Abstract
Lake water is a crucial resource in the global hydrological cycle, providing substantial freshwater resources and regulating regional climates. High-resolution remote sensing satellites, such as Landsat, provide unprecedented opportunities for the continuous monitoring of lake area changes. However, limitations imposed by revisit cycles and cloud cover often result in only a few usable images being taken per month for a single lake, restricting our understanding of daily-scale lake dynamics. Leveraging recent advancements in AI-driven remote sensing technologies, we developed an innovative deep learning algorithm, MosaicFormer, a Transformer-based model designed for spatiotemporal fusion across diverse remote sensing applications. We used it to integrate observations from MODIS and Landsat, producing seamless daily Landsat-scale images. To demonstrate its effectiveness, we applied the model to lake monitoring, showcasing its ability to reconstruct high-resolution water body dynamics with limited Landsat data. This approach combines Masked Autoencoders (MAEs) with the Swin Transformer architecture, effectively capturing latent relationships between images. Testing on public benchmarks demonstrated that our method outperforms all traditional approaches, achieving robust data fusion with an overall R2 of 0.77. A case study on lake water monitoring reveals that our method captures daily variations in the surface area of Hala Lake, providing accurate and robust results. The results indicate that our method demonstrates significant advantages and holds substantial potential for large-scale remote sensing-based environmental monitoring.
1. Introduction
Lakes play a crucial role in freshwater systems, providing essential services such as water supply, flood control, disaster mitigation, and ecological security [1]. Additionally, they serve as indicators of regional environmental changes, help regulate local climates, and support biodiversity and ecosystems. In arid and semi-arid regions, lakes are particularly significant as indicators of regional climatic changes and as essential resources for human survival, as well as economic and social development [2]. Changes in lake area are closely linked to global climate and environmental variations [3]. However, due to the combined effects of climate change and human interventions, many lakes have undergone significant transformations, with several studies highlighting reductions in lake area and water volume [4]. Consequently, monitoring lake dynamics has become increasingly important. Advances in remote sensing (RS) and geographic information technologies (GIS and GPS) now offer effective tools for monitoring changes in lake water bodies across large spatial areas [5,6].
Rapid changes in inland water bodies demand high spatial and temporal resolution from sensors to effectively monitor and analyze lake dynamics. Some high-resolution optical satellite time series data, offering both fine spatial and temporal detail, are crucial for the accurate modeling and monitoring of the dynamics of surface water bodies. However, a significant challenge arises from the inherent tradeoff between spatial resolution and temporal revisit rates, which limits the ability of satellites to capture the Earth’s surface at high spatiotemporal resolution [7]. For instance, the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS), a widely used sensor, offers images with resolutions ranging from 250 m to 1000 m. While its resolution may not be adequate for the precise mapping of water bodies, MODIS provides daily image coverage. In contrast, Landsat, which has the longest continuous space-based observation data since the 1970s, delivers images with a spatial resolution of 30 m [8]. However, its 16-day revisit cycle and frequent cloud cover limit its effectiveness for capturing rapid changes in surface water change [9]. Continuous daily-scale observations are crucial for lake monitoring, as they provide critical insights into hydrological processes and improve our understanding of the local water cycle. To overcome the challenge of limited temporal resolution, Landsat, known for its high spatial resolution but low temporal resolution, must be integrated with MODIS. This integration facilitates the generation of high-resolution, temporally continuous daily images.
To address this issue, previous research has proposed spatiotemporal fusion (STF) methods for improving spatiotemporal resolution. These techniques combine high-spatial-resolution images, which are often temporally sparse, with low-spatial-resolution images, captured more frequently, to obtain more accurate and detailed information on water body dynamics. Typically, STF approaches are categorized into four main approaches: spatiotemporal weighting function methods, such as the spatial and temporal adaptive reflectance fusion model (STARFM) [7]; wavelet transformation [10,11]; unmixing-based data fusion [12]; sparse representation [13,14]; and machine learning methods [15]. Specifically, STF is employed to generate multispectral images that resemble Landsat data, which are then analyzed using various classification algorithms—unsupervised, supervised, or object-based—to create surface water maps [16,17,18,19,20]. The STF algorithm combines the advantages of various sensors to reconstruct high-quality image time series, addressing the issue of image loss due to data limitations [21]. One of the earliest methods developed for this purpose is the Spatio-Temporal Adaptive Reflectance Fusion Model (STARFM) [7], which is likely the most widely used algorithm for generating synthetic surface reflectance. This method is favored for its ability to achieve both high spatial and temporal resolutions, particularly due to its reliable prediction performance [22]. The STARFM algorithm identifies similar neighborhoods for the target pixel and makes predictions by weighing these neighborhoods according to their spatial, spectral, and temporal proximity while disregarding the mixture and changes in land cover types within coarse-resolution pixels. However, STARFM encounters several limitations. First, it struggles with abnormal scenarios involving land cover-type changes or disturbance events not captured in a single Landsat image. Second, it is less effective in making predictions in heterogeneous landscapes [23]. Subsequently, numerous studies have suggested improvements to the STARFM algorithm, leading to the development of various modified versions of the model. Hilker et al. [24] introduced the Spatial and Temporal Adaptive Algorithm for Reflectance Change Mapping (STAARCH), which utilizes a dense set of MODIS data to identify temporal variations to improve STARFM, enhancing the level of detail in the generated synthetic Landsat images. However, the STAARCH neither specifically investigates the impact of cloud shadows on surface reflectance nor allows for the detection or monitoring of individual disturbance events. ESTARFM, proposed by Zhu et al. [25], introduced several enhancements to the original STARFM algorithm, with the most notable being the use of a conversion coefficient to improve prediction accuracy in heterogeneous landscapes. Wang, Liu, Li, He, and Zheng [5] employed ESTARFM to fuse Landsat and MODIS images for extracting lake water bodies and analyzing the relationship between lake water level changes over the past two decades. Similarly, Dao, Mong, and Chan [17] applied ESTARFM to generate cloudless Landsat/MODIS composite data, which were used to delineate inundation areas during flood events. Nevertheless, ESTARFM needs the manual selection of cloud-free image pairs, limiting its use for dense time series generation. Additionally, Li, et al. [26] proposed the STSWM method, which integrates surface water occurrence (SWO) and a digital elevation model (DEM) to provide topographic information above and below the water surface. This approach, combined with MODIS/Landsat image pairs, produces surface water maps with 30 m spatial resolution, which can be used to effectively detect surface water changes due to cloud cover and data-deficient areas. Despite this, in the STSWM method, the higher the percentage of cloud and shadow areas in MODIS scenes, the lower the accuracy of STSWM maps. Table 1 summarizes some image fusion methods and information from 2006.

Table 1.
Summary of recent remote sensing data fusion methods. (N/A: not performed; √: performed).
With the increasing popularity of deep learning (DL) in recent years, learning-based STF methods have emerged. Deep learning techniques, with their ability to automatically learn and extract features, have been widely applied to water body extraction, surpassing the accuracy of traditional machine learning-based and threshold-based approaches, particularly in high-resolution imagery [33,34,35,36,37]. Notably, convolutional neural network (CNN) [38], generative adversarial network (GAN) [39], Swin Transformer [40], and other state-of-the-art DL network architectures continue to emerge [41,42], facilitating the continuous improvement in water body extraction methods and providing unprecedented opportunities for remote sensing image fusion.
The CNN-based fusion method primarily establishes a nonlinear mapping relationship between inputs and outputs, typically involving feature extraction, feature fusion, and image reconstruction. Song et al. [43] proposed a spatiotemporal fusion method via a deep convolutional neural network (STFDCNN), which was the first deep learning-based spatiotemporal fusion approach. It generates high-resolution target images by integrating a nonlinear mapping convolutional neural network (CNN) with a super-resolution CNN. However, this method fails to predict the missing spatial details in low-spatial-resolution MODIS images. Subsequent research introduced several improved fusion accuracy methods, including the deep convolutional spatiotemporal fusion network (DCSTFN) [44], enhanced deep convolutional spatiotemporal fusion network (EDCSTFN) [45], two-stream CNN (StfNet) [46], and spatiotemporal temperature fusion network (STTFN) [47]. However, all these CNN-based methods train each spectral band independently without considering spectral correlations between bands. To address this limitation, Chen et al. [48] proposed a multi-scale two-stream CNN (STFMCNN) method, integrating multi-scale CNNs and temporal consistency into a unified framework. Additionally, they introduced a local fusion strategy to combine the predictions from both streams. Recently, Ran et al. [49] fully considered the scale differences between data from different sources and proposed a two-stage coarse-to-fine STF approach (SIFnet). This approach effectively utilizes the concept of scale transformation to improve feature extraction and enhance the accuracy of the reconstructed image. Compared with various advanced STF algorithms, the structural similarity of SIFnet improved by an average of 2%, demonstrating the effectiveness of the method. However, these main methods rely on using dual-time auxiliary fine images to achieve more accurate fusion results, which poses significant limitations in practical applications. In image fusion work involving GANs, fusion images are generated primarily through an alternating training method between two neural networks, which feeds all spectral bands into a trainable network. Shang et al. [50] proposed a novel spatiotemporal fusion model using a generative adversarial network (GASTFN). In GASTFN, the end-to-end network (including both the generator and discriminator networks) is trained simultaneously for all frequency bands. The proposed model can be applied to single-pair cases, considering the spectral correlation of each band, and improves the process of generating super-resolution images by employing a discriminator network based on image reflectance values rather than the temporal variation in reflectance. Liu et al. [51] proposed a progressive spatiotemporal attention fusion model (PSTAF-GAN) based on a generative adversarial network with a multi-band training approach. Specifically, a flexible multi-scale feature extraction architecture was designed to capture multi-scale feature hierarchies, and spatiotemporal variations were then computed within different feature hierarchies. The quantitative and qualitative experimental results on two publicly available benchmark datasets demonstrate that the proposed PSTAF-GAN achieves superior performance compared to state-of-the-art methods. More recently, Filali Boubrahimi et al. [52] proposed Hydro-GAN, a novel deep learning approach that improves boundary accuracy when mapping low-resolution MODIS data to high-resolution Landsat-8 images, thereby enhancing the accuracy of generating water body polygons. They proposed a novel unsaturated loss function for the Hydro-GAN generator, which maximizes the logarithm of the discriminator’s probability to promote stable updates and aid convergence. Moreover, recent Transformer-based approaches have gained significant attention in the fields of remote sensing and spatiotemporal fusion. Compared with CNNs with multi-scale skip connections and the ability to extract features at multiple hierarchical levels, the primary goal of Transformers is to mitigate the local perception limitations of CNNs by capturing global dependencies and establishing more abstract nonlinear relationships [53]. Therefore, the integration of Transformer models and multi-scale CNNs has potential for further investigation and exploration [54]. Chen et al. [55] proposed a spatiotemporal fusion model (SwinSTFM) that generates high-quality images by integrating the Swin Transformer with the linear spectral mixing theory. Despite its performance improvements, this method requires a large number of parameters and faces challenges in obtaining image pairs without registration errors in practical applications, necessitating further improvements in the future. Luo et al. [56] introduced a Laplacian Pyramid Hybrid (LapH) network, which leverages the advantages of both CNN and Transformer architectures for multimodal image fusion tasks. Zhao et al. [57] proposed the Transformer-based universal fusion (TUFusion) algorithm, which employs a Transformer/CNN encoder architecture and a fusion strategy based on a composite attention module. This approach enables multi-source images to retain more details by integrating global and local features. However, for specific fusion tasks, TUFusion may not outperform specialized fusion algorithms. Zhang et al. [58] introduced a Swin local/global feature extractor in the image enhancement module to integrate both local and long-range dependency features from different source images, allowing for the exploration of potential color and detail features in visible images. In these studies, due to the lack of ground truth (GT) in fusion tasks, existing Transformer-based fusion methods still rely on loss functions with multiple constraints to preserve the intrinsic characteristics of source images. However, hyperparameters are essential for balancing various losses in constraint-based loss functions. Different fusion tasks may require different hyperparameter settings, and while a specific balance coefficient may yield better results for one task, achieving optimal fusion performance across different tasks remains a challenge.
To more effectively and efficiently obtain satellite images with high spatial and temporal resolution for monitoring dynamic changes in lakes, this study leverages the capabilities of a novel Transformer-based deep learning model and the innovative concept of Masked Autoencoders (MAEs), a self-supervised learning framework designed for feature extraction and representation learning in deep learning models, to advance remote sensing data fusion, proposing a new model named MosaicFormer. The MAE’s random masking strategy improves the model’s ability to reconstruct high-resolution details by learning spatial dependencies from incomplete observations, while its hierarchical structure enhances feature extraction efficiency, reducing computational costs without compromising fine-grained details. Furthermore, the MAE’s concept of the random masking of low-frequency information is particularly suitable for image fusion tasks. In such tasks, coarse-resolution input images often contain significant redundancy in pixels and information. The “less is more” approach of MAEs aligns well with this challenge, making them highly effective for image fusion. Consequently, we innovatively incorporate this process into the proposed model. This work represents the first integration of MAEs with Swin Transformers for remote sensing image fusion. We introduce a novel concept, “less is more”, which involves the random masking of low-frequency information during the encoding phase using MAEs. While this approach may seem counterintuitive, especially for tasks requiring precise temporal variations, it effectively guides the neural network to prioritize learning higher-frequency features, improving the efficiency of image super-resolution tasks. By discarding low-frequency information, the network focuses on reconstructing fine-grained details, which is crucial for remote sensing applications where high-resolution images are needed to monitor dynamic changes in water bodies [59,60]. Tests on publicly available image fusion benchmarks demonstrate that our method surpasses all traditional and commonly used deep learning approaches. Furthermore, a case study on lake surface area monitoring highlights the method’s potential for applications in hydrology and large-scale remote sensing-based ecological monitoring. Spatiotemporal fusion plays a crucial role in enhancing the temporal resolution of high-resolution satellite imagery by integrating frequent low-resolution observations. This technique is essential in remote sensing for accurately monitoring environmental changes across diverse landscapes. While this model was used in the context of lake monitoring, its design is versatile and adaptable to various remote sensing applications, including vegetation dynamics, land cover changes, and urban expansion.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data
Landsat and MODIS remote sensing data were fused to achieve enhanced image resolution and temporal coverage. The high-resolution dataset comprises Landsat-8 OLI images with a spatial resolution of 30 m and six spectral bands, including the blue band (0.45–0.51 μm), the green band (0.53–0.59 μm), the red band (0.64–0.67 μm), the near-infrared band (0.85–0.88 μm), the short-wave infrared-1 band (1.57–1.65 μm), and the short-wave infrared-2 band (2.11–2.29 μm). The coarse-resolution dataset consists of MODIS09GA images with a spatial resolution of 500 m. The bands from MODIS images were selected and reordered to align with the corresponding Landsat bands for data fusion. During both the testing phase and the lake application stage, the same data sources were utilized, maintaining consistent band selection but varying image sizes and regions. Table 2 provides a detailed summary of the benchmark dataset and the lake water dataset.

Table 2.
Summary of two remote sensing datasets in this study.
2.2. Model Design
Our MosaicFormer model draws inspiration from integrating MAEs with the Swin-Transformer. While the Swin Transformer has been previously applied to spatiotemporal fusion [55], our approach introduces a novel integration of Masked Autoencoders (MAEs) with Swin Transformers. This combination leverages MAEs’ ability to focus the model on higher-frequency spatial features by randomly masking low-frequency information, thereby improving feature extraction and enhancing the accuracy of spatiotemporal fusion. This addition significantly differentiates our method from previous work, where MAEs were not utilized. The structure of the model is illustrated in Figure 1. It comprises an encoder section that incorporates an improved MAE encoder and a Vector Quantized Variational Autoencoder (VQ-VAE) encoder. The MAE encoder processes input images by encoding them into tokens and randomly masking certain windows, as shown in Figure 1a. The MAE encoder was specifically improved for remote sensing tasks by modifying the masking strategy to preserve important temporal features while enhancing the model’s focus on higher-frequency spatial details. This modification allows the model to better capture both temporal and spatial variations, which are crucial for accurate spatiotemporal fusion. Additionally, we employed pretrained weights for the MAE encoder, which were fine-tuned on remote sensing datasets to help the model learn more generalized features before applying it to our specific fusion tasks. Subsequently, the VQ-VAE encoder maps these tokens into a high-dimensional latent space. The MAE encoder and VQ-VAE work in tandem to encode input images. The MAE encoder masks certain regions of the image to focus the model on learning more discriminative features, while the VQ-VAE encoder maps the encoded information into a high-dimensional latent space. This combination enables the model to more effectively capture spatial and temporal dependencies, providing more accurate fusion results. While the MosaicFormer model’s design was evaluated using lake water monitoring data, its architecture is inherently flexible and adaptable to a wide range of spatiotemporal fusion tasks. The feature extraction and temporal modeling strategies utilized in the MAE encoder and Swin Transformer were designed to enable generalization across various environmental scenarios. Although certain modifications were implemented to improve the model’s ability to capture dynamic water body changes, these enhancements are not exclusive to lake monitoring. MosaicFormer’s modular design allows it to be readily adapted for other applications such as vegetation monitoring, land cover change detection, and urban expansion analysis. This flexibility ensures that the model maintains robust performance across diverse remote sensing tasks.
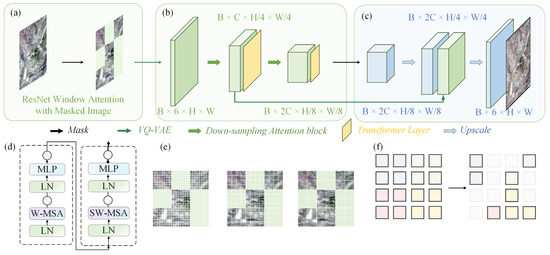
Figure 1.
Model structure of MosaicFormer. (a) The MAE stage within the encoder, showing ResNet window attention with masked image input. (b) Main structure of the Swin-Transformer in the downscaling path. (c) Main structure of the Swin-Transformer in the upscaling path. (d) Detailed architecture of the Swin-Transformer blocks, comparing standard Window Multi-head Self-Attention (W-MSA) with Shifted Window Multi-head Self-Attention (SW-MSA), both containing Layer Normalization (LN) and Multi-Layer Perceptron (MLP) components. (e) Conceptual visualization of the Swin-Transformer’s windowed attention mechanism across different scales. (f) Conceptual illustration of the MAE.
The input image dimensions are B × 6 × H × W (batch × band × height × width). After processing through the VQ-VAE encoder, the image is divided into fixed-size patches, and the channel number C is converted to 64. A 4 × 4 convolution kernel with no overlapping regions is applied, using a stride of 4. Following the encoding stage, the model applies the Swin Transformer with an integrated MAE. During this phase, a standard Swin Transformer block processes the masked windows. In the Window Multi-head Self-Attention (W-MSA) and Shifted Window Multi-Head Self-Attention (SW-MSA) stages, attention is calculated within individual patches and across sliding windows to capture inter-window relationships. The attention mechanism employed follows the framework proposed by Vaswani et al. [61], which operates by transforming the input patch matrix Y into a query matrix (), a key matrix (), and a value matrix (), where h = 1, …, H denotes H parallel attention heads. The parameters , , and are learnable. The attention output Oh is calculated as the dot product of the query and key matrices, scaled and weighted by the value matrix, as follows:
where M is an adjustment parameter utilized to filter out rightward attention, and dk is the dimensionality of the key vectors. Subsequently, Oh values are directed to a linear layer following the attention output. Following the encoding and processing stages, the data undergo an upscaling phase to restore their original resolution. This stage resembles the structure of a U-Net, incorporating skip connections to retain detailed spatial information from earlier layers. After applying the skip connections, the data dimensions become B × 128 × H/4 × W/4. Subsequently, the model utilizes the VQ-VAE decoder to reconstruct the data back to their original resolution, resulting in an output with dimensions B × 6 × H × W. Figure 1d illustrates the structure of the Swin Transformer, while Figure 1e presents the integration of an MAE with the Swin Transformer. Additionally, Figure 1f provides a visual representation of the masked window concept, showcasing how the model leverages masked regions for efficient learning and reconstruction.
2.3. Training and Evaluation Strategy
The MosaicFormer model processes data in batches (B = 1), with each batch consisting of six bands as three-dimensional input. The high-resolution Landsat remote sensing images from the same region serve as the target output for training. The benchmark dataset comprises a total of 27 image pairs (27 input MODIS images and 27 corresponding Landsat target images). These images are organized in chronological order, with the first 21 pairs allocated for training, the next 3 pairs for validation, and the final 3 pairs for testing. This division results in a training, validation, and testing set ratio of approximately 8:1:1. All evaluation results are reported exclusively on the testing set. For the lake monitoring data, the same splitting strategy as the used for the benchmark dataset is applied.
To train the model efficiently and ensure a fair comparison, the primary evaluation metric used is the Mean Squared Error (MSE). This metric assesses the model’s overall capability in accurate data fusion without emphasizing specific bands, including the three bands commonly visualized. The loss function used for evaluation is defined as follows:
In this context, and represent the actual and predicted values of the remote sensing images, respectively. The loss function Lfmse is designed to quantify the model’s ability to recover fine-resolution images effectively. Model optimization is performed using the Adam optimization algorithm, with an initial learning rate of 1.0 × 10−4. A cosine decay strategy is employed to adjust the learning rate dynamically during training. The training process is conducted on a high-performance H800 GPU with 80 GB of memory, offering substantial computational capacity to manage the billions of parameters in the Swin Transformer architecture.
We assessed two metrics, the Root Mean Square Error (RMSE) and Determination score (R2), defined as follows:
where is the mean of the actual values Xi. The R2 score reflects how well the model explains the variance in the data, with values closer to 1 indicating better performance.
To evaluate the MosaicFormer model’s performance, we define improvement as an increasing R2 percentage from benchmark data. For a comprehensive comparison with the benchmark, we also examine recently widely tested and outperformed super-resolution models: SwinIR [62], SRGAN [63], and ROSTF [64]. SwinIR is based on the Swin Transformer architecture, which utilizes a hierarchical Transformer framework with shifted windows to model local and global dependencies efficiently. It excels in high-resolution image restoration tasks by combining advanced attention mechanisms and multi-scale feature representation. In contrast, SRGAN operates within a generative adversarial network (GAN) framework, where a generator creates high-resolution images from low-resolution inputs, and a discriminator ensures the realism of the images by distinguishing between real and generated ones. ROSTF is a robust optimization-based framework for spatiotemporal fusion, designed to handle noise and missing data. It combines high-resolution image restoration with temporal fusion through a constrained convex optimization approach, demonstrating superior performance, particularly in noisy scenarios. ROSTF is also used to perform spatial comparisons with the fusion results from MosaicFormer to evaluate the improvements in spatial detail reconstruction.
3. Results
3.1. Evaluation of Benchmark Dataset
Our implementation of MosaicFormer on the benchmark test dataset allows for a comprehensive comparison with the latest models and the benchmark data. Figure 2 illustrates the validation results and overall prediction accuracy across different bands. In Figure 2a, a bar chart compares the performance of MosaicFormer (white), SwinIR (pink), SRGAN (dark yellow), ROSTF (light purple), and the benchmark method (yellow) across four spectral bands. MosaicFormer consistently demonstrates the highest prediction accuracy in all bands, with R2 values of 0.774, 0.782, 0.807, and 0.695 across Bands 1 to 4, respectively, indicating its superiority in maintaining spatial and spectral details. Compared with the next best-performing model (SwinIR), MosaicFormer shows an improvement of 3.7% in Band 1, 3.0% in Band 2, 0.9% in Band 3, and 1.3% in Band 4. Compared with the benchmark method, the improvement is even more significant, with an increase of 30.8%, 17.2%, 16.6%, and 5.1% in Bands 1 to 4, respectively. These results indicate MosaicFormer’s superiority in maintaining spatial and spectral details. In Figure 2b, a scatter density plot shows the correlation between the predicted values and ground truth for different bands. With an R2 value of 0.767 and a low RMSE of 3.549, MosaicFormer’s performance can be validated, confirming its effectiveness in generating high-resolution predictions. The blue lines represent the 95% prediction confidence intervals, with the majority of the data points falling within this range. MosaicFormer closely aligns with the 1:1 line, indicating a strong agreement between the predicted and actual values.
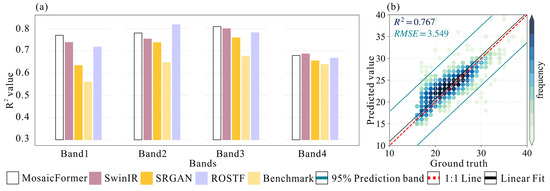
Figure 2.
Comparison and validation stage. (a) Comparison with benchmark (yellow) and widely tested and outperformed super-resolution models, SwinIR (pink), SRGAN (dark yellow), and ROSTF (light purple). (b) Scatter density diagrams and prediction accuracy with different image band versus Landsat ground truth. Blue line represents 95% confidence intervals (upper and lower whiskers) of R2 and RMSE, the red dashed line represents the 1:1 line, and the black line denotes the linear fit.
These results demonstrate that MosaicFormer outperforms both traditional methods and advanced models such as SwinIR, SRGAN, and ROSTF in terms of pixel-level accuracy and overall performance consistency. With R2 improvements of up to 30.8 percentage points for Band 1 over the benchmark model, MosaicFormer underscores its capability in high-precision spatiotemporal data fusion.
3.2. Spatial Fusion Map
We then compare the spatial fusion map results with the ground truth ones. Figure 3 illustrates the results of the spatial fusion process, comparing the generated high-resolution image with the ground truth one. Figure 3a presents the low-resolution MODIS image, which serves as the initial input for the spatial fusion process. Although it provides frequent temporal coverage, its relatively low spatial resolution (500 m) limits the precision of spatial features. Figure 3b shows the high-resolution image produced by the pretrained AI model, MosaicFormer. This high-resolution output, with a spatial resolution of 30 m, clearly illustrates the model’s capability to reconstruct fine spatial details. The image generated by MosaicFormer enhances features like surface water boundaries, landforms, and other small-scale environmental elements that are not discernible in the low-resolution input. We can see that Figure 3c displays the ground truth Landsat image, which serves as the target high-resolution data for comparison. The accuracy of the generated image is evident when we compare it with the Landsat image; the super-resolved details in Figure 3b closely align with the ground truth, validating the performance of the MosaicFormer model. This comparison emphasizes the model’s ability to effectively capture small-scale features that are crucial for high-precision monitoring in remote sensing applications. With reference to Figure 3e,f, they provide detailed examples that further showcase the performance of the MosaicFormer model in generating super-resolution results, demonstrating the superior performance of the AI model in tasks such as water body monitoring and land cover classification.
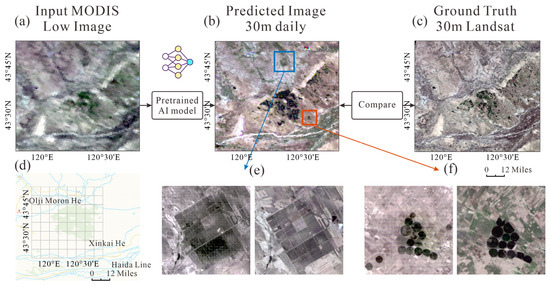
Figure 3.
The spatial fusion map results compared with the ground truth. (a) The input low-resolution MODIS image used as the initial input for the spatial fusion process. (b) The high-resolution image generated by the pretrained AI model, MosaicFormer, showcasing its ability to produce fine spatial details. (c) The ground truth Landsat image, representing the target high-resolution data for comparison. (d) The benchmark dataset location, indicating the specific region used for testing and evaluation. (e,f) Two detailed examples highlighting the predicted results.
The results in Figure 3 provide compelling evidence that the MosaicFormer model significantly improves spatial resolution compared to the low-resolution MODIS input. The fusion process not only recovers finer details but also enhances the overall quality of the spatial data, making it more suitable for applications that require high-resolution, temporally continuous satellite images.
To further evaluate the effectiveness of our proposed method, we also conducted a comparison with a recently published spatiotemporal fusion method, ROSTF. Figure S3 in the Supplementary Materials shows the results of comparing our model, MosaicFormer, with ROSTF. Our method demonstrates significant advantages in reconstructing high-resolution details, particularly in complex terrains where our model can more accurately recover fine spatial details. This comparison highlights the superior performance of MosaicFormer in spatiotemporal fusion tasks, where the accurate recovery of temporal and spatial information is crucial.
3.3. Application in Lake Area
A simple regional application case is presented using our MosaicFormer model. Hala Lake (97°24′–97°47′E, 38°12′–38°25′N) is the third largest lake in Qinghai Province, located in Qinghai Province on the Tibetan Plateau within the Qilian Mountains, and it is a representative case of a hydrological area with limited or no observational data. The absence of hydrological and meteorological stations, coupled with the scarcity of observed data, highlights the critical need for hydrological research in this data-deficient region.
In this case study of Hala Lake, the low-resolution MODIS image (Figure 4a) serves as a starting point, but its coarse resolution (500 m) is insufficient for capturing the fine spatial details necessary for the accurate monitoring of lake dynamics. However, the high-resolution output generated by the MosaicFormer model (Figure 4b) demonstrates a clear improvement, revealing enhanced spatial details such as the precise boundaries of the water body and the surrounding landforms. This leap in spatial resolution—30 m from 500 m—shows the potential of leveraging AI-driven models for image super-resolution, which is a crucial capability for monitoring rapidly changing environments like lakes.
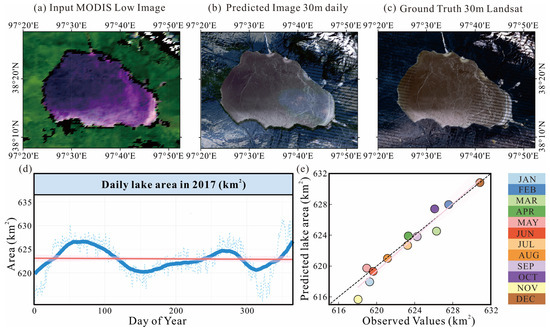
Figure 4.
A simple regional application case is lake water tracking. (a) The input low-resolution MODIS image in Hala Lake. (b) The high-resolution image generated by the pretrained AI model, MosaicFormer. (c) The ground truth Landsat image. (d) The daily high-resolution images produced by MosaicFormer, with water surface areas extracted using the Otsu algorithm. The red line is the trend, the blue line is the true value, and solid line is the smooth value (e) A comparison of monthly water surface areas for 2017, derived from true Landsat observations and the MosaicFormer-generated results, showcasing the model’s accuracy in replicating observed variations.
Another significant aspect of the model’s performance is its robustness in producing reliable high-resolution images from a combination of high-frequency input data (MODIS) and low-frequency high-resolution images (Landsat). Unlike conventional methods that may struggle with inconsistent temporal data or high variability in the landscape, MosaicFormer excels by learning spatial–temporal dependencies from a sequence of images. This ability to capture complex spatiotemporal patterns allows the model to create continuous, accurate daily-scale observations, which are crucial for understanding short-term dynamics like seasonal water fluctuations and anomalies due to climatic or environmental changes. The comparison between the MosaicFormer-generated high-resolution images and the ground truth Landsat data (Figure 4c) highlights the model’s effectiveness in mimicking observed spatial structures. More importantly, the daily high-resolution images (Figure 4d) generated for Hala Lake demonstrate how the model enables the continuous, real-time monitoring of lake dynamics. This capability is particularly critical for regions with sparse or non-existent in situ data, where satellite observations are the primary data source.
Furthermore, the comparison of monthly water surface areas (Figure 4e) between the true Landsat observations and the MosaicFormer-generated results reveals that the model captures the seasonal and short-term variations with remarkable accuracy. These capabilities go beyond traditional approaches by offering both spatial and temporal resolution, filling a significant gap in hydrological studies where data are often limited by either the spatial resolution or frequency of observations.
MosaicFormer, by providing a seamless integration of MODIS and Landsat data, thus bridges the gap between high spatial resolution and high temporal frequency, offering a promising solution for remote sensing-based environmental monitoring.
4. Discussion
4.1. Ablation Studies
In this study, we introduced the MosaicFormer model, which incorporates a Masked Autoencoders (MAE) and the Swin Transformer for spatiotemporal fusion. To assess the impact of different components on the model’s performance, we conducted ablation studies that systematically removed key modules, such as the MAE architecture and VQ-VAE encoder.
The results of the ablation experiments (shown in Figure S2, Supplementary Materials) demonstrate the pivotal role that the MAE module plays in enhancing the model’s ability to reconstruct finer spatial and temporal details. The removal of the MAE significantly increased the error, resulting in a performance drop of approximately 5.1%. This underscores the importance of the MAE in improving fusion accuracy, particularly in regions where high spatiotemporal resolution is essential. Additionally, these findings highlight MosaicFormer’s generalizability, as it performs well in lake monitoring tasks and has the potential for use in other remote sensing applications, such as vegetation monitoring, urban expansion detection, and land cover classification. While the Swin Transformer has been applied in previous spatiotemporal fusion methods (e.g., Chen et al.), MosaicFormer introduces new features that significantly enhance its performance, improving both spatial detail reconstruction and temporal coherence, distinguishing MosaicFormer from existing approaches.
4.2. Comparison with SDC Products
To further validate the performance of MosaicFormer, we conducted a comparison with the Global 30 m Daily Seamless Data Cube (SDC) [65,66]. SDC provides high-frequency remote sensing data on a global scale, making it valuable for large-scale environmental monitoring. However, for more refined regional monitoring, we found that MosaicFormer demonstrated superior spatiotemporal detail preservation and radiometric consistency compared with SDC. As shown in Figure S4 in the Supplementary Materials, our approach performs better in reconstructing water body boundaries and fine spatiotemporal details in the Hala Lake region. Additionally, we observed slight spectral shifts in some areas. In contrast, MosaicFormer maintains better radiometric consistency during multitemporal image fusion. This indicates that MosaicFormer is not only well suited for high spatiotemporal resolution fusion tasks but also offers advantages for fine-scale regional water body monitoring.
However, two key sources of uncertainty need to be considered in the application of MosaicFormer. First, the lack of high-resolution images (i.e., missing Landsat ground truth) poses a significant limitation. In cases where only MODIS images are available, the absence of corresponding Landsat observations prevents effective training, leading to increased uncertainty in predictions. Such missing data scenarios are common due to cloud cover, sensor limitations, and long revisit intervals, making it difficult to ensure continuous high-resolution monitoring.
Second, the time interval between consecutive high-resolution images can affect the model’s ability to capture temporal changes. For instance, in our dataset, the training sequence includes images from 5 January 2017, 10 January 2017, 22 February 2017, and 5 April 2017, where a significant gap occurs between February and April. During this period, lake dynamics may undergo substantial changes that are not well represented in the available training data, reducing the model’s ability to infer intermediate variations. Such temporal gaps introduce challenges in capturing rapid seasonal changes in lake surface area, highlighting a potential limitation of the current approach.
To mitigate these uncertainties, future research may explore the integration of additional data sources, such as Sentinel-2 imagery, which provides higher temporal resolution compared with Landsat. Further advancements in model design, such as incorporating temporal attention mechanisms, may also enhance the ability to predict environmental changes over extended time intervals.
4.3. Challenges in Handling Lake Boundaries with Mixed Pixels
In MODIS data, mixed pixels often occur at lake boundaries, especially when the boundary changes are less distinct. This can lead to the learning of inaccurate features by the model. Our method works effectively in these scenarios, but there are still cases where it may be affected.
Firstly, when the changes in the lake boundary are not obvious (e.g., minor water level fluctuations or no clear desiccation), our model performs well and maintains high accuracy. In these cases, since there is less mixing of water and surrounding land cover at the boundary, the model can learn effective spatial features more easily. However, when the lake boundary undergoes significant changes (such as desiccation, overflow, or substantial morphological changes), the impact of mixed pixels increases, and the model might be more susceptible to interference. In these cases, our method could benefit from further optimization, potentially by incorporating additional high-resolution data or by introducing more robust boundary adaptation mechanisms.
Overall, while our method performs well in handling lake boundaries, additional strategies are needed to ensure robustness in regions with more dynamic boundary changes.
4.4. Application in Other Regions and Data Fusion
There are several aspects that warrant further exploration. While the model performs well in regions with relatively consistent landscapes, its performance may degrade in highly heterogeneous environments where land cover types change rapidly. In these areas, MosaicFormer may face challenges in accurately predicting water bodies, as the relationships between MODIS and Landsat images become more complex. However, integrating additional data sources, such as Sentinel-2 or higher-frequency MODIS data, can potentially address these challenges and improve the model’s ability to handle complex land cover changes. Future improvements in the model architecture and data fusion strategies will be crucial for enhancing its robustness in dynamic environments.
Another limitation of this study is the relatively small number of training images, which increases the risk of overfitting. The model may perform well on the training dataset but struggle to be generalized to unseen data. To overcome this, future research should focus on expanding the training dataset by incorporating a broader range of geographical areas, including diverse environmental conditions. Additionally, employing data augmentation techniques could further enhance the model’s robustness and generalization ability.
Looking ahead, future research could aim to improve the model’s adaptability to diverse geographical and environmental conditions. Incorporating advanced machine learning techniques, such as attention mechanisms or reinforcement learning, could refine the model’s capacity to handle complex spatiotemporal patterns. These advancements could also improve the model’s ability to predict extreme events, such as floods or droughts, which are essential for effective water resource management and disaster preparedness.
5. Conclusions
This study introduces MosaicFormer, a model integrating MODIS and Landsat data for effective lake water monitoring. By combining MODIS’s daily coverage with Landsat’s high spatial resolution, MosaicFormer overcomes the limitations of each sensor, providing continuous daily observations at 30 m resolution—significantly finer than MODIS’s 500 m. On the benchmark dataset, MosaicFormer achieved an R2 of 0.767 and RMSE of 3.549 for Hala Lake, demonstrating its ability to capture spatiotemporal variations in water surface area. The model’s daily-scale observations are particularly valuable in data-sparse regions, enabling the precise tracking of rapid lake dynamics.
MosaicFormer excels in preserving fine-scale spatial details, sharp boundaries, and consistent temporal transitions, outperforming traditional methods in both visual and radiometric accuracy. While ROSTF serves as a useful mechanism-based benchmark, its reliance on constrained optimization limits its ability to capture complex patterns compared to MosaicFormer’s data-driven approach. Future work will expand comparisons to include additional methods (e.g., STARFM, ESTARFM, SwinIR) and address challenges such as overfitting and performance in heterogeneous landscapes. Overall, MosaicFormer shows great potential for large-scale remote sensing applications, advancing water resource monitoring and management.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/rs17071138/s1, Figure S1: Illustration of the four improved 3D-MAE concepts; Figure S2: The ablation study results of the model, where VQ-VAE and MAE are added to the base model (Swin Transformer), ultimately resulting in the MosaicFormer model; Figure S3: Comparison with the ROSTF model. (a) ROSTF model (b) MosaicFormer (c) Landsat Ground Truth; Figure S4: Accuracy comparison between MosaicFormer and SDC product at Hala Lake. Points are randomly selected from the first band, with the y-axis representing the model’s predicted values and the x-axis representing the ground truth values. (a) & (c) Global 30 m daily seamless data cube (SDC) of land surface reflectance. (b) & (d) Land surface reflectance derived from MosaicFormer; Figure S5: Technical workflow diagram of this study. (a) Detailed architecture of the MosaicFormer model. (b) Implementation framework comprising benchmark data extraction, preprocessing protocols, and lacustrine application methodology.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.L. and D.Z.; methodology, D.Z.; formal analysis, D.Z.; visualization, D.Z.; validation, D.Z.; writing—original draft preparation, D.Z.; writing—review and editing, A.L. and D.Z.; supervision, A.L.; project administration and funding acquisition, A.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Science and Technology Department of Qinghai Province (2024ZY029).
Data Availability Statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors on request.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank the editors and anonymous reviewers for their constructive comments and suggestions. Thanks also go to the teams at NASA and Jun Li who have made their datasets available and use for free. Special thanks to Longhao Wang for sharing the model architecture and providing assistance with the implementation code.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| STF | Spatiotemporal fusion |
| DL | Deep learning |
| MAE | Masked Autoencoders |
| VQ-VAE | Vector Quantized Variational Autoencoder |
References
- Liu, Y.; Yang, J.; Chen, Y.; Fang, G.; Li, W. The temporal and spatial variations in lake surface areas in Xinjiang, China. Water 2018, 10, 431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Xu, J.; Zheng, L. Long-Term Change of Lake Water Storage and Its Response to Climate Change for Typical Lakes in Arid Xinjiang, China. Water 2023, 15, 1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamazaki, D.; Trigg, M.A.; Ikeshima, D. Development of a global ~90m water body map using multi-temporal Landsat images. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 171, 337–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, F.; Livneh, B.; Rajagopalan, B.; Wang, J.; Crétaux, J.-F.; Wada, Y.; Berge-Nguyen, M. Satellites reveal widespread decline in global lake water storage. Science 2023, 380, 743–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Liu, X.; Li, W.; He, S.; Zheng, T. Temporal and Spatial Variation Analysis of Lake Area Based on the ESTARFM Model: A Case Study of Qilu Lake in Yunnan Province, China. Water 2023, 15, 1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Dong, L.n.; Wang, L.; Jin, J. Satellite Reveals a Coupling between Forest Displacement and Landscape Fragmentation across the Economic Corridor of the Eurasia Continent. Forests 2024, 15, 1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, G.; Masek, J.; Schwaller, M.; Hall, F. On the blending of the Landsat and MODIS surface reflectance: Predicting daily Landsat surface reflectance. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2006, 44, 2207–2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, D.P.; Wulder, M.A.; Loveland, T.R.; Woodcock, C.E.; Allen, R.G.; Anderson, M.C.; Helder, D.; Irons, J.R.; Johnson, D.M.; Kennedy, R.; et al. Landsat-8: Science and product vision for terrestrial global change research. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 145, 154–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Li, J.; Liu, Y.; Pan, T.; Shi, K.; Cai, X. Synthesizing Landsat images using time series model-fitting methods for China’s coastal areas against sparse and irregular observations. GIScience Remote Sens. 2024, 61, 2421574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malenovský, Z.; Bartholomeus, H.M.; Acerbi-Junior, F.W.; Schopfer, J.T.; Painter, T.H.; Epema, G.F.; Bregt, A.K. Scaling dimensions in spectroscopy of soil and vegetation. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2007, 9, 137–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acerbi-Junior, F.W.; Clevers, J.G.P.W.; Schaepman, M.E. The assessment of multi-sensor image fusion using wavelet transforms for mapping the Brazilian Savanna. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2006, 8, 278–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gevaert, C.M.; García-Haro, F.J. A comparison of STARFM and an unmixing-based algorithm for Landsat and MODIS data fusion. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 156, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Song, H. Spatiotemporal Reflectance Fusion via Sparse Representation. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2012, 50, 3707–3716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Q.; Bioucas-Dias, J.; Dobigeon, N.; Tourneret, J.Y. Hyperspectral and Multispectral Image Fusion Based on a Sparse Representation. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2015, 53, 3658–3668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moosavi, V.; Talebi, A.; Mokhtari, M.H.; Shamsi, S.R.F.; Niazi, Y. A wavelet-artificial intelligence fusion approach (WAIFA) for blending Landsat and MODIS surface temperature. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 169, 243–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Chen, L.; Huang, B.; Michishita, R.; Xu, B. Dynamic monitoring of the Poyang Lake wetland by integrating Landsat and MODIS observations. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2018, 139, 75–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dao, P.D.; Mong, N.T.; Chan, H.-P. Landsat-MODIS image fusion and object-based image analysis for observing flood inundation in a heterogeneous vegetated scene. GISci. Remote Sens. 2019, 56, 1148–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heimhuber, V.; Tulbure, M.G.; Broich, M. Addressing spatio-temporal resolution constraints in Landsat and MODIS-based mapping of large-scale floodplain inundation dynamics. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 211, 307–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Z.; Wang, X.; Chen, B.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Q. Surface water connectivity of seasonal isolated lakes in a dynamic lake-floodplain system. J. Hydrol. 2019, 579, 124154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Zhu, X.; Liu, D. Blending MODIS and Landsat images for urban flood mapping. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2014, 35, 3237–3253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeh, Y.; Zhu, X.; Dunkerley, D.; Walker, J.P.; Zhang, Y.; Rozenstein, O.; Manivasagam, V.S.; Chenu, K. Fusion of Sentinel-2 and PlanetScope time-series data into daily 3 m surface reflectance and wheat LAI monitoring. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2021, 96, 102260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emelyanova, I.V.; McVicar, T.R.; Van Niel, T.G.; Li, L.T.; van Dijk, A.I.J.M. Assessing the accuracy of blending Landsat–MODIS surface reflectances in two landscapes with contrasting spatial and temporal dynamics: A framework for algorithm selection. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 133, 193–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, Y.; He, L.; Chen, J.; Plaza, A. Spatio-temporal fusion for remote sensing data: An overview and new benchmark. Sci. China Inf. Sci. 2020, 63, 140301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilker, T.; Wulder, M.A.; Coops, N.C.; Linke, J.; McDermid, G.; Masek, J.G.; Gao, F.; White, J.C. A new data fusion model for high spatial- and temporal-resolution mapping of forest disturbance based on Landsat and MODIS. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 1613–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Chen, J.; Gao, F.; Chen, X.; Masek, J.G. An enhanced spatial and temporal adaptive reflectance fusion model for complex heterogeneous regions. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 2610–2623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Ling, F.; Foody, G.M.; Boyd, D.S.; Jiang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, P.; Wang, Y.; Chen, R.; Du, Y. Monitoring high spatiotemporal water dynamics by fusing MODIS, Landsat, water occurrence data and DEM. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 265, 112680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, D.P.; Ju, J.; Lewis, P.; Schaaf, C.; Gao, F.; Hansen, M.; Lindquist, E. Multi-temporal MODIS–Landsat data fusion for relative radiometric normalization, gap filling, and prediction of Landsat data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 3112–3130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Helmer, E.H.; Gao, F.; Liu, D.; Chen, J.; Lefsky, M.A. A flexible spatiotemporal method for fusing satellite images with different resolutions. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 172, 165–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Huang, B.; Song, H. A robust adaptive spatial and temporal image fusion model for complex land surface changes. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 208, 42–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Song, H.; Sun, L.; Wu, Z.; Jeon, B. Spatiotemporal Fusion of Satellite Images via Very Deep Convolutional Networks. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Tang, Y.; Tong, X.; Atkinson, P.M. Virtual image pair-based spatio-temporal fusion. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 249, 112009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Guan, K.; Peng, J.; Wang, S.; Huang, Y. STAIR 2.0: A Generic and Automatic Algorithm to Fuse Modis, Landsat, and Sentinel-2 to Generate 10 m, Daily, and Cloud-/Gap-Free Surface Reflectance Product. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, F.; Xia, G.-S.; Hu, J.; Zhang, L. Transferring Deep Convolutional Neural Networks for the Scene Classification of High-Resolution Remote Sensing Imagery. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 14680–14707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Wu, P.; Wang, B.; Park, H.; Yang, H.; Wu, Y. A Deep Learning Method of Water Body Extraction From High Resolution Remote Sensing Images With Multisensors. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2021, 14, 3120–3132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Dang, B.; Zhang, Y.; Du, Z. Water body classification from high-resolution optical remote sensing imagery: Achievements and perspectives. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2022, 187, 306–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, W.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Wang, L.; Huang, X.; Li, J.; Wang, S.; Chen, W.; Li, X.; Feng, R.; et al. A survey of machine learning and deep learning in remote sensing of geological environment: Challenges, advances, and opportunities. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2023, 202, 87–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wu, J.; Li, R.; Song, Y.; Zhou, J.; Rui, X.; Xu, H. A Weight Assignment Algorithm for Incomplete Traffic Information Road Based on Fuzzy Random Forest Method. Symmetry 2021, 13, 1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Meng, X.; Li, X.; Shao, F. Detail Injection-Based Spatio-Temporal Fusion for Remote Sensing Images With Land Cover Changes. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 61, 5401514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Song, Y.; Han, C.; Zhang, L. Remote Sensing Image Spatiotemporal Fusion Using a Generative Adversarial Network. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 59, 4273–4286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Lin, Y.; Cao, Y.; Hu, H.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, S.; Guo, B. Swin transformer: Hierarchical vision transformer using shifted windows. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Virtual, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 10012–10022. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, X.; Leung, L.R.; Chiew, F.H.; AghaKouchak, A.; Ying, K.; Zhang, Y. CAS-Canglong: A skillful 3D Transformer model for sub-seasonal to seasonal global sea surface temperature prediction. arXiv 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, Y. Filling GRACE data gap using an innovative transformer-based deep learning approach. Remote Sens. Environ. 2024, 315, 114465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Liu, Q.; Wang, G.; Hang, R.; Huang, B. Spatiotemporal Satellite Image Fusion Using Deep Convolutional Neural Networks. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2018, 11, 821–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Z.; Yue, P.; Di, L.; Tang, J. Deriving High Spatiotemporal Remote Sensing Images Using Deep Convolutional Network. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Z.; Di, L.; Zhang, M.; Guo, L.; Gao, M. An Enhanced Deep Convolutional Model for Spatiotemporal Image Fusion. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Deng, C.; Chanussot, J.; Hong, D.; Zhao, B. StfNet: A Two-Stream Convolutional Neural Network for Spatiotemporal Image Fusion. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 6552–6564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z.; Wu, P.; Foody, G.M.; Wu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Du, Y.; Ling, F. Spatiotemporal Fusion of Land Surface Temperature Based on a Convolutional Neural Network. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 59, 1808–1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Shi, K.; Ge, Y.; Zhou, Y. Spatiotemporal Remote Sensing Image Fusion Using Multiscale Two-Stream Convolutional Neural Networks. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 4402112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, Q.; Wang, Q.; Zheng, K.; Li, J. Multiscale Attention Spatiotemporal Fusion Model Based on Pyramidal Network Constraints. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2024, 21, 5004305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, C.; Li, X.; Yin, Z.; Li, X.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Du, Y.; Ling, F. Spatiotemporal Reflectance Fusion Using a Generative Adversarial Network. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 5400915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Meng, X.; Shao, F.; Li, S. PSTAF-GAN: Progressive Spatio-Temporal Attention Fusion Method Based on Generative Adversarial Network. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 5408513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filali Boubrahimi, S.; Neema, A.; Nassar, A.; Hosseinzadeh, P.; Hamdi, S.M. Spatiotemporal Data Augmentation of MODIS-Landsat Water Bodies Using Adversarial Networks. Water Resour. Res. 2024, 60, e2023WR036342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Wang, N.; Shao, F.; Li, S. Vision Transformer for Pansharpening. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 5409011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, Y.; Chen, H.; Sun, J.; Wang, M.; Chen, L. WTFusion: Wavelet-Assisted Transformer Network for Multisensor Image Fusion. IEEE Sens. J. 2024, 24, 37152–37168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Jiao, P.; Hu, Q.; Xiao, L.; Ye, Z. SwinSTFM: Remote Sensing Spatiotemporal Fusion Using Swin Transformer. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 5410618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Fu, G.; Yang, J.; Cao, Y.; Cao, Y. Multi-Modal Image Fusion via Deep Laplacian Pyramid Hybrid Network. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2023, 33, 7354–7369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zheng, Q.; Zhu, P.; Zhang, X.; Ma, W. TUFusion: A Transformer-Based Universal Fusion Algorithm for Multimodal Images. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2024, 34, 1712–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, X.; Yan, C.; Sun, Q. EV-Fusion: A Novel Infrared and Low-Light Color Visible Image Fusion Network Integrating Unsupervised Visible Image Enhancement. IEEE Sens. J. 2024, 24, 4920–4934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Wright, J.; Huang, T.S.; Ma, Y. Image Super-Resolution Via Sparse Representation. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2010, 19, 2861–2873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, Ł.; Polosukhin, I. Attention is all you need. In Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017; pp. 6000–6010. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, J.; Cao, J.; Sun, G.; Zhang, K.; Gool, L.V.; Timofte, R. SwinIR: Image Restoration Using Swin Transformer. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops (ICCVW), Montreal, BC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 1833–1844. [Google Scholar]
- Ledig, C.; Theis, L.; Huszár, F.; Caballero, J.; Cunningham, A.; Acosta, A.; Aitken, A.; Tejani, A.; Totz, J.; Wang, Z.; et al. Photo-Realistic Single Image Super-Resolution Using a Generative Adversarial Network. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 105–114. [Google Scholar]
- Isono, R.; Naganuma, K.; Ono, S. Robust Spatiotemporal Fusion of Satellite Images: A Constrained Convex Optimization Approach. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2024, 62, 5404516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Wang, J.; Gong, P. ROBOT: A spatiotemporal fusion model toward seamless data cube for global remote sensing applications. Remote Sens. Environ. 2023, 294, 113616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Wang, J.; Liu, Q.; Liang, X.; Liu, R.; Qin, P.; Yuan, J.; Wei, J.; Yuan, S.; Huang, H.; et al. Global 30 m seamless data cube (2000–2022) of land surface reflectance generated from Landsat 5, 7, 8, and 9 and MODIS Terra constellations. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2024, 16, 5449–5475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).