Inferring River Channel Geometry Based on Multi-Satellite Datasets and Hydraulic Modeling
Highlights
- An innovative method integrating multi-source satellite images and hydraulic modeling is proposed to develop channel geometry.
- Both channel widths and bottom elevations are well predicted.
- The predicted channel geometry leads to good hydrodynamic simulations.
- Channel geometry for inland rivers can be derived from satellite data instead of ground surveys.
- The derived channel geometry can be used to drive hydrodynamic simulations, which provide critical bathymetry for data-scarce watersheds.
Abstract
1. Introduction
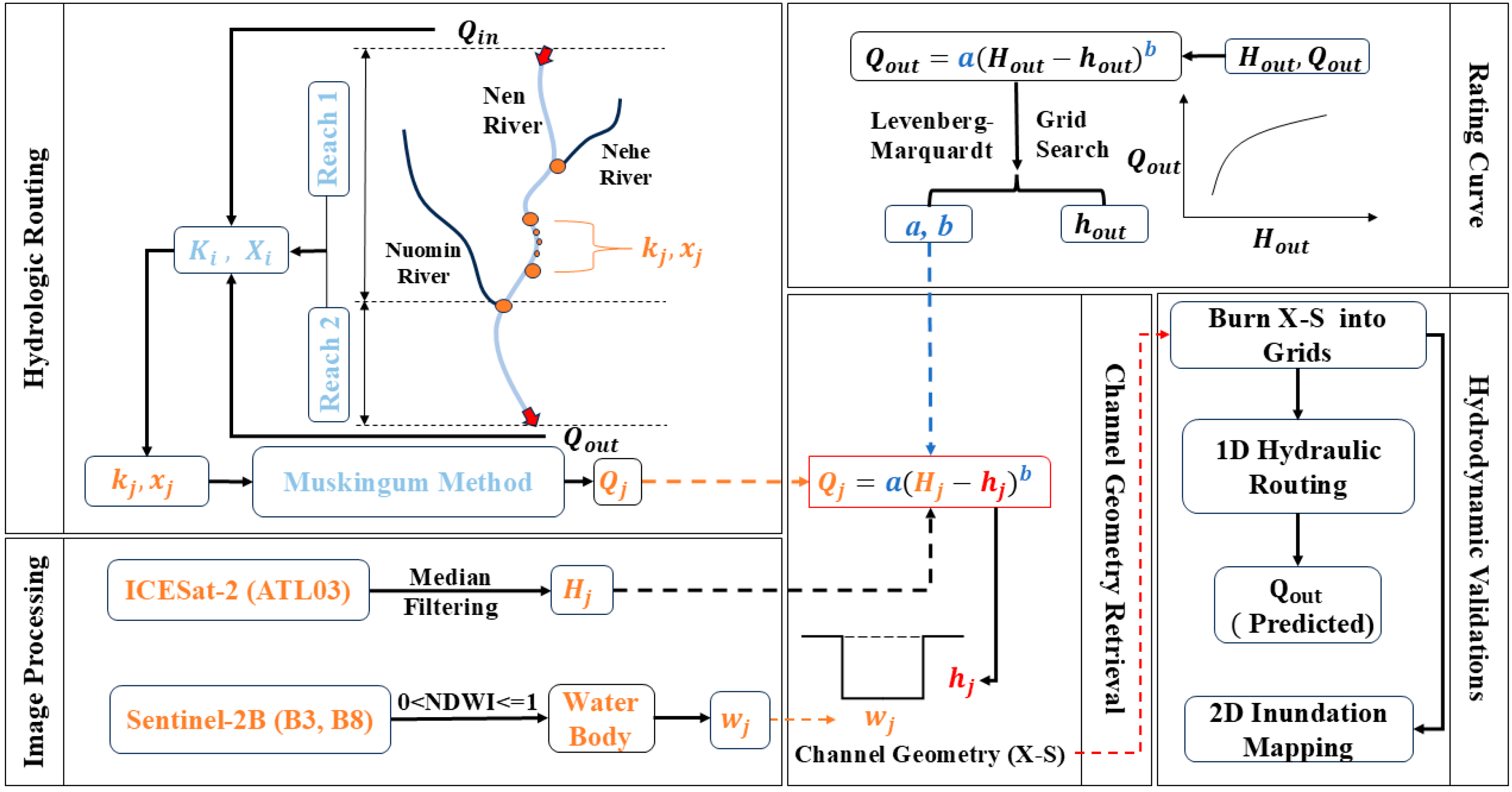
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
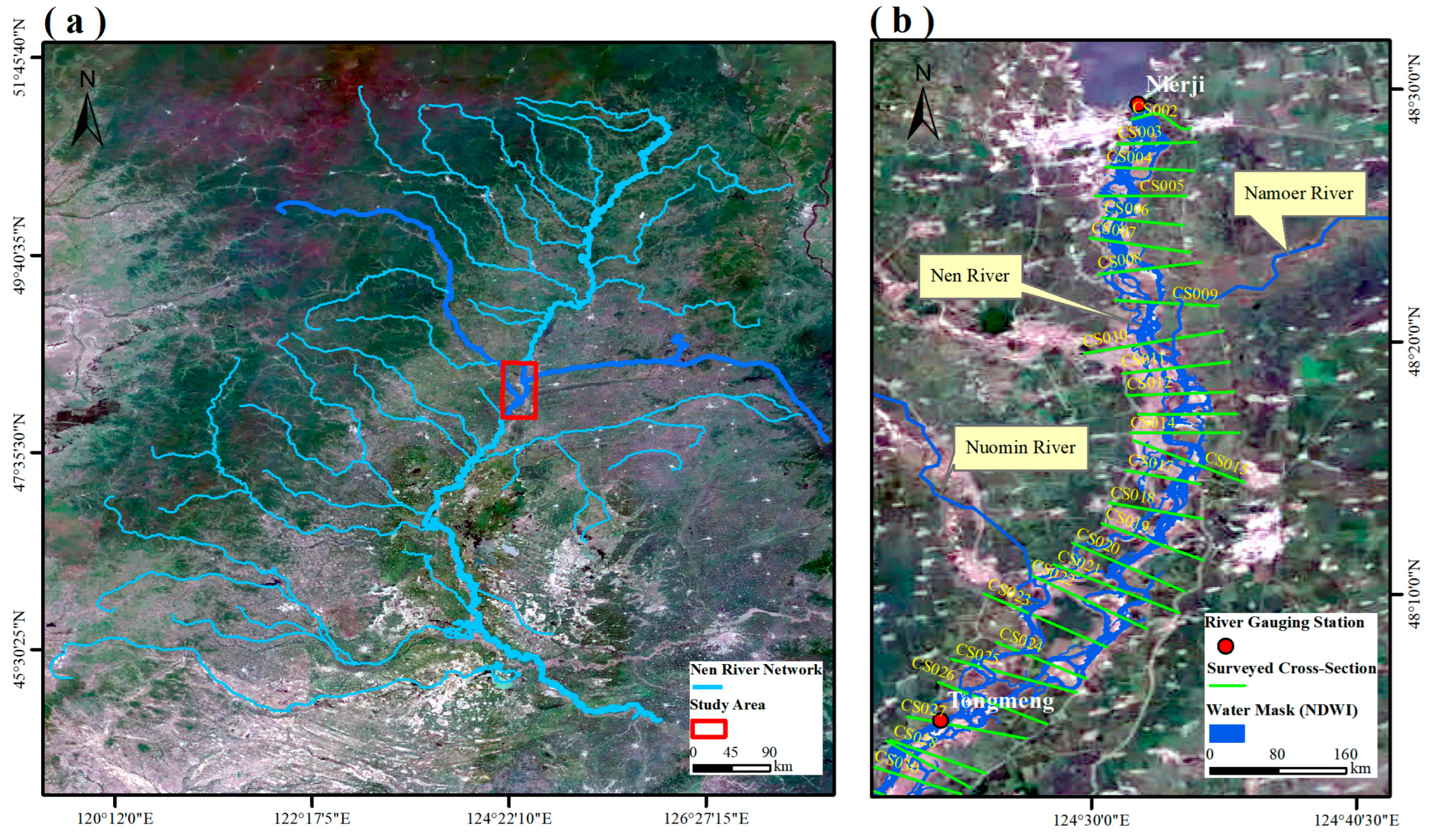
2.1.1. Study Area
2.1.2. Streamflow Data
2.1.3. Cross Section Surveys
2.1.4. Satellite Data
2.2. Satellite Image Processing
2.2.1. Water Body Retrieval and Width Calculation
2.2.2. Water Surface Elevation Retrieval
2.3. Retrieving Riverbed Elevation
2.3.1. Hydrologic Routing
2.3.2. Developing Rating Curve
2.3.3. Deriving Channel Geometry
2.4. Hydrodynamic Validations
2.4.1. One-Dimensional Hydraulic Routing
2.4.2. Two-Dimensional Inundation Mapping
2.5. Accuracy Evaluation
3. Results
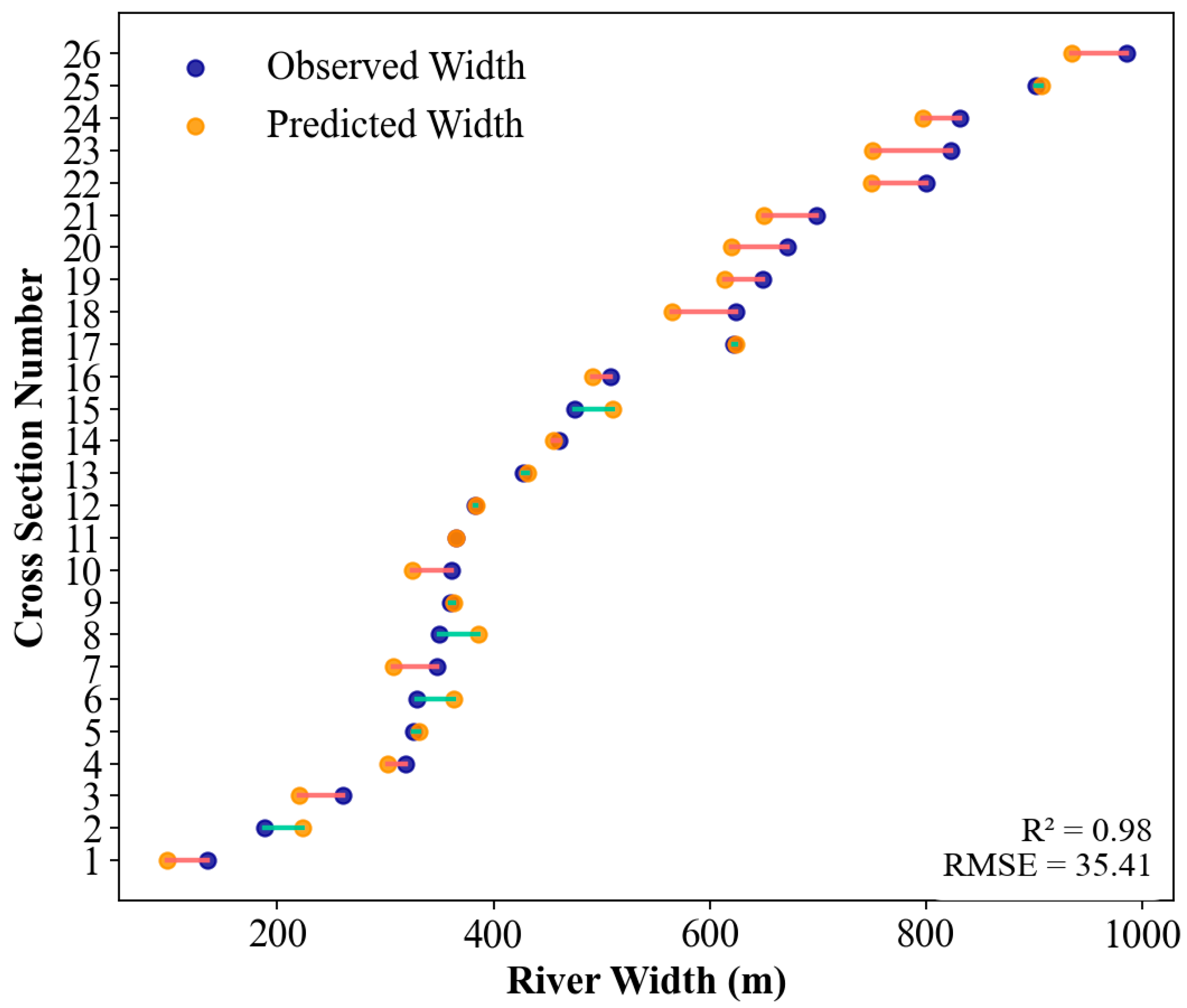
3.1. River Width Retrieval
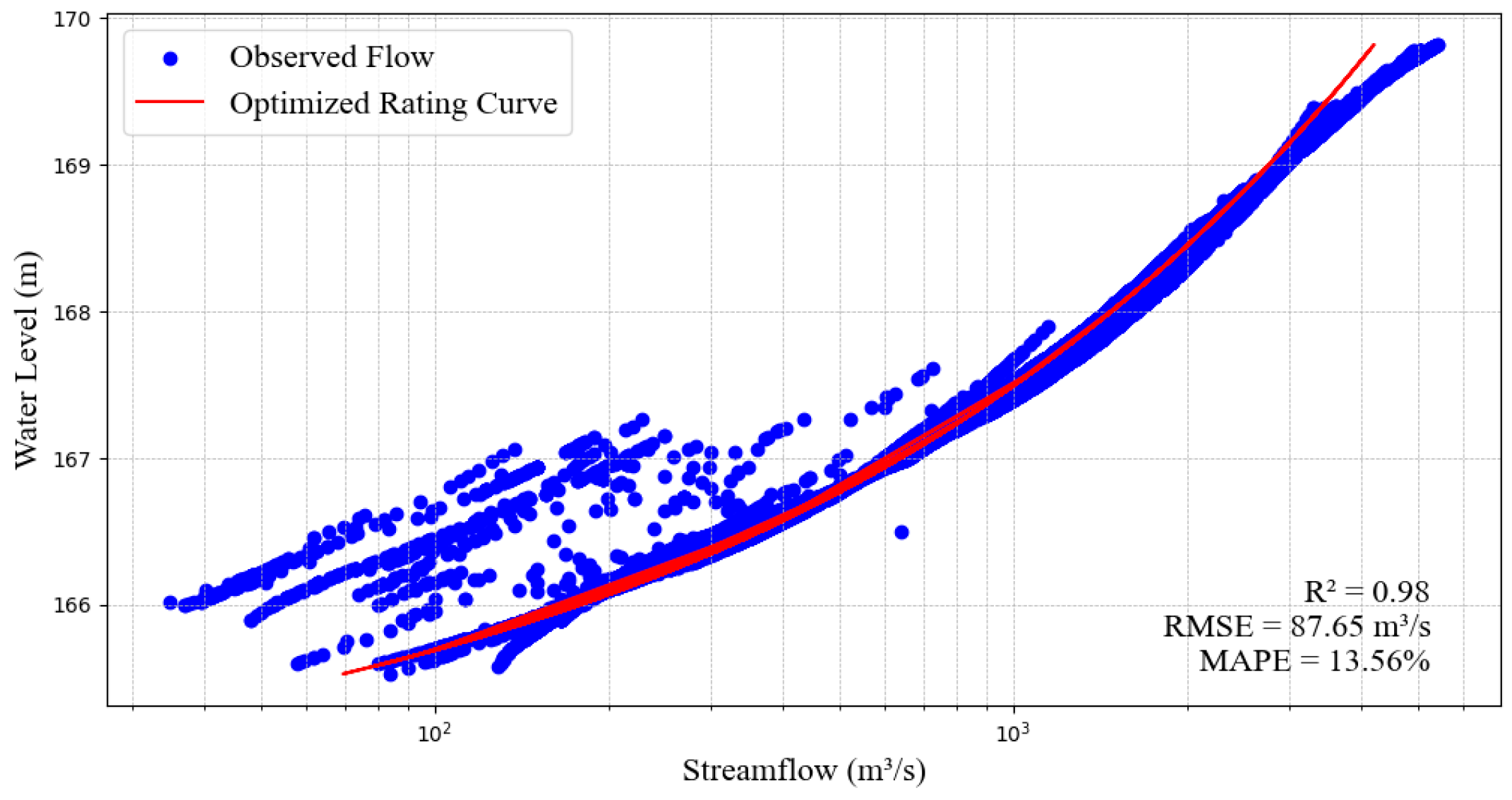
3.2. Developed Rating Curve
3.3. Calibrated Muskingum Parameters
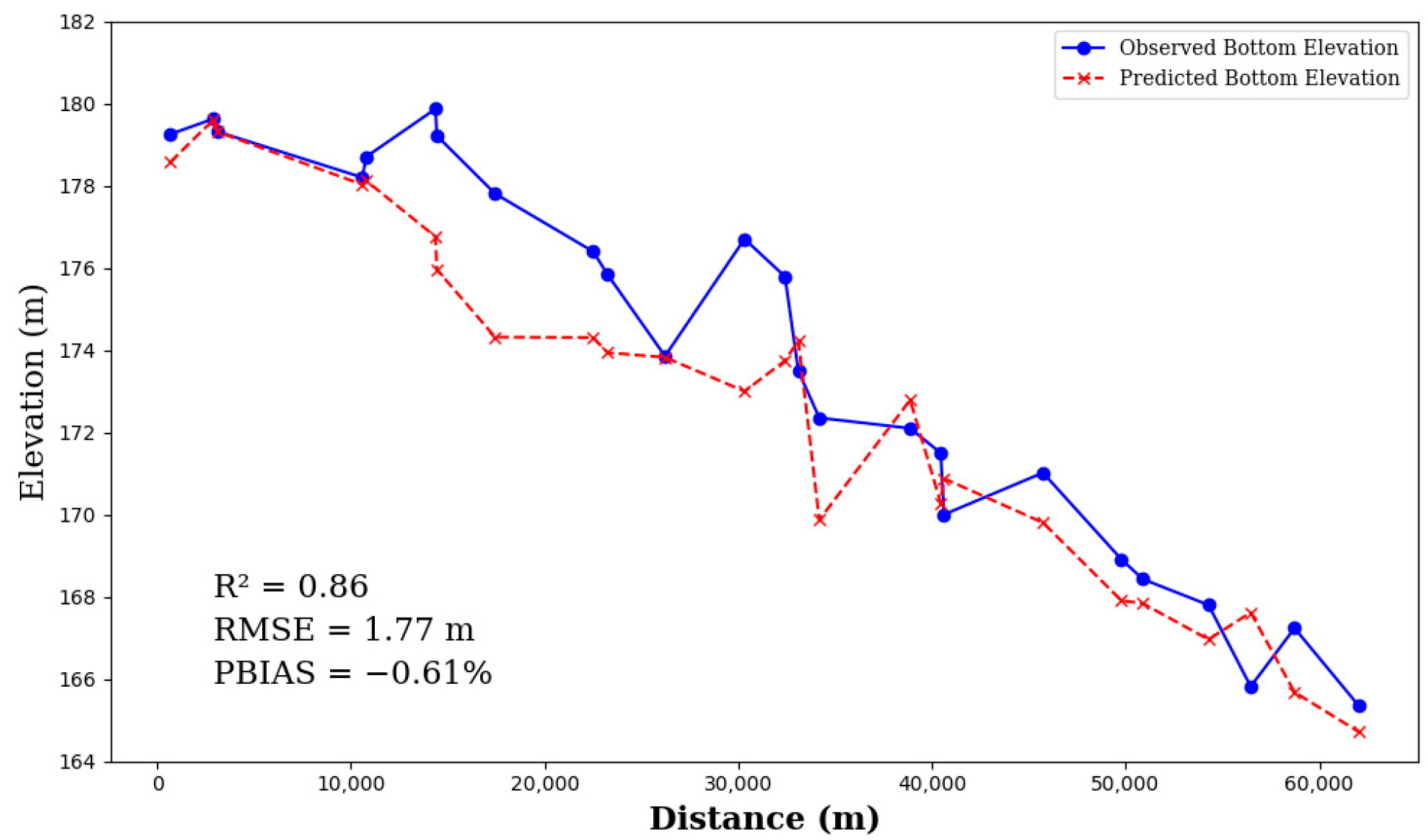
3.4. Back-Calculated Riverbed Elevations
3.5. One-Dimensional Hydraulic Validation
4. Discussion
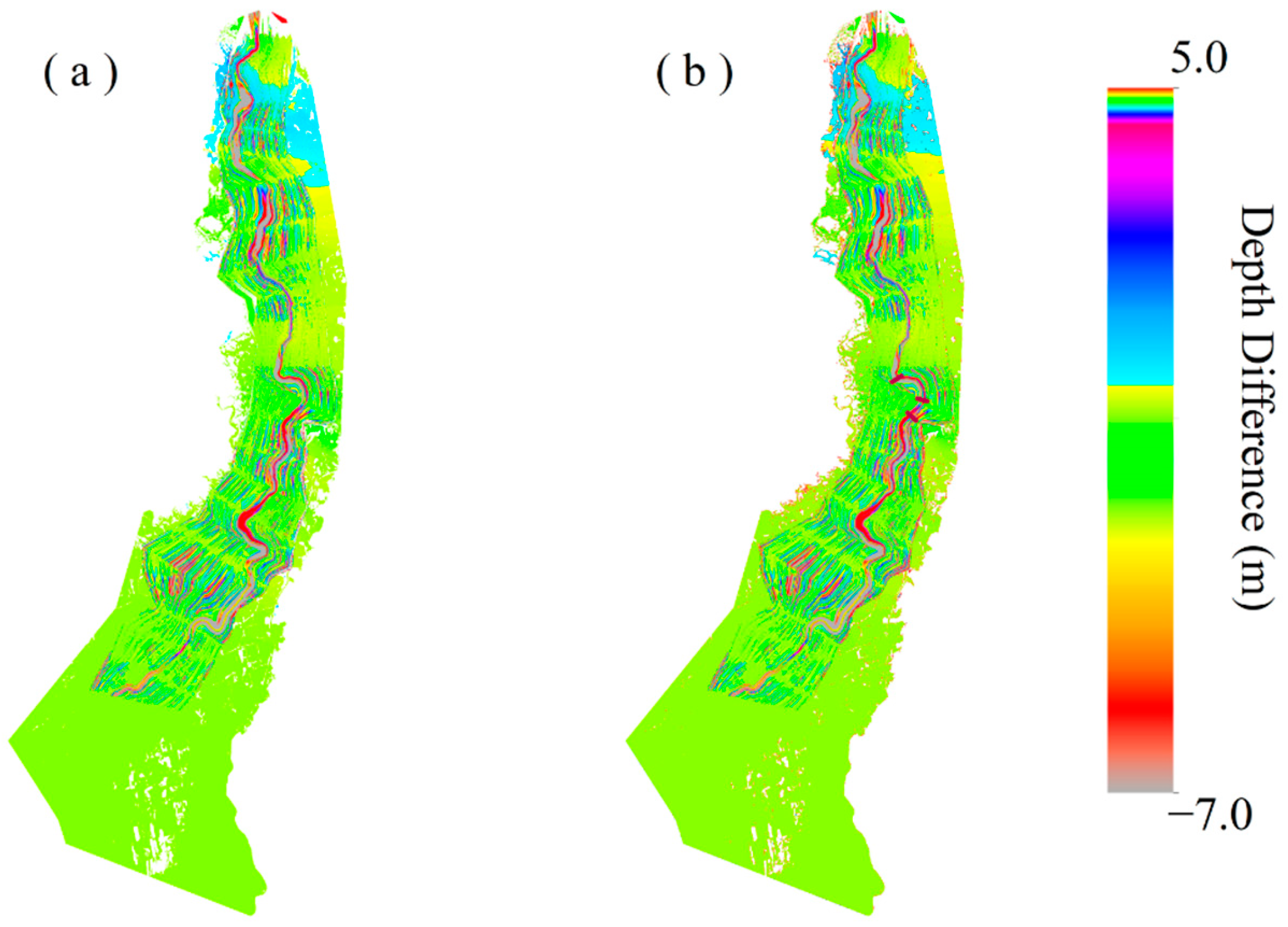
4.1. Influence of Channel Geometry on 2D Inundation Mapping
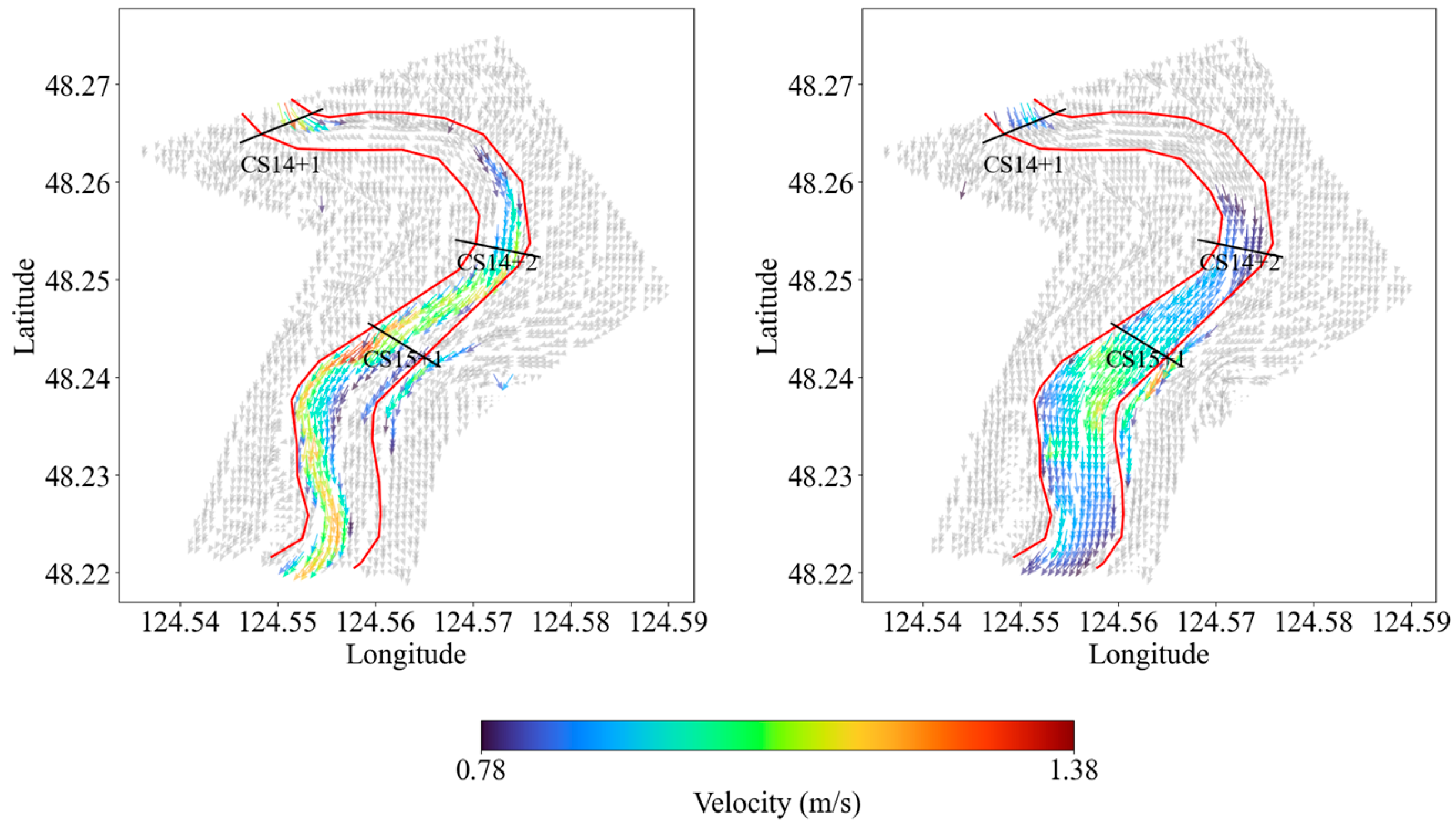
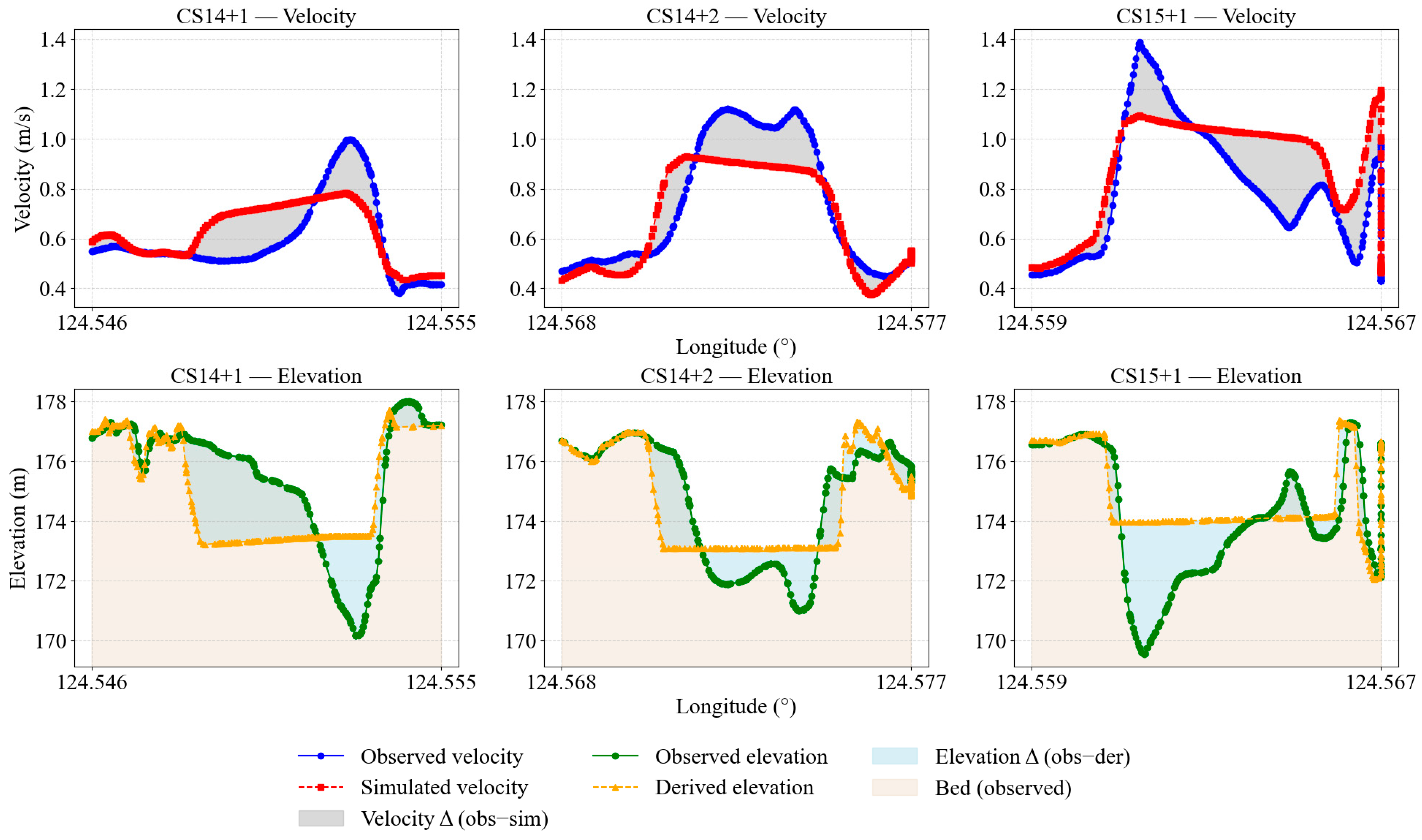
4.2. Velocity Fields at the Channel Bend
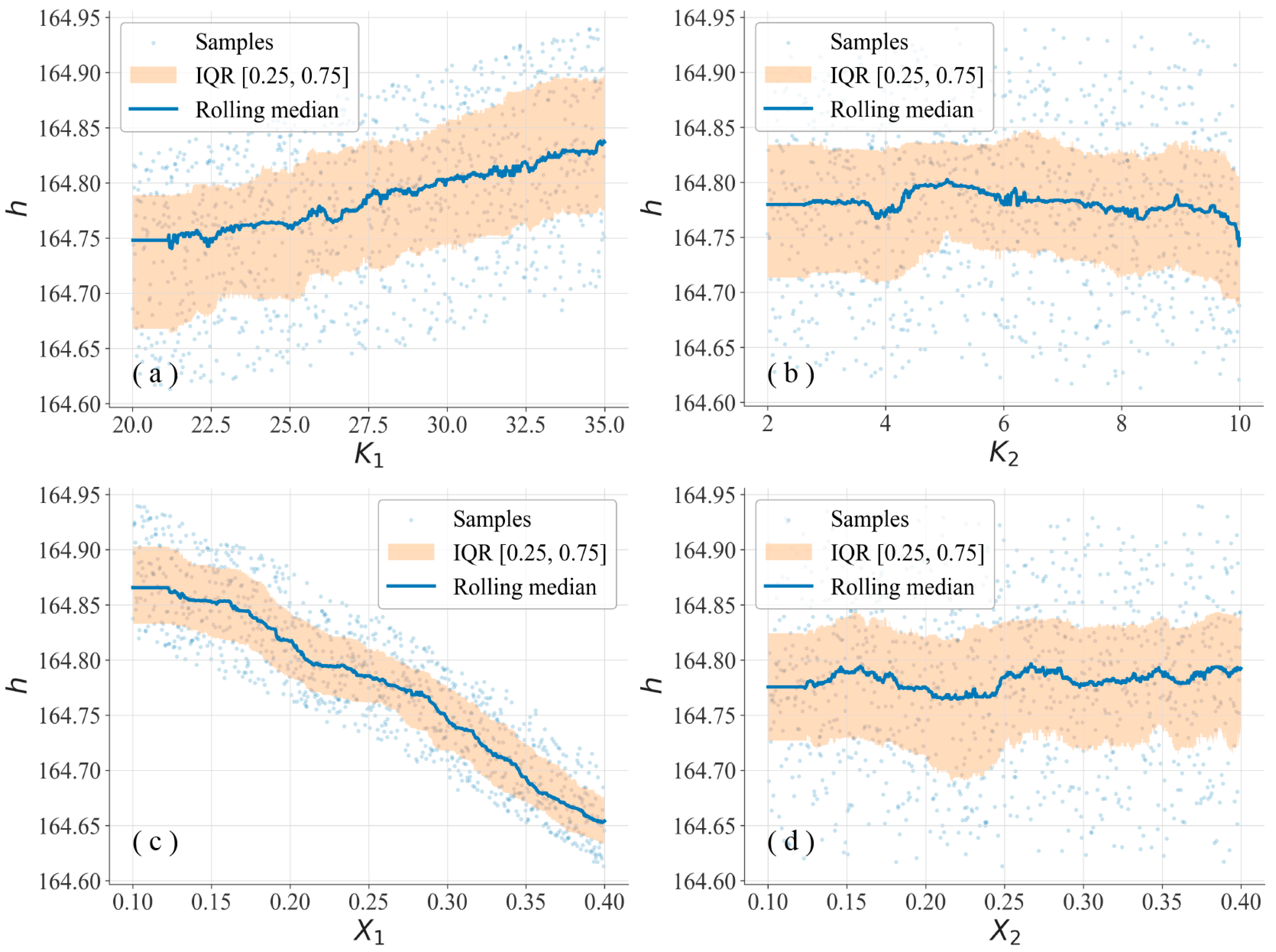
4.3. Uncertainty Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ICESat-2 | Ice, Cloud, and Land Elevation Satellite-2 |
| ADCP | Acoustic Doppler Current Profiler |
| ATLAS | Advanced Terrain Laser Altimeter System |
| ATL03 | ATLAS Level-3A Global Geolocated Photon Data |
| CS | Cross Section |
| DEM | Digital Elevation Model |
| EGM2008 | Earth Gravity Model 2008 |
| HEC-RAS | Hydrologic Engineering Center’s River Analysis System |
| MAPE | Mean Absolute Percentage Error |
| MSI | Multispectral Instrument (Sentinel-2) |
| NDWI | Normalized Difference Water Index |
| NSE | Nash–Sutcliffe Efficiency |
| PBIAS | Percent Bias |
| R2 | Coefficient of Determination |
| RMSE | Root Mean Square Error |
| RTK | Real-Time Kinematics |
| USVs | Unmanned Surface Vehicles |
| 1D | One-dimensional (hydrodynamic model) |
| 2D | Two-dimensional (hydrodynamic model) |
| GA | Genetic Algorithm |
| DEAP | Distributed Evolutionary Algorithms in Python |
References
- Neal, J.; Hawker, L.; Savage, J.; Durand, M.; Bates, P.; Sampson, C. Estimating River Channel Bathymetry in Large Scale Flood Inundation Models. Water Resour. Res. 2021, 57, e2020WR028301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zazo, S.; Rodríguez-Gonzálvez, P.; Molina, J.-L.; González-Aguilera, D.; Agudelo-Ruiz, C.A.; Hernández-López, D. Flood Hazard Assessment Supported by Reduced Cost Aerial Precision Photogrammetry. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garzon, L.F.L.; Johnson, M.F.; Mount, N.; Gomez, H. Exploring the effects of catchment morphometry on overland flow response to extreme rainfall using a 2D hydraulic-hydrological model (IBER). J. Hydrol. 2023, 627, 130405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Lee, A.C.; Alip, A.E.; Dieu, H.T.; Leong, Y.L.; Ooi, S.K. Robust Bathymetric Mapping in Shallow Waters: A Digital Surface Model-Integrated Machine Learning Approach Using UAV-Based Multispectral Imagery. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 3066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Bai, Y.; Paik, J.K. Optimal coverage path planning for USV-assisted coastal bathymetric survey: Models, solutions, and lake trials. Ocean Eng. 2024, 296, 116921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavelsky, T.M.; Smith, L.C. RivWidth: A Software Tool for the Calculation of River Widths From Remotely Sensed Imagery. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2008, 5, 70–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, G.H.; Pavelsky, T.M. Patterns of river width and surface area revealed by the satellite-derived North American River Width data set. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2015, 42, 395–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, G.H.; Pavelsky, T.M. Global extent of rivers and streams. Science 2018, 361, 585–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isikdogan, F.; Bovik, A.; Passalacqua, P. RivaMap: An automated river analysis and mapping engine. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 202, 88–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Huang, X.; Tang, Q. Satellite-derived river width and its spatiotemporal patterns in China during 1990–2015. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 247, 111918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamazaki, D.; O’Loughlin, F.; Trigg, M.A.; Miller, Z.F.; Pavelsky, T.M.; Bates, P.D. Development of the Global Width Database for Large Rivers. Water Resour. Res. 2014, 50, 3467–3480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Li, J.; Lin, Y.; Meng, Y.; Liu, J. GrabRiver: Graph-Theory-Based River Width Extraction From Remote Sensing Imagery. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2022, 19, 1500505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-J.; Kim, H.-S.; Yun, H.-S.; Lee, S.-H. Satellite-Derived Bathymetry Using Sentinel-2 and Airborne Hyperspectral Data: A Deep Learning Approach with Adaptive Interpolation. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 2594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhao, J.; Deng, R.; Liang, Y.; Gao, Y.; Chen, Q.; Xiong, L.; Liu, Y.; Tang, Y.; Tang, D. A downscaled bathymetric mapping approach combining multitemporal Landsat-8 and high spatial resolution imagery: Demonstrations from clear to turbid waters. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2021, 180, 65–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, J.; Parrish, C.E.; Magruder, L.A.; Herrmann, J.; Yoo, S.; Perry, J.S. ICESat-2 bathymetry algorithms: A review of the current state-of-the-art and future outlook. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2025, 223, 413–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Jin, X.; Jin, S. Shallow Water Bathymetry Mapping from ICESat-2 and Sentinel-2 Based on BP Neural Network Model. Water 2022, 14, 3862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, L.-L.; Pavelsky, T.; Cretaux, J.-F.; Morrow, R.; Farrar, J.T.; Vaze, P.; Sengenes, P.; Vinogradova-Shiffer, N.; Sylvestre-Baron, A.; Picot, N.; et al. The Surface Water and Ocean Topography Mission: A Breakthrough in Radar Remote Sensing of the Ocean and Land Surface Water. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2024, 51, e2023GL107652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Zheng, R.; Ma, D.; Huang, X. Associating reservoir operations with 2D inundation risk and climate uncertainty. Water Supply 2024, 24, 2598–2613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Huang, X.; Ma, D.; Gao, Z.; Liu, J. Shifting patterns of Pareto fronts for multi-objective reservoir operations in response to extreme flood events and uncertain climates. J. Water Clim. Change 2025, 16, 2134–2152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, F.; Chen, J.; Chen, J.; Wang, T.; Han, L.; Zhang, X.; Yan, J. Evolution of the hydro-ecological environment and its natural and anthropogenic causes during 1985–2019 in the Nenjiang River basin. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 799, 149256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, W.; Zhang, G.; Cui, H.; Chen, Z.; Wei, S.; Zhu, C.; Xie, Z. Extraction of high-accuracy control points using ICESat-2 ATL03 in urban areas. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2022, 115, 103116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, Y.; Hu, M.; Chen, Y.; Yan, Q.; Zhang, D.; Li, S.; Zhang, X.; Wang, L. Investigating the Shallow-Water Bathymetric Capability of Zhuhai-1 Spaceborne Hyperspectral Images Based on ICESat-2 Data and Empirical Approaches: A Case Study in the South China Sea. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrmann, I.; Pimstein, A.; Karnieli, A.; Cohen, Y.; Alchanatis, V.; Bonfil, D.J. LAI assessment of wheat and potato crops by VENμS and Sentinel-2 bands. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 2141–2151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, C.S.; King, O.; Miles, E.S.; Quincey, D.J. Optimising NDWI supraglacial pond classification on Himalayan debris-covered glaciers. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 217, 414–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Tang, L.; Wang, H. An improved approach for monitoring urban built-up areas by combining NPP-VIIRS nighttime light, NDVI, NDWI, and NDBI. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 328, 129488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Shen, X.; Cao, L. An Advanced Terrain Vegetation Signal Detection Approach for Forest Structural Parameters Estimation Using ICESat-2 Data. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nezhadarya, E.; Wang, Z.J.; Ward, R.K. Robust Image Watermarking Based on Multiscale Gradient Direction Quantization. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2011, 6, 1200–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Wang, H.; Wang, B.; Chen, S.; Li, H. Performance Comparison of Geoid Refinement between XGM2016 and EGM2008 Based on the KTH and RCR Methods: Jilin Province, China. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlis, N.K.; Holmes, S.A.; Kenyon, S.C.; Factor, J.K. The development and evaluation of the Earth Gravitational Model 2008 (EGM2008). J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2012, 117, B04406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, B.; Perumal, M.; Moramarco, T.; Barbetta, S. Rating Curve Development at Ungauged River Sites using Variable Parameter Muskingum Discharge Routing Method. Water Resour. Manag. 2014, 28, 3783–3800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, S.; Zhang, F.; Yu, L.; Cao, S.; Zhou, Y.; Wu, Y.; Hou, L. Optimization of a combined cooling, heating and power system using CO2 as main working fluid driven by gas turbine waste heat. Energy Convers. Manag. 2018, 178, 235–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perumal, M.; Moramarco, T.; Sahoo, B.; Barbetta, S. On the practical applicability of the VPMS routing method for rating curve development at ungauged river sites. Water Resour. Res. 2010, 46, W03522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Jiang, Z.; Que, Y. Hierarchical recursive Levenberg–Marquardt algorithm for radial basis function autoregressive models. Inf. Sci. 2023, 647, 119506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karakaya, D.; Ozturk, B.; Elçi, S. Hydrokinetic power potential assessment of the Çoruh River Basin. Energy Sustain. Dev. 2024, 82, 101533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rather, A.F.; Ahmed, R.; Bansal, J.K.; Mir, R.A.; Ahmed, P.; Malik, I.H.; Varade, D. Glacial lake outburst flood risk assessment of a rapidly expanding glacial lake in the Ladakh region of Western Himalaya, using hydrodynamic modeling. Geomat. Nat. Hazards Risk 2024, 15, 2413893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mejia, A.I.; Reed, S.M. Evaluating the effects of parameterized cross section shapes and simplified routing with a coupled distributed hydrologic and hydraulic model. J. Hydrol. 2011, 409, 512–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fereshtehpour, M.; Esmaeilzadeh, M.; Alipour, R.S.; Burian, S.J. Impacts of DEM type and resolution on deep learning-based flood inundation mapping. Earth Sci. Inform. 2024, 17, 1125–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, M.; Wilson, M.D.; Lane, E.M.; Brasington, J.; Pearson, R.A. Quantifying Uncertainty in Flood Predictions in Fixed Cartesian Flood Model Due To Arbitrary Conventions in Grid Alignment. Water Resour. Res. 2025, 61, e2024WR038919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthusamy, M.; Casado, M.R.; Butler, D.; Leinster, P. Understanding the effects of Digital Elevation Model resolution in urban fluvial flood modelling. J. Hydrol. 2021, 596, 126088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoch, J.M.; Eilander, D.; Ikeuchi, H.; Baart, F.; Winsemius, H.C. Evaluating the impact of model complexity on flood wave propagation and inundation extent with a hydrologic–hydrodynamic model coupling framework. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2019, 19, 1723–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, S.; Saksena, S.; Winter, D.; Merwade, V.; McMillan, S. Incorporating Network Scale River Bathymetry to Improve Characterization of Fluvial Processes in Flood Modeling. Water Resour. Res. 2022, 58, e2020WR029521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demiral, D.; Boes, R.M.; Albayrak, I. Effects of Secondary Currents on Turbulence Characteristics of Supercritical Open Channel Flows at Low Aspect Ratios. Water 2020, 12, 3233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bali, M.; Kolahdoozan, M.; Zarrati, A.; Alaee, M. Vertical velocity in rectangular channel bends: Numerical study and development of a prediction formula. J. Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng. 2019, 41, 489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, M.; Wright, N.G.; Sleigh, P.A.; Ahilan, S.; Lamb, R. Physical complexity to model morphological changes at a natural channel bend. Water Resour. Res. 2016, 52, 6348–6364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalid, Z.; de Souza de Lima, A.; Ruess, P.J.; Khalid, A.; Miesse, T.; Veronez, D.; Ferreira, C.M.; Kinter, J.L. DEMend: Automating Hydrological Correction of Digital Elevation Models for Enhanced Urban Flood Modeling. Water Resour. Manag. 2025, 39, 5751–5768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neal, J.; Schumann, G.; Bates, P. A subgrid channel model for simulating river hydraulics and floodplain inundation over large and data sparse areas. Water Resour. Res. 2012, 48, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Feng, Y.; Liu, J.; Huang, X.; Zhao, S.; Ma, D.; Lee, S.; Cao, R. Inferring River Channel Geometry Based on Multi-Satellite Datasets and Hydraulic Modeling. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 3753. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17223753
Feng Y, Liu J, Huang X, Zhao S, Ma D, Lee S, Cao R. Inferring River Channel Geometry Based on Multi-Satellite Datasets and Hydraulic Modeling. Remote Sensing. 2025; 17(22):3753. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17223753
Chicago/Turabian StyleFeng, Youcan, Junhui Liu, Xin Huang, Shaohua Zhao, Donghe Ma, Seungyub Lee, and Ruibo Cao. 2025. "Inferring River Channel Geometry Based on Multi-Satellite Datasets and Hydraulic Modeling" Remote Sensing 17, no. 22: 3753. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17223753
APA StyleFeng, Y., Liu, J., Huang, X., Zhao, S., Ma, D., Lee, S., & Cao, R. (2025). Inferring River Channel Geometry Based on Multi-Satellite Datasets and Hydraulic Modeling. Remote Sensing, 17(22), 3753. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17223753








