Spatial Downscaling of Satellite Sea Surface Wind with Soft-Sharing Multi-Task Learning
Abstract
1. Introduction
- A spatial downscaling method for satellite SSW with multi-task learning is proposed. It takes the downscaling of sea surface temperature (SST) and water vapor (WV) as an auxiliary task and incorporates the implicit correlations among variables into downscaling for performance enhancement.
- A soft-sharing mechanism with bridge modules has been developed to facilitate the sharing of and interaction between tasks.
- GAN and dual-learning structures have been incorporated into the presented multi-task downscaling network to enhance performance.
- The results in terms of accuracy compared with buoy observations and reconstruction quality demonstrate the superior performance of the proposed downscaling network.
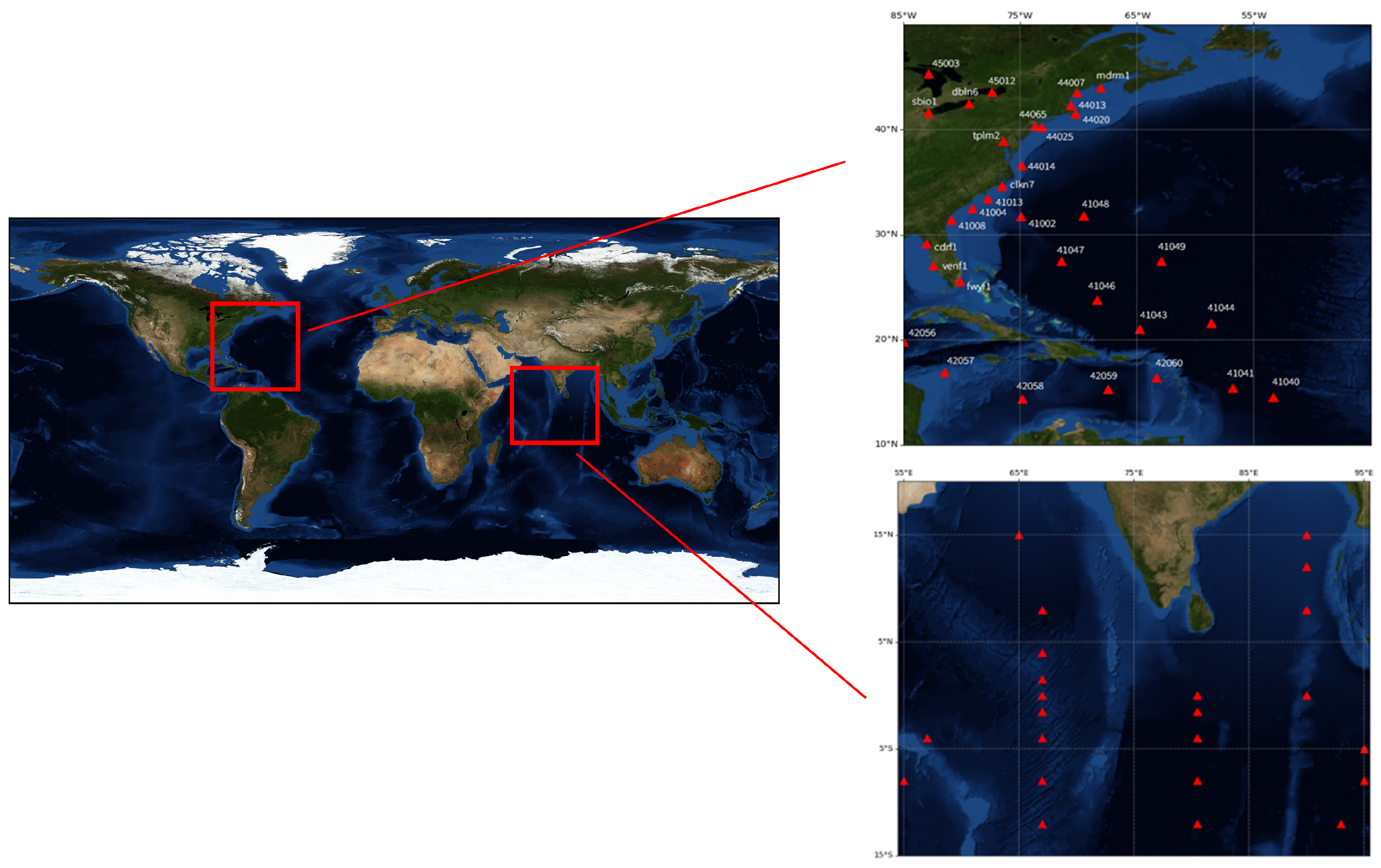
2. Study Area and Dataset
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Dataset
2.2.1. Buoy Data
2.2.2. Satellite Observations
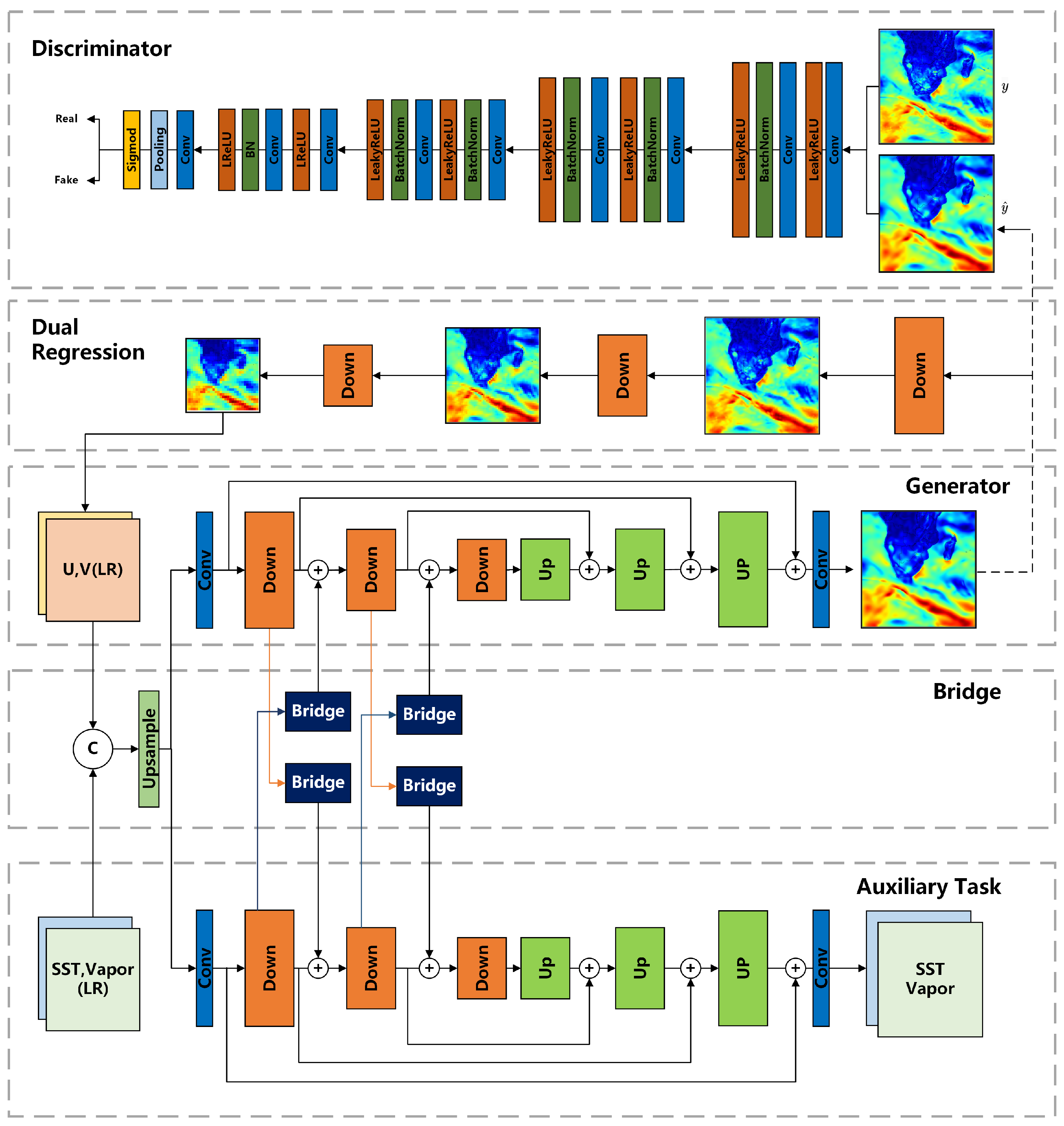
3. Methodology
3.1. Baseline with GAN and Dual Learning
3.2. Auxiliary Variables and Auxiliary Task
3.3. Downscaling Architecture with Soft-Sharing Multi-Task Learning
3.4. Loss Function and Model Training
| Algorithm 1 Model training for spatial downscaling of satellite SSW with auxiliary task |
| Input SSW, SST, WV as LR: unpaired data ; The corresponding synthetic data as LR and HR : paired data Ensure: Downscaled SSW results 1: Initialization models: generator (G), dual regression () and discriminator () 2: while not convergent do 3: UnpairedTraining if random(0, 1) <, vice versa 4: if not Unpaired Training then 5: Update by minimizing the objective: 6: Update G by minimizing the objective: 7: Update by minimizing the objective: 8: else 9: Update by minimizing the objective: 10: end if 11: end while |
4. Experiments and Discussion
4.1. Experimental Setup
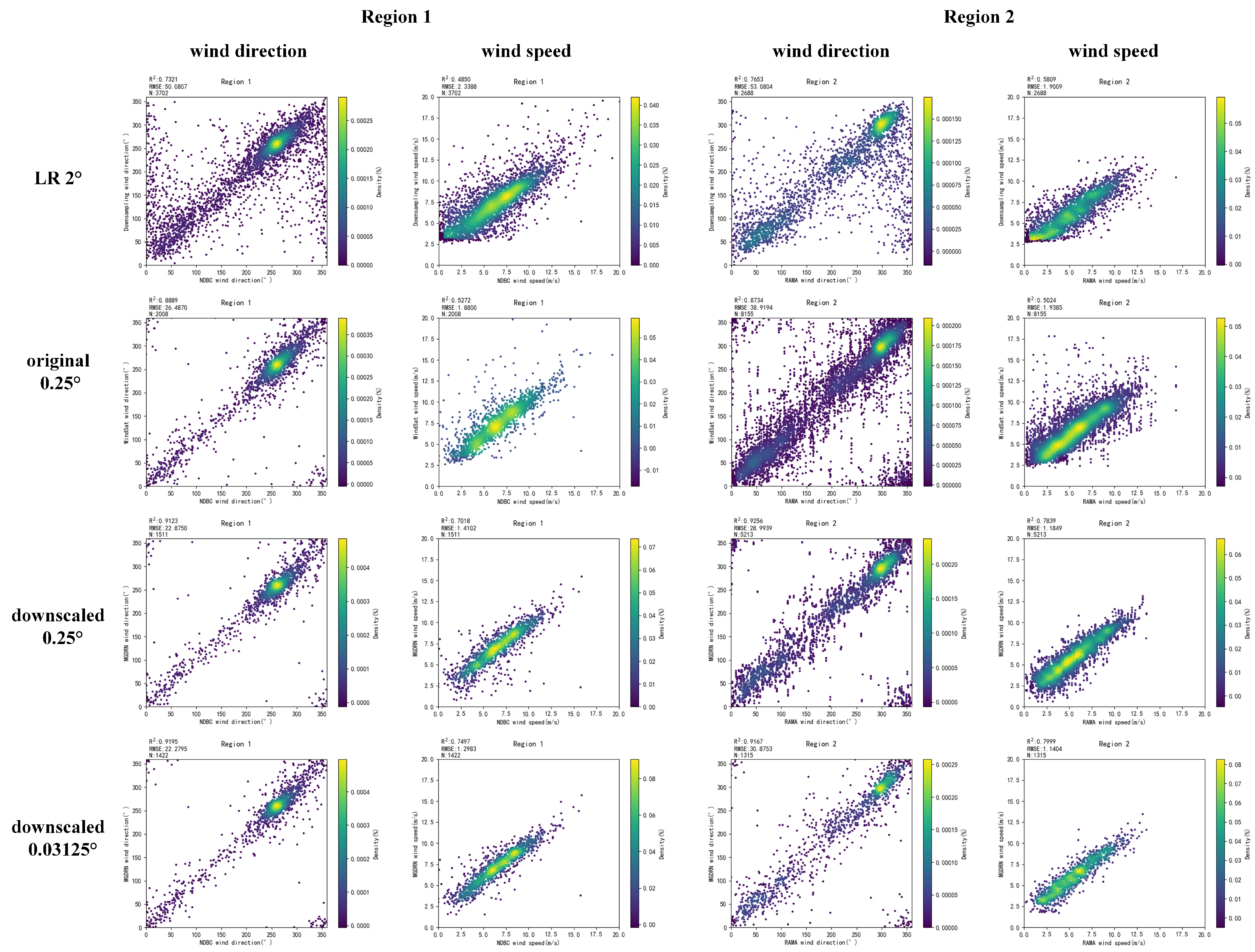
4.2. Validation with Buoy Measurements
4.3. Impacts of Auxiliary Variables and Task
4.4. Comparison of Downscaling Methods
4.5. Computational Efficiency
4.6. Model Transferability
4.7. Robustness Evaluation Under Noisy Low-Quality Data
4.8. Uncertainty Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, G.; Yang, X.; Li, X.; Zhang, B.; Pichel, W.; Li, Z.; Zhou, X. A Systematic Comparison of the Effect of Polarization Ratio Models on Sea Surface Wind Retrieval From C-Band Synthetic Aperture Radar. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2013, 6, 1100–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Xu, X.; Han, B.; Mansaray, L.R.; Guo, Q.; Huang, J. The Influence of Different Spatial Resolutions on the Retrieval Accuracy of Sea Surface Wind Speed with C-2PO Models Using Full Polarization C-Band SAR. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2017, 55, 5015–5025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, T.; Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, D. Retrieval of Sea Surface Wind Fields Using Multi-Source Remote Sensing Data. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, F.; Li, Y.; Zheng, Z.; Yan, H.; Du, Q. Online emergency mapping based on disaster scenario and data integration. Int. J. Image Data Fusion 2021, 12, 282–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuai, P.; Chen, X.Y.; Mital, U.; Coon, E.T.; Dwivedi, D. The effects of spatial and temporal resolution of gridded meteorological forcing on watershed hydrological responses. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2022, 26, 2245–2276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Caceres, M.; Martin-StPaul, N.; Turco, M.; Cabon, A.; Granda, V. Estimating daily meteorological data and downscaling climate models over landscapes. Environ. Model. Softw. 2018, 108, 186–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapiador, F.J.; Navarro, A.; Moreno, R.; Sanchez, J.L.; Garcia-Ortega, E. Regional climate models: 30 years of dynamical downscaling. Atmos. Res. 2020, 235, 104785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.F.; Han, Y.; Yang, Z.L. Dynamical downscaling of regional climate: A review of methods and limitations. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2019, 62, 365–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.M.; Luo, Y.M.; Li, X.; Yang, K.X.; Liu, Q.; Luo, X.B.; Li, X.H. Downscaling land surface temperature based on non-linear geographically weighted regressive model over urban areas. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.P.; Niu, X.R.; Wang, S.Y.; Gao, H.X.; Wang, X.Y.; Wu, J. Statistical downscaling and dynamical downscaling of regional climate in China: Present climate evaluations and future climate projections. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2016, 121, 2110–2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sachindra, D.A.; Ahmed, K.; Rashid, M.M.; Shahid, S.; Perera, B.J.C. Statistical downscaling of precipitation using machine learning techniques. Atmos. Res. 2018, 212, 240–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camus, P.; Menéndez, M.; Méndez, F.J.; Izaguirre, C.; Espejo, A.; Cánovas, V.; Pérez, J.; Rueda, A.; Losada, I.J.; Medina, R. A weather-type statistical downscaling framework for ocean wave climate. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2014, 119, 7389–7405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, S.; Zhu, W.; Lu, A.; Yan, T. A statistical spatial downscaling algorithm of TRMM precipitation based on NDVI and DEM in the Qaidam Basin of China. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 3069–3079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skourkeas, A.; Kolyva-Machera, F.; Maheras, P. Improved statistical downscaling models based on canonical correlation analysis, for generating temperature scenarios over Greece. Environ. Ecol. Stat. 2013, 20, 445–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, Y.; Yu, W.; Lin, H. A New Statistical-Dynamical Downscaling Procedure Based on EOF Analysis for Regional Time Series Generation. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2013, 52, 935–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Chen, H.; Tian, B.; Sheng, S.; Wang, J.; Kim, J.S. A Downscaling-Merging Scheme for Improving Daily Spatial Precipitation Estimates Based on Random Forest and Cokriging. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sa’adi, Z.; Shahid, S.; Pour, S.H.; Ahmed, K.; Chung, E.S.; Yaseen, Z.M. Multi-variable model output statistics downscaling for the projection of spatio-temporal changes in rainfall of Borneo Island. J. Hydro-Environ. Res. 2020, 31, 62–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, T.C.M.; Rocha, H.R.; Perez, G.M.P. Fine scale surface climate in complex terrain using machine learning. Int. J. Climatol. 2021, 41, 233–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.M.; Zhang, X.C.; Tian, Y.P.; Wang, W.; Xue, J.H.; Liao, Q.M. Deep learning for single image super-resolution: A brief review. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2019, 21, 3106–3121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hohlein, K.; Kern, M.; Hewson, T.; Westermann, R. A comparative study of convolutional neural network models for wind field downscaling. Meteorol. Appl. 2020, 27, e1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dujardin, J.; Lehning, M. Wind-Topo: Downscaling near-surface wind fields to high-resolution topography in highly complex terrain with deep learning. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2022, 148, 1368–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, T.; Yang, R.; Huang, Y.; Gao, J.; Kuang, Q. Terrain-guided flatten memory network for deep spatial wind downscaling. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2022, 15, 9468–9481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.Y.; Li, X.C. Future projections of offshore wind energy resources in China using CMIP6 simulations and a deep learning-based downscaling method. Energy 2021, 217, 119321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stengel, K.; Glaws, A.; Hettinger, D.; King, R.N. Adversarial super-resolution of climatological wind and solar data. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 16805–16815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Sun, Y.J.; Ren, K.J.; Zhao, Y.L.; Deng, K.F.; Wang, L.Z. A spatial downscaling approach for WindSat satellite sea surface wind based on generative adversarial networks and dual learning scheme. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerges, F.; Boufadel, M.C.; Bou-Zeid, E.; Nassif, H.; Wang, J.T.L. A Novel Bayesian Deep Learning Approach to the Downscaling of Wind Speed with Uncertainty Quantification. In Proceedings of the Advances in Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, PAKDD 2022, PT III, Chengdu, China, 16–19 May 2022; Gama, J., Li, T., Yu, Y., Chen, E., Zheng, Y., Teng, F., Eds.; Lecture Notes in Artificial Intelligence. Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; Volume 13282, pp. 55–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doury, A.; Somot, S.; Gadat, S.; Ribes, A.; Corre, L. Regional climate model emulator based on deep learning: Concept and first evaluation of a novel hybrid downscaling approach. Clim. Dyn. 2023, 60, 1751–1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rampal, N.; Gibson, P.B.; Sood, A.; Stuart, S.; Fauchereau, N.C.; Brandolino, C.; Noll, B.; Meyers, T. High-resolution downscaling with interpretable deep learning: Rainfall extremes over New Zealand. Weather Clim. Extrem. 2022, 38, 100525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Deng, K.; Ren, K.; Liu, J.; Deng, C.; Jin, Y. Deep learning in statistical downscaling for deriving high spatial resolution gridded meteorological data: A systematic review. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2024, 208, 14–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Tian, D.; Lowe, L.; Kalin, L.; Lehrter, J. Deep learning for daily precipitation and temperature downscaling. Water Resour. Res. 2021, 57, e2020WR029308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandal, T.; Kodra, E.; Ganguly, S.; Michaelis, A.; Nemani, R.; Ganguly, A.R. DeepSD: Generating high resolution climate change projections through single image super-resolution. In Proceedings of the 23rd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining (KDD ’17), Halifax, NS, Canada, 13–17 August 2017; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 1663–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sha, Y.K.; Gagne, D.J.; West, G.; Stull, R. Deep-learning-based gridded downscaling of surface meteorological variables in complex terrain. Part II: Daily precipitation. J. Appl. Meteorol. Clim. 2020, 59, 2075–2092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tie, R.; Shi, C.; Wan, G.; Hu, X.; Kang, L.; Ge, L. CLDASSD: Reconstructing fine textures of the temperature field using super-resolution technology. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2022, 39, 117–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sha, Y.K.; Gagne, D.J.; West, G.; Stull, R. Deep-learning-based gridded downscaling of surface meteorological variables in complex terrain. Part I: Daily maximum and minimum 2-m temperature. J. Appl. Meteorol. Clim. 2020, 59, 2057–2073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, L.; McRae, A.T.T.; Chantry, M.; Dueben, P.D.; Palmer, T.N. A generative deep learning approach to stochastic downscaling of precipitation forecasts. J. Adv. Model. Earth Syst. 2022, 14, e2022MS003120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hewson, T.D.; Pillosu, F.M. A low-cost post-processing technique improves weather forecasts around the world. Commun. Earth Environ. 2021, 2, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bano-Medina, J.; Manzanas, R.; Gutierrez, J.M. Configuration and intercomparison of deep learning neural models for statistical downscaling. Geosci. Model Dev. 2020, 13, 2109–2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bano-Medina, J.; Manzanas, R.; Manuel Gutierrez, J. On the suitability of deep convolutional neural networks for continental-wide downscaling of climate change projections. Clim. Dyn. 2021, 57, 2941–2951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Lan, Y. Statistical downscaling of daily temperature and precipitation over China using deep learning neural models: Localization and comparison with other methods. Int. J. Climatol. 2021, 41, 1128–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, W.; Luo, Y.; Wu, T.; Huang, X.; Xue, W.; Yu, C. Deep learning for seasonal precipitation prediction over China. J. Meteorol. Res. 2022, 36, 271–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, B.; Hsu, K.; AghaKouchak, A.; Sorooshian, S. Improving precipitation estimation using convolutional neural network. Water Resour. Res. 2019, 55, 2301–2321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adewoyin, R.A.; Dueben, P.; Watson, P.; He, Y.L.; Dutta, R. TRU-NET: A deep learning approach to high resolution prediction of rainfall. Mach. Learn. 2021, 110, 2035–2062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Xu, J.; Tasaka, K.; Chen, Z. Multi-task Learning-based All-in-one Collaboration Framework for Degraded Image Super-resolution. ACM Trans. Multimed. Comput. Commun. Appl. 2021, 17, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yang, Q. A Survey on Multi-Task Learning. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 2022, 34, 5586–5609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thung, K.H.; Wee, C.Y. A brief review on multi-task learning. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2018, 77, 29705–29725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilburn, K.A.; Meissner, T.; Wentz, F.J.; Brown, S.T. Ocean Vector Winds From WindSat Two-Look Polarimetric Radiances. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2016, 54, 918–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, M.; Li, X.M.; Sha, J. Comparison of sea surface wind field measured by HY-2A scatterometer and WindSat in global oceans. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2019, 37, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, R.A.; Jordan, M.I.; Nowlan, S.J.; Hinton, G.E. Adaptive mixtures of local experts. Neural Comput. 1991, 3, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creswell, A.; White, T.; Dumoulin, V.; Arulkumaran, K.; Sengupta, B.; Bharath, A.A. Generative adversarial networks: An overview. IEEE Signal Process Mag. 2018, 35, 53–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makin, V. Air-sea exchange of heat in the presence of wind waves and spray. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 1998, 103, 1137–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, K.; Li, K.; Wang, L.; Zhong, B.; Fu, Y. Image Super-Resolution Using Very Deep Residual Channel Attention Networks. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision—ECCV 2018, Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; Ferrari, V., Hebert, M., Sminchisescu, C., Weiss, Y., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 294–310. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, Z.; Xue, Z.; He, R.; Bao, X.; Song, J. Statistical downscaling of IPCC sea surface wind and wind energy predictions for US east coastal ocean, Gulf of Mexico and Caribbean Sea. J. Ocean Univ. China 2016, 15, 577–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Alvarez, J.C.; Costoya, X.; Pérez-Alarcón, A.; Rahimi, S.; Nieto, R.; Gimeno, L. Dynamic downscaling of wind speed over the North Atlantic Ocean using CMIP6 projections: Implications for offshore wind power density. Energy Rep. 2023, 9, 873–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolukula, S.S.; Murty, P.; Baduru, B.; Sharath, D.; PA, F. Downscaling of wind fields on the east coast of India using deep convolutional neural networks and their applications in storm surge computations. J. Water Clim. Chang. 2024, 15, 1612–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Type | Resolution | Method | Component | Region 1 | Region 2 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RMSE | R2 | RMSE | R2 | ||||
| LR | 2° | Bicubic down-sample 8× | Direction | 50.08 | 0.73 | 53.08 | 0.77 |
| Speed | 2.34 | 0.49 | 1.90 | 0.58 | |||
| Downscaling HR | 0.25° | SSW | Direction | 24.87 | 0.90 | 35.02 | 0.90 |
| Speed | 1.69 | 0.62 | 1.68 | 0.63 | |||
| SSW + Auxiliary Variable | Direction | 23.25 | 0.91 | 30.31 | 0.92 | ||
| Speed | 1.58 | 0.62 | 1.49 | 0.66 | |||
| Multi-Task Downscaling (ours) | Direction | 22.88 | 0.91 | 28.99 | 0.93 | ||
| Speed | 1.41 | 0.70 | 1.18 | 0.78 | |||
| Downscaling SR | 0.03125° | SSW | Direction | 25.19 | 0.90 | 37.63 | 0.88 |
| Speed | 1.78 | 0.58 | 1.75 | 0.60 | |||
| SSW + Auxiliary Variable | Direction | 23.49 | 0.91 | 31.45 | 0.91 | ||
| Speed | 1.40 | 0.71 | 1.40 | 0.70 | |||
| Multi-Task Downscaling (ours) | Direction | 22.28 | 0.92 | 30.88 | 0.92 | ||
| Speed | 1.30 | 0.75 | 1.14 | 0.80 | |||
| Method | PSNR | SSIM |
|---|---|---|
| SSW | 40.16 | 0.982 |
| SSW + Auxiliary Variable | 40.28 | 0.971 |
| Multi-Task Downscaling (ours) | 42.62 | 0.986 |
| Type | Resolution | Method | Component | Region 1 | Region 2 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RMSE | R2 | RMSE | R2 | ||||
| LR | 2° | Bicubic down-sample 8× | Direction | 50.08 | 0.73 | 53.08 | 0.77 |
| Speed | 2.34 | 0.49 | 1.90 | 0.58 | |||
| Downscaling HR | 0.25° | Bicubic interpolation | Direction | 34.53 | 0.81 | 44.14 | 0.83 |
| Speed | 1.90 | 0.52 | 1.85 | 0.55 | |||
| DeepSD | Direction | 34.38 | 0.81 | 44.28 | 0.83 | ||
| Speed | 2.12 | 0.40 | 1.96 | 0.49 | |||
| Adversarial DeepSD | Direction | 28.72 | 0.87 | 38.32 | 0.88 | ||
| Speed | 2.08 | 0.42 | 1.87 | 0.54 | |||
| DRN | Direction | 26.11 | 0.89 | 36.48 | 0.89 | ||
| Speed | 1.91 | 0.51 | 1.66 | 0.63 | |||
| GAN-Downscaling | Direction | 24.42 | 0.91 | 34.07 | 0.90 | ||
| Speed | 1.62 | 0.65 | 1.57 | 0.67 | |||
| Multi-Task Downscaling (ours) | Direction | 22.88 | 0.91 | 28.99 | 0.93 | ||
| Speed | 1.41 | 0.70 | 1.18 | 0.78 | |||
| Type | Resolution | Method | Component | Region 1 | Region 2 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RMSE | R2 | RMSE | R2 | ||||
| Original HR | 0.25° | Original HR | Direction | 26.49 | 0.89 | 38.92 | 0.87 |
| Speed | 1.88 | 0.53 | 1.94 | 0.50 | |||
| Downscaling SR | 0.03125° | Bicubic interpolation | Direction | 26.07 | 0.90 | 38.71 | 0.88 |
| Speed | 1.82 | 0.57 | 1.96 | 0.49 | |||
| DeepSD | Direction | 29.44 | 0.87 | 42.48 | 0.85 | ||
| Speed | 2.21 | 0.36 | 2.16 | 0.38 | |||
| Adversarial DeepSD | Direction | 32.28 | 0.84 | 45.26 | 0.83 | ||
| Speed | 2.16 | 0.39 | 2.24 | 0.34 | |||
| DRN | Direction | 31.01 | 0.85 | 44.24 | 0.84 | ||
| Speed | 2.09 | 0.43 | 2.16 | 0.38 | |||
| GAN-Downscaling | Direction | 30.80 | 0.86 | 43.96 | 0.84 | ||
| Speed | 1.82 | 0.56 | 2.02 | 0.46 | |||
| Multi-Task Downscaling (ours) | Direction | 22.28 | 0.92 | 30.88 | 0.92 | ||
| Speed | 1.30 | 0.75 | 1.14 | 0.80 | |||
| Method | PSNR | SSIM |
|---|---|---|
| Bicubic | 38.34 | 0.973 |
| DeepSD | 36.75 | 0.951 |
| Adversarial DeepSD | 36.89 | 0.958 |
| DRN | 39.43 | 0.977 |
| GAN-Downscaling | 39.96 | 0.980 |
| Multi-Task Downscaling (ours) | 42.62 | 0.986 |
| Resolution | Method | Parameters | FLOPs |
|---|---|---|---|
| 8× downscaling | Bicubic interpolation | 0 | 102.4 K |
| DeepSD | 207,825 | 16.4 G | |
| Adversarial DeepSD | 207,825 | 16.4 G | |
| DRN | 10,000,772 | 63.57 G | |
| GAN-Downscaling | 10,000,772 | 63.57 G | |
| Multi-Task Downscaling (ours) | 22,800,202 | 154.25 G |
| Type | Resolution | Method | Component | Region 1 | Region 2 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RMSE | R2 | RMSE | R2 | ||||
| LR | 2° | Bicubic down-sample 8× | Direction | 50.08 | 0.73 | 53.08 | 0.77 |
| Speed | 2.53 | 0.40 | 2.16 | 0.46 | |||
| Downscaling HR | 0.25° | Bicubic interpolation | Direction | 34.41 | 0.81 | 44.37 | 0.83 |
| Speed | 2.11 | 0.41 | 1.99 | 0.47 | |||
| DeepSD | Direction | 34.54 | 0.81 | 44.33 | 0.83 | ||
| Speed | 2.18 | 0.36 | 2.00 | 0.47 | |||
| Adversarial DeepSD | Direction | 28.85 | 0.87 | 38.79 | 0.87 | ||
| Speed | 2.17 | 0.37 | 1.94 | 0.50 | |||
| DRN | Direction | 26.28 | 0.89 | 37.25 | 0.88 | ||
| Speed | 2.14 | 0.39 | 1.84 | 0.55 | |||
| GAN-Downscaling | Direction | 26.65 | 0.88 | 36.14 | 0.90 | ||
| Speed | 1.91 | 0.51 | 1.82 | 0.60 | |||
| Multi-Task Downscaling (ours) | Direction | 23.02 | 0.91 | 28.74 | 0.93 | ||
| Speed | 1.42 | 0.70 | 1.18 | 0.79 | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yue, Y.; Liu, J.; Sun, Y.; Ren, K.; Deng, K.; Deng, K. Spatial Downscaling of Satellite Sea Surface Wind with Soft-Sharing Multi-Task Learning. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 587. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17040587
Yue Y, Liu J, Sun Y, Ren K, Deng K, Deng K. Spatial Downscaling of Satellite Sea Surface Wind with Soft-Sharing Multi-Task Learning. Remote Sensing. 2025; 17(4):587. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17040587
Chicago/Turabian StyleYue, Yinlei, Jia Liu, Yongjian Sun, Kaijun Ren, Kefeng Deng, and Ke Deng. 2025. "Spatial Downscaling of Satellite Sea Surface Wind with Soft-Sharing Multi-Task Learning" Remote Sensing 17, no. 4: 587. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17040587
APA StyleYue, Y., Liu, J., Sun, Y., Ren, K., Deng, K., & Deng, K. (2025). Spatial Downscaling of Satellite Sea Surface Wind with Soft-Sharing Multi-Task Learning. Remote Sensing, 17(4), 587. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17040587





