Structural Deformation Style and Seismic Potential of the Maoyaba Fault, Southeastern Margin of the Tibet Plateau
Abstract
1. Introduction
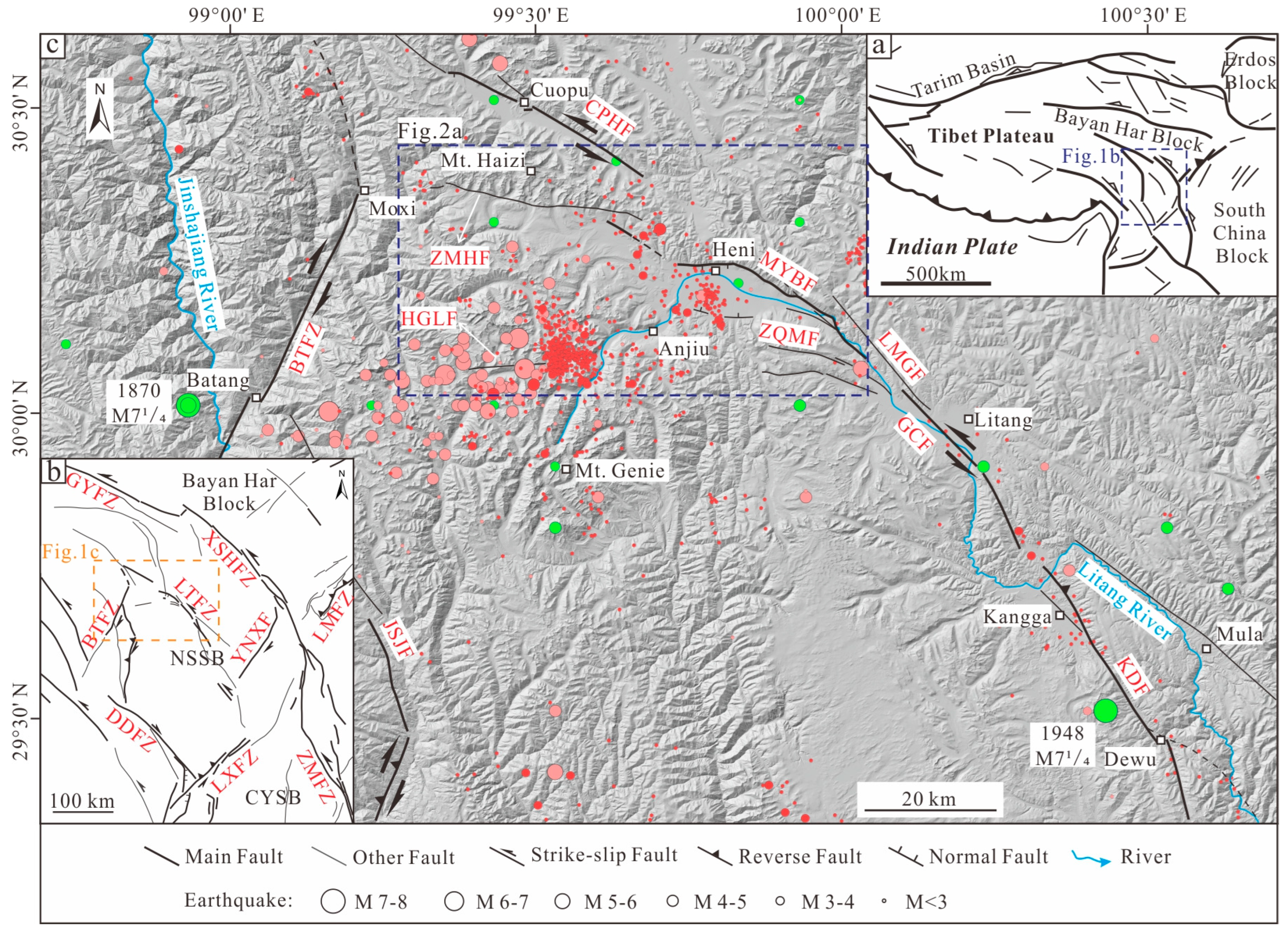
2. Geological Setting
3. Methods and Materials
4. Results
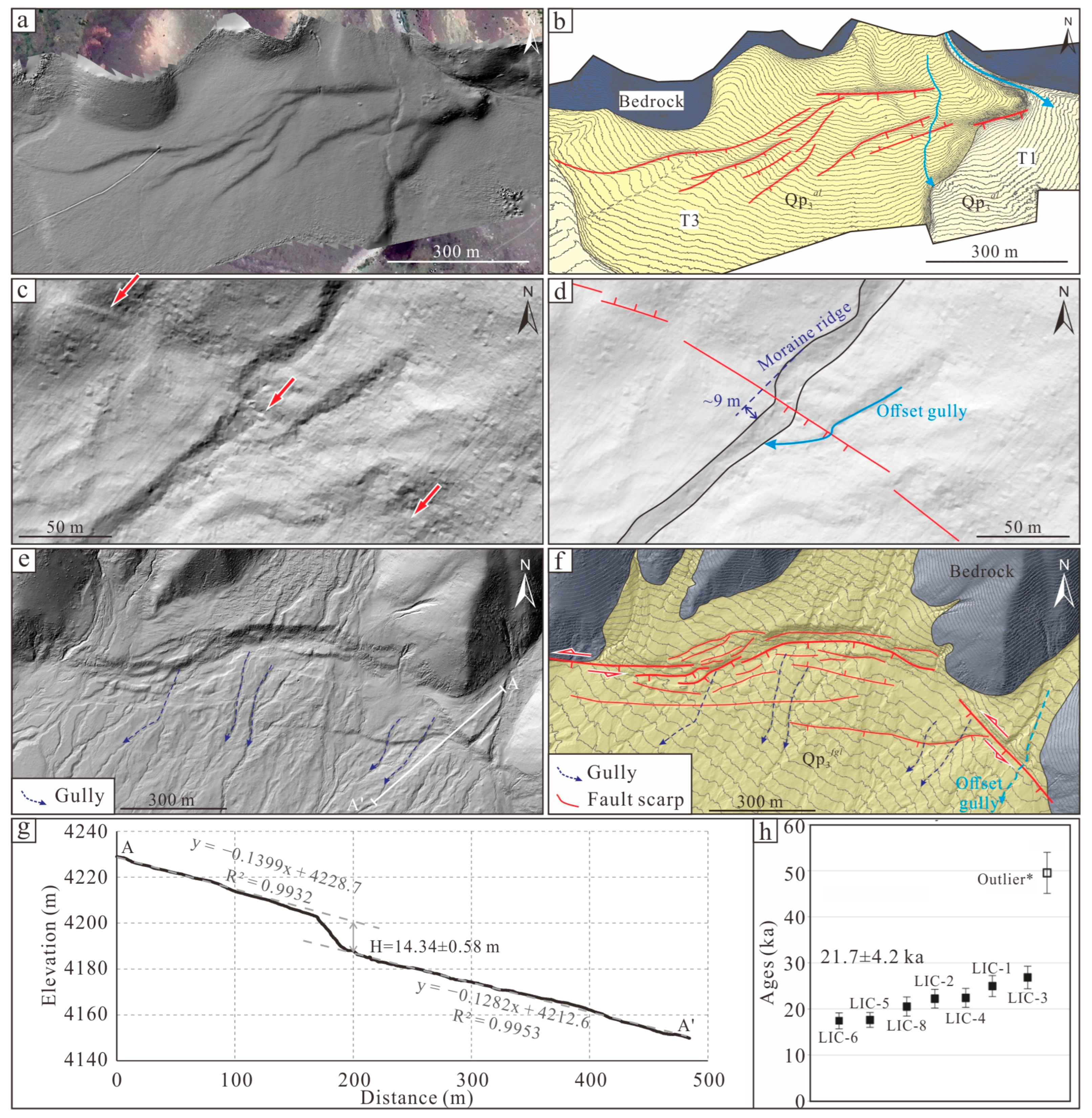
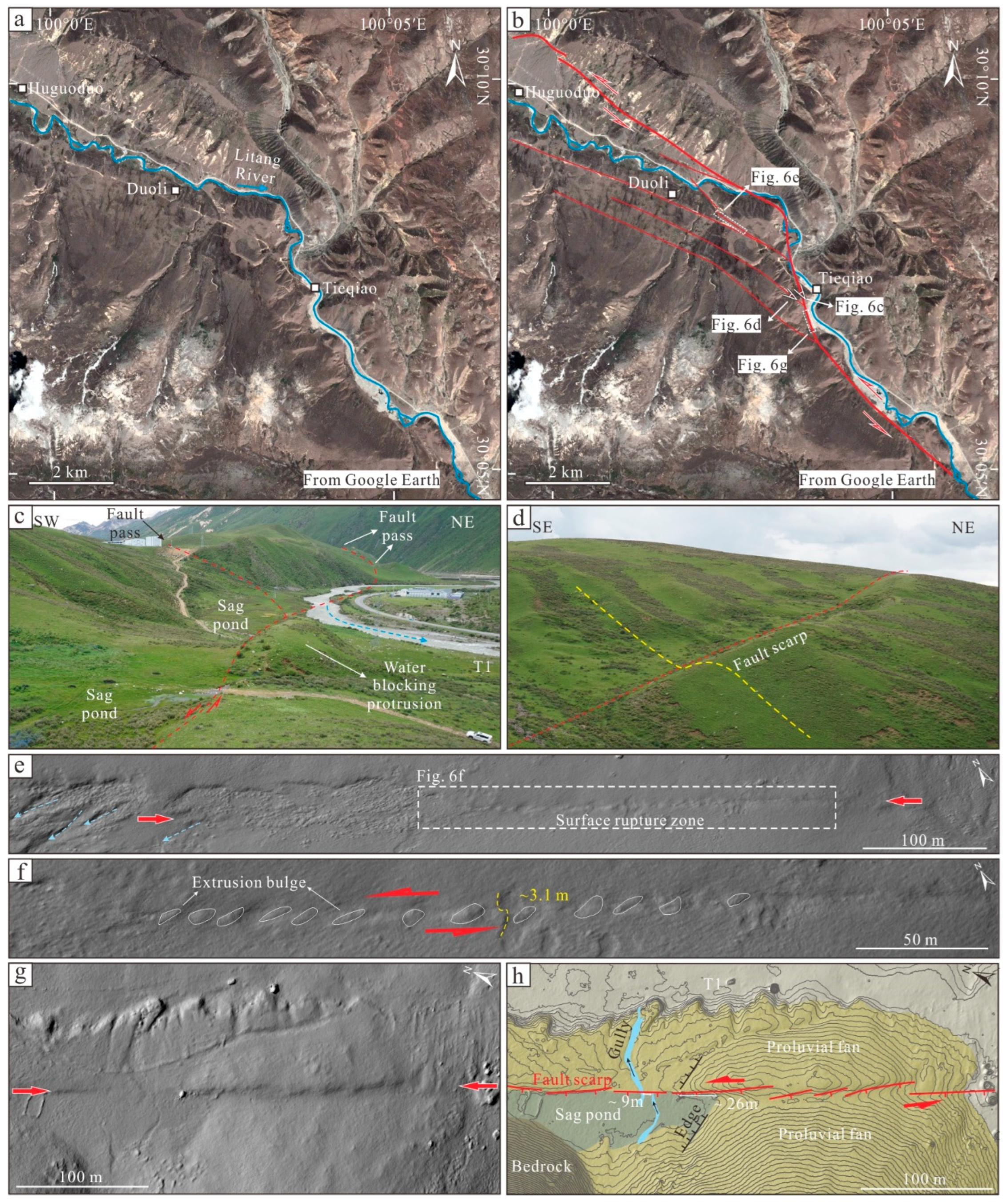
4.1. Geometric Structure and Kinematic Characteristics of the MYBF
4.1.1. M-F1
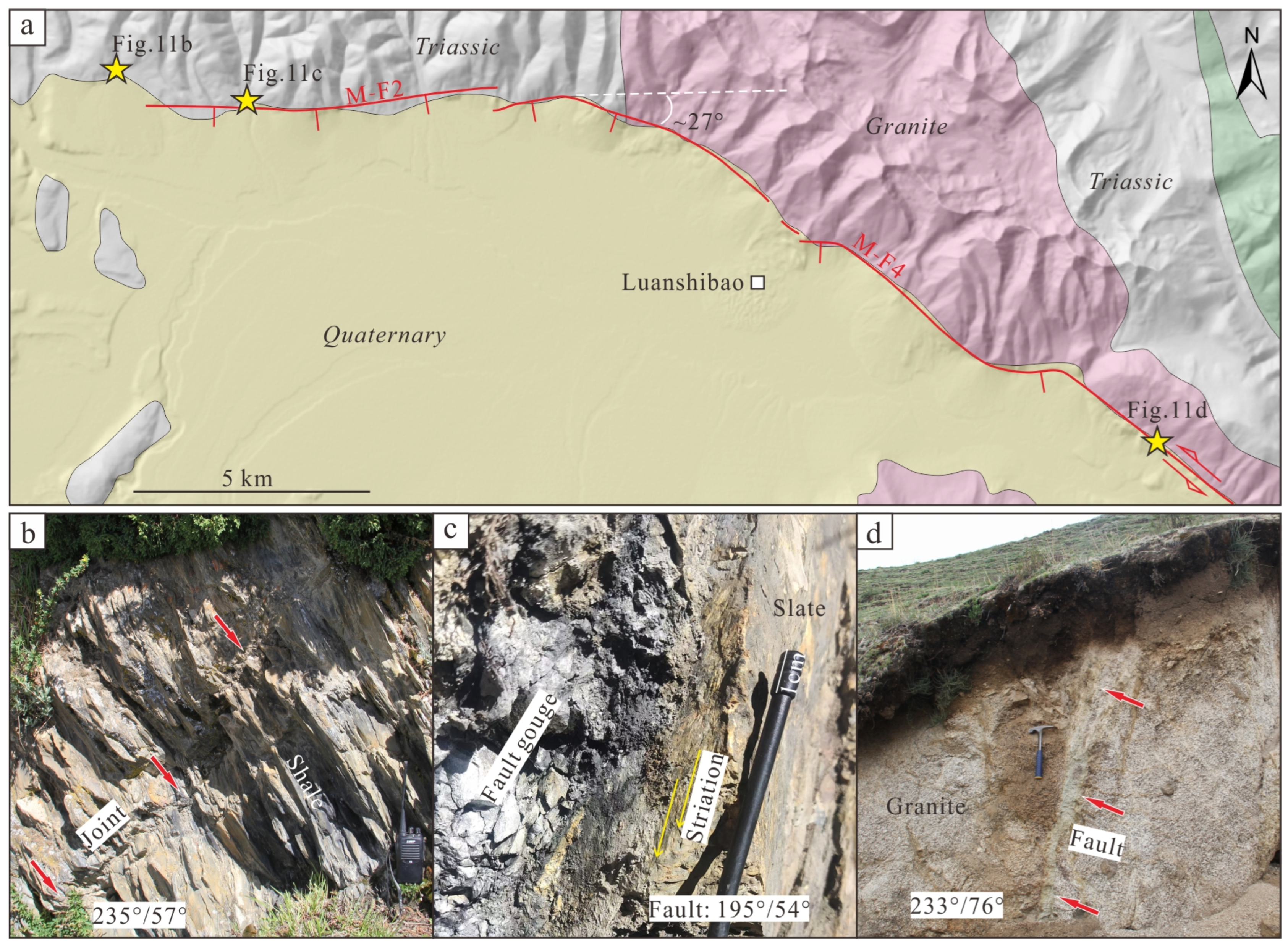
4.1.2. M-F2
4.1.3. M-F3
4.1.4. M-F4
4.1.5. M-F5
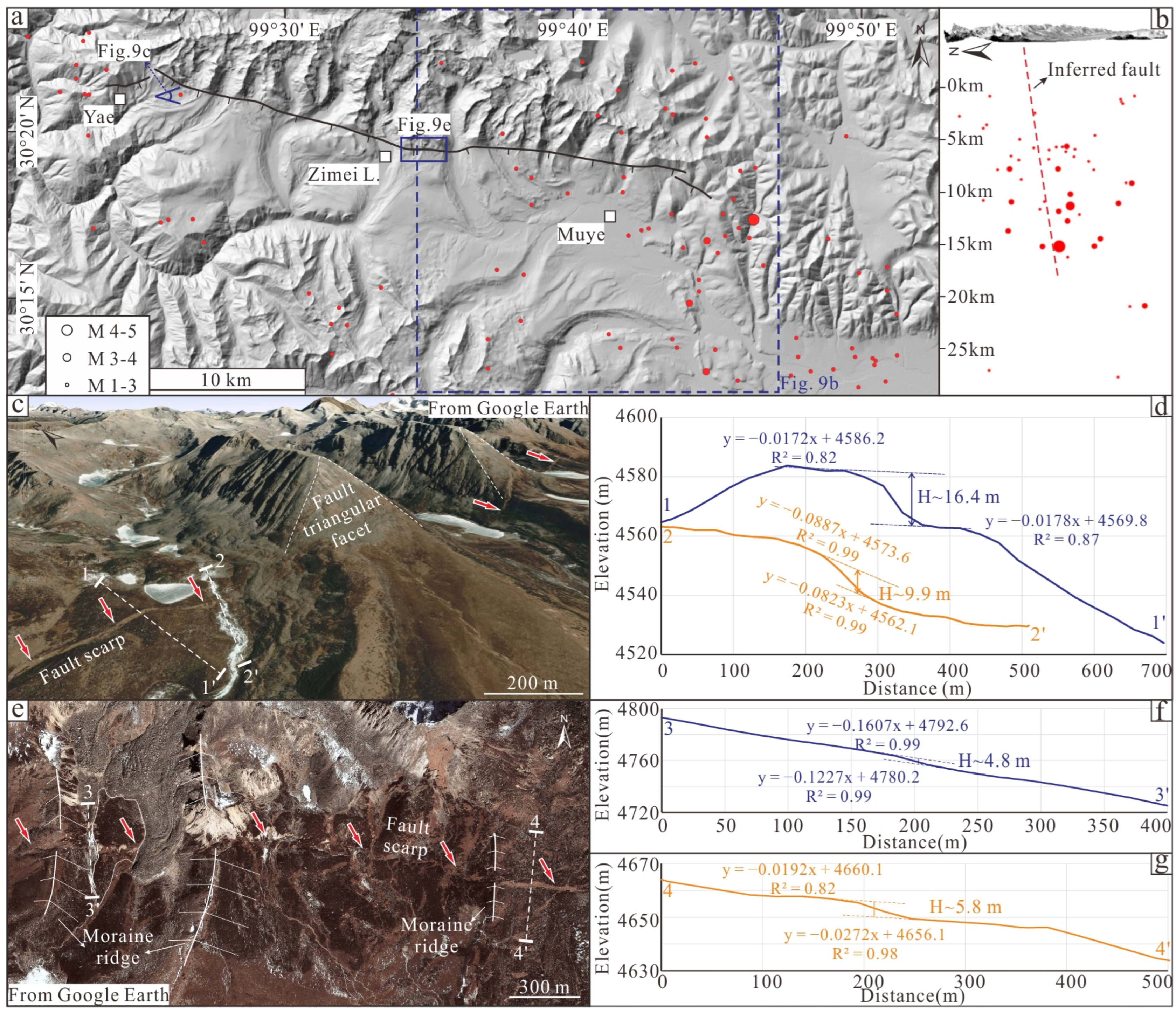
4.2. Offset Cluster Characteristics of the MYBF
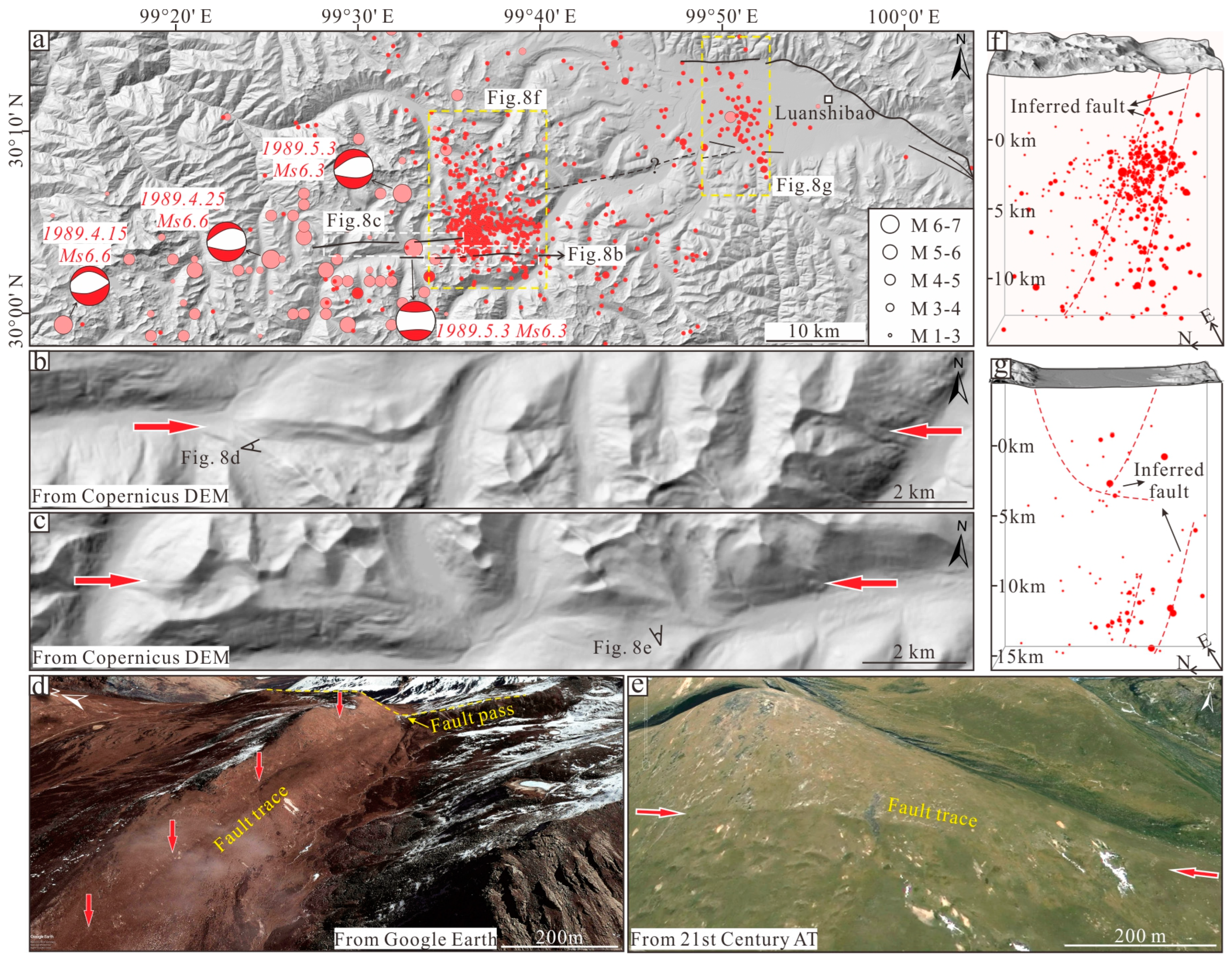
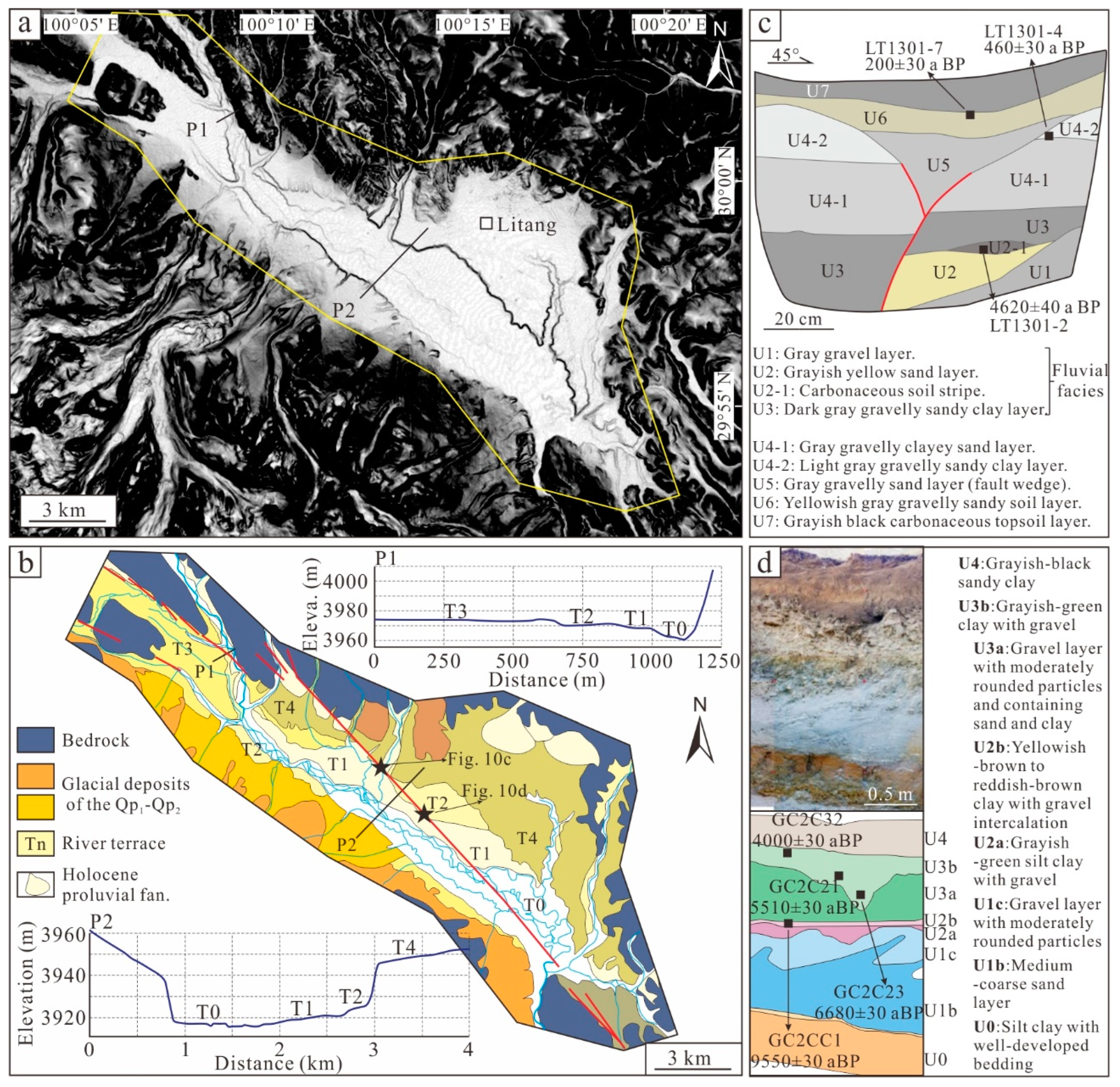
4.3. Geometric Distribution and Kinematic Property of the HGLF
4.4. Geometric Distribution and Kinematic Properties of the ZMHF
5. Discussion
5.1. Paleoearthquakes Recorded by the Fault Scarps of the MYBF
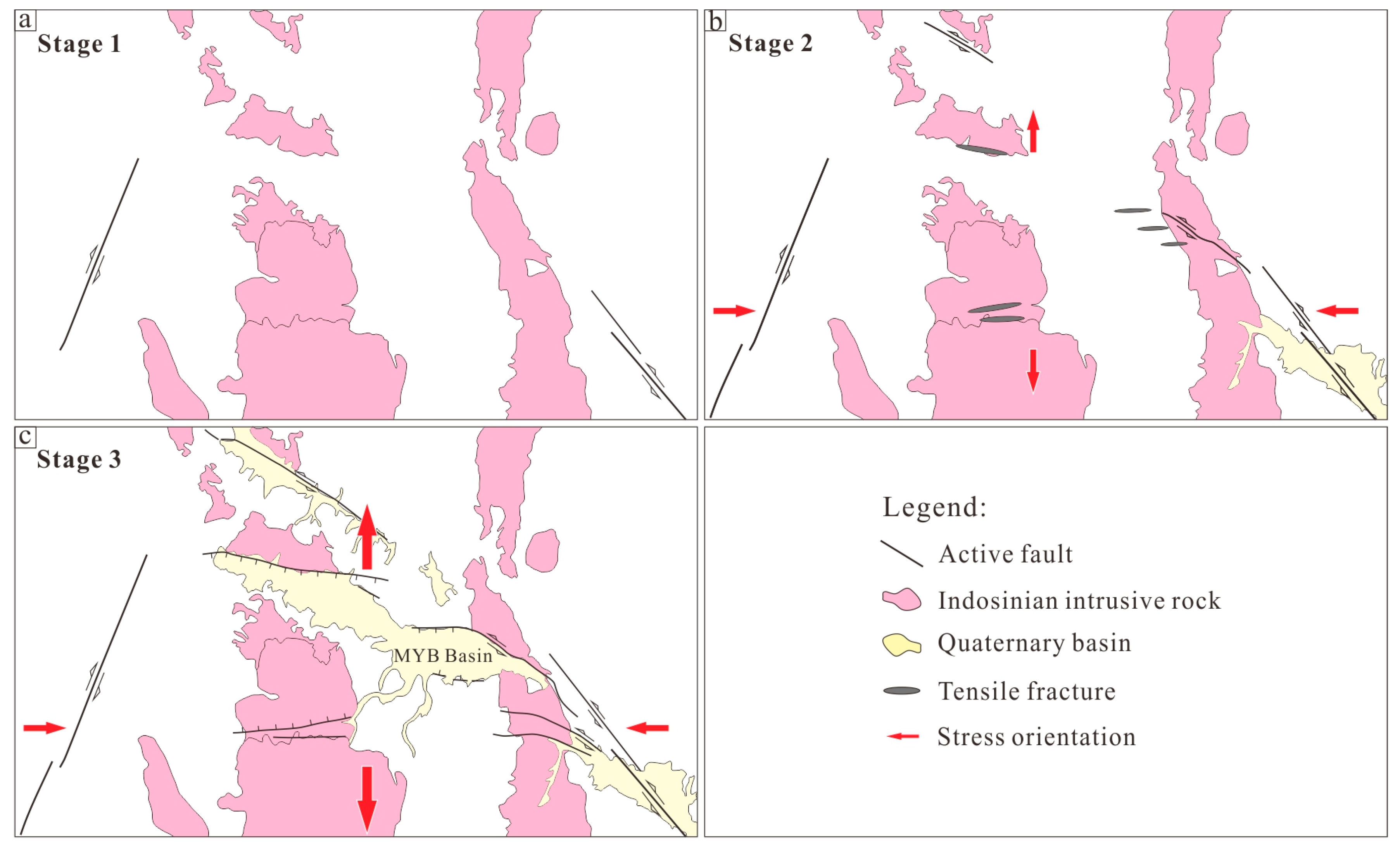
5.2. Characteristics and Formation Mechanism of Structure Deformation in MYB Area
5.3. Seismic Potential in the MYB Area
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, P.Z.; Shen, Z.; Wang, M.; Gan, W.J.; Burgmann, R.; Molnar, P.; Wang, Q.; Niu, Z.; Sun, J.; Wu, J. Continuous deformation of the Tibetan Plateau from global positioning system data. Geology 2004, 32, 809–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.J.; Wang, Y.; Liu, L.J.; Shao, Z.G.; Cheng, F.; Zhang, J.J.; Gan, W.J.; Hao, M. Lithospheric deformation and corresponding deep geodynamic process of the SE Tibetan Plateau. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2024, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.W.; Wen, X.Z.; Yu, G.H.; Zheng, R.Z.; Luo, H.Y.; Zheng, B. Average slip rate, earthquake rupturing segmentation and recurrence behavior on the Litang fault zone, western Sichuan Province, China. Sci. China Ser. D Earth Sci. 2005, 48, 1183–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, R.J.; Chen, G.X.; Li, Y.; Zhou, Z.H.; Gong, Y.; He, Y.L.; Li, X.G. Research on Active Faults in Litang—Batang Region, Western Sichuan Province, and the Seismogenic Structures of the 1989 Batang M6.7 Earthquake Swarm. Seismol. Geol. 2005, 27, 31–43, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Chevalier, M.L.; Leloup, P.H.; Replumaz, A.; Pan, J.W.; Liu, D.L.; Li, H.B.; Gourbet, L.; Métois, M. Tectonic-geomorphology of the Litang fault system, SE Tibetan Plateau, and implication for regional seismic hazard. Tectonophysics 2016, 682, 278–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.Y.; Zhou, R.J.; Liang, M.J.; Liu, S.; Liu, N.; Long, J.Y. Co-seismic surface rupture and recurrence interval of large earthquakes along Damaoyaba-Litang segment of the Litang fault on the Eastern Margin of the Tibetan Plateau in China. J. Earth Sci. 2021, 32, 1139–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.P.; Chen, L.C.; Li, Y.B.; Wang, H.; Han, M.M.; Feng, J.H.; Lu, L.L.; Peng, S.X.; Jin, C.; Liu, L.T. Rupture behavior of the Litang fault within the Sichuan-Yunnan active block, southeastern Tibetan Plateau. Lithosphere 2022, 2021, 8773676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.T.; Zhou, W.J.; Dong, G.C.; Xian, F.X.; Fu, Y.C.; Zhang, L.; Tang, L.; Ding, P.K.; Zhao, G.Q. Timing and seismic origin of the historic Luanshibao rock avalanche in the Maoyaba basin, SE Tibetan Plateau: New evidence from 10Be exposure-ages. Quat. Geochronol. 2023, 75, 101430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.B.; Zhang, Y.S.; Montgomery, D.R.; Du, Y.B.; Zhang, G.Z.; Wang, S.F. How unusual is the long-runout of the earthquake-triggered giant Luanshibao landslide, Tibetan Plateau, China? Geomorphology 2016, 259, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Q.L.; Yuan, G.X.; Davies, T.; Xu, B.; Wei, R.Q.; Xue, X.Y.; Zhang, L.Q. 10Be dating and seismic origin of Luanshibao rock avalanche in SE Tibetan Plateau and implications on Litang active fault. Landslides 2020, 17, 1091–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, P.; Ge, Y.G.; Li, S.J.; Li, Z.H.; Xu, X.W.; Zhou, G.G.D.; Chen, H.Y.; Wang, H.; Lei, Y.; Zhou, L.B.; et al. Scientific challenges in disaster risk reduction for the Sichuan–Tibet Railway. Eng. Geol. 2022, 309, 106837. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, J.J.; Xu, X.W.; Lv, Y.W.; Wang, Q.X.; Li, A.; Li, K.; Zhu, J.L.; Cai, J.T.; Liu, S. Late Quaternary slip rate of the northern Lancangjiang fault zone in eastern Tibet: Seismic hazards for the Sichuan-Tibet Railway and regional tectonic implications. Eng. Geol. 2022, 306, 106748. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, N.; Zhang, X.B.; Guo, C.B.; Yang, Z.; Yu, H.; Wu, R.A.; Wang, Y.; Li, H.B. Geological risk assessment of traffic engineering construction among 7.0–8.5 magnitude earthquake areas: Practice from the Sichuan-Tibet transport corridor in the eastern Tibetan Plateau. China Geol. 2024, 7, 605–629. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, X.W.; Wen, X.Z.; Zheng, R.Z.; Ma, W.T.; Song, F.M.; Yu, G.H. Pattern of latest tectonic motion and its dynamics for active blocks in Sichuan-Yunnan region, China. Sci. China Ser. D Earth Sci. 2003, 46, 210–226. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, J.J.; Qi, S.W.; Xu, Z.X.; Kang, W.J.; Su, Q.; Lv, Y.W. Timing of the Luanshibao Giant Landslide in eastern Tibet: The evidence from paleoseismology. In IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2021; Volume 861, p. 052002. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, J.; Xu, X.W.; Gan, W.J.; Ma, W.T.; Chen, W.T.; Zhang, Y. Block model and dynamic implication from the earthquake activities and crustal motion in the southeastern margin of Tibetan Plateau. Chinese J. Geophys. 2012, 55, 1198–1212, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Bai, M.K.; Chevalier, M.L.; Pan, J.W.; Replumaz, A.; Leloup, P.H.; Métois, M.; Li, H.B. Southeastward increase of the Late Quaternary slip-rate of the Xianshuihe fault, eastern Tibet. Geodynamic and seismic hazard implications. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2018, 485, 19–31. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, M.K.; Chevalier, M.L.; Leloup, P.H.; Li, H.B.; Pan, J.W.; Replumaz, A.; Wang, S.G.; Li, K.Y.; Wu, Q.; Liu, F.C.; et al. Spatial slip rate distribution along the SE Xianshuihe fault, eastern Tibet, and earthquake hazard assessment. Tectonics 2021, 40, e2021TC006985. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, X.W.; Zhang, P.Z.; Wen, X.Z.; Qin, Z.L.; Chen, G.H.; Zhu, A.L. Features of Active Tectonics and Recurrence Behaviors of Strong Earthquakes in the Western Sichuan Province and Its Adjacent Regions. Seismol. Geol. 2005, 27, 446–461, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Huang, W.L.; Zhang, J.L.; Xiang, W.; Yang, Q.H. The Late Quaternary Activity Characteristics and Slip Rate of Batang Fault in SE Tibetan Plateau. Seismol. Geol. 2023, 45, 1265–1285, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, R.J.; Ye, Y.Q.; Li, Y.; Li, X.G.; He, Y.L.; Ge, T.Y. Late-Quaternary Activity of the Shawan Segment of the Litang Faults. Quat. Sci. 2007, 27, 45–53, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Gu, G.X.; Lin, T.H.; Shi, Z.L. Catalogue of Chinese Earthquakes (1831 BC-1969 AD); Science Press: Beijing, China, 1983. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Su, Z.; Wang, E.; Furlong, K.P.; Shi, X.H.; Wang, G.; Fan, C. Young, active conjugate strike–slip deformation in West Sichuan: Evidence for the stress–strain pattern of the southeastern Tibetan plateau. Int. Geol. Rev. 2012, 54, 991–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.H.; Shi, X.H.; Chen, H.L.; Yang, R.; Zhang, F.Q.; Cheng, X.G.; Rao, G.; Deng, H.D.; Gong, J.F.; Shu, Y.H. V-Shaped Conjugate Strike-Slip Faults: Characteristics, Formation Mechanisms and Implications for the Late Cenozoic Deformation in the Southeastern Tibetan Plateau. J. Earth Sci. 2023, 48, 1421–1440, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Schäfer, J.M.; Tschudi, S.; Zhao, Z.Z.; Wu, X.H.; Ivy-Ochs, S.; Wieler, R.; Baur, H.; Kubik, P.W.; Schlüchter, C. The limited influence of glaciations in Tibet on global climate over the past 170 000 yr. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2002, 194, 287–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Airbus. Copernicus DEM: Copernicus Digital Elevation Model Product Handbook-Report; AO/1-9422/18/I-LG Version 5.0; Airbus: Leiden, The Netherlands, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Zhao, J.Y.; Yan, B.Q.; Yue, L.W.; Wang, L.C. Global DEMs vary from one to another: An evaluation of newly released Copernicus, NASA and AW3D30 DEM on selected terrains of China using ICESat-2 altimetry data. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2022, 15, 1149–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bielski, C.; López-Vázquez, C.; Grohmann, C.H.; Guth, P.L.; Hawker, L.; Gesch, D.; Trevisani, S.; Herrera-Cruz, V.; Riazanoff, S.; Corseaux, A.; et al. Novel approach for ranking DEMs: Copernicus DEM improves one arc second open global topography. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2024, 62, 4503922. [Google Scholar]
- Bi, H.Y.; Zheng, W.J.; Ren, Z.K.; Zeng, J.Y.; Yu, J.X. Using an unmanned aerial vehicle for topography mapping of the fault zone based on structure from motion photogrammetry. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2017, 38, 2495–2510. [Google Scholar]
- Radaideh, O.M.; Grasemann, B.; Melichar, R.; Mosar, J. Detection and analysis of morphotectonic features utilizing satellite remote sensing and GIS: An example in SW Jordan. Geomorphology 2016, 275, 58–79. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, R.Z.; Xu, X.W.; Wang, F.; Li, J.P.; Ji, F.J. The Thrust Activity of the Altyn Fault Zone Since the Middle and Late Pleistocene. Seismol. Geol. 2005, 27, 361–373, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Yi, G.X.; Long, F.; Liang, M.J.; Zhang, Z.W.; Zhao, M.; Qi, Y.P.; Gong, Y.; Qiao, H.Z.; Wang, Z.; Wang, S.W. Seismogenic Structure of the M4. 9 and M5. 1 Litang Earthquakes on 23 September 2016 in Southwestern China. Seismol. Geol. 2017, 39, 949–963, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zielke, O.; Arrowsmith, J.R.; Ludwig, L.G.; Akçiz, S.O. Slip in the 1857 and earlier large earthquakes along the Carrizo Plain, San Andreas fault. Science 2010, 327, 1119–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klinger, Y.; Etchebes, M.; Tapponnier, P.; Narteau, C. Characteristic slip for five great earthquakes along the Fuyun fault in China. Nat. Geosci. 2011, 4, 389–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z.K.; Zhang, Z.Q.; Chen, T.; Yan, S.L.; Yin, J.H.; Zhang, P.Z.; Zheng, W.J.; Zhang, H.P.; Li, C.Y. Clustering of offsets on the Haiyuan fault and their relationship to paleoearthquakes. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 2016, 128, 3–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Zhou, B.G.; Wang, M.M.; Guo, P.; Liu, J.R.; Ha, G.H.; Fan, J. Surface rupture and slip distribution along the Zheduotang fault in the Kangding section of the Xianshuihe fault zone. Lithosphere 2022, 2021, 6500707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.F.; Luo, S.L.; Yang, M.W. An Analysis for Sedimentary System, Evolution, and Paleoclimate in the Litang Basin in West Sichuan in Quaternary. Acta Geol. Sichuan 2004, 24, 194–197, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- You, Z.C. Fine Study on Surface Rupture Features of the Litang Fault Zone Based on High-Resolution Remote Sensing Images. Master’s Thesis, Institute of Geology, China Earthquake Administration, Beijing, China, 2023. (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, C.J.; Wu, Z.H.; Zhang, K.Q.; Li, J.C.; Jiang, Y.; Tian, T.T.; Liu, Y.H.; Huang, X.J. New Chronological Constraint on the Co-seismic Surface Rupture Segments Associated with the Litang Fault. Seismol. Geol. 2015, 37, 13, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Gao, S.P. Late Quaternary Paleoseismology and Faulting Behavior of the Internal and Western Boundary Faults of Northwest Sichuan Subblock. Ph.D. Thesis, Institute of Geology, China Earthquake Administration, Beijing, China, 2021. (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham, W.D.; Mann, P. Tectonics of Strike-Slip Restraining and Releasing Bends; Geological Society of London: London, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.; Shen, Z.K. Present-day crustal deformation of continental China derived from GPS and its tectonic implications. J. Geophys. Res. Solid. Earth 2020, 125, e2019JB018774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Paola, N.; Holdsworth, R.E.; McCaffrey, K.J.W. The influence of lithology and pre-existing structures on reservoir-scale faulting patterns in transtensional rift zones. J. Geol. Soc. 2005, 162, 471–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrill, D.A.; Morris, A.P.; McGinnis, R.N.; Smart, K.J.; Wigginton, S.S.; Hill, N.J. Mechanical stratigraphy and normal faulting. J. Struct. Geol. 2017, 94, 275–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.F. Rupture behavior of the North Qilian Shan frontal thrust-Case studies from Fodongmiao-Hongyazi and Minle-damaying thrusts (NE Tibet). Ph.D. Thesis, Institute of Geology, China Earthquake Administration, Beijing, China, 2021. (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Editorial Board of Engineering Geology Handbook. Engineering Geology Handbook, 5th ed.; China Architecture and Building Press: Beijing, China, 2018. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Tong, H.M.; Cai, D.S.; Wu, Y.P.; Li, X.G.; Li, X.S.; Meng, L.J. Activity criterion of pre-existing fabrics in non-homogeneous deformation domain. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2010, 53, 1115–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.Q.; Yao, H.J.; Yang, Y. Shear wave velocity structure of the crust and upper mantle in Southeastern Tibet and its geodynamic implications. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2020, 63, 1278–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Yao, H.J.; Wu, H.X.; Zhang, P.; Wang, M.M. A new crustal shear-velocity model in Southwest China from joint seismological inversion and its implications for regional crustal dynamics. Geophys. J. Int. 2020, 220, 1379–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wells, D.L.; Coppersmith, K.J. New empirical relationships among magnitude, rupture length, rupture width, rupture area, and surface displacement. Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 1994, 84, 974–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| No. | Location | Area (km2) | Point Clouds | Resolution (m) | Date | Method |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | NE margin of MYB basin | 35.00 | 124689038 | 0.20 | 18 June 2021 | UAV + LiDAR |
| 2 | North of Muye | 0.20 | 34826813 | 0.08 | 2 September 2021 | UAV + SfM |
| 3 | North of Jinqing | 0.47 | 7197241 | 0.24 | 30 May 2023 | UAV + SfM |
| 4 | East of Jinqing | 0.48 | 10626496 | 0.22 | 25 June 2021 | UAV + SfM |
| 5 | South of Duoli | 0.55 | 16946515 | 0.18 | 23 June 2021 | UAV + SfM |
| 6 | South of Tieqiao | 0.22 | 6044270 | 0.24 | 23 June 2021 | UAV + SfM |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, X.; Zhong, N.; Yu, X.; Yang, G.; Li, H. Structural Deformation Style and Seismic Potential of the Maoyaba Fault, Southeastern Margin of the Tibet Plateau. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 1288. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17071288
Zhang X, Zhong N, Yu X, Yang G, Li H. Structural Deformation Style and Seismic Potential of the Maoyaba Fault, Southeastern Margin of the Tibet Plateau. Remote Sensing. 2025; 17(7):1288. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17071288
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Xianbing, Ning Zhong, Xiao Yu, Guifang Yang, and Haibing Li. 2025. "Structural Deformation Style and Seismic Potential of the Maoyaba Fault, Southeastern Margin of the Tibet Plateau" Remote Sensing 17, no. 7: 1288. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17071288
APA StyleZhang, X., Zhong, N., Yu, X., Yang, G., & Li, H. (2025). Structural Deformation Style and Seismic Potential of the Maoyaba Fault, Southeastern Margin of the Tibet Plateau. Remote Sensing, 17(7), 1288. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17071288








