Abstract
Soil erosion is a global issue that threatens food security and causes environmental degradation. Management of water erosion requires accurate estimates of the spatial and temporal variations in the erosive power of rainfall (erosivity). Rainfall erosivity can be estimated from rain gauge stations and satellites. However, the time series rainfall data that has a high temporal resolution are often unavailable in many areas of the world. Satellite remote sensing allows provision of the continuous gridded estimates of rainfall, yet it is generally characterized by significant bias. Here we present a methodology that merges daily rain gauge measurements and the Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission (TRMM) 3B42 data using collocated cokriging (ColCOK) to quantify the spatial distribution of rainfall and thereby to estimate rainfall erosivity across China. This study also used block kriging (BK) and TRMM to estimate rainfall and rainfall erosivity. The methodologies are evaluated based on the individual rain gauge stations. The results from the present study generally indicate that the ColCOK technique, in combination with TRMM and gauge data, provides merged rainfall fields with good agreement with rain gauges and with the best accuracy with rainfall erosivity estimates, when compared with BK gauges and TRMM alone.
1. Introduction
Water erosion is one of the most important environmental threats worldwide in addition to soil degradation, food security, and natural ecosystem deterioration [1]. The rainfall erosivity factor (R) in the Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation (RUSLE) is one the most important indicators of potential water erosion which combines the effects of the duration, magnitude, and intensity of rainfall events. High resolution precipitation data are essential for the evaluation of rainfall erosivity. Traditionally, rainfall erosivity is determined by a function of a storm’s kinetic energy, E, and its maximum 30 minute rainfall intensity, I30, known as the EI30 [2], and is observed with conventional instruments such as rain gauges. High temporal resolution rainfall measurements, for example 15 min or 30 min, are important for the calculation of erosivity since heavy rainfall and extreme events are typically rare events of short duration [3,4,5,6]. However, information on these records is rarely available with good spatial and temporal coverage, especially in developing countries, and processing these data is time-consuming and laborious [7,8,9]. Statistical relationships were subsequently established between R and precipitation in order to solve this problem, based on annual precipitation [1,10], monthly precipitation [11], daily precipitation [9,12], and storm events [13,14]. Compared to annual and monthly rainfall data, daily rainfall data include more detailed and accurate information about ground rainfall characteristics, and the accuracy of the R factor calculated from daily rainfall data has been widely verified and applied [7,8,9].
Rain gauges provide valuable information about the amount and frequency of rainfall. However, uneven spatial distribution and spatial incoherencies limit the implication of rain gauges in the estimation of precipitation [15]. In this context, precipitation retrievals from a satellite provide an alternative solution to this problem by providing spatially distributed precipitation estimation over large areas. Various aspects of remotely-sensed rainfall have been explored and reported [16,17,18,19,20]. Among them, Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission (TRMM) multisatellite precipitation analysis (TMPA) has been used, since the launch of TRMM in November 1997, to produce a range of quasi-global precipitation products. These products are widely used in various climate and hydrological applications [17,19,21,22,23,24], and have been considered for the spatial assessment of erosivity [20,25,26]. Numerous studies have evaluated the performance of TRMM by comparing precipitation estimates from TRMM products with rain gauge precipitations or ground-based radar estimates [27,28,29]. However, it is well recognized that rainfall estimates from TRMM satellites involve their own uncertainties. De Goncalves et al. [30] used three satellite-derived products to estimate daily rainfall across South America and found that TRMM tends to underestimate areas without rainfall and overestimate areas with small amounts of rainfall. Tang et al. [31] reported that the TRMM-based precipitation estimates show obvious overestimation over most inland water bodies, which is caused by the systematic anomalies of the TRMM product stemming from deficiencies in the TRMM’s assumptions about water surface emissivity. The uncertainties of TRMM products that are encountered when measuring ground level rainfall therefore influence the accuracy of rainfall erosivity estimates.
The merging of rain gauge and satellite measurements offers considerable potential for improvement of the quality of rainfall data. Several attempts have previously been made to merge rain gauge observations with satellite rainfall data [32,33,34,35,36]. Among them, one popular and simple alternative approach for spatial modelling and mapping of sparsely sampled (rain gauge) data, which makes use of extensive gridded (satellite) data, is collocated cokriging (ColCOK) [37]. This approach makes estimates at a spatial resolution of the gridded data. In this case, the outcome would be at approximately 25 × 25 km2—the spatial resolution of the satellite product. However, none of the studies has measured and mapped rainfall erosivity with merged rainfall data by ColCOK technique at a national scale.
The aim of this study is to assess the improvement of the estimation of daily rainfall by merging TRMM 3B42 and rain gauge data using the ColCOK technique and thereby estimate rainfall erosivity in China at a fine resolution. To achieve this aim, this study employed three approaches that use TRMM 3B42 and/or rain gauge data as supporting information: (1) use TRMM 3B42 only to define the spatial variability of daily rainfall and to estimate rainfall erosivity; (2) use rain gauge data to estimate the rainfall and rainfall erosivity with the same support as in (1) by using block kriging (BK); and (3) use TRMM 3B42 fields as in (1) but also include rain gauge observations at the target pixels in the estimation equations by using ColCOK. The analysis involves estimated daily rainfall maps and thereby estimates mean annual rainfall erosivity across China using the three alternative methods and assesses improvements introduced by the ColCOK technique. The performance of each one of these estimators was analyzed, compared, and discussed using several independent rain gauges in China.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Rain Gauge Measurements
Daily observed precipitation data are provided by the National Climate Centre of the China Meteorological Administration (CMA). The homogeneity and reliability of the daily meteorological data are checked and filtered by the CMA to remove spurious data before its release [33]. A day is defined as from 20:00 of the previous day to 20:00 of the current day in local time (i.e., 12:00 UTC previous day to 12:00 UTC current day). Although the number of stations in service has changed over the years, 650 of the 752 stations in the original data set have maintained daily rainfall data since the 1960s. Thus, daily rain gauge data at 650 stations across China for the 12-year period from 2002 to 2013 are used (Figure 1).
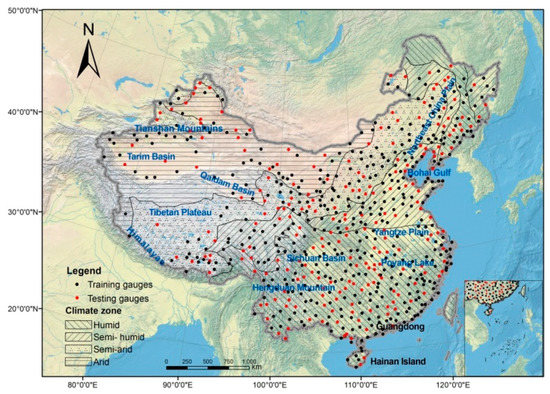
Figure 1.
Spatial distribution of rain gauges used in this study and their relation to the climate zones. The black circles show the locations of 433 training rain gauges and the red circles represent the locations of the 217 testing rain gauges used in our study.
The rain gauges are separated into two parts as described in the following steps: (1) rain gauges are divided according to the four climate regions; (2) rain gauges in each climate region are ordered according to the mean daily precipitation over the 2002–2013 period; (3) the training data set is randomly selected and consisted of two-thirds of the rain gauges in each climate region; (4) the remaining third of rain gauges in each climate region is used as an independent set against which to test the performance of the results. The training data set used in this study consists of 433 rain gauges in China. The remaining 217 rain gauges are used as the testing data set (Table 1).

Table 1.
Number of rain gauges in each climate region and each region’s percentage of total number of rain gauge stations across China.
2.2. Satellite-Based Rainfall Measurements
The Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission (TRMM) satellite is designed to measure tropical and subtropical precipitation and to estimate its associated latent heat using passive and active microwave sensors [38]. The TRMM multisatellite precipitation analysis (TMPA) is produced by the NASA Goddard Space Flight Center (GSFC), and is the result of a combination of precipitation-related instruments (precipitation radar, PR; TRMM microwave imager, TMI; visible and infrared scanner, VIRS, with the special sensor microwave imager, SSM/I) [39]. It is designed to combine precipitation estimates from various satellite systems, in addition to rain gauge data. Rainfall estimates from TMPA provided by algorithm 3B42 Version 7 were used in this study, with a spatial resolution of 0.25° × 0.25° and a temporal resolution of 3 h (00:00, 03:00, 06:00, ..., 21:00 UTC) for coverage between 50° S and 50° N. Huffman et al. [40] provides details of this product.
To be consistent with daily rain gauge data, it is necessary to construct daily 3B42-based estimates of precipitation for China using a consistent 24 h accumulation period. That is, the estimation of TRMM-derived daily precipitation for China is the accumulation of the rainfall falling in the 12:00 UTC previous day to 12:00 UTC current day.
2.3. Merging Daily Rain Gauge and Satellite Data
One of the main objectives of this study is to map the primary and sparsely sampled rain gauge data using the secondary, collocated TRMM gridded rainfall estimates. ColCOK uses the single collocated secondary variable (Z2) directly in the kriging equation for each estimation. The means of the primary variable (m1) and secondary variable (m2) are used in rescaling the secondary variable to eliminate potential bias. The ColCOK estimator of the primary variable (Z1) at location u follows Goovaerts [41]
where is the number of measurements at location u; are weights associated with the n(u) known rainfall values of the rain gauges, , and is the weight related to the known rainfall value of the TRMM field at the target point and the single constraint that all weights must sum to one
The weights of this estimator can therefore be computed by solving the following linear equation system
where and are the spatial covariances of gauge and TRMM, respectively; is the cross-variance between gauge and TRMM; and is the Lagrange multiplier.
Covariances and and the cross-covariances = can be obtained by developing cross-variograms under a valid linear model at lag distance h. However, this linear model is an unattractive procedure because variogram models cannot be built independently from each other. By applying a Markov–type approximation, the requirement for the secondary data variogram and full cross-covariance can be defined as a factor of the correlogram of the primary data [41]
where is the standard primary covariance of gauges , is the cross-correlogram function between gauge and TRMM data, and is the linear correlation coefficient inferred from collocated data , .
The experimental (semi-)variogram of the rain gauge point data is calculated and fitted with a range of authorized functions. The best fit is chosen using least squares weighted to the number of comparisons at each lag separation n(u). The spatial correlation of the rain gauge data and collocated TRMM is established to provide the spatial correlation model of the merged rainfall. The TRMM correlation map approximates the cross-correlogram model using the Markov approach. Following Equation (4), the cross-correlogram can be estimated directly from correlogram and from the correlation coefficient between and .
The main assumption underlying the Markov–type model is that the variogram of the gauge data is proportional to the cross-variogram. The results section shows how this proportionality assumption holds.
2.4. Estimation of Gauge-Based Rainfall by Block Kriging
In this study, block kriging (BK) was used to upscale the rain gauge observations (from points to approx. 25 km2 blocks). BK uses a moving neighborhood—or block—of given dimensions to estimate the average Z value over a surface. The average value of attribute Z over a block V centered at u, the block mean value is defined as
The block value is a linear average of the N point estimators and has a minimum variance of estimation error. The block ordinary kriging system is written as [41]
where μ is a Lagrange multiplier, is approximated by the arithmetic average of the point support covariances defined between location and the points discretizing the block .
2.5. Calculation of Rainfall Erosivity from Merged Daily Rainfall Data
The rainfall erosivity in the RUSLE is calculated from the total kinetic energy and the maximum 30 min intensity of individual events. However, continuous long-term rainfall data with high temporal resolutions are often unavailable in many areas of the world. For that reason, many efforts have been made to estimate rainfall erosivity by using daily rainfall data [42,43]. Zhang et al. [44] developed a power function model to estimate rainfall erosivity based on daily rainfall data that is widely used in China, including in the First National Water Conservancy Survey [8,12,45,46]. Zhang and Fu [47] estimated rainfall erosivity from daily, monthly, and annual rainfall and verified each model by EI30. Their results indicated that the performance of a daily-based model was obviously better with an average coefficient of determination of 0.718 and an average relative error of 4.2% [44]. This method obtains annual and monthly rainfall erosivity by aggregating rainfall erosivity of each half-month
where is the rainfall erosivity of the i half-month (MJ mm ha−1 h−1); k is the number of days in the i half month; is the effective rainfall for day j of the i half-month, which is equivalent to the actual rainfall if the rainfall is larger than the threshold value of 12 mm, which has become a standard value widely used for China’s erosive rainfall [12,48]. Otherwise, is equal to zero. The parameters α and β are defined as
where Pd12 is the average daily rainfall that is larger than 12 mm and Py12 is the yearly average rainfall for days with rainfall larger than 12 mm.
The R factor for each year is calculated as the sum of the half-month rainfall erosivity in a year and, in this study, is subsequently averaged to obtain the long-term mean R value for the period from 2002 to 2013. Using the daily rainfall formula (Equation (9)), the mean annual rainfall erosivity is calculated for each of the 0.25° × 0.25° pixel as well as for 650 rain gauges across China and for each time step. As mentioned above, TRMM is a rainfall product with a global coverage between 50° S and 50° N. The use of TRMM with the proposed methodology excludes a small part of China. To facilitate direct comparisons with the TRMM data, all the analysis in this study will be consistent with the spatial resolution and coverage of TRMM.
2.6. Uncertainty Estimation
Rain gauge measurements at 217 rain gauges are used as the testing data set for assessment of the performance of the BK-based rain gauge data (hereafter BK gauges) and the TRMM and ColCOK rainfall data. Comparison criteria are calculated, including root mean square error (RMSE), bias, and coefficient of determination (R2).
where n is the total number of gauges in the analysis, and and represent the observed and estimated rainfall at a particular rain gauge, respectively.
3. Results
3.1. Spatial Distribution of Daily Rainfall
In this study, collocated cokriging (ColCOK) was used to merge the rain gauge and TRMM measurements to improve the quality of the daily rainfall data for the period from 2002 to 2013. Two days (3 June 2012 and 9 November 2012) are chosen to show the type of outcomes from the methodology and to make comparisons of the rainfall datasets. On these two days rainfall occurs in every climate region across China. The variograms of the BK gauges rainfall data are shown in Figure 2a,b. The cross-correlogram between the BK gauges and TRMM data are shown in Figure 2c,d.
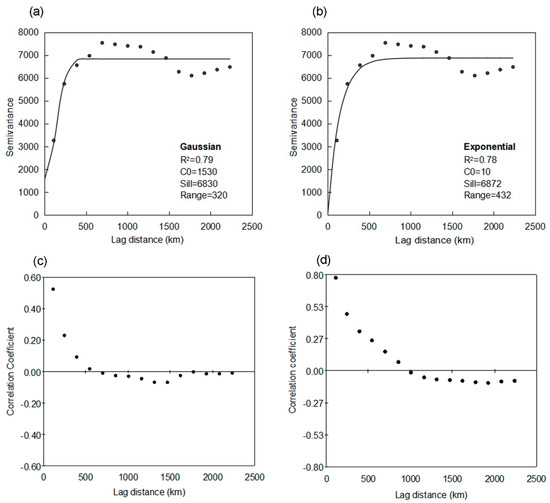
Figure 2.
Semi-variogram of block-kriging (BK) gauges rainfall data for (a) 3 June 2012 and (b) 9 November 2012; cross-correlogram between the BK gauges and TRMM data for (c) 3 June 2012 and (d) 9 November 2012.
The spatial distribution maps of daily rainfall for 3 June 2012 and 9 November 2012 are shown in Figure 3. On 3 June 2012, large areas of southwest China—for example Hengduan Mountain and Sichuan Basin—have recorded rainfall. Heavy rainfall also occurs in the areas around the border of the Northeast China Plain and in southern China (Figure 3a–c). On 9 November 2012, rainfall mainly occured in the humid regions of southeastern China. There is a broadly similar pattern of rainfall estimated by BK gauges, TRMM, and ColCOK (Figure 3d–f). The inclusion of the TRMM data using ColCOK does not change the general pattern of BK gauges. However, it improves the visual impression of the rainfall map estimates, particularly in the arid areas (Figure 3c,f). This pattern suggests that the TRMM rainfall data provide important information in areas where the rain gauge network is sparse. Notwithstanding those similarities, there is a difference between these three measures over China and the uncertainty of these data sets should be estimated.
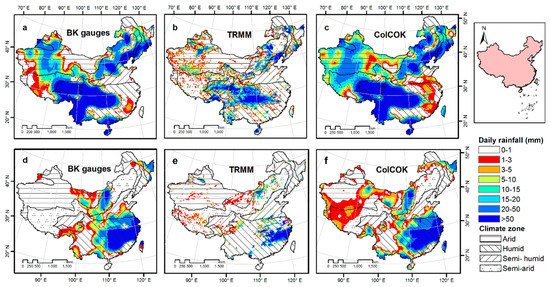
Figure 3.
Maps of daily rainfall (mm) measured at (a) BK gauges, (b) Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission (TRMM), and (c) collocated cokriging (ColCOK) for 3 June 2012; and (d) BK gauges, (e) TRMM, and (f) ColCOK for 9 November 2012 at 0.25° × 0.25° grid across China.
Table 2 presents the validation results of the BK gauges, TRMM, and ColCOK estimates in comparison with the 217 rain gauge measurements (Figure 1) for the 3 June 2012 and 9 November 2012 across China. The technique explicitly improves the estimation accuracy compared with that of the BK gauges and TRMM data alone (Table 2) and the patches of rainfall evident in the gauge and satellite data are matched by the merged estimates (Figure 3). Overall, there are differences between daily rainfall estimates produced with and without the ColCOK method. The highest correlation between BK gauges and testing rain gauges was obtained in the humid regions, while the lowest correlation between them was obtained in the arid regions. TRMM estimates alone are likely to underestimate rainfall (evident by the positive biases for these two days), especially for the semi-humid and semi-arid regions, while ColCOK tends to overestimate daily rainfall only slightly for nearly all the climate regions and China as a whole (Table 2). The rainfall estimates from ColCOK produce less error than those from BK gauges and TRMM with respect to error statistics. Compared with estimates from TRMM alone, ColCOK improved the value of R2 by more than 40% from 0.47 to 0.66 across China for 3 June 2012, and decreased the value of bias by more than 16 times from 2.67 to −0.16 across China for 9 November 2012.

Table 2.
Overall performance of the validation results of TRMM and ColCOK estimates in comparison to rain gauge measurements for 3 June 2012 and 9 November 2012 for each of the 217 testing rain gauges across China.
3.2. Mean Annual Rainfall Erosivity over China
The maps of spatial distribution of mean annual rainfall erosivity (2002–2013), estimated by BK gauges, TRMM, and ColCOK at 0.25° × 0.25° resolution are shown in Figure 4a–c. Based on the estimation of BK gauges, TRMM, and ColCOK, the largest erosivity (>10,000 MJ mm ha−1 h−1 yr−1) is found in areas where the rainfall is most intense and frequent, for example along the southern coast of humid regions, on the Hainan Island, and in parts of Guangdong Province. Medium erosivity (5000–10,000 MJ mm ha−1 h−1 yr−1) occurs in the south of the Yangtze Plain (Figure 4c). Arid areas, such as Tarim Basin and Qaidam Basin, show the smallest erosivity below 100 MJ mm ha−1 h−1 yr−1. A map of interquartile range (IQR; 75th minus 25th percentile) of rainfall erosivity that was calculated by ColCOK for each 0.25° × 0.25° pixel is shown in Figure 4d. The map of IQR shows the spatial uncertainty of rainfall erosivity. Figure 4d shows that rainfall erosivity over China, estimated by ColCOK, has a minimum uncertainty (IQR < 10 MJ mm ha−1 h−1 yr−1) in the northwest and increases gradually towards the southeast of China.
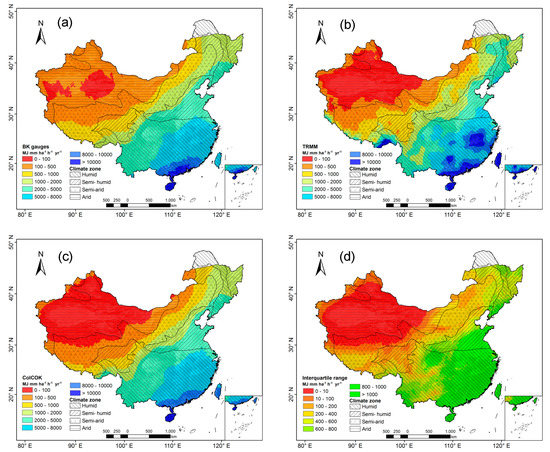
Figure 4.
Spatial distribution maps of annual rainfall erosivity based on: (a) BK gauges, (b) TRMM, (c) ColCOK, and (d) interquartile range (IQR) of rainfall erosivity based on ColCOK at 0.25° × 0.25° for the 2002 to 2013 period, across China.
The yearly time series of precipitation and rainfall erosivity during 2002–2013 across the climate regions of China are shown in Figure 5. The yearly precipitation and rainfall erosivity values are calculated based on 650 rain gauges stations across China. Rainfall in humid regions has a larger erosivity value than that in the other regions. Generally, winter and summer monsoons are distinctly developed in the humid regions. The monthly and inter-annual variations in precipitation are obvious over these regions, which in turn contribute to the highest annual rainfall erosivity. The annual rainfall erosivity value estimated by BK gauges, TRMM, and ColCOK is 3204.26 MJ mm ha−1 h−1 yr−1, 3425.29 MJ mm ha−1 h−1 yr−1, and 2838.63 MJ mm ha−1 h−1 yr−1, respectively, while the value calculated by rain gauges is 2854.48 MJ mm ha−1 h−1 yr−1. TRMM based rainfall erosivity shows larger values than that calculated by BK gauges and ColCOK in the humid, semi-humid, and semi-arid regions. Rainfall erosivity calculated by ColCOK is less than that estimated by BK gauges and TRMM and is similar to the values calculated by rain gauges.
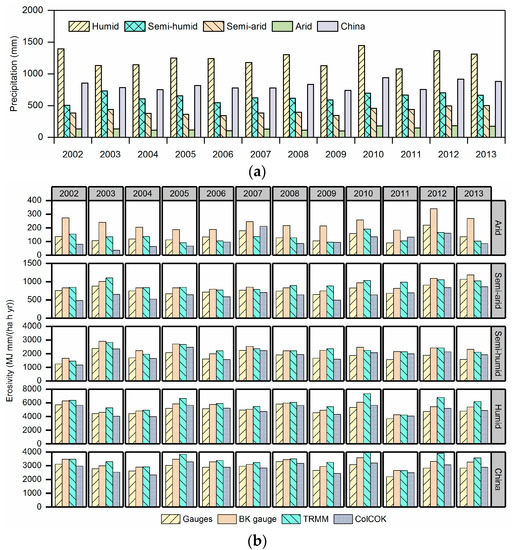
Figure 5.
Temporal distribution of (a) annual precipitation and (b) rainfall erosivity in different climate regions and across the whole of China for 2002–2013.
Figure 6 provides a summary of the evaluation by comparing the estimates of the BK gauges, TRMM, and ColCOK in this study and the calculated annual rainfall erosivity at the location of the 217 testing rain gauges. The IQR of rainfall erosivity that was estimated by BK gauges, TRMM, and ColCOK is 4189.51 MJ mm ha−1 h−1 yr−1, 4334.07 MJ mm ha−1 h−1 yr−1, and 4189.03 MJ mm ha−1 h−1 yr−1, respectively, while the IQR of gauge-based rainfall erosivity is 4365.3 MJ mm ha−1 h−1 yr−1. Table 3 shows the overall performance of the estimated results in this study. In general, ColCOK improves R2 and decreases RMSE in each climate region and across China. ColCOK underestimates rainfall erosivity values in the humid regions.
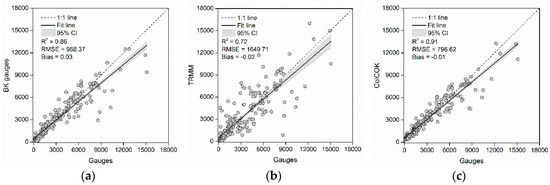
Figure 6.
Scatter plot between the rain gauge calculated annual R factor and the estimated annual R factor from: (a) BK gauges, (b) TRMM, and (c) ColCOK, based on the 217 testing data set for 2002–2013.

Table 3.
Overall performance of validation results of the BK gauge-, TRMM-, and ColOCK-based yearly rainfall erosivity estimates in comparison with the 217 testing rain gauges.
4. Discussion
The spatial characteristics of rainfall are essential for the mapping of its erosive force and should be considered before calculating rainfall erosivity. Few studies have assessed rainfall characteristics using gauge-satellite merged products [32,33,34,35,49] and none of these studies have measured and mapped rainfall erosivity using precipitation estimates obtained from these merged techniques. Several attempts have been made to evaluate and map rainfall erosivity on a national scale using gauge data, for example in Brazil [50,51,52], Korea [1] and the United States [53]. Due to the limitations of field measurements and surveys, most efforts have been made to estimate regional rainfall erosivity in China [12,39,45,54,55] and only a few studies have focused on the national scale of China [3,46,56]. The spatial pattern of our R factor in China is similar to that of Zhu and Yu [56] and Qin et al. [46]. The relationship between our estimates and those of Zhu and Yu [56]—who estimated the R factor using the mean annual precipitation for 22 locations in mainland China—has an R2 of 0.84 and an RMSE of 1211 MJ mm ha−1 h−1 yr−1. Compared to Qin et al. [46] (R = 2434 MJ mm ha−1 h−1 yr−1) and Panagos et al. [3] (R = 1600 MJ mm ha−1 h−1 yr−1), our estimates of rainfall erosivity (R = 2838.63 MJ mm ha−1 h−1 yr−1) are larger because we used a different rainfall dataset for the estimations of rainfall erosivity. Daily rainfall data from 756 stations and hourly rainfall records from 387 stations were used by Qin et al. [46] and Panagos et al. [3], respectively. However, the rainfall data that we used was based on the daily gauge-satellite merged products.
The results from the present study indicate that the ColCOK provides an appropriate method to estimate daily rainfall. The technique explicitly improves estimation accuracy compared to TRMM data (Table 2) and the patches of rainfall evident in the gauge and satellite data are matched by the merged estimates (Figure 3). TRMM tends to severely underestimate daily rainfall, especially for humid and semi-humid regions, while ColCOK tends to overestimate daily rainfall only slightly for all climate regions and China as a whole (Figure 3 and Table 2). The ColCOK estimates provide more reliable results than TRMM alone at the rain gauge locations (Table 2). However, the BK gauge estimates are subject to measurement errors, particularly over semi-arid and arid regions, due to the difficulty of interpolating sparse rain gauge measurements. The inclusion of the TRMM data using ColCOK does not change the general pattern of BK gauges. However, it improves the visual impression of the rainfall map estimates, particularly in the semi-arid and arid areas (Figure 3c,f). This pattern suggests that the TRMM rainfall data provide important information for areas where the rain gauge network is sparse.
Figure 5a shows a concentration of heavy rainfall in the wet season, overlapping with the tropical monsoon period, and contributing more than 80% of the annual rainfall. Evidently, wet seasonal rainfall strongly influences rainfall erosivity across China. Winter and summer monsoons are distinctly developed in the humid regions of southern China. The monthly and inter-annual variations in precipitation are striking over these regions, which in turn contribute to the highest annual rainfall erosivity (Table 3). Rainfall in the semi-humid region has a similar temporal distribution trend to the rainfall for the whole of China (Figure 5). The rainfall records during the winter and spring months come from several precipitation events of relatively small intensity. In contrast, the precipitation in summer and autumn is typically caused by a few very intense events (Figure 5a). The intense summer rainfall in the humid regions, especially along the East Asian monsoon climate zone, should be a focus for soil conservation to prevent soil erosion and ensure food security.
The areas around the China–India border, the southern Himalayas and Hengduan Mountains, are located in the subtropical monsoon humid climate region and have a complex topography. Fan et al. [57] investigated the characteristics of rainfall erosivity in Tibet and found a peak value of annual rainfall erosivity (about 1600 MJ mm ha−1 h−1 yr−1) in these regions. The large rainfall erosivity is likely caused by the intense rainfall between May and September. However, compared with ColCOK based annual rainfall erosivity, the annual rainfall erosivity calculated using the TRMM data showed large overestimates over this region (Figure 4b). These results suggest that TRMM may not provide a precipitation estimate suitable for these regions due to the complex effects of wind, wetting loss, and other factors. Similar annual rainfall erosivity was estimated in the arid regions by both ColCOK and TRMM. For these regions, annual rainfall erosivity was estimated at less than 100 MJ mm ha−1 h−1 yr−1. As mentioned above, the rain gauge data is not evenly distributed over the arid regions (Figure 1). This similarity is attributed to the spatial overlap between ColCOK and TRMM data at unsampled locations in the cokriging procedure. In addition, it may also be caused by the limited rainfall in these areas.
5. Conclusions
This study explored and mapped rainfall erosivity based on merged daily rainfall data at 0.25° × 0.25° spatial resolution across China (2002–2013). The application of ColCOK is an attempt to produce improved daily rainfall data at a finer spatial resolution with higher accuracy. The merged daily rainfall was applied to estimate rainfall erosivity across China, in which precipitation is highly variable in time and space. The rainfall data used are the most up-to-date and rigorously quality-controlled data available for China. Daily rainfall estimates based on the merged rainfall data have a higher accuracy than BK gauges and TRMM alone. Compared with estimated rainfall by TRMM alone, ColCOK improved the value of R2 by more than 40% from 0.47 to 0.66 across China for 3 June 2012, and decreased the value of bias by more than 16 times from 2.67 mm to −0.16 mm across China for 9 November 2012. Compared with estimated rainfall by BK gauges, ColCOK improved the performance of validation results for almost all the climate regions for 3 June 2012 and 9 November 2012. The limited rain gauges, particularly in western China, influence the accuracy of rainfall estimates by BK gauges. The ColCOK estimates, which incorporate the TRMM data, improve upon BK estimates in the regions where gauge densities are less than one gauge per pixel.
The average annual rainfall erosivity across China, based on the ColCOK, is estimated to be 2838.63 MJ mm ha−1 h−1 yr−1. Humid regions affected by the tropical climate in China have the largest average annual rainfall erosivity values, while the arid regions have the smallest average annual erosivity values. The striking changes of rainfall amount, rainfall intensity, and rainfall spatio-temporal distribution in the humid regions contribute to the highest annual rainfall erosivity. The estimates of rainfall erosivity based on the ColCOK methodology showed a strong correlation with those estimates based on the testing data set (R2 = 0.91). The overall performance of the estimated rainfall erosivity in comparison to the testing rain gauges showed that ColCOK improved the value of R2 from 0.86 and 0.72 to 0.91 in China, and decreased the value of RMSE from 988.37 MJ mm ha−1 h−1 yr−1 and 1649.71 MJ mm ha−1 h−1 yr−1 to 796.62 MJ mm ha−1 h−1 yr−1. The rainfall erosivity maps and technique used in this study provide a useful tool for erosion assessments, especially in the otherwise data-poor environments of China and elsewhere in the world.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 41461063, 41571339), and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities of Zhejiang.
Author Contributions
Hongfen Teng and Zhou Shi conceived and designed the experiments; Hongfen Teng, Ziqiang Ma, Zongzheng Liang and Wu Yu performed the experiments and analyzed the data; Hongfen Teng wrote the paper; Adrian Chappell contributed to discussions and revisions, providing important feedbacks and suggestions.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Lee, J.H.; Heo, J.H. Evaluation of estimation methods for rainfall erosivity based on annual precipitation in Korea. J. Hydrol. 2011, 409, 30–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wischmeier, W.H.; Smith, D.D. Predicting Rainfall Erosion Losses: A Guide to Conservation Planning; US Department of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 1978.
- Panagos, P.; Borrelli, P.; Meusburger, K.; Yu, B.F.; Klik, A.; Lim, K.J.; Yang, J.E.; Ni, J.R.; Miao, C.Y.; Chattopadhyay, N.; et al. Global rainfall erosivity assessment based on high-temporal resolution rainfall records. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, S.; Xie, Y.; Nearing, M.A.; Wang, C. Estimation of rainfall erosivity using 5 to 60 minute fixed–interval rainfall data from China. Catena 2007, 70, 306–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meusburger, K.; Steel, A.; Panagos, P.; Montanarella, L.; Alewell, C. Spatial and temporal variability of rainfall erosivity factor for Switzerland. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2012, 16, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panagos, P.; Ballabio, C.; Borrelli, P.; Meusburger, K.; Klik, A.; Rousseva, S.; Tadic, M.P.; Michaelides, S.; Hrabalikova, M.; Olsen, P.; et al. Rainfall erosivity in Europe. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 511, 801–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, C.G.; Chen, X.H.; Wang, Z.L.; Wu, X.S.; Zhao, S.W.; Wu, X.Q.; Bai, W.K. Spatio-temporal variation in rainfall erosivity during 1960–2012 in the Pearl River Basin, China. Catena 2016, 137, 382–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Z.J.; Duan, X.W.; Liu, B.; Hu, J.M.; He, J.N. The spatial distribution and temporal variation of rainfall erosivity in the Yunnan Plateau, Southwest China: 1960–2012. Catena 2016, 145, 291–300. [Google Scholar]
- Angulo-Martinez, M.; Begueria, S. Estimating rainfall erosivity from daily precipitation records: A comparison among methods using data from the Ebro Basin (NE Spain). J. Hydrol. 2009, 379, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikhailova, E.A.; Bryant, R.B.; Schwager, S.J.; Smith, S.D. Predicting rainfall erosivity in Honduras. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1997, 61, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renard, K.G.; Freimund, J.R. Using monthly precipitation data to estimate the R-factor in the revised USLE. J. Hydrol. 1994, 157, 287–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; He, Y.; Xu, J.; van Noordwijk, M.; Lu, X. Spatial and temporal variation in rainfall erosivity in a Himalayan watershed. Catena 2014, 121, 248–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghi, S.H.R.; Moatamednia, M.; Behzadfar, M. Spatial and temporal variations in the rainfall erosivity factor in Iran. J. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2011, 13, 451–464. [Google Scholar]
- Bonilla, C.A.; Vidal, K.L. Rainfall erosivity in central Chile. J. Hydrol. 2011, 410, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhnlein, M.; Appelhans, T.; Thies, B.; Nauss, T. Improving the accuracy of rainfall rates from optical satellite sensors with machine learning—A random forests-based approach applied to MSG SEVIRI. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 141, 129–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maidment, R.I.; Grimes, D.; Black, E.; Tarnavsky, E.; Young, M.; Greatrex, H.; Allan, R.P.; Stein, T.; Nkonde, E.; Senkunda, S.; et al. Data descriptor: A new, long-term daily satellite-based rainfall dataset for operational monitoring in Africa. Sci. Data 2017, 4, 170063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimani, M.W.; Hoedjes, J.C.B.; Su, Z.B. An assessment of satellite-derived rainfall products relative to ground observations over East Africa. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satge, F.; Xavier, A.; Zola, R.P.; Hussain, Y.; Timouk, F.; Garnier, J.; Bonnet, M.P. Comparative assessments of the latest GPM mission’s spatially enhanced satellite rainfall products over the main Bolivian watersheds. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, A.K.; Sheffield, J.; Pan, M.; Wood, E.F. Evaluation of the tropical rainfall measuring mission multi-satellite precipitation analysis (TMPA) for assessment of large-scale meteorological drought. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 159, 181–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrieling, A.; Sterk, G.; de Jong, S.M. Satellite-based estimation of rainfall erosivity for Africa. J. Hydrol. 2010, 395, 235–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.X.; Sha, W.M.; Iwasaki, T.; Ueno, K. Diurnal variation of rainfall in the Yangtze River Valley during the spring–summer transition from TRMM measurements. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2012, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, R.T.; Buarque, D.C. Statistically combining rainfall characteristics estimated from remote-sensed and rain gauge data sets in the Brazilian Amazon-Tocantins Basins. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 7467–7480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, M.F.; Thompson, S.E. Bias adjustment of satellite rainfall data through stochastic modeling: Methods development and application to Nepal. Adv. Water Resour. 2013, 60, 121–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Moreno, J.F.; Mannaerts, C.M.; Jetten, V. Applicability of satellite rainfall estimates for erosion studies in small offshore areas: A case study in Cape Verde Islands. Catena 2014, 121, 365–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrieling, A.; Hoedjes, J.C.B.; van der Velde, M. Towards large-scale monitoring of soil erosion in Africa: Accounting for the dynamics of rainfall erosivity. Global Planet. Chang. 2014, 115, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, H.F.; Rossel, R.A.V.; Shi, Z.; Behrens, T.; Chappell, A.; Bui, E. Assimilating satellite imagery and visible-near infrared spectroscopy to model and map soil loss by water erosion in Australia. Environ. Model. Softw. 2016, 77, 156–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Varma, A.K.; Mishra, A.; Gairola, R.M.; Das, I.M.L.; Sarkar, A.; Agarwal, V.K. Comparison of TRMM TMI and PR version 5 and 6 precipitation data products under cyclonic weather conditions. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2009, 6, 378–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Hong, Y.; Cao, Q.; Gourley, J.J.; Kirstetter, P.E.; Yong, B.; Tian, Y.D.; Zhang, Z.X.; Shen, Y.; Hu, J.J.; et al. Similarity and difference of the two successive V6 and V7 TRMM multisatellite precipitation analysis performance over China. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 13060–13074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, B.; Chen, B.; Gourley, J.J.; Ren, L.L.; Hong, Y.; Chen, X.; Wang, W.G.; Chen, S.; Gong, L.Y. Intercomparison of the Version-6 and Version-7 TMPA precipitation products over high and low latitudes basins with independent gauge networks: Is the newer version better in both real-time and post-real-time analysis for water resources and hydrologic extremes? J. Hydrol. 2014, 508, 77–87. [Google Scholar]
- De Goncalves, L.G.G.; Shuttleworth, W.J.; Nijssen, B.; Burke, E.J.; Marengo, J.A.; Chou, S.C.; Houser, P.; Toll, D.L. Evaluation of model-derived and remotely sensed precipitation products for continental South America. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2006, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, G.Q.; Long, D.; Hong, Y. Systematic anomalies over inland water bodies of High Mountain Asia in TRMM precipitation estimates: No longer a problem for the GPM era? IEEE Geosci. Remote. Sens. Lett. 2016, 13, 1762–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Shao, Q.X. An improved statistical approach to merge satellite rainfall estimates and raingauge data. J. Hydrol. 2010, 385, 51–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Zhao, P.; Pan, Y.; Yu, J.J. A high spatiotemporal gauge-satellite merged precipitation analysis over China. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2014, 119, 3063–3075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woldemeskel, F.M.; Sivakumar, B.; Sharma, A. Merging gauge and satellite rainfall with specification of associated uncertainty across Australia. J. Hydrol. 2013, 499, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chappell, A.; Renzullo, L.J.; Raupach, T.H.; Haylock, M. Evaluating geostatistical methods of blending satellite and gauge data to estimate near real-time daily rainfall for Australia. J. Hydrol. 2013, 493, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velasco-Forero, C.A.; Sempere-Torres, D.; Cassiraga, E.F.; Gomez-Hernandez, J.J. A non-parametric automatic blending methodology to estimate rainfall fields from rain gauge and radar data. Adv. Water Resour. 2009, 32, 986–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goovaerts, P. Using elevation to aid the geostatistical mapping of rainfall erosivity. Catena 1999, 34, 227–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, R.T.; Buarque, D.C.; de Paiva, R.C.D.; Collischonn, W. Issues of spatial correlation arising from the use of TRMM rainfall estimates in the Brazilian Amazon. Water Resour. Res. 2011, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Chen, X.W.; Fan, Q.X.; Jin, H.P.; Li, J.R. A new procedure to estimate the rainfall erosivity factor based on Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission (TRMM) data. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 2011, 54, 2437–2445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huffman, G.J.; Adler, R.F.; Bolvin, D.T.; Gu, G.J.; Nelkin, E.J.; Bowman, K.P.; Hong, Y.; Stocker, E.F.; Wolff, D.B. The TRMM multisatellite precipitation analysis (TMPA): Quasi-global, multiyear, combined-sensor precipitation estimates at fine scales. J. Hydrometeorol. 2007, 8, 38–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goovaerts, P. Geostatistics for Natural Resources Evaluation; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, B. Rainfall erosivity and its estimation for Australia’s tropics. Aust. J. Soil Res. 1998, 36, 143–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Yin, S.Q.; Liu, B.Y.; Nearing, M.A.; Zhao, Y. Models for estimating daily rainfall erosivity in China. J. Hydrol. 2016, 535, 547–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.B.; Xie, Y.; Liu, B.Y. Rainfall erosivity estimation using daily rainfall amounts. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 2002, 22, 705–711. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, W.Y.; Shao, Q.Q.; Liu, J.Y.; Zhai, J. Assessing the effects of land use and topography on soil erosion on the Loess Plateau in China. Catena 2014, 121, 151–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, W.; Guo, Q.K.; Zuo, C.Q.; Shan, Z.J.; Ma, L.; Sun, G. Spatial distribution and temporal trends of rainfall erosivity in mainland China for 1951–2010. Catena 2016, 147, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.B.; Fu, J.S. Rainfall erosivity estimation under different rainfall amount. Resour. Sci. 2003, 25, 35–41. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, Y.; Liu, B.Y.; Zhang, W.B. Study on standard of erosive rainfall. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2000, 14, 6–11. [Google Scholar]
- Shin, D.B.; Kim, J.H.; Park, H.J. Agreement between monthly precipitation estimates from TRMM satellite, NCEP reanalysis, and merged gauge-satellite analysis. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2011, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, A.M. Rainfall erosivity map for Brazil. Catena 2004, 57, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mello, C.R.; Viola, M.R.; Beskow, S.; Norton, L.D. Multivariate models for annual rainfall erosivity in Brazil. Geoderma 2013, 202–203, 88–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, P.T.S.; Wendland, E.; Nearing, M.A. Rainfall erosivity in Brazil: A review. Catena 2013, 100, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanal, S.; Anex, R.P.; Anderson, C.J.; Herzmann, D.E.; Jha, M.K. Implications of biofuel policy-driven land cover change for rainfall erosivity and soil erosion in the United States. GCB Bioenergy 2013, 5, 713–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schonbrodt-Stitt, S.; Bosch, A.; Behrens, T.; Hartmann, H.; Shi, X.Z.; Scholten, T. Approximation and spatial regionalization of rainfall erosivity based on sparse data in a mountainous catchment of the Yangtze River in Central China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 20, 6917–6933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, S.; Xie, Y.; Liu, B.; Nearing, M.A. Rainfall erosivity estimation based on rainfall data collected over a range of temporal resolutions. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2015, 19, 4113–4126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Yu, B. Validation of rainfall erosivity estimators for mainland China. Trans. ASABE 2015, 58, 61–71. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, J.R.; Chen, Y.; Yan, D.; Guo, F.F. Characteristics of rainfall erosivity based on tropical rainfall measuring mission data in Tibet, China. J. Mt. Sci. 2013, 10, 1008–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).