Land Spatial Development Intensity and Its Ecological Effect on Soil Carbon Sinks in Large-Scale Coastal Areas
Abstract
1. Introduction
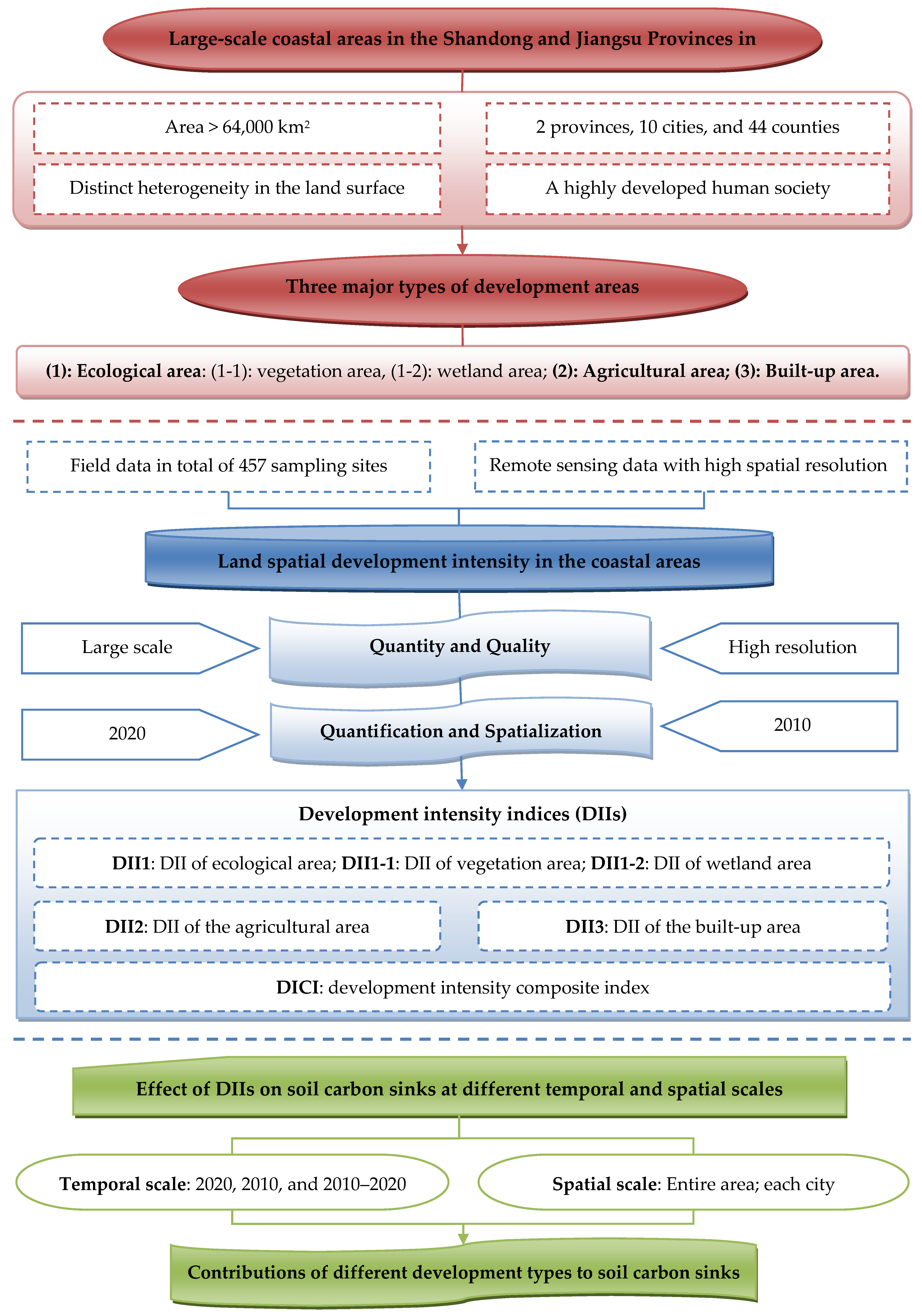
2. Materials and Methods
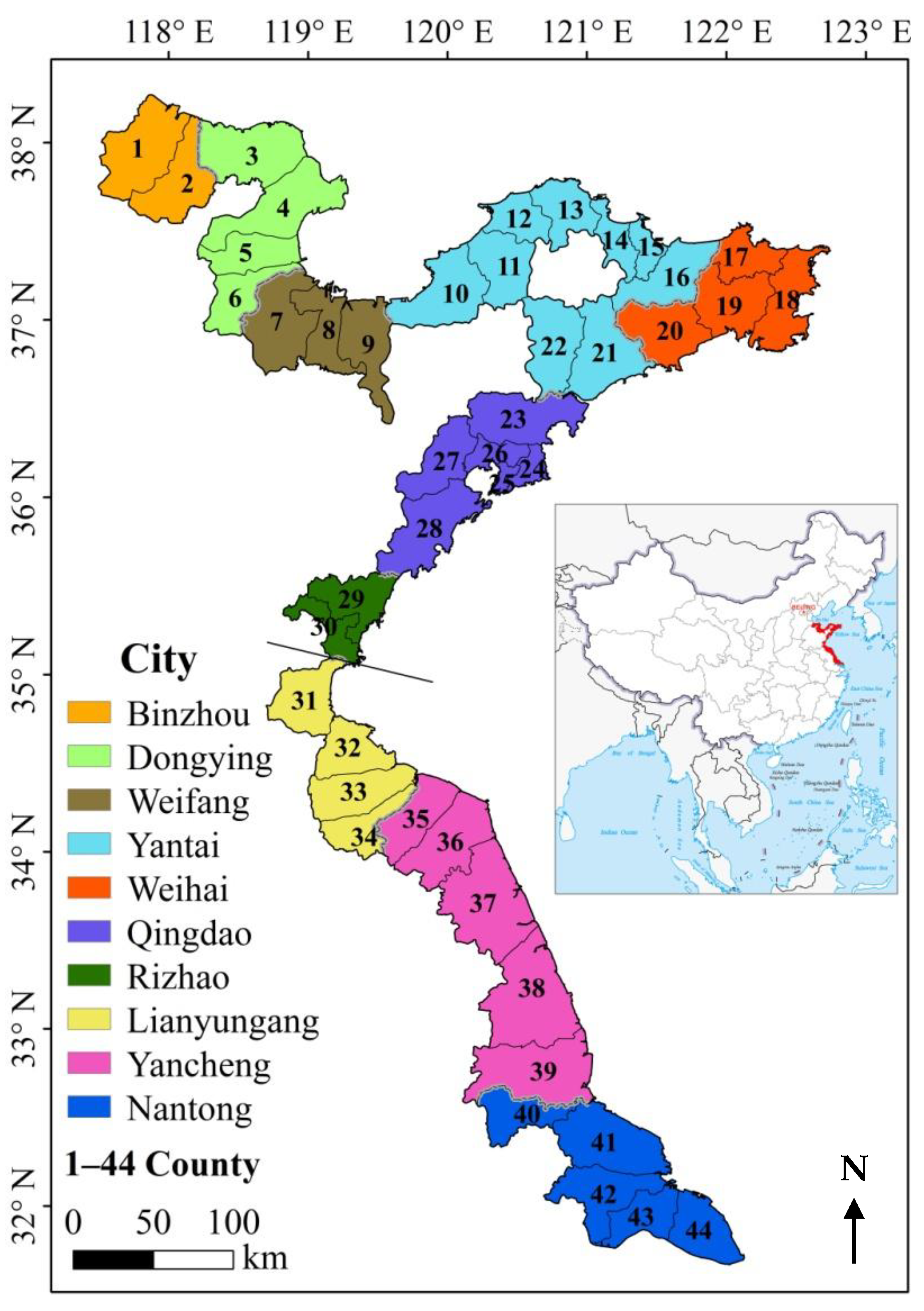
2.1. Study Area and Data Sources
2.1.1. Study Area
2.1.2. Data Sources
2.2. Quantification of Land Spatial Development Intensity
2.2.1. Scale and Resolution
2.2.2. Quantity and Quality
- (1)
- Quantity
- (2)
- Quality
2.2.3. Development Intensity Indices
2.3. Effects of Land Spatial Development Intensity on Soil Carbon Sinks
3. Results
3.1. Land Spatial Development Intensity in Large-Scale Coastal Areas
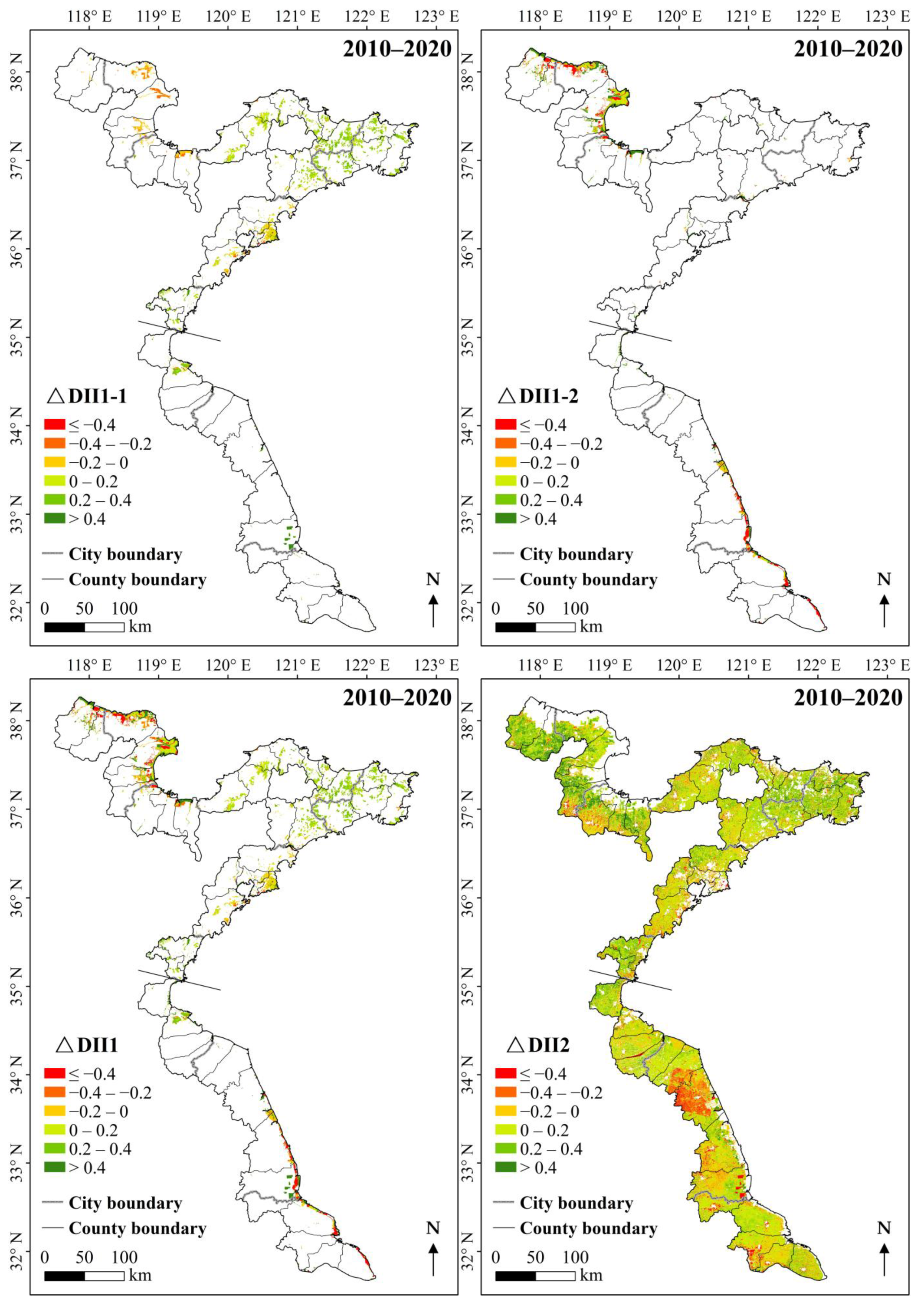
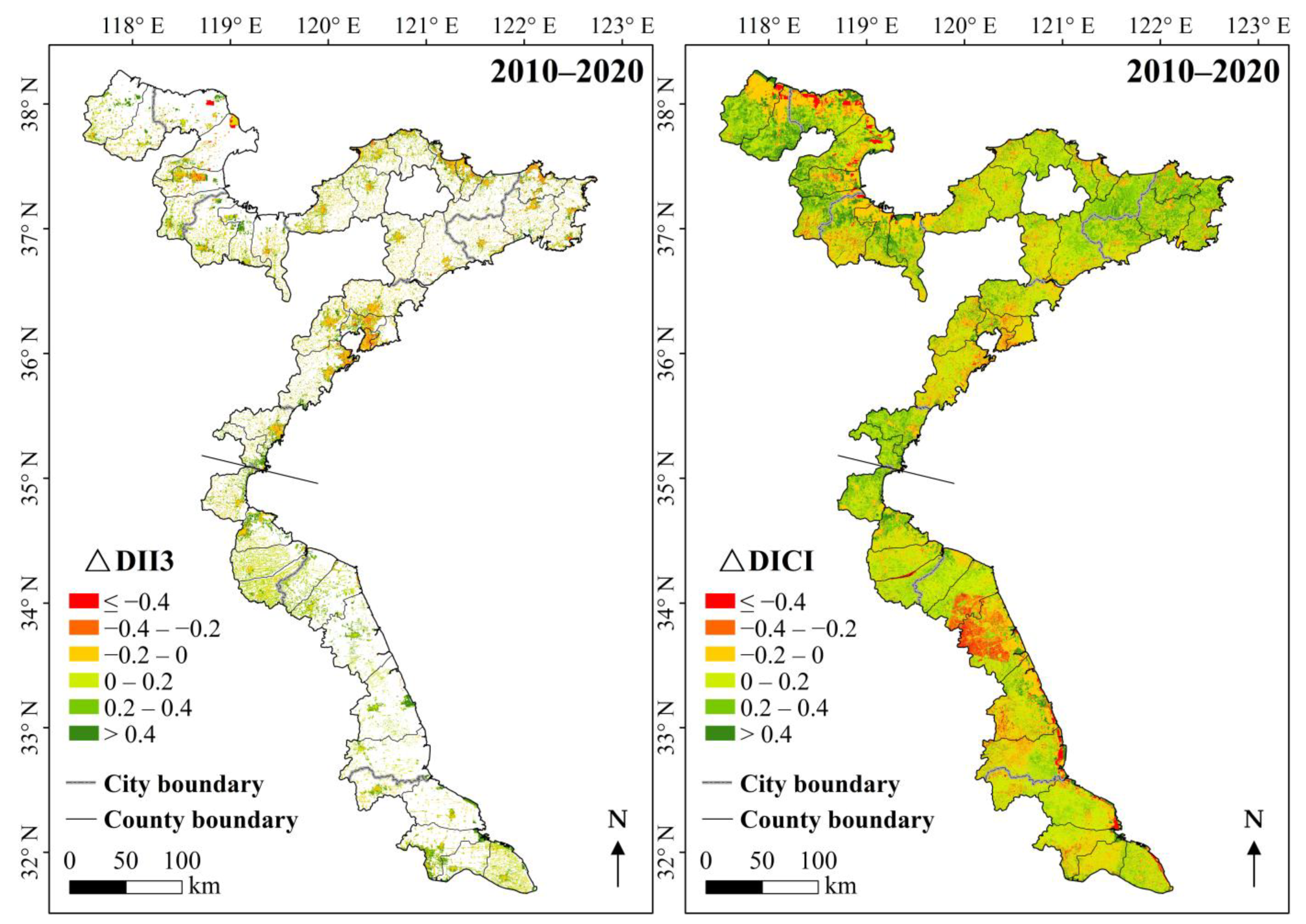
3.1.1. Spatial Distributions of Land Spatial Development Intensity
3.1.2. Land Spatial Development Intensity Along Multiple Gradients and Across Administrative Divisions
3.2. Soil Carbon Sink Effect of Land Spatial Development Intensity
3.2.1. Overall Effect of Different Development Types
3.2.2. Gradient Analyses Within Two Scopes
3.2.3. Correlation Analyses Within Two Scopes Using Two Analysis Schemes
4. Discussion
4.1. Optimization of Method for Quantifying Land Spatial Development Intensity in Large-Scale Coastal Areas
4.2. Spatial Patterns and Influencing Factors of Land Spatial Development Intensity
4.2.1. Spatial Patterns of Land Spatial Development Intensity
4.2.2. Factors Influencing Spatial Patterns of Land Spatial Development Intensity
4.3. Contributions of Different Development Types to Spatiotemporal Variations of Soil Carbon Sinks
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Merkens, J.-L.; Reimann, L.; Hinkel, J.; Vafeidis, A.T. Gridded Population Projections for the Coastal Zone under the Shared Socioeconomic Pathways. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2016, 145, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Y.; Li, W.; Wen, J.; Xu, H.; Du, S. Population Pattern and Exposure under Sea Level Rise: Low Elevation Coastal Zone in the Yangtze River Delta, 1990–2100. Clim. Risk Manag. 2021, 33, 100348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pizarro, B.; de Andrés, M.; Barragán, J.M. Coastal Zone in Central Chile, Delimitation Proposal of Valparaiso Region. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2024, 254, 107176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazant-Fabre, O.; Bonilla-Moheno, M.; Martínez, M.L.; Lithgow, D.; Muñoz-Piña, C. Land Planning and Protected Areas in the Coastal Zone of Mexico: Do Spatial Policies Promote Fragmented Governance? Land Use Policy 2022, 121, 106325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Luan, W.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Tian, C. Multi-Scenario Simulation of Land Use and Land Cover Based on Shared Socioeconomic Pathways: The Case of Coastal Special Economic Zones in China. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 335, 117536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, Y.; Liu, D.; Wang, C.; Xing, W.; Gao, J. Island development suitability evaluation for supporting the spatial planning in archipelagic areas. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 829, 154679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Megías, C.; Rico, A. Biodiversity Impacts by Multiple Anthropogenic Stressors in Mediterranean Coastal Wetlands. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 818, 151712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Jiang, W.; Peng, K.; Wu, Z.; Ling, Z.; Li, Z. Assessment of the Impact of Wetland Changes on Carbon Storage in Coastal Urban Agglomerations from 1990 to 2035 in Support of SDG15.1. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 877, 162824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Zhu, K.-H.; Ge, Z.-M.; Lv, Q.; Liu, S.-X.; Zhang, W.; Xin, P. Effects of Plastic Contamination on Carbon Fluxes in a Subtropical Coastal Wetland of East China. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 345, 118654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faber-Langendoen, D.; Lemly, J.; Nichols, W.; Rocchio, J.; Walz, K.; Smyth, R. Development and Evaluation of NatureServe’s Multi-Metric Ecological Integrity Assessment Method for Wetland Ecosystems. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 104, 764–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.W.; Chi, Y.; Liu, D.H.; Qu, Y.B.; Ma, X.J.; Xing, W.X.; Liu, Z.H. Spatiotemporal Pattern of Landscape Ecological Sensitivity in Coastal Zone in the Last 30 Years: An Empirical Study of Shandong Peninsula, China. J. Coast. Conserv. 2022, 26, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cradock-Henry, N.A.; Flood, S.; Buelow, F.; Blackett, P.; Wreford, A. Adaptation Knowledge for New Zealand’s Primary Industries: Known, Not Known and Needed. Clim. Risk Manag. 2019, 25, 100190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, S.D.; Fang, B. Cultivated Land Protection System in China from 1949 to 2019: Historical Evolution, Realistic Origin Exploration and Path Optimization. China Land Sci. 2019, 33, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.L.; Wu, D.X.; Zhou, K.; Liao, L.W. The Urban Space and Urban Development Boundary under the Framework of Territory Spatial Planning. Geogr. Res. 2019, 38, 2458–2472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Xie, Z.; Wang, J. How Human Activities Influence the Island Ecosystem through Damaging the Natural Ecosystem and Supporting the Social Ecosystem? J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 248, 119203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, W.; Hou, B.; Ye, G.; Wang, Z. China’s Land-Sea Coordination Practice in Territorial Spatial Planning. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2023, 237, 106545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.X.; Liang, L.W.; Wang, Z.B.; Zhang, W.Z.; Yu, J.H.; Liang, Y. Geographical Thinking on the Relationship between Beautiful China and Land Spatial Planning. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2019, 74, 2467–2481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crowder, L.B.; Osherenko, G.; Young, O.R.; Airamé, S.; Norse, E.A.; Baron, N.; Day, J.C.; Douvere, F.; Ehler, C.N.; Halpern, B.S.; et al. Resolving Mismatches in U.S. Ocean Governance. Science 2006, 313, 617–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Yu, L.; Du, Z.; Xu, Y.; Zhao, J.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, G.; Peng, D.; Gong, P. Distribution of Ecological Restoration Projects Associated with Land Use and Land Cover Change in China and Their Ecological Impacts. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 825, 153938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, Y.; Liu, D.; Gao, J.; Sun, J.; Zhang, Z.; Xing, W.; Qu, Y.; Ma, X.; Zha, B. Coastal Surface Soil Carbon Stocks Have Distinctly Increased under Extensive Ecological Restoration in Northern China. Commun. Earth Environ. 2023, 4, 373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, M.T.; Vivas, M.B. Landscape Development Intensity Index. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2005, 101, 289–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, S.; Wang, S. Do Development Zones Increase Urban Land Use Intensity? Empirical Analysis from 235 Cities in China. Appl. Geogr. 2023, 156, 103001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Peng, J.; Qiu, S.; Xu, Z.; Zhou, F.; Xia, P.; Adalibieke, W. Distinguishing the Impacts of Land Use Change in Intensity and Type on Ecosystem Services Trade-Offs. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 316, 115206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, Y.; Zhang, Z.W.; Gao, J.H.; Xie, Z.L.; Zhao, M.W.; Wang, E.K. Evaluating Landscape Ecological Sensitivity of an Estuarine Island Based on Landscape Pattern across Temporal and Spatial Scales. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 101, 221–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canelas, J.V.; Pereira, H.M. Impacts of Land-Use Intensity on Ecosystems Stability. Ecol. Model. 2022, 472, 110093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wu, K.; Yang, Q.; Hao, S.; Feng, Z.; Ma, J. Quantitative Assessment of Cultivated Land Use Intensity in Heilongjiang Province, China, 2001–2015. Land Use Policy 2023, 125, 106505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Xu, X.; Tang, Q. Human Activity Intensity of Land Surface: Concept, Methods and Application in China. J. Geogr. Sci. 2016, 26, 1349–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano, O.; Lovelock, C.E.; Atwood, T.B.; Macreadie, P.I.; Canto, R.; Phinn, S.; Arias-Ortiz, A.; Bai, L.; Baldock, J.; Bedulli, C.; et al. Australian Vegetated Coastal Ecosystems as Global Hotspots for Climate Change Mitigation. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 4313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Fu, C.C.; Wang, W.Q.; Zeng, L.; Tu, C.; Luo, Y.M. An Overlooked Soil Carbon Pool in Vegetated Coastal Ecosystems: National-Scale Assessment of Soil Organic Carbon Stocks in Coastal Shelter Forests of China. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 876, 162823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deb, S.; Mandal, B. Soils and Sediments of Coastal Ecology: A Global Carbon Sink. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2021, 214, 105937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, Y.; Sun, J.K.; Liu, D.H.; Xie, Z.L. Reconstructions of Four-Dimensional Spatiotemporal Characteristics of Soil Organic Carbon Stock in Coastal Wetlands during the Last Decades. Catena 2022, 218, 106553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owers, C.J.; Rogers, K.; Mazumder, D.; Woodroffe, C.D. Temperate Coastal Wetland Near-Surface Carbon Storage: Spatial Patterns and Variability. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2020, 235, 106584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Wang, T.; Gustave, W.; Wang, J.J.; Zhou, Y.H.; Chen, J.Q. Spatial-Temporal Patterns of Organic Carbon Sequestration Capacity after Long-Term Coastal Wetland Reclamation. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2023, 341, 108209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendriks, H.C.M.; van Prooijen, B.C.; Aarninkhof, S.G.J.; Winterwerp, J.C. How Human Activities Affect the Fine Sediment Distribution in the Dutch Coastal Zone Seabed. Geomorphology 2020, 367, 107314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhou, Y.; Wu, J.; Wang, C.; Zhang, R.; Xiong, X.; Xu, C. Human Activities Dominate a Staged Degradation Pattern of Coastal Tidal Wetlands in Jiangsu Province, China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 154, 110579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Bureau of Statistics. Bulletin of the Seventh National Population Census in China; National Bureau of Statistics: Beijing, China, 2021.
- De Gruijter, J.J.; Brus, D.J.; Bierkens, M.F.P.; Knotters, M. Sampling for Natural Resource Monitoring; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Saurette, D.D.; Berg, A.A.; Laamrani, A.; Heck, R.J.; Gillespie, A.W.; Voroney, P.; Biswas, A. Effects of Sample Size and Covariate Resolution on Field-Scale Predictive Digital Mapping of Soil Carbon. Geoderma 2022, 425, 116054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Z.; Chen, S.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, R.; Shi, Z.; Viscarra Rossel, R.A. National Digital Soil Map of Organic Matter in Topsoil and Its Associated Uncertainty in 1980’s China. Geoderma 2019, 335, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Q.; Wang, G.; Liu, T.; Xue, B.-L. Controls of Carbon Flux in a Semi-Arid Grassland Ecosystem Experiencing Wetland Loss: Vegetation Patterns and Environmental Variables. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2018, 259, 196–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huete, A.R. A Soil-Adjusted Vegetation Index (SAVI). Remote Sens. Environ. 1988, 25, 295–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douaoui, A.E.K.; Nicolas, H.; Walter, C. Detecting Salinity Hazards within a Semiarid Context by Means of Combining Soil and Remote-Sensing Data. Geoderma 2006, 134, 217–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H. A New Index for Delineating Built-up Land Features in Satellite Imagery. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2008, 29, 4269–4276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Essaadia, A.; Abdellah, A.; Ahmed, A.; Abdelouahed, F.; Kamal, E. The Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI) of the Zat Valley, Marrakech: Comparison and Dynamics. Heliyon 2022, 8, e12204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, L.; Yan, M.; Zhang, L.; Fan, X.; Yang, H. Spatial-Temporal NDVI Pattern of Global Mangroves: A Growing Trend during 2000–2018. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 844, 157075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venancio, L.P.; Mantovani, E.C.; do Amaral, C.H.; Usher Neale, C.M.; Gonçalves, I.Z.; Filgueiras, R.; Campos, I. Forecasting Corn Yield at the Farm Level in Brazil Based on the FAO-66 Approach and Soil-Adjusted Vegetation Index (SAVI). Agric. Water Manag. 2019, 225, 105779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, H.; Zhou, G.; Zhang, F. Using Negative Soil Adjustment Factor in Soil-Adjusted Vegetation Index (SAVI) for Aboveground Living Biomass Estimation in Arid Grasslands. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 209, 439–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.S.; Xu, H.Q. A New Remote Sensing Index for Assessing the Spatial Heterogeneity in Urban Ecological Quality: A Case from Fuzhou City, China. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 89, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Zhang, H.; Yao, B.; Lin, H.; An, X.; Liu, Y. Spatiotemporal Changes of Wetlands in China during 2000–2015 Using Landsat Imagery. J. Hydrol. 2023, 621, 129590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, J.G.; Sparrius, J.; Robinson, T.; Hale, S.; Lupone, L.; Healey, T.; Cooke, R.; Rendall, A.R. Can NDVI Identify Drought Refugia for Mammals and Birds in Mesic Landscapes? Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 851, 158318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Zhu, J.; Zhao, S.; Su, F. Coastal Wetland Degradation and Ecosystem Service Value Change in the Yellow River Delta, China. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2023, 44, e02501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, Y.; Sun, J.; Liu, W.; Wang, J.; Zhao, M. Mapping Coastal Wetland Soil Salinity in Different Seasons Using an Improved Comprehensive Land Surface Factor System. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 107, 105517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wang, G.; Dai, L.; Liu, H.; Li, Y.; Qiu, C.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, H.; Dong, B.; Zhao, Y.; et al. Study on the Effect of Habitat Function Change on Waterbird Diversity and Guilds in Yancheng Coastal Wetlands Based on Structure–Function Coupling. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 122, 107223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Shen, J.; Xiao, Y.; Li, S.; Cao, M. Habitat Suitability and Potential Biological Corridors for Waterbirds in Yancheng Coastal Wetland of China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 148, 110090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, W.; Song, X.; Liu, M.; Shan, B.; Ma, M.; Liu, Y. Spatio-Temporal Evolution of Resources and Environmental Carrying Capacity and Its Influencing Factors: A Case Study of Shandong Peninsula Urban Agglomeration. Environ. Res. 2023, 234, 116469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Wang, J.; Cheng, H. Spatiotemporal Changes in Ecological Network Resilience in the Shandong Peninsula Urban Agglomeration. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 339, 130681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.Y.; Webster, R.; Shi, Z. Mapping Soil Salinity in the Yangtze Delta: REML and Universal Kriging (E-BLUP) Revisited. Geoderma 2015, 237–238, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.P.; Long, X.H.; Shao, H.B.; Liu, Z.P.; Tao, Y.; Zhou, Q.S.; Zong, J.Q. Ameliorants Improve Saline–Alkaline Soils on a Large Scale in Northern Jiangsu Province, China. Ecol. Eng. 2015, 81, 328–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, B.; Yang, X.; Yang, M.; Sun, D.; Zhu, W.; Zhu, D.; Wang, J. Mapping Soil Salinity Using a Combination of Vegetation Index Time Series and Single-Temporal Remote Sensing Images in the Yellow River Delta, China. Catena 2023, 231, 107313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Chen, S.; Ji, H.; Fan, Y.; Li, P. The Modern Yellow River Delta in Transition: Causes and Implications. Mar. Geol. 2021, 436, 106476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, S.; Hu, Y.; Li, J.; Tian, P.; Pu, R.; Liu, Y.; Fan, H. Tracking Economic-Driven Coastal Wetland Change along the East China Sea. Appl. Geogr. 2023, 156, 102995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halpern, B.S.; Walbridge, S.; Selkoe, K.A.; Kappel, C.V.; Micheli, F.; D’Agrosa, C.; Bruno, J.F.; Casey, K.S.; Ebert, C.; Fox, H.E.; et al. A Global Map of Human Impact on Marine Ecosystems. Science 2008, 319, 948–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, S.H.; Gan, T.Y. Impact of Anthropogenic Climate Change and Human Activities on Environment and Ecosystem Services in Arid Regions. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 633, 1329–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, Y.; Mo, S.; Wu, H.; Qu, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, L. Influence of Human Activities and Climate Change on Wetland Landscape Pattern—A Review. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 879, 163112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Hou, F.; Angerer, J.P.; Yi, S. Effects of Topography and Land-Use Patterns on the Spatial Heterogeneity of Terracette Landscapes in the Loess Plateau, China. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 109, 105839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, Y.; Sun, J.; Xie, Z.; Wang, J. Soil-Landscape Relationships in a Coastal Archipelagic Ecosystem. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2022, 216, 105996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacior, S.; Prus, B. Infrastructure Development and Its Influence on Agricultural Land and Regional Sustainable Development. Ecol. Inform. 2018, 44, 82–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Guo, H.; Corbane, C.; Li, Q. Urban Sprawl in Provincial Capital Cities in China: Evidence from Multi-Temporal Urban Land Products Using Landsat Data. Sci. Bull. 2019, 64, 955–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.; Zhao, R. China’s New Era of Ecological Civilization. Science 2017, 358, 1008–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Fang, F.; Li, Y. Key Issues of Land Use in China and Implications for Policy Making. Land Use Policy 2014, 40, 6–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Song, Y.; Tang, L.; Shi, L.; Shao, G. China’s Cities Need to Grow in a More Compact Way. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 8607–8608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


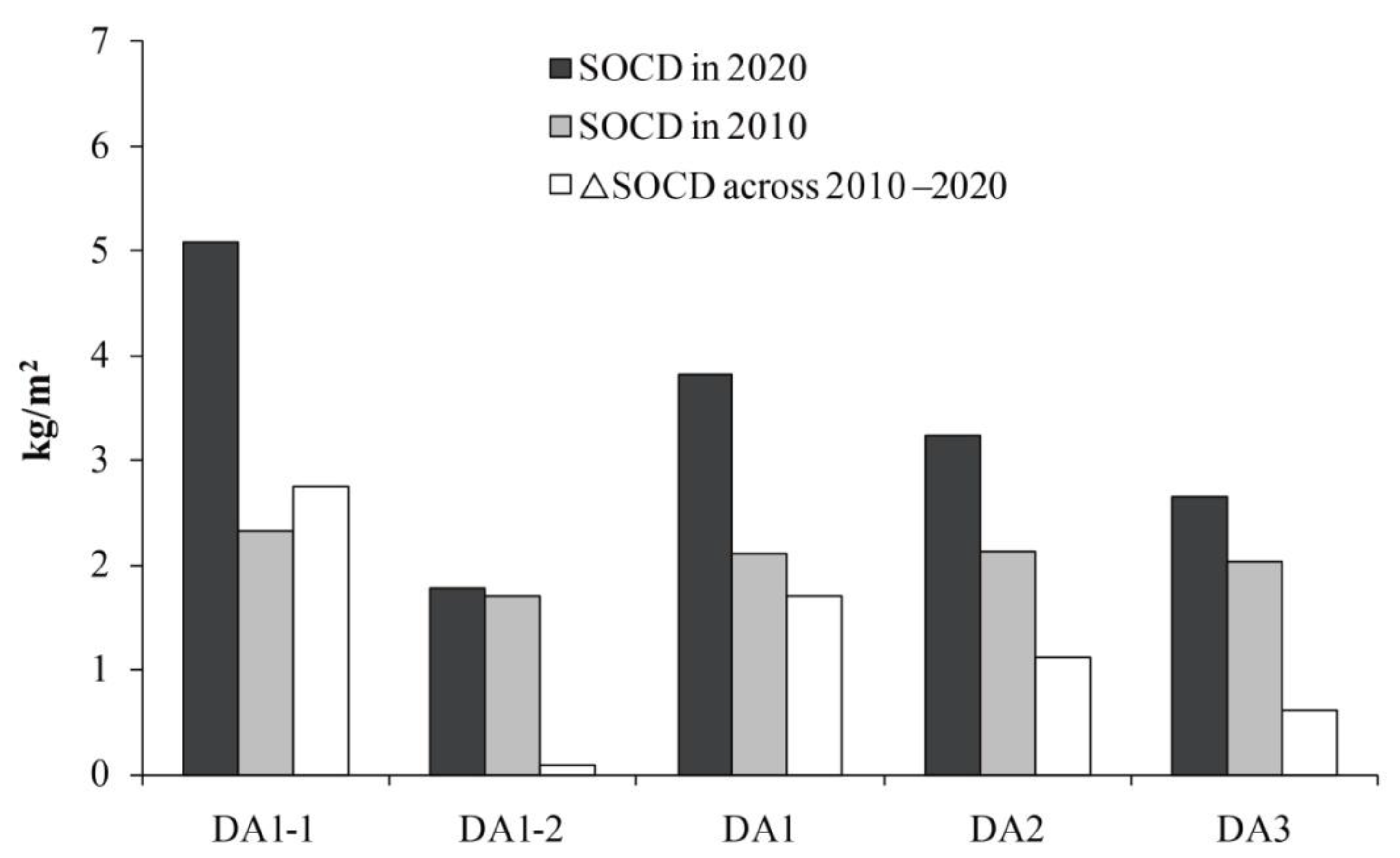

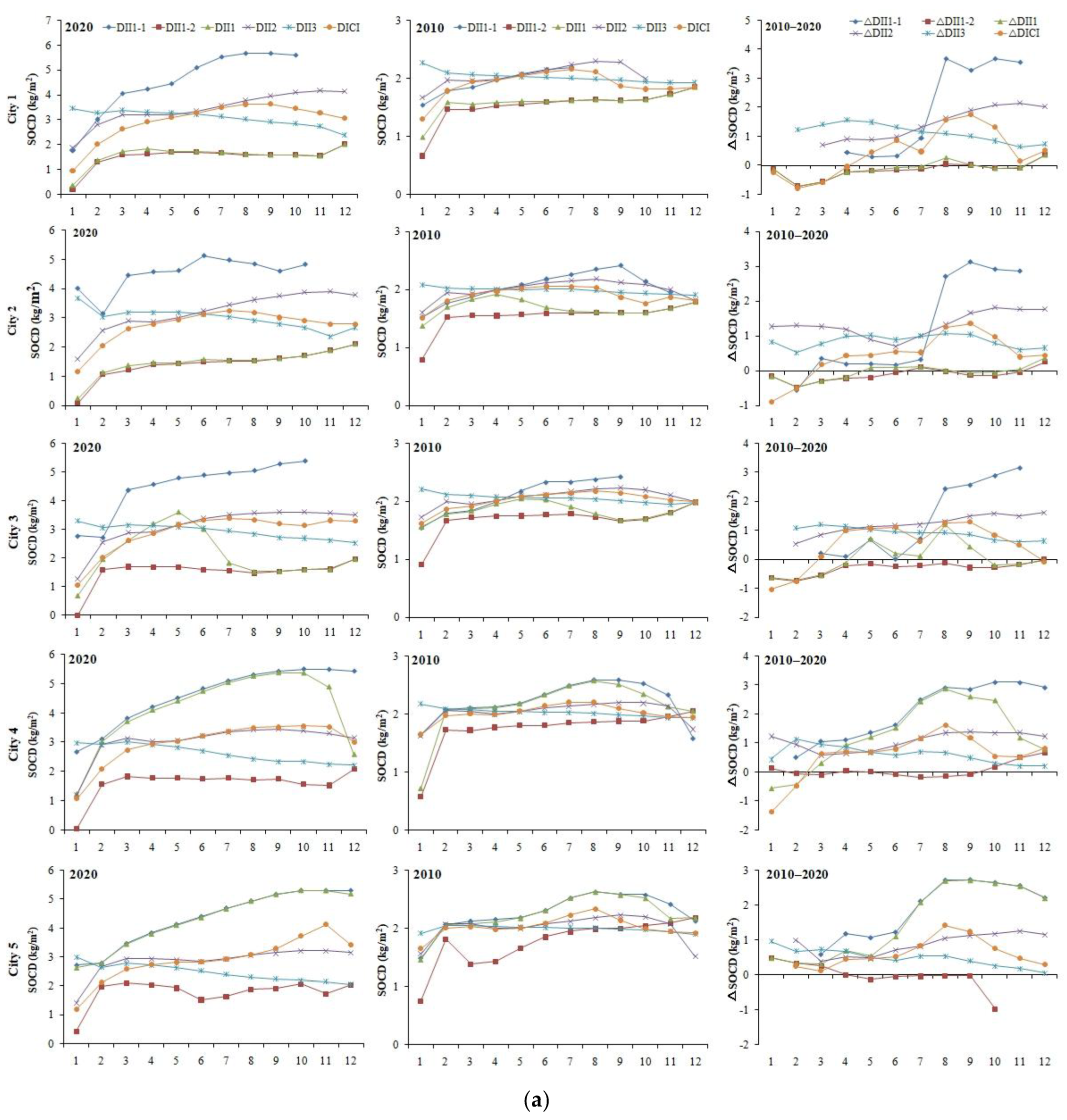

| Region | 2020 | 2010 | 2010–2020 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DA1-1 | DA1-2 | DA2 | DA3 | DA1-1 | DA1-2 | DA2 | DA3 | DA1-1 | DA1-2 | DA2 | DA3 | |
| % | % | % | % | % | % | % | % | % | % | % | % | |
| EA | 30.02 + | 10.35 − | 44.73 + | 14.90 − | 22.18 + | 12.83 − | 55.43 + | 9.56 − | 43.53 + | 1.59 + | 40.87 + | 14.01 − |
| City 1 | 2.33 + | 11.64 − | 84.87 + | 1.15 + | 1.07 + | 5.70 − | 89.36 + | 3.87 + | 5.39 + | 7.01 + | 80.57 + | 7.04 − |
| City 2 | 3.22 + | 10.01 − | 83.90 + | 2.86 + | 10.65 + | 20.82 − | 61.32 + | 7.20 + | 13.70 + | 11.65 + | 72.89 + | 1.76 + |
| City 3 | 8.81 + | 14.35 − | 71.24 + | 5.60 − | 0.50 − | 8.18 − | 88.50 + | 2.82 − | 25.29 + | 4.29 − | 56.40 + | 14.02 − |
| City 4 | 47.69 + | 6.19 − | 19.43 + | 26.69 − | 48.23 + | 3.98 − | 31.49 + | 16.31 − | 49.48 + | 1.89 − | 33.52 + | 15.11 − |
| City 5 | 54.82 + | 2.14 − | 18.71 + | 24.33 − | 61.97 + | 3.06 − | 21.03 + | 13.94 − | 60.26 + | 3.13 + | 26.30 + | 10.30 − |
| City 6 | 33.37 + | 5.92 − | 36.13 + | 24.58 − | 40.68 + | 1.10 − | 37.34 + | 20.88 − | 13.84 + | 3.83 − | 61.80 + | 20.53 − |
| City 7 | 48.59 + | 5.75 − | 20.54 + | 25.11 − | 38.58 + | 1.56 − | 46.01 + | 13.85 − | 66.57 + | 7.63 − | 0.27 + | 25.53 − |
| City 8 | 23.19 + | 10.32 − | 49.15 + | 17.34 − | 14.21 + | 3.35 − | 64.89 + | 17.55 − | 32.97 + | 13.54 − | 33.67 + | 19.81 − |
| City 9 | 20.90 + | 10.22 − | 58.38 + | 10.51 − | 0.74 − | 18.28 − | 67.45 + | 13.52 − | 60.80 + | 6.62 + | 6.31 − | 26.27 − |
| City 10 | 7.49 + | 14.71 − | 55.80 + | 22.00 − | 0.33 − | 23.99 − | 57.09 + | 18.60 − | 17.22 + | 7.92 + | 49.32 + | 25.54 − |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xing, W.; Chi, Y.; Zhang, Z. Land Spatial Development Intensity and Its Ecological Effect on Soil Carbon Sinks in Large-Scale Coastal Areas. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 1197. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17071197
Xing W, Chi Y, Zhang Z. Land Spatial Development Intensity and Its Ecological Effect on Soil Carbon Sinks in Large-Scale Coastal Areas. Remote Sensing. 2025; 17(7):1197. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17071197
Chicago/Turabian StyleXing, Wenxiu, Yuan Chi, and Zhiwei Zhang. 2025. "Land Spatial Development Intensity and Its Ecological Effect on Soil Carbon Sinks in Large-Scale Coastal Areas" Remote Sensing 17, no. 7: 1197. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17071197
APA StyleXing, W., Chi, Y., & Zhang, Z. (2025). Land Spatial Development Intensity and Its Ecological Effect on Soil Carbon Sinks in Large-Scale Coastal Areas. Remote Sensing, 17(7), 1197. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17071197







