Spatiotemporal Patterns of Chlorophyll-a Concentration in a Hypersaline Lake Using High Temporal Resolution Remotely Sensed Imagery
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Training Data
2.3. Imagery
2.4. Image Processing and Data Extraction
3. Results
3.1. Satellite Product Comparisons
3.2. Spatial-Temporal Variation in Chlorophyll
4. Discussion
4.1. Remote Sensing
4.2. Spatial-Temporal Changes in Chlorophyll
4.2.1. Broad Scale Patterns in Gilbert Bay
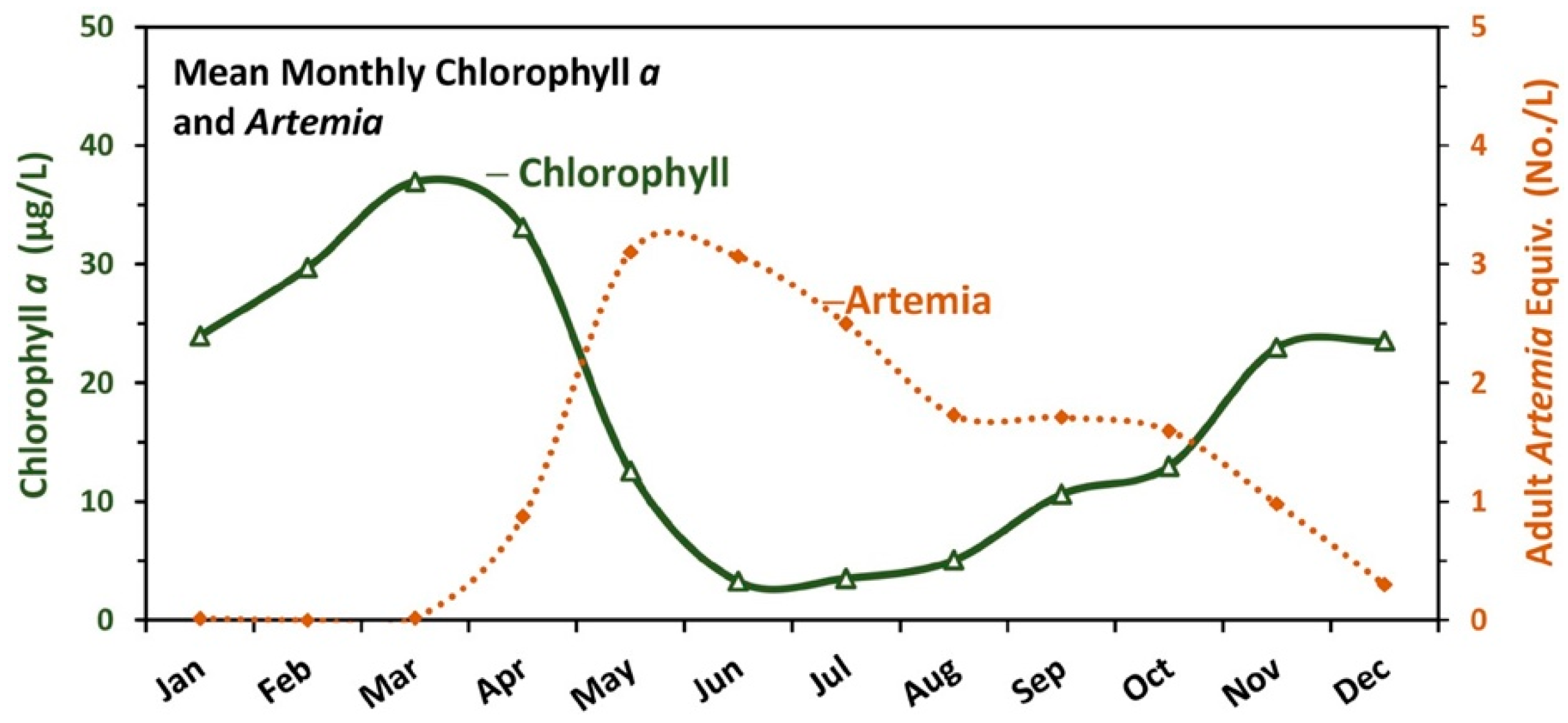
4.2.2. Temporal Changes in Chl a
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A

References
- Huot, Y.; Babin, M.; Bruyant, F.; Grob, C.; Twardowski, M.S.; Claustre, H. Does Chlorophyll a Provide the Best Index of Phytoplankton Biomass for Primary Productivity Studies? Biogeosci. Discuss. 2007, 4, 707–745. [Google Scholar]
- Messager, M.L.; Lehner, B.; Grill, G.; Nedeva, I.; Schmitt, O. Estimating the Volume and Age of Water Stored in Global Lakes Using a Geo-Statistical Approach. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 13603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammer, U.T. Primary Production in Saline Lakes. Hydrobiologia 1981, 81, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timms, B.V. Waterbirds of the Saline Lakes of the Paroo, Arid-Zone Australia: A Review with Special Reference to Diversity and Conservation. Nat. Resour. Environ. Issues 2009, 15, 46. [Google Scholar]
- Roberts, A.J. Avian Diets in a Saline Ecosystem: Great Salt Lake, Utah, USA. Hum.-Wildl. Interact. 2013, 7, 158–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, D.K.; Kimball, J.S.; Larson, R.; DiGirolamo, N.E.; Casey, K.A.; Hulley, G. Intensified Warming and Aridity Accelerate Terminal Lake Desiccation in the Great Basin of the Western United States. Earth Space Sci. 2023, 10, e2022EA002630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wurtsbaugh, W.A.; Miller, C.; Null, S.E.; DeRose, R.J.; Wilcock, P.; Hahnenberger, M.; Howe, F.; Moore, J. Decline of the World’s Saline Lakes. Nat. Geosci. 2017, 10, 816–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassibe, W.R.; Keck, W.G. The Great Salt Lake; General Information Product: Washington, DC, USA, 1991; p. 28. [Google Scholar]
- Tarboton, D. Collection of Great Salt Lake Data; HydroShare: Arlington, MA, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Division of Forestry, Fire & State Lands. U.D. of N.R. Final Great Salt Lake Comprehensive Management Plan and Record of Decision; SWCA: Phoenix, AZ, USA, 2013; p. 391.
- Great Salt Lake Advisory Council Economic Significance of the Great Salt Lake to the State of Utah. Available online: https://lf-public.deq.utah.gov/WebLink/DocView.aspx?id=392799&eqdocs=DWQ-2012-006864 (accessed on 15 November 2024).
- Paul, D.S.; Manning, A.E. Great Salt Lake Waterbird Survey Five-Year Report (1997–2001); Utah Division of Wildlife Resources: Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 2002; p. 64. [Google Scholar]
- Sorensen, E.D.; Hoven, H.M.; Neill, J. Great Salt Lake Shorebirds, Their Habitats, and Food Base. In Great Salt Lake Biology: A Terminal Lake in a Time of Change; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 263–309. ISBN 3030403513. [Google Scholar]
- Castellino, M.; Carle, R.; Lesterhuis, A.; Clay, R. Conservation Plan for Wilson’s Phalarope (Phalaropus Tricolor), Version 2.0; Western Hemisphere Shorebird Reserve Network; Manomet Inc.: Manomet, MA, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Matthews, M.W. A Current Review of Empirical Procedures of Remote Sensing in Inland and Near-Coastal Transitional Waters. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2011, 32, 6855–6899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behrenfeld, M.J.; Falkowski, P.G. Photosynthetic Rates Derived from Satellite-Based Chlorophyll Concentration. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1997, 42, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tebbs, E.J.; Remedios, J.J.; Harper, D.M. Remote Sensing of Chlorophyll-a as a Measure of Cyanobacterial Biomass in Lake Bogoria, a Hypertrophic, Saline–Alkaline, Flamingo Lake, Using Landsat ETM+. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 135, 92–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, C.H.; Williams, G.P. Evaluating Remote Sensing Model Specification Methods for Estimating Water Quality in Optically Diverse Lakes throughout the Growing Season. Hydrology 2018, 5, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wurtsbaugh, W.; Naftz, D.; Bradt, S. Spatial Analyses of Trophic Linkages Between Basins in the Great Salt Lake; Forestry, Fire & State Lands: Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Hansen, C.H.; Burian, S.J.; Dennison, P.E.; Williams, G.P. Evaluating Historical Trends and Influences of Meteorological and Seasonal Climate Conditions on Lake Chlorophyll a Using Remote Sensing. Lake Reserv. Manag. 2020, 36, 45–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baskin, R.L. Occurrence and Spatial Distribution of Microbial Bioherms in Great Salt Lake, Utah. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Utah, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Lindsay, M.R.; Anderson, C.; Fox, N.; Scofield, G.; Allen, J.; Anderson, E.; Bueter, L.; Poudel, S.; Sutherland, K.; Munson-McGee, J.H.; et al. Microbialite Response to an Anthropogenic Salinity Gradient in Great Salt Lake, Utah. Geobiology 2017, 15, 131–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brothers, S.; Cobb, M.; Ramsey, R.D.; Wurtsbaugh, W.A.; Rivers, E. A Multi-Tiered Assessment of Primary Production in Great Salt Lake; Utah Division of Forestry, Fire, and State Lands: Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 2023; p. 49. [Google Scholar]
- Pilati, A.; Wurtsbaugh, W.A. Importance of Zooplankton for the Persistence of a Deep Chlorophyll Layer: A Limnocorral Experiment. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2003, 48, 249–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 23rd ed.; 10200 Plankton; APHA Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2023.
- Crawford, C.J.; Roy, D.P.; Arab, S.; Barnes, C.; Vermote, E.; Hulley, G.; Gerace, A.; Choate, M.; Engebretson, C.; Micijevic, E.; et al. The 50-Year Landsat Collection 2 Archive. Sci. Remote Sens. 2023, 8, 100103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaaf, C.; Wang, Z. MCD43A4 MODIS/Terra + Aqua BRDF/Albedo Nadir BRDF Adjusted Ref Daily L3 Global—500m V006. Available online: https://lpdaac.usgs.gov/products/mcd43a4v006/ (accessed on 15 November 2024).
- Vermote, E.; Wolfe, R. MOD09GA MODIS/Terra Surface Reflectance Daily L2G Global 1 km and 500 m SIN Grid V006. Available online: https://lpdaac.usgs.gov/products/mod09gav006/ (accessed on 15 November 2024).
- Gorelick, N.; Hancher, M.; Dixon, M.; Ilyushchenko, S.; Thau, D.; Moore, R. Google Earth Engine: Planetary-Scale Geospatial Analysis for Everyone. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 202, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakovljević, G.; Govedarica, M.; Álvarez-Taboada, F. Waterbody Mapping: A Comparison of Remotely Sensed and GIS Open Data Sources. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2019, 40, 2936–2964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belovsky, G.E.; Stephens, D.; Perschon, C.; Birdsey, P.; Paul, D.; Naftz, D.; Baskin, R.; Larson, C.; Mellison, C.; Luft, J.; et al. The Great Salt Lake Ecosystem (Utah, USA): Long Term Data and a Structural Equation Approach. Ecosphere 2011, 2, art33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brivio, P.A.; Giardino, C.; Zilioli, E. Determination of Chlorophyll Concentration Changes in Lake Garda Using an Image-Based Radiative Transfer Code for Landsat TM Images. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2001, 22, 487–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Jordan, K.J. Estimating and Mapping Chlorophyll-a Concentration in Pensacola Bay, Florida Using Landsat ETM+ Data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2005, 26, 5245–5254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, B.; Pahlevan, N.; Schalles, J.; Ruberg, S.; Errera, R.; Ma, R.; Giardino, C.; Bresciani, M.; Barbosa, C.; Moore, T.; et al. A Chlorophyll-a Algorithm for Landsat-8 Based on Mixture Density Networks. Front. Remote Sens. 2021, 1, 623678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Xu, M.; Liu, Y.; Liu, H.; Beck, R.; Reif, M.; Emery, E.; Young, J.; Wu, Q. Mapping Freshwater Chlorophyll-a Concentrations at a Regional Scale Integrating Multi-Sensor Satellite Observations with Google Earth Engine. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markogianni, V.; Kalivas, D.; Petropoulos, G.P.; Dimitriou, E. Estimating Chlorophyll-a of Inland Water Bodies in Greece Based on Landsat Data. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buma, W.G.; Lee, S.-I. Evaluation of Sentinel-2 and Landsat 8 Images for Estimating Chlorophyll-a Concentrations in Lake Chad, Africa. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, X.-G.; Zhao, D.-Z.; Liu, Y.-G.; Yang, J.-H.; Xiu, P.; Wang, L. An Overview of Remote Sensing of Chlorophyll Fluorescence. Ocean Sci. J. 2007, 42, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutser, T.; Pierson, D.C.; Kallio, K.Y.; Reinart, A.; Sobek, S. Mapping Lake CDOM by Satellite Remote Sensing. Remote Sens. Environ. 2005, 94, 535–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wurtsbaugh, W.A.; Marcarelli, A.M.; Boyer, G.L. Eutrophication and Metal Concentrations in Three Bays of the Great Salt Lake (USA); Watershed Sciences Faculty Publications: Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 2012; p. 70. [Google Scholar]
- Baxter, B.K.; Litchfield, C.D.; Sowers, K.; Griffith, J.D.; Dassarma, P.A.; Dassarma, S. Microbial Diversity of Great Salt Lake. In Adaptation to Life at High Salt Concentrations in Archaea, Bacteria, and Eukarya; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2005; pp. 9–25. [Google Scholar]
- Wurtsbaugh, W.A. The Great Salt Lake Ecosystem (Utah, USA): Long Term Data and a Structural Equation Approach: Comment. Ecosphere 2014, 5, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wurtsbaugh, W.A. Food-Web Modification by an Invertebrate Predator in the Great Salt Lake (USA). Oecologia 1992, 89, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Great Salt Lake Ecosystem Program Algae: A Contributing Factor to the Lake’s Color (and Smell). Available online: https://wildlife.utah.gov/gslep/wildlife/algae.html (accessed on 15 November 2024).
- Adams, H.; Ye, J.; Persaud, B.D.; Slowinski, S.; Kheyrollah Pour, H.; Van Cappellen, P. Rates and Timing of Chlorophyll- a Increases and Related Environmental Variables in Global Temperate and Cold-Temperate Lakes. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2022, 14, 5139–5156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Chen, F.; Hu, W.; Lu, X.; Xu, B.; Hamilton, D.P. Variations in the Distribution of Chl-a and Simulation Using a Multiple Regression Model. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 4553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spall, R.E. A Hydrodynamic Model of the Circulation within the South Arm of the Great Salt Lake. Int. J. Model. Simul. 2009, 29, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crosman, E.T.; Horel, J.D. MODIS-Derived Surface Temperature of the Great Salt Lake. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyngsgaard, M.M.; Markager, S.; Richardson, K.; Møller, E.F.; Jakobsen, H.H. How Well Does Chlorophyll Explain the Seasonal Variation in Phytoplankton Activity? Estuaries Coasts 2017, 40, 1263–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rae, R.; Vincent, W.F. Phytoplankton Production in Subarctic Lake and River Ecosystems: Development of a Photosynthesis-Temperature-Irradiance Model. J. Plankton Res. 1998, 20, 1293–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephens, D.W.; Gillespie, D.M. Phytoplankton Production in the Great Salt Lake, Utah, and a Laboratory Study of Algal Response to Enrichment1: Production in Great Salt Lake. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1976, 21, 74–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wurtsbaugh, W.A. Iron, Molybdenum and Phosphorus Limitation of N2 Fixation Maintains Nitrogen Deficiency of Plankton in the Great Salt Lake Drainage (Utah, USA). SIL Proc. 1922–2010 1988, 23, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcarelli, A.M.; Wurtsbaugh, W.A.; Griset, O. Salinity Controls Phytoplankton Response to Nutrient Enrichment in the Great Salt Lake, Utah, USA. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2006, 63, 2236–2248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogata, E.M.; Wurtsbaugh, W.A.; Smith, T.N.; Durham, S.L. Bioassay Analysis of Nutrient and Artemia Franciscana Effects on Trophic Interactions in the Great Salt Lake, USA. Hydrobiologia 2017, 788, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wurtsbaugh, W.A.; Epstein, D. Impact of the Farmington Bay Eutrophication Plume on the Plankton Ecology of Gilbert Bay, Great Salt Lake. In Aquatic Ecology Practicum Class Report; College of Natural Resources, Utah State University: Logan, UT, USA, 2011; Volume 41. [Google Scholar]
- Carlson, R.E. A Trophic State Index for Lakes1. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1977, 22, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wurtsbaugh, W.A.; Gliwicz, Z.M. Limnological Control of Brine Shrimp Population Dynamics and Cyst Production in the Great Salt Lake, Utah. In Saline Lakes; Melack, J.M., Jellison, R., Herbst, D.B., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2001; pp. 119–132. ISBN 978-90-481-5995-6. [Google Scholar]
- Fontana, C.G.; Maybruck, V.G.; Billings, R.M.; Mansfeldt, C.B.; Trower, E.J. Modeling the Microbiome of Utah’s Great Salt Lake: A Regression Analysis of Key Abiotic Factors Impacting Growth of Dunaliella Green Algae in the GSL’s South Arm. bioRxiv 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leavitt, P.R.; Bunting, L.; Moser, K.; Woodward, C. Effects of Wastewater Influx and Hydrologic Modification on Algal Production in the Great Salt Lake of Utah, USA; The University of Queensland: Brisbane, Australia, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Gunnell, N.; Nelson, S.; Rushforth, S.; Rey, K.; Hudson, S.M.; Carling, G.; Miller, T.; Meyers, L.; Engstrom, D. From Hypersaline to Fresh-Brackish: Documenting the Impacts of Human Intervention on a Natural Water Body from Cores, Farmington Bay, UT, USA. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2022, 233, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrne, A.; Tebbs, E.J.; Njoroge, P.; Nkwabi, A.; Chadwick, M.A.; Freeman, R.; Harper, D.; Norris, K. Productivity Declines Threaten East African Soda Lakes and the Iconic Lesser Flamingo. Curr. Biol. 2024, 34, 1786–1793.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, L.; Devey, M.; Leavitt, P.R.; Power, M.J.; Brothers, S.; Brahney, J. Anthropogenic Forcing Leads to an Abrupt Shift to Phytoplankton Dominance in a Shallow Eutrophic Lake. Freshw. Biol. 2024, 69, 335–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wurtsbaugh, W.A.; Berry, T.S. Cascading Effects of Decreased Salinity on the Plankton Chemistry, and Physics of the Great Salt Lake (Utah). Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1990, 47, 100–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maszczyk, P.; Wurtsbaugh, W.A. Brine Shrimp Grazing and Fecal Production Increase Sedimentation to the Deep Brine Layer (Monimolimnion) of Great Salt Lake, Utah. Hydrobiologia 2017, 802, 7–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jellison, R.; Melack, J.M. Algal Photosynthetic Activity and Its Response to Meromixis in Hypersaline Mono Lake, California. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1993, 38, 818–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wurtsbaugh, W.A.; Paerl, H.W.; Dodds, W.K. Nutrients, Eutrophication and Harmful Algal Blooms along the Freshwater to Marine Continuum. WIREs Water 2019, 6, e1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conover, M.R.; Bell, M.E. Importance of Great Salt Lake to Pelagic Birds: Eared Grebes, Phalaropes, Gulls, Ducks, and White Pelicans. In Great Salt Lake Biology; Baxter, B.K., Butler, J.K., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 239–262. ISBN 978-3-030-40351-5. [Google Scholar]
- Marden, B.; Brown, P.; Bosteels, T. Great Salt Lake Artemia: Ecosystem Functions and Services with a Global Reach. In Great Salt Lake Biology; Baxter, B.K., Butler, J.K., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 175–237. ISBN 978-3-030-40351-5. [Google Scholar]
- Richards, D.C. Nutrient Atmospheric Deposition on Utah Lake and Great Salt Lake Locations 2020, Including Effects of Sampler Type Statistical Analyses and Results. Ph.D. Thesis, Brigham Young University, Provo, UT, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong, T.; Wurtsbaugh, W.A. Impacts of Eutrophication on Benthic Invertebrates & Fish Prey of Birds in Farmington and Bear River Bays of Great Salt Lake; Utah State University: Logan, UT, USA, 2019; p. 41. [Google Scholar]









Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ramsey, R.D.; Brothers, S.M.; Cobo, M.; Wurtsbaugh, W.A. Spatiotemporal Patterns of Chlorophyll-a Concentration in a Hypersaline Lake Using High Temporal Resolution Remotely Sensed Imagery. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 430. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17030430
Ramsey RD, Brothers SM, Cobo M, Wurtsbaugh WA. Spatiotemporal Patterns of Chlorophyll-a Concentration in a Hypersaline Lake Using High Temporal Resolution Remotely Sensed Imagery. Remote Sensing. 2025; 17(3):430. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17030430
Chicago/Turabian StyleRamsey, R. Douglas, Soren M. Brothers, Melissa Cobo, and Wayne A. Wurtsbaugh. 2025. "Spatiotemporal Patterns of Chlorophyll-a Concentration in a Hypersaline Lake Using High Temporal Resolution Remotely Sensed Imagery" Remote Sensing 17, no. 3: 430. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17030430
APA StyleRamsey, R. D., Brothers, S. M., Cobo, M., & Wurtsbaugh, W. A. (2025). Spatiotemporal Patterns of Chlorophyll-a Concentration in a Hypersaline Lake Using High Temporal Resolution Remotely Sensed Imagery. Remote Sensing, 17(3), 430. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17030430






