A Robust and Reliable Positioning Method for Complex Environments Based on Quality-Controlled Multi-Sensor Fusion of GNSS, INS, and LiDAR
Highlights
- A robust and reliable positioning method based on quality-controlled multi-sensor fusion of GNSS, INS, and LiDAR is proposed for large-scale tunnel, urban, campus, and mountain environments.
- The proposed algorithm reduces the risk of degradation and demonstrates superior adaptability in large-scale, long-duration complex environments, significantly enhancing both reliability and robustness.
- This study can improve the reliability and robustness of positioning of unmanned vehicles in real-world complex environments.
- This study provides a new method for solving the localization of lidar point cloud in scenes with sparse features and repeated features.
Abstract
1. Introduction
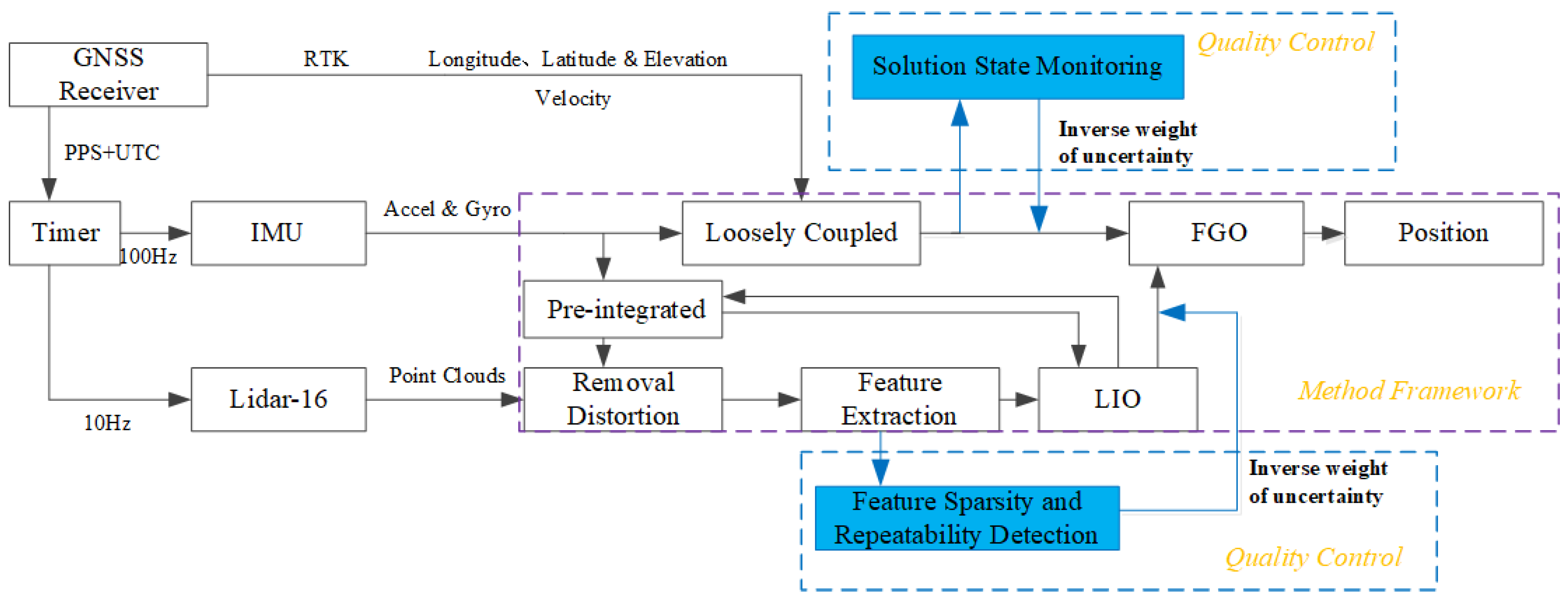
2. System Overview
2.1. The Primary Contributions of This Paper
- (1)
- The uncertainty measurement weights in real time and quality-control fusion positioning framework are proposed, which include GNSS/INS integrated navigation for absolute position measurement and LIO (LiDAR-Inertial Odometry) for relative motion estimation.
- (2)
- The front-end is augmented with a GNSS availability status monitoring model and a LIO quality control model, enhancing the adaptability of sensors in complex environments.
- (3)
- A verification platform has been developed for satellite navigation, inertial navigation, and LiDAR, enabling synchronized timing among sensors. Real-time processing is facilitated by software implemented on the platform computer.
- (4)
- Experiments are conducted in real-world environments, including mountainous areas, tunnels, campus, and urban environments, and the robustness and reliability of the algorithm are verified on the experimental vehicle platform.
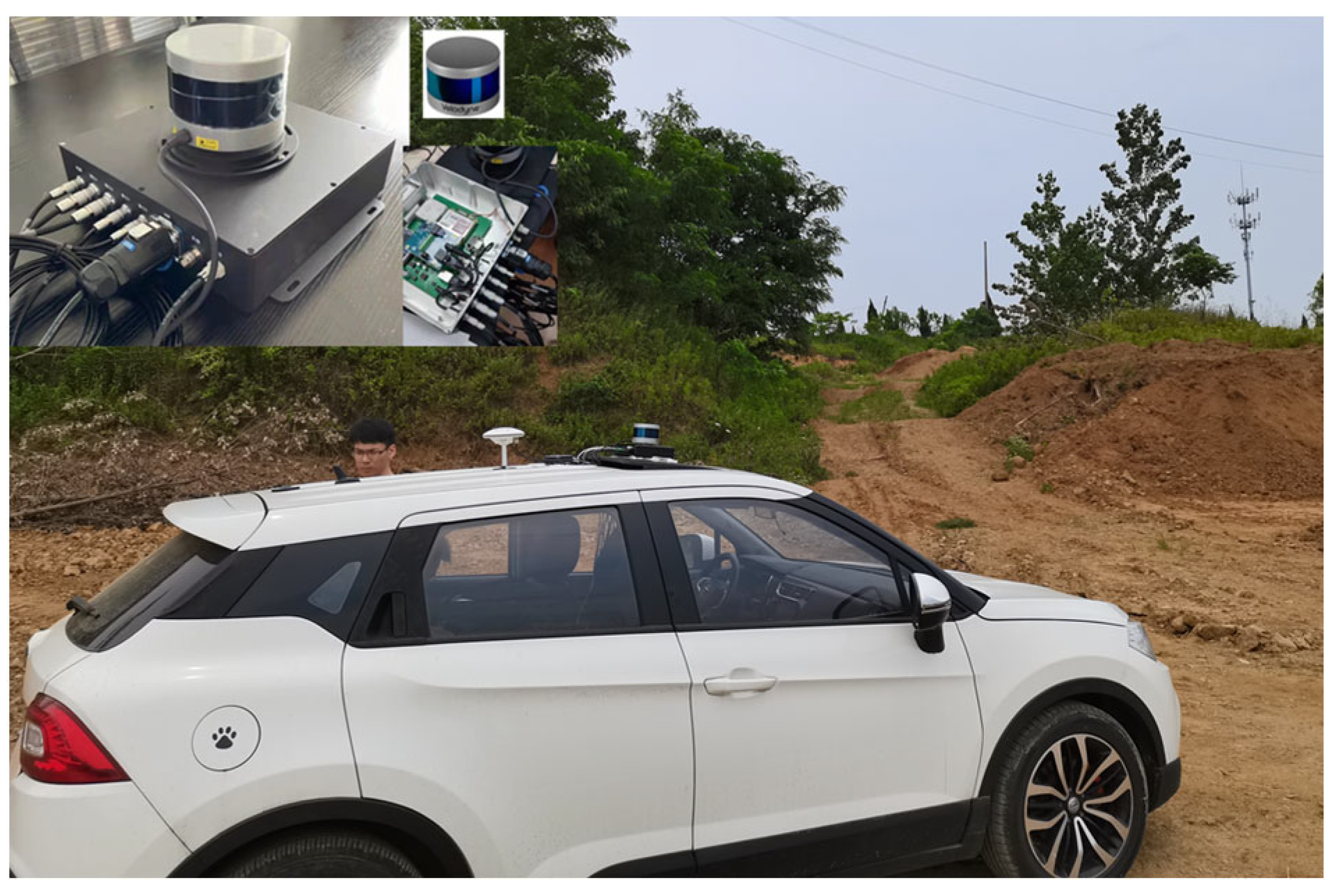
2.2. Platform System
2.3. Unified Coordinate System
3. Fusion Methods
3.1. GNSS/INS Factor
3.2. LIO Factor
3.2.1. Distortion Correction
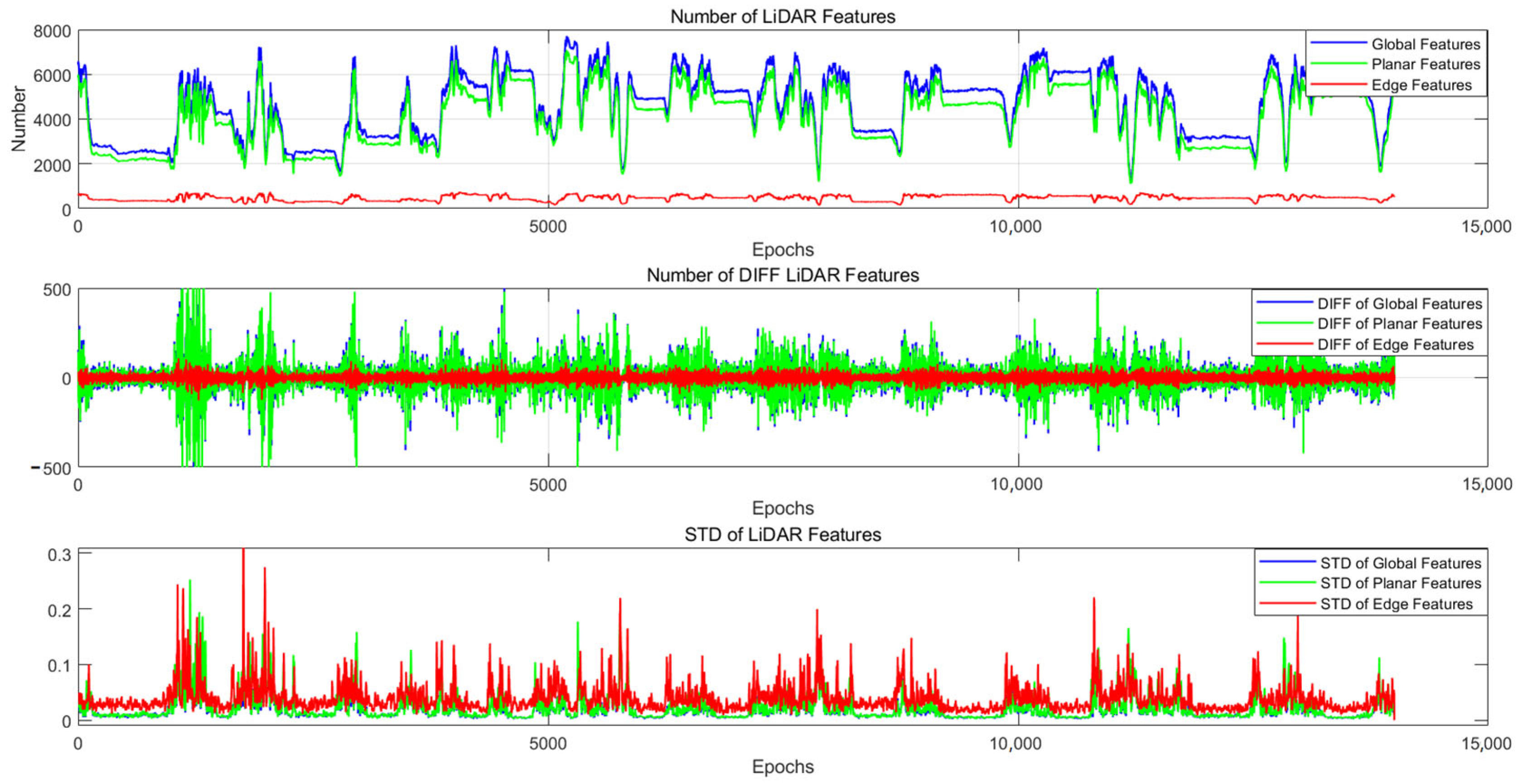
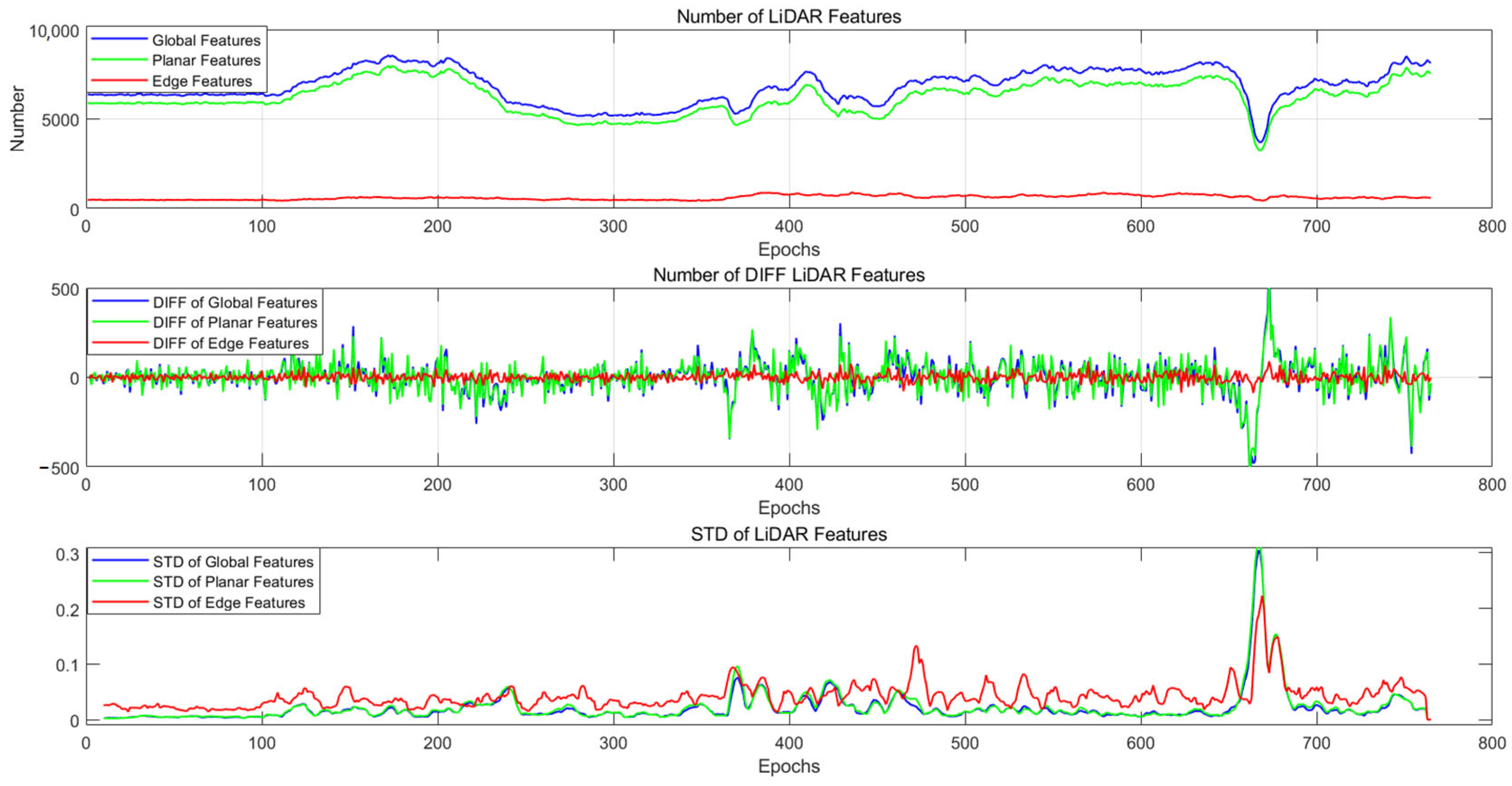
3.2.2. Feature Extraction
3.2.3. LiDAR Odometer
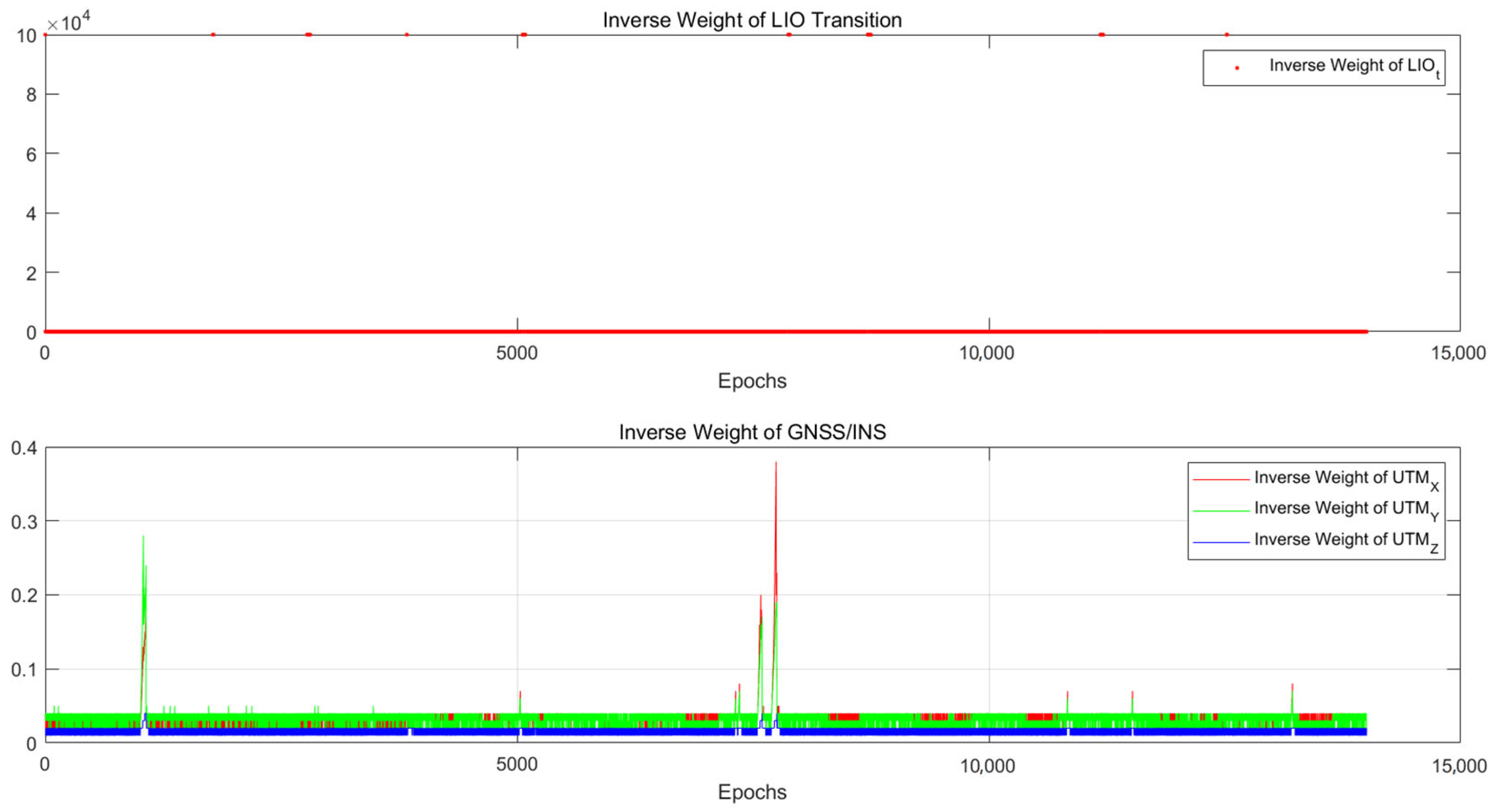
3.3. Quality Control
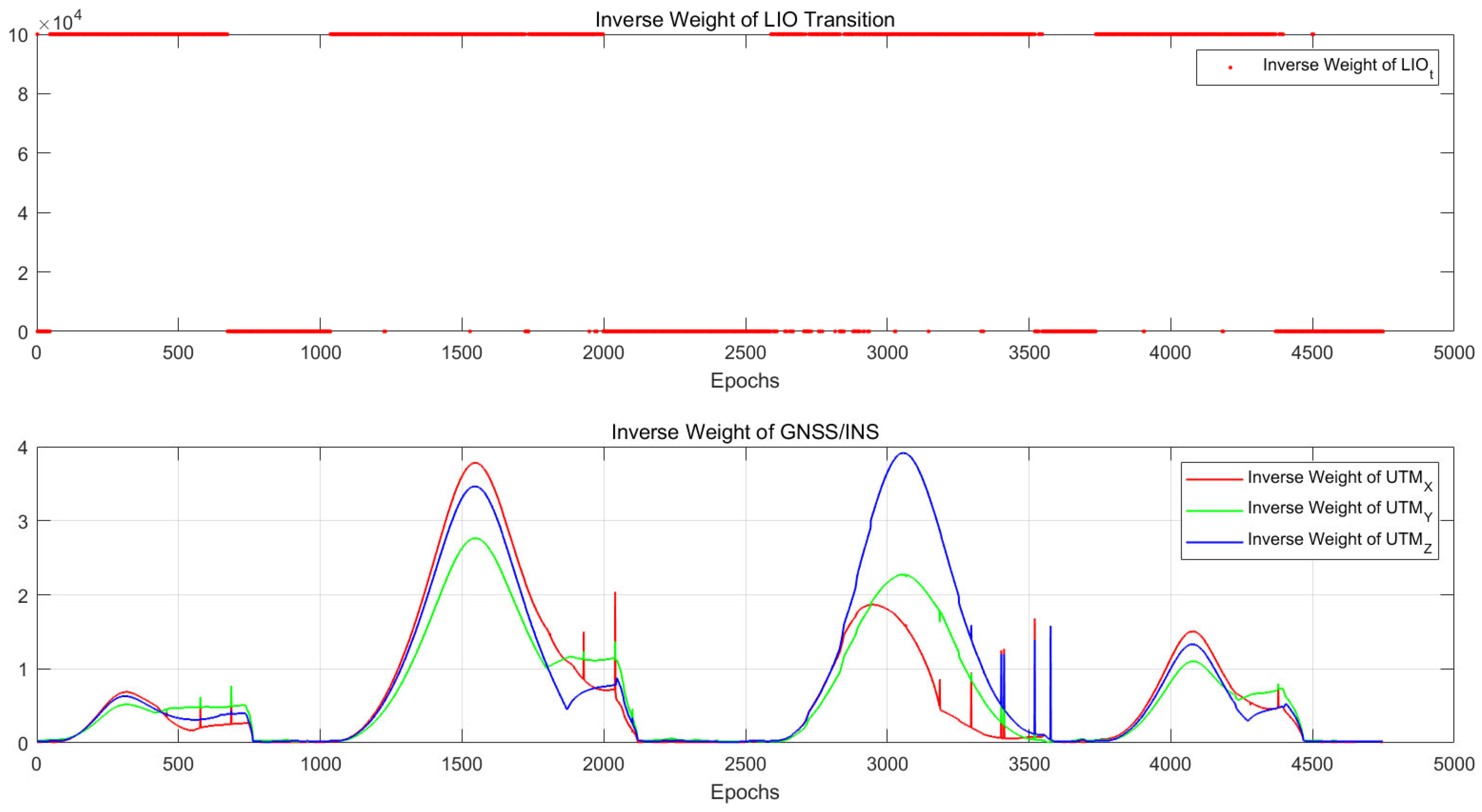
3.3.1. GNSS/INS Quality Control
3.3.2. LIO Quality Control
3.4. Fusion
3.4.1. Factor Graph Optimization
3.4.2. Inverse Weight of Uncertainty
4. Experiments and Analysis
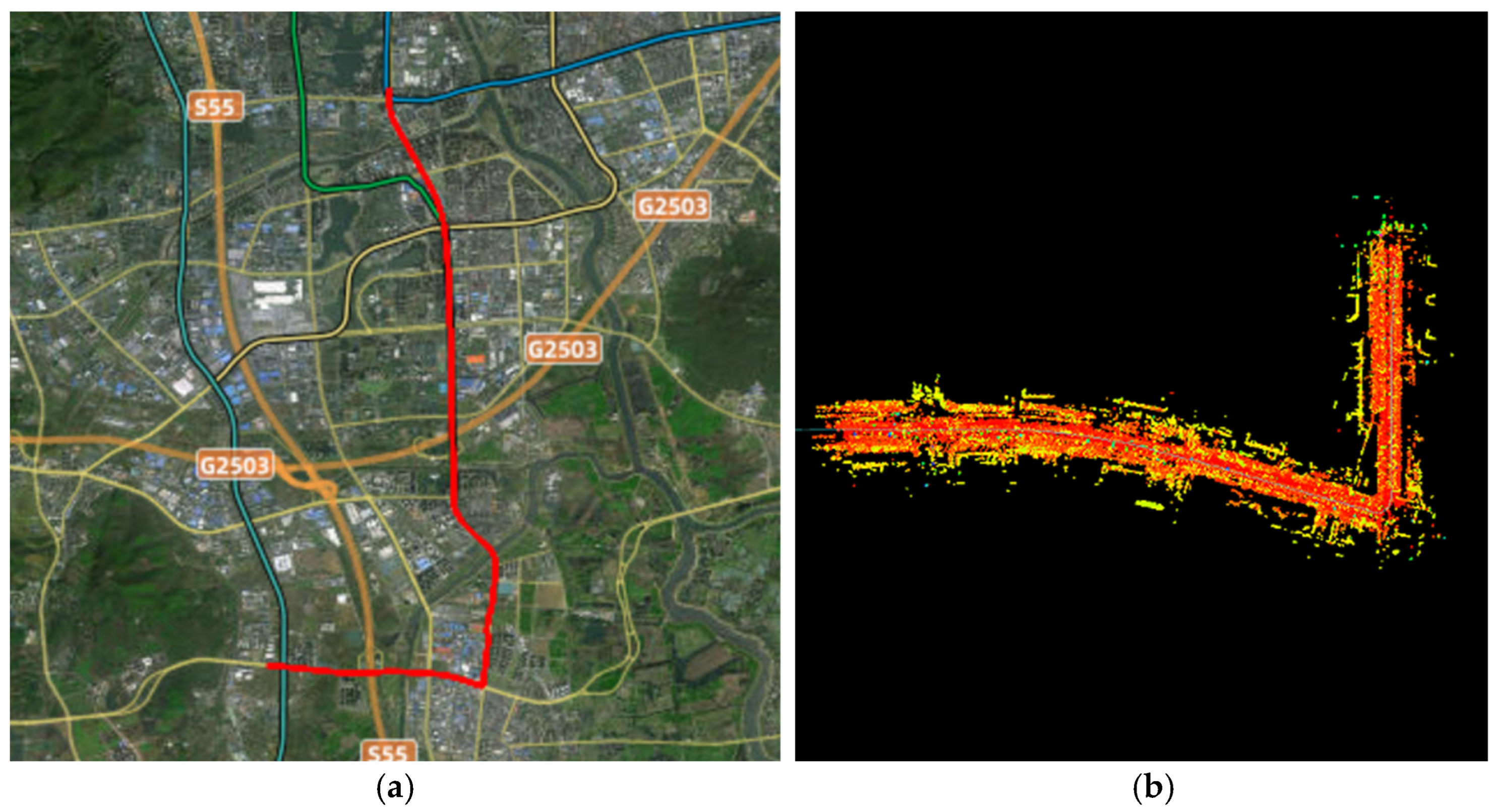
4.1. Tunnel Environment Experiment
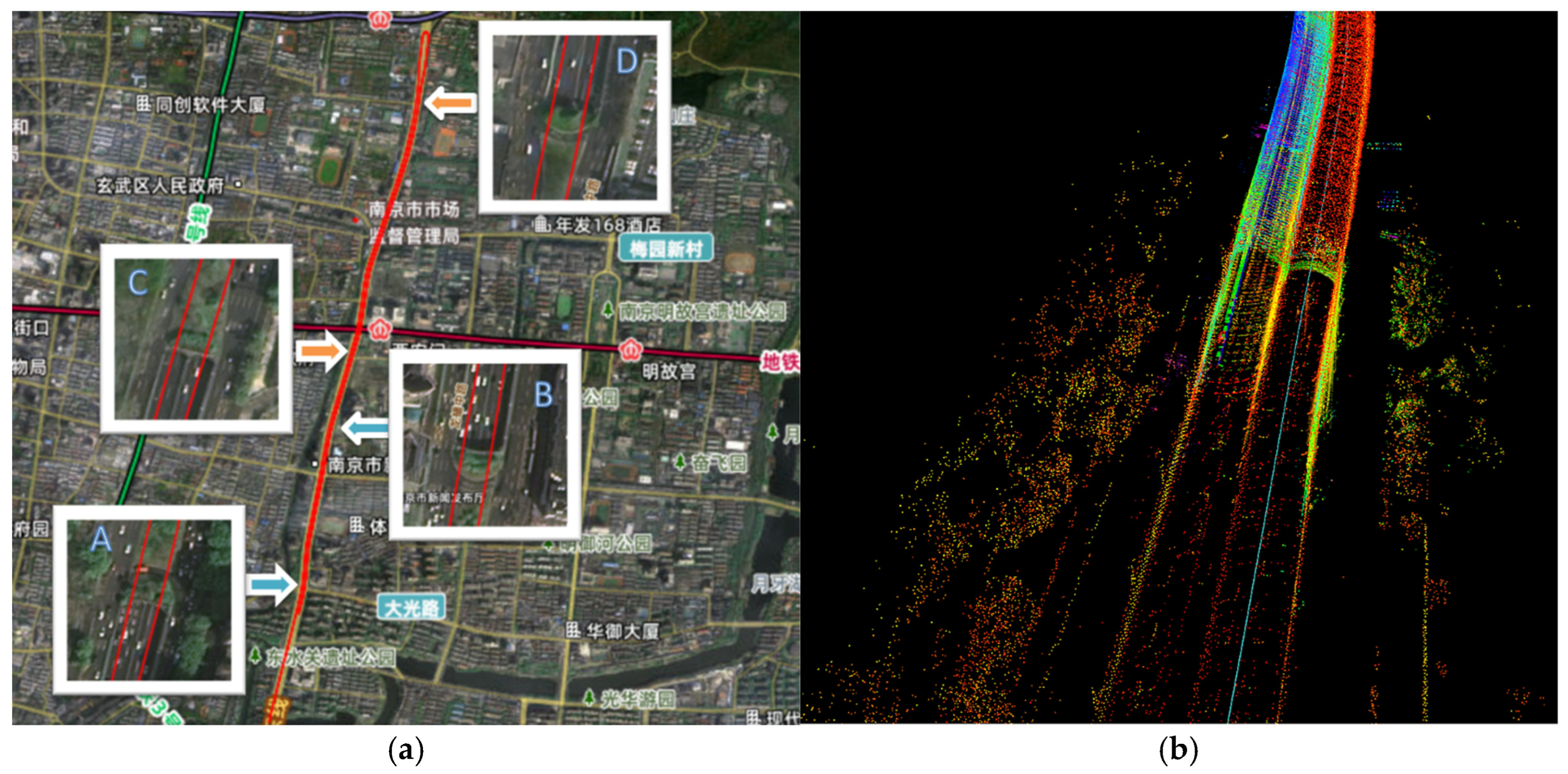
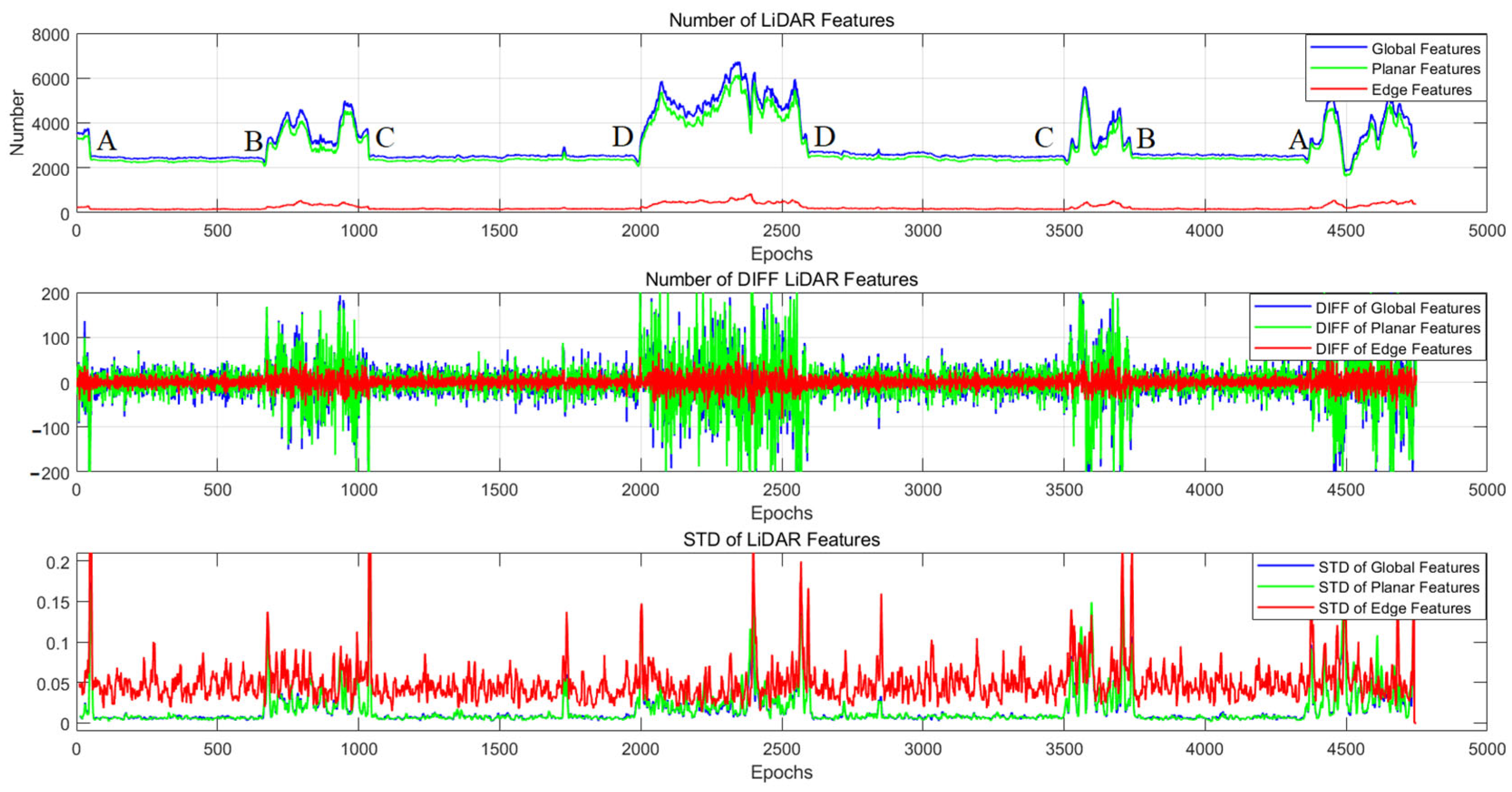
4.2. Urban Environment Experiment
4.3. Campus Environment Experiment
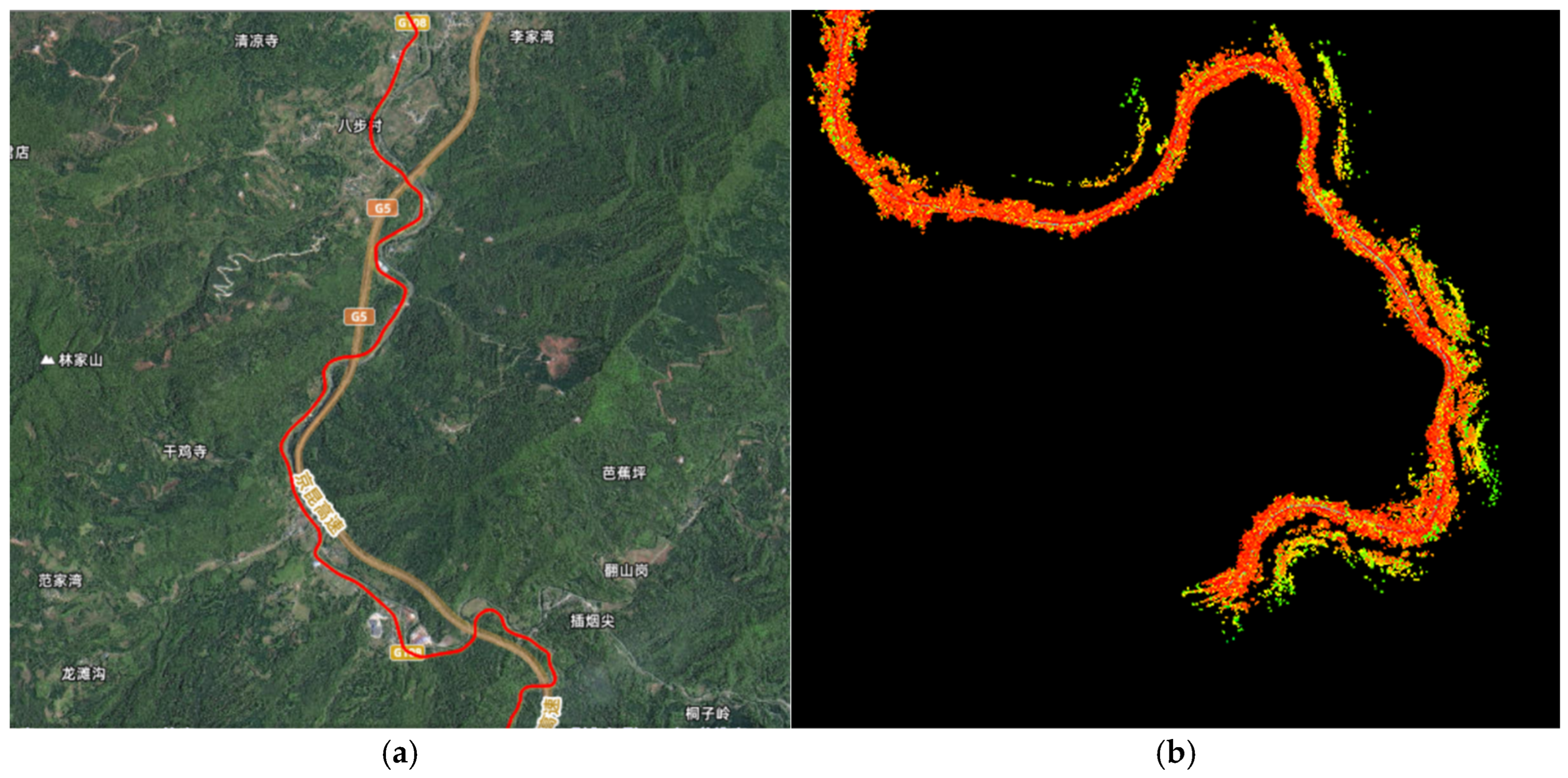
4.4. Mountain Environment Experiment
4.5. Accuracy of Positioning and Mapping
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, X.; Xu, Q.; Li, X.; Xin, H.; Yuan, Y.; Shen, Z.; Zhou, Y. Improving PPP-RTK-based vehicle navigation in urban environments via multilayer perceptron-based NLOS signal detection. GPS Solut. 2023, 28, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zhang, Z.; Sheng, C.; Yu, B.; Gao, W.; Meng, X. Fast and Reliable Network RTK Positioning Based on Multi-Frequency Sequential Ambiguity Resolution under Significant Atmospheric Biases. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 2320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Sukkarieh, S. 6DOF SLAM aided GNSS/INS navigation in GNSS denied and unknown environments. J. Glob. Position. Syst. 2005, 4, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Nie, W.; Zong, W.; Xu, T.; Li, M.; Jiang, N.; Zhang, W. High-Precision Multi-Source Fusion Navigation Solutions for Complex and Dynamic Urban Environments. Remote. Sens. 2025, 17, 1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Zhang, S.; Wang, J.; Li, J. An innovation-based cycle-slip, multipath estimation, detection and mitigation method for tightly coupled GNSS/INS/Vision navigation in urban areas. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2409.03433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, T.; Li, P.; Shen, S. VINS-Mono: A Robust and Versatile Monocular Visual-Inertial State Estimator. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2018, 34, 1004–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, C.; Elvira, R.; Rodriguez, J.J.G.; Montiel, J.M.M.; Tardos, J.D. ORB-SLAM3: An Accurate Open-Source Library for Visual, Visual-Inertial and Multi-Map SLAM. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2021, 37, 1874–1890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhu, F.; Tao, X.; Duan, R. New optimal smoothing scheme for improving relative and absolute accuracy of tightly coupled GNSS/SINS integration. Gps Solut. 2017, 21, 861–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, G.; Wang, J.; Zhou, X. High-Precision Simulator for Strapdown Inertial Navigation Systems Based on Real Dynamics from GNSS and IMU Integration. In Proceedings of the China Satellite Navigation Conference (CSNC), Xi’an, China, 13–15 May 2015; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obst, M.; Bauer, S.; Reisdorf, P.; Wanielik, G. Multipath Detection with 3D Digital Maps for Robust Multi-Constellation GNSS/INS Vehicle Localization in Urban Areas. In Proceedings of the Intelligent Vehicles Symposium (IV), Madrid, Spain, 3–7 June 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.H.; Jho, C.W.; Hong, H.K. Automatic Registration Method for Multiple 3D Range Data Sets. J. KISS Softw. Appl. 2003, 30, 1239–1246. [Google Scholar]
- Dellenbach, P.; Deschaud, J.-E.; Jacquet, B.; Goulette, F. CT-ICP: Real-time Elastic LiDAR Odometry with Loop Closure. In Proceedings of the 2022 International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Philadelphia, PA, USA, 23–27 May 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koide, K.; Miura, J.; Menegatti, E. A Portable 3D LIDAR-based System for Long-term and Wide-area People Behavior Measurement. Int. J. Adv. Robot. Syst. 2019, 16, 1729881419841532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koide, K.; Miura, J.; Menegatti, E. Hdl_Graph_Slam[EB/OL]. 2018. Available online: https://github.com/koide3/hdl_graph_slam (accessed on 5 December 2020).
- Zhang, J.; Singh, S. Low-drift and Real-time LiDAR Odometry and Mapping. Auton. Robot. 2017, 41, 401–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wang, C.; Chen, C.; Xie, L. F-LOAM: Fast LiDAR Odometry and Mapping. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Prague, Czech Republic, 27 September–1 October 2021; pp. 4390–4396. [Google Scholar]
- Shan, T.; Englot, B. Lego-loam: Lightweight and ground-optimized LiDAR odometry and mapping on variable terrain. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Madrid, Spain, 1–5 October 2018; pp. 4758–4765. [Google Scholar]
- Kaess, M.; Johannsson, H.; Roberts, R.; Ila, V.; Leonard, J.J.; Dellaert, F. iSAM2: Incremental smoothing and mapping using the Bayes tree. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2021, 31, 216–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, T.; Englot, B.; Meyers, D.; Wang, W.; Ratti, C.; Rus, D. LIO-SAM: Tightly-coupled Lidar Inertial Odometry via Smoothing and Mapping. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 24 October 2020–24 January 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Zhang, F. FAST-LIO: A Fast, Robust LiDAR-inertial Odometry Package by Tightly-Coupled Iterated Kalman Filter. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2021, 6, 3317–3324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Cai, Y.; He, D.; Lin, J.; Zhang, F. FAST-LIO2: Fast Direct LiDAR-Inertial Odometry. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2022, 38, 2053–2073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, C.; Ye, H.; Pranata, C.E.; Han, J.; Zhang, S.; Liu, M. LINS: A LiDAR-Inertial State Estimator for Robust and Efficient Navigation. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Paris, France, 31 May–31 August 2020; pp. 8899–8906. [Google Scholar]
- Shan, T.; Englot, B.; Ratti, C.; Rus, D. LVI-SAM: Tightly-coupled LiDAR-Visual-Inertial Odometry via Smoothing and Mapping. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Xi’an, China, 30 May–5 June 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, C.; Zhu, Q.; Xu, W.; Liu, X.; Guo, Q.; Zhang, F. FAST-LIVO: Fast and Tightly-coupled Sparse-Direct LiDAR-Inertial-Visual Odometry. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Kyoto, Japan, 23–27 October 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Titterton, D.; Weston, J. Strapdown Inertial Navigation Technology, 2nd ed.; IET: London, UK, 2005; Volume 20, pp. 33–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, X.J.; Zhang, Q.; Gong, L.L.; Liu, C.; Zhang, H.; Shi, C.; Wang, J.; Coleman, M. Development and evaluation of GNSS/INS data processing software for position and orientation systems. Surv. Rev. 2014, 47, 87–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forster, C.; Carlone, L.; Dellaert, F.; Scaramuzza, D. On-Manifold Preintegration for Real-Time Visual-Inertial Odometry. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2016, 33, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triggs, B.; McLauchlan, P.F.; Hartley, R.I.; Fitzgibbon, A.W. Bundle adjustment—A modern synthesis. In Proceedings of the International Workshop on Vision Algorithms, Corfu, Greece, 21–22 September 1999; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1999; pp. 298–372. [Google Scholar]
- Indelman, V.; Williams, S.; Kaess, M.; Dellaert, F. Information Fusion in Navigation Systems via Factor Graph Based Incremental Smoothing. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2013, 61, 721–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, S.; Mierle, K. Ceres-Solver[EB/OL]. 2015. Available online: http://www.ceres-solver.org (accessed on 10 May 2022).
- Kaess, M.; Ranganathan, A.; Dellaert, F. iSAM: Incremental Smoothing and Mapping. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2008, 24, 1365–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sturm, J.; Engelhard, N.; Endres, F.; Burgard, W.; Cremers, D. A benchmark for the evaluation of RGB-D SLAM systems. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Vilamoura-Algarve, Portugal, 7–12 October 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


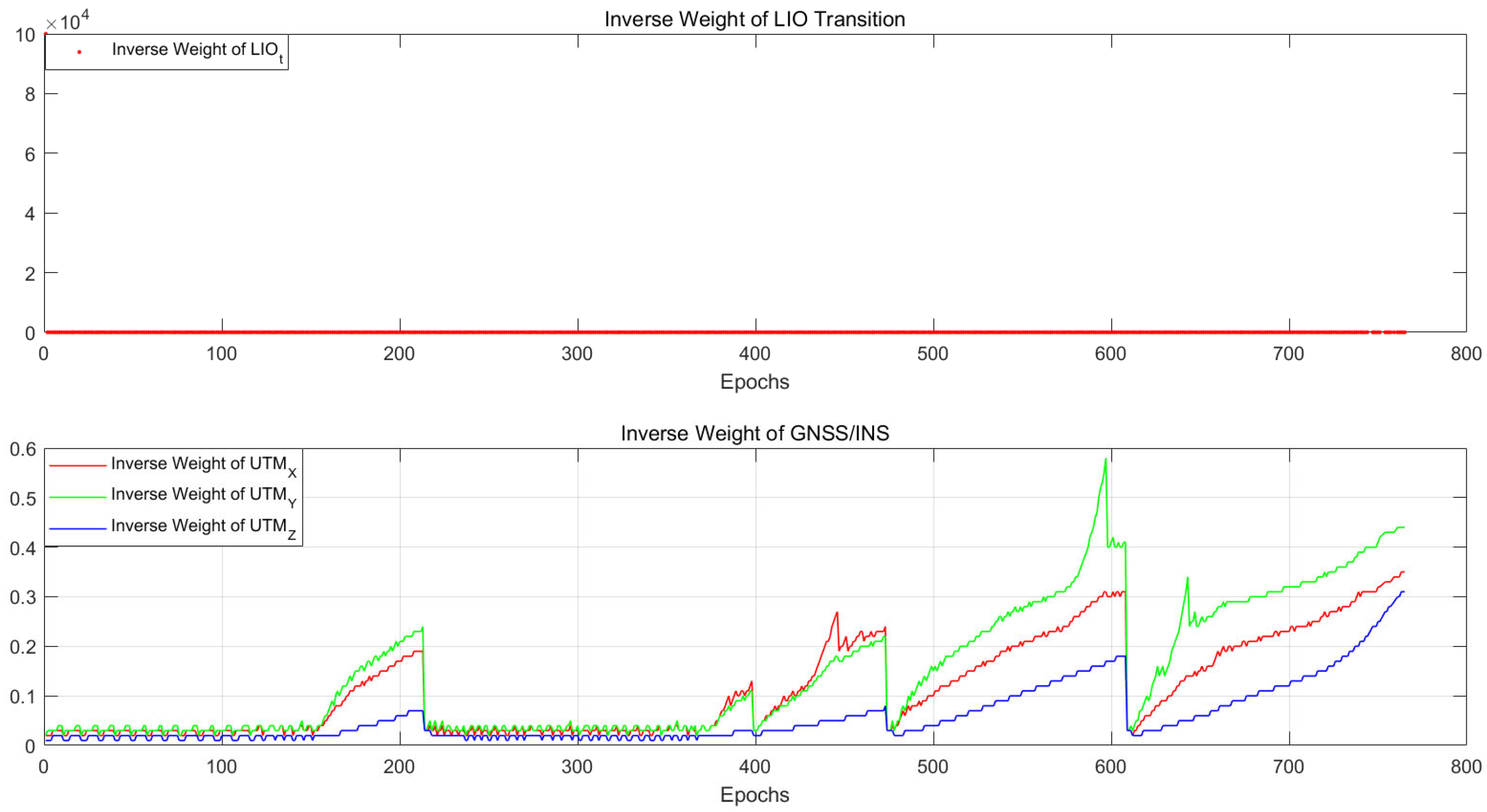

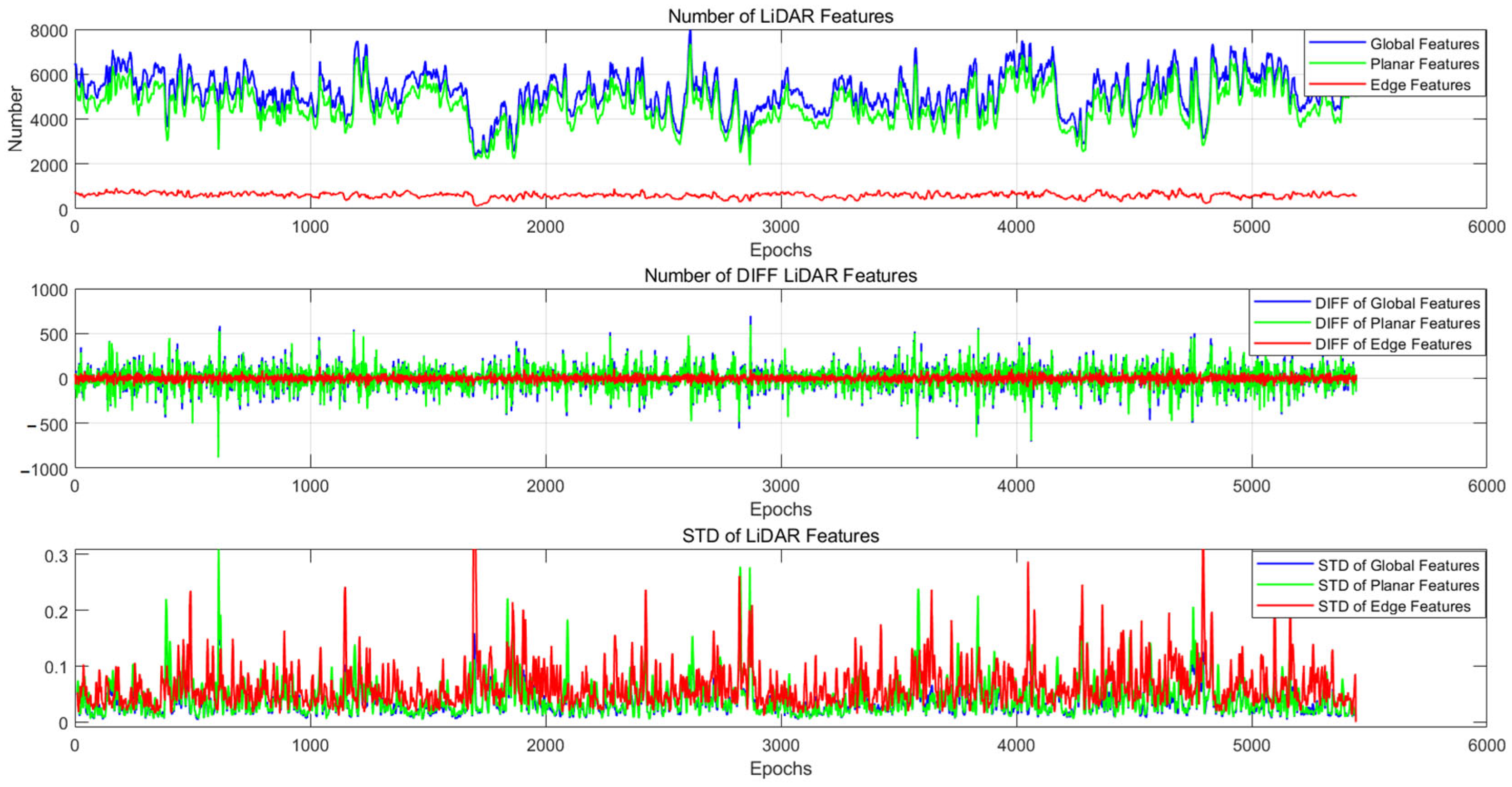
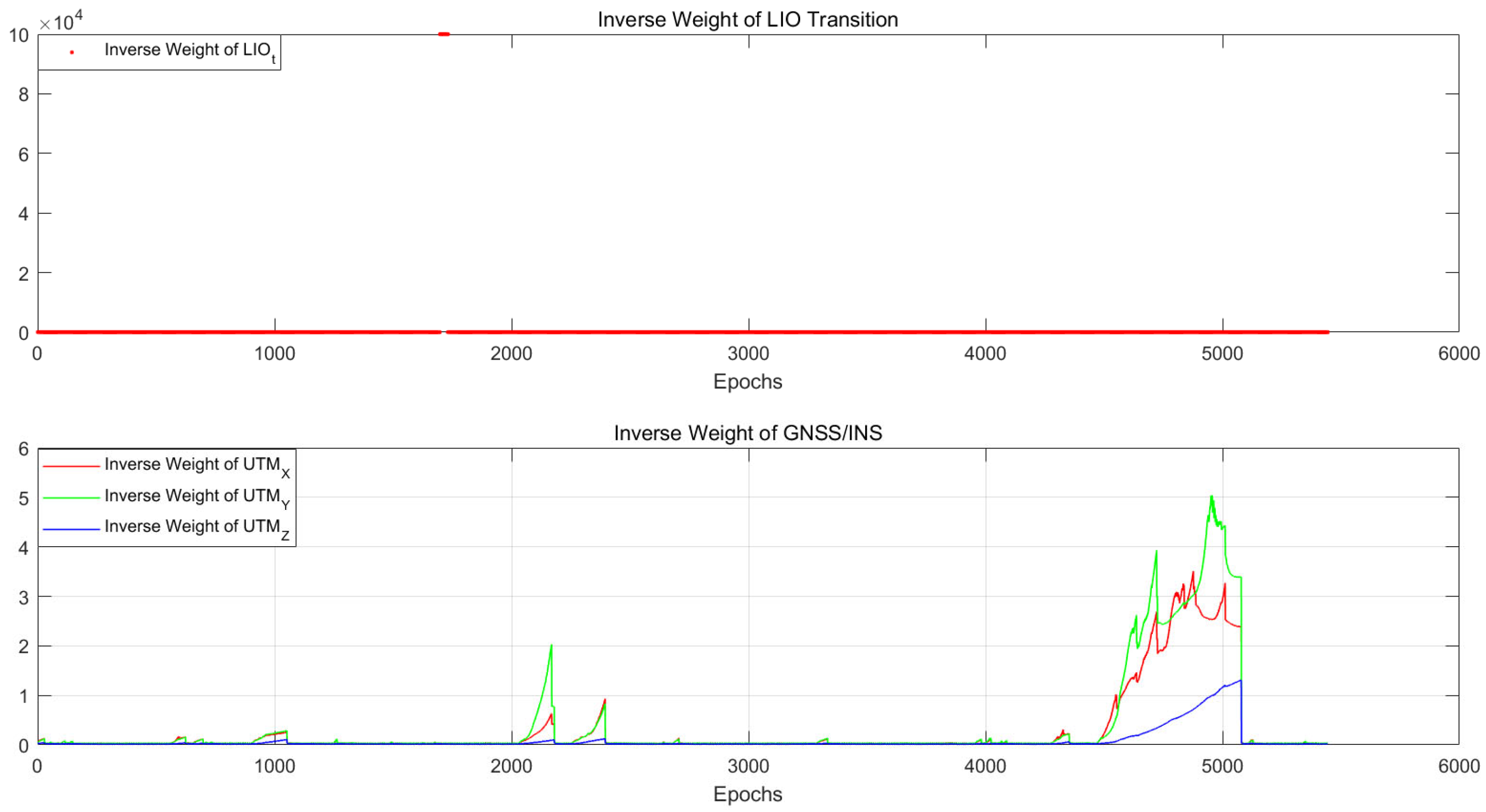
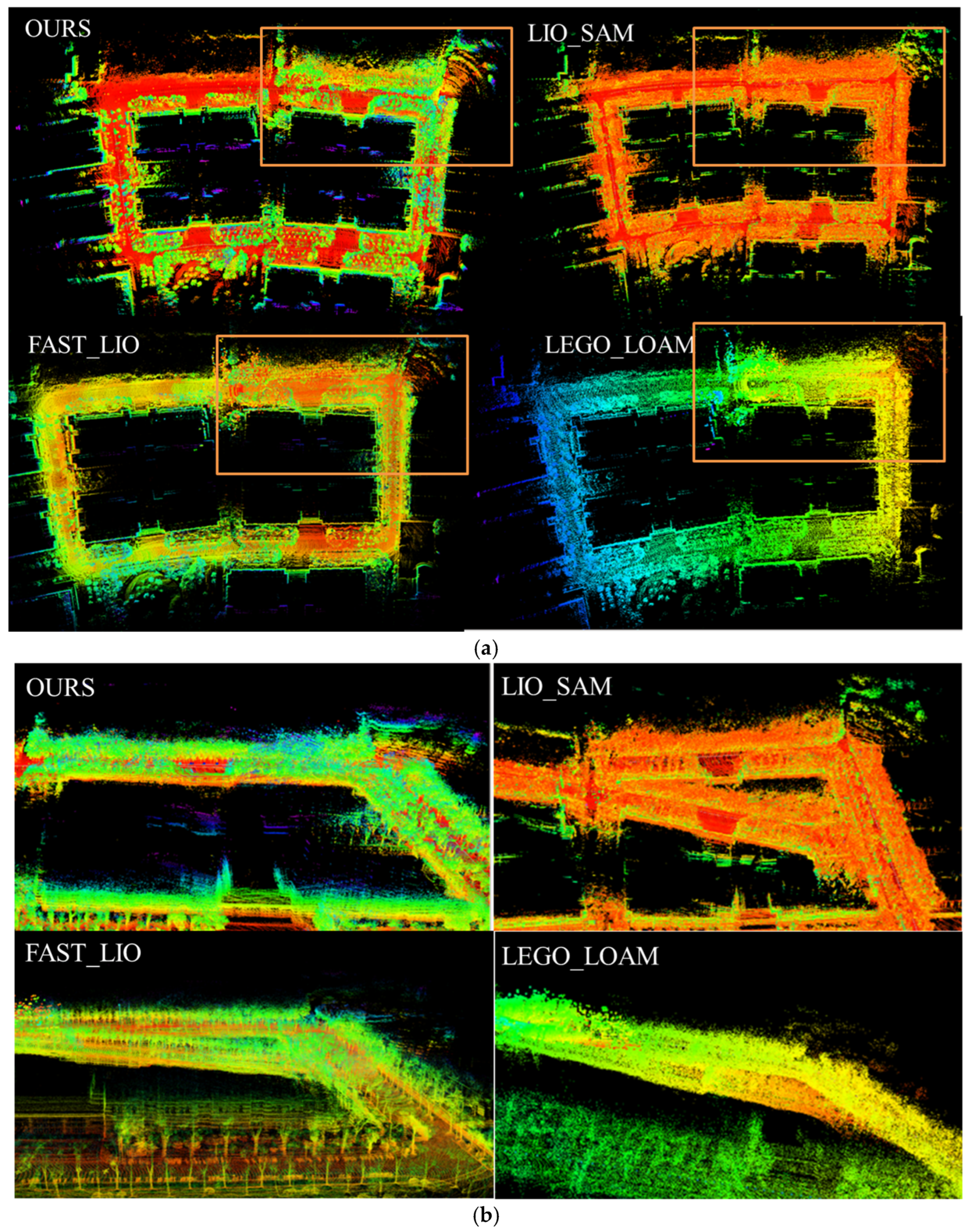
| Dataset | OURS (With QC Module) | LIO_SAM (Without QC Module) | LIO_SAM (gps) (Without QC Module) | FAST-LIO | LEGO_LOAM | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RMSE | Max | Min | RMSE | Max | Min | RMSE | Max | Min | RMSE | Max | Min | RMSE | Max | Min | ||
| Tunnel (628s) | Continuous and smooth | False (16s) | False (7s) | False | False | |||||||||||
| Urban (2014s) | 0.18 | 0.48 | 0.01 | False (1133s) | False (165s) | False | >1000 | |||||||||
| Urban (180s) | 0.14 | 0.24 | 0.11 | 19.73 | 28.98 | 10.03 | False (74s) | 27.22 | 63.86 | 3.04 | 143.96 | 196.92 | 35.99 | |||
| Campus (180s) | 0.23 | 0.29 | 0.15 | 1.82 | 2.58 | 1.22 | 0.49 | 0.77 | 0.24 | 4.17 | 8.13 | 1.70 | 1.31 | 1.86 | 0.92 | |
| Mountain (760s) | 0.21 | 1.76 | 0.01 | >1000 | False | >1000 | >1000 | |||||||||
| Dataset | Urban | Tunnel | Campus | Mountain | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Global | Planar | Edge | Global | Planar | Edge | Global | Planar | Edge | Global | Planar | Edge | |
| 80.66 | 79.38 | 20.51 | 23.73 | 21.73 | 9.649 | 99.1 | 94.62 | 25 | 119.3 | 114 | 30 | |
| 2.10% | 2.23% | 3.92% | 0.79% | 0.78% | 4.68% | 2.14% | 2.28% | 4.16% | 3.95% | 4.20% | 6.43% | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Z.; Sheng, C.; Pan, S.; Wang, X.; Yu, B.; Zhang, J. A Robust and Reliable Positioning Method for Complex Environments Based on Quality-Controlled Multi-Sensor Fusion of GNSS, INS, and LiDAR. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 3760. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17223760
Zhang Z, Sheng C, Pan S, Wang X, Yu B, Zhang J. A Robust and Reliable Positioning Method for Complex Environments Based on Quality-Controlled Multi-Sensor Fusion of GNSS, INS, and LiDAR. Remote Sensing. 2025; 17(22):3760. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17223760
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Ziteng, Chuanzhen Sheng, Shuguo Pan, Xingxing Wang, Baoguo Yu, and Jingkui Zhang. 2025. "A Robust and Reliable Positioning Method for Complex Environments Based on Quality-Controlled Multi-Sensor Fusion of GNSS, INS, and LiDAR" Remote Sensing 17, no. 22: 3760. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17223760
APA StyleZhang, Z., Sheng, C., Pan, S., Wang, X., Yu, B., & Zhang, J. (2025). A Robust and Reliable Positioning Method for Complex Environments Based on Quality-Controlled Multi-Sensor Fusion of GNSS, INS, and LiDAR. Remote Sensing, 17(22), 3760. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17223760





