S2GL-MambaResNet: A Spatial–Spectral Global–Local Mamba Residual Network for Hyperspectral Image Classification
Highlights
- S2GL-MambaResNet, a lightweight Mamba-based HSI classification network that tightly couples improved Mamba encoders with progressive residual fusion, ensures high-quality classification of hyperspectral images.
- By employing Global_Local Spatial_Spectral Mamba Encoder and Hierarchical Spectral Mamba Encoder to strengthen multi-scale global and local spatial-spectral modeling, and by using Progressive Residual Fusion Block to fuse Mamba output features, the network substantially improves classification performance while maintaining a lightweight architecture.
- This approach enhances the classification performance of hyperspectral images under few-shot and class-imbalanced conditions.
- The proposed Global_Local Spatial_Spectral Mamba Encoder and Hierarchical Spectral Mamba Encoder address the insufficient extraction of spatial–spectral features caused by the intrinsic high spectral dimensionality, information redundancy, and spatial heterogeneity of hyperspectral images (HSI).
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- S2GL-MambaResNet is designed, a lightweight Mamba-based HSI classification network tightly coupling improved Mamba encoders with progressive residual fusion, specifically designed for few-shot and class-imbalanced classification. Through coordinated design across serialization, spectral-domain encoding, spatial-domain modeling, and multi-scale residual fusion, our approach effectively couples the near-linear global sequence modeling strengths of traditional Mamba with local spatial–spectral perceptual mechanisms, reducing overfitting risk and enhancing feature discriminability while preserving computational efficiency.
- (2)
- The Global_Local Spatial_Spectral Mamba Encoder (GLS2ME) is employed to comprehensively extract global and local spatial–spectral features. GLS2ME employs a global Mamba branch together with a non-overlapping sliding-window local Mamba branch to capture long-distance global spatial–spectral context and richly exploit local spatial–spectral structures, respectively. This complementary modeling significantly improves characterization of complex spatial–spectral correlations and spatial edge details, addressing the insufficiency of feature extraction in HSI due to high spectral dimensionality, information redundancy, and spatial heterogeneity.
- (3)
- The Hierarchical Spectral Mamba Encoder (HSME) is proposed to capture spectral features at multiple scales. HSME first extracts spectral semantics at short, medium, and long scales using multi-scale 1D convolutions, then groups spectral channels and feeds each group into intra-group Mamba encoders for long-distance context modeling. This hierarchical scheme preserves fine intra-spectral details while efficiently capturing inter-group long-distance dependencies, thereby enhancing the completeness and discriminability of spectral features.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preliminaries
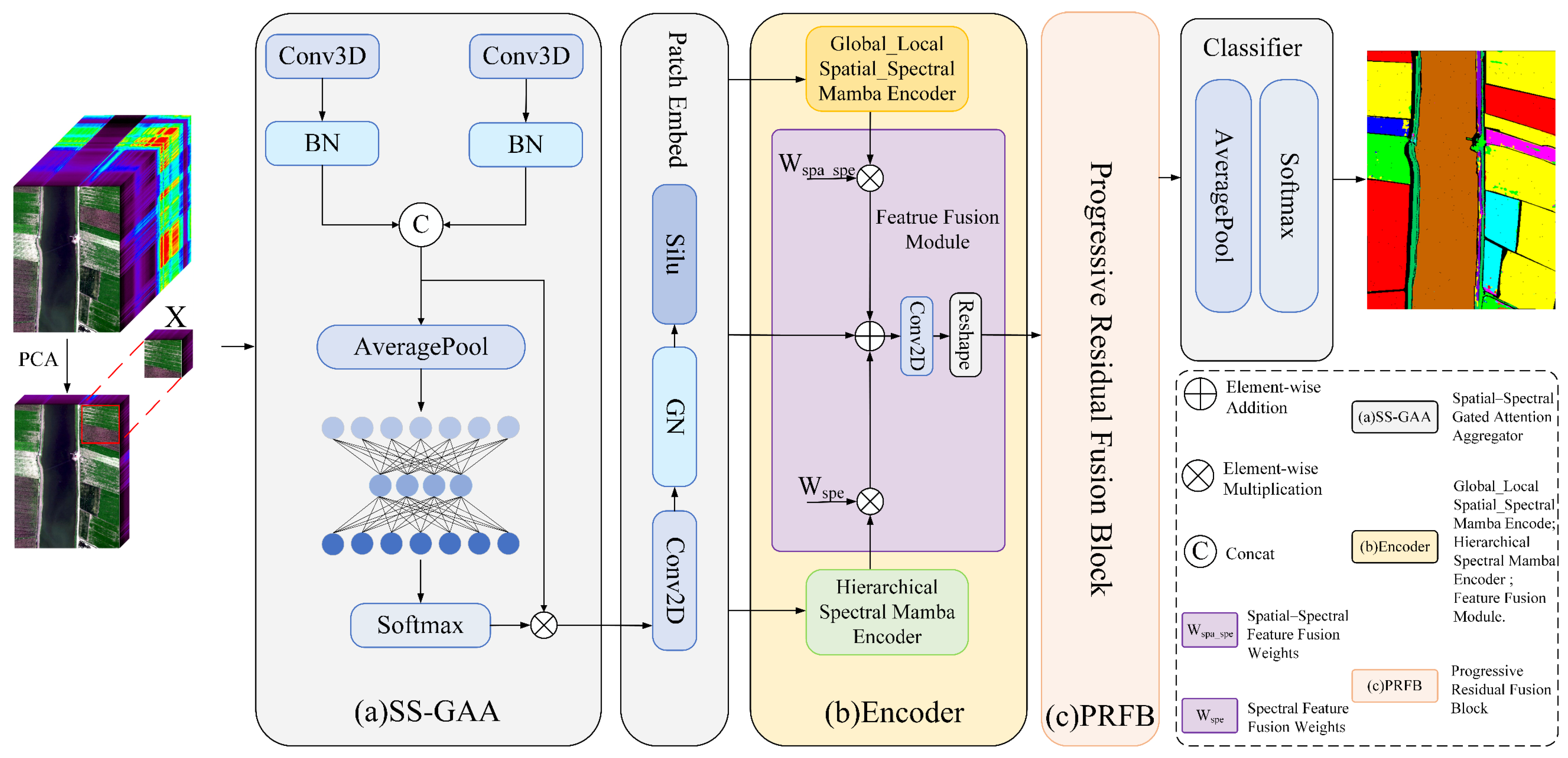
2.2. Overall Framework
2.3. Module Synergy and Functional Decomposition
2.4. Spatial–Spectral Gated Attention Aggregator
- Step 1: Let the input tensor be . After the initial 3D convolution, the spatial feature map and the spectral feature map are obtained:
- Step 2: The branches are summed element-wise to produce the channel-level aggregated representation :
- Step 3: A operation is applied along the branch dimension to obtain the normalized branch–channel weights . The final attention-weighted and fused feature is denoted as :
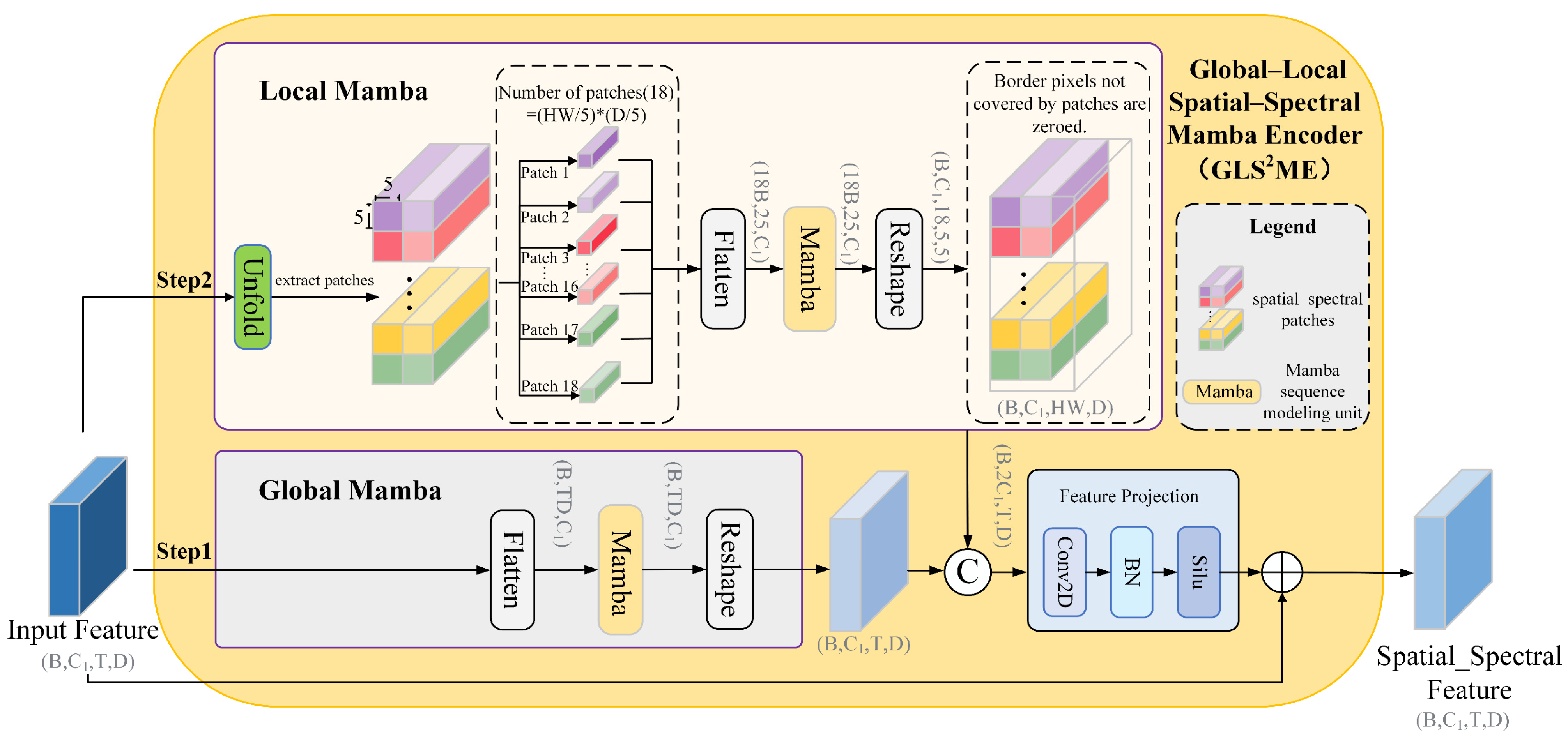
2.5. Global_Local Spatial_Spectral Mamba Encoder
- Step 1: The output features from the embedding layer are fed into the global path (as illustrated by the Global Mamba in Figure 2). The features are first flattened along the spatial dimension to form a sequence, which is then processed by the global Mamba to capture long-range dependencies across both spatial and spectral domains. The resulting features are subsequently reshaped back to the original spatial structure to preserve the integrity of discriminative patterns and structural consistency. Let the pixel-level embeddings be denoted as ; the specific computation is listed as follows:
- Step 2: The output features from the embedding layer are fed into the local path (as illustrated by the Local Mamba in Figure 2). First, the input is divided into multiple non-overlapping local patches (in this work ) of size (in this work ). Each patch is then flattened within the patch and processed by the local Mamba to model intra-patch dependencies, resulting in (where , , , ). If the spatial dimension or the spectral dimension is not divisible by the window size , the edge pixels that are not fully covered are excluded from local path computation; their positions in the local feature map are set to zero (As shown by the final scatter-add operation in the Local Mamba in Figure 2) and subsequently compensated by the global path and residual connections. After processing, each patch is restored to its original spatial location, and overlapping regions (if any) are averaged to produce the final local feature map. The detailed procedure is listed as follows:
- Step 3: The global and local features are concatenated along the channel dimension, projected by a 1 × 1 convolution, and then processed by batch normalization and a nonlinear activation to form the fused representation. The fused representation is subsequently added to the input via a residual connection to achieve integration of global and local features. The detailed structure is shown in the remaining parts of Figure 2. The fusion process is listed as follows:
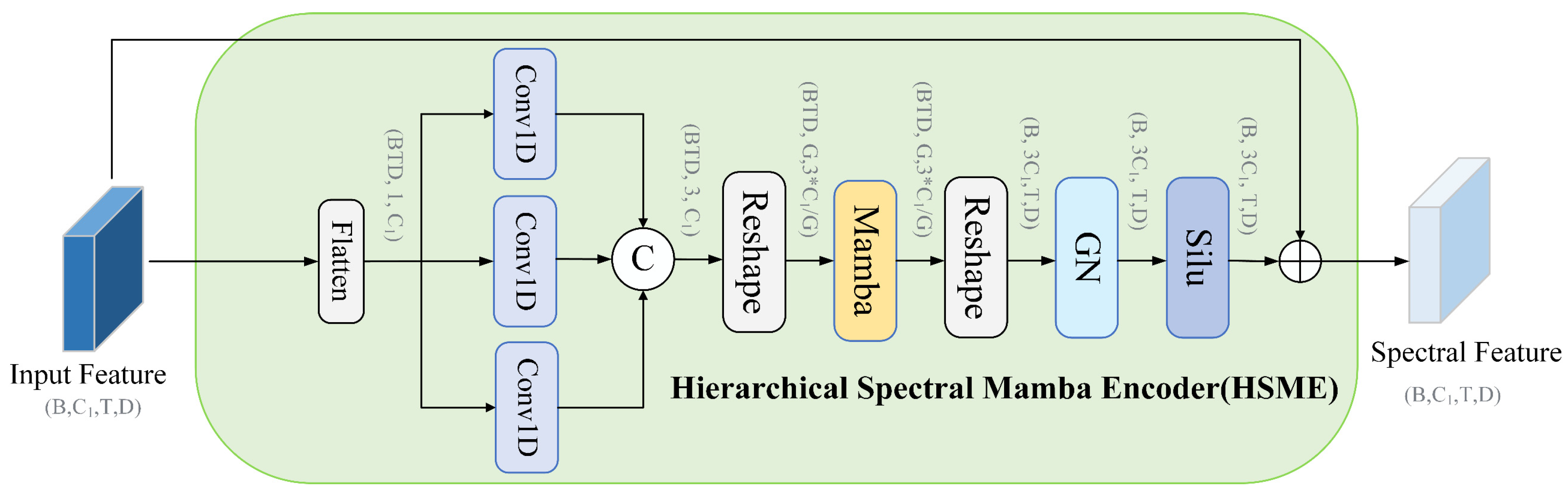
2.6. Hierarchical Spectral Mamba Encoder
- Step 1: Let denote the input data. Three 1D convolutions with different receptive fields are applied to extract spectral responses at fine, medium, and coarse scales, respectively.
- Step 2: The Mamba-based group-level feature extraction models semantic relationships among groups along the token dimension.
- Step 3: The output of Mamba is reconstructed according to the channel layout to form a multi-scale channel representation, and its expressive capacity is further enhanced through normalization and activation.
2.7. Feature Fusion Module
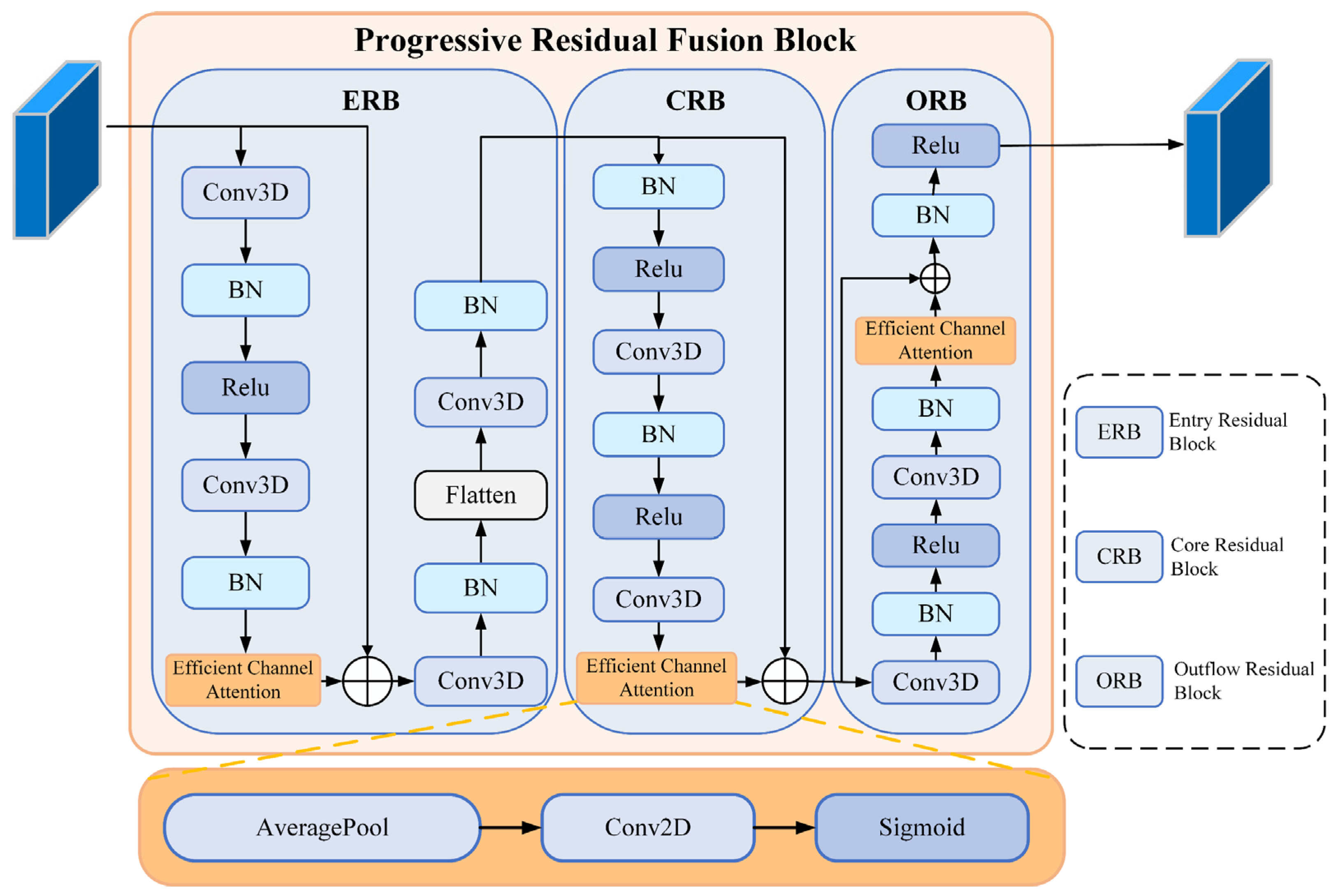
2.8. Progressive Residual Fusion Block
- Step 1 (Entry Residual Block): The ERB transforms the input into a compact, multi-scale spatial–spectral representation that preserves fine detail and suppresses noise. It expands channels with a convolution, aggregates along the spectral axis, reorders feature axes for cross-axis interaction, applies a second convolution, and concludes with spatial and spectral downsampling (see Figure 4 ERB)
- Step 2 (Core Residual Block): A stack of 3D convolutions with residual links progressively extracts deeper spatial–spectral features and improves channel discrimination (see Figure 4 CRB):
- Step 3 (Outflow Residual Block): The ORB serves as a feature organizer and stabilizer, ensuring that the output features exhibit stable statistical distributions and well-separated decision boundaries before the pooling and fully connected stages (see Figure 4 ORB):
3. Experimental Details
3.1. Dataset Description
3.2. Experimental Parameter Settings
3.3. Comparison Methods
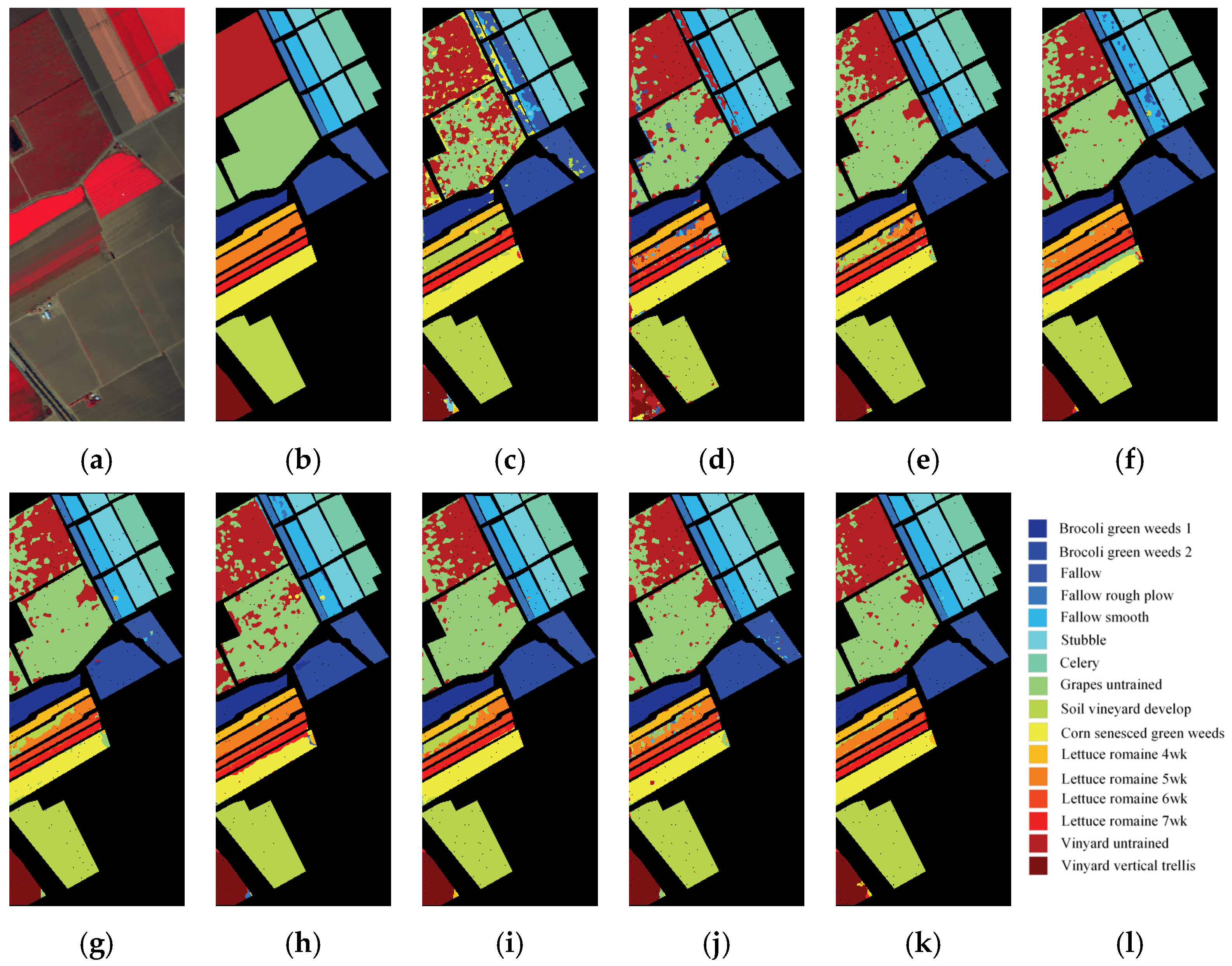
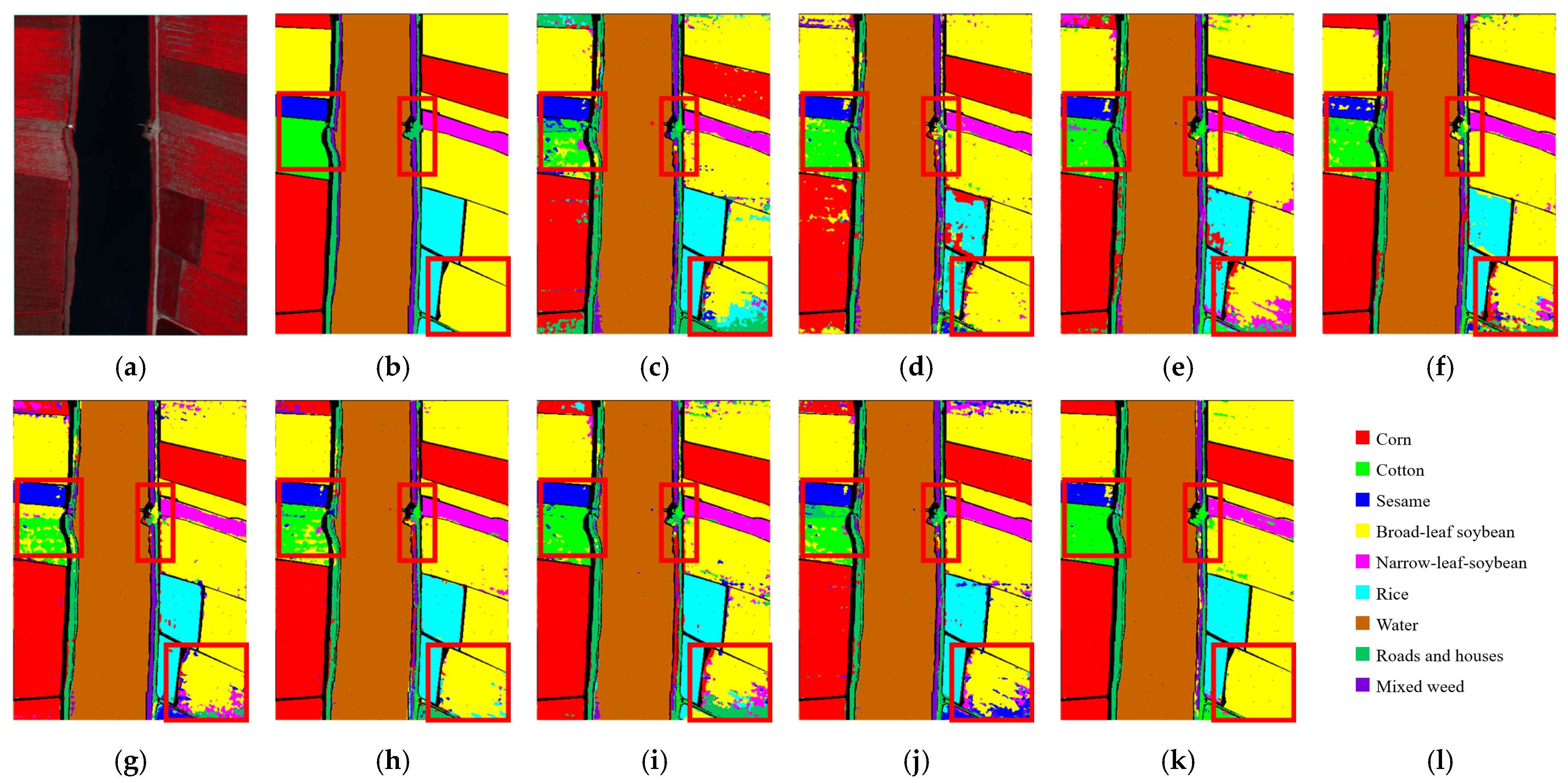
3.4. Quantitative Experimental Results
3.4.1. Comparison of Classification Metrics
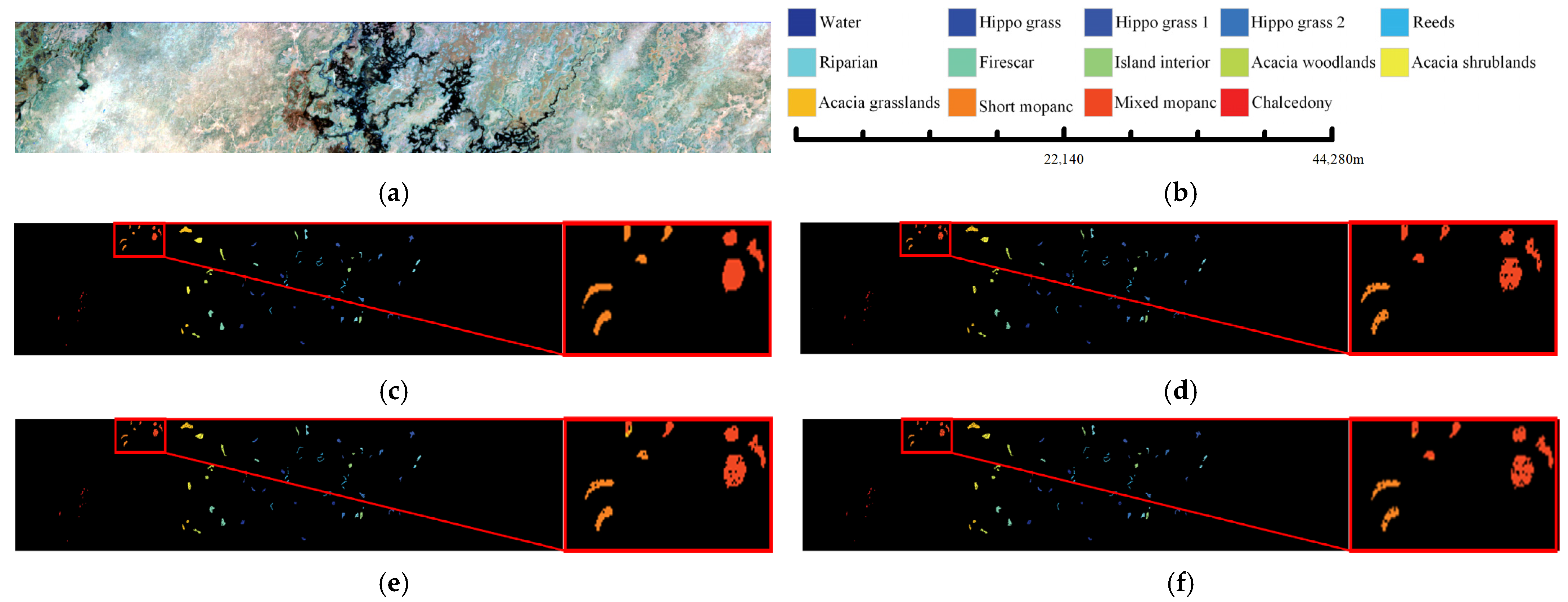
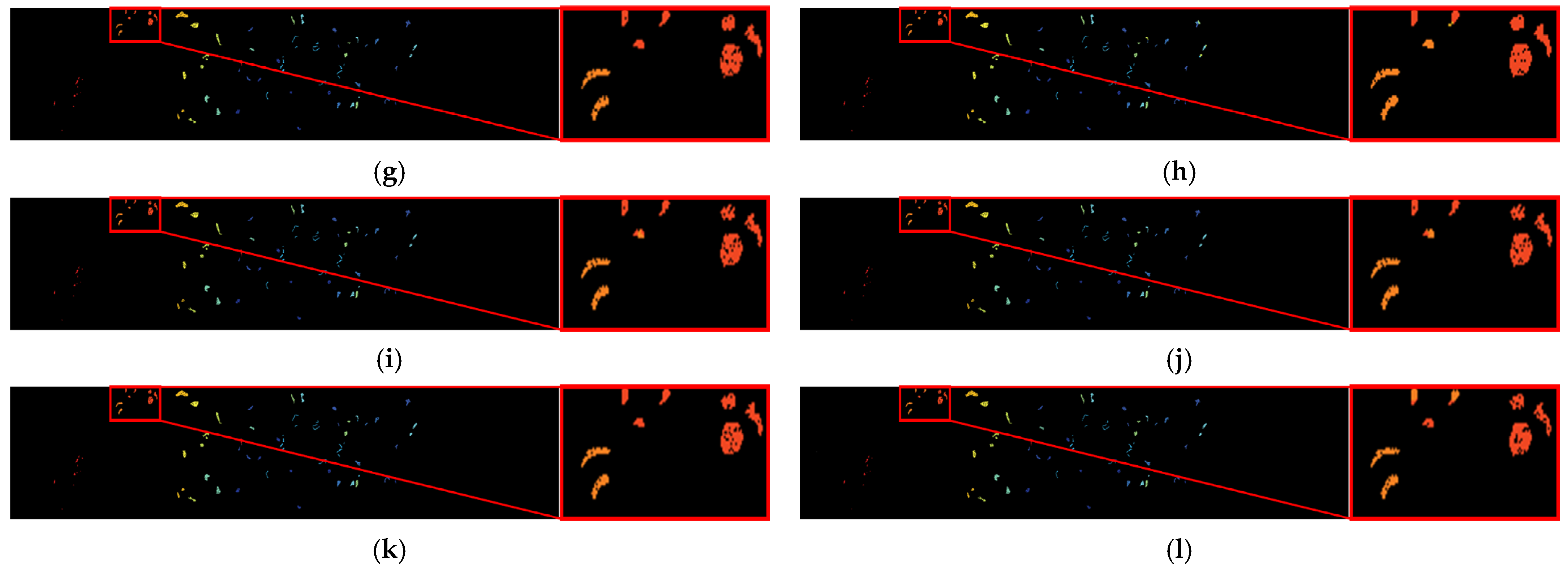
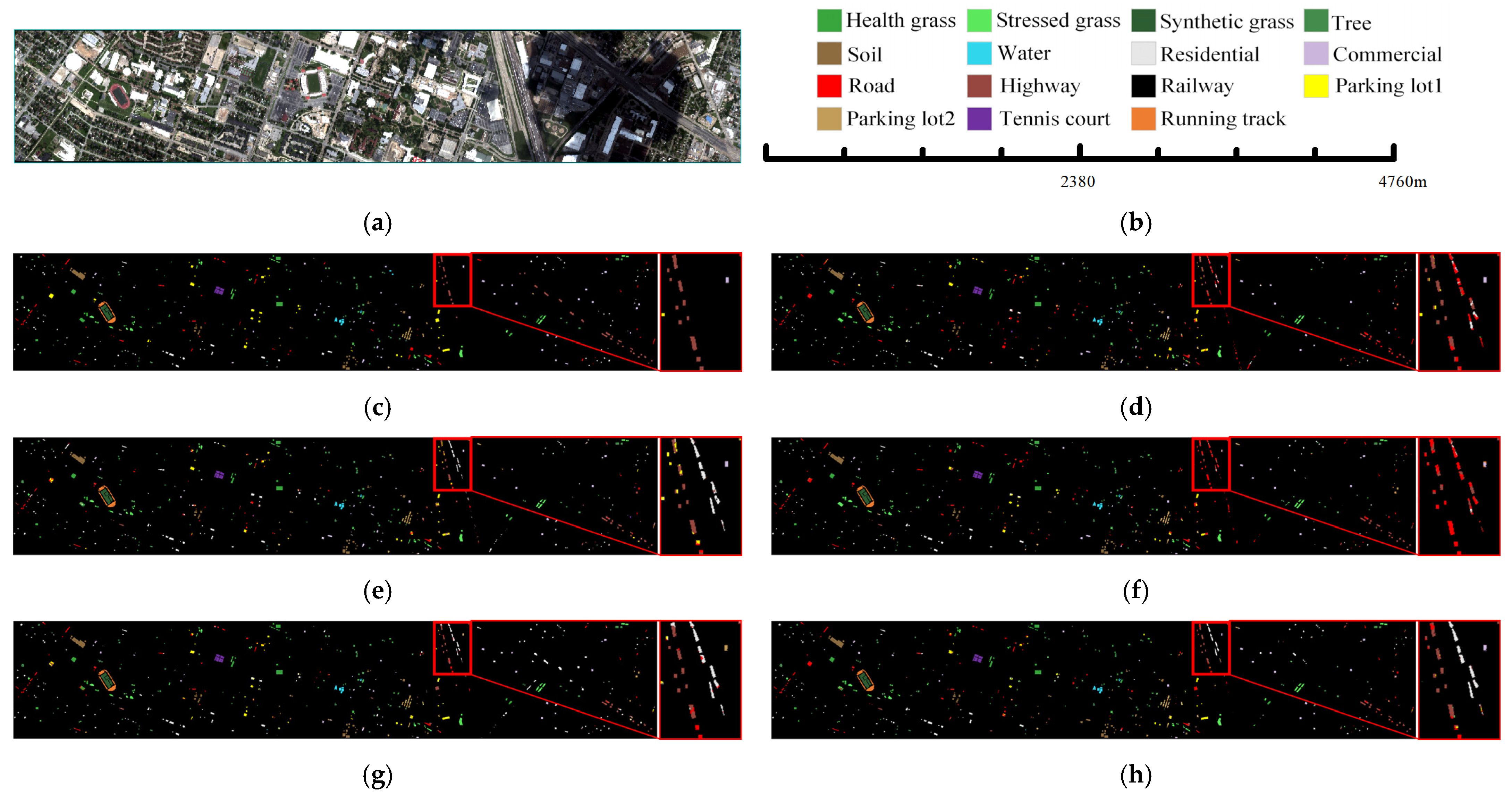
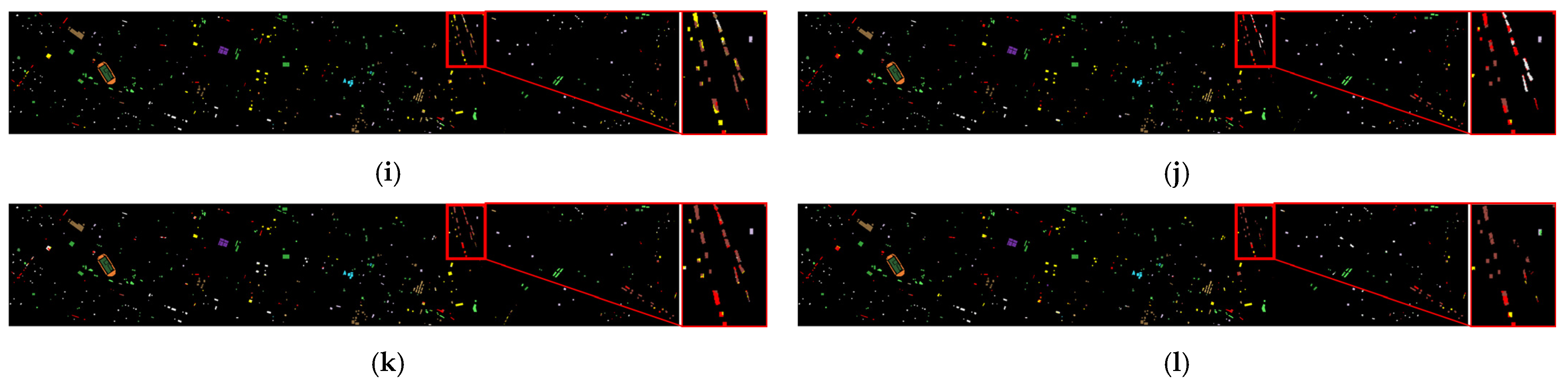
3.4.2. Comparison of Classification Maps
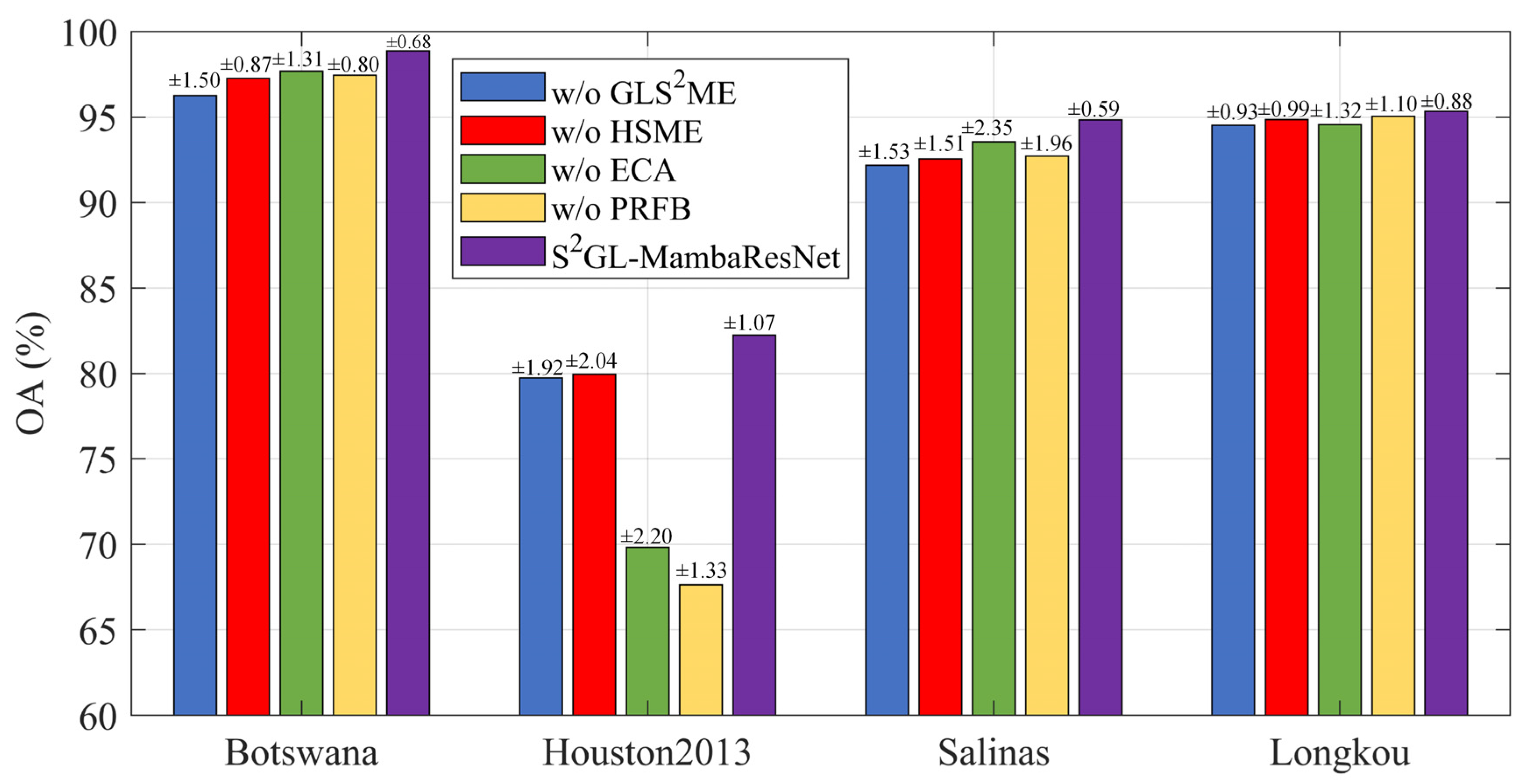
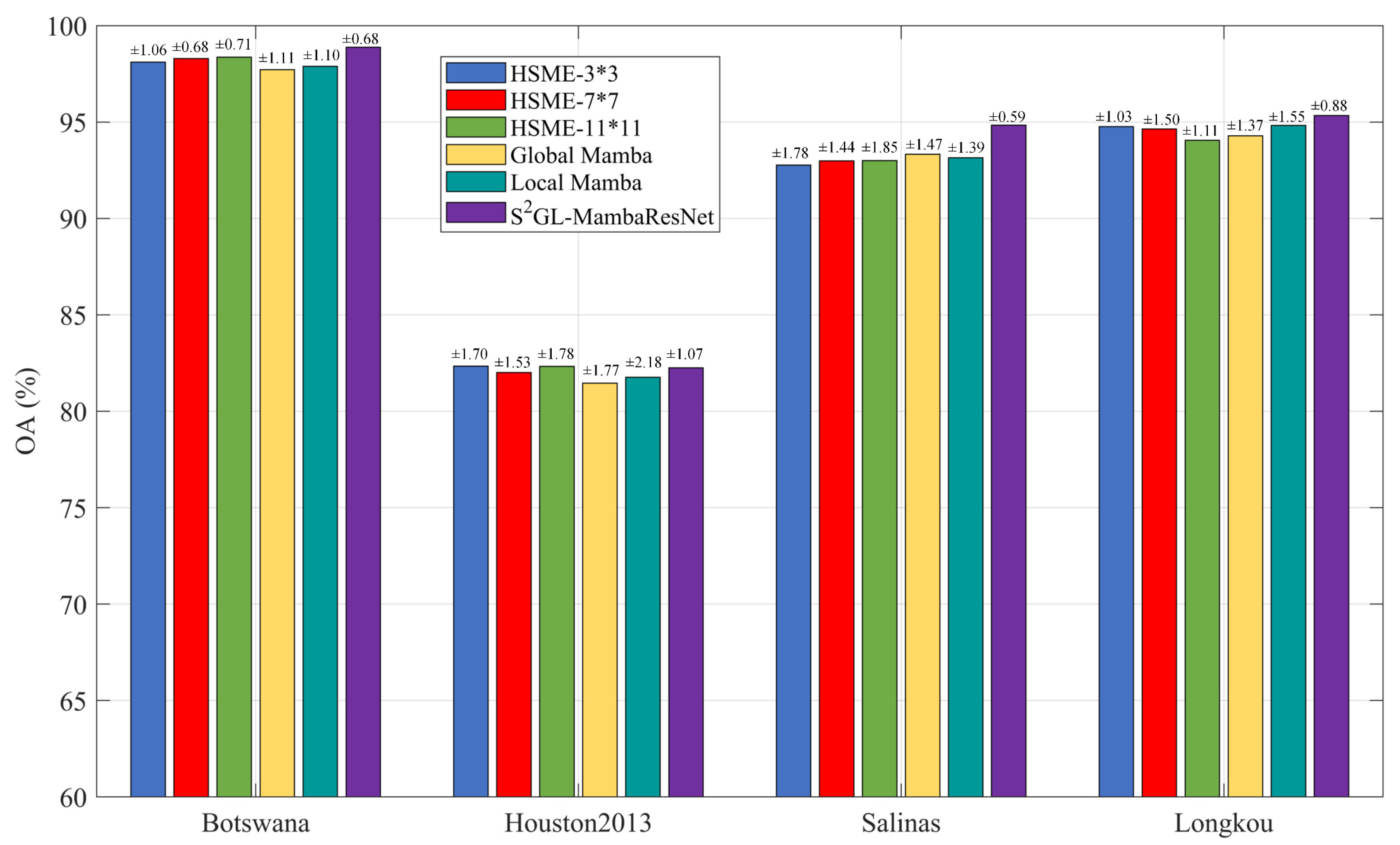
3.5. Ablation Experiments
- (1)
- w/o GLS2ME: The Global_Local Spatial_Spectral Mamba Encoder was removed from S2GL-MambaResNet.
- (2)
- w/o HSME: The Hierarchical Spectral Mamba Encoder was removed.
- (3)
- w/o ECA: The Efficient Channel Attention within the Progressive Residual Fusion Block was removed.
- (4)
- w/o PRFB: Both the Efficient Channel Attention and the residual summation within the Progressive Residual Fusion Block were removed.
- (1)
- HSME-3*3: Only the 3*3 small-scale convolutional kernels were used in the HSME.
- (2)
- HSME-7*7: Only the 7*7 medium-scale convolutional kernels were used in the HSME.
- (3)
- HSME-11*11: Only the 11*11 large-scale convolutional kernels were used in the HSME.
- (4)
- Global Mamba: Only the global path was retained in the GLS2ME.
- (5)
- Local Mamba: Only the local path was retained in the GLS2ME.
3.6. Effect of Patch Size
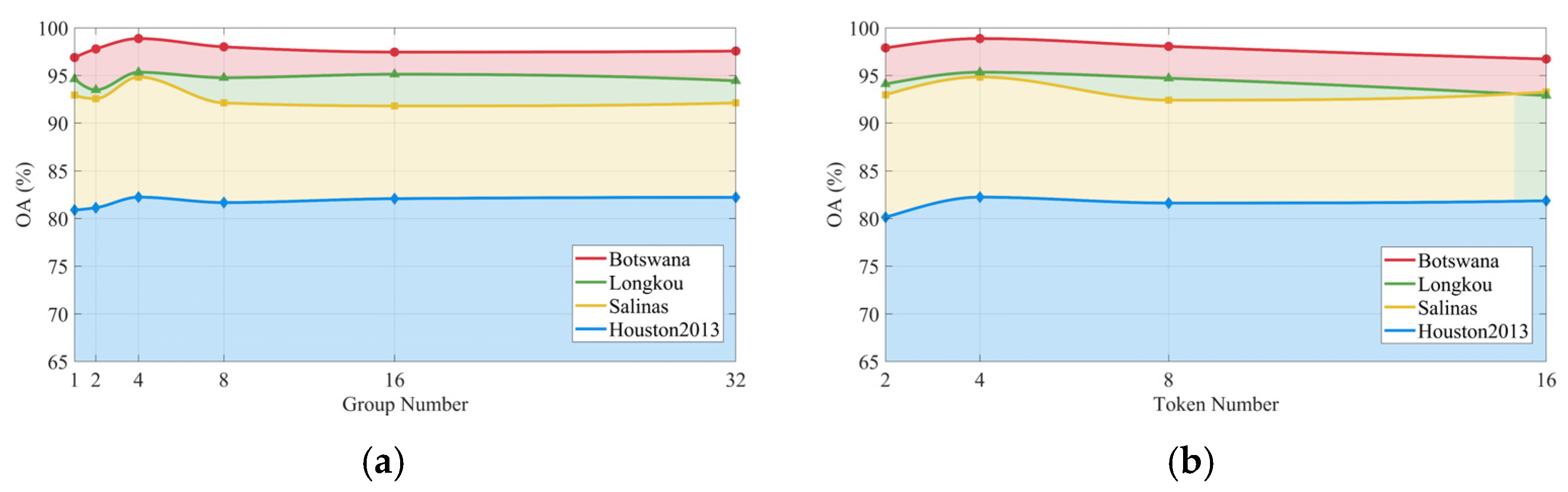
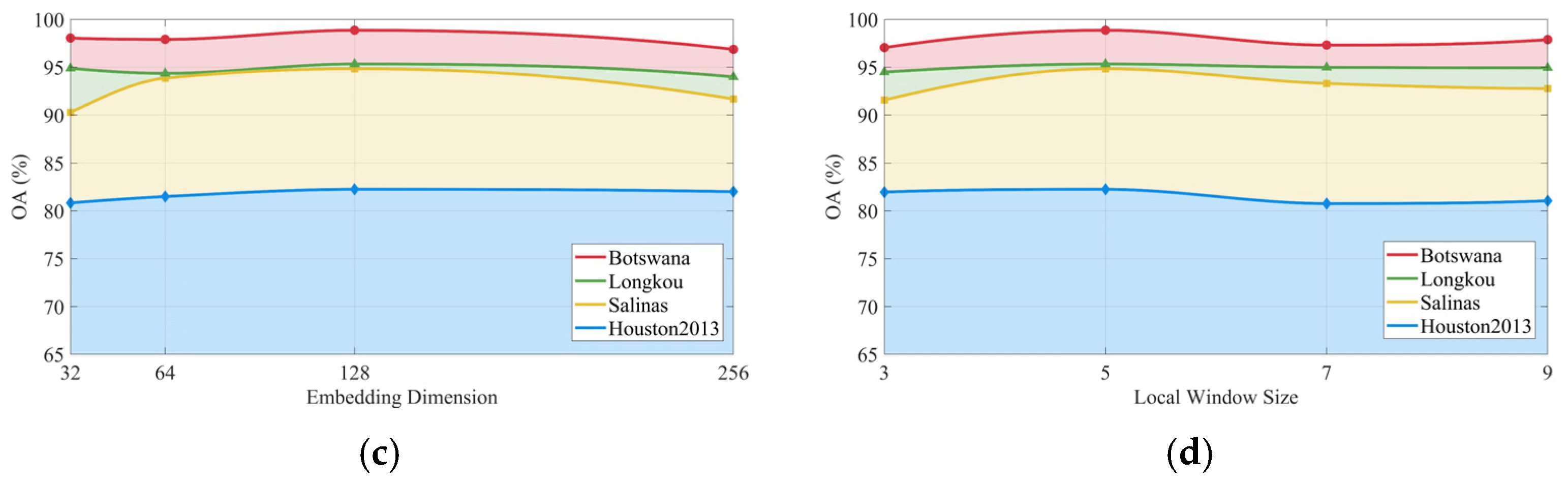
3.7. Hyper-Parameter Analysis
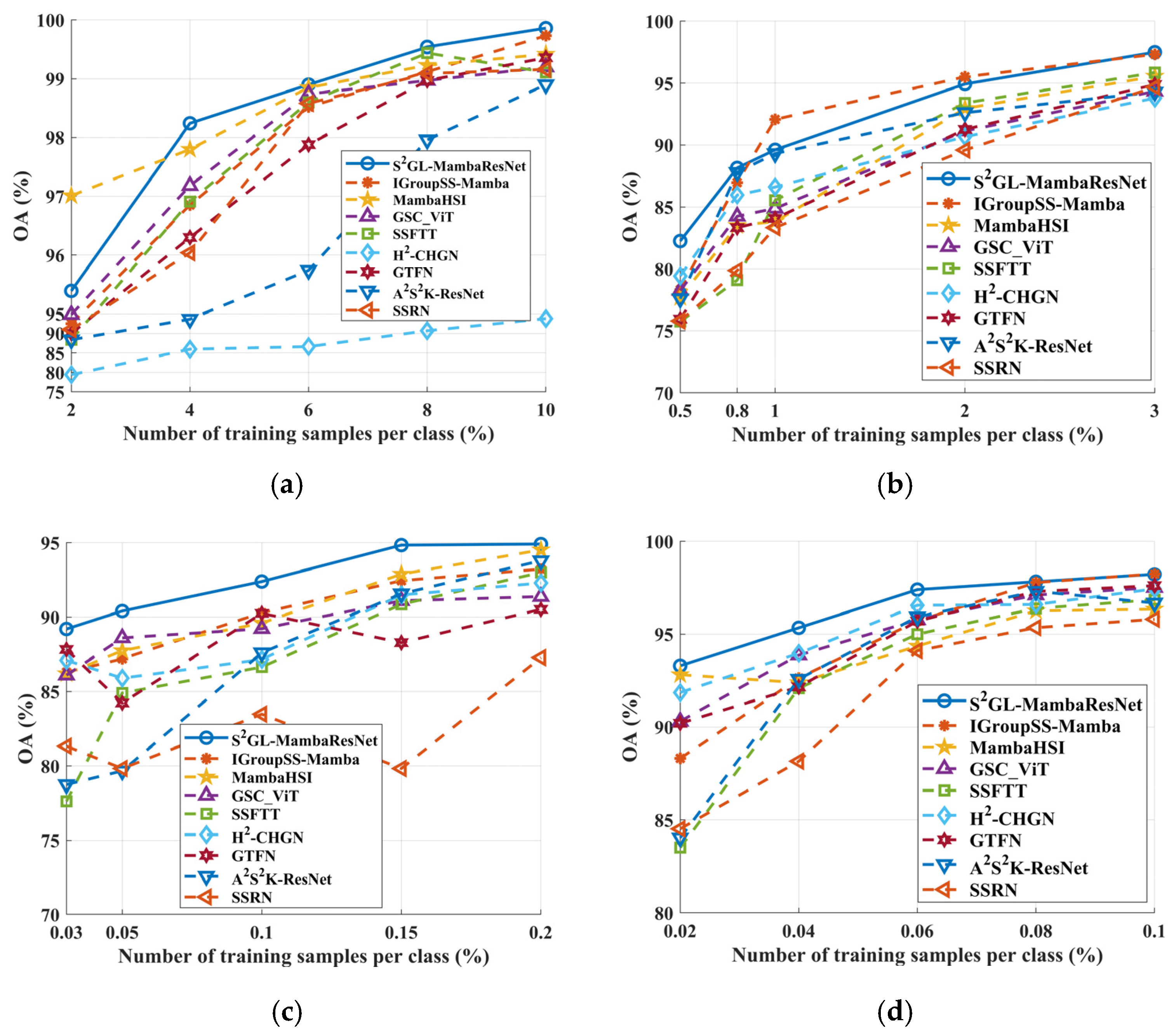
3.8. Sample Sensitivity Verification
4. Discussion
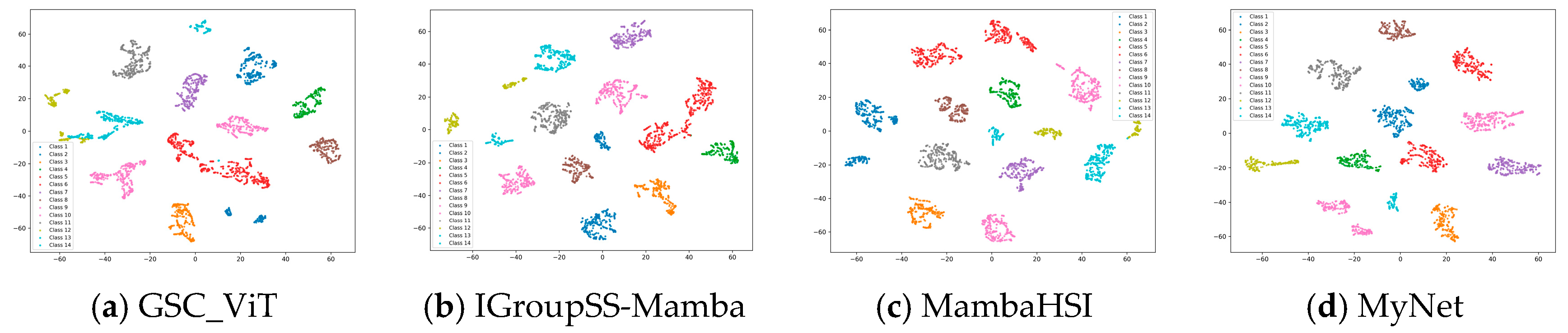
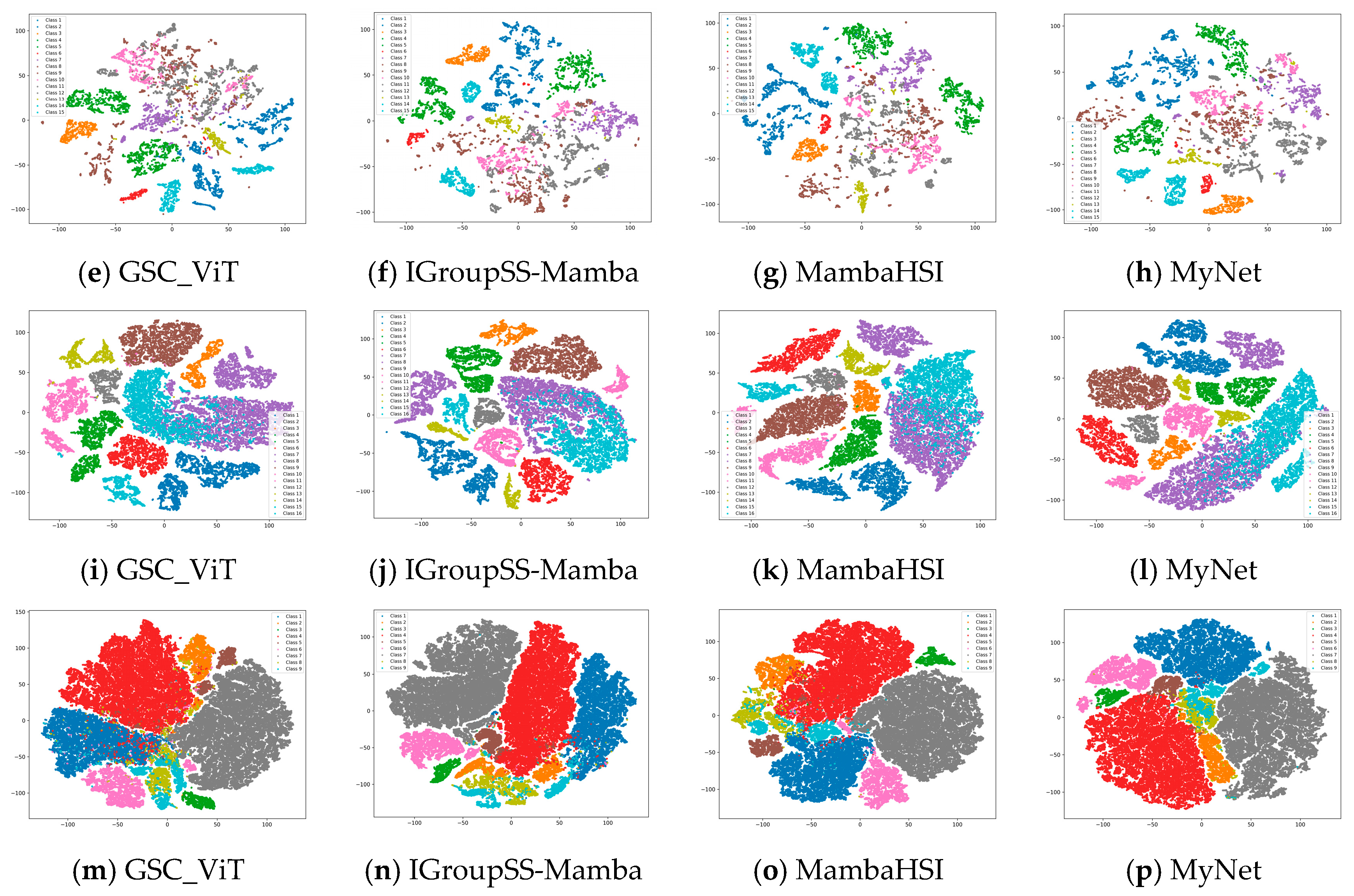
4.1. Learned Feature Visualizations by T-SNE
4.2. Discussion of Computational Complexity
4.3. Outlook and Future Work
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Long, H.; Chen, T.; Chen, H.; Zhou, X.; Deng, W. Principal space approximation ensemble discriminative marginalized least-squares regression for hyperspectral image classification. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2024, 133, 108031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horita, H. Optimizing runtime business processes with fair workload distribution. J. Compr. Bus. Adm. Res. 2025, 2, 162–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, D.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, J.; Yang, B.; Lin, Y. Exploring contextual knowledge-enhanced speech recognition in air traffic control communication: A comparative study. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2025, 36, 16085–16099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Chen, Y.; Lu, Z.; Ding, F.; Hu, B. ADED: Method and device for automatically detecting early depression using multimodal physiological signals evoked and perceived via various emotional scenes in virtual reality. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2025, 74, 2524016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Song, C. Adaptive evolutionary multitask optimization based on anomaly detection transfer of multiple similar sources. Expert Syst. Appl. 2025, 283, 127599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Chen, S.; Chen, L.; Chen, H.; Zheng, B.; Deng, W. Joint classification of hyperspectral and LiDAR data via multiprobability decision fusion method. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 4317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, H.; Shen, Q. Spectral–spatial classification of hyperspectral imagery with 3D convolutional neural network. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopatin, A. Intelligent system of estimation of total factor productivity (TFP) and investment efficiency in the economy with external technology gaps. J. Compr. Bus. Adm. Res. 2023, 1, 160–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Ye, Y.; Li, X.; Lau, R.Y.K.; Zhang, X.; Huang, X. Hyperspectral image classification with deep learning models. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2018, 56, 5408–5423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chhapariya, K.; Buddhiraju, K.M.; Kumar, A. A Deep Spectral–Spatial Residual Attention Network for Hyperspectral Image Classification. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Observ. Remote Sens. 2024, 17, 15393–15406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Yin, W.; Xue, J.; Fu, Y.; Jia, S. Global–Local Residual Fusion Network for Hyperspectral Image Classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2025, 63, 5522217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.; Dong, X.-M.; Li, W.; Peng, J.; Sun, W.; Xu, Y. DBCTNet: Double branch convolution-transformer network for hyperspectral image classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2024, 62, 5509915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, E.; Zhang, Q.; Lu, X. Concern With Center-Pixel Labeling: Center-Specific Perception Transformer Network for Hyperspectral Image Classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2025, 63, 5514614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Arshad, T.; Peng, B. Spectral Spatial Window Attention Transformer for Hyperspectral Image Classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2025, 63, 5519413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Song, Y.; Ma, H.; Zhou, X.; Deng, W. A multiple level competitive swarm optimizer based on dual evaluation criteria and global optimization for large-scale optimization problem. Inf. Sci. 2025, 708, 122068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Xu, H.; Liu, J.; Hou, M.; Li, Y.; Qiu, S.; Sun, M.; Zhao, H.; Deng, W. A hybridizing-enhanced quantum-inspired differential evolution algorithm with multi-strategy for complicated optimization. J. Artif. Intell. Soft Comput. Res. 2025, 16, 5–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, D.; Zhang, J.; Yang, B.; Lin, Y. Multi-modal intelligent situation awareness in real-time air traffic control: Control intent understanding and flight trajectory prediction. Chin. J. Aeronaut. 2025, 38, 103376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, W.; Shang, S.; Zhang, L.; Lin, Y.; Huang, C.; Zhao, H.; Ran, X.; Zhou, X.; Chen, H. Multi-strategy quantum differential evolution algorithm with cooperative co-evolution and hybrid search for capacitated vehicle routing. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2025, 26, 18460–18470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Chen, Y.; Wang, X.; Wang, D.; Xu, H.; Deng, W. Joint optimization scheduling using AHMQDE-ACO for key resources in smart operations. IEEE Trans. Consum. Electron. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, A.; Dao, T. Mamba: Linear-time sequence modeling with selective state spaces. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2312.00752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dao, T.; Gu, A. Transformers are SSMS: Generalized models and efficient algorithms through structured state space duality. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2405.21060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.X.; Zhou, J.; Wang, J.; Tian, H.; Liew, A.W.C. Hsimamba: Hyperpsectral imaging efficient feature learning with bidirectional state space for classification. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2404.00272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Tu, B.; Liu, B.; Li, J.; Plaza, A. 3DSS-Mamba: 3D-Spectral-Spatial Mamba for Hyperspectral Image Classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2024, 62, 5534216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Tu, B.; Jiang, P.; Liu, B.; Li, J.; Plaza, A. IGroupSS-Mamba: Interval Group Spatial–Spectral Mamba for Hyperspectral Image Classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2024, 62, 5538817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J.; Plaza, A.; Benediktsson, J.A. SpiralMamba: Spatial–Spectral Complementary Mamba With Spatial Spiral Scan for Hyperspectral Image Classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2025, 63, 5510319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Liu, C.; Dang, X.; Xu, J.; Deng, W. Few-shot cross-domain fault diagnosis of transportation motor bearings using MAML-GA. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; Agrawal, S.; Dongre, S. Blockchain-based NFT warranty system: A software implementation. J. Compr. Bus. Adm. Res. 2024, 1, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, W.; Xu, H.; Guan, Z.; Sun, Y.; Ran, X.; Ma, H.; Zhou, X.; Zhao, H. PSO-K-means clustering-based NSGA-III for delay recovery. IEEE Trans. Consum. Electron. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Gu, M.; Qiu, S.; Zhao, A.; Deng, W. Dynamic path planning for space-time optimization cooperative tasks of multiple unmanned aerial vehicles in uncertain environment. IEEE Trans. Consum. Electron. 2025, 71, 7673–7682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhao, H.; Xu, J.; Zhu, G.; Deng, W. APDPFL: Anti-poisoning attack decentralized privacy enhanced federated learning scheme for flight operation data sharing. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2024, 23, 19098–19109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, W.; Li, X.; Xu, J.; Li, W.; Zhu, G.; Zhao, H. BFKD: Blockchain-based federated knowledge distillation for aviation internet of things. IEEE Trans. Reliab. 2025, 7, 2626–2639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, R.; Zhao, H.; Zhao, Z.; Guo, C.; Deng, W. Parallel convolutional transfer network for bearing fault diagnosis under varying operation states. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2024, 73, 3540713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Luo, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Z.; Du, B. MambaHSI: Spatial–Spectral Mamba for Hyperspectral Image Classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2024, 62, 5524216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Wu, B.; Zhu, P.; Li, P.; Zuo, W.; Hu, Q. ECA-Net: Efficient Channel Attention for Deep Convolutional Neural Networks. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1910.03151. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, Y.; Hu, X.; Luo, C.; Wang, X.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, L. WHU-Hi: UAV-borne hyperspectral with high spatial resolution (H2) benchmark datasets and classifier for precise crop identification based on deep convolutional neural network with CRF. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 250, 112012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Z.; Li, J.; Luo, Z.; Chapman, M. Spectral–spatial residual network for hyperspectral image classification: A 3-D deep learning framework. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2017, 56, 847–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.K.; Manna, S.; Song, T.; Bruzzone, L. Attention-based adaptive spectral–spatial kernel ResNet for hyperspectral image classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 59, 7831–7843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, A.; Li, M.; Ding, Y.; Hong, D.; Lv, Y.; He, Y. GTFN: GCN and transformer fusion network with spatial-spectral features for hyperspectral image classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 61, 6600115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Wang, T.; Chen, H.; Zheng, B.; Deng, W. Cross-Hopping Graph Networks for Hyperspectral–High Spatial Resolution (H2) Image Classification. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 3155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Zhao, G.; Zheng, Y.; Wu, Z. Spectral–spatial feature tokenization transformer for hyperspectral image classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 5522214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Xu, X.; Li, S.; Plaza, A. Hyperspectral image classification using groupwise separable convolutional vision transformer network. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2024, 62, 5511817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Zhang, X.; Peng, Z.; Zhang, T.; Jiao, L. S2Mamba: A Spatial–Spectral State Space Model for Hyperspectral Image Classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2025, 63, 5511413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maaten, L.; Hinton, G. Visualizing data using t-SNE. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2008, 9, 2579–2605. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, K.; Zhao, Z.; Yang, Q.; Feng, R. SCSU–GDO: Superpixel Collaborative Sparse Unmixing with Graph Differential Operator for Hyperspectral Imagery. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 3088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cañada, C.; Paoletti, M.E.; García-Flores, M.B.; Tao, X.; Pastor-Vargas, R.; Haut, J.M. Distributed Parallel Hyperspectral Unmixing for Large-Scale Data in Spark Environments via Geometric Distance. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2025, 63, 5531719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, K.; Li, R.; Polk, S.L.; Lin, Y.; Zhang, H.; Murphy, J.M.; Plemmons, R.J.; Chan, R.H. Superpixel-based and spatially regularized diffusion learning for unsupervised hyperspectral image clustering. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2024, 62, 4405818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Mi, P.; Han, D. CPMFFormer: Class-Aware Progressive Multiscale Fusion Transformer for Hyperspectral Image Classification. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 3684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, A.; Feng, R.; Li, X. ThiefCloud: A Thickness Fused Thin Cloud Removal Network for Optical Remote Sensing Image With Self-Supervised Learnable Cloud Prior. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Yu, W.; Ghamisi, P.; Kopp, M.; Hochreiter, S. Txt2Img-MHN: Remote sensing image generation from text using modern Hopfield networks. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2023, 32, 5737–5750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Wu, D.; Zhou, X.; Song, Y.; Chen, H.; Deng, W. Competitive swarm optimizer with dynamic multi-competitions and convergence accelerator for large-scale optimization problems. Appl. Soft Comput. 2024, 167, 112252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Zhang, J.; Lin, L.; Wang, J.; Gao, S.; Zhang, Z. Locally linear unbiased randomization network for cross-scene hyperspectral image classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 61, 5526512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.; Li, X.; Miao, J.; Shen, H. A front-back view fusion strategy and a novel dataset for super tiny object detection in remote sensing imagery. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2025, 326, 114051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.; Geng, J.; Jiang, W. Spectral-Spatial Enhancement and Causal Constraint for Hyperspectral Image Cross-Scene Classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2024, 62, 5507013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Zhen, H.; Zhang, X.; Bai, X.; Li, X. SEMA-YOLO: Lightweight Small Object Detection in Remote Sensing Image via Shallow-Layer Enhancement and Multi-Scale Adaptation. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.; Zhang, W.; Tian, C.; Rong, X.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, H.; Fu, K.; Sun, X. Remote sensing cross-modal text-image retrieval based on global and local information. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 5620616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Yu, J.G.; Zhang, Y. Learning deep cross-modal embedding networks for zero-shot remote sensing image scene classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 59, 10590–10603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.K.; Jamali, A.; Chanussot, J.; Ghamisi, P.; Ghaderpour, E.; Shahabi, H. SimPoolFormer: A two-stream vision transformer for hyperspectral image classification. Remote Sens. Appl. Soc. Environ. 2025, 37, 101478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkhatib, M.Q.; Al-Saad, M.; Aburaed, N.; Almansoori, S.; Zabalza, J.; Marshall, S.; Al-Ahmad, H. Tri-CNN: A three branch model for hyperspectral image classification. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Yao, J.; Xu, Z.; Meng, D. Hyperspectral image classification with convolutional neural network and active learning. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 58, 4604–4616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, C.; Zhou, L.; Ding, S.; Lu, M.; Zhou, X. Research on self-propulsion simulation of a polar ship in a brash ice channel based on body force model. Int. J. Nav. Archit. Ocean Eng. 2023, 15, 100557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, W.; Li, K.; Zhao, H. A flight arrival time prediction method based on cluster clustering-based modular with deep neural network. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2024, 25, 6238–6247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Yan, L.; Sun, J.; Ding, S.; Li, F.; Diao, F.; Zhou, L. Hybrid trajectory planning and tracking for automatic berthing: A grid-search and optimal control integration approach. Ocean Eng. 2025, 317, 120002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, X.; Suyaroj, N.; Tepsan, W.; Lei, M.; Ma, H.; Zhou, X.; Deng, W. A novel fuzzy system-based genetic algorithm for trajectory segment generation in urban global positioning system. J. Adv. Res. 2025; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Sun, J.; Yan, L.; Ding, S.; Zhou, L. Research on effective trajectory planning, tracking, and reconstruction for USV formation in complex environments. Ocean Eng. 2025, 341, 122488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.J.; Jiang, J.; Liu, X.M.; Ma, J.Y. Learning a 3D-CNN and Transformer Prior for Hyperspectral Image Super-Resolution. Inf. Fusion 2023, 100, 101907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Information | Botswana | Houston2013 | Salinas | WHU-Hi-LongKou |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Size (pixels) | 1476 × 256 | 349 × 1905 | 512 × 217 | 550 × 400 |
| Bands | 145 | 144 | 204 | 270 |
| Spatial-res (m) Spectral-wave (nm) | 30 380–1050 | 2.5 380–1050 | 3.7 400–2500 | 0.463 400–1000 |
| Sensor | Hyperion | CASI-1500 | AVIRIS | DJI M600 Pro |
| Class | 14 | 15 | 16 | 9 |
| Training sample ratio | 4% | 0.5% | 0.15% | 0.04% |
| Training sample ratio | 96% | 99.5% | 99.85% | 99.96% |
| Class | Name | Train | Test |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Water | 10 | 260 |
| 2 | Hippo grass | 4 | 97 |
| 3 | Floodplain grasses1 | 10 | 241 |
| 4 | Floodplain grasses2 | 8 | 207 |
| 5 | Reeds | 10 | 259 |
| 6 | Riparian | 10 | 259 |
| 7 | Firescar | 10 | 249 |
| 8 | island interior | 8 | 195 |
| 9 | Accacia woodlands | 12 | 302 |
| 10 | Acacia shrublands | 9 | 239 |
| 11 | Accacia grasslands | 12 | 293 |
| 12 | Short mopane | 7 | 174 |
| 13 | Mixed mopane | 10 | 258 |
| 14 | Exposed soils | 3 | 92 |
| Total | 123 | 3125 |
| Class | Name | Train | Test |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Grass_healthy | 6 | 1245 |
| 2 | Grass_stressed | 6 | 1248 |
| 3 | Grass_synthetic | 3 | 694 |
| 4 | Tree | 6 | 1238 |
| 5 | Soil | 6 | 1236 |
| 6 | Water | 1 | 324 |
| 7 | Residential | 6 | 1262 |
| 8 | Commercial | 6 | 1238 |
| 9 | Road | 6 | 1246 |
| 10 | Highway | 6 | 1221 |
| 11 | Railway | 6 | 1229 |
| 12 | Parking_lot1 | 6 | 1227 |
| 13 | Parking_lot2 | 2 | 467 |
| 14 | Tennis_court | 2 | 426 |
| 15 | Running_track | 3 | 657 |
| Total | 71 | 14,958 |
| Class | Name | Train | Test |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Brocoli green weeds 1 | 3 | 2006 |
| 2 | Brocoli green weeds 2 | 5 | 3721 |
| 3 | Fallow | 2 | 1974 |
| 4 | Fallow rough plow | 2 | 1392 |
| 5 | Fallow smooth | 4 | 2674 |
| 6 | Stubble | 5 | 3954 |
| 7 | Celery | 5 | 3574 |
| 8 | Grapes untrained | 16 | 11,255 |
| 9 | Soil vineyard develop | 9 | 6194 |
| 10 | Corn senesced green weeds | 4 | 3274 |
| 11 | Lettuce romaine 4 wk | 1 | 1067 |
| 12 | Lettuce romaine 5 wk | 2 | 1925 |
| 13 | Lettuce romaine 6 wk | 1 | 915 |
| 14 | Lettuce romaine 7 wk | 1 | 1069 |
| 15 | Vinyard untrained | 10 | 7258 |
| 16 | Vinyard vertical trellis | 2 | 1805 |
| Total | 72 | 54,057 |
| Class | Name | Train | Test |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Corn | 13 | 34,498 |
| 2 | Cotton | 3 | 8371 |
| 3 | Sesame | 1 | 3030 |
| 4 | Broad-leaf soybean | 25 | 63,187 |
| 5 | Narrow-leaf-soybean | 1 | 4150 |
| 6 | Rice | 4 | 11,850 |
| 7 | Water | 26 | 67,030 |
| 8 | Roads and houses | 2 | 7122 |
| 9 | Mixed weed | 2 | 5227 |
| Total | 77 | 204,465 |
| Class | CNN (Residual Network)-Based Methods | GCN-Based Methods | Transformer- Based Methods | SSM-Based | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SSRN | A2S2K-ResNet | GTFN | H2-CHGN | SSFTT | GSC_ViT | MambaHSI | IGroupSS-Mamba | S2Mamba | MyNet | |
| TGRS2018 | TGRS2022 | TGRS2023 | RS2024 | TGRS2021 | TGRS2024 | TGRS2024 | TGRS2024 | TGRS2025 | Ours | |
| 1 | 99.15 ± 0.94 | 99.64 ± 0.33 | 99.69 ± 0.38 | 96.50 ± 3.88 | 99.07 ± 1.85 | 99.02 ± 1.37 | 99.94 ± 0.14 | 100.00 ± 0.00 | 100.00 ± 0.00 | 99.80 ± 0.20 |
| 2 | 99.13 ± 1.93 | 100.00 ± 0.00 | 99.79 ± 0.41 | 100.00 ± 0.00 | 92.58 ± 9.66 | 100.00 ± 0.00 | 85.96 ± 14.77 | 100.00 ± 0.00 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 98.60 ± 1.88 |
| 3 | 99.04 ± 2.38 | 98.55 ± 2.64 | 100.00 ± 0.00 | 95.46 ± 10.70 | 90.04 ± 9.69 | 99.91 ± 0.18 | 99.20 ± 1.14 | 92.03 ± 10.72 | 95.73 ± 4.48 | 99.84 ± 0.30 |
| 4 | 95.48 ± 4.32 | 95.24 ± 2.87 | 99.03 ± 0.61 | 100.00 ± 0.00 | 99.61 ± 0.77 | 99.38 ± 0.82 | 98.99 ± 1.17 | 99.32 ± 1.06 | 85.44 ± 4.16 | 99.57 ± 0.79 |
| 5 | 90.79 ± 6.61 | 88.75 ± 4.37 | 93.36 ± 3.06 | 92.85 ± 4.94 | 91.09 ± 9.61 | 93.55 ± 5.28 | 89.34 ± 4.05 | 96.59 ± 1.60 | 92.11 ± 3.88 | 96.21 ± 3.24 |
| 6 | 92.29 ± 7.14 | 94.02 ± 7.82 | 98.38 ± 0.75 | 98.24 ± 1.40 | 89.38 ± 11.47 | 93.31 ± 5.86 | 96.44 ± 1.87 | 97.67 ± 1.26 | 19.14 ± 13.96 | 97.06 ± 3.37 |
| 7 | 97.62 ± 4.21 | 99.33 ± 1.75 | 99.92 ± 0.16 | 92.55 ± 7.95 | 100.00 ± 0.00 | 99.92 ± 0.17 | 100.00 ± 0.00 | 100.00 ± 0.00 | 98.68 ± 0.31 | 99.95 ± 0.14 |
| 8 | 99.32 ± 1.13 | 98.65 ± 2.70 | 74.67 ± 4.12 | 100.00 ± 0.00 | 99.79 ± 0.41 | 99.78 ± 0.43 | 99.70 ± 0.48 | 100.00 ± 0.00 | 95.02 ± 4.91 | 99.53 ± 0.82 |
| 9 | 94.90 ± 6.33 | 94.75 ± 3.96 | 99.93 ± 0.13 | 100.00 ± 0.00 | 92.98 ± 9.75 | 95.52 ± 3.58 | 99.03 ± 2.24 | 99.93 ± 0.15 | 87.09 ± 2.18 | 98.94 ± 1.50 |
| 10 | 99.47 ± 0.81 | 97.86 ± 4.80 | 98.24 ± 2.07 | 100.00 ± 0.00 | 99.08 ± 0.97 | 97.96 ± 3.45 | 99.88 ± 0.30 | 99.75 ± 0.38 | 62.46 ± 8.15 | 99.34 ± 0.44 |
| 11 | 98.28 ± 2.67 | 98.80 ± 2.34 | 99.80 ± 0.41 | 93.01 ± 6.43 | 95.63 ± 5.35 | 99.06 ± 1.20 | 99.24 ± 1.87 | 99.25 ± 1.01 | 98.00 ± 1.34 | 98.88 ± 1.40 |
| 12 | 98.55 ± 3.36 | 97.08 ± 4.15 | 98.28 ± 1.78 | 100.00 ± 0.00 | 59.20 ± 9.12 | 98.18 ± 3.04 | 99.91 ± 0.21 | 72.07 ± 6.67 | 75.62 ± 11.84 | 99.55 ± 0.65 |
| 13 | 91.75 ± 7.70 | 94.29 ± 5.23 | 100.00 ± 0.00 | 93.99 ± 6.26 | 100.00 ± 0.00 | 99.59 ± 0.82 | 100.00 ± 0.00 | 99.53 ± 1.04 | 85.33 ± 2.32 | 99.02 ± 1.46 |
| 14 | 100.00 ± 0.00 | 99.88 ± 0.35 | 83.26 ± 2.53 | 96.50 ± 3.88 | 92.97 ± 5.84 | 90.23 ± 7.38 | 91.49 ± 6.18 | 96.48 ± 1.43 | 9.78 ± 10.70 | 98.52 ± 2.59 |
| OA (%) | 96.04 ± 1.74 | 96.30 ± 1.03 | 96.91 ± 0.41 | 97.18 ± 1.20 | 93.63 ± 2.08 | 97.67 ± 0.90 | 97.80 ± 0.51 | 96.85 ± 0.96 | 78.30 ± 1.36 | 98.88 ± 0.64 |
| AA (%) | 96.84 ± 1.14 | 96.92 ± 0.84 | 96.05 ± 0.48 | 97.33 ± 1.22 | 92.96 ± 1.97 | 97.53 ± 1.03 | 97.08 ± 0.93 | 96.40 ± 0.97 | 71.74 ± 1.58 | 98.91 ± 0.66 |
| Kappa | 95.70 ± 1.89 | 95.99 ± 1.12 | 96.65 ± 0.45 | 96.95 ± 1.29 | 93.09 ± 2.25 | 97.47 ± 0.98 | 97.82 ± 1.04 | 96.59 ± 1.04 | 76.39 ± 1.48 | 98.78 ± 0.70 |
| Class | CNN (Residual Network)-Based Methods | GCN-Based Methods | Transformer- Based Methods | SSM-Based | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SSRN | A2S2K-ResNet | GTFN | H2-CHGN | SSFTT | GSC_ViT | MambaHSI | IGroupSS-Mamba | S2Mamba | MyNet | |
| TGRS2018 | TGRS2021 | TGRS2023 | RS2024 | TGRS2022 | TGRS2024 | TGRS2024 | TGRS2024 | TGRS2025 | Ours | |
| 1 | 87.80 ± 8.58 | 89.23 ± 9.79 | 89.08 ± 4.07 | 87.07 ± 4.59 | 76.92 ± 7.41 | 91.50 ± 6.51 | 91.50 ± 5.21 | 78.72 ± 3.46 | 64.35 ± 33.76 | 91.78 ± 8.16 |
| 2 | 88.92 ± 8.92 | 90.45 ± 3.01 | 85.62 ± 9.15 | 68.99 ± 22.13 | 82.14 ± 4.35 | 79.66 ± 7.99 | 85.91 ± 5.77 | 83.97 ± 2.46 | 47.26 ± 27.64 | 92.92 ± 2.98 |
| 3 | 99.09 ± 1.53 | 98.88 ± 2.87 | 99.28 ± 0.27 | 99.40 ± 1.25 | 93.57 ± 3.53 | 93.40 ± 6.32 | 89.13 ± 14.20 | 97.30 ± 1.57 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 99.90 ± 0.11 |
| 4 | 88.00 ± 8.13 | 84.05 ± 12.59 | 89.19 ± 6.94 | 87.52 ± 9.33 | 75.34 ± 7.33 | 94.89 ± 3.46 | 93.38 ± 2.62 | 73.71 ± 3.65 | 87.56 ± 15.25 | 85.15 ± 12.92 |
| 5 | 94.65 ± 2.97 | 92.45 ± 4.14 | 99.76 ± 0.18 | 95.86 ± 5.37 | 96.47 ± 6.45 | 97.38 ± 4.39 | 99.11 ± 1.83 | 99.45 ± 0.58 | 93.93 ± 0.77 | 95.06 ± 2.78 |
| 6 | 95.57 ± 5.50 | 95.56 ± 6.69 | 4.79 ± 4.47 | 52.98 ± 24.56 | 79.88 ± 4.61 | 81.49 ± 2.80 | 83.09 ± 6.78 | 76.62 ± 0.78 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 91.72 ± 5.55 |
| 7 | 74.81 ± 12.76 | 68.92 ± 11.85 | 78.39 ± 7.06 | 88.17 ± 4.73 | 75.30 ± 6.64 | 83.61 ± 8.84 | 78.53 ± 7.71 | 70.26 ± 9.00 | 77.27 ± 18.04 | 75.39 ± 6.50 |
| 8 | 87.27 ± 9.26 | 75.75 ± 22.15 | 56.50 ± 14.14 | 39.12 ± 12.07 | 49.62 ± 8.53 | 45.17 ± 11.60 | 33.46 ± 4.91 | 45.88 ± 4.58 | 10.90 ± 7.08 | 80.14 ± 11.83 |
| 9 | 65.99 ± 16.95 | 59.77 ± 11.04 | 52.49 ± 12.34 | 71.96 ± 17.29 | 65.63 ± 10.83 | 78.71 ± 4.68 | 69.87 ± 8.37 | 69.04 ± 1.44 | 79.27 ± 4.40 | 71.49 ± 3.44 |
| 10 | 64.70 ± 13.56 | 62.90 ± 11.96 | 66.85 ± 7.46 | 67.70 ± 14.94 | 67.11 ± 8.00 | 65.46 ± 13.22 | 68.89 ± 10.87 | 66.03 ± 4.08 | 13.94 ± 14.89 | 70.81 ± 4.55 |
| 11 | 49.62 ± 15.74 | 68.33 ± 9.30 | 67.62 ± 9.20 | 83.78 ± 10.34 | 94.92 ± 3.33 | 69.36 ± 8.77 | 70.14 ± 6.41 | 90.25 ± 6.73 | 53.85 ± 7.52 | 80.33 ± 5.43 |
| 12 | 72.49 ± 17.24 | 71.13 ± 18.00 | 78.87 ± 9.94 | 73.01 ± 9.14 | 73.48 ± 8.20 | 63.98 ± 14.97 | 66.20 ± 12.57 | 81.22 ± 10.54 | 5.82 ± 14.24 | 75.71 ± 7.35 |
| 13 | 74.50 ± 10.02 | 74.91 ± 12.17 | 39.88 ± 21.15 | 73.19 ± 20.06 | 51.90 ± 26.81 | 78.32 ± 11.93 | 63.98 ± 16.78 | 73.87 ± 5.93 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 66.60 ± 7.58 |
| 14 | 89.52 ± 2.62 | 95.86 ± 2.80 | 61.45 ± 35.70 | 96.55 ± 6.16 | 99.40 ± 1.30 | 96.13 ± 5.66 | 99.97 ± 0.08 | 100.00 ± 0.00 | 54.48 ± 1.88 | 91.38 ± 2.82 |
| 15 | 90.12 ± 7.88 | 95.99 ± 3.98 | 98.59 ± 0.44 | 96.22 ± 5.11 | 99.74 ± 0.34 | 98.90 ± 0.88 | 95.46 ± 2.95 | 99.96 ± 0.08 | 82.31 ± 9.99 | 88.46 ± 10.24 |
| OA (%) | 75.79 ± 4.68 | 75.94 ± 3.24 | 75.74 ± 2.43 | 78.26 ± 1.80 | 77.60 ± 2.42 | 79.43 ± 1.50 | 77.71 ± 2.95 | 78.32 ± 1.08 | 49.54 ± 4.71 | 82.25 ± 1.07 |
| AA (%) | 81.54 ± 3.03 | 81.61 ± 1.97 | 72.48 ± 3.12 | 78.77 ± 1.79 | 78.76 ± 2.76 | 81.20 ± 1.27 | 79.24 ± 3.09 | 80.23 ± 0.74 | 44.73 ± 3.83 | 83.79 ± 0.67 |
| Kappa | 73.83 ± 5.07 | 73.99 ± 3.51 | 73.73 ± 2.62 | 76.49 ± 1.94 | 75.78 ± 2.62 | 77.77 ± 1.62 | 79.31 ± 6.50 | 76.58 ± 1.16 | 45.15 ± 5.13 | 80.83 ± 1.16 |
| Class | CNN (Residual Network)- Based Methods | GCN-Based Methods | Transformer- Based Methods | SSM-Based | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SSRN | A2S2K-ResNet | GTFN | H2-CHGN | SSFTT | GSC_ViT | MambaHSI | IGroupSS-Mamba | S2Mamba | MyNet | |
| TGRS2018 | TGRS2022 | TGRS2023 | RS2024 | TGRS2021 | TGRS2024 | TGRS2024 | TGRS2024 | TGRS2025 | Ours | |
| 1 | 93.17 ± 9.81 | 97.99 ± 4.42 | 98.27 ± 1.74 | 95.73 ± 2.92 | 97.01 ± 1.87 | 98.91 ± 1.76 | 94.26 ± 9.32 | 96.88 ± 1.77 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 98.67 ± 2.47 |
| 2 | 99.02 ± 1.46 | 98.47 ± 1.28 | 99.80 ± 0.16 | 99.99 ± 0.01 | 93.96 ± 7.13 | 99.96 ± 0.03 | 97.37 ± 4.12 | 100.00 ± 0.00 | 96.17 ± 9.26 | 99.48 ± 0.50 |
| 3 | 91.79 ± 16.43 | 97.24 ± 5.76 | 91.28 ± 14.50 | 97.17 ± 5.66 | 99.90 ± 0.12 | 80.93 ± 10.40 | 70.21 ± 14.58 | 99.97 ± 0.05 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 98.75 ± 1.20 |
| 4 | 81.40 ± 23.84 | 93.02 ± 6.20 | 90.86 ± 7.44 | 97.67 ± 2.97 | 87.49 ± 8.00 | 91.50 ± 10.28 | 97.39 ± 1.24 | 89.30 ± 5.08 | 15.66 ± 27.10 | 97.40 ± 3.60 |
| 5 | 74.92 ± 21.47 | 82.84 ± 33.92 | 94.68 ± 2.09 | 95.60 ± 3.10 | 95.34 ± 2.51 | 95.88 ± 3.31 | 94.65 ± 2.59 | 97.13 ± 0.62 | 99.61 ± 0.21 | 98.16 ± 0.84 |
| 6 | 90.69 ± 17.20 | 97.04 ± 2.50 | 99.72 ± 0.35 | 98.46 ± 2.18 | 99.93 ± 0.09 | 99.53 ± 0.57 | 99.29 ± 1.49 | 100.00 ± 0.00 | 99.83 ± 0.05 | 99.61 ± 0.43 |
| 7 | 95.50 ± 3.22 | 94.96 ± 8.44 | 98.79 ± 1.01 | 99.45 ± 0.76 | 99.84 ± 0.12 | 99.88 ± 0.18 | 98.31 ± 0.99 | 99.86 ± 0.11 | 89.60 ± 11.78 | 99.15 ± 0.73 |
| 8 | 71.04 ± 7.85 | 79.82 ± 7.29 | 91.25 ± 2.77 | 85.50 ± 6.96 | 87.42 ± 1.93 | 85.54 ± 3.20 | 91.34 ± 1.49 | 88.95 ± 3.07 | 97.14 ± 2.33 | 89.73 ± 3.54 |
| 9 | 79.84 ± 13.95 | 90.16 ± 12.01 | 99.98 ± 0.03 | 99.98 ± 0.04 | 99.86 ± 0.22 | 99.66 ± 0.44 | 99.22 ± 0.76 | 100.00 ± 0.00 | 99.94 ± 0.07 | 97.64 ± 1.43 |
| 10 | 94.74 ± 3.43 | 97.85 ± 2.74 | 78.76 ± 5.55 | 90.41 ± 9.61 | 94.38 ± 1.48 | 80.54 ± 11.57 | 75.34 ± 4.57 | 91.42 ± 3.57 | 5.99 ± 11.74 | 97.99 ± 0.80 |
| 11 | 94.18 ± 6.18 | 97.00 ± 2.68 | 86.45 ± 10.72 | 87.37 ± 5.92 | 100.00 ± 0.00 | 66.72 ± 13.00 | 95.39 ± 3.60 | 99.36 ± 0.75 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 91.92 ± 2.54 |
| 12 | 80.72 ± 26.53 | 83.91 ± 34.37 | 78.09 ± 5.95 | 99.27 ± 1.46 | 93.35 ± 2.35 | 96.47 ± 6.25 | 97.01 ± 7.35 | 94.73 ± 4.63 | 4.39 ± 6.83 | 98.86 ± 0.91 |
| 13 | 78.29 ± 17.73 | 85.74 ± 8.10 | 70.49 ± 20.29 | 46.26 ± 44.75 | 44.59 ± 15.29 | 100.00 ± 0.00 | 99.10 ± 1.45 | 67.78 ± 25.59 | 41.06 ± 20.31 | 91.25 ± 10.36 |
| 14 | 78.55 ± 23.98 | 94.58 ± 4.30 | 82.27 ± 12.44 | 92.38 ± 7.43 | 92.30 ± 6.11 | 90.35 ± 6.06 | 99.70 ± 0.16 | 94.29 ± 1.71 | 3.63 ± 3.90 | 97.36 ± 1.36 |
| 15 | 78.06 ± 14.79 | 76.46 ± 11.37 | 81.09 ± 2.99 | 76.16 ± 26.70 | 78.03 ± 7.70 | 87.50 ± 3.33 | 89.82 ± 5.40 | 75.72 ± 7.70 | 1.55 ± 2.32 | 87.50 ± 3.23 |
| 16 | 93.60 ± 12.94 | 99.89 ± 0.18 | 83.49 ± 11.54 | 97.87 ± 1.28 | 97.69 ± 0.39 | 87.13 ± 10.32 | 95.26 ± 3.62 | 99.21 ± 0.46 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 99.49 ± 0.46 |
| OA (%) | 79.83 ± 5.47 | 88.28 ± 3.30 | 90.86 ± 0.72 | 91.10 ± 2.73 | 91.57 ± 0.65 | 91.49 ± 1.55 | 92.89 ± 1.04 | 92.45 ± 1.15 | 58.35 ± 0.97 | 94.84 ± 0.59 |
| AA (%) | 85.97 ± 7.03 | 91.68 ± 4.31 | 89.31 ± 1.10 | 91.21 ± 3.80 | 91.32 ± 0.77 | 91.28 ± 1.71 | 93.35 ± 1.06 | 93.43 ± 1.99 | 40.91 ± 1.95 | 96.43 ± 0.69 |
| Kappa | 77.29 ± 6.24 | 86.89 ± 3.71 | 89.80 ± 0.82 | 90.08 ± 3.09 | 90.60 ± 0.73 | 90.52 ± 1.74 | 92.96 ± 1.36 | 91.58 ± 1.30 | 52.04 ± 1.04 | 94.25 ± 0.66 |
| Class | CNN (Residual Network)-Based Methods | GCN-Based Methods | Transformer- Based Methods | SSM-Based | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SSRN | A2S2K-ResNet | GTFN | H2-CHGN | SSFTT | GSC_ViT | MambaHSI | IGroupSS-Mamba | S2Mamba | MyNet | |
| TGRS2018 | TGRS2022 | TGRS2023 | RS2024 | TGRS2021 | TGRS2024 | TGRS2024 | TGRS2024 | TGRS2025 | Ours | |
| 1 | 86.76 ± 11.53 | 90.81 ± 1.85 | 98.76 ± 0.98 | 97.74 ± 2.02 | 97.40 ± 1.93 | 96.94 ± 1.57 | 99.29 ± 0.13 | 98.76 ± 1.47 | 92.71 ± 2.84 | 95.26 ± 1.84 |
| 2 | 77.95 ± 35.16 | 78.24 ± 11.17 | 85.21 ± 7.44 | 97.31 ± 1.78 | 84.08 ± 5.97 | 83.17 ± 9.71 | 80.82 ± 4.64 | 89.28 ± 2.97 | 57.42 ± 3.18 | 81.98 ± 10.49 |
| 3 | 69.55 ± 21.88 | 83.34 ± 13.72 | 60.24 ± 30.98 | 60.52 ± 24.21 | 91.65 ± 2.78 | 71.01 ± 15.29 | 82.36 ± 4.73 | 86.65 ± 1.93 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 87.20 ± 16.28 |
| 4 | 84.68 ± 3.63 | 93.20 ± 4.08 | 97.99 ± 0.99 | 96.71 ± 2.68 | 94.65 ± 1.23 | 97.34 ± 1.15 | 89.95 ± 5.95 | 95.79 ± 2.70 | 95.12 ± 0.33 | 96.34 ± 1.94 |
| 5 | 71.77 ± 11.37 | 87.40 ± 10.27 | 25.78 ± 16.65 | 70.09 ± 25.66 | 69.57 ± 4.69 | 55.24 ± 20.37 | 74.72 ± 16.11 | 66.14 ± 8.07 | 0.01 ± 0.01 | 86.27 ± 9.22 |
| 6 | 94.59 ± 6.37 | 97.47 ± 1.98 | 92.75 ± 5.89 | 88.26 ± 9.17 | 93.28 ± 4.58 | 86.90 ± 17.30 | 95.51 ± 0.99 | 96.72 ± 0.83 | 71.97 ± 2.48 | 97.58 ± 1.87 |
| 7 | 97.60 ± 1.67 | 97.60 ± 3.02 | 99.33 ± 0.57 | 99.97 ± 0.03 | 99.30 ± 0.61 | 99.75 ± 0.32 | 99.95 ± 0.04 | 99.27 ± 0.57 | 100.00 ± 0.00 | 99.27 ± 0.55 |
| 8 | 73.71 ± 16.17 | 82.78 ± 13.11 | 52.56 ± 28.17 | 62.51 ± 12.75 | 42.67 ± 3.81 | 90.54 ± 7.79 | 50.05 ± 3.60 | 37.80 ± 3.05 | 2.05 ± 5.53 | 81.62 ± 9.68 |
| 9 | 66.14 ± 23.36 | 71.19 ± 14.34 | 36.71 ± 31.73 | 44.01 ± 21.44 | 47.84 ± 10.01 | 41.70 ± 15.75 | 67.84 ± 2.20 | 38.88 ± 1.83 | 0.41 ± 0.41 | 86.53 ± 8.81 |
| OA (%) | 88.15 ± 3.30 | 92.15 ± 1.52 | 92.08 ± 2.66 | 93.87 ± 1.67 | 92.57 ± 0.97 | 93.97 ± 1.35 | 92.38 ± 1.67 | 92.63 ± 1.34 | 84.42 ± 0.66 | 95.34 ± 0.88 |
| AA (%) | 80.30 ± 8.94 | 86.89 ± 3.20 | 70.31 ± 11.27 | 79.68 ± 7.84 | 80.05 ± 2.57 | 80.29 ± 5.69 | 82.28 ± 1.10 | 77.90 ± 2.21 | 46.64 ± 0.87 | 90.22 ± 1.97 |
| Kappa | 84.09 ± 4.50 | 89.61 ± 2.03 | 89.45 ± 3.59 | 91.86 ± 2.29 | 90.18 ± 1.32 | 92.05 ± 1.80 | 93.12 ± 0.01 | 90.21 ± 1.81 | 78.99 ± 0.90 | 93.85 ± 1.17 |
| Patch Sizes | Botswana | Houston2013 | Salinas | WHU-Hi-LongKou |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OA (%) | OA (%) | OA (%) | OA (%) | |
| 7 × 7 | 98.88 | 82.25 | 94.84 | 95.34 |
| 9 × 9 | 97.10 | 81.15 | 91.33 | 93.18 |
| 11 × 11 | 95.22 | 78.53 | 89.13 | 92.28 |
| Methods | Trainable Params (MB) | Memory (MB) | Training (s) | Inference (s) | FLOPs (G) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SSRN | 0.28 | 10.26 | 28.89 | 3.78 | 0.1392 |
| A2S2K-ResNet | 0.29 | 11.39 | 35.91 | 0.66 | 0.1073 |
| GTFN | 0.28 | 332.78 | 79.58 | 3.38 | 0.7427 |
| H2-CHGN | 0.237 | 7777.88 | 15.55 | 0.02 | 38.8191 |
| SSFTT | 0.15 | 9.77 | 13.66 | 0.22 | 0.0236 |
| GSC_ViT | 0.178 | 9.89 | 518.81 | 21.39 | 0.0132 |
| MambaHSI | 0.42 | 6535.36 | 222.60 | 0.34 | 38.5625 |
| IGroupSS-Mamba | 0.14 | 9.78 | 43.30 | 1.78 | 0.0095 |
| S2Mamba | 0.11 | 9.55 | 16.72 | 0.87 | 0.0285 |
| MyNet | 0.93 | 41.87 | 215.31 | 5.96 | 0.7313 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, T.; Ye, H.; Li, G.; Peng, Y.; Ding, J.; Chen, H.; Zhou, X.; Deng, W. S2GL-MambaResNet: A Spatial–Spectral Global–Local Mamba Residual Network for Hyperspectral Image Classification. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 3917. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17233917
Chen T, Ye H, Li G, Peng Y, Ding J, Chen H, Zhou X, Deng W. S2GL-MambaResNet: A Spatial–Spectral Global–Local Mamba Residual Network for Hyperspectral Image Classification. Remote Sensing. 2025; 17(23):3917. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17233917
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Tao, Hongming Ye, Guojie Li, Yaohan Peng, Jianming Ding, Huayue Chen, Xiangbing Zhou, and Wu Deng. 2025. "S2GL-MambaResNet: A Spatial–Spectral Global–Local Mamba Residual Network for Hyperspectral Image Classification" Remote Sensing 17, no. 23: 3917. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17233917
APA StyleChen, T., Ye, H., Li, G., Peng, Y., Ding, J., Chen, H., Zhou, X., & Deng, W. (2025). S2GL-MambaResNet: A Spatial–Spectral Global–Local Mamba Residual Network for Hyperspectral Image Classification. Remote Sensing, 17(23), 3917. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17233917











