Estimating and Mapping Aboveground Biomass of Vegetation in Typical Lake Flooding Wetland Based on MODIS and Landsat Images Fusion
Highlights
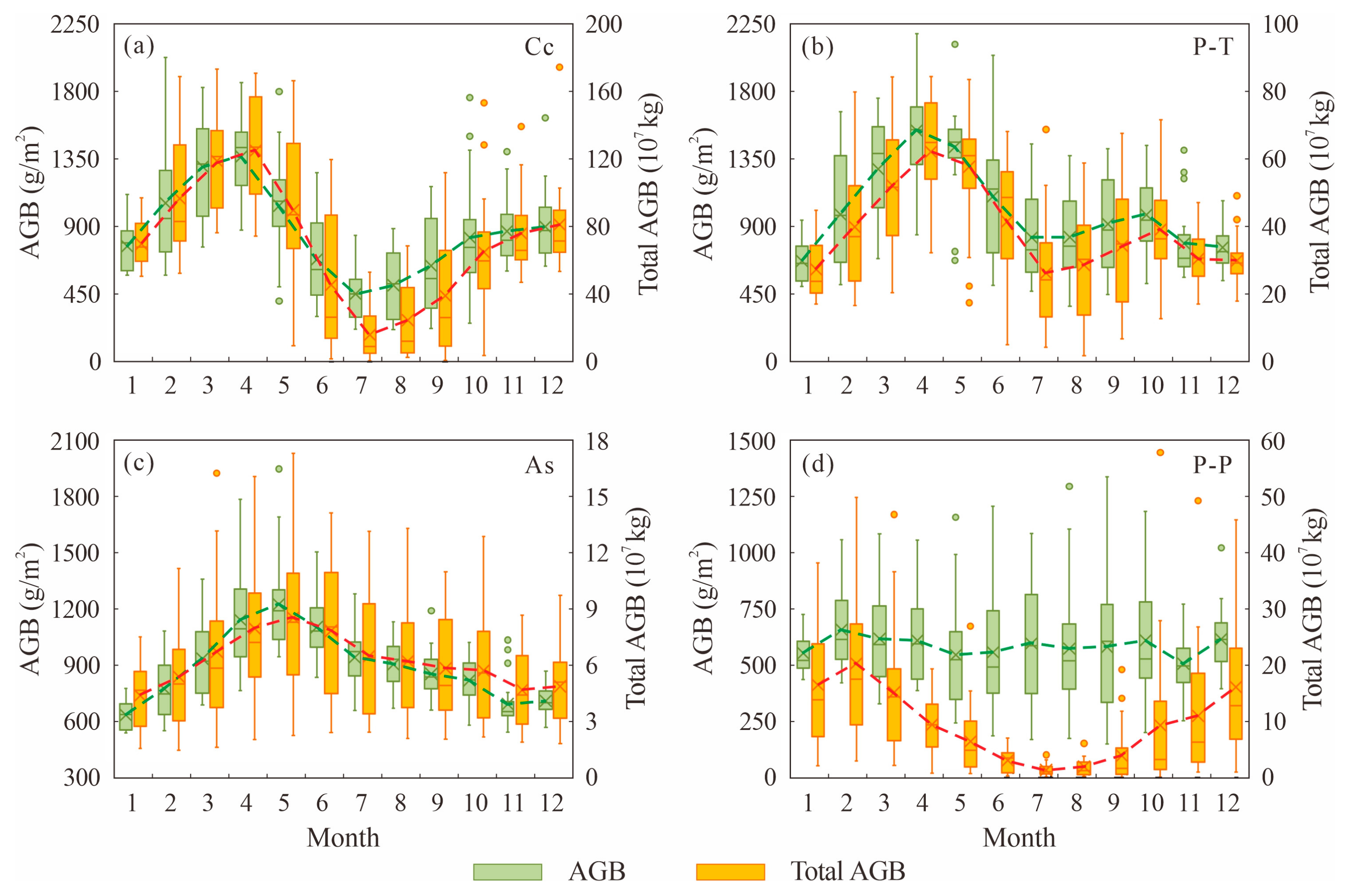
- The biomass of Carex cinerascens and Phragmites australis-Triarrhena lutarioriparia communities in Poyang Lake wetland during the spring growth period is greater than that during the autumn growth period.
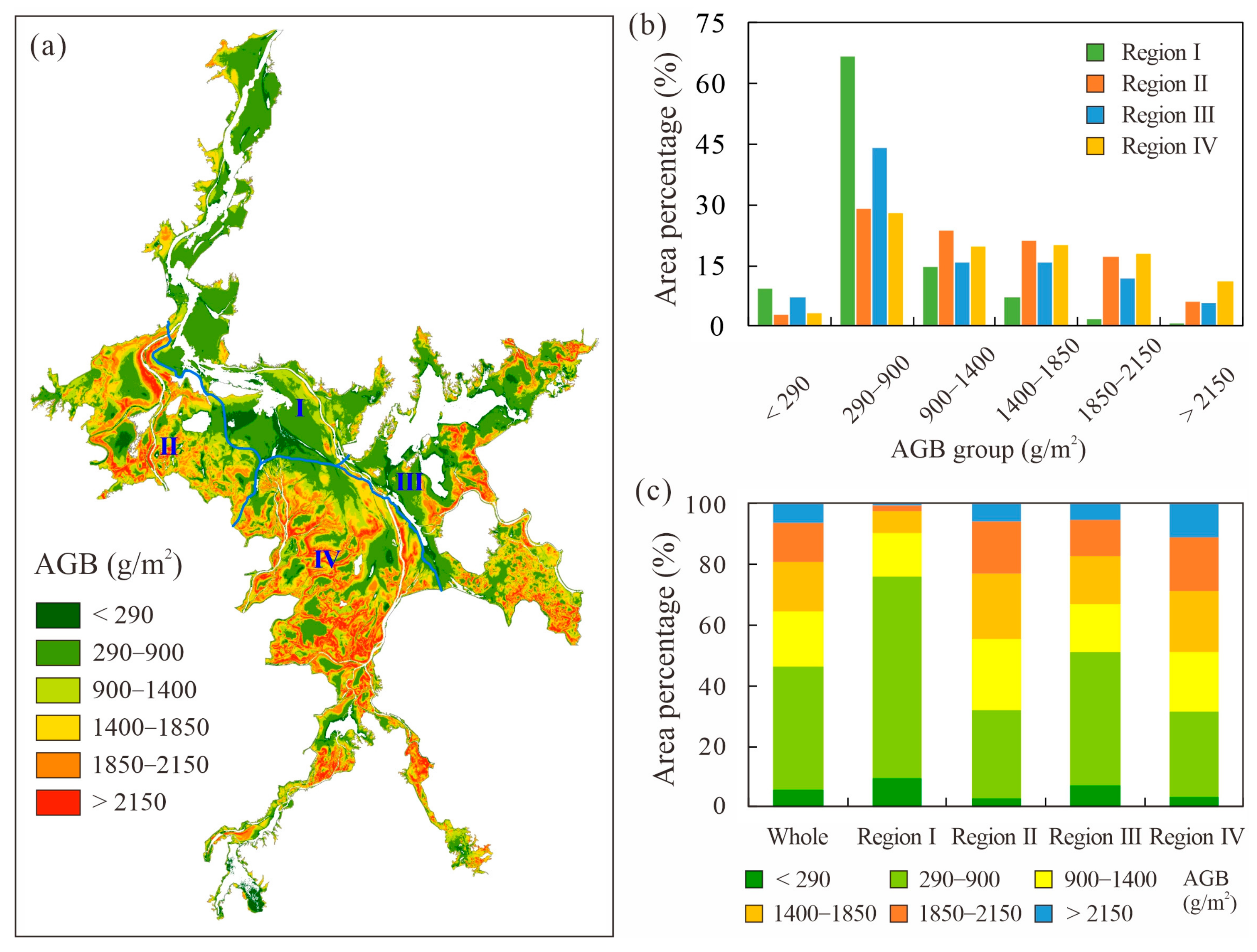
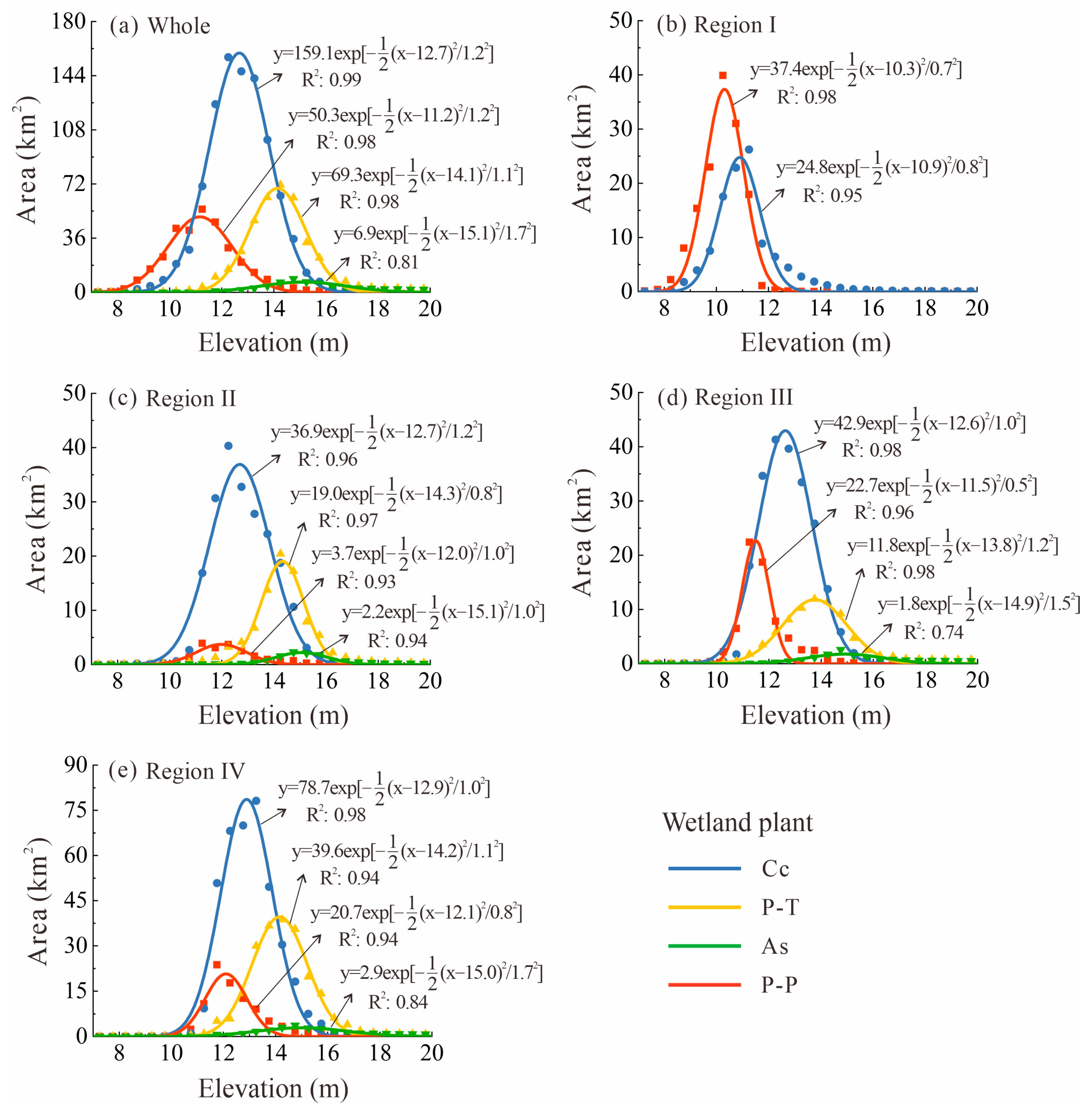
- The biomass is highest in the Southern part of the wetland and lowest in the Northern part, with over 78% of the total biomass distributed in areas with elevations of 11.0–15.0 m.
- The spatial distribution and seasonal physiological characteristics of different wetland plants should be considered when estimating the aboveground biomass in the Poyang Lake wetland.
- The hydrological condition of oyang Lake plays a dominant role in the spatial pattern and seasonal distribution of biomass of wetland plant communities.
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
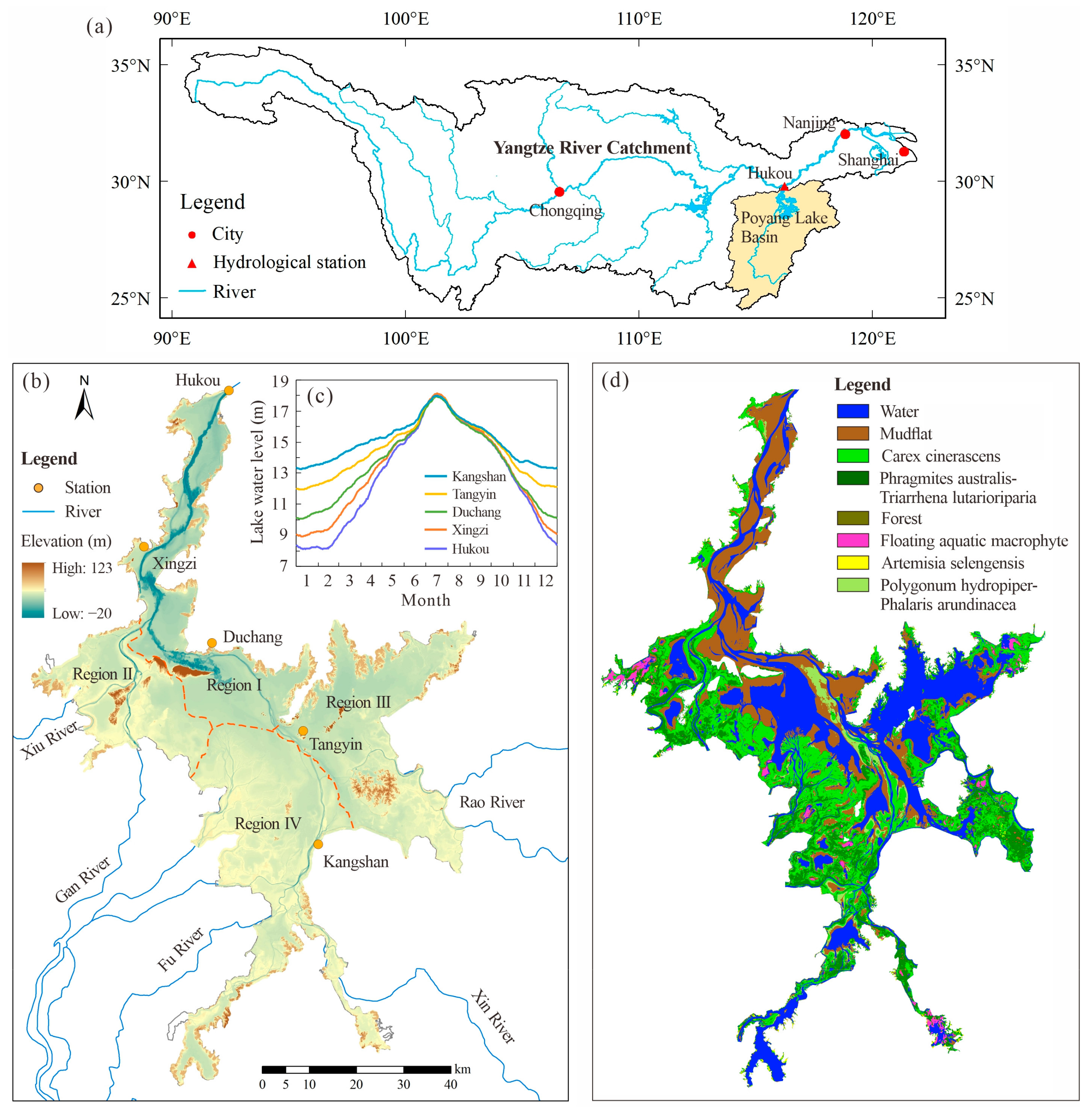
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data
2.3. Methods
2.3.1. STAFFN Model
2.3.2. Method for Estimating AGB of Wetland Vegetation
2.3.3. Gaussian Regression Model
3. Results
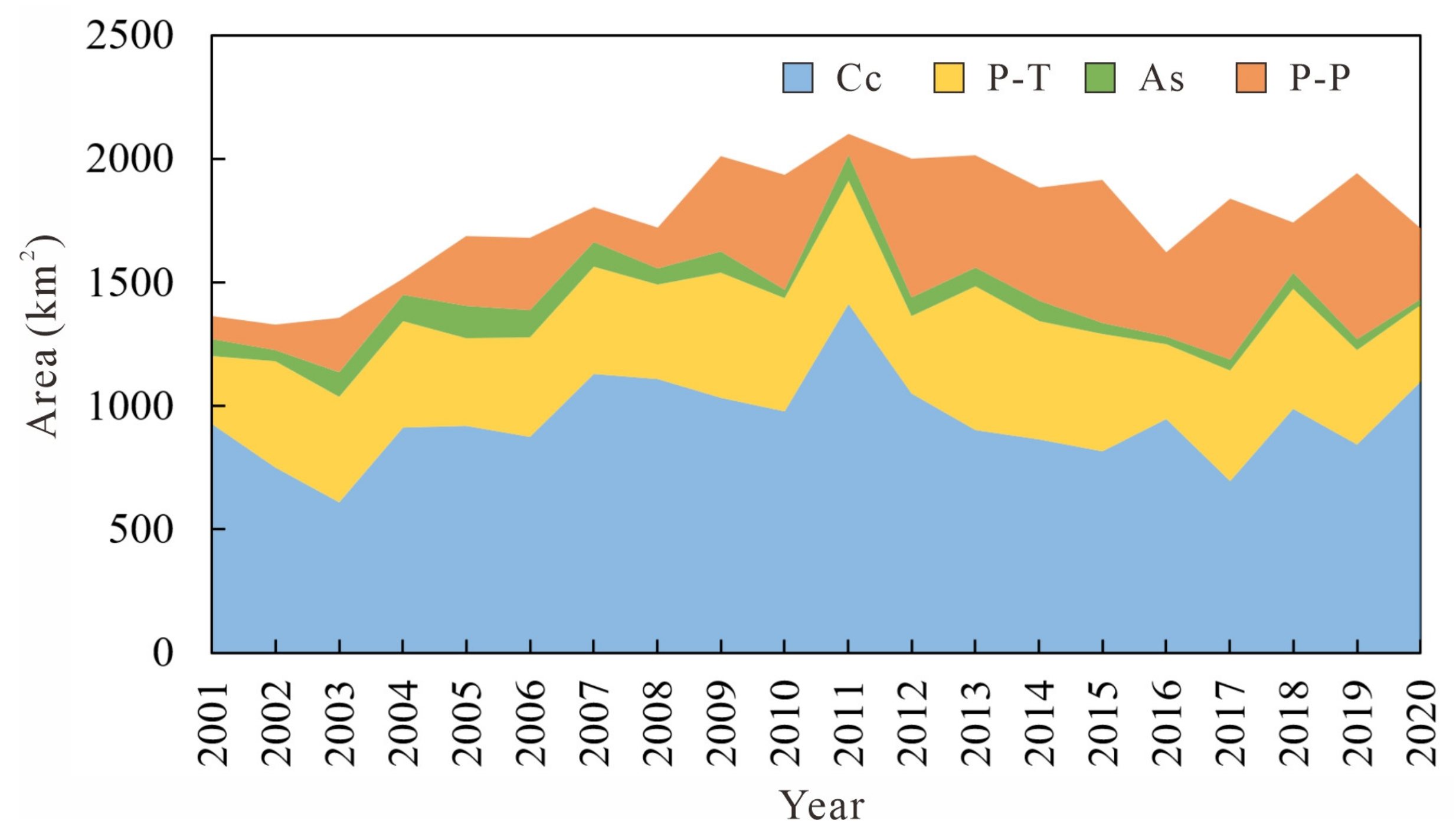
3.1. Monthly and Annual Changes in AGB of Wetland Vegetation
3.2. Spatial Distribution of Wetland Vegetation AGB
3.3. Changes in AGB of Wetland Vegetation Along Elevation Gradients
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bridgham, S.D.; Megonigal, J.P.; Keller, J.K.; Bliss, N.B.; Trettin, C. The carbon balance of North American wetlands. Wetlands 2006, 26, 889–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desta, H.; Lemma, B.; Fetene, A. Aspects of climate change and its associated impacts on wetland ecosystem functions—A review. J. Am. Sci. 2012, 8, 582–596. [Google Scholar]
- Costanza, R.; d’Arge, R.; de Groot, R.; Farber, S.; Grasso, M.; Hannon, B.; Limburg, K.; Naeem, S.; ONeill, R.V.; Paruelo, J.; et al. The value of the world’s ecosystem services and natural capital. Nature 1997, 387, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Cao, C.X.; Liu, D.; Tian, R.; Wu, C.Y.; Wang, Y.Q.; Qian, Y.F.; Ma, G.Q.; Bao, D.M. An evaluating system for wetland ecological health: Case study on nineteen major wetlands in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 666, 1080–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehner, B.; Döll, P. Development and validation of a global database of lakes, reservoirs and wetlands. J. Hydrol. 2004, 296, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutanga, O.; Adam, E.; Cho, M.A. High density biomass estimation for wetland vegetation using WorldView-2 imagery and random forest regression algorithm. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2012, 18, 399–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, W.L.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Z.H. Radial oxygen loss, photosynthesis, and nutrient removal of 35 wetland plants. Ecol. Eng. 2012, 39, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.Y.; Yan, W.; Sun, X.Y.; Shao, J.J.; Zhang, P.P.; Zhou, G.Y.; He, Y.H.; Liu, H.Y.; Fu, Y.L.; Zhou, X.H. Regulation of climate, soil and hydrological factors on macrophyte biomass allocation for coastal and inland wetlands in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 774, 145317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, Z.C.; Chen, Y.S.; Shen, R.C.; Cai, Y.J.; Luo, H.; Jin, B.S.; Chen, J.K. Effects of flooding duration on wetland plant biomass: The importance of soil nutrients and season. Freshw. Biol. 2021, 66, 211–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barya, M.P.; Kumar, A.; Thakur, T.K. Utilization of constructed wetland for the removal of heavy metal through fly ash bricks manufactured using harvested plant biomass. Ecohydrology 2022, 15, E2424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.Y.; Zhang, Z.M.; Zhang, M.X.; Huang, P.S.; Dai, L.Y.; Ma, Z.W.; Liu, J.K. Climate vs. nutrient control: A global analysis of driving environmental factors of wetland plant biomass allocation strategy. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 406, 136983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, W.C.; Li, R.; Tang, T.H.; Zuh, A.A. Removal, distribution and plant uptake of perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS) in a simulated constructed wetland system. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2021, 15, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.P.; Ye, C.; Liu, Y.B. Spatial distribution of wetland vegetation biomass in the Poyang Lake National Nature Reserve, China. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2015, 35, 361–369. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klemas, V. Remote Sensing of Coastal Wetland Biomass: An Overview. J. Coast. Res. 2013, 29, 1016–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adam, E.; Mutanga, O.; Rugege, D. Multispectral and hyperspectral remote sensing for identification and mapping of wetland vegetation: A review. Wetl. Ecol. Manag. 2010, 18, 281–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrachina, M.; Cristóbal, J.; Tulla, A.F. Estimating above-ground biomass on mountain meadows and pastures through remote sensing. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2015, 38, 184–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asner, G.P.; Powell, G.V.N.; Mascaro, J.; Knapp, D.E.; Clark, J.K.; Jacobson, J.; Kennedy-Bowdoin, T.; Balaji, A.; Paez-Acosta, G.; Victoria, E.; et al. High-resolution forest carbon stocks and emissions in the Amazon. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 16738–16742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, S.Z.; Wang, C.; Xi, X.H.; Pan, F.F.; Peng, D.L.; Zou, J.; Nie, S.; Qin, H.M. Fusion of airborne LiDAR data and hyperspectral imagery for aboveground and belowground forest biomass estimation. Ecol. Indic. 2017, 73, 378–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naicker, R.; Mutanga, O.; Peerbhay, K.; Odebiri, O. Estimating high-density aboveground biomass within a complex tropical grassland using Worldview-3 imagery. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2024, 196, 370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrd, K.B.; Ballanti, L.; Thomas, N.; Nguyen, D.; Holmquist, J.R.; Simard, M.; Windham-Myers, L. A remote sensing-based model of tidal marsh aboveground carbon stocks for the conterminous United States. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2018, 139, 255–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buffington, K.J.; Dugger, B.D.; Thorne, K.M. Climate-related variation in plant peak biomass and growth phenology across Pacific Northwest tidal marshes. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2018, 202, 212–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amarsaikhan, E.; Erdenebaatar, N.; Amarsaikhan, D.; Otgonbayar, M.; Bayaraa, B. Estimation and mapping of pasture biomass in Mongolia using machine learning methods. Geocarto Int. 2023, 38, 2195824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Tuya, H.; Zhang, S.W.; Zhao, X.Y.; Liu, Z.Q.; Li, R.S.; Lin, X. Random forest method for analysis of remote sensing inversion of aboveground biomass and grazing intensity of grasslands in Inner Mongolia, China. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2023, 44, 2867–2884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.K.; Biradar, C.M.; Behera, M.D.; Prakash, A.J.; Das, P.; Mohanta, M.R.; Krishna, G.; Dogra, A.; Dhyani, S.K.; Rizvi, J. Optimising carbon fixation through agroforestry: Estimation of aboveground biomass using multi-sensor data synergy and machine learning. Ecol. Inform. 2024, 79, 102408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belloli, T.F.; Guasselli, L.A.; Kuplich, T.M.; Ruiz, L.F.C.; de Arruda, D.C.; Etchelar, C.B.; Simioni, J.D. Estimation of aboveground biomass and carbon in palustrine wetland using bands and multispectral indices derived from optical satellite imageries PlanetScope and Sentinel-2A. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2022, 16, 034516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gou, F.Z.; Zhao, C.Z.; Yang, J.C.; Ren, J.; Ma, J.Y.; Li, Z.Q. Spatial Heterogeneity of Above-ground Biomass in Sugan Lake Wetland Vegetation. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2021, 41, 7774–7784. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramoelo, A.; Cho, M.A.; Mathieu, R.; Madonsela, S.; van de Kerchove, R.; Kaszta, Z.; Wolff, E. Monitoring grass nutrients and biomass as indicators of rangeland quality and quantity using random forest modelling and World View-2 data. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2015, 43, 43–54. [Google Scholar]
- Nakano, T.; Bavuudorj, G.; Urianhai, N.G.; Shinoda, M. Monitoring aboveground biomass in semiarid grasslands using MODIS images. J. Agric. Meteorol. 2013, 69, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunliffe, A.M.; Assmann, J.J.; Daskalova, G.N.; Kerby, J.T.; Myers-Smith, I.H. Aboveground biomass corresponds strongly with drone-derived canopy height but weakly with greenness (NDVI) in a shrub tundra landscape. Environ. Res. Lett. 2020, 15, 125004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alegria, C. Aboveground Biomass Mapping and Fire Potential Severity Assessment: A Case Study for Eucalypts and Shrubland Areas in the Central Inland Region of Portugal. Forests 2023, 14, 1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dashpurev, B.; Dorj, M.; Phan, T.N.; Bendix, J.; Lehnert, L.W. Estimating fractional vegetation cover and aboveground biomass for land degradation assessment in eastern Mongolia steppe: Combining ground vegetation data and remote sensing. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2023, 44, 452–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Ma, X.H.; Chen, A.; Guo, J.; Xing, X.Y.; Yang, D.; Xu, B.; Lan, X.Y.; Yang, X.C. A spatio-temporal fusion strategy for improving the estimation accuracy of the aboveground biomass in grassland based on GF-1 and MODIS. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 157, 111276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.J.; Liu, T.X.; Batelaan, O.; Duan, L.M.; Wang, Y.X.; Li, X.; Li, M.Y. Spatiotemporal fusion of multi-source remote sensing data for estimating aboveground biomass of grassland. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 146, 109892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Pei, L.; Du, J. Remote Sensing Inversion of Aboveground Biomass over the Honghe Wetland. Remote Sens. Technol. Appl. 2014, 29, 224–231. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, T.G.; Yu, R.H.; Zhang, Z.L. Estimation of wetland vegetation aboveground biomass based on remote sensing data: A review. Chin. J. Ecol. 2016, 35, 1936–1946. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- O’Donnell, J.P.R.; Schalles, J.F. Examination of Abiotic Drivers and Their Influence on Biomass over a Twenty-Eight Year Period Using Landsat 5 TM Satellite Imagery of the Central Georgia Coast. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Ye, X.C.; Werner, A.D.; Li, Y.L.; Yao, J.; Li, X.H.; Xu, C.Y. An investigation of enhanced recessions in Poyang Lake: Comparison of Yangtze River and local catchment impacts. J. Hydrol. 2014, 517, 425–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Hu, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, R. Response of rainfall erosivity to changes in extreme precipitation in the Poyang Lake basin, China. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2020, 75, 537–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.H.; Zhang, Q.; Hu, Q.; Zhang, D.; Ye, X.C. Lake flooding sensitivity to the relative timing of peak flows between upstream and downstream waterways: A case study of Poyang Lake, China. Hydrol. Process. 2017, 31, 4217–4228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Li, L.; Wang, Y.G.; Werner, A.D.; Xin, P.; Jiang, T.; Barry, D.A. Has the Three-Gorges Dam made the Poyang Lake wetlands wetter and drier? Geophys. Res. Lett. 2012, 39, L20402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.H.; Ye, X.C.; Yao, J.; Lin, Y.L.; Xu, C.Y.; Yuan, C.Y. Influences of increasing water release of the Three Gorges Reservoir during dry season on water regimes of downstream lake. Hydrol. Process. 2023, 37, e14895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.H.; Ye, X.C.; Yuan, C.Y.; Xu, C.Y. Can water release from local reservoirs cope with the droughts of downstream lake in a large river-lake system? J. Hydrol. 2023, 625, 130172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.P.; Lin, Y.R. Analysis of evolution process and driving factors for aquatic vegetations of Poyang Lake in 30 years. Resour. Environ. Yangtze Basin 2019, 28, 1947–1955. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, R.; Li, X.H.; Zhang, Q.; Cheng, J.X.; Li, J.F.; Zhang, D.; Liu, Y.B. Projection of drought-flood abrupt alternation in a humid subtropical region under changing climate. J. Hydrol. 2023, 624, 129875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.L.; Li, X.H.; Tan, Z.Q.; Song, Y.Y.; Xu, C.Y. Dynamic characteristics of vegetation communities in the floodplain wetland of Poyang Lake based on spatiotemporal fusion of remote sensing data. J. Lake Sci. 2023, 35, 1408–1422. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Xu, L.G.; Xu, W.M.; Wang, X.L. Research on the Ecological Environment of Poyang Lake; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2023. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Y.X.; Huang, J.L.; Du, Y.; Han, P.P.; Wang, J.L.; Huang, W. Monitoring wetland vegetation pattern response to water-level change resulting from the Three Gorges Project in the two largest freshwater lakes of China. Ecol. Eng. 2015, 74, 274–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.X.; Feng, L.; Hu, C.M.; Chen, X.L. Wetland changes of China’s largest freshwater lake and their linkage with the Three Gorges Dam. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 204, 799–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, R.R.; Wang, P.; Wang, X.L.; Yao, X.; Dai, X. Mapping Aboveground Biomass of Four Typical Vegetation Types in the Poyang Lake Wetlands Based on Random Forest Modelling and Landsat Images. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, X.; Wan, R.R.; Yang, G.S.; Wang, X.L.; Xu, L.G.; Li, Y.Y.; Li, B. Impact of seasonal water-level fluctuations on autumn vegetation in Poyang Lake wetland, China. Front. Earth Sci. 2019, 13, 398–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yu, X.B.; Guo, Q.; Liu, Y.; Xia, S.X.; Zhang, G.S.; Zhang, Q.J.; Duan, H.L.; Zhao, L. Estimating the biomass of Carex cinerascens (Cyperaceae) in floodplain wetlands in Poyang Lake, China. J. Freshw. Ecol. 2019, 34, 379–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.P.; Ge, G.; Liu, C.L.; Chen, F.S.; Li, S. Structure of Poyang Lake wetland plants ecosystem and influence of lake water level for the structure. Resour. Environ. Yangtze Basin 2010, 19, 597–605. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Q.; Feng, S.; Guo, H.; Chen, G.; Jiang, T. Interactions of the Yangtze river flow and hydrologic processes of the Poyang Lake, China. J. Hydrol. 2007, 347, 90–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.B.; Wan, J.B.; Jiang, J.H. The Impact of Water Level Changes in Poyang Lake on Its Ecosystem; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2011. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chen, B.; Chen, L.F.; Huang, B.; Michishita, R.; Xu, B. Dynamic monitoring of the Poyang Lake wetland by integrating Landsat and MODIS observations. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2018, 139, 75–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todd, M.J.; Muneepeerakul, R.; Pumo, D.; Azaele, S.; Miralles-Wilhelm, F.; Rinaldo, A.; Rodriguez-Iturbe, I. Hydrological drivers of wetland vegetation community distribution within Everglades National Park, Florida. Adv. Water Resour. 2010, 33, 1279–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.X. The effects of changes in hydrological regimes and salinity on wetland vegetation: A review. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2012, 32, 4254–4260. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hebb, A.J.; Mortsch, L.D.; Deadman, P.J.; Cabrera, A.R. Modeling wetland vegetation community response to water-level change at Long Point, Ontario. J. Great Lakes Res. 2013, 39, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Li, E.H.; Cai, X.B.; Wang, Z.; Wang, X.L. Research Progress in Response of Plants in Wetlands to Water Level Change. Wetl. Sci. 2014, 12, 807–813. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Xie, D.M.; Zheng, P.; Deng, H.B.; Zhao, J.Z.; Fan, Z.W.; Fang, Y. Landscape responses to changes in water levels at Poyang Lake wetlands. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2011, 31, 1269–1276. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.H.; Ye, X.C.; Li, Z.; Zhang, D. Hydrological drought in two largest river-connecting lakes in the middle reaches of the Yangtze River, China. Hydrol. Res. 2023, 54, 82–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.H.; Lin, Y.L.; Ye, X.C.; Yuan, C.Y.; Tan, Z.Q.; Sun, T. The impacts of drought on the ecological niches of typical wetland plants in Poyang Lake, China. Hydrol. Res. 2024, 55, 890–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.X.; Chen, X.L.; Feng, L. Four decades of winter wetland changes in Poyang Lake based on Landsat observations between 1973 and 2013. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 156, 426–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, X.Y.; Xie, Y.H.; Chen, X.S. Competition and facilitation among wetland plants: A review. Chin. J. Ecol. 2010, 29, 117–123. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Meng, B.; Liu, J.L.; Bao, K.; Sun, B. Methodologies and Management Framework for Restoration of Wetland Hydrologic Connectivity: A Synthesis. Integr. Environ. Assess. Manag. 2020, 16, 438–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Cohen, M.J.; Kaplan, D.A.; Acharya, S.; Larsen, L.G.; Nungesser, M.K. Linking metrics of landscape pattern to hydrological process in a lotic wetland. Landsc. Ecol. 2015, 30, 1893–1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Liao, J.J. Estimation of wetland vegetation biomass in the Poyang Lake area using Landsat TM and Envisat ASAR data. In Proceedings of the Sixth International Symposium on Digital Earth: Data Processing and Applications, Beijing, China, 9–12 September 2009; Volume 7841, pp. 420–429. [Google Scholar]
- Li, R.; Liu, J. Wetland vegetation biomass estimation and mapping from Landsat ETM data: A case study of Poyang Lake. J. Geogr. Sci. 2002, 12, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Plant Community | Region I | Region II | Region III | Region IV | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean (g/m2) | SD (g/m2) | Mean (g/m2) | SD (g/m2) | Mean (g/m2) | SD (g/m2) | Mean (g/m2) | SD (g/m2) | |
| Cc | 1368 | 368 | 1634 | 319 | 1556 | 272 | 1700 | 244 |
| P-T | 1443 | 233 | 1771 | 314 | 1692 | 226 | 1838 | 231 |
| As | 1331 | 193 | 1433 | 217 | 1342 | 181 | 1462 | 271 |
| P-P | 795 | 189 | 1075 | 289 | 833 | 196 | 924 | 201 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, X.; Lin, Y.; Lv, Z.; Song, Y.; Huang, X. Estimating and Mapping Aboveground Biomass of Vegetation in Typical Lake Flooding Wetland Based on MODIS and Landsat Images Fusion. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 3754. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17223754
Li X, Lin Y, Lv Z, Song Y, Huang X. Estimating and Mapping Aboveground Biomass of Vegetation in Typical Lake Flooding Wetland Based on MODIS and Landsat Images Fusion. Remote Sensing. 2025; 17(22):3754. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17223754
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Xianghu, Yaling Lin, Zhenhe Lv, Yani Song, and Xing Huang. 2025. "Estimating and Mapping Aboveground Biomass of Vegetation in Typical Lake Flooding Wetland Based on MODIS and Landsat Images Fusion" Remote Sensing 17, no. 22: 3754. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17223754
APA StyleLi, X., Lin, Y., Lv, Z., Song, Y., & Huang, X. (2025). Estimating and Mapping Aboveground Biomass of Vegetation in Typical Lake Flooding Wetland Based on MODIS and Landsat Images Fusion. Remote Sensing, 17(22), 3754. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17223754







