Graph-Based Relaxation for Over-Normalization Avoidance in Reflectance Normalization of Multi-Temporal Satellite Imagery
Highlights
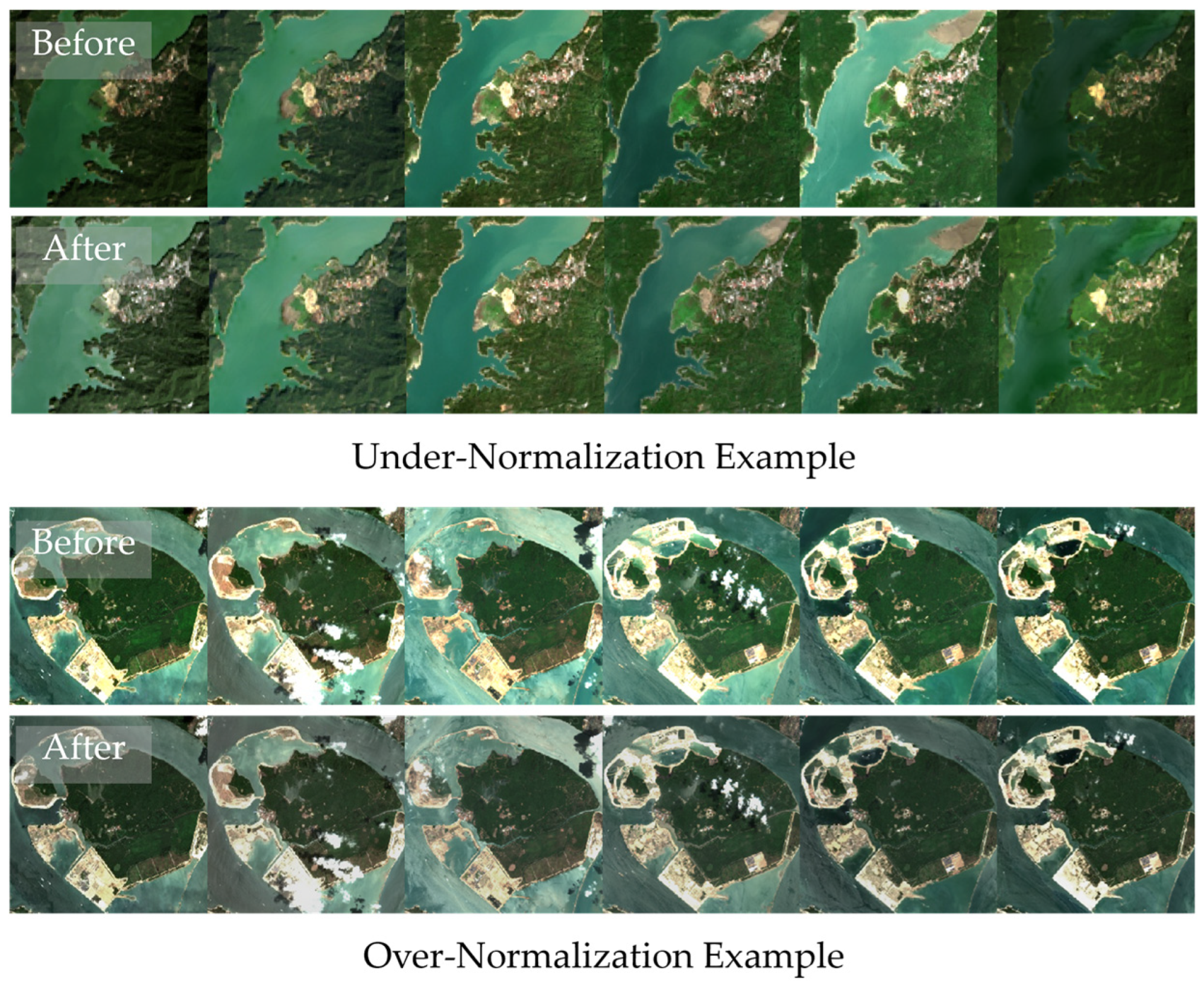
- The proposed graph-based relaxation demonstrates a strong ability to balance reflectance consistency and temporal variability. The method successfully addresses under-normalization and over-normalization, two significant difficulties that commonly distort temporal assessments in multitemporal satellite data through the incorporation of intra-normalization and inter-normalization into a graph-based framework. This balance allows the model to maintain radiometric consistency across different acquisition periods and sensors while preserving the seasonal characteristics of each image, resulting in accurate normalization without significant variance loss.
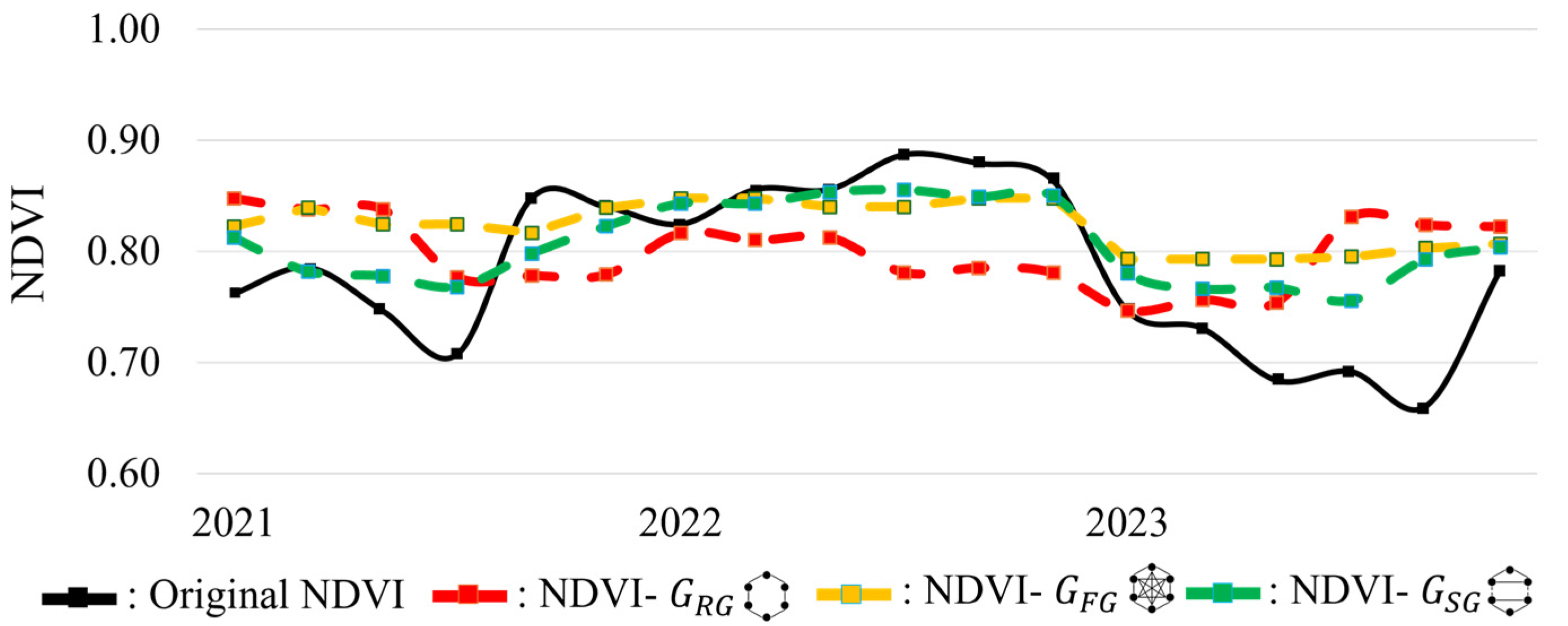
- The proposed method also demonstrated remarkable capability in preserving seasonal and environmental dynamics, particularly in maintaining NDVI trends that reflect natural vegetation cycles. Compared to standard normalization procedures, which frequently result in over-smoothing or temporal discontinuities, the proposed graph-based relaxation preserved seasonal variability while ensuring smooth transitions between distinct periods. As a result, it generated clearer and more realistic representations of vegetation and environmental changes over time, providing higher confidence for long-term monitoring and ecosystem trend assessments.
- By maintaining both temporal stability and seasonal variability, the proposed method increases confidence in long term environmental monitoring results. It minimizes temporal distortions caused by under-normalization and over-normalization, ensuring that reflectance trends represent environmental and phenological changes over time. The framework also achieves consistent reflectance alignment across Landsat 8, Landsat 9, and Sentinel 2 imagery, enabling smooth cross-sensor harmonization through robust linear radiometric alignment necessary for temporal studies and supporting the integration of multi-sensor satellite archives.
- The graph-based relaxation framework demonstrates strong scalability and automation potential. Its adaptable structure supports integration into machine learning workflows or AI-assisted preprocessing pipelines, specifically by decomposing the time series into parallelizable subgraphs, allowing for efficient handling of large-scale datasets. This makes the method suitable for operational use in long-term, spatiotemporal Earth observation projects that require consistent, season-aware reflectance normalization.
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
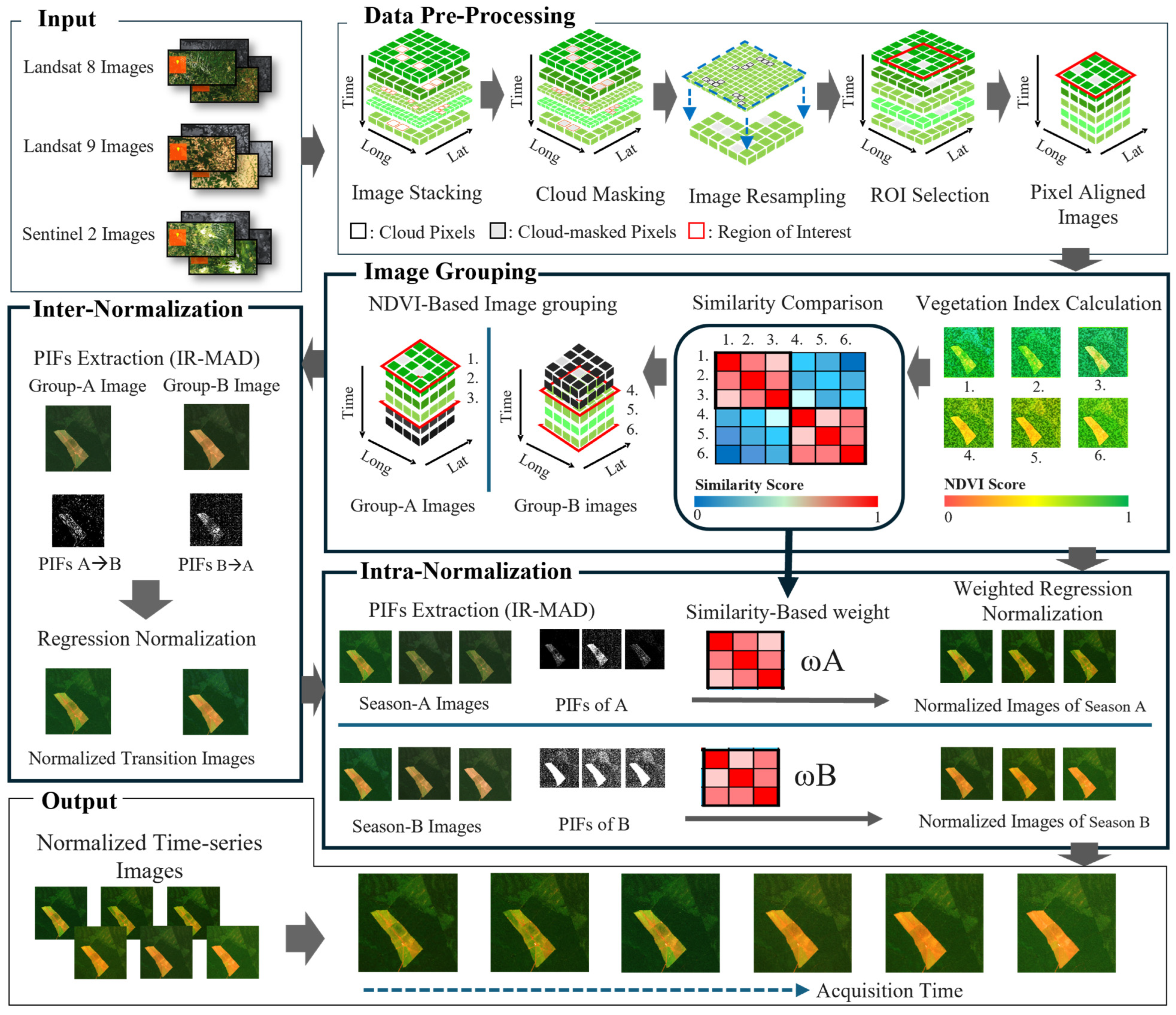
2.1. System Overview
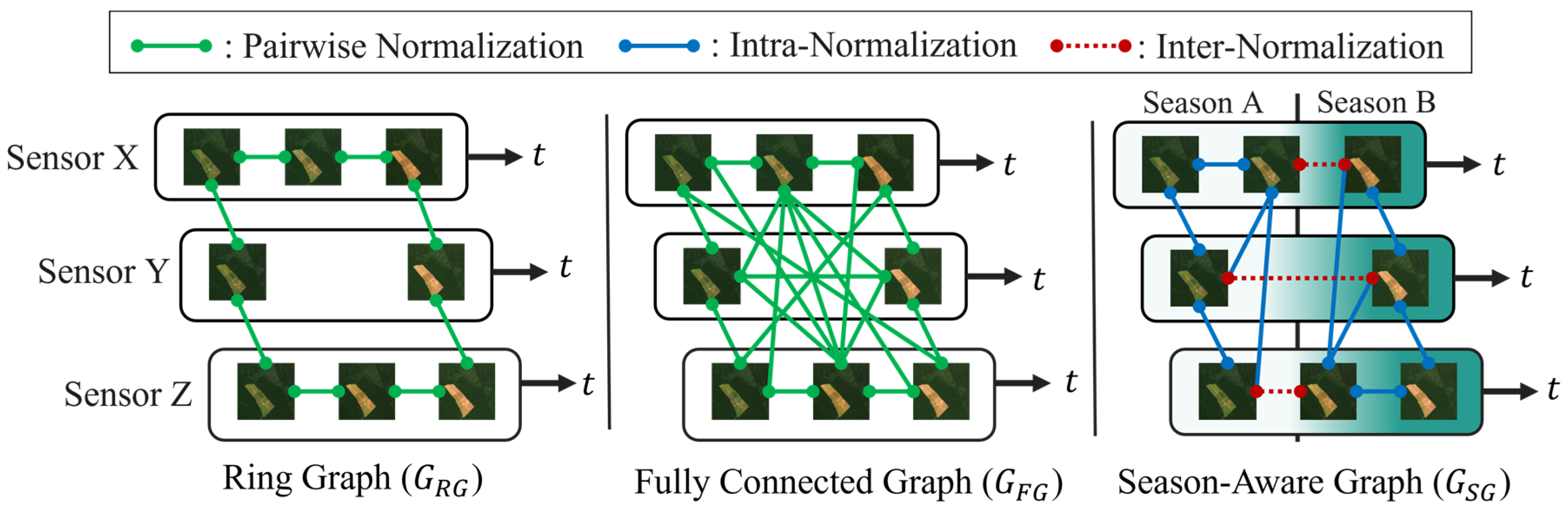
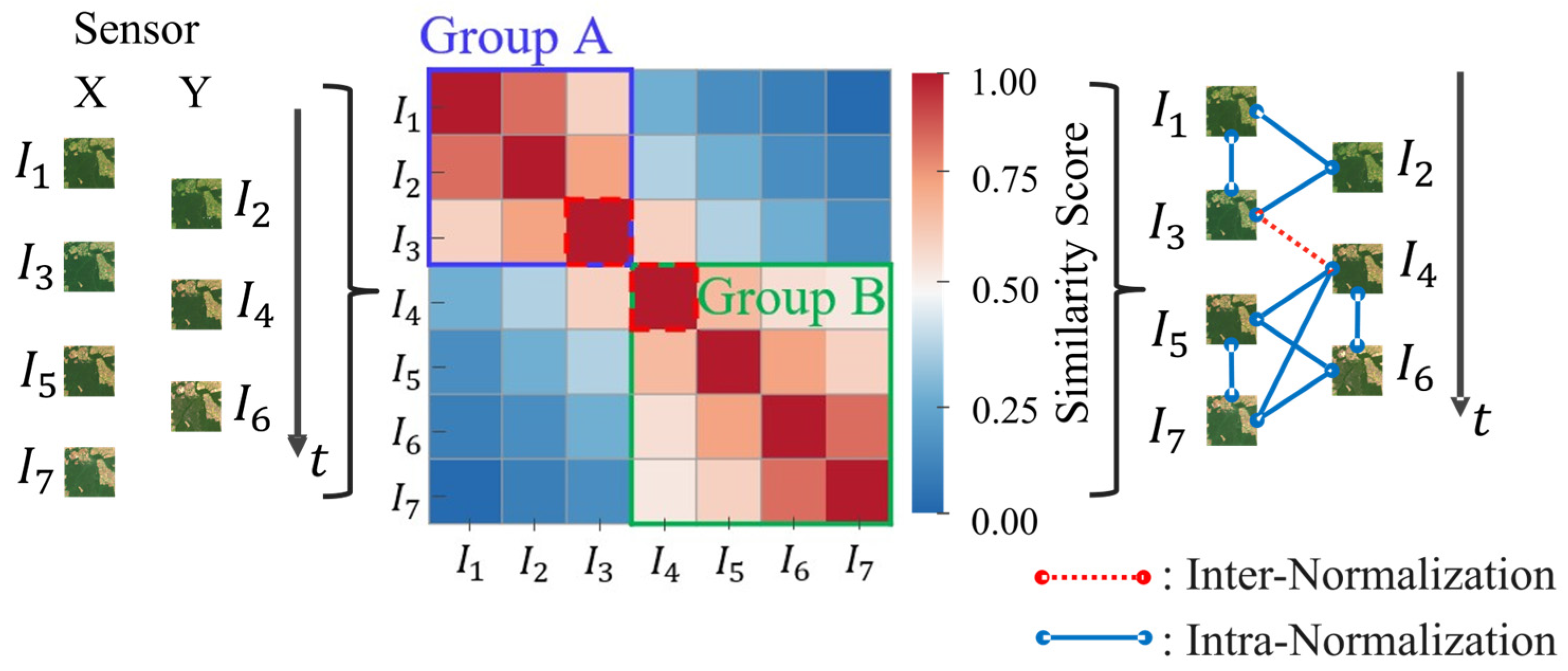
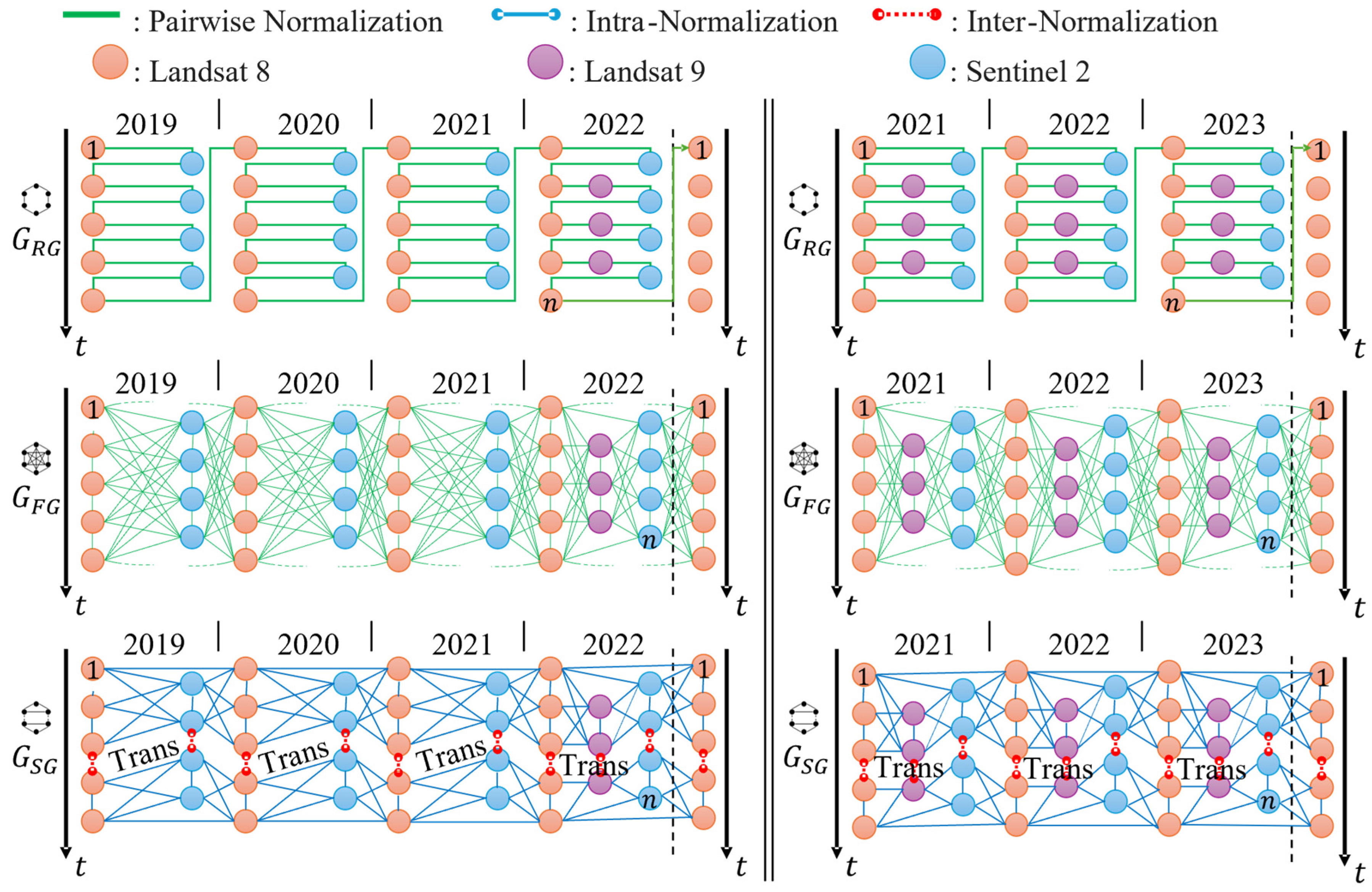
2.2. Graph Design and Image Grouping
2.3. Image Normalization
2.3.1. Inter-Normalization
| Algorithm 1 Inter-normalization (Graph ) |
| //Input: (a inter subgraph containing a set of transition images and a set of edges ) //Output: (the set of normalized transition images) // Relaxation-based normalization For each image-pair (, ) in : // : the reference image (act as an anchor for radiometric alignment) // : the target image to be normalized based on Set Iteration count = 0; Set convergence = false; Set = […]; While convergence = false: // Step 1: Extract PIFs using IR-MAD (Equations (1)–(3)) PIFs = IRMAD (, ); // Step 2: Perform regression-based normalization (Equations (4) and (5)) = Regression_Normalization (PIFs, , ); // Step 3: Assess convergence If Convergence_check (norm_img, ) = true: = norm_img; convergence = true; Else: = norm_img; // update target image for next iteration iteration count + = 1; End While // Save result Add to ; End For Return |
2.3.2. Intra-Normalization
| Algorithm 2 Intra-normalization (Vertices , Graph ) |
| //Input: (the set of normalized transition images) // (an intra-subgraph containing a set of similar images and a set of edges can be a ring graph or fully connected graph) // Output: (The set of normalized same season group images) For each target image in : // : the target image to be normalized based on Set PairResults = […]; Set SSIMscores = […]; // Pairwise relaxation-based normalization and store SSIM (see Relaxation in Procedure Inter-normalization) For each reference image in , ≠ ): // : the reference image Normalized = Relaxation-based Normalization(, ); Z = SSIM(, ); Add (Normalized, Z) to PairResults; Add Z to SSIMscores; End For Zsum = Sum(SSIMscores); //Compute the sum of SSIMs for weighting WeightedSet = […]; For each (Normalized, Z) in PairResults: = Normalized × (Z/Zsum); // Equation (6) Add to WeightedSet; End For = Sum(WeightedSet); //Final weighted normalization (Equation (7)) Add to ; End For Return |
3. Experimental Results and Discussion
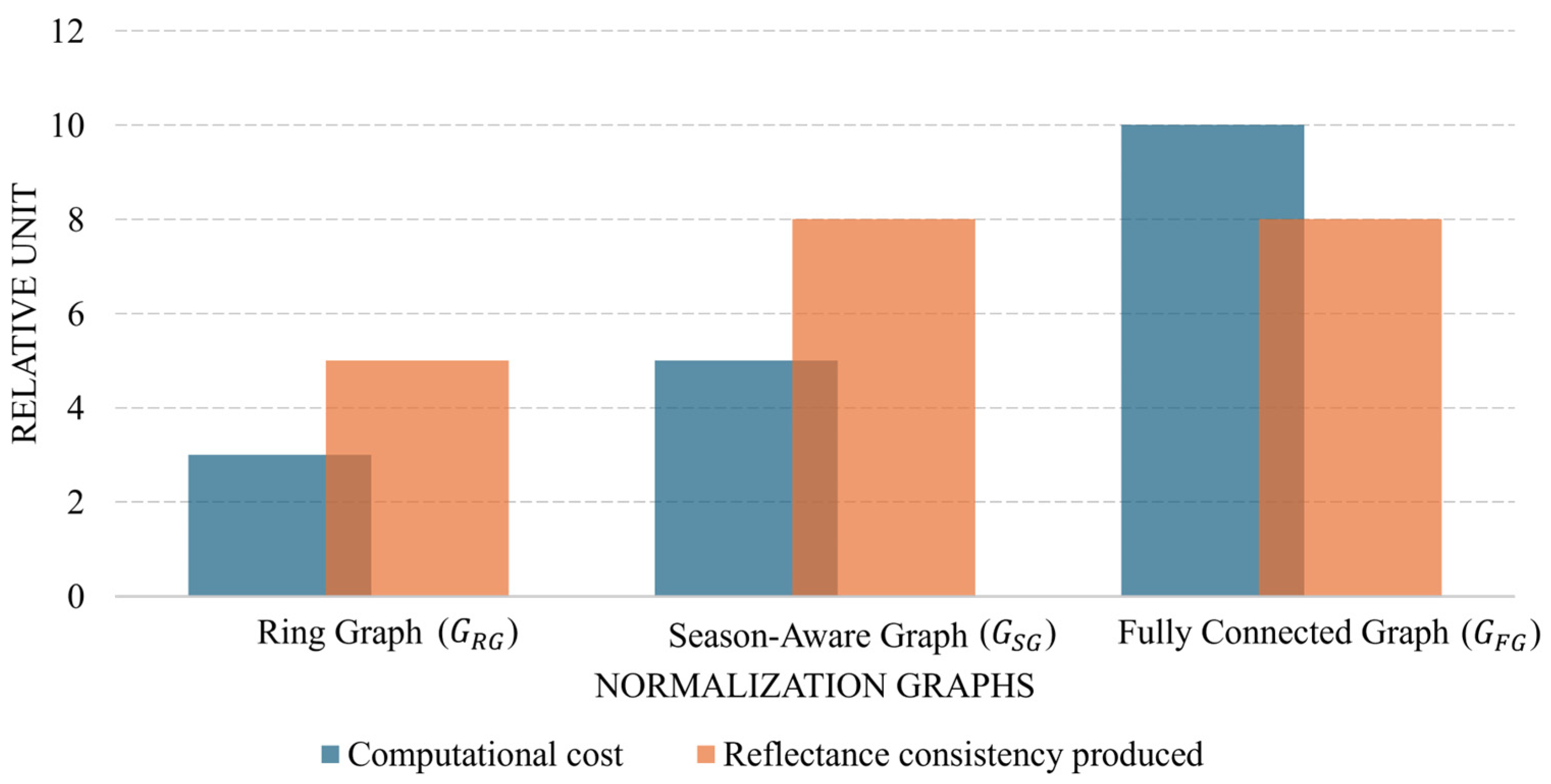
3.1. Normalization Graph Configuration
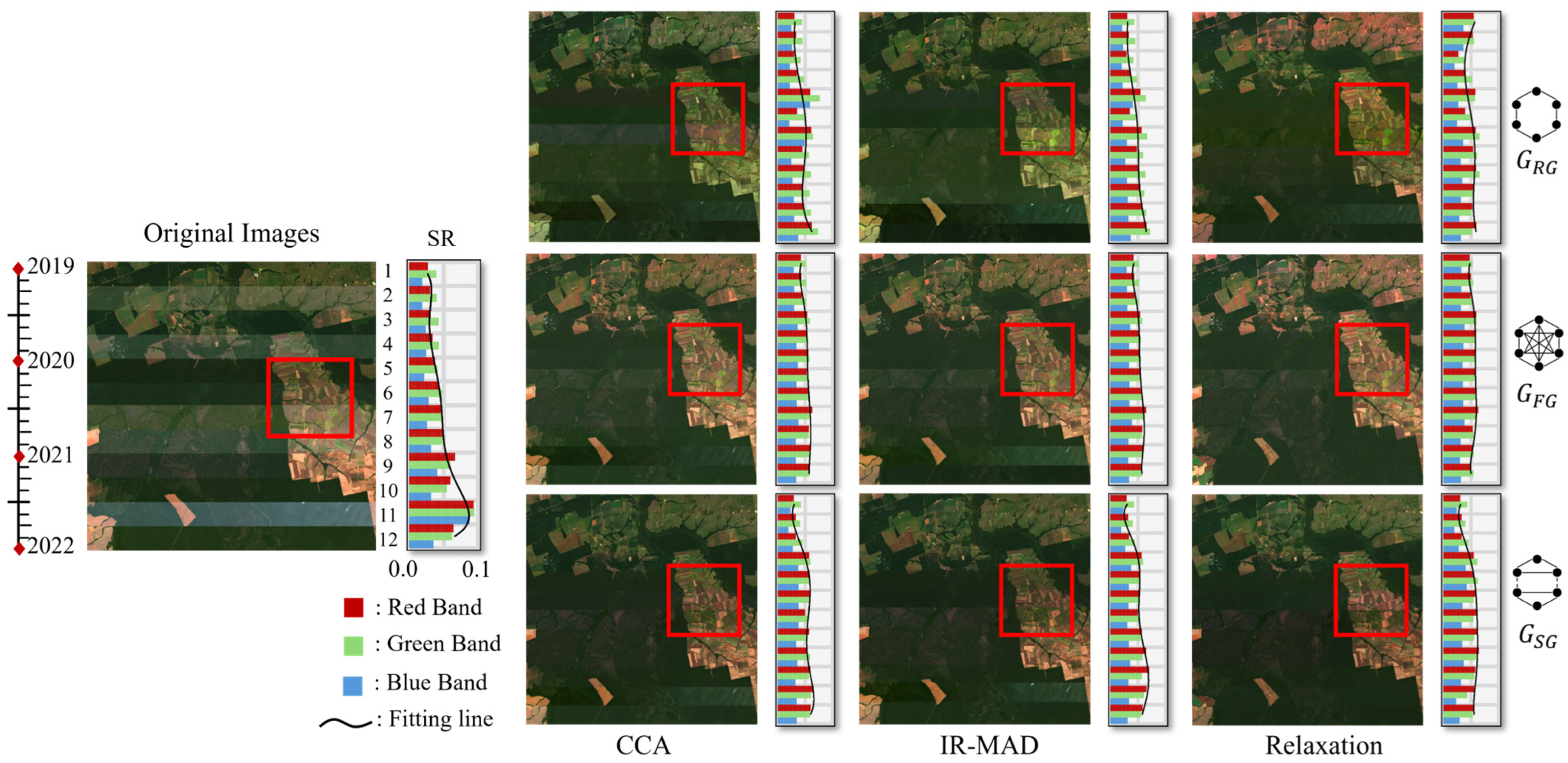
3.2. Visual Assessment of Graph-Based Reflectance Normalization
3.3. Statistical Assessment of Graph-Based Reflectance Normalization
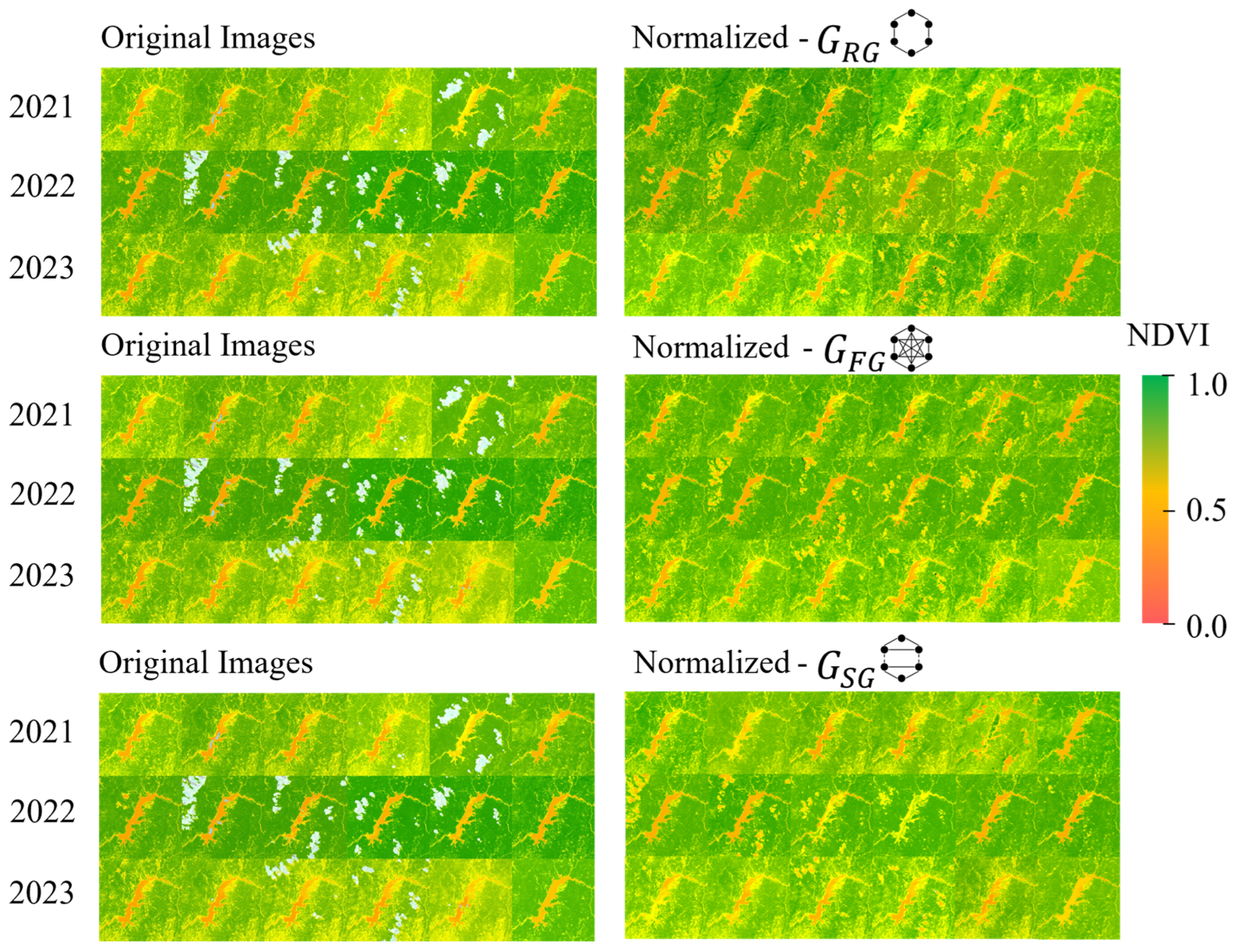
3.4. Comparisons of NDVIs from Normalized Images
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Smith, G.M.; Milton, E.J. The Use of the Empirical Line Method to Calibrate Remotely Sensed Data to Reflectance. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1999, 20, 2653–2662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemingway, B.L.; Frazier, A.E. Cross-Sensor Radiometric Normalization of Planet Smallsat Data Using Sentinel-2 to Improve Consistency across Scenes and Environments. In Proceedings of the Image and Signal Processing for Remote Sensing XXVII, Online, Spain, 12 September 2021; Bruzzone, L., Bovolo, F., Benediktsson, J.A., Eds.; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2021; p. 1186204. [Google Scholar]
- Broncano-Mateos, C.J.; Pinilla, C.; Gonzalez-Crespo, R.; Castillo-Sanz, A. Relative Radiometric Normalization of Multitemporal Images. IJIMAI 2010, 1, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anees, S.A.; Zhang, X.; Shakeel, M.; Al-Kahtani, M.A.; Khan, K.A.; Akram, M.; Ghramh, H.A. Estimation of Fractional Vegetation Cover Dynamics Based on Satellite Remote Sensing in Pakistan: A Comprehensive Study on the FVC and Its Drivers. J. King Saud Univ.—Sci. 2022, 34, 101848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asokan, A.; Anitha, J. Change Detection Techniques for Remote Sensing Applications: A Survey. Earth Sci. Inf. 2019, 12, 143–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.; Liu, Z.; Li, J.; Zeng, Z. Challenges in Remote Sensing Based Climate and Crop Monitoring: Navigating the Complexities Using AI. J. Cloud Comp. 2024, 13, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Liu, L.; Liu, L.; Jiao, Q. Comparison of absolute and relative radiometric normalization use Landsat time series images. In Proceedings of the Comparison of Absolute and Relative Radiometric Normalization Use Landsat Time Series Images, Guilin, China, 20 November 2011; Liu, J., Tian, J., Sang, H., Ma, J., Eds.; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2011; p. 800616. [Google Scholar]
- Farhad, M.M.; Kaewmanee, M.; Leigh, L.; Helder, D. Radiometric Cross Calibration and Validation Using 4 Angle BRDF Model between Landsat 8 and Sentinel 2A. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, G.P.; Felde, G.W.; Hoke, M.L.; Ratkowski, A.J.; Cooley, T.W.; Chetwynd, J.H., Jr.; Gardner, J.A.; Adler-Golden, S.M.; Matthew, M.W.; Berk, A.; et al. MODTRAN4-based atmospheric correction algorithm: FLAASH (fast line-of-sight atmospheric analysis of spectral hypercubes). In Proceedings of the MODTRAN4-Based Atmospheric Correction Algorithm: FLAASH (Fast Line-of-Sight Atmospheric Analysis of Spectral Hypercubes), Orlando, FL, USA, 1 August 2002; Shen, S.S., Lewis, P.E., Eds.; Exelis Visual Information Solutions: McLean, WV, USA, 2002; pp. 65–71. [Google Scholar]
- Maher, A. Evaluation of Atmospherically Gases Using Models FLAASH and QUAC to Hyper-Spectral Imagery. Karbala Int. J. Mod. Sci. 2019, 5, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawes, F.T.; Berk, A.; Van Den Bosch, J.; Fortin, G. MODTRAN7: A Polarimetric Extension of the MODTRAN6 Radiometric Atmospheric Radiative Transfer Model. In Proceedings of the Polarization: Measurement, Analysis, and Remote Sensing XV, Orlando, FL, USA, 3–7 April 2022; Chenault, D.B., Kupinski, M.K., Eds.; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2022; p. 9. [Google Scholar]
- Jasso-Garduño, A.E.; Muñoz-Máximo, I.; Pinto, D.; Ramírez-Cortés, J.M. Deep Learning Based Emulation of Radiative Transfer Code for Atmospheric Correction of Satellite Images. CyS 2024, 28, 2327–2341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassani, C.; Manzo, C.; Zakey, A.; Cuevas-Agulló, E. Effect of the Aerosol Type Selection for the Retrieval of Shortwave Ground Net Radiation: Case Study Using Landsat 8 Data. Atmosphere 2016, 7, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Carvalho, O.; Guimarães, R.; Silva, N.; Gillespie, A.; Gomes, R.; Silva, C.; de Carvalho, A. Radiometric Normalization of Temporal Images Combining Automatic Detection of Pseudo-Invariant Features from the Distance and Similarity Spectral Measures, Density Scatterplot Analysis, and Robust Regression. Remote Sens. 2013, 5, 2763–2794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghimi, A.; Celik, T.; Mohammadzadeh, A.; Kusetogullari, H. Comparison of Keypoint Detectors and Descriptors for Relative Radiometric Normalization of Bitemporal Remote Sensing Images. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2021, 14, 4063–4073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayegani, B.; Barati, S.; Sarkheil, H. A Simple Model for PIFs Extraction at Digital Change Detection Approach. Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 2021, 7, 1769–1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Ma, Y.; Lian, Y.; Zhang, H.; Yu, Y.; Lin, Y. Radiometric Normalization Using a Pseudo−Invariant Polygon Features−Based Algorithm with Contemporaneous Sentinel−2A and Landsat−8 OLI Imagery. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 2525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Tang, P.; Hu, C. kCCA Transformation-Based Radiometric Normalization of Multi-Temporal Satellite Images. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denaro, L.G.; Lin, C.-H. Hybrid Canonical Correlation Analysis and Regression for Radiometric Normalization of Cross-Sensor Satellite Imagery. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2020, 13, 976–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, H.; Shi, J.; Wang, Y.; Wei, L. An improved dark-object subtraction technique for atmospheric correction of Landsat 8. In Proceedings of the An Improved Dark-Object Subtraction Technique for Atmospheric Correction of Landsat 8, Enshi, China, 14 December 2015; Liu, J., Sun, H., Eds.; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2015; p. 98150K. [Google Scholar]
- Nicolau, R.; Basos, N.; Marcelino, F.; Caetano, M.; Pereira, J.M.C. Harmonization of Categorical Maps by Alignment Processes and Thematic Consistency Analysis. AIMS Geosci. 2020, 6, 473–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Fan, J.; Zhang, M.; Liu, Q.; Li, Y.; Zhang, D.; Zhou, Y. Relative Radiation Correction Based on CycleGAN for Visual Perception Improvement in High-Resolution Remote Sensing Images. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 106627–106640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sambandham, V.T.; Kirchheim, K.; Ortmeier, F.; Mukhopadhaya, S. Deep Learning-Based Harmonization and Super-Resolution of Landsat-8 and Sentinel-2 Images. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2024, 212, 274–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Wang, L.; Lian, J.; Liu, C.; Zhan, X.; Liu, J.; Wang, T.; Geng, D.; Duan, H.; Zou, S. Auto-Robust Relative Radiometric Normalization via Latent Change Noise Modeling. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2024, 62, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koczkodaj, W.W.; Magnot, J.-P.; Mazurek, J.; Peters, J.F.; Rakhshani, H.; Soltys, M.; Strzałka, D.; Szybowski, J.; Tozzi, A. On Normalization of Inconsistency Indicators in Pairwise Comparisons. Int. J. Approx. Reason. 2017, 86, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Sun, X.; Wang, X.; Fan, J.; Luo, J.; Shen, Y.; Yang, Y. A Long Time-Series Radiometric Normalization Method for Landsat Images. Sensors 2018, 18, 4505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, R.J. Introduction to Graph Theory, 4th ed.; Nachdr; Prentice Hall: Harlow, UK; Munich, Germany, 2009; ISBN 978-0-582-24993-6. [Google Scholar]
- Ghanbari, H.; Homayouni, S.; Ghamisi, P.; Safari, A. Radiometric Normalization of Multitemporal and Multisensor Remote Sensing Images Based on a Gaussian Mixture Model and Error Ellipse. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2018, 11, 4526–4533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y. Improved Relative Radiometric Normalization Method of Remote Sensing Images for Change Detection. J. Appl. Rem. Sens. 2018, 12, 045018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, W.; Albanwan, H.; Qin, R. Radiometric Normalization of Multitemporal Landsat and Sentinel-2 Images Using a Reference MODIS Product Through Spatiotemporal Filtering. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2021, 14, 4000–4013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canty, M.J.; Nielsen, A.A. Automatic Radiometric Normalization of Multitemporal Satellite Imagery with the Iteratively Re-Weighted MAD Transformation. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 1025–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marpu, P.R.; Gamba, P.; Canty, M.J. Improving Change Detection Results of IR-MAD by Eliminating Strong Changes. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2011, 8, 799–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barazzetti, L.; Gianinetto, M.; Scaioni, M. Radiometric normalization with multi-image pseudo-invariant features. In Proceedings of the Radiometric Normalization with Multi-Image Pseudo-Invariant Features, Paphos, Cyprus, 12 August 2016; Themistocleous, K., Hadjimitsis, D.G., Michaelides, S., Papadavid, G., Eds.; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2016; p. 968807. [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen, A.A. The Regularized Iteratively Reweighted MAD Method for Change Detection in Multi- and Hyperspectral Data. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2007, 16, 463–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Choi, S.-K.; Han, Y.-K.; Lee, S.-K.; Choi, J.-W. Application of IR-MAD Using Synthetically Fused Images for Change Detection in Hyperspectral Data. Remote Sens. Lett. 2015, 6, 578–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryadi, G.Y.I.; Syariz, M.A.; Lin, C.-H. Relaxation-Based Radiometric Normalization for Multitemporal Cross-Sensor Satellite Images. Sensors 2023, 23, 5150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabino, M.; Da Silva, A.C.; De Almeida, F.T.; De Souza, A.P. Reference Evapotranspiration in Climate Change Scenarios in Mato Grosso, Brazil. Hydrology 2024, 11, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Commar, L.F.S.; Louzada, L.; Costa, M.H.; Brumatti, L.M.; Abrahão, G.M. Mato Grosso’s Rainy Season: Past, Present, and Future Trends Justify Immediate Action. Environ. Res. Lett. 2024, 19, 114065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunlap, W.P.; Brody, C.J.; Greer, T. Canonical Correlation and Chi-Square: Relationships and Interpretation. J. Gen. Psychol. 2000, 127, 341–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Sensor | 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | 2022 | 2023 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BR | TW | BR | TW | BR | TW | BR | TW | BR | TW | |
| Landsat 8 (LANDSAT/LC08/C02/T1_L2) | 11 | - | 11 | - | 9 | 17 | 10 | 8 | - | 12 |
| Landsat 9 (LANDSAT/LC09/C02/T1_L2) | - | - | - | - | - | 13 | 11 | 9 | - | 8 |
| Sentinel 2 (COPERNICUS/S2_SR_HARMONIZED) | 14 | - | 14 | - | 13 | 30 | 9 | 13 | - | 13 |
| Total Images | 25 | 0 | 25 | 0 | 22 | 60 | 30 | 30 | 0 | 33 |
| MAE/RMSE | CCA | ||
| Wet Seasons | Transitions | Dry Seasons | |
| Original Image | 0.557/0.198 | 0.605/0.206 | 0.994/0.231 |
 | 0.474/0.170 | 1.144/0.286 | 0.727/0.220 |
 | 0.465/0.164 | 0.483/0.177 | 0.475/0.174 |
 | 0.465/0.165 | 0.497/0.177 | 0.469/0.166 |
| MAE/RMSE | IR-MAD | ||
| Wet Seasons | Transitions | Dry Seasons | |
| Original Image | 0.557/0.198 | 0.605/0.206 | 0.994/0.231 |
 | 0.481/0.167 | 0.769/0.208 | 0.690/0.198 |
 | 0.473/0.160 | 0.479/0.161 | 0.473/0.161 |
 | 0.468/0.160 | 0.486/0.166 | 0.470/0.158 |
| MAE/RMSE | Relaxation-Based | ||
| Wet Seasons | Transitions | Dry Seasons | |
| Original Image | 0.557/0.198 | 0.605/0.206 | 0.994/0.231 |
 | 0.484/0.185 | 0.759/0.217 | 0.630/0.214 |
 | 0.457/0.158 | 0.461/0.160 | 0.456/0.158 |
 | 0.453/0.157 | 0.461/0.160 | 0.446/0.144 |
| SSIM | CCA | ||
| Wet Seasons | Transitions | Dry Seasons | |
| Original Image | 0.79 | 0.876 | 0.907 |
 | 0.835 | 0.832 | 0.873 |
 | 0.836 | 0.878 | 0.913 |
 | 0.868 | 0.877 | 0.931 |
| SSIM | IR-MAD | ||
| Wet Seasons | Transitions | Dry Seasons | |
| Original Image | 0.79 | 0.876 | 0.907 |
 | 0.829 | 0.846 | 0.863 |
 | 0.837 | 0.879 | 0.913 |
 | 0.843 | 0.878 | 0.930 |
| SSIM | Relaxation-Based | ||
| Wet Seasons | Transitions | Dry Seasons | |
| Original Image | 0.79 | 0.876 | 0.907 |
 | 0.825 | 0.844 | 0.883 |
 | 0.852 | 0.878 | 0.916 |
 | 0.856 | 0.880 | 0.935 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ryadi, G.Y.I.; Lin, C.-H.; Lin, B.-Y. Graph-Based Relaxation for Over-Normalization Avoidance in Reflectance Normalization of Multi-Temporal Satellite Imagery. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 3877. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17233877
Ryadi GYI, Lin C-H, Lin B-Y. Graph-Based Relaxation for Over-Normalization Avoidance in Reflectance Normalization of Multi-Temporal Satellite Imagery. Remote Sensing. 2025; 17(23):3877. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17233877
Chicago/Turabian StyleRyadi, Gabriel Yedaya Immanuel, Chao-Hung Lin, and Bo-Yi Lin. 2025. "Graph-Based Relaxation for Over-Normalization Avoidance in Reflectance Normalization of Multi-Temporal Satellite Imagery" Remote Sensing 17, no. 23: 3877. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17233877
APA StyleRyadi, G. Y. I., Lin, C.-H., & Lin, B.-Y. (2025). Graph-Based Relaxation for Over-Normalization Avoidance in Reflectance Normalization of Multi-Temporal Satellite Imagery. Remote Sensing, 17(23), 3877. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17233877






