Formal Quantification of Spatially Differential Characteristics of PSI-Derived Vertical Surface Deformation Using Regular Triangle Network: A Case Study of Shixi in the Northwest Xuzhou Coalfield
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Quantification Framework
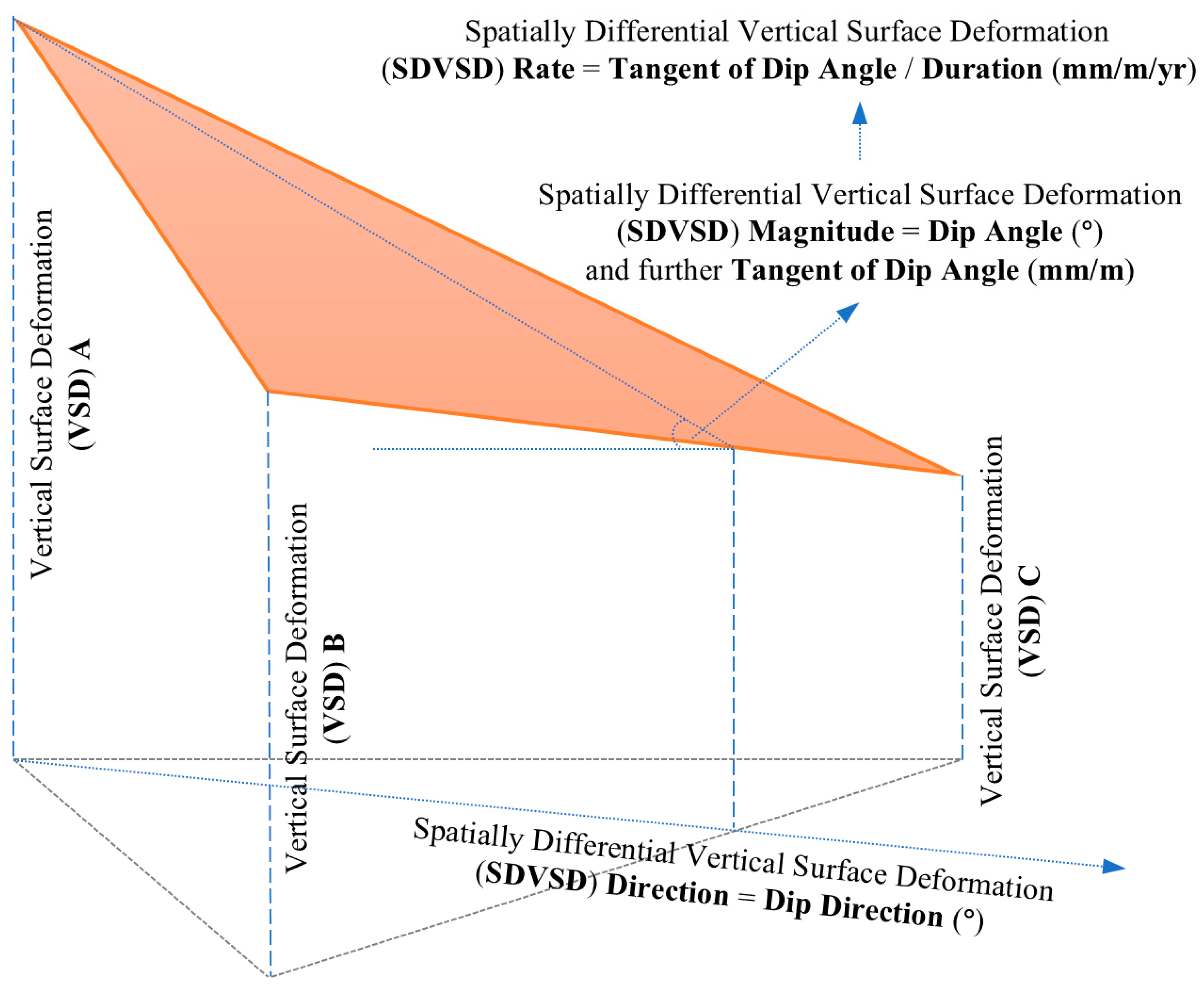
2.1. Principles of SDVSD Quantification
2.2. Construction of Regular Triangle Network
3. Study Area and Data
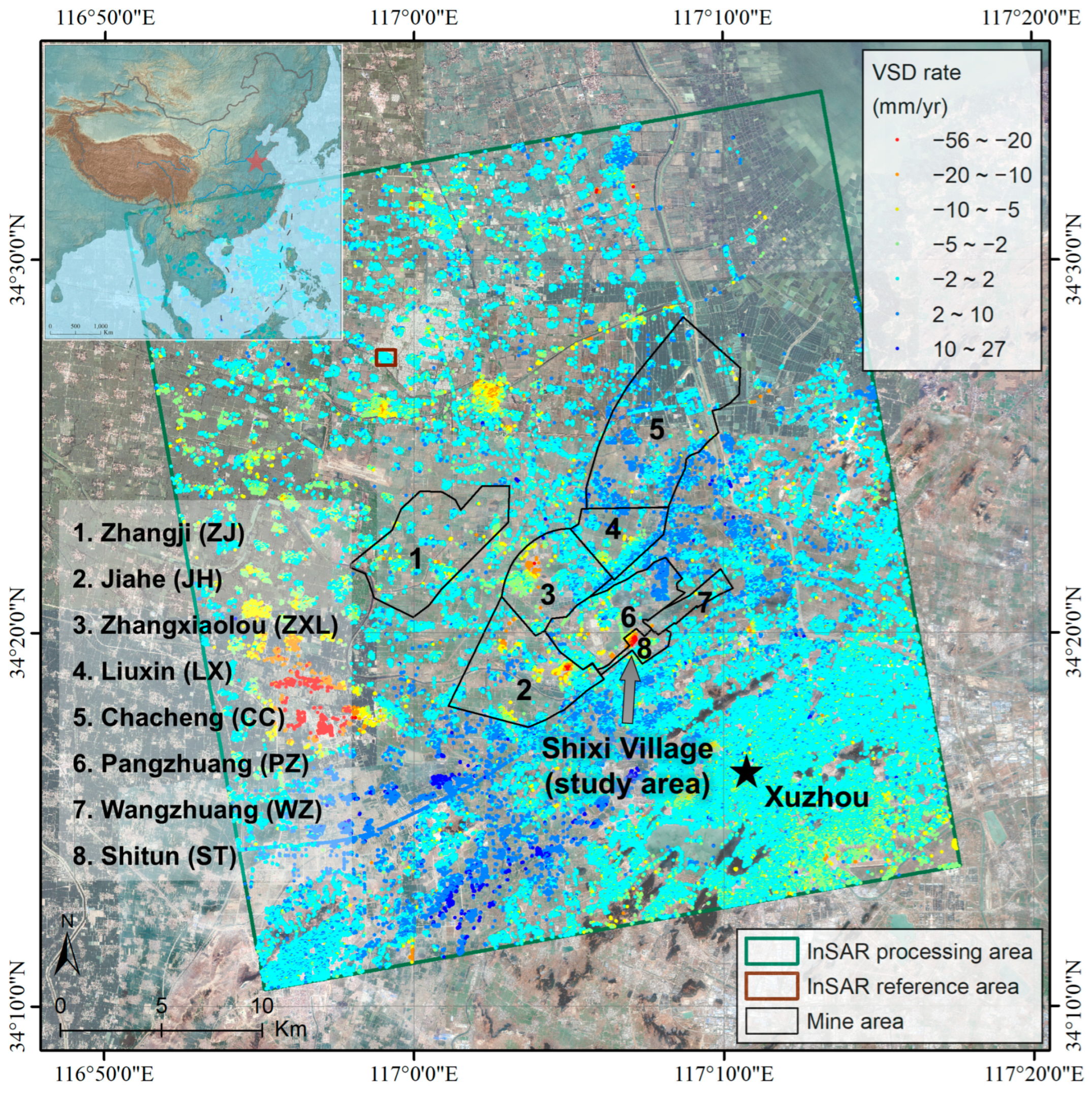
3.1. Study Area
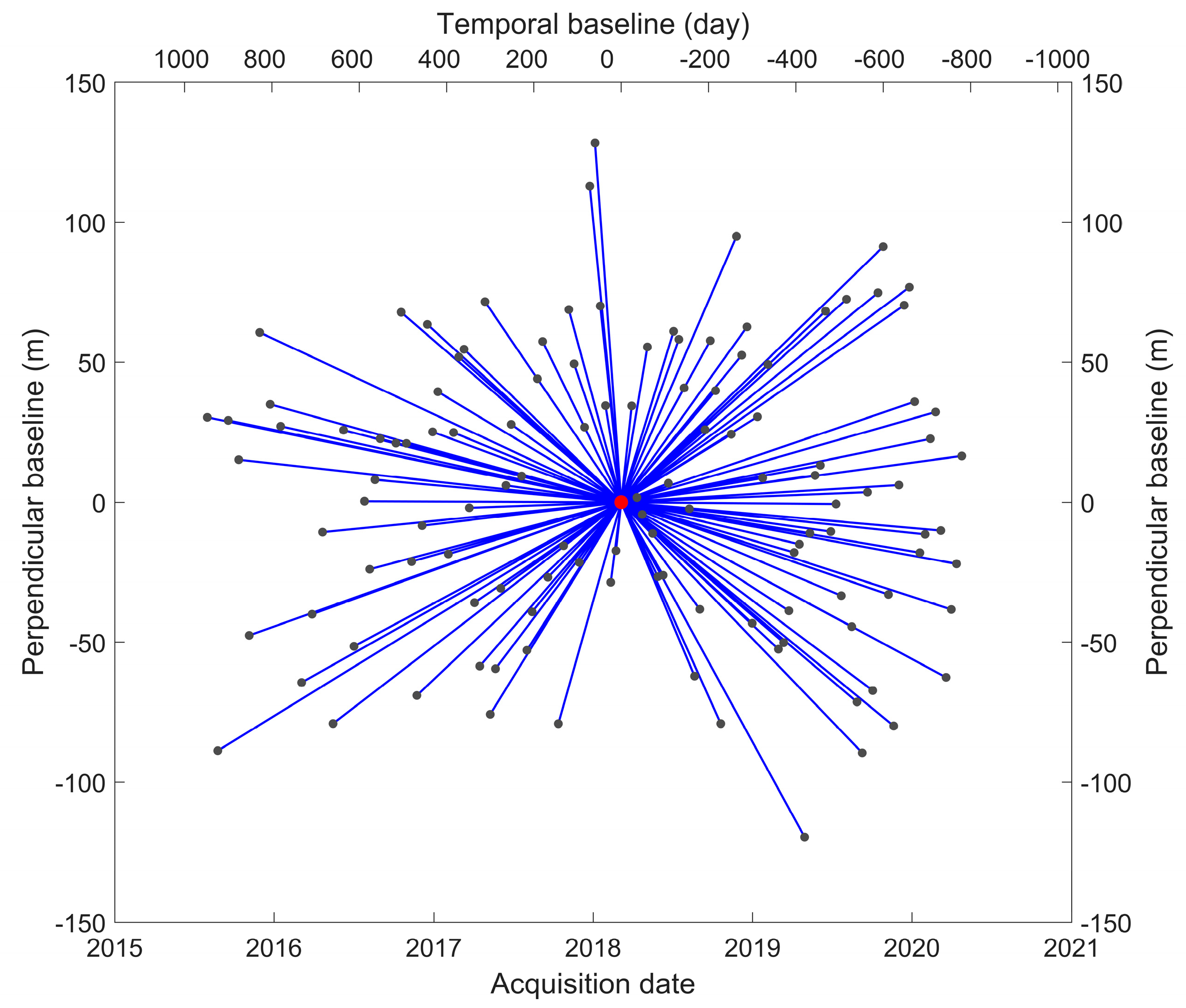
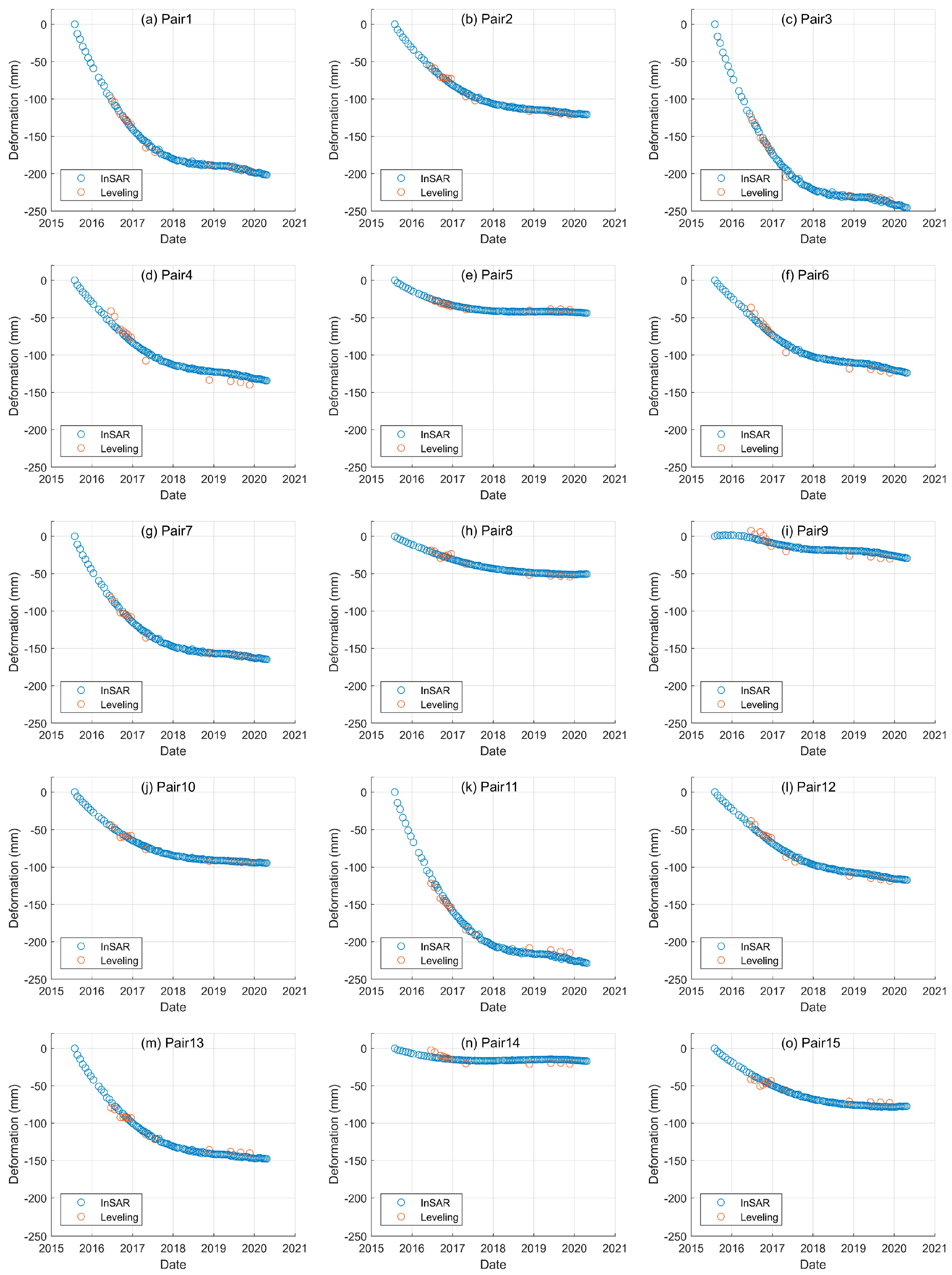
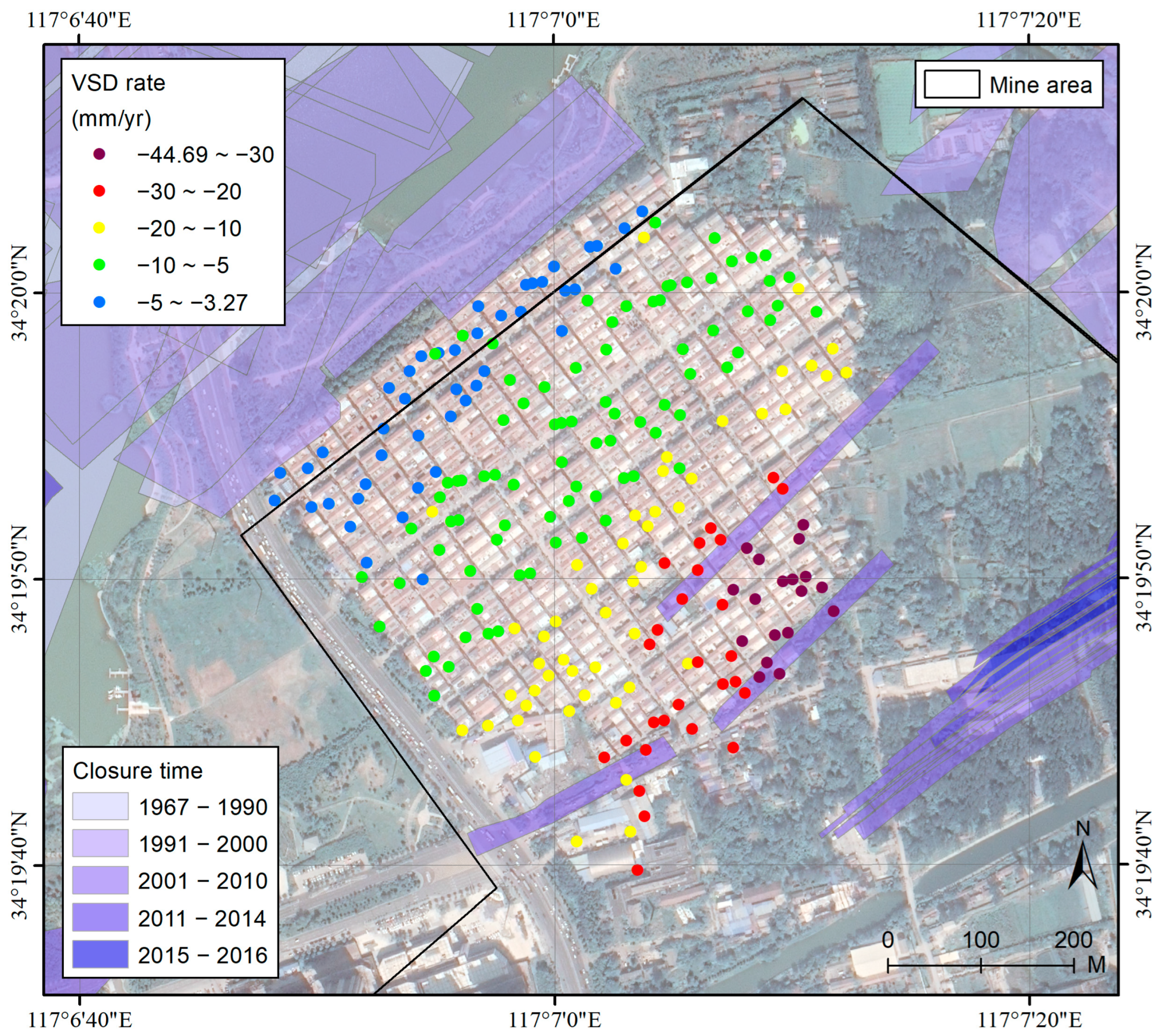
3.2. PSI-Derived VSD Data
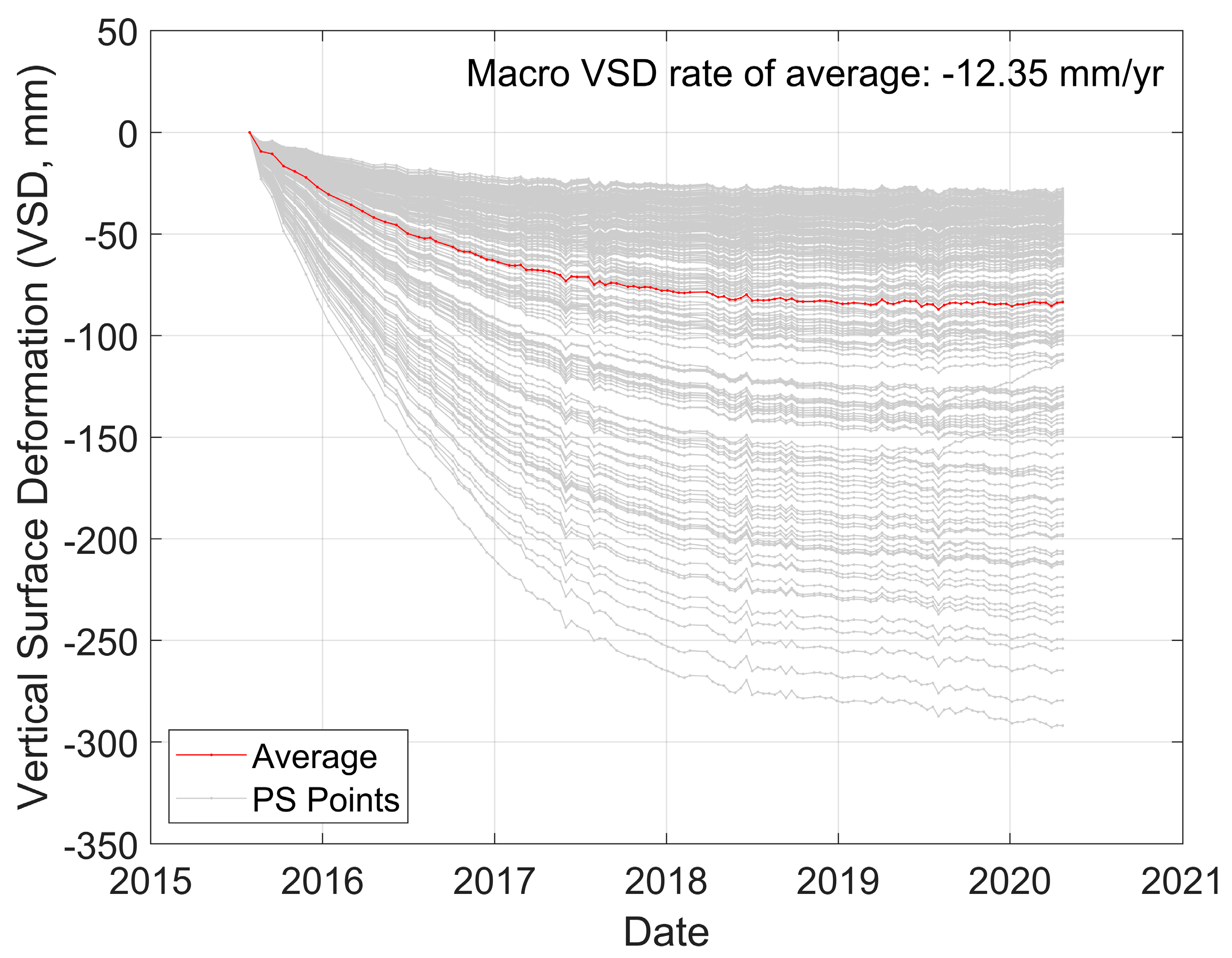
4. Results
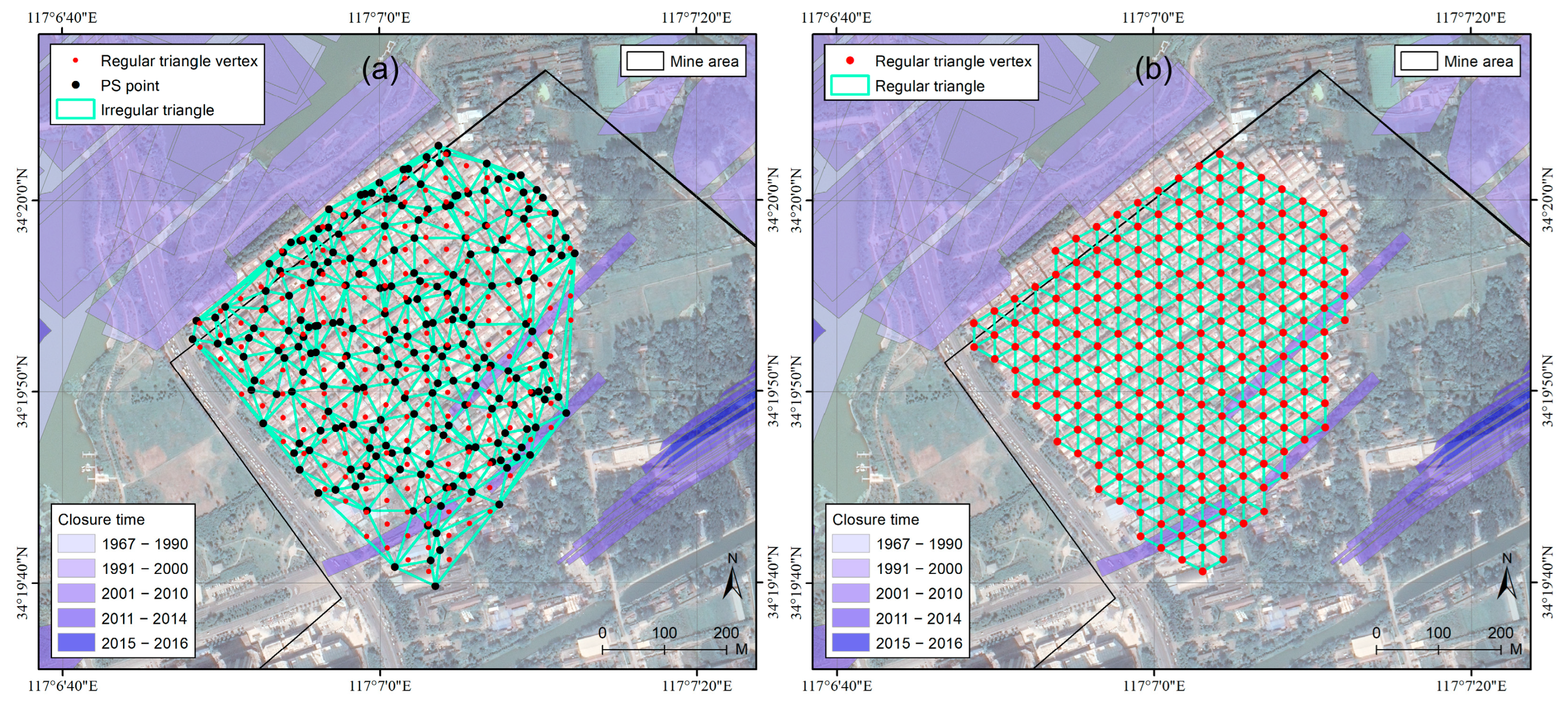
4.1. Regular Triangle Network
4.2. SDVSD Characteristics
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A

References
- Holzer, T.L.; Pampeyan, E.H. Earth fissures and localized differential subsidence. Water Resour. Res. 1981, 17, 223–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.; Miao, X.; Yang, S.; Liu, H.; Song, Y.; Liu, H.; Hu, X. Improved prediction of differential subsidence caused by underground mining. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2000, 37, 615–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, M.; Chen, B.; Gong, H.; Li, X.; Chen, W.; Gao, M.; Zhou, C.; Lei, K. Monitoring differential subsidence along the beijing–tianjin intercity railway with multiband SAR data. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 4453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Figueroa-Miranda, S.; Hernández-Madrigal, V.M.; Tuxpan-Vargas, J.; Villaseñor-Reyes, C.I. Evolution assessment of structurally-controlled differential subsidence using SBAS and PS interferometry in an emblematic case in Central Mexico. Eng. Geol. 2020, 279, 105860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Wit, K.; Lexmond, B.R.; Stouthamer, E.; Neussner, O.; Dörr, N.; Schenk, A.; Minderhoud, P.S. Identifying causes of urban differential subsidence in the Vietnamese Mekong Delta by combining InSAR and field observations. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Torres, E.A.; Cabral-Cano, E.; Salazar-Tlaczani, L.; Solano-Rojas, D. Economic risk of differential subsidence in Mexico City (2014–2022). Nat. Hazards 2024, 121, 2507–2534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rateb, A.; Abotalib, A.Z. Inferencing the land subsidence in the Nile Delta using Sentinel-1 satellites and GPS between 2015 and 2019. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 729, 138868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirzaei, M.; Freymueller, J.; Tornqvist, T.E.; Galloway, D.L.; Dura, T.; Minderhoud, P.S.J. Measuring, modelling and projecting coastal land subsidence. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2021, 2, 40–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cigna, F.; Tapete, D. Urban growth and land subsidence: Multi-decadal investigation using human settlement data and satellite InSAR in Morelia, Mexico. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 811, 152211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, K.; Kumar, D.; Perissin, D.; Pradhan, B. Estimation of ground subsidence of New Delhi, India using PS-InSAR technique and Multi-sensor Radar data. Adv. Space Res. 2022, 69, 1863–1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perissin, D.; Wang, Z.; Lin, H. Shanghai subway tunnels and highways monitoring through Cosmo-SkyMed Persistent Scatterers. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2012, 73, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueroa-Miranda, S.; Tuxpan-Vargas, J.; Ramos-Leal, J.A.; Hernández-Madrigal, V.M.; Villaseñor-Reyes, C.I. Land subsidence by groundwater over-exploitation from aquifers in tectonic valleys of Central Mexico: A review. Eng. Geol. 2018, 246, 91–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, C.P.; Arrowsmith, J.R.; Nissen, E.; Lajoie, L.; Maruyama, T.; Chiba, T. The M7 2016 Kumamoto, Japan, Earthquake: 3-D Deformation Along the Fault and Within the Damage Zone Constrained from Differential Lidar Topography. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2018, 123, 6138–6155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlögl, M.; Widhalm, B.; Avian, M. Comprehensive time-series analysis of bridge deformation using differential satellite radar interferometry based on Sentinel-1. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2021, 172, 132–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawluszek-Filipiak, K.; Borkowski, A. Integration of DInSAR and SBAS Techniques to Determine Mining-Related Deformations Using Sentinel-1 Data: The Case Study of Rydułtowy Mine in Poland. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, T.; Han, K.; Yao, X.; Chen, X.; Wu, Z.; Yao, C.; Tian, X.; Zhou, Z.; Ren, K. Identification of Ground Fissure Development in a Semi-Desert Aeolian Sand Area Induced from Coal Mining: Utilizing UAV Images and Deep Learning Techniques. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellazzi, P.; Garfias, J.; Martel, R. Assessing the efficiency of mitigation measures to reduce groundwater depletion and related land subsidence in Querétaro (Central Mexico) from decadal InSAR observations. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2021, 105, 102632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, L.; Zhao, Z.; Zhou, D.; Cao, J.; Qin, J.; Cao, Y.; He, Y. Study on the Relationship between Groundwater and Land Subsidence in Bangladesh Combining GRACE and InSAR. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 3715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, T.J.; Parsons, B.E.; Lu, Z. Toward mapping surface deformation in three dimensions using InSAR. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2004, 31, L01607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perissin, D.; Wang, T. Time-Series InSAR Applications Over Urban Areas in China. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2011, 4, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.W.; Lu, Z.; Jung, H.S. Simulation of time-series surface deformation to validate a multi-interferogram InSAR processing technique. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2012, 33, 7075–7087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, M.S.; Tang, J.; Wang, T.; Balz, T.; Zhang, L. Landslide monitoring with high-resolution SAR data in the Three Gorges region. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2012, 55, 590–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Li, Z.W.; Ding, X.L.; Zhu, J.J.; Zhang, L.; Sun, Q. Resolving three-dimensional surface displacements from InSAR measurements: A review. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2014, 133, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Y.; Lan, H.; Li, L.; Wu, Y.; Li, Q. Characteristics of surface deformation detected by X-band SAR interferometry over sichuan-tibet grid connection project area, China. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 12265–12281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Guo, H.; Ma, P.; Lin, H.; Wang, C.; Ishwaran, N.; Hang, P. Radar interferometry offers new insights into threats to the Angkor site. Sci. Adv. 2017, 3, e1601284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Li, Z.; Zhu, J.; Yi, H.; Hu, J.; Feng, G. Deriving Dynamic Subsidence of Coal Mining Areas Using InSAR and Logistic Model. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, K.; Liu, G.; Li, Z.; Ma, D.; Wang, X.; Zhang, B.; Tang, J.; Li, G. Monitoring highway stability in permafrost regions with X-band temporary scatterers stacking InSAR. Sensors 2018, 18, 1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Liu, C.; Zhang, Q.; Lu, Z.; Yang, C. Deformation of Linfen-Yuncheng Basin (China) and its mechanisms revealed by Π-RATE InSAR technique. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 218, 221–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Yao, X.; Yao, J.; Zhou, Z.; Feng, X.; Liu, X. Analysis of deformation characteristics for a reservoir landslide before and after impoundment by multiple D-InSAR observations at Jinshajiang River, China. Nat. Hazards 2019, 98, 719–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Zhao, C.; Zhang, Q.; Peng, M. Sequential InSAR time series deformation monitoring of land subsidence and rebound in Xi’an, China. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, H.; Wang, C.; Tang, Y.; Zhang, B.; Wu, F.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Z. Time-series InSAR monitoring of permafrost freeze-thaw seasonal displacement over Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau using sentinel-1 data. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Jin, M.; Jing, Y.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Sun, W.; Wei, J.; Chen, Y. Monitoring land subsidence in wuhan city (China) using the SBAS-INSAR method with radarsat-2 imagery data. Sensors 2019, 19, 743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Zou, J.; Lu, Z.; Qu, F.; Kang, Y.; Li, J. Ground Deformation of Wuhan, China, Revealed by Multi-Temporal InSAR Analysis. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Lan, H.; Li, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, C. A Multiple-Regression Model Considering Deformation Information for Atmospheric Phase Screen Compensation in Ground-Based SAR. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 58, 777–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Gong, H.; Chen, B.; Gao, M.; Cao, Q.; Cao, J.; Duan, L.; Zuo, J.; Shi, M. Land subsidence response to dierent land use types and water resource utilization in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei, China. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Lan, H.; Gong, H.; Zhang, Y.; Warner, T.A.; Clague, J.J.; Wu, Y. Reduced rate of land subsidence since 2016 in Beijing, China: Evidence from Tomo-PSInSAR using RadarSAT-2 and Sentinel-1 datasets. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2020, 41, 1259–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, J.; Xing, K.; Wang, L.; Guo, H.; Wang, D.; Peng, Y.; Xiang, X.; Ciren, D.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, L.; et al. Air-Space-Ground Synergistic Observations for Rapid Post-Seismic Disaster Assessment of 2025 Ms6.8 Xigazê Earthquake, Xizang. J. Earth Sci. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferretti, A.; Prati, C.; Rocca, F. Permanent scatterers in SAR interferometry. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2001, 39, 8–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilley, G.E.; Bürgmann, R.; Ferretti, A.; Novali, F.; Rocca, F. Dynamics of slow-moving landslides from permanent scatterer analysis. Science 2004, 304, 1952–1955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooper, A.; Segall, P.; Zebker, H. Persistent scatterer interferometric synthetic aperture radar for crustal deformation analysis, with application to Volcán Alcedo, Galápagos. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2007, 112, B07407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, J.J.; Hooper, A.J.; Hanssen, R.F.; Bastos, L.C.; Ruiz, A.M. Persistent Scatterer InSAR: A comparison of methodologies based on a model of temporal deformation vs. spatial correlation selection criteria. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 2652–2663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, H.; Li, L.; Liu, H.; Yang, Z. Complex urban infrastructure deformation monitoring using high resolution PSI. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2012, 5, 643–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, H.; Gao, X.; Liu, H.; Yang, Z.; Li, L. Integration of TerraSAR-X and PALSAR PSI for detecting ground deformation. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2013, 34, 5393–5408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crosetto, M.; Monserrat, O.; Cuevas-González, M.; Devanthéry, N.; Crippa, B. Persistent Scatterer Interferometry: A review. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2016, 115, 78–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, D.; Zhang, L.; Li, M.; Liu, B.; Wang, Y. Beijing subway tunnelings and high-speed railway subsidence monitoring with PSInSAR and TerraSAR-X data. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Beijing, China, 10–15 July 2016; pp. 6883–6886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Peng, J.; Wang, B.; Song, Y.; Zhang, D.; Li, L. Ground deformation monitoring of Zhengzhou city from 2012 to 2013 using an improved IPTA. Nat. Hazards 2016, 80, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Wu, Q.; Zhang, B.; Tang, Y. Seasonal deformation features on Qinghai-Tibet railway observed using time-series InSAR technique with high-resolution TerraSAR-X images. Remote Sens. Lett. 2017, 8, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiaschi, S.; Holohan, E.P.; Sheehy, M.; Floris, M. PS-InSAR analysis of Sentinel-1 data for detecting ground motion in temperate oceanic climate zones: A case study in the Republic of Ireland. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wang, Y.; Yan, S.; Shao, Y.; Zhou, H.; Li, Y. Ground subsidence characteristics associated with urbanization in East China analyzed with a Sentinel-1A-based InSAR time series approach. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2019, 78, 4003–4015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, F.; Lv, X.; Dou, F.; Yun, Y. A Review of Time-Series Interferometric SAR Techniques: A Tutorial for Surface Deformation Analysis. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Mag. 2020, 8, 22–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Dou, J.; Merghadi, A.; Liang, W.; Dong, A.; Xiong, D.; Zhang, L. Advanced Prediction of Landslide Deformation through Temporal Fusion Transformer and Multivariate Time Series Clustering of InSAR: Insights from the Badui Region, Eastern Tibet. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2024, 62, 4514219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Wang, R.; Li, M.; Liao, M. A PSI targets characterization approach to interpreting surface displacement signals: A case study of the Shanghai metro tunnels. Remote Sens. Environ. 2022, 280, 113150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Chen, J. Accurate persistent scatterer identification based on phase similarity of radar pixels. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 5118513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Kang, Y.; Wei, J.; Lu, Z.; Yan, W.; Wang, H.; Liu, Z.; Lv, X.; Zhou, M. SAR interferometry on full scatterers: Mapping ground deformation with ultra-high density from space. Remote Sens. Environ. 2024, 302, 113965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Zhao, Z. Optimal algorithm for distributed scatterer InSAR phase estimation based on cross-correlation complex coherence matrix. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2024, 134, 104214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mora, O.; Lanari, R.; Mallorqui, J.J.; Berardino, P.; Sansosti, E. A new algorithm for monitoring localized deformation phenomena based on small baseline differential SAR interferogram. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Toronto, ON, Canada, 24–28 June 2002; pp. 1237–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhang, G.; Chen, Z.; Cui, H.; Zheng, Y.; Xu, Z.; Li, Q. Surface deformation extraction from small baseline subset synthetic aperture radar interferometry (SBAS-InSAR) using coherence-optimized baseline combinations. GISci. Remote Sens. 2022, 59, 295–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, M.; Zhao, C.; Liu, X.; Wang, B. Sequential SBAS-InSAR Backward Estimation of Deformation Time Series. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2024, 21, 4001505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azadnejad, S.; Esmaeili, M.; Maghsoudi, Y.; Donohue, S.; Azar, M.K. Extending polarimetric optimization of multi-temporal InSAR techniques on dual polarized Sentinel-1 data. Adv. Space Res. 2023, 72, 349–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giorgini, E.; Orellana, F.; Arratia, C.; Tavasci, L.; Montalva, G.; Moreno, M.; Gandolfi, S. InSAR Monitoring Using Persistent Scatterer Interferometry (PSI) and Small Baseline Subset (SBAS) Techniques for Ground Deformation Measurement in Metropolitan Area of Concepción, Chile. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 5700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado Blasco, J.M.; Foumelis, M.; Stewart, C.; Hooper, A. Measuring Urban Subsidence in the Rome Metropolitan Area (Italy) with Sentinel-1 SNAP-StaMPS Persistent Scatterer Interferometry. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sang, H.; Shi, B.; Zhang, D.; Liu, S.; Lu, Y. Monitoring land subsidence with the combination of persistent scatterer interferometry techniques and distributed fiber optic sensing techniques: A case study in Suzhou, China. Nat. Hazards 2023, 116, 2135–2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alizadeh, N.; Maghsoudi, Y.; Managhebi, T.; Azadnejad, S. Collapse Hotspot Detection in Urban Area Using Sentinel-1 and TerraSAR-X Dataset with SBAS and PSI Techniques. Land 2024, 13, 2237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Refice, A.; Spalluto, L.; Bovenga, F.; Fiore, A.; Miccoli, M.N.; Muzzicato, P.; Nitti, D.O.; Nutricato, R.; Pasquariello, G. Integration of persistent scatterer interferometry and ground data for landslide monitoring: The Pianello landslide (Bovino, Southern Italy). Landslides 2019, 16, 447–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eker, R.; Aydın, A.; Görüm, T. Tracking deformation velocity via PSI and SBAS as a sign of landslide failure: An open-pit mine-induced landslide in Himmetoğlu (Bolu, NW Turkey). Nat. Hazards 2024, 120, 7701–7724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Dai, H.; Yan, Y.; Liu, J.; Ren, J. Combination of InSAR with a Depression Angle Model for 3D Deformation Monitoring in Mining Areas. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Kou, P.; Dong, X.; Xia, Y.; Gu, Q.; Tao, Y.; Feng, J.; Ji, Q.; Wang, W.; Avtar, R. Reservoir water level decline accelerates ground subsidence: InSAR monitoring and machine learning prediction of surface deformation in the Three Gorges Reservoir area. Front. Earth Sci. 2025, 12, 1503634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witkowski, W.T.; Łukosz, M.A.; Guzy, A.; Hejmanowski, R. Estimation of mining-induced horizontal strain tensor of land surface applying insar. Minerals 2021, 11, 788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, P.; Liu, Y.; Wang, W.; Lin, H. Optimization of PSInSAR networks with application to TomoSAR for full detection of single and double persistent scatterers. Remote Sens. Lett. 2019, 10, 717–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalaitzis, P.; Foumelis, M.; Mouratidis, A.; Kavroudakis, D.; Soulakellis, N. Multiscale Visualization of Surface Motion Point Measurements Associated with Persistent Scatterer Interferometry. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2024, 13, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhao, C.; Huang, J.; Huan, C.; Wu, H.; Xu, P.; Yuan, L.; Chen, Y. Complex surface deformation of the coalfield in the northwest suburbs of Xuzhou from 2015 to 2020 revealed by time series InSAR. Can. J. Remote Sens. 2021, 47, 697–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, J.; Liu, F.; Bi, R.; Zhu, H.; Lv, C.; Yu, J. Effect of underground coal mining on the regional soil organic carbon pool in farmland in a mining subsidence area. Sustainability 2019, 11, 4961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, A.H.M.; Ge, L.; Zhang, K.; Chang, H.; Li, X.; Rizos, C.; Omura, M. Deformation mapping in three dimensions for underground mining using InSAR—Southern highland coalfield in New South Wales, Australia. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2011, 32, 7227–7256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samsonov, S.; D’Oreye, N.; Smets, B. Ground deformation associated with post-mining activity at the French-German border revealed by novel InSAR time series method. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2013, 23, 142–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diao, X.; Wu, K.; Chen, R.; Yang, J. Identifying the Cause of Abnormal Building Damage in Mining Subsidence Areas Using InSAR Technology. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 172296–172304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Xia, H.; Hu, J. Surface deformation monitoring in coal mine area based on psi. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 29672–29678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, M.; Deng, K.; Fan, H.; Du, S. Monitoring and analysis of surface deformation in mining area based on InSAR and GRACE. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Deng, K.; Fan, H.; Zhou, F. Monitoring of large-scale deformation in mining areas using sub-band InSAR and the probability integral fusion method. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2019, 40, 2602–2622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Zhu, L.; Wang, W.; Guo, L.; Chen, B. Land subsidence related to coal mining in China revealed by L-band InSAR analysis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Tian, Z.; Wang, B.; Li, W.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, Z. Monitoring and Assessment of SBAS-InSAR Deformation for Sustainable Development of Closed Mining Areas—A Case of Nanzhuang Mining Area. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 22935–22947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, M.; Zhang, H.; Deng, K.; Du, S.; Wang, L. Analysis of pre- and post-mine closure surface deformations in western Xuzhou coalfield from 2006 to 2018. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 124158–124172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Tan, K.; Yan, S.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, H.; Liu, X.; Li, H.; Sun, Y. Monitoring land surface displacement over Xuzhou (China) in 2015–2018 through PCA-based correction Applied to SAR interferometry. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, M.; Deng, K.; Fan, H.; Zhang, H.; Qin, X. Retrieving surface secondary subsidence in closed mines with time-series SAR interferometry combining persistent and distributed scatterers. Environ. Earth Sci. 2023, 82, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooper, A.; Zebker, H.; Segall, P.; Kampes, B. A new method for measuring deformation on volcanoes and other natural terrains using InSAR persistent scatterers. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2004, 31, L23611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooper, A.; Bekaert, D.; Hussain, E.; Spaans, K. StaMPS/MTI Manual Version 4.1b. 2018. Available online: https://homepages.see.leeds.ac.uk/~earahoo/stamps/ (accessed on 24 July 2019).
- Zhao, F.; Wang, Y.; Yan, S.; Lin, L. Reconstructing the Vertical Component of Ground Deformation from Ascending ALOS and Descending ENVISAT Datasets—A Case Study in the Cangzhou Area of China. Can. J. Remote Sens. 2016, 42, 147–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kositsky, A.P.; Avouac, J.-P. Inverting geodetic time series with a principal component analysis-based inversion method. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2010, 115, B03401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remy, D.; Froger, J.L.; Perfettini, H.; Bonvalot, S.; Gabalda, G.; Albino, F.; Cayol, V.; Legrand, D.; De Saint Blanquat, M. Persistent uplift of the Lazufre volcanic complex (Central Andes): New insights from PCAIM inversion of InSAR time series and GPS data. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 2014, 15, 3591–3611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
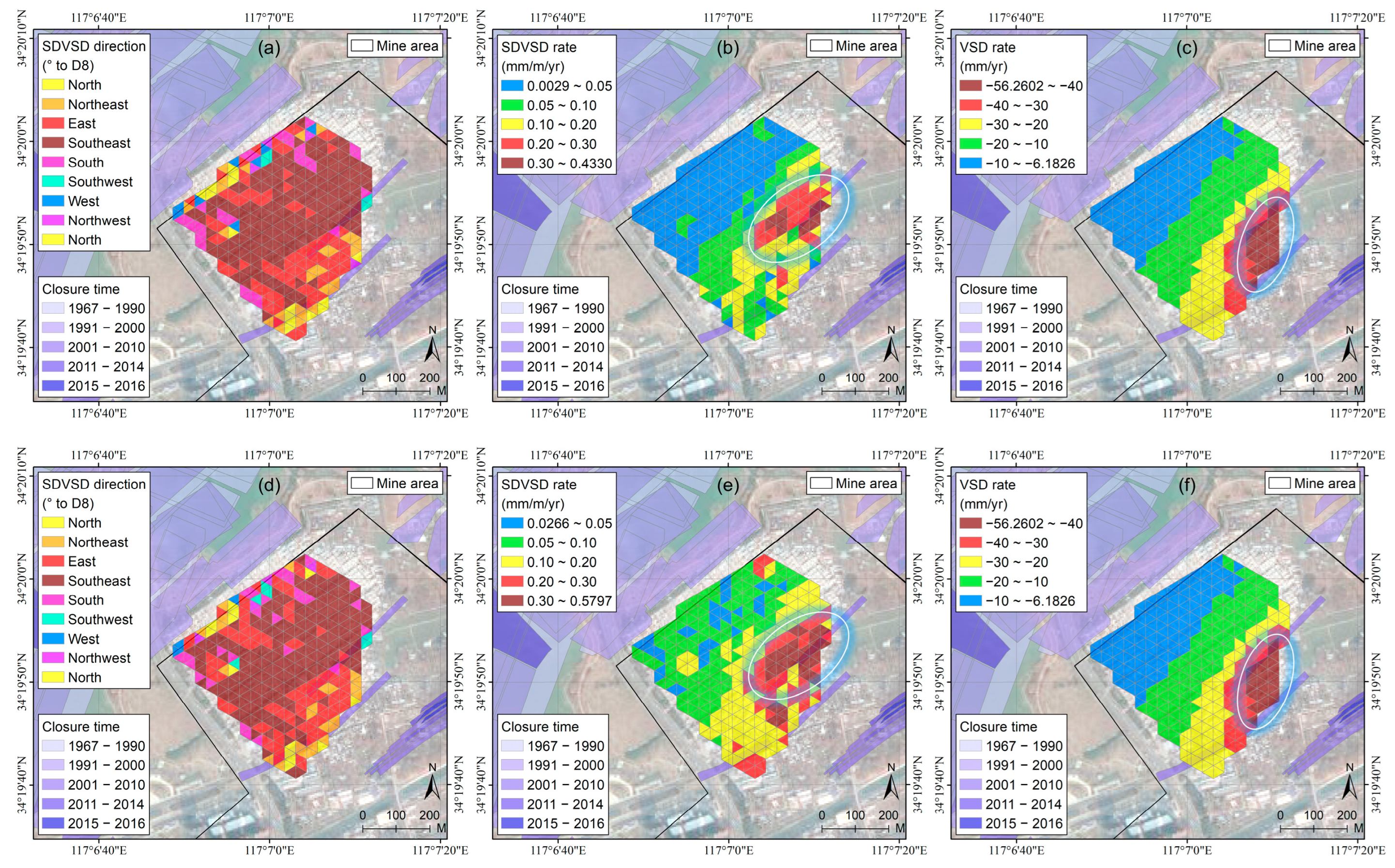
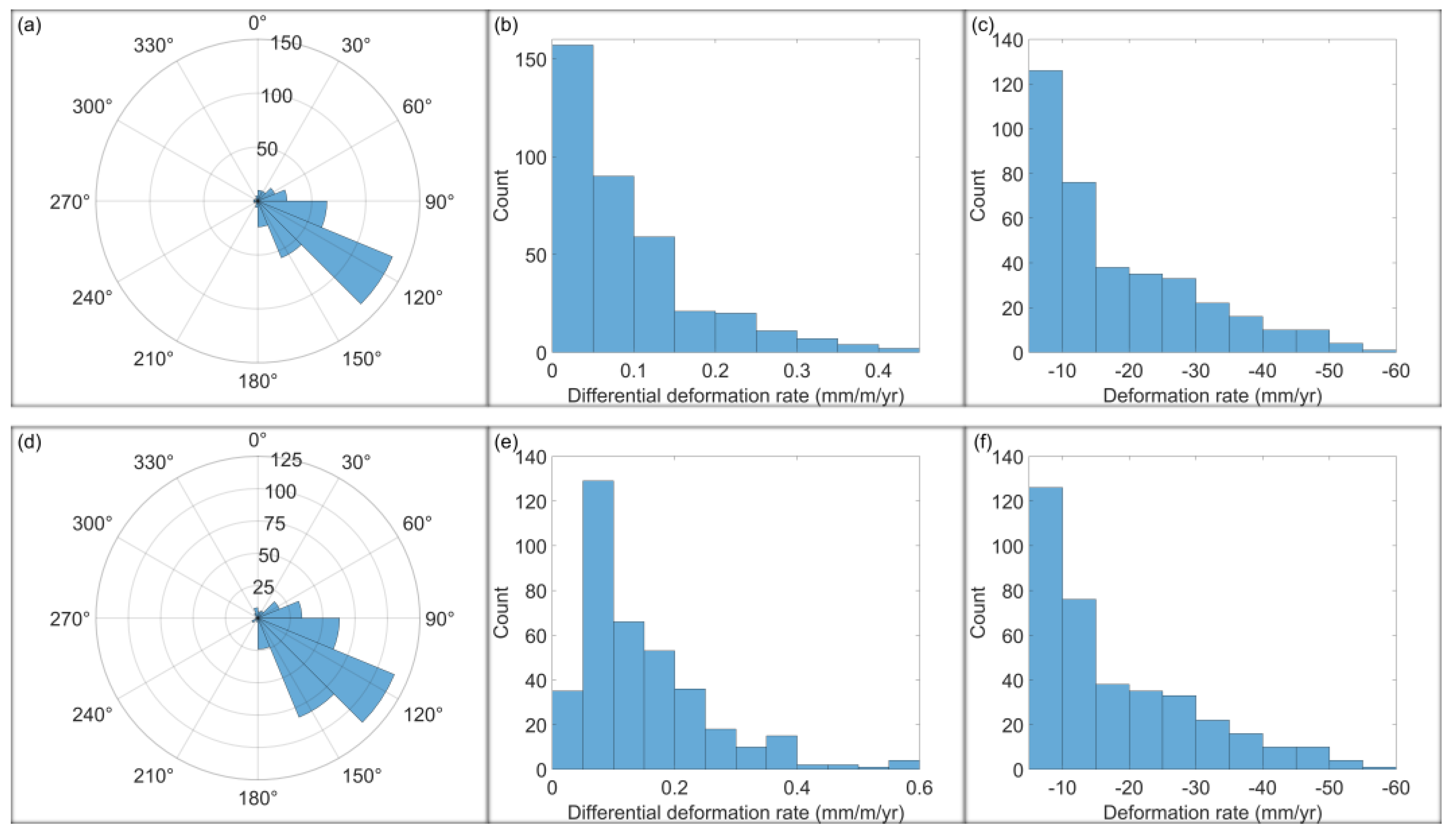

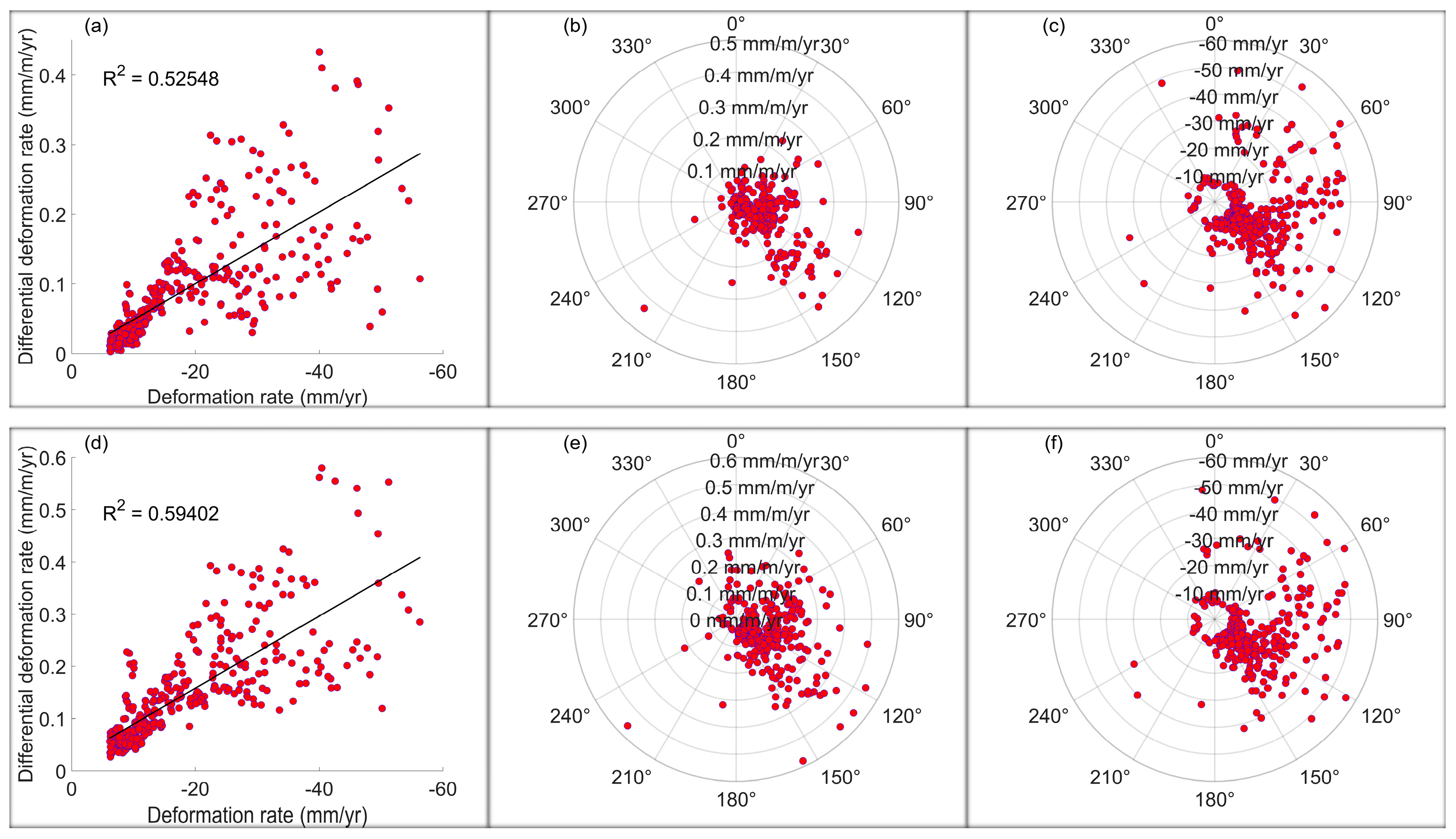
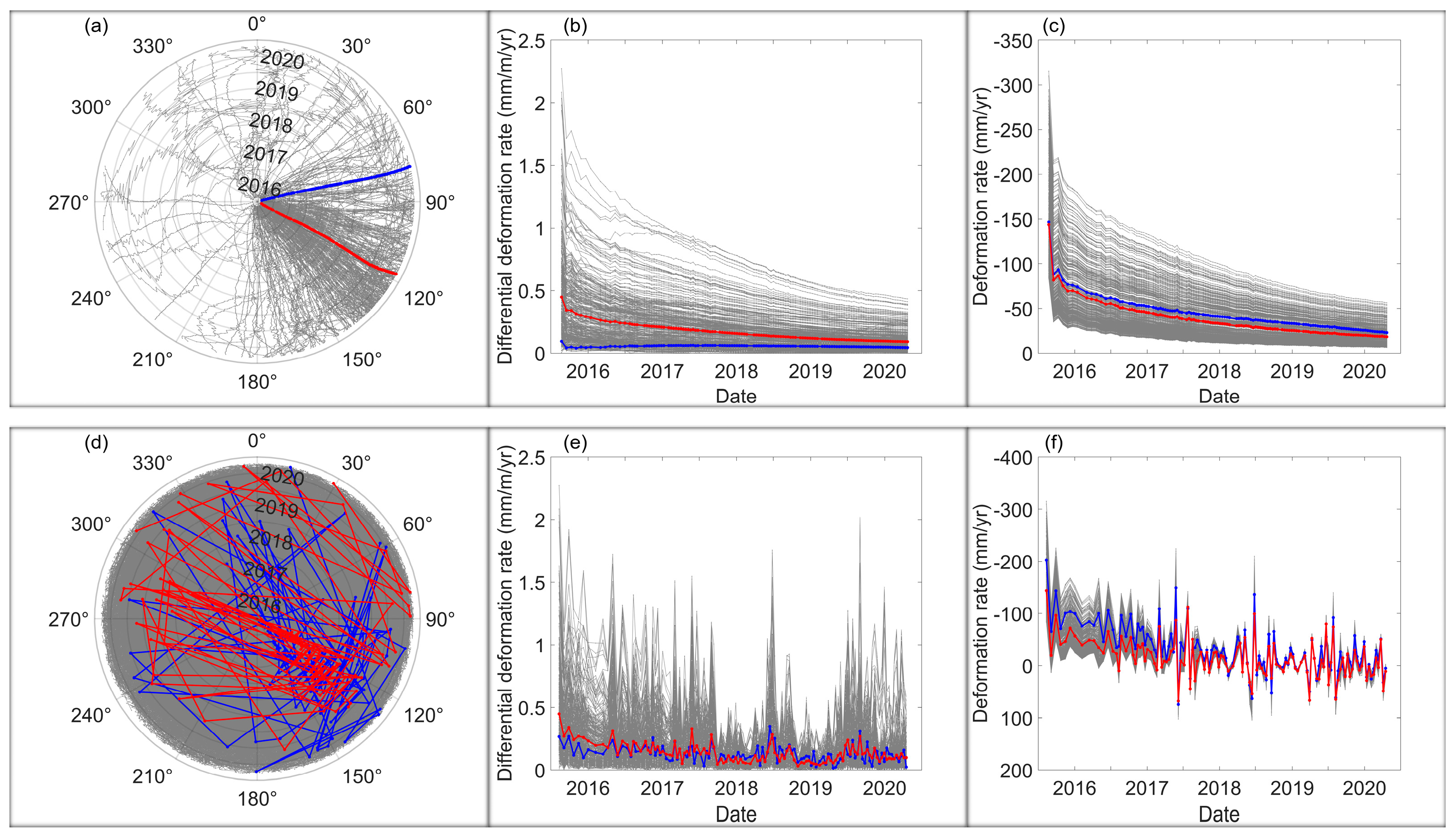
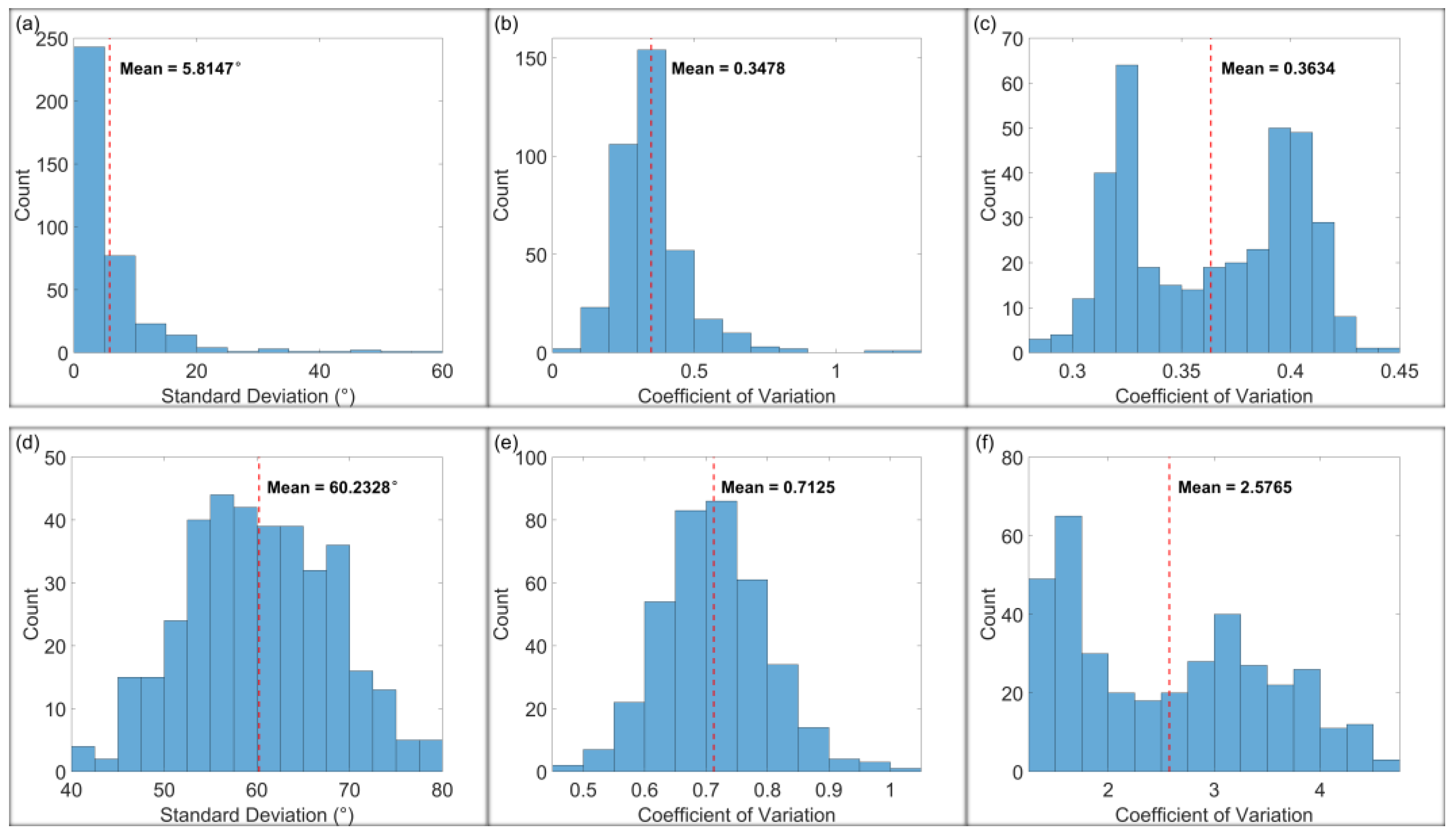
| Interval | Quantity | MIN | MAX | Range | Median | Mean | STD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cumulative for the whole observation period | SDVSD direction (°) | N.A. | N.A. | N.A. | 122.8951 | 117.6373 | 40.5183 |
| SDVSD rate (mm/m/yr) | 0.0029 | 0.4330 | 0.4301 | 0.0643 | 0.0908 | 0.0828 | |
| VSD rate (mm/yr) | −56.2602 | −6.1826 | 50.0776 | −13.3122 | −18.2019 | 11.6495 | |
| Weighted mean of all incremental intervals | SDVSD direction (°) | N.A. | N.A. | N.A. | 124.1070 | 119.7484 | 39.0982 |
| SDVSD rate (mm/m/yr) | 0.0266 | 0.5797 | 0.5531 | 0.1233 | 0.1457 | 0.1044 | |
| VSD rate (mm/yr) | −56.2602 | −6.1826 | 50.0776 | −13.3122 | −18.2019 | 11.6495 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, C.; Li, L.; Yin, H.; Zhao, G.; Wang, W.; Huang, J.; Fan, Q. Formal Quantification of Spatially Differential Characteristics of PSI-Derived Vertical Surface Deformation Using Regular Triangle Network: A Case Study of Shixi in the Northwest Xuzhou Coalfield. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 1388. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17081388
Zhao C, Li L, Yin H, Zhao G, Wang W, Huang J, Fan Q. Formal Quantification of Spatially Differential Characteristics of PSI-Derived Vertical Surface Deformation Using Regular Triangle Network: A Case Study of Shixi in the Northwest Xuzhou Coalfield. Remote Sensing. 2025; 17(8):1388. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17081388
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Cunfa, Langping Li, Huiyong Yin, Guanhua Zhao, Wei Wang, Jianxue Huang, and Qi Fan. 2025. "Formal Quantification of Spatially Differential Characteristics of PSI-Derived Vertical Surface Deformation Using Regular Triangle Network: A Case Study of Shixi in the Northwest Xuzhou Coalfield" Remote Sensing 17, no. 8: 1388. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17081388
APA StyleZhao, C., Li, L., Yin, H., Zhao, G., Wang, W., Huang, J., & Fan, Q. (2025). Formal Quantification of Spatially Differential Characteristics of PSI-Derived Vertical Surface Deformation Using Regular Triangle Network: A Case Study of Shixi in the Northwest Xuzhou Coalfield. Remote Sensing, 17(8), 1388. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17081388






