mainly eastward with the maximum value of 55.4 mm (see Figure 11a) and southward with the peak deformation of −56.2 mm (see Figure 11b). In addition, the G315 Highway also suffered serious subsidence up to 73.0 mm at the edge of SB1 gas field. It is apparent that SB2 gas field has much more damaging contribution to the G315 Highway than SB1 gas field does. Besides the SB1 and SB2 gas fields, the production activities of the Salt Lake have also a certain impact on the G315 Highway with the southward deformation up to 50 mm and subsidence up to ~47 mm. More importantly, it should be noted that three special critical points A, B and C of the G315 Highway (see Figure 11b) are suffering the E–W deformations with opposite directions at both sides, which can produce shear force to the critical points of the G315 Highway. The shear force can cause very serious damage to the parts of G315 Highway near the critical points. Therefore, the serious deformations would crack the highway pavement, and possess potential and non-negligible threat to the safe operation of the G315 Highway. The knowledge of the dynamic spatial and temporal distribution of derived 3-D deformations can be utilized to predict and mitigate the negative influence of deformations resulting from future gas extraction. Hence, the InSAR-derived 3-D time-series surface deformations, with the significant advantages of lower cost and higher automation level, should be considered in the management of the further extraction of the Sebei gas fields.
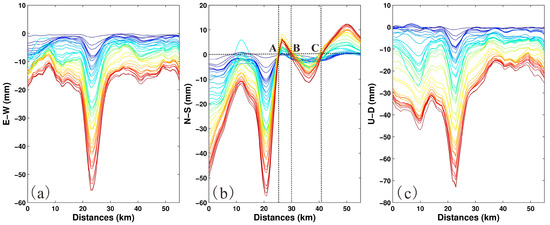
Figure 11.
The 3-D time-series accumulated deformations along the G315 Highway: (a) the E–W component; (b) the N–S component; and (c) the U–D component. The beginning and ending of the G315 Highway are by the edge of the Salt Lake and the SB2 gas field, respectively. Points A, B and C specified by the intersections of the dashed lines are three special critical points of the G315 Highway.
In addition to 3-D time-series deformations, the changes in underground fluid reservoirs are derived in the study. We estimate a decrease of underground gas volume of approximate during the investigation period. According to the PQOCYs of 2011–2016, the actual gas productions in TN, SB1 and SB2 gas fields are summarized in Table 1, which shows the yearly productions of the three primary gas fields of Sebei. The total gas productions of 5.499 billion m3 of TN, SB1 and SB2 gas fields between the beginning of the study and the end of 2015 are estimated according to the real statistics data of 2010–2015 (see Table 1). There is a tremendous gap between the real productions of 5.499 billion m3 and the estimated gas volume change of 49.12 million m3 in the same period, which is ascribed to the different circumstances (e.g., temperature and pressure). We estimated gas volume change of underground under the conditions of the mean pressures of 13.3 MPa, 9.2 MPa and 9.1 Mpa and the average temperatures of 326.15 K, 319.26 K and 318.89 K for TN, SB1 and SB2 gas fields, respectively [65,66,67,68,69,70], while the statistical result from the PQOCYs is calculated on the standard state of China with the temperature of 293.15 K and the pressure of 101.325 KPa. To effectively evaluate the reliability of the result, a conversion is performed based on Ideal-Gas Equation of State to derive the gas volume change from the underground conditions to the standard state of China. The converted gas volume change result is 5.022 billion m3, which is consistent with the contemporaneous statistical result of 5.499 billion m3 from the PQOCYs. The comparisons between the actual and InSAR-derived gas volume change result of each year are detailed in Table 1. It can be observed that for the overlapped period the differences between the gas volume change results from the PQOCYs and the study are very small for all the three gas fields, where the largest discrepancy of 0.169 billion m3 occurs for the SB2 gas field in 2015. The root-mean-square error (RMSE) of 0.131 billion m3 of the differences is calculated to quantitatively assess the performance of the proposed method in the monitoring of the underground gas volume change. Therefore, the InSAR-derived volume changes are reliable, and can be used to assess the gas production ability of the Sebei gas fields. In addition, there are four reasons that could be responsible for the differences between the estimated gas volume change and the recorded gas production of PQOCYs. Firstly, an average depth and thickness within a unique source are employed in the model. This will inevitably bring some errors since the gas reservoir has numerous layers with variable depths and thicknesses. Secondly, the gas extraction is usually accompanied by a small amount of water and sand, causing a certain contribution to the differences. Thirdly, as described by the poro-elastic theory [84], a decrease of underground gas pressure may counteract a certain subsurface volume change. Finally, the natural compaction of the gas reservoir is not considered in the study.

Table 1.
The annual gas productions of TN, SB1 and SB2 gas fields from PQOCYs or this study between 2011 and 2017.
The method can be applied to monitor 3-D ground deformations caused by subsurface fluid flux such as groundwater withdrawal, oil or natural gas exploitation and geothermal extraction. It however should be noted that the method assumes the surrounding earth medium within a homogeneous and elastic half space, which might be inapplicable for completely heterogeneous medium. In addition, the method requires some a priori information about the underground fluid (e.g., depth and thickness), which sometimes are quite difficult to obtain.
6. Conclusions
Based on the Green’s function, this paper presents how to retrieve the 3-D time series deformations from single track InSAR measurements, as well as to estimate the corresponding fluids volume changes. In this study, we monitor the time-series LOS displacements induced by the dynamic gas production of the Sebei gas field by employing the WLS InSAR algorithm and the Sentinel-1 images data acquired from November 2014 to July 2017. The dynamic 3-D time series deformations and corresponding contemporaneous subsurface gas volume changes with unprecedented spatial-temporal resolution are estimated at the Sebei gas field from the WLS InSAR-derived LOS displacements. The results are vital for the relevant geo-hazards prevention as well as the sustainable development of the gas exploitation. Two main conclusions can be drawn in this study as follows:
- The 3-D time-series deformations allow us to understand the ground deformation features under high-intensity gas-exploitation, and have unique insight into the corresponding damages and threats. The time-series analysis of 3-D deformations reflects that the main 3-D time-series surface displacements patterns of the Sebei gas fields are heterogeneous, of up to 73.4 mm/year, 23.5 mm/year and 31.3 mm/year in the investigation period along the U–D, E–W and N–S directions, respectively. These heterogeneous displacements will induce varied stress and strain in different directions, which well explain the damages of the gas wells and pipelines, and indicates potential threats to the G315 Highway. In addition, the knowledge of the patterns of 3-D time-series deformations can be used to predict the extent of the gas-extraction-derived deformation such that some measures can be taken to prevent gas wells and pipelines from being damaged or to control the potential geo-hazards.
- The estimated volume change rates reveal that underground gas of about had been exploited in the Sebei gas systems during the period of November 2014–July 2017. The estimated gas production of 5.022 billion m3 under the conditions of standard state of China in this case coincides with the actual gas productions of 5.499 billion m3 from the PQOCYs between the beginning of this study and the end of 2015, which signifies that the proposed method can not only estimate reliable 3-D time-series deformations, but also the corresponding underground fluids’ volume changes if some a priori information (such as the depths and thickness of the underground fluids) is available or can be estimated. Moreover, the InSAR-derived volume changes can be used to assess the gas production ability, and to assist related departments to ensure the long-term development of Sebei gas field.
The method used in the study can be applied in other fields. For instance, in volcanic research, the estimated 3-D time series deformations are very helpful to comprehensively describe the intrusion and eruption of volcano, and the estimated magma variation is a good indication for the source model. In the monitoring of subsurface reservoir, the estimated groundwater volume change can provide scientific evidence for ensuring a sustainable use of the fresh water resource.
Acknowledgments
The Sentinel-1 data are provided by the European Space Agency. This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 41404011, 41674010, and 41704001), the Science and Technology Project of Hunan Province (No. 2016SK2002), the National Key Basic Research and Development Program of China (No. 2013CB733303), the Project of Education Department of Hunan Province (No. 16K053), Major Projects of High Resolution Earth Observation (Civil Part) (Grant No. 03-Y20A11-9001-15/16), the Demonstration System of High-Resolution Remote Sensing Application in Surveying and Mapping of China (grant No. AH1601-8), the Land and Resources Research Project of Hunan Province (No. 2017-13) and the Advanced Project of Civil Aerospace Research of China: Earth Application and Key Technology Research of 20 m-Resolution Geosynchronous SAR Satellite. The comments and suggestions from the anonymous reviewers and academic editor greatly improve the quality of the manuscript.
Author Contributions
Xiaoge Liu and Jun Hu conceived and designed the study; Xiaoge Liu performed the experiments; Jun Hu supervised the research; Xiaoge Liu, Jun Hu and Qian Sun analyzed the data and the results; Zhiwei Li and Jianjun Zhu contributed to the discussions of the results; and Xiaoge Liu wrote the paper. All authors have reviewed and approved the final manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Geertsma, J. The effect of fluid pressure decline on volumetric changes of porous rocks. Trans. AIME 1957, 210, 331–340. [Google Scholar]
- Han, W.S.; Lu, M.; McPherson, B.J.; Keating, E.H.; Moore, J.; Park, E.; Watson, Z.T.; Jung, N.H. Characteristics of CO2-driven cold-water geyser, Crystal Geyser in Utah: Experimental observation and mechanism analyses. Geofluids 2013, 13, 283–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathias, S.A.; Hardisty, P.E.; Trudell, M.R.; Zimmerman, R.W. Screening and selection of sites for CO2 sequestration based on pressure buildup. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control 2009, 3, 577–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez, A.; Foxall, W. Stochastic inversion of InSAR data to assess the probability of pressure penetration into the lower caprock at In Salah. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control 2014, 27, 42–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Berk, W.; Fu, Y.; Schulz, H.-M. Temporal and spatial development of scaling in reservoir aquifers triggered by seawater injection: Three-dimensional reactive mass transport modeling of water-rock-gas interactions. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2015, 135, 206–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.J.; Fang, Y.L.; Scheibe, T.D.; Bonneville, A. A fluid pressure and deformation analysis for geological sequestration of carbon dioxide. Comput. Geosci. 2012, 46, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomas, R.; Marquez, Y.; Lopez-Sanchez, J.M.; Delgado, J.; Blanco, P.; Mallorqui, J.J.; Martinez, M.; Herrera, G.; Mulas, J. Mapping ground subsidence induced by aquifer overexploitation using advanced Differential SAR Interferometry: Vega Media of the Segura River (SE Spain) case study. Remote Sens. Environ. 2005, 98, 269–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferretti, A.; Prati, C.; Rocca, F. Nonlinear subsidence rate estimation using permanent scatterers in differential SAR interferometry. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2000, 38, 2202–2212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferretti, A.; Prati, C.; Rocca, F. Permanent scatterers in SAR interferometry. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2001, 39, 8–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berardino, P.; Fornaro, G.; Lanari, R.; Sansosti, E. A new algorithm for surface deformation monitoring based on small baseline differential SAR interferograms. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2002, 40, 2375–2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanari, R.; Mora, O.; Manunta, M.; Mallorqui, J.J.; Berardino, P.; Sansosti, E. A small-baseline approach for investigating deformations on full-resolution differential SAR interferograms. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2004, 42, 1377–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zebker, H.A.; Villasenor, J. Decorrelation in interferometric radar echoes. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1992, 30, 950–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanssen, R.F.; Weckwerth, T.M.; Zebker, H.A.; Klees, R. High-resolution water vapor mapping from interferometric radar measurements. Science 1999, 283, 1297–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaussard, E.; Amelung, F.; Abidin, H.; Hong, S.-H. Sinking cities in Indonesia: ALOS PALSAR detects rapid subsidence due to groundwater and gas extraction. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 128, 150–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cigna, F.; Osmanoglu, B.; Cabral-Cano, E.; Dixon, T.H.; Avila-Olivera, J.A.; Garduno-Monroy, V.H.; DeMets, C.; Wdowinski, S. Monitoring land subsidence and its induced geological hazard with Synthetic Aperture Radar Interferometry: A case study in Morelia, Mexico. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 117, 146–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heleno, S.I.N.; Oliveira, L.G.S.; Henriques, M.J.; Falcao, A.P.; Lima, J.N.P.; Cooksley, G.; Ferretti, A.; Fonseca, A.M.; Lobo-Ferreira, J.P.; Fonseca, J.F.B.D. Persistent Scatterers Interferometry detects and measures ground subsidence in Lisbon. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 2152–2167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera, G.; Fernandez, J.A.; Tomas, R.; Cooksley, G.; Mulas, J. Advanced interpretation of subsidence in Murcia (SE Spain) using A-DInSAR data - modelling and validation. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2009, 9, 647–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, W.-C.; Hwang, C.; Chen, Y.-A.; Chang, C.-P.; Yen, J.-Y.; Hooper, A.; Yang, C.-Y. Surface deformation from persistent scatterers SAR interferometry and fusion with leveling data: A case study over the Choushui River Alluvial Fan, Taiwan. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 957–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, A.H.-M.; Ge, L.; Li, X.; Zhang, K. Monitoring ground deformation in Beijing, China with persistent scatterer SAR interferometry. J. Geodesy 2012, 86, 375–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osmanoglu, B.; Dixon, T.H.; Wdowinski, S.; Cabral-Cano, E.; Jiang, Y. Mexico City subsidence observed with persistent scatterer InSAR. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2011, 13, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teatini, P.; Tosi, L.; Strozzi, T.; Carbognin, L.; Wegmuller, U.; Rizzetto, F. Mapping regional land displacements in the Venice coastland by an integrated monitoring system. Remote Sens. Environ. 2005, 98, 403–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghaddam, N.F.; Sahebi, M.R.; Matkan, A.A.; Roostaei, M. Subsidence rate monitoring of Aghajari oil field based on Differential SAR Interferometry. Adv. Space Res. 2013, 51, 2285–2296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Zhao, W.; Dixon, T.H.; Amelung, F.; Han, W.S.; Li, P. InSAR monitoring of ground deformation due to CO2 injection at an enhanced oil recovery site, West Texas. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control 2015, 41, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deschamps, B.; Henschel, M.D.; Walter, G.; Chen, J.; Sato, S.; Gravelle, S. Multi-sensor/multi-beam InSAR ground deformation monitoring of water-flood oil fields. In Proceedings of the Multitemp 2013 7th International Workshop on the Analysis of Multi-Temporal Remote Sensing Images, Banff, AB, Canada, 25–27 June 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Higgins, S.; Overeem, I.; Tanaka, A.; Syvitski, J.P.M. Land subsidence at aquaculture facilities in the Yellow River delta, China. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2013, 40, 3898–3902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, A.H.-M.; Ge, L.; Li, X. Assessments of land subsidence in the Gippsland Basin of Australia using ALOS PALSAR data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 159, 86–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Zhang, Q.; Zhao, C.; Yang, C.; Sun, Q.; Chen, W. Monitoring land subsidence in the southern part of the lower Liaohe plain, China with a multi-track PS-InSAR technique. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 188, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.-Z.; Huang, H.-J.; Bi, H.-B. Land subsidence in the modern Yellow River Delta based on InSAR time series analysis. Nat. Hazards 2015, 75, 2385–2397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Xin, Y.; Li, J. Detecting land uplift associated with enhanced oil recovery using InSAR in the Karamay oil field, Xinjiang, China. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2016, 37, 1527–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikhailov, V.; Kiseleva, E.; Dmitriev, P.; Golubev, V.; Smolyaninova, E.; Timoshkina, E. On reconstruction of the three displacement vector components from SAR LOS displacements for oil and gas producing fields. Procedia Technol. 2014, 16, 385–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasiliev, Y.V.; Yevtyushkin, A.V.; Martynov, O.S.; Radchenko, A.V.; Filatov, A.V. Use PALSAR images by geodynamics monitoring gas and oil fields. Curr. Probl. Remote Sens. Earth Space 2010, 7, 122–128. [Google Scholar]
- Matsunaga, T.; Mialdun, A.; Nishino, K.; Shevtsova, V. Measurements of gas/oil free surface deformation caused by parallel gas flow. Phys. Fluids 2012, 24, 062101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Codegone, G.; Rocca, V.; Verga, F.; Coti, C. Subsidence Modeling Validation Through Back Analysis for an Italian Gas Storage Field. Geotech. Geol. Eng. 2016, 34, 1749–1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Guo, K.; Christianson, M.; Konietzky, H. Deformation characteristics of rock salt with mudstone interbeds surrounding gas and oil storage cavern. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2011, 48, 871–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filatov, A.V.; Yevtyushkin, A.V.; Vasiliev, Y.V. Long-term geodynamic monitoring of oil and gas fields in Western Siberia by InSAR technique. Curr. Probl. Remote Sens. Earth Space 2012, 9, 39–47. [Google Scholar]
- Fokker, P.A.; Wassing, B.B.T.; van Leijen, F.J.; Hanssen, R.F.; Nieuwland, D.A. Application of an ensemble smoother with multiple data assimilation to the Bergermeer gas field, using PS-InSAR. Geomech. Energy Environ. 2016, 5, 16–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gee, D.; Sowter, A.; Novellino, A.; Marsh, S.; Gluyas, J. Monitoring land motion due to natural gas extraction: Validation of the Intermittent SBAS (ISBAS) DInSAR algorithm over gas fields of North Holland, The Netherlands. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2016, 77, 1338–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.T.; Akerley, J.; Baluyut, E.C.; Cardiff, M.; Davatzes, N.C.; Feigl, K.L.; Foxall, W.; Fratta, D.; Mellors, R.J.; Spielman, P.; et al. Time-series analysis of surface deformation at Brady Hot Springs geothermal field (Nevada) using interferometric synthetic aperture radar. Geothermics 2016, 61, 114–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishitsuka, K.; Tsuji, T.; Matsuoka, T.; Nishijima, J.; Fujimitsu, Y. Heterogeneous surface displacement pattern at the Hatchobaru geothermal field inferred from SAR interferometry time-series. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2016, 44, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Wang, Q.; Li, Z.; Zhao, R.; Sun, Q. Investigating the Ground Deformation and Source Model of the Yangbajing Geothermal Field in Tibet, China with the WLS InSAR Technique. Remote Sens. 2016, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koros, W.K.; Agustin, F. Subsidence surveys at Olkaria geothermal field, Kenya. J. Spat. Sci. 2017, 62, 195–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarychikhina, O.; Glowacka, E. Spatio-temporal evolution of aseismic ground deformation in the Mexicali Valley (Baja California, Mexico) from 1993 to 2010, using differential SAR interferometry. In Prevention and Mitigation of Natural and Anthropogenic Hazards Due to Land Subsidence; Daito, K., Galloway, D., Eds.; Copernicus Publications: Göttingen, Germany, 2015; Volume 372, pp. 335–341. [Google Scholar]
- Han, J.-Y.; Forster, R.R.; Moser, D.E.; Ford, A.L.J.; Ramirez-Hernandez, J.; Tiampo, K.F. The spatial and temporal subsidence variability of the East Mesa Geothermal Field, California, USA, and its potential impact on the All American Canal System. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2011, 32, 3427–3449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lubitz, C.; Motagh, M.; Wetzel, H.U.; Kaufmann, H. Remarkable Urban Uplift in Staufen im Breisgau, Germany: Observations from TerraSAR-X InSAR and Leveling from 2008 to 2011. Remote Sens. 2013, 5, 3082–3100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samsonov, S.; van der Kooij, M.; Tiampo, K. A simultaneous inversion for deformation rates and topographic errors of DInSAR data utilizing linear least square inversion technique. Comput. Geosci. 2011, 37, 1083–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Ding, X.-L.; Zhang, L.; Sun, Q.; Li, Z.-W.; Zhu, J.-J.; Lu, Z. Estimation of 3-D Surface Displacement Based on InSAR and Deformation Modeling. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2017, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raucoules, D.; de Michele, M.; Malet, J.P.; Ulrich, P. Time-variable 3D ground displacements from high-resolution synthetic aperture radar (SAR). application to La Valette landslide (South French Alps). Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 139, 198–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michel, R.; Avouac, J.P.; Taboury, J. Measuring near field coseismic displacements from SAR images: Application to the Landers earthquake. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1999, 26, 3017–3020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michel, R.; Avouac, J.P.; Taboury, J. Measuring ground displacements from SAR amplitude images: Application to the Landers earthquake. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1999, 26, 875–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Li, Z.W.; Ding, X.L.; Zhu, J.J.; Zhang, L.; Sun, Q. Resolving three-dimensional surface displacements from InSAR measurements: A review. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2014, 133, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singleton, A.; Li, Z.; Hoey, T.; Muller, J.-P. Evaluating sub-pixel offset techniques as an alternative to D-InSAR for monitoring episodic landslide movements in vegetated terrain. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 147, 133–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Wu, L.; Liu, S.; Wang, Z.; Su, C.; Liu, S.-N. Mapping Two-Dimensional Deformation Field Time-Series of Large Slope by Coupling DInSAR-SBAS with MAI-SBAS. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 12440–12458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bechor, N.B.D.; Zebker, H.A. Measuring two-dimensional movements using a single InSAR pair. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samsonov, S.; Tiampo, K.; Rundle, J.; Li, Z. Application of DInSAR-GPS Optimization for Derivation of Fine-Scale Surface Motion Maps of Southern California. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2007, 45, 512–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guglielmino, F.; Nunnari, G.; Puglisi, G.; Spata, A. Simultaneous and Integrated Strain Tensor Estimation From Geodetic and Satellite Deformation Measurements to Obtain Three-Dimensional Displacement Maps. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2011, 49, 1815–1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vollrath, A.; Zucca, F.; Bekaert, D.; Bonforte, A.; Guglielmino, F.; Hooper, A.J.; Stramondo, S. Decomposing DInSAR Time-Series into 3-D in Combination with GPS in the Case of Low Strain Rates: An Application to the Hyblean Plateau, Sicily, Italy. Remote Sens. 2017, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozawa, T.; Ueda, H. Advanced interferometric synthetic aperture radar (InSAR) time series analysis using interferograms of multiple-orbit tracks: A case study on Miyake-jima. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2011, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, T.J.; Parsons, B.E.; Lu, Z. Toward mapping surface deformation in three dimensions using InSAR. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2004, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Ding, X.-L.; Li, Z.-W.; Zhu, J.-J.; Sun, Q.; Zhang, L. Kalman-filter-based approach for multisensor, multitrack, and multitemporal InSAR. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2013, 51, 4226–4239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raw Precipitation Data. Available online: http://data.cma.cn/data/cdcindex/cid/6d1b5efbdcbf9a58.html (accessed on 10 March 2017).
- Jin, Q.; Cheng, F.Q.; Su, A.G.; Zhu, G.Y.; Wang, L.; Cao, Q. Biogas charging and dissipating process and its accumulation in the Sebei gasfield, Qaidam Basin, China. Sci. China Ser. D Earth Sci. 2008, 51, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, C.H. Fluid typing extends production in Chinese gas reservoir. Oil Gas J. 2015, 113, 54–61. [Google Scholar]
- Ou, C.H.; Wang, X.L.; Li, C.C.; He, Y. Three-Dimensional Modelling of a Multi-Layer Sandstone Reservoir: The Sebei Gas Field, China. Acta Geol. Sin. Engl. Ed. 2016, 90, 209–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.T.; Gao, J.F.; Tian, H.M.; Qian, Z.H.; Sun, Y.Q. Calculation and Evaluation of Dynamic Reserves in Sebei No. 1 Gas Field. Nat. Gas Ind. 2009, 29, 95–98. [Google Scholar]
- Petro China Qinghai Oilfield Company (PCQOC). Petro China Qinghai Oilfield Company Yearbook, 2008–2009; Tongxin Press: Beijing, China, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Petro China Qinghai Oilfield Company (PCQOC). PetroChina Qinghai Oilfield Company Yearbook, 2011–2012; Dunhuang Literature and Art Publishing House: Lanzhou, China, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Petro China Qinghai Oilfield Company (PCQOC). PetroChina Qinghai Oilfield Company Yearbook, 2013; Dunhuang Literature and Art Publishing House: Lanzhou, China, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Petro China Qinghai Oilfield Company (PCQOC). PetroChina Qinghai Oilfield Company Yearbook, 2014; Gansu Culture Publishing House: Lanzhou, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Petro China Qinghai Oilfield Company (PCQOC). PetroChina Qinghai Oilfield Company Yearbook, 2015; Gansu Culture Publishing House: Lanzhou, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Petro China Qinghai Oilfield Company (PCQOC). PetroChina Qinghai Oilfield Company Yearbook, 2016; Gansu Culture Publishing House: Lanzhou, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, C.R.; Wang, Y.Z.; Li, Z.C. Calibration of recoverable reserves of three large gas fields in Qaidam Basin. Nat. Gas Ind. 2000, 20, 69–72. [Google Scholar]
- Rabus, B.; Eineder, M.; Roth, A.; Bamler, R. The shuttle radar topography mission—A new class of digital elevation models acquired by spaceborne radar. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2003, 57, 241–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massonnet, D.; Rossi, M.; Carmona, C.; Adragna, F.; Peltzer, G.; Fiegl, K.; Rabaute, T. The displacement field of the Landers earthquake mapped by radar interferometry. Nature 1993, 364, 138–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sentinel1 Orbit State Vectors. Available online: https://qc.sentinel1.eo.esa.int/ (accessed on 10 March 2017).
- Li, Z.W.; Ding, X.L.; Zheng, D.W.; Huang, C. Least squares-based filter for remote sensing image noise reduction. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2008, 46, 2044–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.W.; Zebker, H.A. Phase unwrapping for large SAR interferograms: Statistical segmentation and generalized network models. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2002, 40, 1709–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanssen, R.F. Radar Interferometry: Data Interpretation and Error Analysis; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin, Germany, 2001; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Lei, M.F.; Wang, Q.J.; Liu, X.L.; Xu, B.; Zhang, H.Q. Influence of ocean tidal loading on InSAR offshore areas deformation monitoring. Geodesy Geodyn. 2017, 8, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasco, D.W.; Puskas, C.M.; Smith, R.B.; Meertens, C.M. Crustal deformation and source models of the Yellowstone volcanic field from geodetic data. J. Geophys. Res. 2007, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mogi, K. Relations between the eruptions of various volcanoes and the deformations of the ground surfaces around them. Bull. Earthquake Res. Inst. 1958, 36, 99–134. [Google Scholar]
- Tarantola, A. Inverse Problem Theory: Method for Data Fitting and Model Parameter Estimation; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1987; 613p. [Google Scholar]
- William, M. Geophysical Data Analysis: Discrete Inverse Theory; Academic Press, Inc.: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.D.; Wang, X.L.; Zhang, D.; Yuan, W.K. Optimum Design of Horizontal Section Length of the Horizontal Wells in Sebei-2 Gas Field. Adv. Eng. Res. 2010, 4, 55–66. [Google Scholar]
- Biot, M.A. General Theory of Three—Dimensional Consolidation. J. Appl. Phys. 1941, 12, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).