Displacement Time Series Forecasting Using Sentinel-1 SBAS-InSAR Results in a Mining Subsidence Case Study—Evaluation of Machine Learning and Deep Learning Methods
Highlights
- Data-driven models, including deep neural networks, successfully captured the temporal course of mining-induced ground subsidence based on SBAS-InSAR time series.
- Model performance varied across different forecast horizons and across the study area, with local outliers and heterogeneous accuracy measures.
- Integrating SBAS-InSAR observations with machine learning models can provide a framework for continuous ground deformation monitoring and prediction.
- A comprehensive assessment of models’ accuracy, in both spatial and temporal domains, is essential for improving model reliability in risk assessment and early-warning scenarios.
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. InSAR Data Processing
2.3. Time Series Forecasting Model Development
2.3.1. Forecasting Strategy
2.3.2. Time Series Preprocessing
2.3.3. Model Development
3. Results
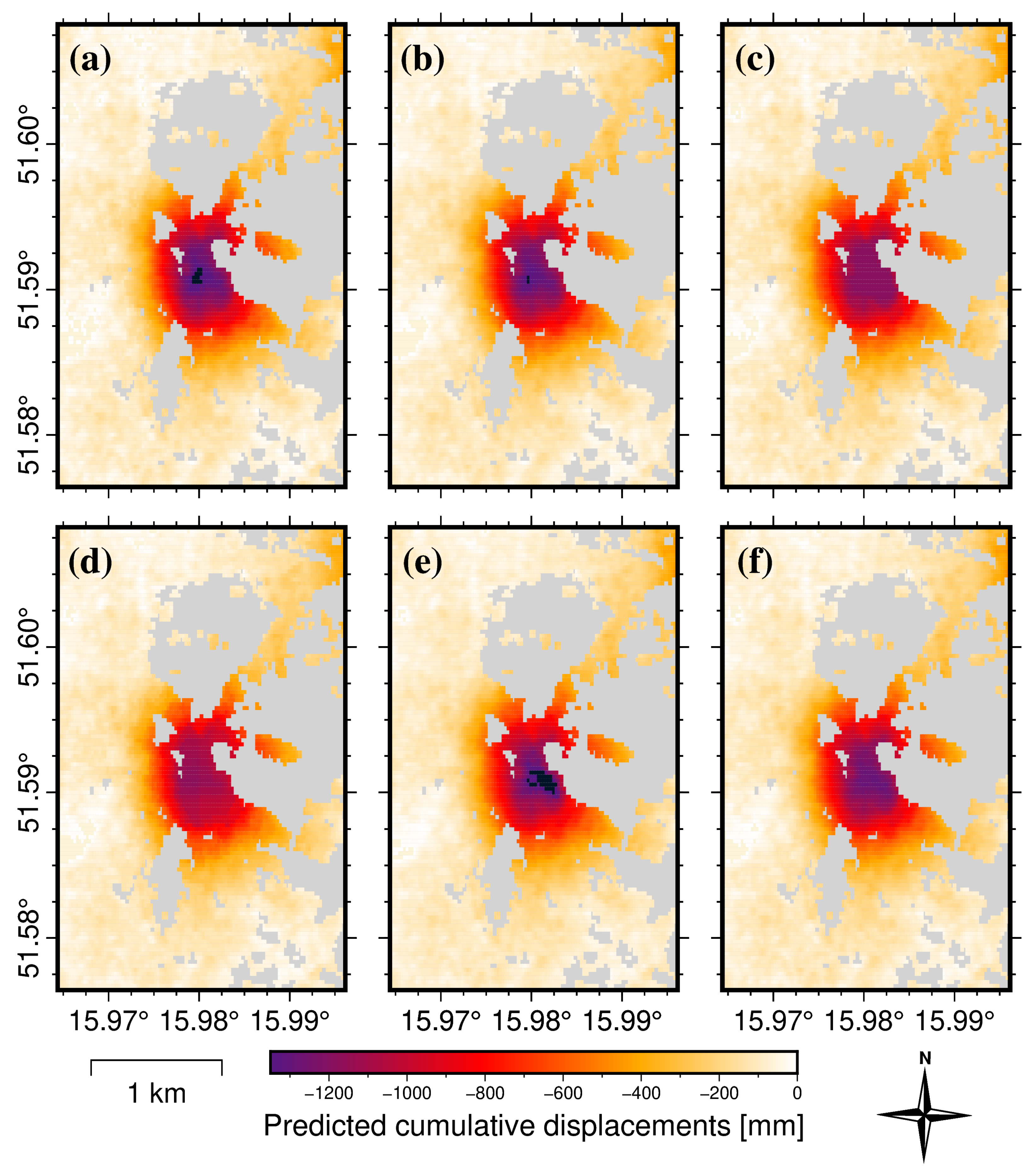
3.1. Ground Surface Displacements
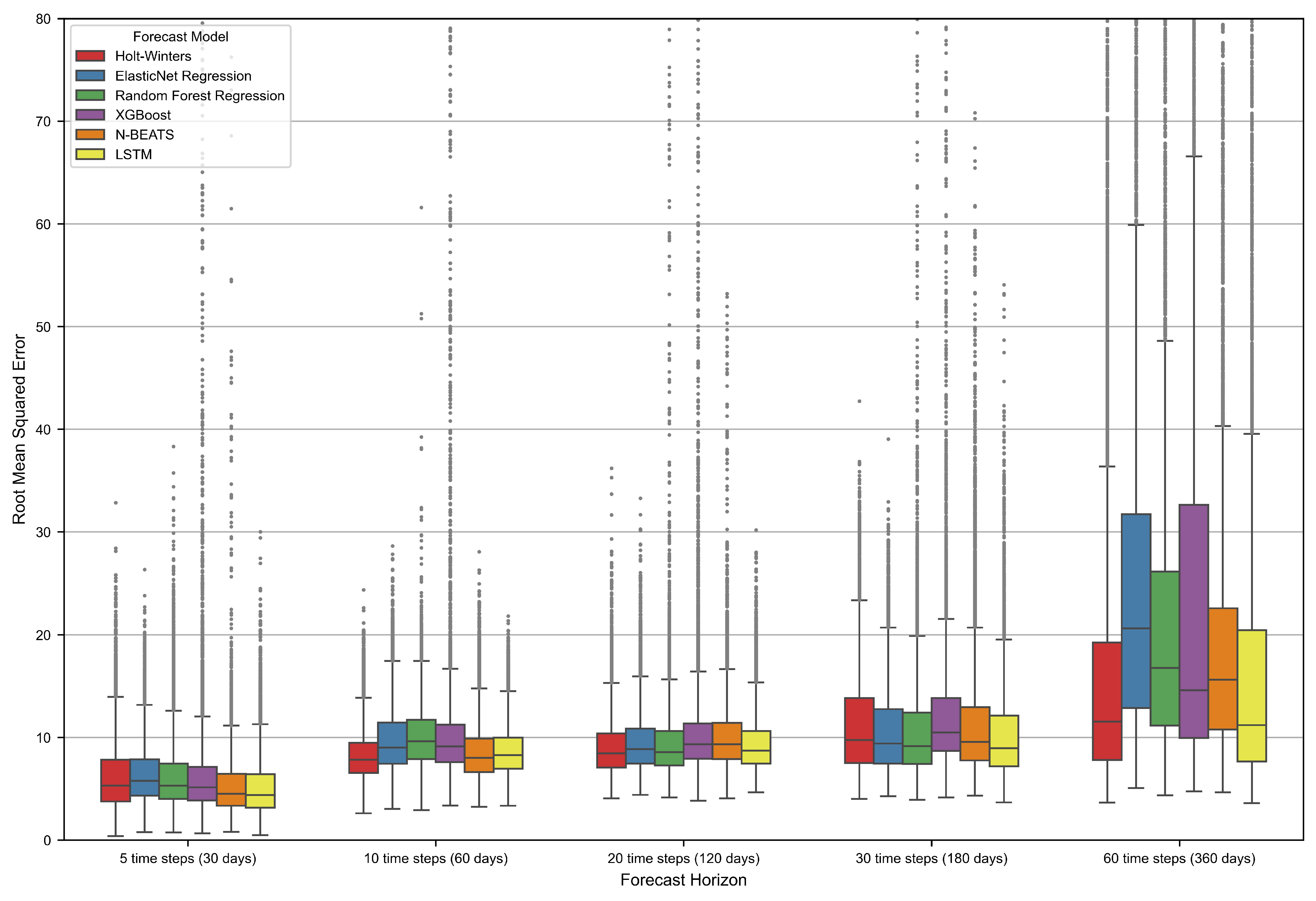
3.2. Displacement Prediction Model Evaluation
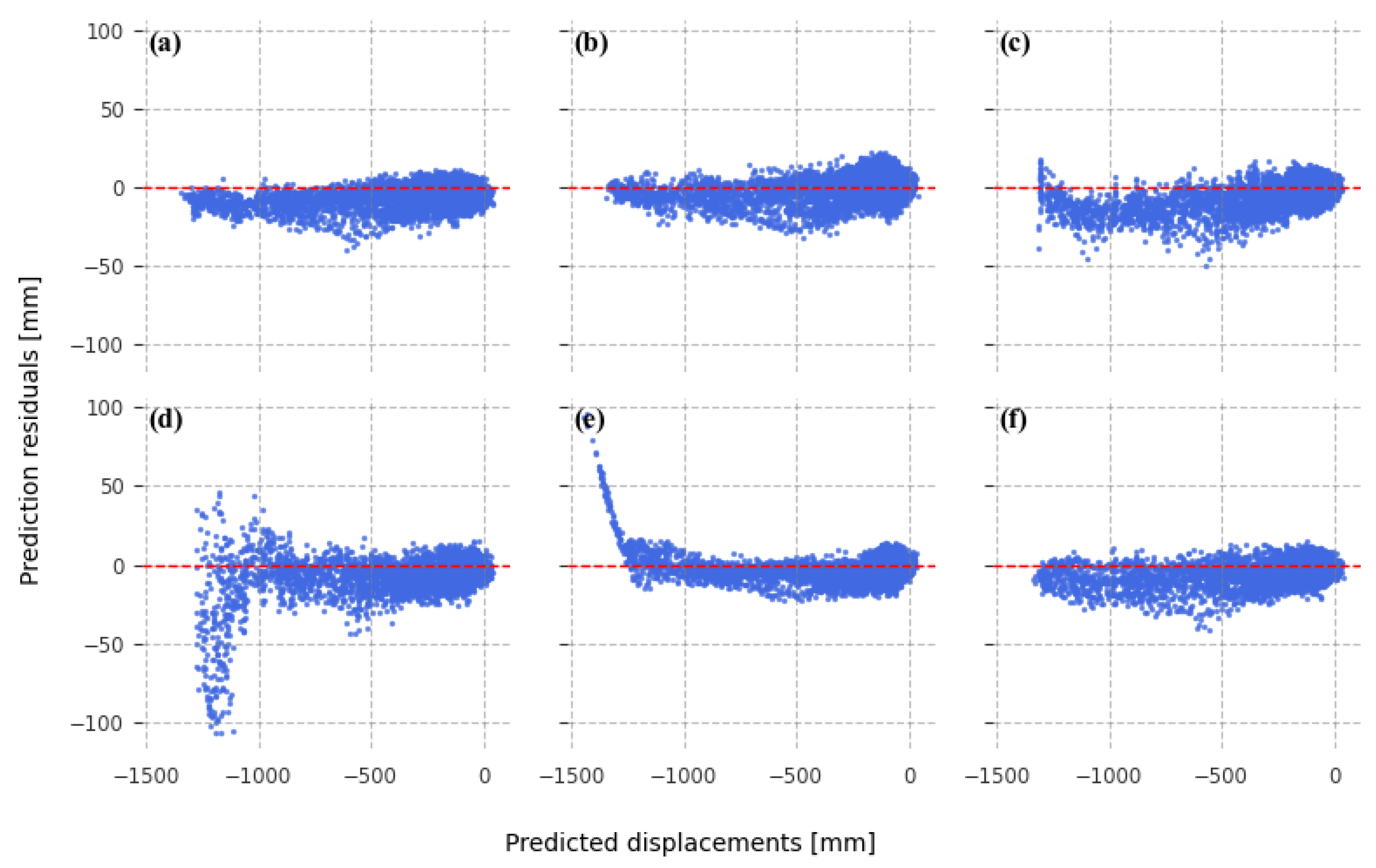
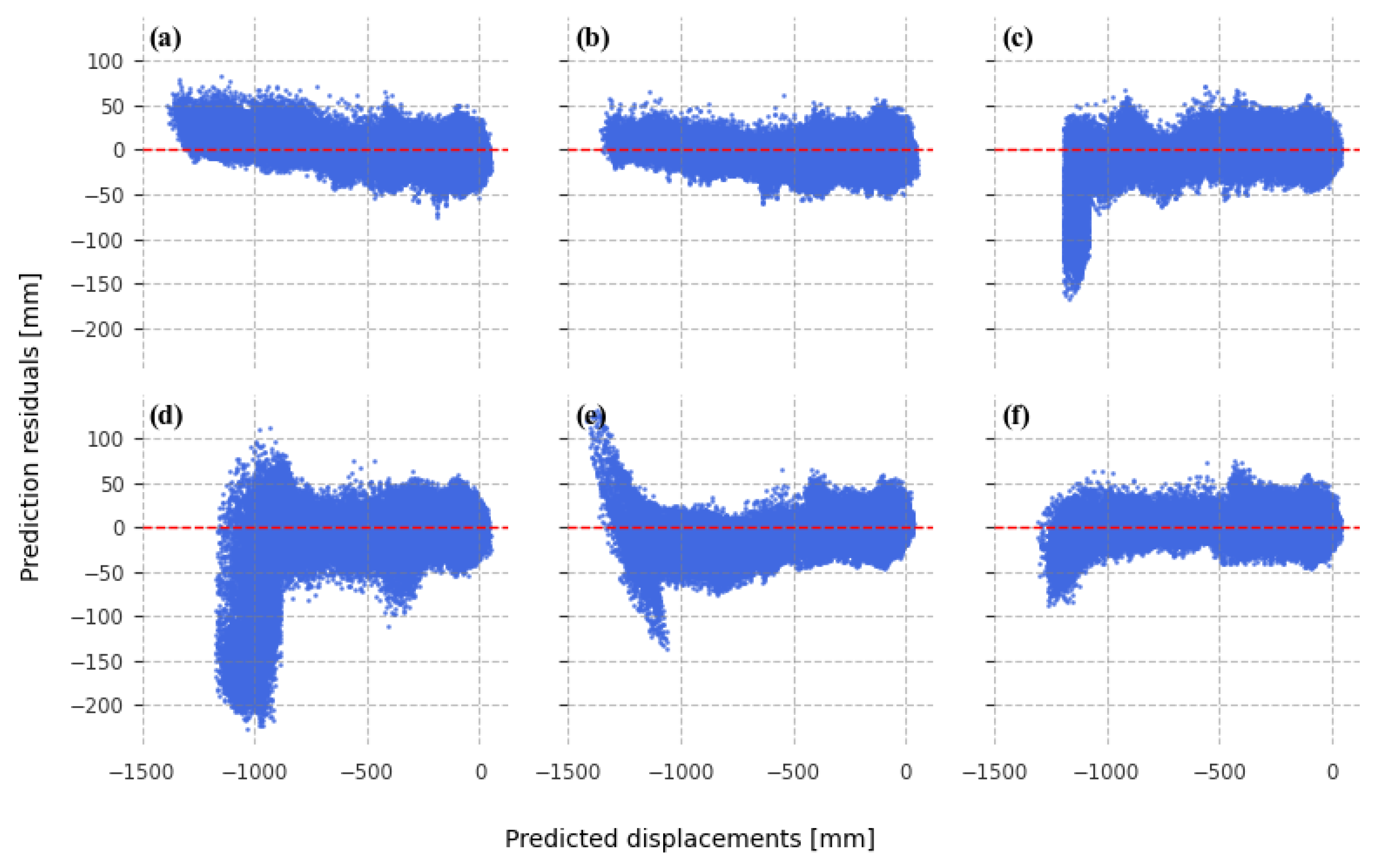
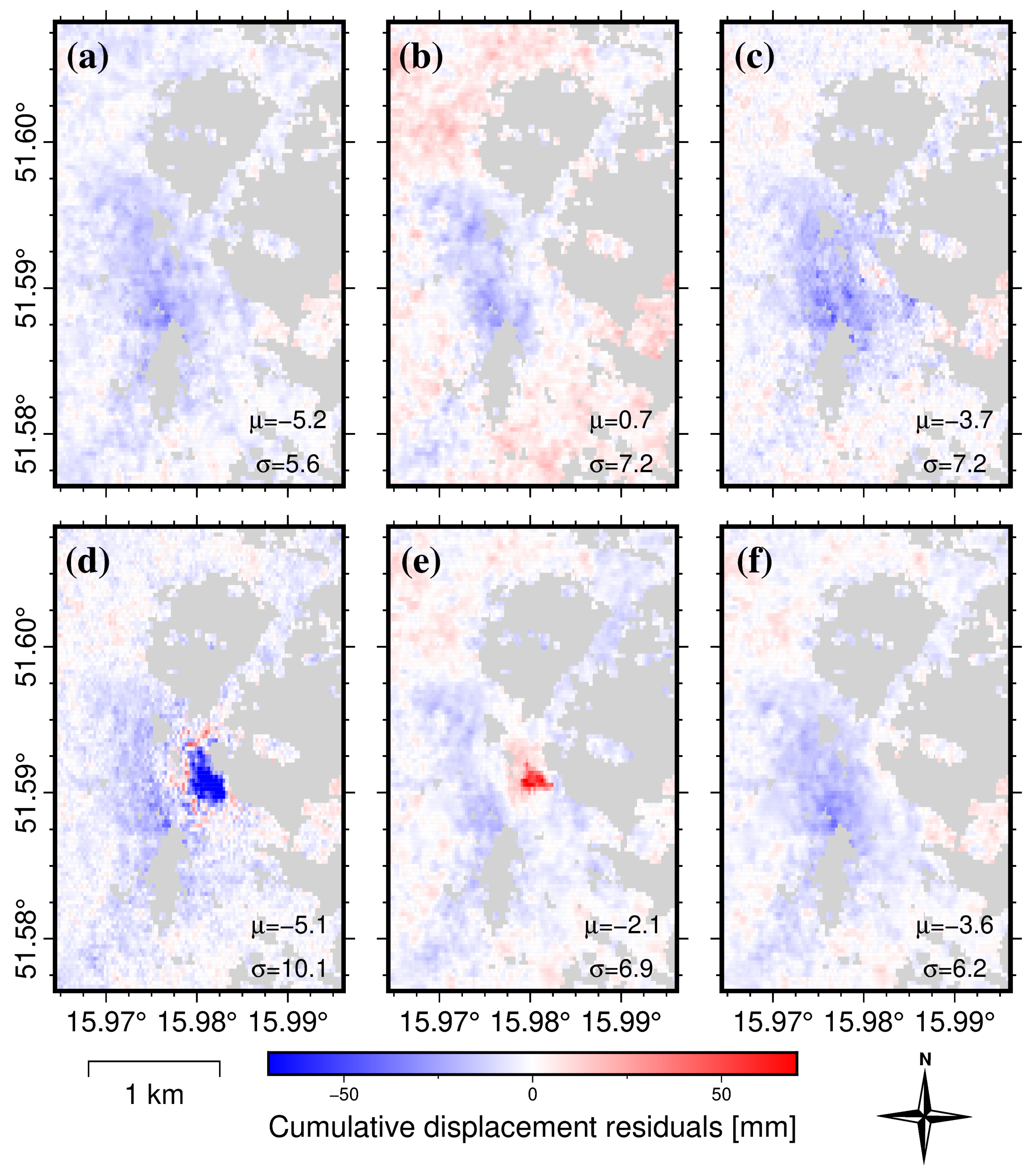
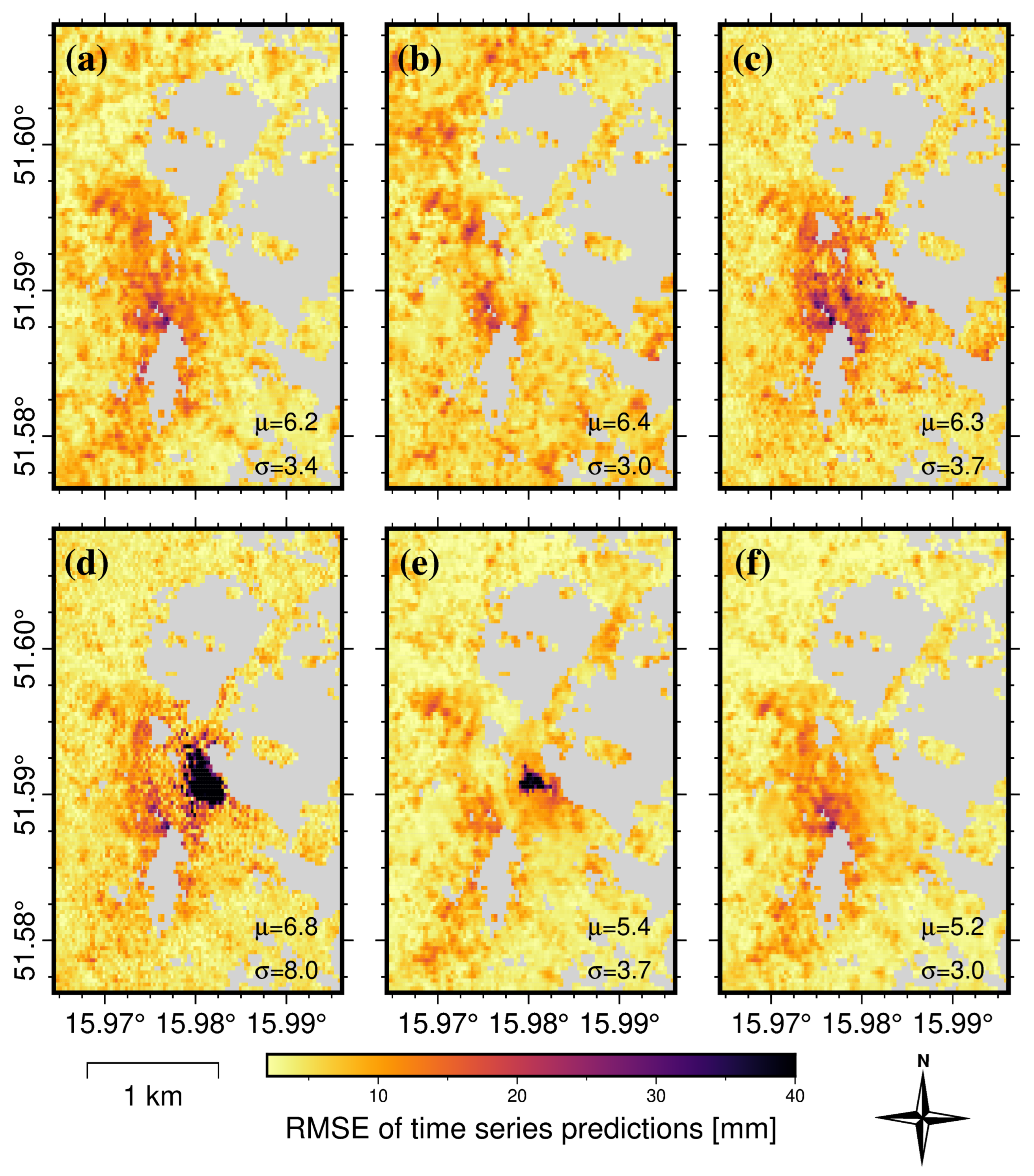
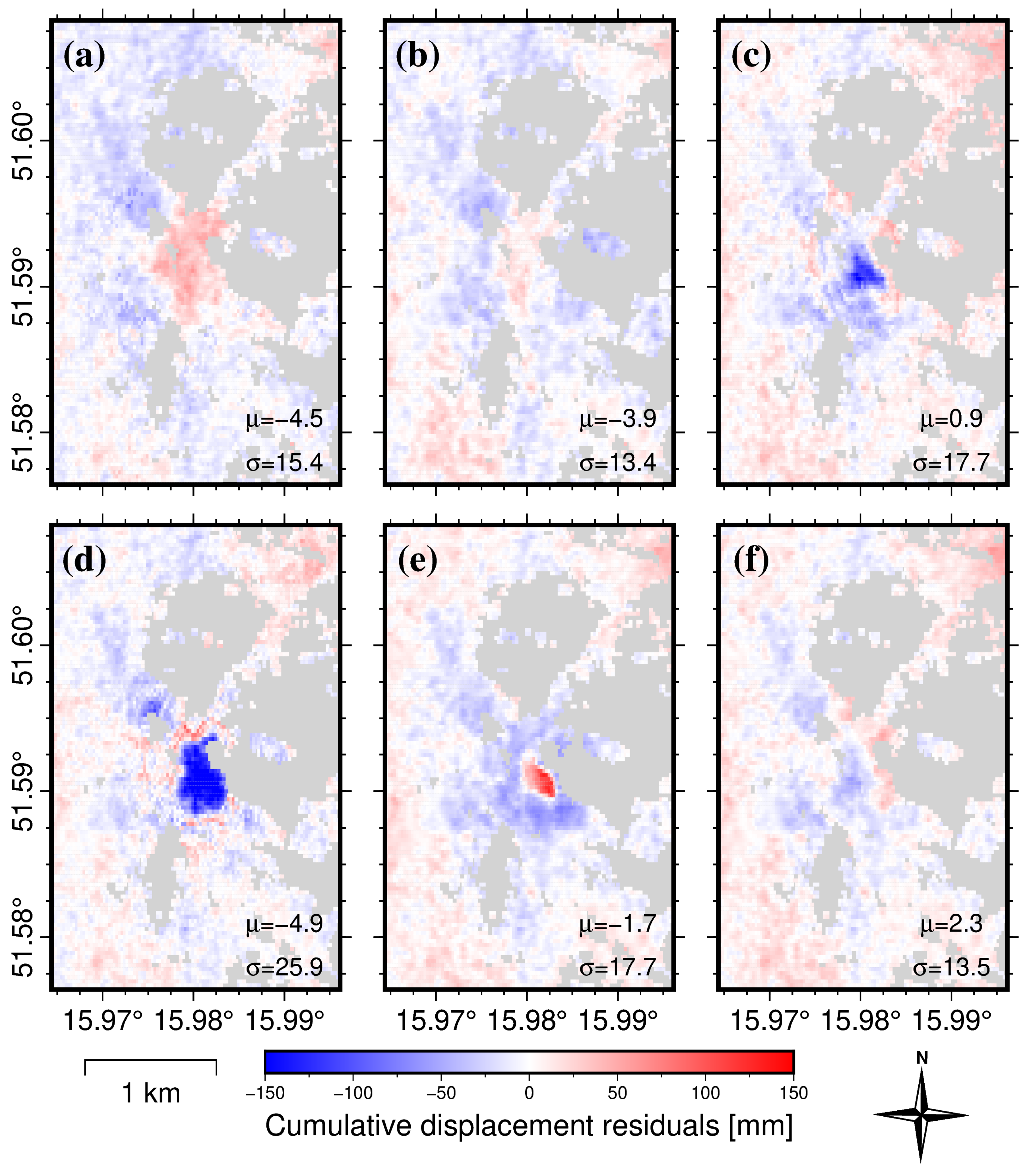
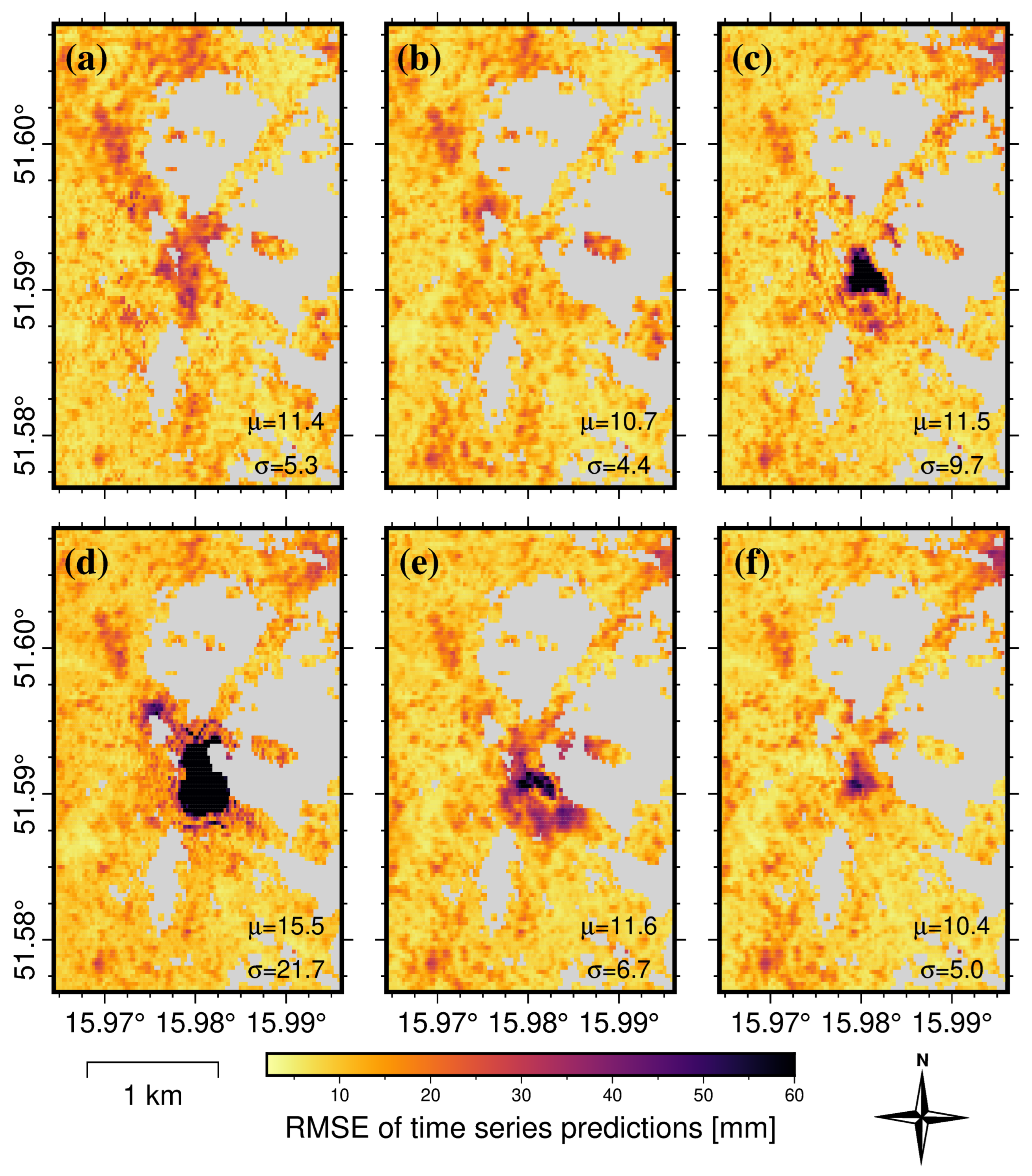
3.3. Displacement-Prediction-Error Analysis in the Spatial Domain
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kratzsch, H. Mining Subsidence Engineering; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tondaś, D.; Kazmierski, K.; Kapłon, J. Real-Time and Near Real-Time Displacement Monitoring With GNSS Observations in the Mining Activity Areas. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2023, 16, 5963–5972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tajduś, K.; Sroka, A.; Misa, R.; Hager, S.; Rusek, J.; Dudek, M.; Wollnik, F. Analysis of Mining-Induced Delayed Surface Subsidence. Minerals 2021, 11, 1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witkowski, W.T.; Łukosz, M.; Guzy, A.; Hejmanowski, R. Estimation of Mining-Induced Horizontal Strain Tensor of Land Surface Applying InSAR. Minerals 2021, 11, 788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ćwiąkała, P.; Gruszczyński, W.; Stoch, T.; Puniach, E.; Mrocheń, D.; Matwij, W.; Matwij, K.; Nędzka, M.; Sopata, P.; Wójcik, A. UAV Applications for Determination of Land Deformations Caused by Underground Mining. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witkowski, W.T.; Mrocheń, D.; Sopata, P.; Stoch, T. Integration of the Leveling Observations and PSInSAR Results for Monitoring Deformations Caused by Underground Mining. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium IGARSS, Brussels, Belgium, 11–16 July 2021; pp. 6614–6617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knothe, S. Równanie Profilu Ostatecznie Wykształconej Niecki Osiadania. Archiwum Górnictwa i Hutnictwa 1953, 1, 22–38. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, Y. An Improved Influence Function Method for Predicting Subsidence Caused by Longwall Mining Operations in Inclined Coal Seams. Int. J. Coal Sci. Technol. 2015, 2, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apanowicz, B.; Milczarek, W.; Kowalski, A. Novel Method for Determining the Time Coefficient c in Knothe’s Function and Disappearance Time of Deformation Increase Using SAR Data. Measurement 2024, 235, 114898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zha, J.; Wang, L. Adaptive Dynamic Prediction Model of Mining Subsidence Aided by Measured Data. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 14754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knothe, S.M. Prognozowanie Wpływów Eksploatacji Górniczej; Wydaw. Śląsk: Katowice, Poland, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Kochmański, T. Całkowa Teoria Ruchów Górotworu Nad Eksploatacją Złoża Pokładowego Na Podstawie Pomiarów Geodezyjnych. Geod. Kartogr. 1955, 2. [Google Scholar]
- Litwiniszyn, J. Przemieszczenia Górotworu w Świetle Teorii Prawdopodobieństwa. Arch. Górnictwa Hut. 1954, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Drzęźla, B. Przybliżona Ocena Niektórych Parametrów Kinematyki Niecki Osiadania Przy Zmianach Prędkości Wybierania i Postojach Ścian. Przegląd Górniczy 1995, 9, 10–16. [Google Scholar]
- Dudek, M.; Mrocheń, D.; Sroka, A.; Tajduś, K. Integrating the Finite Element Method with Python Scripting to Assess Mining Impacts on Surface Deformations. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 7797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Tan, Z.; Yan, L.; Deng, K. Time Series Prediction of Mining Subsidence Based on a SVM. Min. Sci. Technol. 2011, 21, 557–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmati, O.; Falah, F.; Naghibi, S.A.; Biggs, T.; Soltani, M.; Deo, R.C.; Cerdà, A.; Mohammadi, F.; Tien Bui, D. Land Subsidence Modelling Using Tree-Based Machine Learning Algorithms. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 672, 239–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.; Xia, X. Prediction of Mining Subsidence under Thin Bedrocks and Thick Unconsoliyeard Layers Based on Field Measurement and Artificial Neural Networks. Comput. Geosci. 2013, 52, 199–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cieślik, K.; Milczarek, W. Application of Machine Learning in Forecasting the Impact of Mining Deformation: A Case Study of Underground Copper Mines in Poland. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, P.; Biggs, J.; Ponce-López, V.; Bull, D. Time-Series Prediction Approaches to Forecasting Deformation in Sentinel-1 InSAR Data. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2021, 126, e2020JB020176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Yu, H.; Zhang, X.; Li, Z.; Kang, J.; Yu, Y.; Yang, J.; Qin, L. Time-Varying Surface Deformation Retrieval and Prediction in Closed Mines through Integration of SBAS InSAR Measurements and LSTM Algorithm. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moualla, L.; Rucci, A.; Naletto, G.; Anantrasirichai, N.; Da Deppo, V. Hybrid GIS-Transformer Approach for Forecasting Sentinel-1 Displacement Time Series. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 2382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Fan, X.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Nie, W.; Qi, Y.; Zhang, N. Spatiotemporal Mechanism-Based Spacetimeformer Network for InSAR Deformation Prediction and Identification of Retrogressive Thaw Slumps in the Chumar River Basin. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Ye, M.; Xia, Z.; Wang, W.; Luo, C.; Muller, J.P. An Interpretable Attention-Based Deep Learning Method for Landslide Prediction Based on Multi-Temporal InSAR Time Series: A Case Study of Xinpu Landslide in the TGRA. Remote Sens. Environ. 2025, 318, 114580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Zhou, X.; Yan, K. Deep Learning Neural Network Model for Tunnel Ground Surface Settlement Prediction Based on Sensor Data. Math. Probl. Eng. 2021, 2021, 9488892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, P.; Stow, R. Detecting Mining Subsidence from Space. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1999, 20, 1183–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raspini, F.; Caleca, F.; Del Soldato, M.; Festa, D.; Confuorto, P.; Bianchini, S. Review of Satellite Radar Interferometry for Subsidence Analysis. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2022, 235, 104239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferretti, A.; Prati, C.; Rocca, F. Permanent Scatterers in SAR Interferometry. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2001, 39, 8–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonielli, B.; Sciortino, A.; Scancella, S.; Bozzano, F.; Mazzanti, P. Tracking Deformation Processes at the Legnica Glogow Copper District (Poland) by Satellite InSAR—I: Room and Pillar Mine District. Land 2021, 10, 653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berardino, P.; Fornaro, G.; Lanari, R.; Sansosti, E. A New Algorithm for Surface Deformation Monitoring Based on Small Baseline Differential SAR Interferograms. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2002, 40, 2375–2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gee, D.; Bateson, L.; Sowter, A.; Grebby, S.; Novellino, A.; Cigna, F.; Marsh, S.; Banton, C.; Wyatt, L. Ground Motion in Areas of Abandoned Mining: Application of the Intermittent SBAS (ISBAS) to the Northumberland and Durham Coalfield, UK. Geosciences 2017, 7, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samsonov, S.; d’Oreye, N.; Smets, B. Ground Deformation Associated with Post-Mining Activity at the French–German Border Revealed by Novel InSAR Time Series Method. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2013, 23, 142–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hochreiter, S.; Schmidhuber, J. Long Short-Term Memory. Neural Comput. 1997, 9, 1735–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piestrzyński, A. Monografia KGHM Polska Miedź SA, 2nd ed.; KGHM CUPRUM Sp. z o.o. CBR: Wrocław, Poland, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Butra, J.; Kicki, J. Ewolucja Technologii Eksploatacji Złóż Rud Miedzi w Polskich Kopalniach; Biblioteka Szkoły Eksploatacji Podziemnej: Kraków, Poland, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Kudłacik, I.; Kapłon, J.; Lizurek, G.; Crespi, M.; Kurpiński, G. High-Rate GPS Positioning for Tracing Anthropogenic Seismic Activity: The 29 January 2019 Mining Tremor in Legnica- Głogów Copper District, Poland. Measurement 2021, 168, 108396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milczarek, W. Application of a Small Baseline Subset Time Series Method with Atmospheric Correction in Monitoring Results of Mining Activity on Ground Surface and in Detecting Induced Seismic Events. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hejmanowski, R.; Malinowska, A.A.; Witkowski, W.T.; Guzy, A. An Analysis Applying InSAR of Subsidence Caused by Nearby Mining-Induced Earthquakes. Geosciences 2019, 9, 490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosen, P.A.; Gurrola, E.; Sacco, G.F.; Zebker, H. The InSAR Scientific Computing Environment. In Proceedings of the EUSAR 2012, 9th European Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar, Nuremberg, Germany, 23–26 April 2012; pp. 730–733. [Google Scholar]
- Farr, T.G.; Rosen, P.A.; Caro, E.; Crippen, R.; Duren, R.; Hensley, S.; Kobrick, M.; Paller, M.; Rodriguez, E.; Roth, L.; et al. The Shuttle Radar Topography Mission. Rev. Geophys. 2007, 45, 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, R.M.; Werner, C.L. Radar Interferogram Filtering for Geophysical Applications. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1998, 25, 4035–4038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.W.; Zebker, H.A. Network Approaches to Two-Dimensional Phase Unwrapping: Intractability and Two New Algorithms. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 2000, 17, 401–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yunjun, Z.; Fattahi, H.; Amelung, F. Small Baseline InSAR Time Series Analysis: Unwrapping Error Correction and Noise Reduction. Comput. Geosci. 2019, 133, 104331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Li, Z.; Penna, N.T.; Crippa, P. Generic Atmospheric Correction Model for Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar Observations. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2018, 123, 9202–9222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, T.J.; Parsons, B.E.; Lu, Z. Toward Mapping Surface Deformation in Three Dimensions Using InSAR. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2004, 31, L01607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samieie-Esfahany, S.; Hanssen, R.F.; Van Thienen-Visser, K.; Muntendam-Bos, A. On the Effect of Horizontal Deformation on Insar Subsidence Estimates. In Proceedings of the Fringe 2009 Workshop, Frascati, Italy, 30 November–4 December 2009; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Costantini, M.; Minati, F.; Trillo, F.; Ferretti, A.; Novali, F.; Passera, E.; Dehls, J.; Larsen, Y.; Marinkovic, P.; Eineder, M.; et al. European Ground Motion Service (EGMS). In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium IGARSS, Brussels, Belgium, 11–16 July 2021; pp. 3293–3296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyndman, R.J.; Athanasopoulos, G. Forecasting: Principles and Practice, 3rd ed.; OTexts: Melbourne, Australia, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Garza, A.; Canseco, M.M.; Challú, C.; Olivares, K.G. StatsForecast: Lightning Fast Forecasting with Statistical and Econometric Models; PyCon: Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, H.; Hastie, T. Regularization and Variable Selection Via the Elastic Net. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B Stat. Methodol. 2005, 67, 301–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiman, L. Random Forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Guestrin, C. XGBoost: A Scalable Tree Boosting System. In Proceedings of the 22nd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, San Francisco, CA, USA, 13–17 August 2016; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2016; KDD’16, pp. 785–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oreshkin, B.N.; Carpov, D.; Chapados, N.; Bengio, Y. N-BEATS: Neural Basis Expansion Analysis for Interpretable Time Series Forecasting. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1905.10437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witkowski, W.T.; Łucka, M.; Guzy, A.; Sudhaus, H.; Barańska, A.; Hejmanowski, R. Impact of Mining-Induced Seismicity on Land Subsidence Occurrence. Remote Sens. Environ. 2024, 301, 113934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milczarek, W.; Kopeć, A.; Głąbicki, D.; Bugajska, N. Induced Seismic Events—Distribution of Ground Surface Displacements Based on InSAR Methods and Mogi and Yang Models. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owczarz, K.; Blachowski, J. Random Forest—Based Identification of Factors Influencing Ground Deformation Due to Mining Seismicity. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 2742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maghsoudi, Y.; Hooper, A.J.; Wright, T.J.; Lazecky, M.; Ansari, H. Characterizing and Correcting Phase Biases in Short-Term, Multilooked Interferograms. Remote Sens. Environ. 2022, 275, 113022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karami, E.; Shami, S.; Maghsoudi, Y.; Ranjgar, B.; Azadnejad, S. Investigating the InSAR Phase Bias in the SBAS Algorithm and Its Effect on Different Landcovers. IEEE Access 2025, 13, 82514–82526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Q.; Xiao, Y.; Hu, L.; Liu, R.; Li, X. Ground Subsidence Prediction with High Precision: A Novel Spatiotemporal Prediction Model with Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar Technology. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2024, 45, 8649–8671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Gao, J.; Gao, F. Time Series Land Subsidence Monitoring and Prediction Based on SBAS-InSAR and GeoTemporal Transformer Model. Earth Sci. Inform. 2024, 17, 5899–5911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
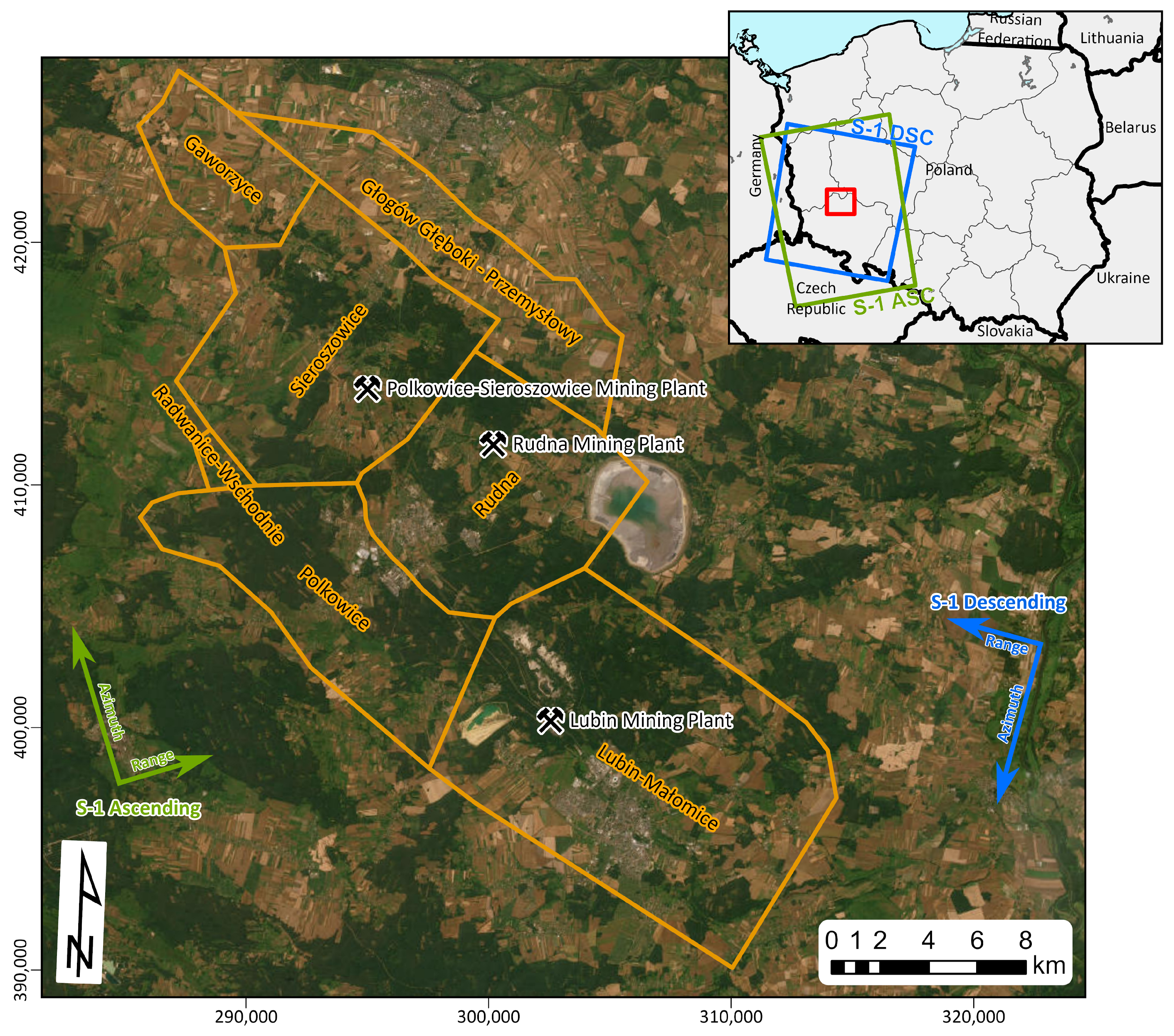
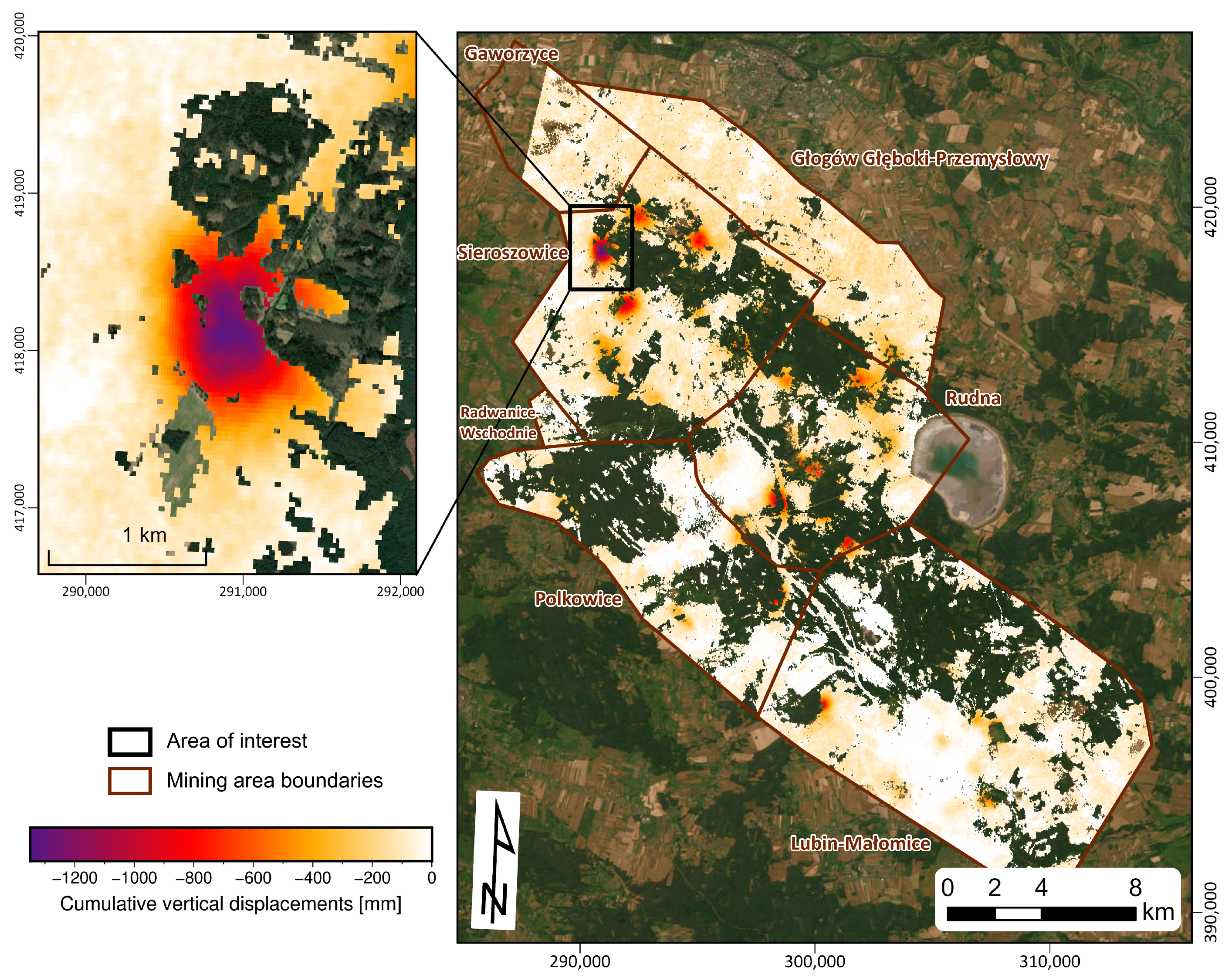
| Flight Direction | Path No. | Start Date * | End Date | Number of Scenes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ascending | 73 | 20 May 2016 | 26 October 2020 | 278 |
| Descending | 22 | 17 May 2016 | 23 October 2020 | 257 |
| Forecast Horizon | Training Data Period | Testing Data Period |
|---|---|---|
| 5 time steps | 20.05.2016–26.09.2020 | 26.09.2020–26.10.2020 |
| 10 time steps | 20.05.2016–27.08.2020 | 27.08.2020–26.10.2020 |
| 20 time steps | 20.05.2016–28.06.2020 | 28.06.2020–26.10.2020 |
| 30 time steps | 20.05.2016–29.04.2020 | 29.04.2020–26.10.2020 |
| 60 time steps | 20.05.2016–01.11.2019 | 01.11.2019–26.10.2020 |
| Model | Hyperparameters |
|---|---|
| ElasticNet | , |
| Random Forest | , , |
| XGBoost | , , |
| N-BEATS | , , , , |
| LSTM | , , , , |
| Model | Metrics | h = 5 | h = 10 | h = 20 | h = 30 | h = 60 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Holt–Winters | RMSE | 6.1 | 8.3 | 9.1 | 11.4 | 16.6 |
| MAE | 5.5 | 6.5 | 7.4 | 9.4 | 13.7 | |
| sMAPE | 7.3 | 8.9 | 10.3 | 13.5 | 15.5 | |
| ElasticNet | RMSE | 6.4 | 9.8 | 9.6 | 10.7 | 25.6 |
| MAE | 5.6 | 8.2 | 7.8 | 8.8 | 22.0 | |
| sMAPE | 7.3 | 11.3 | 10.6 | 12.0 | 21.5 | |
| Random Forest | RMSE | 6.3 | 10.1 | 9.7 | 11.5 | 27.3 |
| MAE | 5.4 | 8.4 | 8.0 | 9.6 | 24.2 | |
| sMAPE | 6.3 | 11.5 | 10.1 | 11.1 | 20.0 | |
| XGBoost | RMSE | 6.8 | 10.9 | 12.5 | 15.5 | 32.9 |
| MAE | 6.0 | 9.2 | 10.6 | 13.3 | 29.3 | |
| sMAPE | 6.4 | 10.9 | 11.1 | 12.5 | 18.9 | |
| N-BEATS | RMSE | 5.4 | 8.6 | 10.2 | 11.6 | 23.0 |
| MAE | 4.7 | 7.0 | 8.3 | 9.6 | 19.8 | |
| sMAPE | 5.7 | 9.1 | 11.0 | 11.8 | 18.4 | |
| LSTM | RMSE | 5.2 | 8.7 | 9.4 | 10.4 | 20.7 |
| MAE | 4.5 | 7.1 | 7.6 | 8.6 | 17.3 | |
| sMAPE | 5.4 | 9.2 | 10.1 | 11.1 | 18.9 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Głąbicki, D. Displacement Time Series Forecasting Using Sentinel-1 SBAS-InSAR Results in a Mining Subsidence Case Study—Evaluation of Machine Learning and Deep Learning Methods. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 3905. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17233905
Głąbicki D. Displacement Time Series Forecasting Using Sentinel-1 SBAS-InSAR Results in a Mining Subsidence Case Study—Evaluation of Machine Learning and Deep Learning Methods. Remote Sensing. 2025; 17(23):3905. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17233905
Chicago/Turabian StyleGłąbicki, Dariusz. 2025. "Displacement Time Series Forecasting Using Sentinel-1 SBAS-InSAR Results in a Mining Subsidence Case Study—Evaluation of Machine Learning and Deep Learning Methods" Remote Sensing 17, no. 23: 3905. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17233905
APA StyleGłąbicki, D. (2025). Displacement Time Series Forecasting Using Sentinel-1 SBAS-InSAR Results in a Mining Subsidence Case Study—Evaluation of Machine Learning and Deep Learning Methods. Remote Sensing, 17(23), 3905. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17233905





