Auto-Scaling of Geo-Based Image Processing in an OpenStack Cloud Computing Environment
Abstract
:1. Introduction
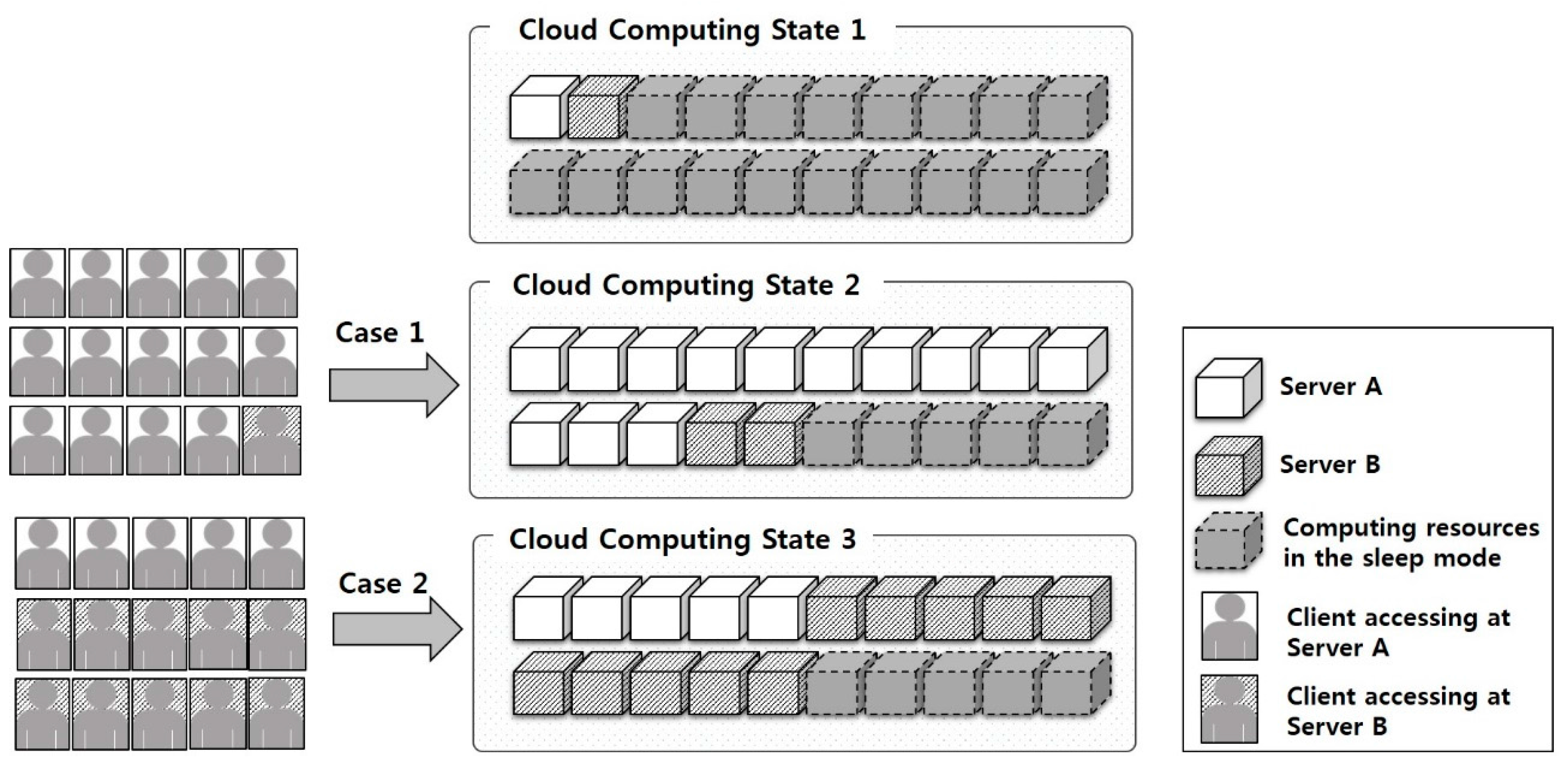
2. Auto-Scaling Concept
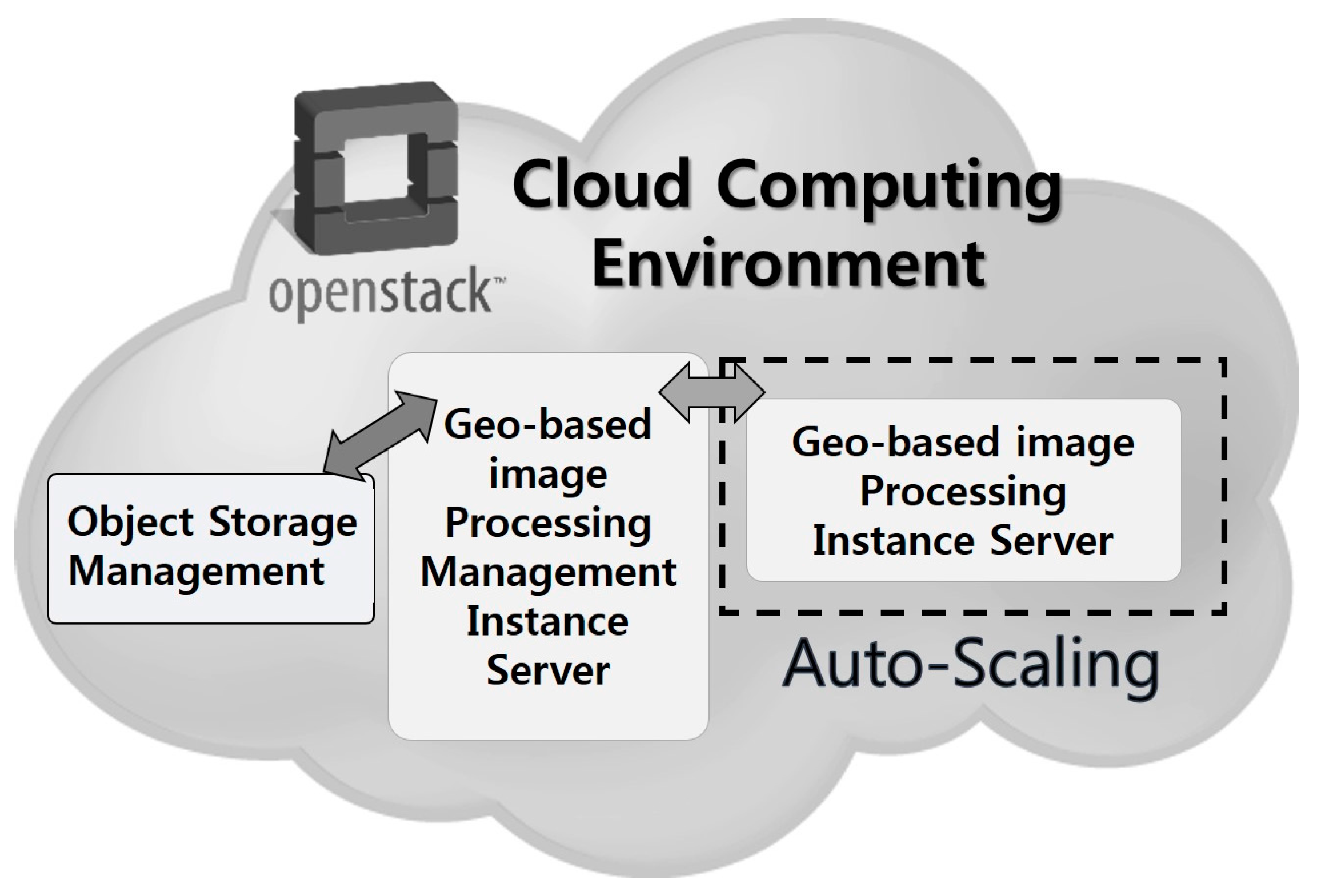
3. Auto-Scaling Application Model for Geo-Based Image Processing Services
3.1. Example Case for Auto-Scaling Application for Geo-Based Image Processing Service
3.2. Experimental Condition for Auto-Scaling
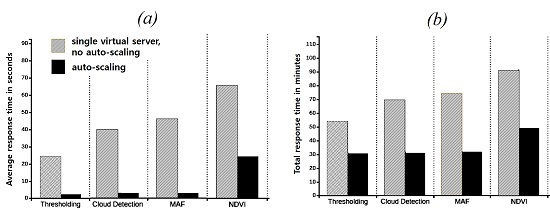
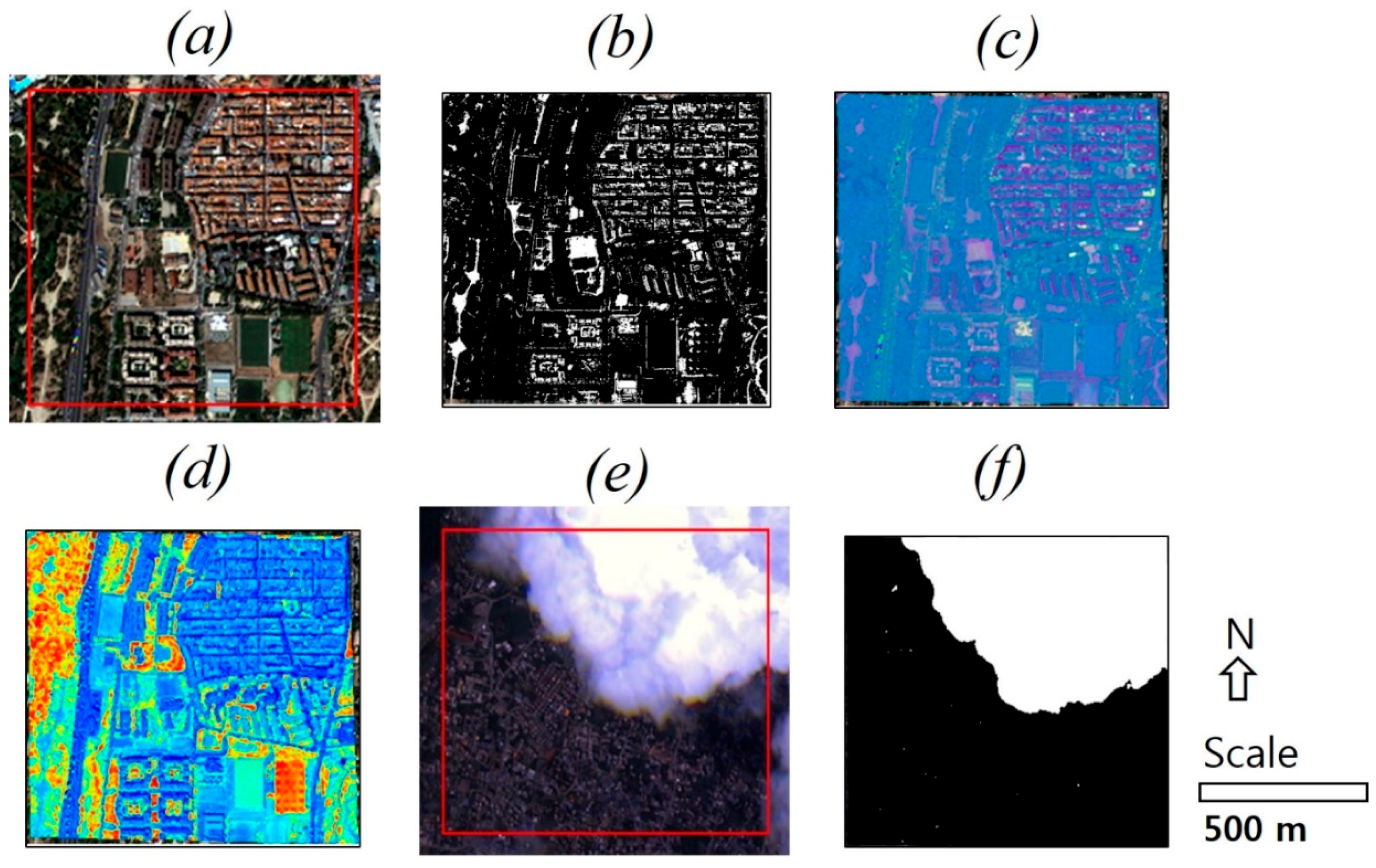
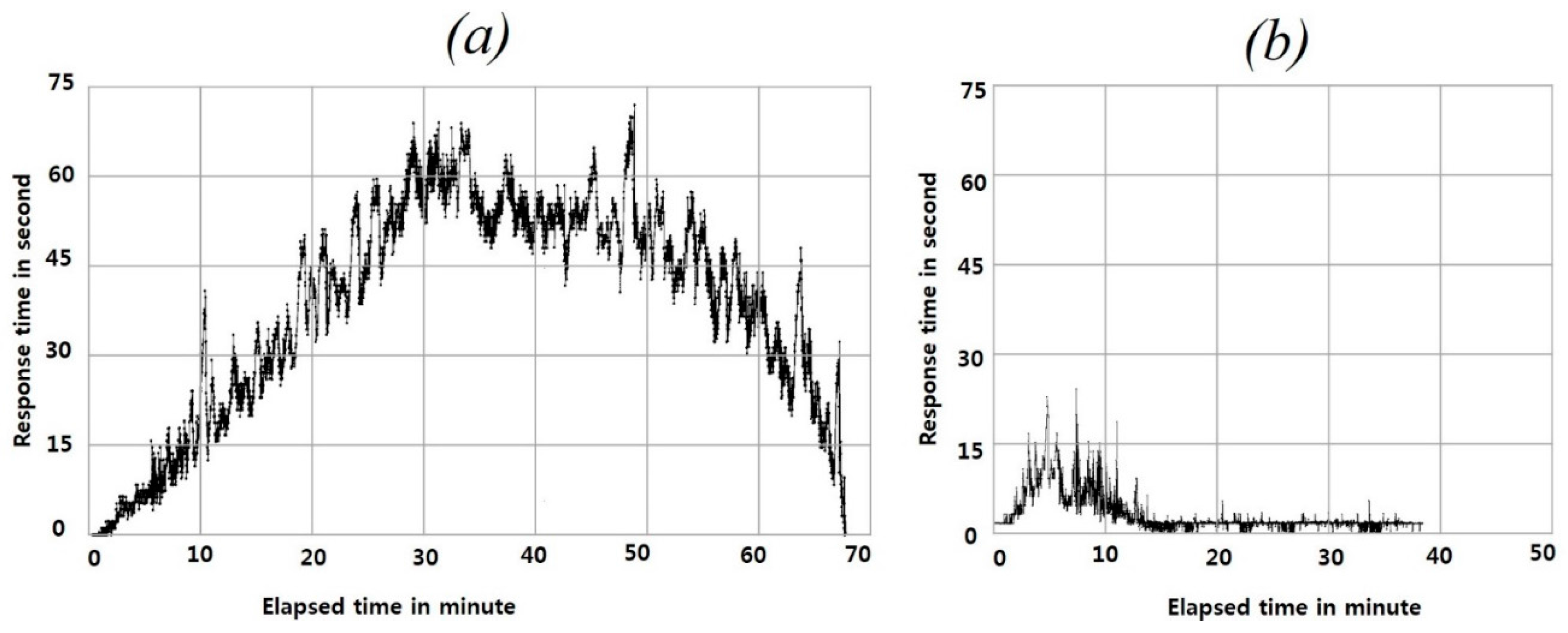
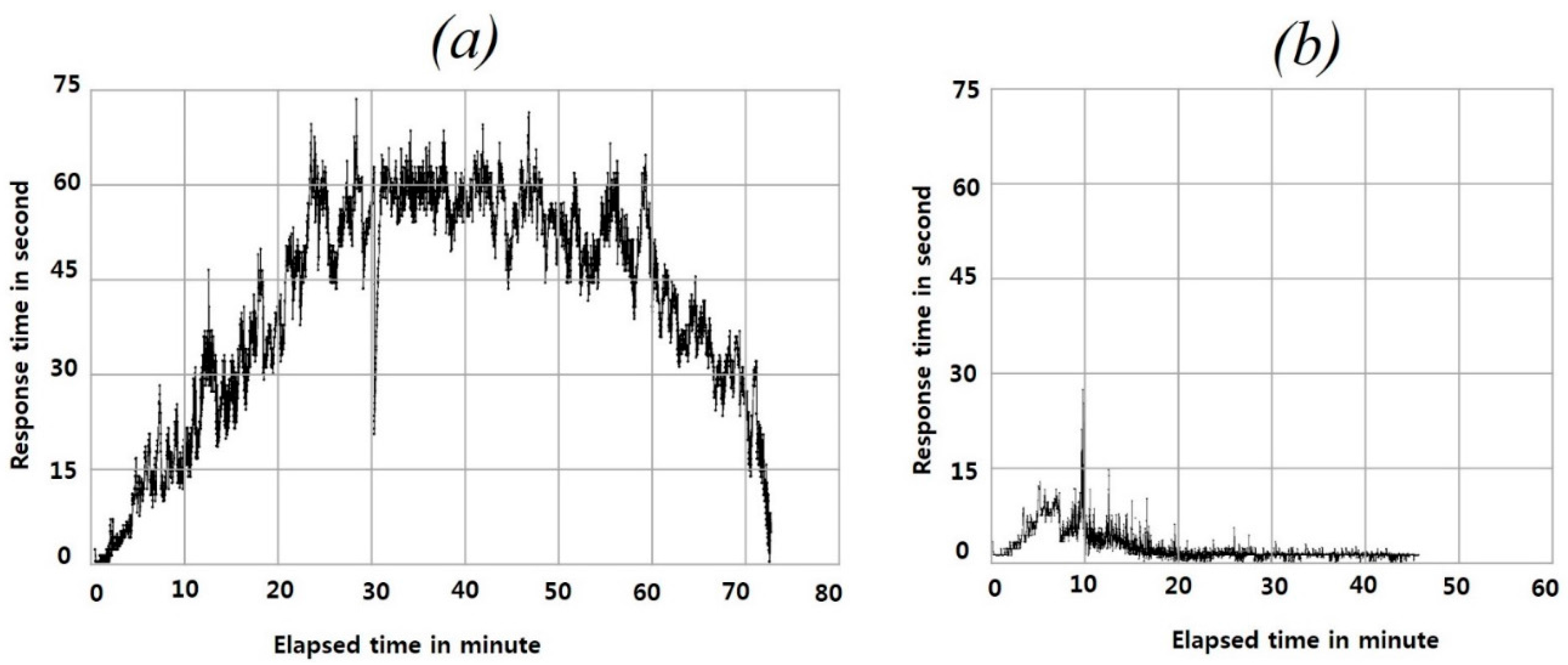
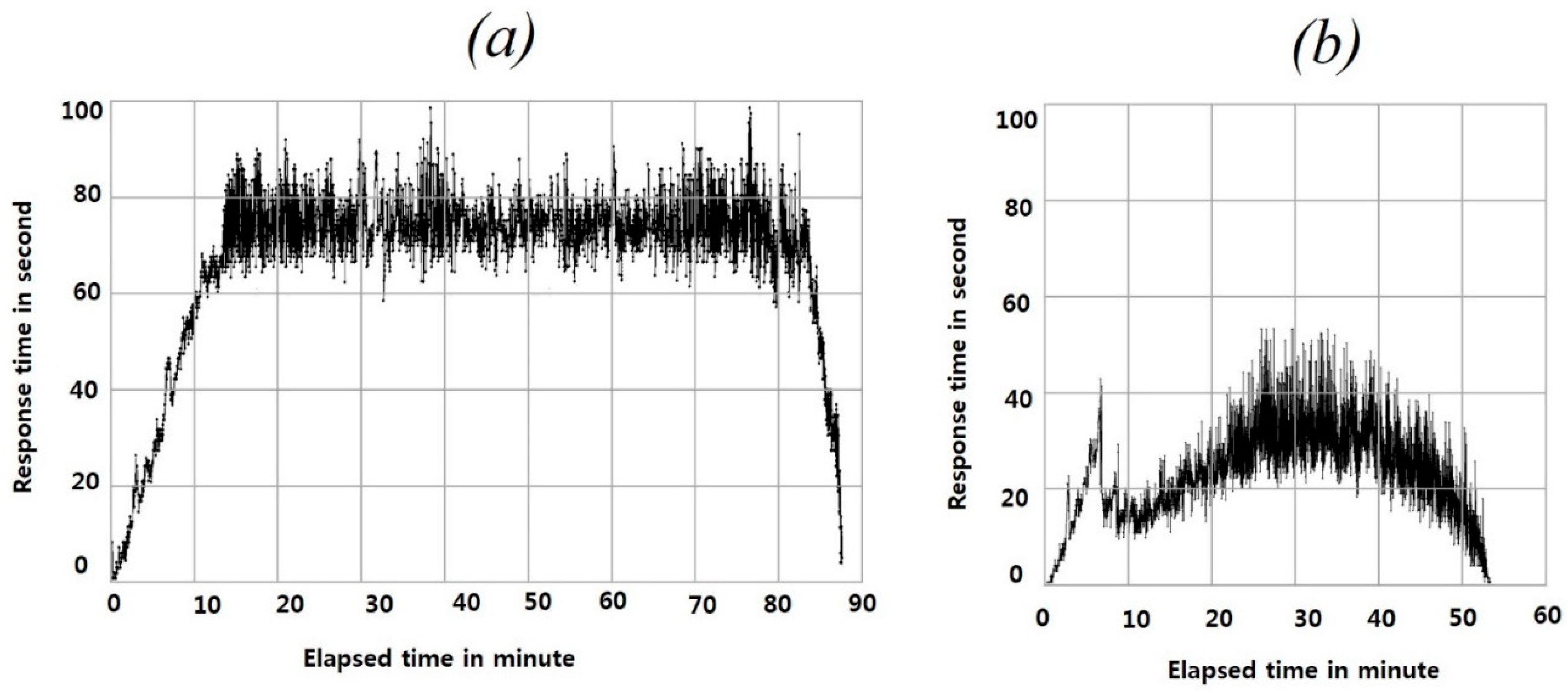
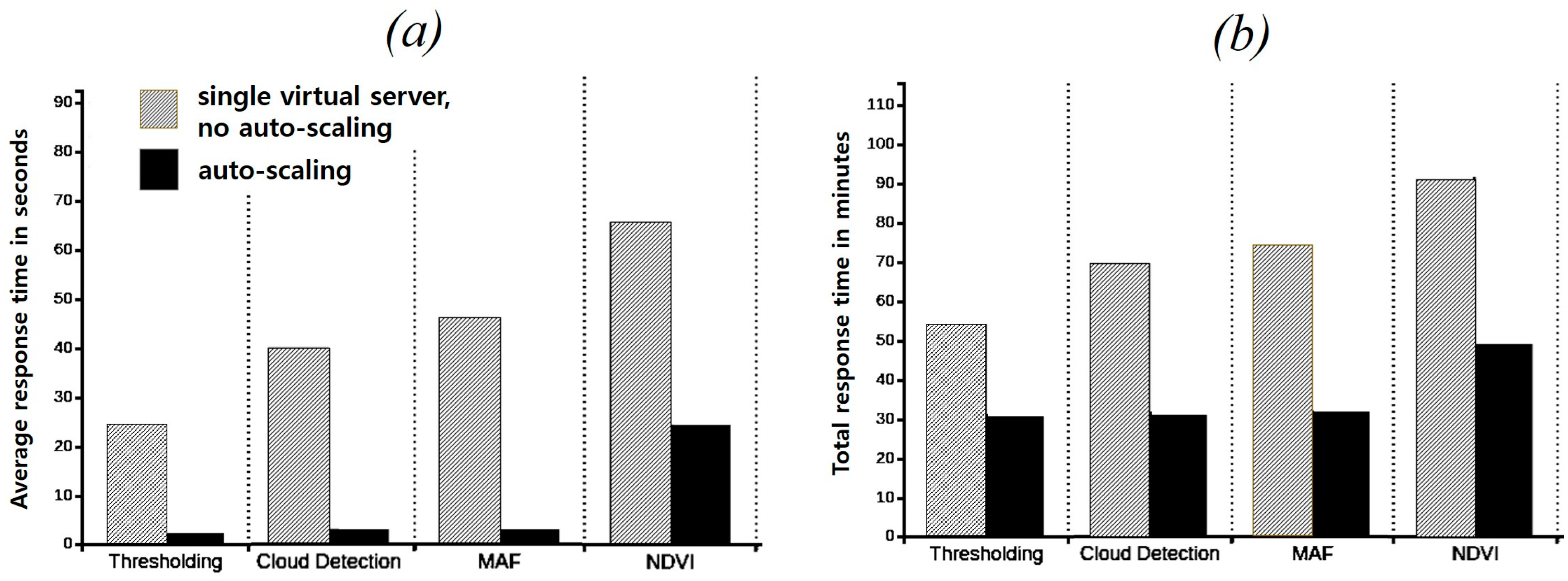
4. Experimental Results and Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mell, P.; Grance, T. The NIST Definition of Cloud Computing, NIST Special Publication 800-145. Available online: http://nvlpubs.nist.gov/nistpubs/Legacy/SP/nistspecialpublication800-145.pdf (accessed on 24 July 2016).
- Diaz, M.; Martin, C.; Rubio, B. State-of-the-art, Challenges, and Open Issues in the Integration of Internet of Things and Cloud Computing. J. Netw. Comput. Appl. 2016, 67, 99–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alipour, H.; Liu, Y.; Hamou-Ihadj, A. Analyzing Auto-Scaling Issues in Cloud Environments, 2014. Available online: https://users.encs.concordia.ca/~abdelw/sba/papers/CASCON14-Autoscaling.pdf (accessed on 20 November 2015).
- Lorido-Botran, T.; Miguel-Alonso, J.J.; Lozano, J.A. A Review of Auto-scaling Techniques for Elastic Applications in Cloud Environments. J. Grid Comput. 2014, 12, 559–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dougherty, B.; White, J.; Schmidt, D.C. Model-driven Auto-scaling of Green Cloud Computing Infrastructure. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2012, 28, 371–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreiger, M.T.; Torreno, O.; Trelles, O.; Kranzlmuller, D. Building an Open Source Cloud Environment with Auto-scaling Resources for Executing Bioinformatics and Biomedical Workflows. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, C.; Calheiros, R.N.; Buyya, R. A Reliable and Cost-efficient Auto-Scaling System for Web Applications using Heterogeneous Spot Instances. J. Netw. Comput. Appl. 2016, 65, 167–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auto Scaling Developer Guide. Available online: http://docs.aws.amazon.com/AutoScaling/latest/DeveloperGuide/as-dg.pdf (accessed on 20 January 2016).
- Evangelidis, K.; Ntouros, K.; Makridis, S.; Papatheodorou, C. Geospatial services in the Cloud. Comput. Geosci. 2014, 63, 116–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navulur, K. Demystifying Cloud Computing for Remote Sensing Applications. Available online: http://eijournal.com/wp-content/uploads/2013/06/cloudcomputing.pdf (accessed on 1 June 2016).
- Wang, P.; Wang, J.; Chen, Y.; Ni, G. Rapid Processing of Remote Sensing Images based on Cloud Computing. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2013, 29, 1963–1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, J.; Yang, C.; Liu, K.; Gui, Z.; Li, Z.; Huang, Q.; Li, R. Adopting Cloud Computing to Optimize Spatial Web Portals for Better Performance to Support Digital Earth and Other Global Geospatial Initiatives. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2015, 8, 451–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, A.A. OpenStack Orchestration; Packt Publication: Birmingham, UK; Mumbai, India, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Auto-Scaling in OpenStack. Available online: http://keithtenzer.com/2015/09/02/auto-scaling-instances-with-openstack/ (accessed on 17 October 2015).
- Singh, K. Learning Ceph; Packt Publication: Birmingham, UK; Mumbai, India, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Radez, D. OpenStack Essentials; Packt Publication: Birmingham, UK; Mumbai, India, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- The ORFEO Tool Box Software Guide, Updated for OTB-5.0. Available online: http://www.orfeo-toolbox.org (accessed on 7 June 2015).
- Kang, S.; Lee, K. Mobile App Approach by Open Source Stack for Satellite Images Utilization. Remote Sens. Lett. 2013, 4, 648–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.; Kang, S. Mobile Cloud Service of Geo-based Image Processing Functions: A Test iPad Implementation. Remote Sens. Lett. 2013, 4, 910–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Openstack. Available online: http://docs.openstack.org/admin-guide-cloud/telemetry-measurements.html (accessed on 15 November 2015).

| System Component | Specification and Version |
|---|---|
| Server operating system | Ubuntu server 64 bit/14.04 LTS |
| Cloud computing | OpenStack Juno/2014.2.3 |
| Database management system | MariaDB/5.5.44 |
| Storage | Ceph Hammer/0.94 |
| Storage access library | librados(python)/0.94.2 |
| Web server | Apache/2.4.7 |
| Web framework | Django/1.6.1 |
| Experimental Condition | |
|---|---|
| Number of users | 100 |
| Number of processing requests | 60 |
| Ramp-up duration | 30 min |
| Applied algorithms | Binary thresholding, NDVI, Cloud Detection, MAF |
| Spatial coverage | 1 km × 1 km |
| Applied Condition | |
|---|---|
| Measurement | Average CPU load check (name: cpu_util, type: gauge, unit: %) |
| Interval | 60 s |
| Scale-out conditions | cpu_util > 40% and 180 s |
| Scale-in conditions | cpu_util < 5% and 3600 s |
| Maximum number of instances | 5 |
| Minimum number of instances | 1 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kang, S.; Lee, K. Auto-Scaling of Geo-Based Image Processing in an OpenStack Cloud Computing Environment. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 662. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs8080662
Kang S, Lee K. Auto-Scaling of Geo-Based Image Processing in an OpenStack Cloud Computing Environment. Remote Sensing. 2016; 8(8):662. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs8080662
Chicago/Turabian StyleKang, Sanggoo, and Kiwon Lee. 2016. "Auto-Scaling of Geo-Based Image Processing in an OpenStack Cloud Computing Environment" Remote Sensing 8, no. 8: 662. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs8080662
APA StyleKang, S., & Lee, K. (2016). Auto-Scaling of Geo-Based Image Processing in an OpenStack Cloud Computing Environment. Remote Sensing, 8(8), 662. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs8080662