Advantage Analysis of Spaceborne SAR Imaging in Very Low Earth Orbit: A Case Study of Haishao-1
Highlights
- The Haishao-1 satellite, operating at an orbital altitude below 350 km, successfully achieved 1-m high-resolution imaging in Stripmap mode, demonstrating the superior imaging capability of VLEO-SAR systems.
- Analysis of system parameters and imaging results confirms that VLEO-SAR enables higher azimuth resolution with a smaller antenna aperture while maintaining a high signal-to-noise ratio.
- The findings validate the potential of VLEO-SAR for designing lower-cost, high-performance payloads, which can significantly reduce satellite development and launch expenses.
- VLEO-SAR platforms offer enhanced suitability for large-scale constellation deployment, enabling shorter revisit intervals and supporting critical applications such as real-time disaster monitoring and military reconnaissance.
Abstract
1. Introduction
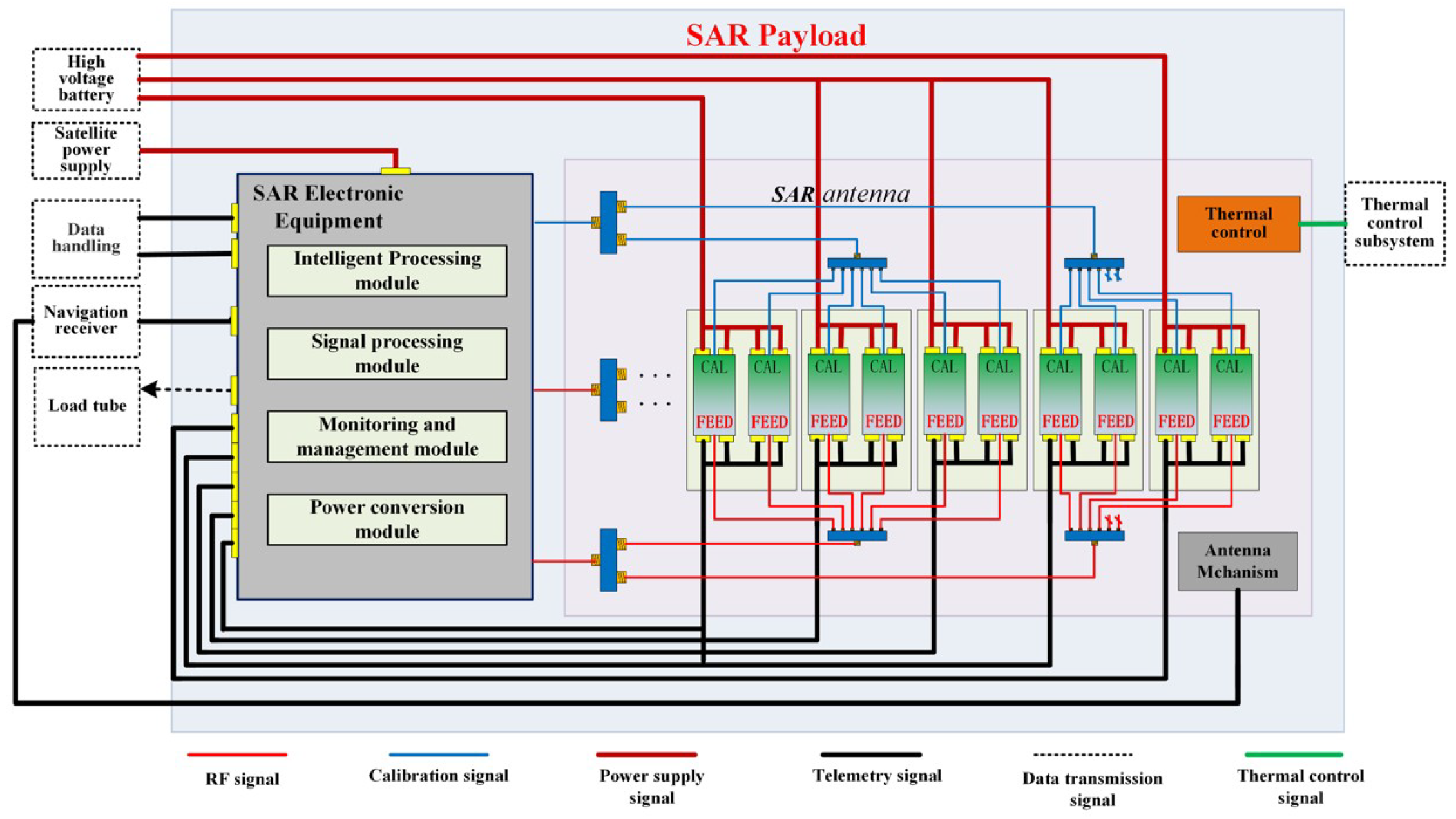
2. Technical Specifications of the Haishao-1 Satellite
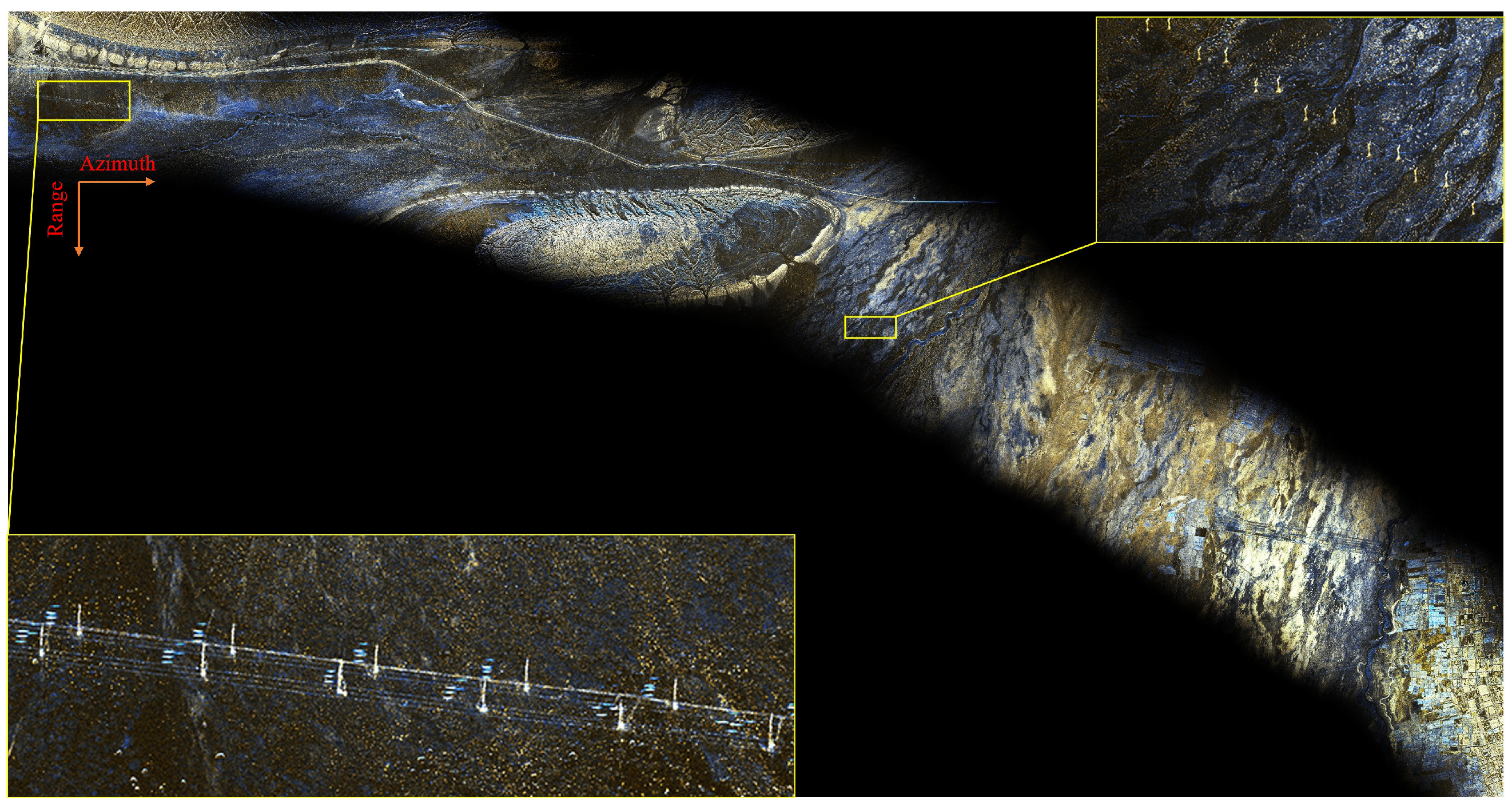
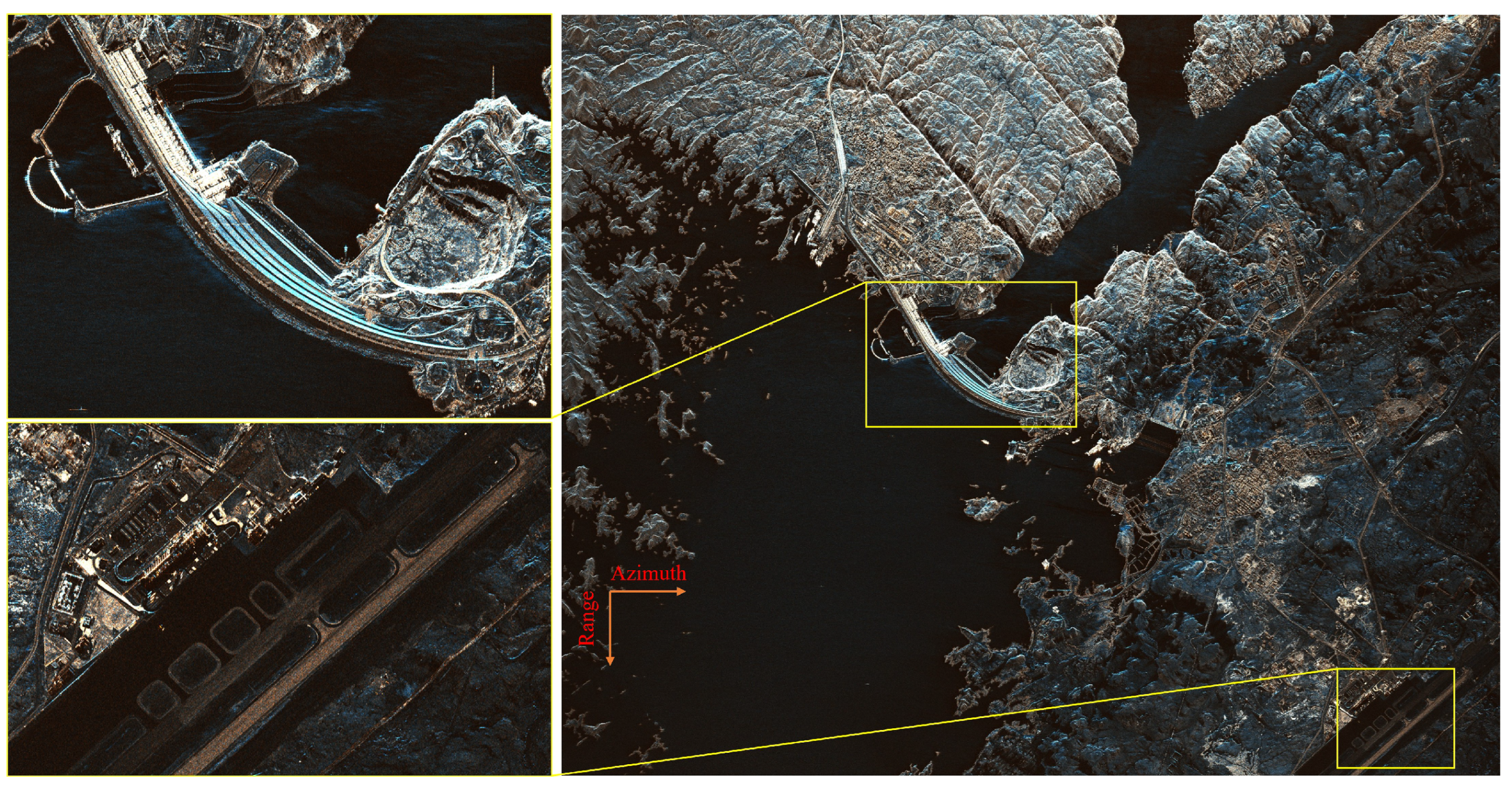
3. Analysis of High-Resolution Advantages in VLEO SAR Satellites
4. Analysis of System Advantages for VLEO SAR Satellites
5. VLEO Challenges and Mission Design Countermeasures
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Moreira, A.; Prats-Iraola, P.; Younis, M.; Krieger, G.; Hajnsek, I.; Papathanassiou, K.P. A tutorial on synthetic aperture radar. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Mag. 2013, 1, 6–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouchi, K. Recent Trend and Advance of Synthetic Aperture Radar with Selected Topics. Remote Sens. 2013, 5, 716–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, D.C.; Speck, R.; Devereux, B.; Schumann, G.J.P.; Neal, J.C.; Bates, P.D. Flood Detection in Urban Areas Using TerraSAR-X. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2010, 48, 882–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, F.; Lv, X.; Dou, F.; Yun, Y. A Review of Time-Series Interferometric SAR Techniques: A Tutorial for Surface Deformation Analysis. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Mag. 2020, 8, 22–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Lv, X.; Huang, Z. Underlying Topography Estimation over Forest Using Maximum a Posteriori Inversion with Spaceborne Polarimetric SAR Interferometry. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafarzadeh, H.; Verma, A.; Mahdianpari, M.; Bhattacharya, A.; Homayouni, S. Enhanced Crop Discrimination and Monitoring Using Compact-Polarimetric SAR Signature Analysis from RADARSAT Constellation Mission. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2024, 17, 6308–6327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Hu, Y.; Yang, J.; Wang, X. Sea Surface Wind Speed Retrieval Using Gaofen-3-02 SAR Full Polarization Data. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milillo, P.; Fielding, E.J.; Shulz, W.H.; Delbridge, B.; Burgmann, R. COSMO-SkyMed Spotlight Interferometry Over Rural Areas: The Slumgullion Landslide in Colorado, USA. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2014, 7, 2919–2926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geudtner, D.; Torres, R.; Snoeij, P.; Davidson, M.; Rommen, B. Sentinel-1 System capabilities and applications. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Quebec City, QC, Canada, 13–18 July 2014; pp. 1457–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werninghaus, R.; Buckreuss, S. The TerraSAR-X Mission and System Design. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2010, 48, 606–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Yu, W.; Deng, Y. The SAR Payload Design and Performance for the GF-3 Mission. Sensors 2017, 17, 2419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Liu, K.; Cai, Y.; Liang, D.; Yu, W.; Liu, D.; Chen, Y.; Yang, Q.; Li, J.; Liu, L. LuTan-1: An Innovative L-band Spaceborne Bistatic Interferometric SAR Mission. In Proceedings of the EUSAR 2024—15th European Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar, Munich, Germany, 23–26 April 2024; pp. 984–988. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, G.; Wu, S.; Deng, Y.; Jiao, J.; Zhang, Q. VLEO Satellite Constellation Design for Regional Aviation and Marine Coverage. IEEE Trans. Netw. Sci. Eng. 2024, 11, 1188–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dakka, S.M. VLEO satellites—A new earth observation space systems commercial and business model. In Proceedings of the 36th International Communications Satellite Systems Conference (ICSSC 2018), Niagara Falls, ON, Canada, 15–18 October 2018; pp. 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez, Y.M. Optimization Approach for a SAR small satellite in Very Low Earth Orbit (VLEO) Demonstrator Mission. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE Aerospace Conference, Big Sky, MT, USA, 2–9 March 2024; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eugenio, F.; Marcello, J.; Martin, J. High-Resolution Maps of Bathymetry and Benthic Habitats in Shallow-Water Environments Using Multispectral Remote Sensing Imagery. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2015, 53, 3539–3549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Liu, C.; Wu, G. Spatial-Temporal Analysis and Stability Investigation of Coastline Changes: A Case Study in Shenzhen, China. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2018, 11, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, N.; Ni, N.; Kapp, P.; Chen, J.; Xiao, A.; Li, H. Structural Analysis of the Hero Range in the Qaidam Basin, Northwestern China, Using Integrated UAV, Terrestrial LiDAR, Landsat 8, and 3-D Seismic Data. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2015, 8, 4581–4591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Dou, A.; Ding, X.; Yuan, X. The Development of Rapid Extraction and Publishing System of Earthquake Damage Based on Remote Sensing. In Proceedings of the IGARSS 2018—2018 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Valencia, Spain, 22–27 July 2018; pp. 2921–2924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, X.; Liao, M.; Zhang, L.; Yang, M. Structural Health and Stability Assessment of High-Speed Railways via Thermal Dilation Mapping With Time-Series InSAR Analysis. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2017, 10, 2999–3010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babu, A.; Baumgartner, S.V. Road Surface Quality Assessment Using Polarimetric Airborne SAR. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE Radar Conference (RadarConf20), Florence, Italy, 21–25 September 2020; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Kang, L.; Liu, J. Spaceborne SAR non-along-track imaging mode: Opportunities and challenges. J. Radars 2022, 11, 1131–1145. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Chen, J.; Wang, P.; Loffeld, O. A Coarse-to-Fine Autofocus Approach for Very High-Resolution Airborne Stripmap SAR Imagery. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2018, 56, 3814–3829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomiyasu, K. Tutorial review of synthetic-aperture radar (SAR) with applications to imaging of the ocean surface. Proc. IEEE 1978, 66, 563–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suess, M.; Grafmueller, B.; Zahn, R. A novel high resolution, wide swath SAR system. IGARSS 2001. Scanning the Present and Resolving the Future. In Proceedings of the IEEE 2001 International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (Cat. No. 01CH37217), Sydney, Australia, 9–13 July 2001; Volume 3, pp. 1013–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Yang, L.; Zhao, L.; Li, P.; Yang, J.; Zhang, L. NESZ Estimation and Calibration for Gaofen-3 Polarimetric Products by the Minimum Noise Envelope Estimator. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 59, 7517–7534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Zhang, H.; Liu, K.; Wang, W.; Ou, N.; Han, H.; Yang, R.; Ren, J.; Wang, J.; Ren, X.; et al. Hongtu-1: The First Spaceborne Single-Pass Multibaseline SAR Interferometry Mission. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2025, 63, 5202518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stangl, M.; Werninghaus, R.; Zahn, R. The TERRASAR-X active phased array antenna. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Symposium on Phased Array Systems and Technology, Boston, MA, USA, 14–17 October 2003; pp. 70–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, D.H.; Yom, I.B.; Kim, D.W. X-band GaN MMIC power amplifier for the SSPA of a SAR system. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Symposium on Radio-Frequency Integration Technology (RFIT), Seoul, Republic of Korea, 30 August–1 September 2017; pp. 93–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hengkang, Q.; Jifeng, H.; Xianhua, W.; Qianlin, Y.; Hong, C.; Baofa, S.; Lisheng, Z.; Kaijian, C. Overview of dual bus solar array design for SAR satellite. In Proceedings of the 2022 3rd China International SAR Symposium (CISS), Shanghai, China, 2–4 November 2022; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
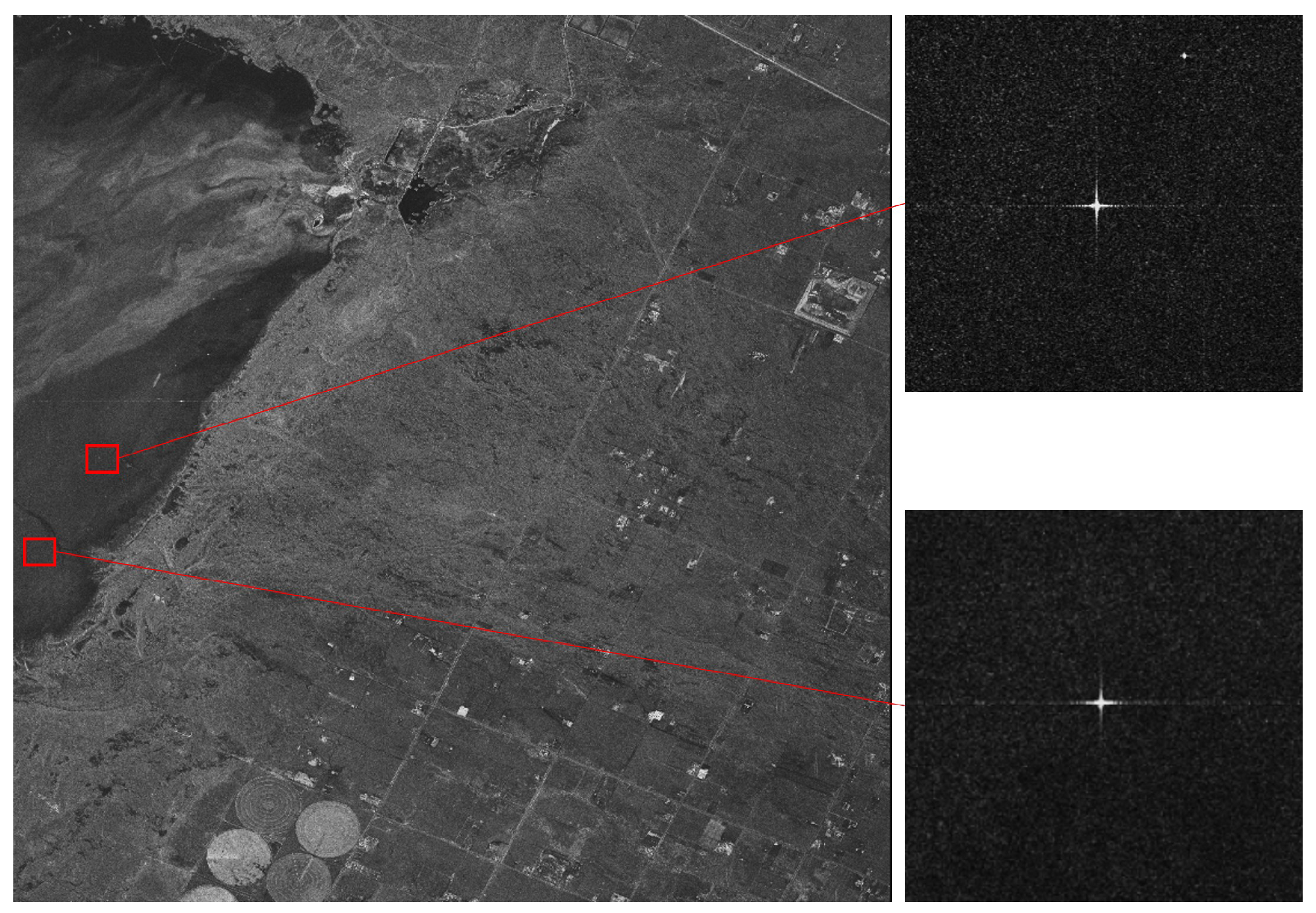




| Observing Mode | Swath Width (km) | Azimuth Resolution (m) | Ground Range Resolution (m) | Polarization |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sliding spotlight | 8 × 8 (R × A) | 0.5 | 0.43–1.03 | single, dual |
| Stripmap | 5–10 (R) | 1 | 0.82–1.03 | single, dual, quad, compact |
| Narrow ScanSAR | 40 (R) | 5 | <5 | single, dual, compact |
| Wide ScanSAR | 160 (R) | 20 | <20 | single, dual |
| Integrated optical-SAR | 110 (R) | 15 | <15 | single, dual |
| Parameters | Value |
|---|---|
| Look Angle (°) | 36.07 |
| Bandwidth (MHz) | 280 |
| Sampling Frequency (MHz) | 400 |
| Pulse width (µs) | 13 |
| PRF (Hz) | 9940 |
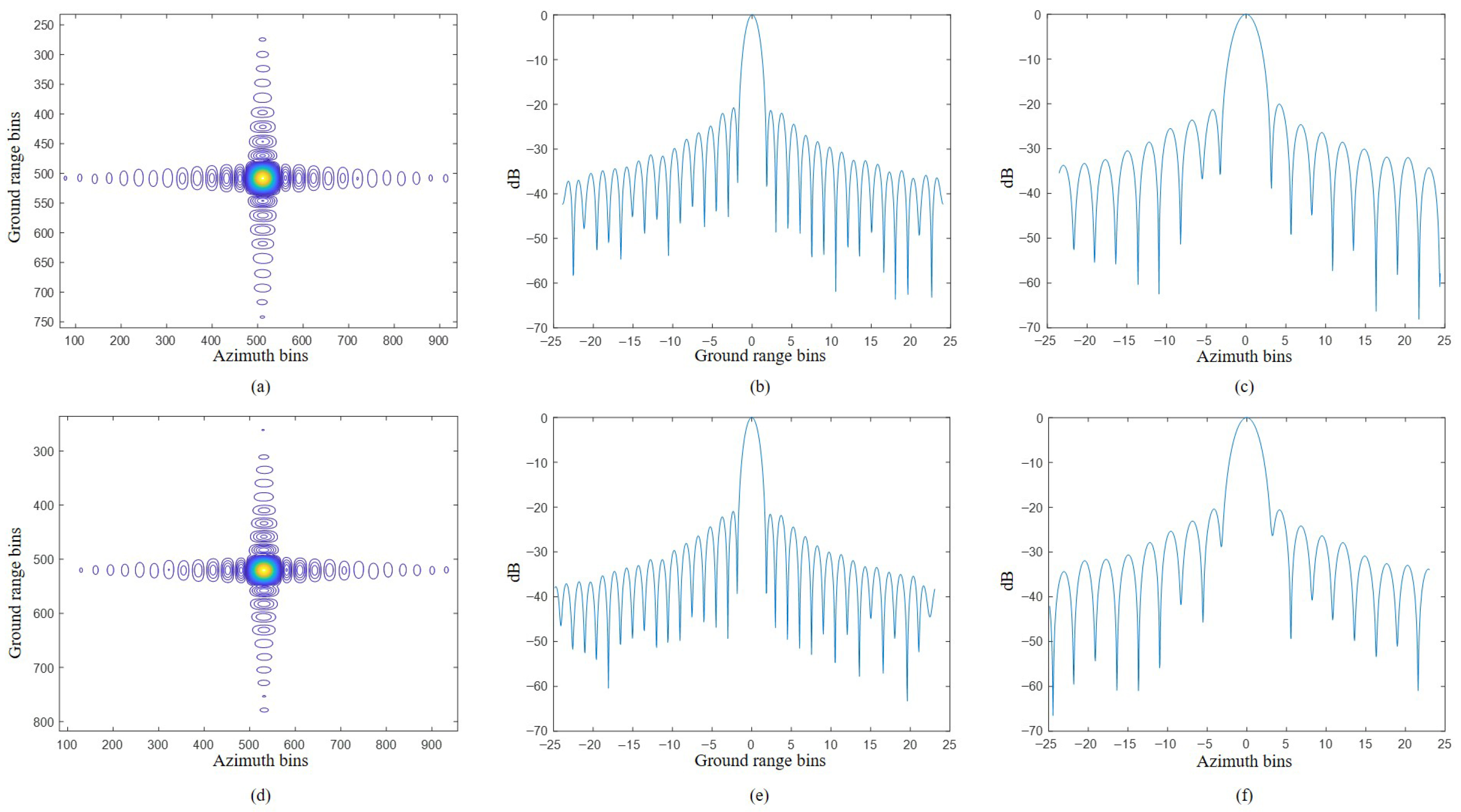
| Resolution (m) | PSLR (dB) | ISLR (dB) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Point 1 | Ground Range | 0.910 | −20.75 | −16.18 |
| Azimuth | 0.926 | −20.13 | −17.66 | |
| Point 2 | Ground Range | 0.910 | −20.94 | −16.24 |
| Azimuth | 0.924 | −20.04 | −17.19 |
| Parameter | TerraSAR | Hongtu-1 | HS-1 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Center Frequency | 9.6 GHz | 9.6 GHz | 9.6 GHz |
| Orbital Altitude | 514 km | 528 km | 350 km |
| Antenna Size | 4784 mm × 754 mm | 3600 mm × 768 mm | 2000 mm × 768 mm |
| Spotlight Mode | 1 m@10 km × 5 km | 1 m@10 km × 20 km 0.5 m@5 km × 5 km | 0.5 m@8 km × 8 km |
| Stripmap Mode | 3 m@30 km | 3 m@20–30 km | 1 m@10 km |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, S.; Sun, J.; Lu, H.; Cheng, S.; Wang, S.; Sun, W. Advantage Analysis of Spaceborne SAR Imaging in Very Low Earth Orbit: A Case Study of Haishao-1. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 3700. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17223700
Yang S, Sun J, Lu H, Cheng S, Wang S, Sun W. Advantage Analysis of Spaceborne SAR Imaging in Very Low Earth Orbit: A Case Study of Haishao-1. Remote Sensing. 2025; 17(22):3700. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17223700
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Shenghui, Jili Sun, Hongliang Lu, Shuohan Cheng, Shuai Wang, and Wen Sun. 2025. "Advantage Analysis of Spaceborne SAR Imaging in Very Low Earth Orbit: A Case Study of Haishao-1" Remote Sensing 17, no. 22: 3700. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17223700
APA StyleYang, S., Sun, J., Lu, H., Cheng, S., Wang, S., & Sun, W. (2025). Advantage Analysis of Spaceborne SAR Imaging in Very Low Earth Orbit: A Case Study of Haishao-1. Remote Sensing, 17(22), 3700. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17223700









