The Global Spatial Pattern of Aerosol Optical, Microphysical and Chemical Properties Derived from AERONET Observations
Highlights
- Coastal aerosol gradients reveal continental outflow’s role in shaping global aerosol patterns.
- The imbalance in observations will introduce systematic errors to the assessment of global aerosol characteristics.
- Anthropogenic aerosols may affect remote uninhabited regions through intercontinental transport.
- Increasing the number of observations in underdeveloped regions is beneficial for understanding the true global distribution of aerosol characteristics.
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Data and Methods
2.1. Data
2.1.1. AERONET Data
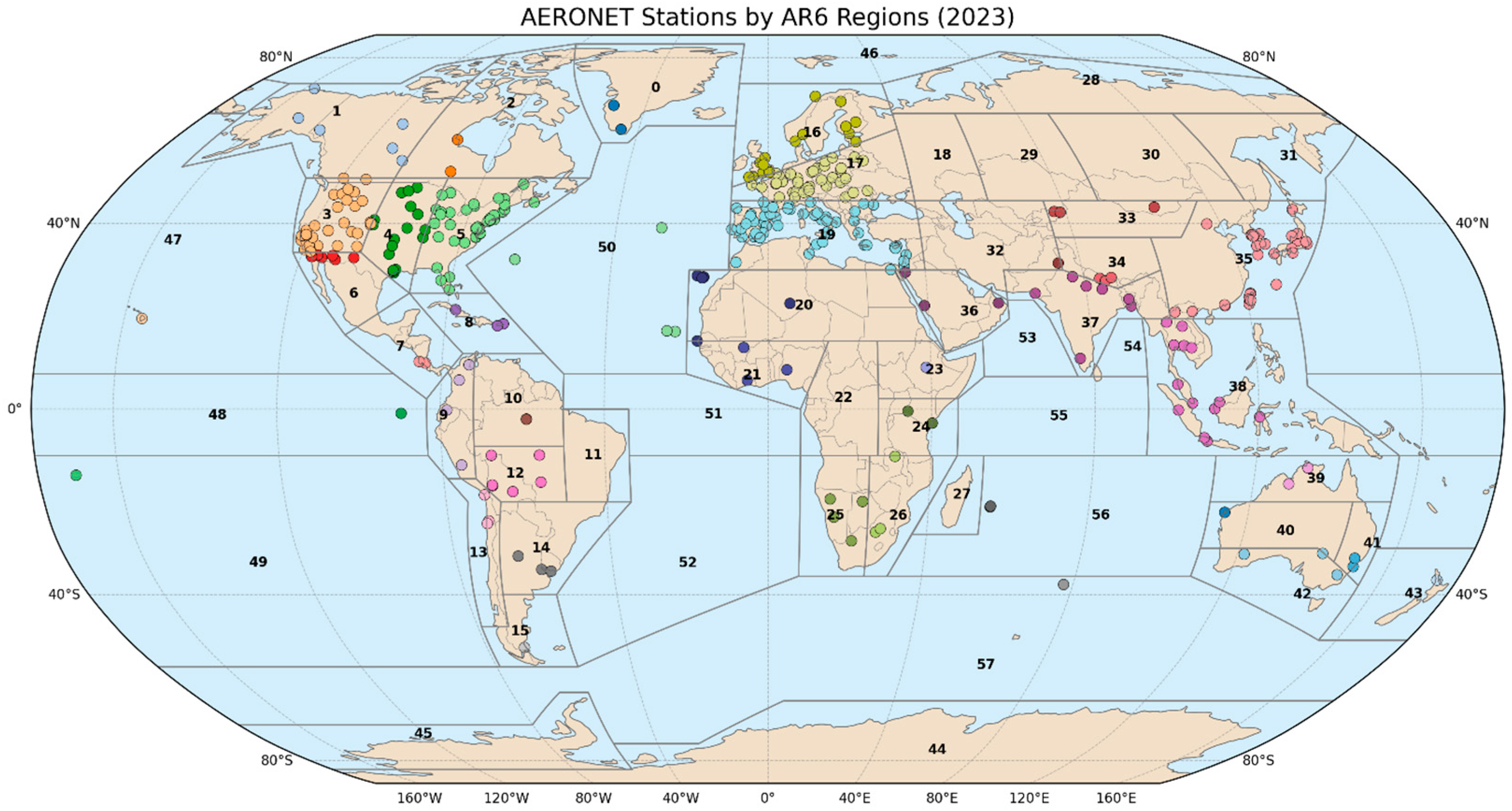
2.1.2. Reference Regions
2.2. Method
2.2.1. Incorporation of the Light-Scattering Organic Components
2.2.2. Determination of CRI in the Multicomponent Liquid System
2.2.3. Comprehensive Characterization of Carbonaceous Components
3. Results and Discussions
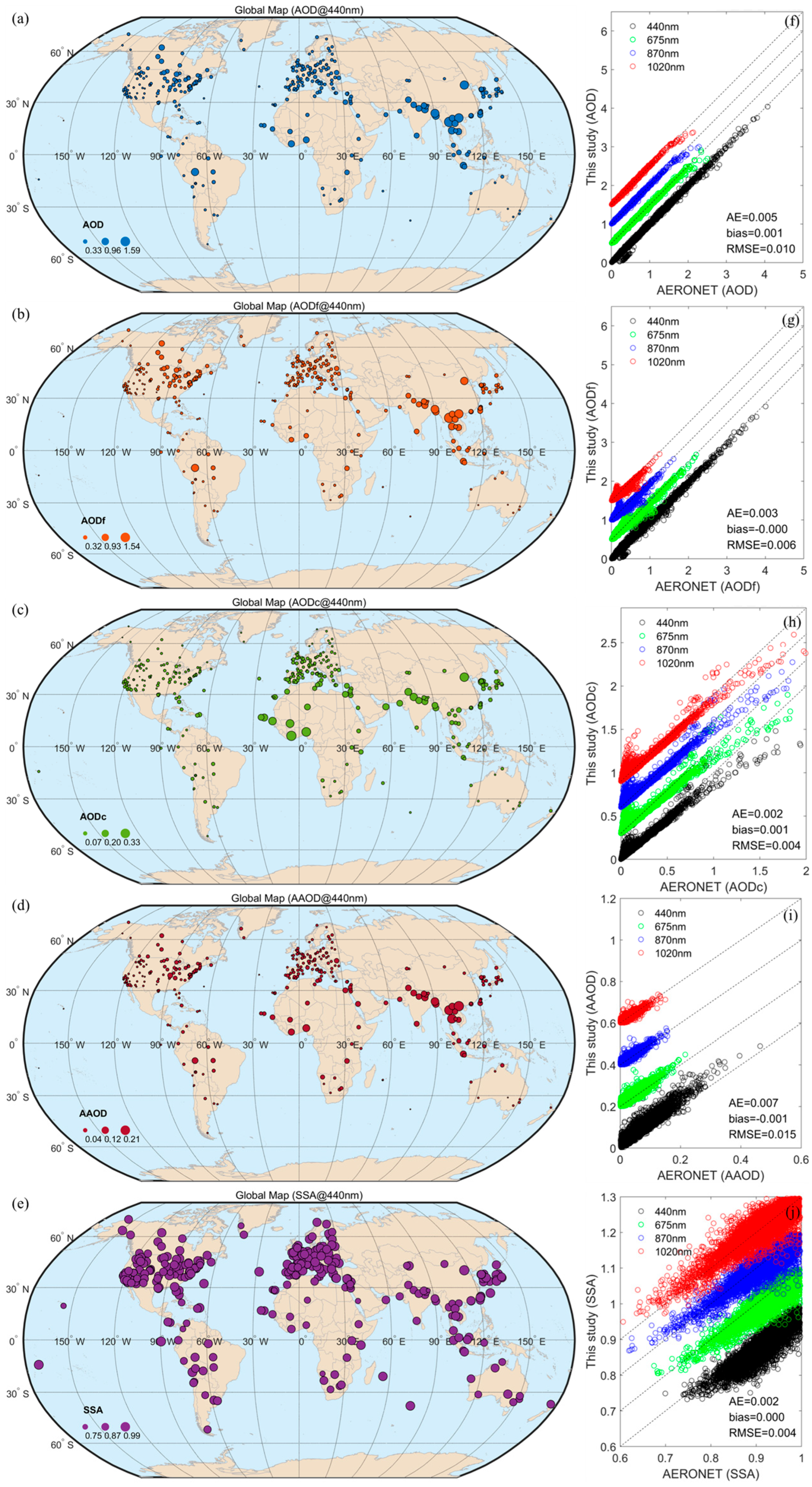
3.1. Aerosol Optical Properties
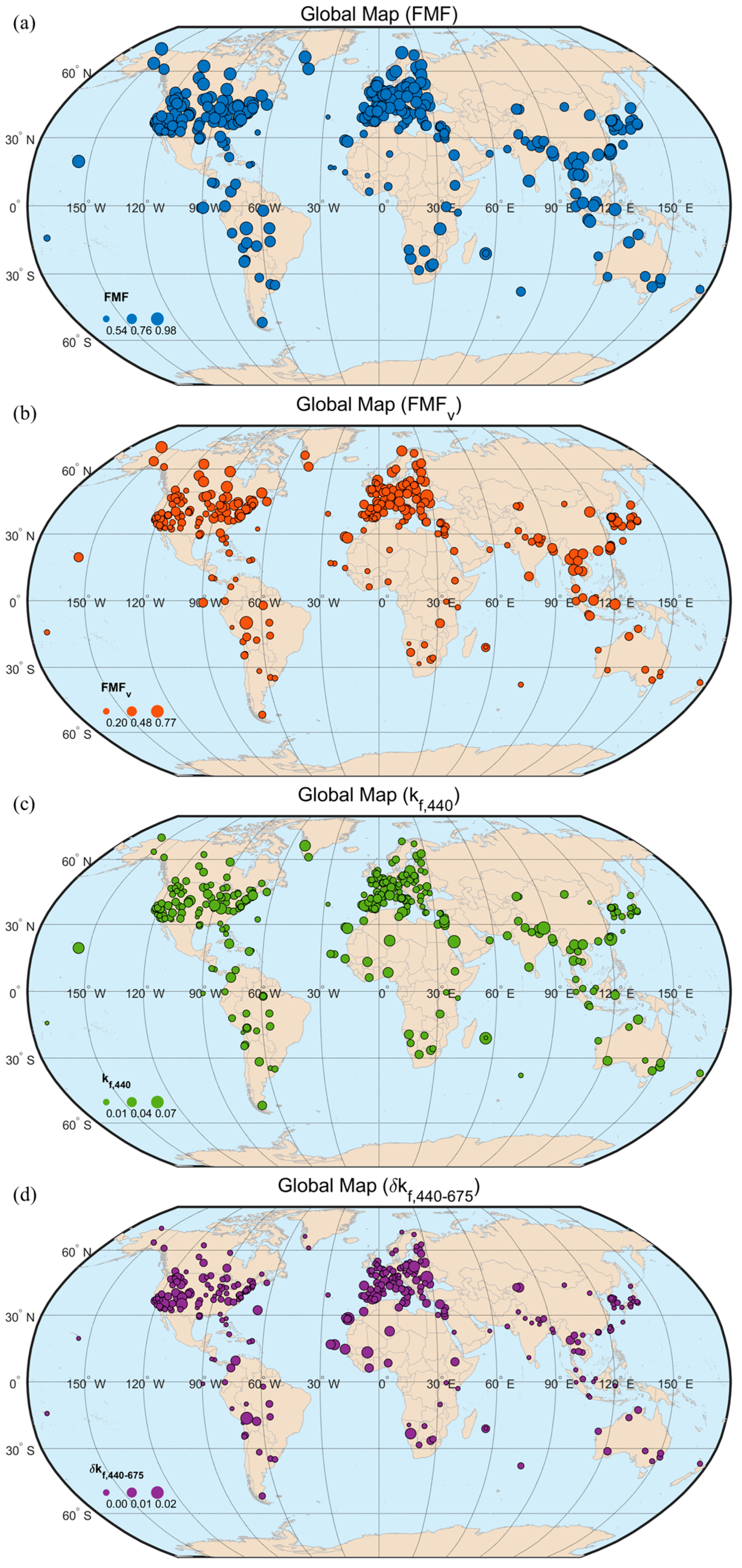
3.2. Aerosol Microphysical Properties
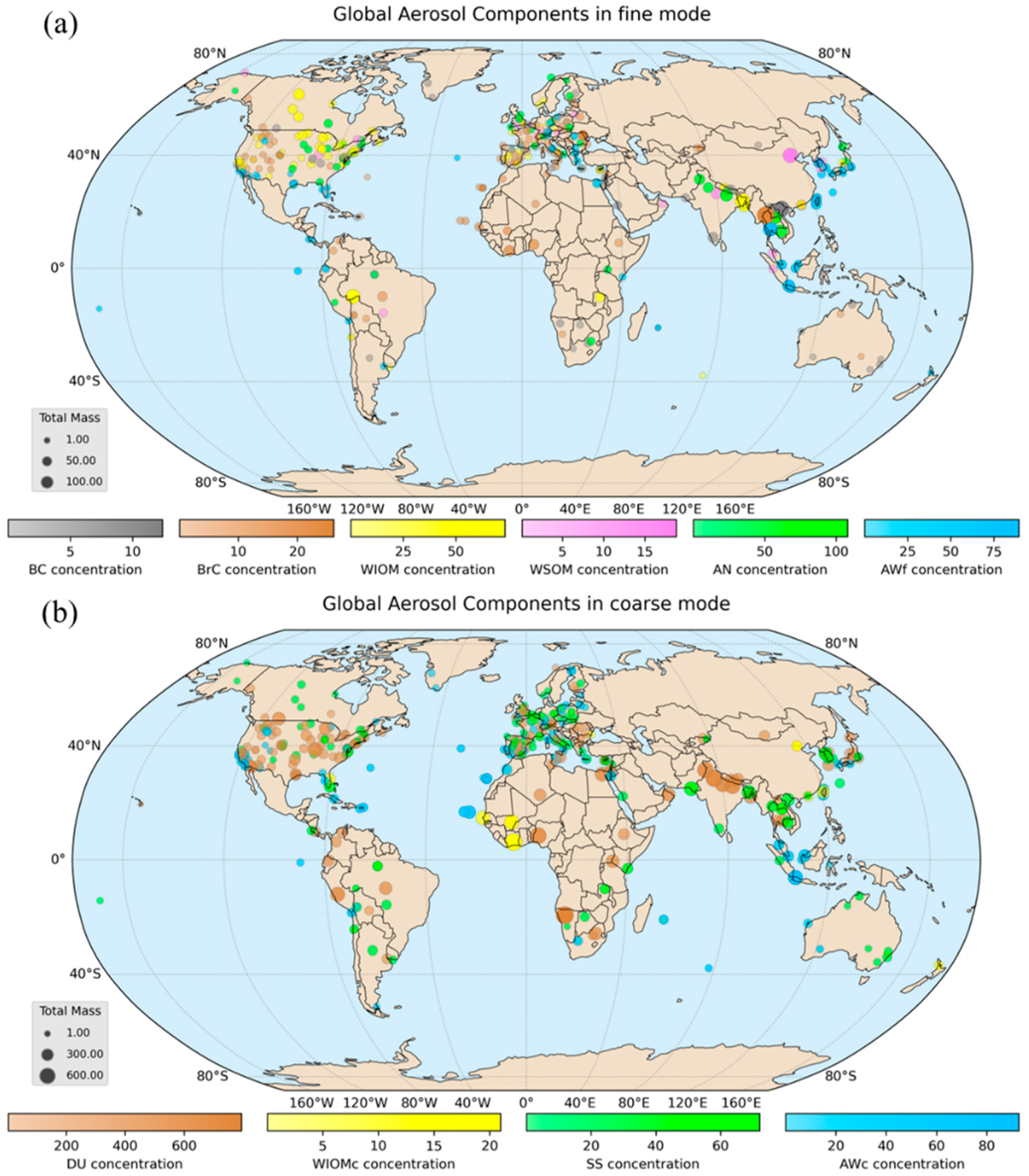
3.3. Aerosol Chemical Properties
3.4. Regional Properties of Aerosols
3.5. Comparison of Aerosol Properties in Hemispheres
3.6. The Observational Imbalance Induced the Global Mean Differences
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AOD | Aerosol Optical Depth |
| AODf | Fine-mode Aerosol Optical Depth |
| AODc | Coarse-mode Aerosol Optical Depth |
| AAOD | Absorbing Aerosol Optical Depth |
| SSA | Single Scattering Albedo |
| FMF | Fine-Mode Fraction (optical) |
| FMFv | Fine-Mode Volume Fraction |
| PVSD | Particle Volume Size Distribution |
| CRI | Complex Refractive Index |
| m | |
| n | Real part of CRI |
| k | Imaginary part of CRI |
| Kf,440 | Imaginary part of CRI in fine mode at 440 nm |
| δkf,440–675 | Imaginary part of the fine-mode aerosol CRI between 440 nm and 675 nm |
| A(λ) | Molar refractive index |
| RH | Relative Humidity |
| fi | Volume fraction of the ith component |
| BC | Black Carbon |
| BrC | Brown Carbon |
| OM | Organic Matter |
| WSOM | Water-Soluble Organic Matter |
| WIOMf | Water-Insoluble Organic Matter in fine mode |
| AN | Ammonium Nitrate |
| AWf | Aerosol Water content (fine mode) |
| DU | Dust |
| SS | Sea Salt |
| WIOMc | Water-Insoluble Organic Matter in coarse mode |
| AWc | Aerosol Water Content(coarse mode) |
| SLCF | Short-Lived Climate Forcer |
| MLMM | Multi-Component Liquid Mixture Model |
| AAC | Apparent Aerosol Component |
| AGS | Average of Global Sites |
| ARR | Average of IPCC AR6 regions |
| RTM | Radiation Transmission Model |
| MERRA-2 | Modern-Era Retrospective analysis for Research and Applications, Version 2 |
| GRASP | Generalized Retrieval of Aerosol and Surface Properties |
| POLDER | Polarization and Directionality of the Earth’s Reflectances |
| PARASOL | Polarization &Anisotropy of Reflectances for Atmospheric Sciences coupled with Observations from a Lidar |
| PHOTONS | PHOtométrie pour le Traitement Opérationnel de Normalisation Satellitaire |
| AE | Average Error |
| RMSE | Root-Mean-Square Error |
| RD | Relative Difference |
References
- Kasoar, M.; Shawki, D.; Voulgarakis, A. Similar spatial patterns of global climate response to aerosols from different regions. npj Clim. Atmos. Sci. 2018, 1, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuster, G.L.; Dubovik, O.; Arola, A. Remote sensing of soot carbon—Part 1: Distinguishing different absorbing aerosol species. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 1565–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aamaas, B.; Berntsen, T.K.; Fuglestvedt, J.S.; Shine, K.P.; Collins, W.J. Regional temperature change potentials for short-lived climate forcers based on radiative forcing from multiple models. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 10795–10809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, D.B.; Ault, A.P.; Moffet, R.C.; Ruppel, M.J.; Cuadra-Rodriguez, L.A.; Guasco, T.L.; Corrigan, C.E.; Pedler, B.E.; Azam, F.; Aluwihare, L.I.; et al. Impact of marine biogeochemistry on the chemical mixing state and cloud forming ability of nascent sea spray aerosol. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 8553–8565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, B.; Wilcox, L.J.; Highwood, E.J.; Sutton, R.T. Impacts of recent decadal changes in Asian aerosols on the East Asian summer monsoon: Roles of aerosol–radiation and aerosol–cloud interactions. Clim. Dyn. 2019, 53, 3235–3256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.H.; Adams, P.J.; Shindell, D.T. Evaluation of the global aerosol microphysical ModelE2-TOMAS model against satellite and ground-based observations. Geosci. Model. Dev. 2015, 8, 631–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Shawki, D.; Voulgarakis, A.; Kasoar, M.; Samset, B.H.; Myhre, G.; Forster, P.M.; Hodnebrog, O.; Sillmann, J.; Aalbergsjo, S.G.; et al. A PDRMIP multi-model study on the impacts of regional aerosol forcings on global and regional precipitation. J. Clim. 2018, 31, 4429–4447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persad, G.; Burney, J.A.; Burke, M.; Heft-Neal, S.; Bendavid, E.; Proctor, J.; Caldeira, K. Dependence of the Global Burden of Aerosol-Driven Societal Impacts on the Geographic Location of Emissions. In Proceedings of the AGU Fall Meeting Abstracts; American Geophysical Union: Washington, DC, USA, 2018; p. GH11C-0924. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.; Dubovik, O.; Schuster, G.L.; Chin, M.; Henze, D.K.; Lapyonok, T.; Li, Z.; Derimian, Y.; Zhang, Y. Multi-angular polarimetric remote sensing to pinpoint global aerosol absorption and direct radiative forcing. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 7459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.S.; Li, Z.Q.; Zhang, Y.X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, D.H.; Li, K.T.; Xu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.Q.; Chen, X.F.; et al. Estimation of atmospheric aerosol composition from ground-based remote sensing measurements of Sun-sky radiometer. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2017, 122, 498–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, Z.; Chen, Y.; de Leeuw, G.; Zhang, C.; Xie, Y.; Li, K. Improved inversion of aerosol components in the atmospheric column from remote sensing data. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 12795–12811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, Z.; Sun, Y.; Lv, Y.; Xie, Y. Estimation of atmospheric columnar organic matter (OM) mass concentration from remote sensing measurements of aerosol spectral refractive indices. Atmos. Environ. 2018, 179, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Li, D.; Qie, L.; Che, H.; Xu, H. Estimation of aerosol complex refractive indices for both fine and coarse modes simultaneously based on AERONET remote sensing products. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2017, 10, 3203–3213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yan, C.; Li, Z.; Gu, H.; Xie, Y. Development of a multiple solution mixing mechanism based aerosol component retrieval method for polarimetric satellite measurements. Atmos. Environ. 2025, 349, 121120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Gu, X.; Wang, L.; Li, D.; Xie, Y.; Li, K.; Dubovik, O.; Schuster, G.; Goloub, P.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Aerosol physical and chemical properties retrieved from ground-based remote sensing measurements during heavy haze days in Beijing winter. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 10171–10183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Li, L.; Zhang, F.; Li, D.; Xie, Y.; Xu, H. Comparison of aerosol properties over Beijing and Kanpur: Optical, physical properties and aerosol component composition retrieved from 12 years ground-based Sun-sky radiometer remote sensing data. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2015, 120, 1520–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Li, Z.; Li, L.; Wang, L.; Li, D.; Chen, C.; Li, K.; Xu, H. Study on influence of different mixing rules on the aerosol components retrieval from ground-based remote sensing measurements. Atmos. Res. 2014, 145, 267–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, Y.; Li, Z.; Chen, C.; Zhang, Y.; Li, K.; Shi, Z.; Dong, J.; Xu, H.; Peng, Z.; Xie, Y.; et al. Evaluation of MERRA-2 Aerosol Optical and Component Properties over China Using SONET and PARASOL/GRASP Data. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubovik, O.; Herman, M.; Holdak, A.; Lapyonok, T.; Tanré, D.; Deuzé, J.L.; Ducos, F.; Sinyuk, A.; Lopatin, A. Statistically optimized inversion algorithm for enhanced retrieval of aerosol properties from spectral multi-angle polarimetric satellite observations. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2011, 4, 975–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Che, H.; Derimian, Y.; Dubovik, O.; Schuster, G.L.; Chen, C.; Li, Q.; Wang, Y.; Guo, B.; Zhang, X. Retrievals of fine mode light-absorbing carbonaceous aerosols from POLDER/PARASOL observations over East and South Asia. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 247, 111913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Che, H.; Zhang, X.; Chen, C.; Chen, X.; Gui, K.; Liang, Y.; Wang, F.; Derimian, Y.; Fuertes, D.; et al. A satellite-measured view of aerosol component content and optical property in a haze-polluted case over North China Plain. Atmos. Res. 2022, 266, 105958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, Y.; Li, L.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Dubovik, O.; Derimian, Y.; Chen, C.; Fuertes, D.; Xie, Y.; Lopatin, A.; et al. Spatio-Temporal Variability of Aerosol Components, Their Optical and Microphysical Properties over North China during Winter Haze in 2012, as Derived from POLDER/PARASOL Satellite Observations. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Li, Z.; Ji, Z.; Xie, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, Z.; Shi, Z.; Qie, L.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Z.; et al. Improvement of Space-Observation of Aerosol Chemical Composition by Synergizing a Chemical Transport Model and Ground-Based Network Data. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 4390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Xie, Y.; Xu, H.; Yan, C.; Hu, T.; Li, Z. Inversion of the global carbonaceous aerosol components (CACs) based on ground-based remote sensing of AERONET. Environ. Int. 2025, 198, 109432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuster, G.L.; Lin, B.; Dubovik, O. Remote sensing of aerosol water uptake. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2009, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holben, B.N.; Eck, T.F.; Slutsker, I.; Tanré, D.; Buis, J.P.; Setzer, A.; Vermote, E.; Reagan, J.A.; Kaufman, Y.J.; Nakajima, T.; et al. AERONET—A Federated Instrument Network and Data Archive for Aerosol Characterization. Remote Sens. Environ. 1998, 66, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubovik, O.; King, M.D. A flexible inversion algorithm for retrieval of aerosol optical properties from Sun and sky radiance measurements. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2000, 105, 20673–20696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubovik, O.; Holben, B.; Eck, T.F.; Smirnov, A.; Kaufman, Y.J.; King, M.D.; Tanré, D.; Slutsker, I. Variability of Absorption and Optical Properties of Key Aerosol Types Observed in Worldwide Locations. J. Atmos. Sci. 2002, 59, 590–608. Available online: https://journals.ametsoc.org/view/journals/atsc/59/3/1520-0469_2002_059_0590_voaaop_2.0.co_2.xml (accessed on 29 October 2025). [CrossRef]
- Dubovik, O.; Smirnov, A.; Holben, B.N.; King, M.D.; Kaufman, Y.J.; Eck, T.F.; Slutsker, I. Accuracy assessments of aerosol optical properties retrieved from Aerosol Robotic Network (AERONET) Sun and sky radiance measurements. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2000, 105, 9791–9806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arola, A.; Schuster, G.; Myhre, G.; Kazadzis, S.; Dey, S.; Tripathi, S.N. Inferring absorbing organic carbon content from AERONET data. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 215–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Li, Z.; Tian, Q.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, Y.; Li, D.; Li, K.; Li, L. Estimate of aerosol absorbing components of black carbon, brown carbon, and dust from ground-based remote sensing data of sun-sky radiometers. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 6534–6543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Zheng, Y.; Shen, X.; Xing, L.; Che, H. Global Aerosol Classification Based on Aerosol Robotic Network (AERONET) and Satellite Observation. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafar, Q.; Zafar, S.; Holben, B. Seasonal assessment and classification of aerosols transported to Lahore using AERONET and MODIS deep blue retrievals. Int. J. Climatol. 2018, 38, 1022–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeb, B.; Alam, K.; Khan, R.; Ditta, A.; Iqbal, R.; Elsadek, M.F.; Raza, A.; Elshikh, M.S. Characteristics and optical properties of atmospheric aerosols based on long-term AERONET investigations in an urban environment of Pakistan. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 8548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, B.; Liu, K. A comparative time series analysis and modeling of aerosols in the contiguous United States and China. Sci. Total Env. 2019, 690, 799–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, V.; Ghosh, S.; Bilal, M.; Dey, S.; Singh, S. Performance of MODIS C6.1 Dark Target and Deep Blue aerosol products in Delhi National Capital Region, India: Application for aerosol studies. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2021, 12, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- She, L.; Xue, Y.; Guang, J.; Mei, L.; Che, Y.; Li, Y.; Fan, C. Aerosol optical and physical properties over beijing. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Fort Worth, Texas, USA, 23–28 July 2017; pp. 5962–5965. [Google Scholar]
- Bui, T.H.; Nguyen, D.L.; Nguyen, H.H. Study of aerosol optical properties at two urban areas in the north of Vietnam with the implication for biomass burning impacts. Env. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2022, 29, 41923–41940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bond, T.C.; Rood, M.J.; Riemer, N. Isolating Weakly and Strongly-Absorbing Classes of Carbonaceous Aerosol: Optical Properties, Abundance and Lifecycle; University of Illinois at Urbana Champaign: Urbana, IL, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, Y.; Ramanathan, V.; Kotamarthi, V.R. Brown carbon: A significant atmospheric absorber of solar radiation? Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 8607–8621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osborne, S.R.; Johnson, B.T.; Haywood, J.M.; Baran, A.J.; Harrison, M.A.J.; McConnell, C.L. Physical and optical properties of mineral dust aerosol during the Dust and Biomass-burning Experiment. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2008, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brocchi, V.; Krysztofiak, G.; Catoire, V.; Guth, J.; Marécal, V.; Zbinden, R.; El Amraoui, L.; Dulac, F.; Ricaud, P. Intercontinental transport of biomass burning pollutants over the Mediterranean Basin during the summer 2014 ChArMEx-GLAM airborne campaign. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 6887–6906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- San-Miguel-Ayanz, J.; Durrant, T.; Boca, R.; Maianti, P.; Libertà, G.; JACOME, F.O.; Branco, A.; DE, R.; Suarez-Moreno, M.; Ferrari, D. Forest Fires in Europe, Middle East and North Africa 2022; JRC Publications Repository: Brussels, Belgium, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- He, C.; Miljevic, B.; Crilley, L.R.; Surawski, N.C.; Bartsch, J.; Salimi, F.; Uhde, E.; Schnelle-Kreis, J.; Orasche, J.; Ristovski, Z.; et al. Characterisation of the impact of open biomass burning on urban air quality in Brisbane, Australia. Environ. Int. 2016, 91, 230–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandey, A.; Patel, S.; Pervez, S.; Tiwari, S.; Yadama, G.; Chow, J.C.; Watson, J.G.; Biswas, P.; Chakrabarty, R.K. Aerosol emissions factors from traditional biomass cookstoves in India: Insights from field measurements. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 13721–13729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sethi, S.S.; Vinoj, V. Transported dust modulates aerosol pollution domes over rapidly urbanizing Indian cities. Commun. Earth Environ. 2025, 6, 554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.Y.; Bauer, S.E.; Tsigaridis, K.; Im, U. Global Influence of Organic Aerosol Volatility on Aerosol Microphysical Processes: Composition and Number. J. Adv. Model. Earth Syst. 2024, 16, e2023MS004185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Li, Z.; Li, L.; Wagener, R.; Abboud, I.; Li, K.; Li, D.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, X.; Xu, H. Aerosol optical, microphysical, chemical and radiative properties of high aerosol load cases over the Arctic based on AERONET measurements. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 9376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Yang, Z.; Yan, C.; Hu, T.; Xie, Y.; Chen, Y.; Xu, H. The Global Spatial Pattern of Aerosol Optical, Microphysical and Chemical Properties Derived from AERONET Observations. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 3624. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17213624
Zhang Y, Wang Q, Yang Z, Yan C, Hu T, Xie Y, Chen Y, Xu H. The Global Spatial Pattern of Aerosol Optical, Microphysical and Chemical Properties Derived from AERONET Observations. Remote Sensing. 2025; 17(21):3624. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17213624
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Ying, Qiyu Wang, Zhuolin Yang, Chaoyu Yan, Tong Hu, Yisong Xie, Yu Chen, and Hua Xu. 2025. "The Global Spatial Pattern of Aerosol Optical, Microphysical and Chemical Properties Derived from AERONET Observations" Remote Sensing 17, no. 21: 3624. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17213624
APA StyleZhang, Y., Wang, Q., Yang, Z., Yan, C., Hu, T., Xie, Y., Chen, Y., & Xu, H. (2025). The Global Spatial Pattern of Aerosol Optical, Microphysical and Chemical Properties Derived from AERONET Observations. Remote Sensing, 17(21), 3624. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17213624






