Highlights
What are the main findings?
- Dual-polarization radar significantly improves quantitative precipitation estimation (QPE) accuracy by utilizing polarimetric variables such as differential reflectivity (ZDR) and specific differential phase (KDP), which provide essential microphysical information about precipitation particles.
- Advanced QPE methods—including composite, hydrometeor classification-based, and drop size distribution (DSD) retrieval approaches—effectively mitigate the uncertainties associated with traditional reflectivity–rain rate (R(ZH)) estimators, especially under diverse precipitation types and conditions.
What is the implication of the main finding?
- The integration of dual-polarization radar data into operational QPE systems (e.g., MRMS in the U.S., SWAN in China, and the French radar network) enhances real-time precipitation monitoring and forecasting, supporting improved hydrological prediction and disaster preparedness.
- Despite progress, challenges remain in complex terrain, snow estimation, and the quality control of polarimetric variables, highlighting the need for continued research and development to achieve a higher accuracy and reliability in global precipitation measurement.
Abstract
Quantitative precipitation estimation (QPE) is one of the primary applications of weather radar. Over the last several decades, dual-polarization radars have significantly improved QPE accuracy by providing additional observational variables that offer more microphysical information about precipitation particles. In this work, we review QPE methods for dual-polarization radars and summarize their advantages and disadvantages from both theoretical and practical perspectives. The development paths and current status of operational QPE systems in the United States, China, and France are examined. We demonstrate how dual-polarization radars have improved QPE accuracy in these systems not only directly through the application of polarimetric QPE methods, but also indirectly through the more accurate identification of non-meteorological echoes, the mitigation of the partial blockage effect, and the detection of melting layers. The challenges are discussed for dual-polarization radar QPE, including the quality of polarimetric variables, QPE quality in complex terrain, estimation of surface precipitation with observations within or above the melting layer, and polarimetric QPE methods for snow.
1. Introduction
Heavy precipitation and associated hazards, such as floods, urban waterlogging, landslides, and debris flows, have caused massive economic losses and casualties worldwide each year. High-quality precipitation measurements are essential for weather and hydrological forecasting, which are also beneficial for governments in formulating policies to prevent or reduce the damages caused by heavy precipitation.
Ever since the introduction of radar into weather monitoring, quantitative precipitation estimation (QPE) has been one of the primary applications. Over the past few decades, many countries have established national radar networks. Initially, these radars were single-polarization radars, which provide only the variable of reflectivity (ZH) that is related to precipitation microphysics, such as particle number concentration and size. After the pioneering work of Seliga and Bringi [1] in measuring rain rates via polarimetric measurements, numerous QPE studies have emerged using dual-polarization radar observations. In 2012, the United States completed the upgrade of its Next Generation Weather Radar network to dual-polarization radars, while other countries such as China, Australia, and Japan are still in the process of upgrading.
In addition to the reflectivity, ZH, dual-polarization radar observations can provide the differential reflectivity (ZDR), the differential phase (ΦDP) and its range derivative specific differential phase (KDP), and the correlation coefficient (CC) in simultaneous transmission/reception (SHV) mode, which significantly improves QPE accuracy. The linear depolarization ratio (LDR) is another polarimetric variable available in the H (horizontal) transmitted and simultaneous H and V (vertical) received (HSHV) mode. As the SHV mode is preferred for operational use and LDR is primarily used to study the particle orientation [2], we focused our discussion on the SHV mode in this study.
The purpose of this paper is to concisely summarize the QPE methods, operational applications, and future challenges of dual-polarization radars. In Section 2, we introduce the radar QPE principles, the prevailing radar QPE methods, and their advantages and disadvantages. Section 3 presents the development history of radar QPE systems, structure considerations, and the current status in several countries. Section 4 discusses the main challenges in operational applications and suggests potential pathways.
2. Dual-Polarization Radar QPE: Principles
In this section, various prevailing QPE methods (Table 1) based on dual-polarization radar observations were reviewed, demonstrating their performances in improving the QPE accuracy. In addition to these QPE methods, it should be noted that polarimetric variables can also improve the QPE accuracy in other ways: (1) the identification of non-precipitation echoes is more accurate and their effects on QPE are mitigated; (2) some polarimetric variables (ΦDP and KDP) are almost immune to radar miscalibration, partial beam blockage, and attenuation; and (3) polarimetric variables are helpful in improving the accuracy of ZH by providing more reliable methods for attenuation correction.

Table 1.
Comparison of primary dual-polarization radar QPE methods.
2.1. The ZH-R Estimator
The ZH-R (rain rate) estimator (R(ZH) hereinafter) is the most widely used radar QPE method worldwide. For the single-polarization radars, R(ZH) is the only way to estimate rain rates due to the fact that ZH is the sole variable providing particle size and number concentration. In radar meteorology, the R(ZH) estimator is generally not considered as a polarimetric radar QPE method because it was developed before the introduction of dual-polarization radar observations in weather surveillance. However, ZH is a variable provided by dual-polarization radars, and therefore the R(ZH) estimator is also one of the most important radar QPE methods for dual-polarization radars. Early studies on the R(ZH) estimator can be dated back to the mid-20th century. In 1947, Marshall et al. [3] proposed the empirical relationship between ZH and R, and R can be estimated by measuring the reflectivity factor (Zh) in the following form:
where Zh is the linear form of ZH. The parameters a and b are constants determined empirically, which were 190 and 1.72, respectively. Later, Marshall et al. [4] slightly revised the values of a and b to 200 and 1.6, respectively, which becomes the classic R(ZH) relationship and is still widely used for the stratiform precipitation estimation.
The accuracy of the R(ZH) estimator is affected by various sources. One is the accuracy of ZH, which usually suffers from miscalibration and attenuation issues. The calibration of ZH is especially crucial for the QPE of heavy precipitation. A radar with a cold (hot) observation of ZH will result in an underestimation (overestimation) of QPE. Traditionally, ZH is usually calibrated by observing a target of known reflectivity, such as a metal sphere. Such methods were well reviewed by Atlas [5]. After the development of dual-polarization radar, researchers found that ZH and two polarimetric variables ZDR and KDP, are not independent. Therefore, ZH can be roughly estimated using ZDR and KDP, and the differences between the observed and estimated ZH can be considered as the ZH bias. Several calibration methods based on this idea were proposed for the polarimetric radar [6,7,8,9,10]. With well-calibrated radars, the systematic bias of QPE is eliminated.
Attenuation is another issue that causes ZH bias. Attenuation can result in the underestimation of QPE, especially for radars operating at shorter wavelengths, such as X- or C-band radar. Attenuation correction for ZH should be applied before generating the radar QPE. The key point of applying attenuation correction is to calculate the path-integrated attenuation, which is proportional to the change in the differential phase, so path-integrated attenuation can be estimated using dual-polarization radar measurement of the differential phase. Many attenuation methods were proposed based on the differential phase, including the linear correction method [11], Z-PHI method [12], self-consistent with constraint method [13], hot-spot method with special attention on heavy convective cells [14], and many others [15,16]. Numerous studies have investigated the performance of attenuation correction methods [12,17,18,19,20]. With applying attenuation correction methods, the underestimation of QPE due to attenuation is significantly reduced.
The accuracy of the R(ZH) estimator is also affected by the drop size distribution (DSD) variability, because the DSD determines the parameters a and b in R(ZH), and the DSD varies in different climatological regions, seasons, and precipitation types [21,22,23,24]. Methods to obtain parameters generally can be referred to as the direct methods and the indirect methods [25]. The direct methods use reflectivity observed by radar and gauge-measured rain rates to obtain parameters. For example, parameters a and b can be calculated with a nonlinear fitting method by comparing gauge-measured rain rates to corresponding radar reflectivity pixels that sit above these rain gauges. The indirect method does not involve radar, while the reflectivity and rain rates are calculated from the DSD information collected by disdrometers. Both the direct and the indirect methods have some limitations in practice. In the direct method, the reflectivity observed by radars and the corresponding rain rates recorded by rain gauges are not collocated. As raindrops fall from the sky, they may experience changes in DSD due to break up, coalescence, evaporation, and drop sorting by updrafts [26]. Therefore, the DSD at the ground may be different from the altitude at which the radar samples it. In addition, the sampling volume of a radar is larger than that of rain gauges, so the rain rates obtained by rain gauges may not be representative of those sampled by a radar. As for the indirect method, the main shortcoming is insufficient DSD samples. Few countries have a national disdrometer network dense enough to provide sufficient DSD samples within their territory.
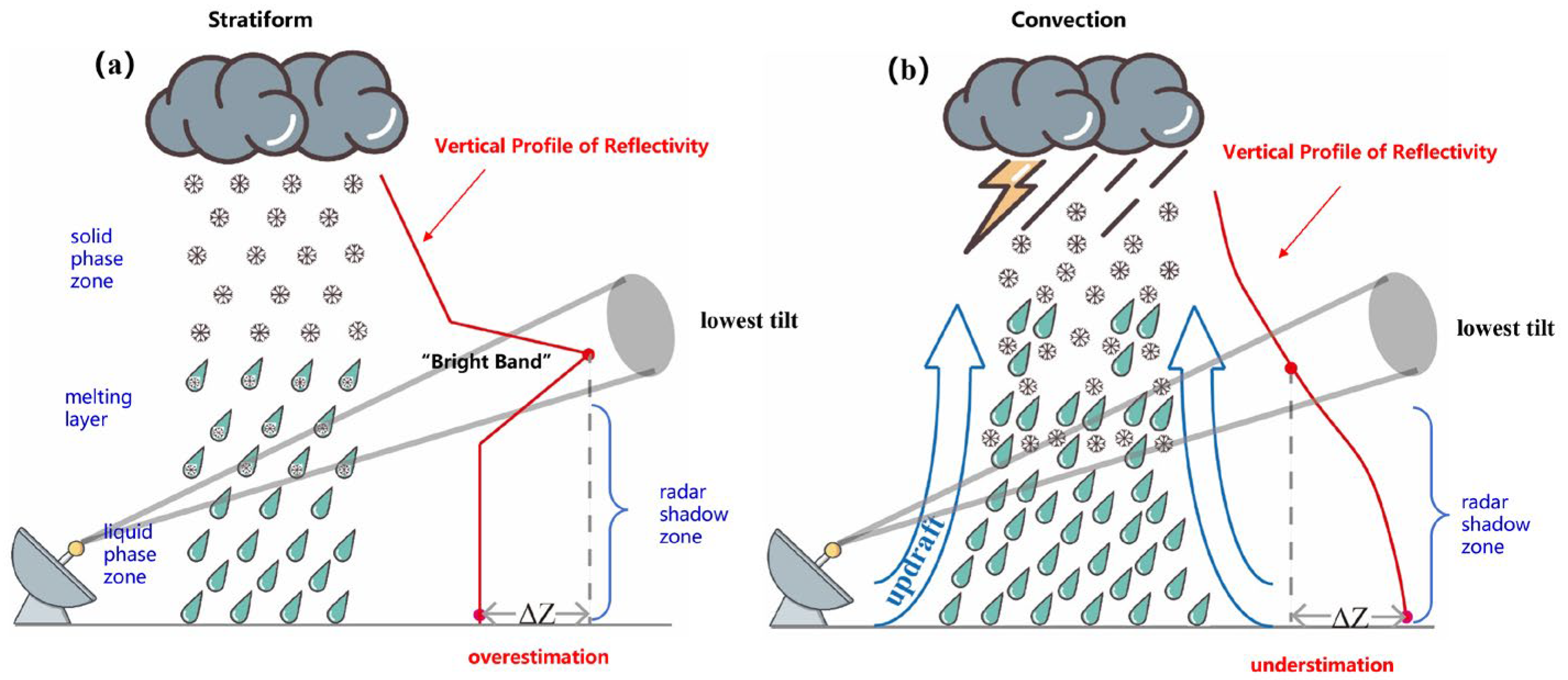
There has been a considerable amount of work on obtaining suitable R(ZH) estimator parameters. Some suggested the use of climatological radar and rain gauge data [27,28,29], and this approach provides a suitable R(ZH) estimator relationship for QPE in a long period. However, for a particular precipitation event, if its DSD characteristics differ greatly from the climatological state, the QPE may have a large bias. One approach is to use adaptive R(ZH) estimator parameters, where a and b values vary from time to time [30,31,32,33]. Radar data and rain gauge data close to the time of analysis (e.g., within one hour of the analysis) are used to obtain parameters. The main problem is the representativeness of the obtained parameters. As these parameters are usually derived from data within a short period of time, the lack of samples may result in unrepresentative parameters, which will lead to instability in the performance of the QPE. Another conventional approach is to use different R(ZH) estimator parameters for different precipitation types, as convection, stratiform, and tropical precipitation exhibit distinctly different DSDs. The accuracy of this approach relies heavily on the correct classification of precipitation types. Some studies proposed precipitation classification schemes based on the difference in the reflectivity field for different precipitation types, including reflectivity intensity, homogeneity, and vertical structure [34,35,36,37,38,39,40]. The bright band, caused by the snow melting to rain, leads to the enhancement in radar reflectivity. The bright band contamination must be eliminated, or the QPE will be greatly overestimated (Figure 1a). Numerous studies were conducted to identify the bright band [41,42,43,44,45,46,47,48,49,50]. Then, the correction of the vertical profile of reflectivity (VPR) can be applied to mitigate the overestimation of QPE due to the bright band [43,46,47,51,52]. On the other hand, convection usually leads to an underestimation of QPE due to the enhancement of precipitation in the low level (Figure 1b); the VPR correction method for convection has also been proposed in recent years [53].
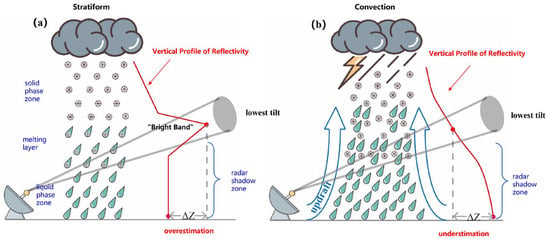
Figure 1.
Conceptual diagram for vertical profile of reflectivity: (a) stratiform, (b) convection.
It has been over half a century since the R(ZH) estimator was proposed. Despite its inherent limitation of being highly sensitive to DSD variability, the R(ZH) estimator remains the most widely used QPE estimator. The high DSD variability in heavy precipitation systems can lead to large errors in QPE using the R(ZH) estimator. However, the R(ZH) estimator can provide stable QPE when the polarimetric signals are weak, and it is the dominant method to estimate surface rain rates at the surface with measurements in or above the melting layer.
2.2. Polarimetric Estimators
Since the introduction of dual-polarization radars into meteorological monitoring, one of the primary goals of the dual-polarization radar is to estimate rain rates with polarimetric variables. In addition to ZH, dual-polarization radars provide polarimetric variables such as ZDR, KDP, and CC, which can inform the size and number concentration of particles. When these polarimetric variables are introduced into the QPE estimator, the high uncertainty of the R(ZH) estimator due to the DSD variability can be mitigated. Among the four variables (ZH, ZDR, KDP, and CC), CC provides little information about particle shape and is usually used to identify non-meteorological echoes and hydrometeors, leaving ZH, ZDR, and KDP for the construction of polarimetric estimators. Furthermore, as ZDR is the ratio of the power estimates for horizontal and vertical polarization signals, it does not contain information about particle concentration and therefore cannot be used alone to estimate rain rates.
The R(ZH, ZDR) estimator was firstly proposed by Seliga et al. [54]. The common form of the R(ZH, ZDR) estimator is as in Equation (2):
where Zdr is the linear form of ZDR. The R(ZH, ZDR) estimator can be considered as an R(ZH) estimator with the adjustment of the particle size information provided by ZDR. Numerous studies were conducted to evaluate the performance of R(ZH, ZDR) in different regions, seasons, and precipitation systems [55,56,57]. These results suggested that R(ZH, ZDR) provided a more accurate estimation of rain rates, especially for R with larger rain rates (e.g., larger than 20 mm h−1 [56]). In practice, the performance of R(ZH, ZDR) could be strongly influenced by the accuracy of the observed ZDR. ZDR should be well-calibrated within at least ± 0.2 dB [54,58]. In addition, ZDR signals are weak in light rain compared to noise, which can cause instability in R(ZH, ZDR). As mentioned in the previous section, attenuation issues affect the accuracy of ZDR, especially in heavy precipitation with short-band radars (e.g., X- or C-band), and so attenuation correction should be performed and evaluated before utilizing the R(ZH, ZDR) estimator.
Later, Seliga and Bringi [59] suggested that the KDP could be used to estimate rain rates. The R(KDP) estimator that we use nowadays was proposed by Sachidananda et al. [60] with the following form:
R(KDP) is less sensitive to the DSD variability than R(ZH) and therefore performs better at higher rain rates [61]. The performance of R(KDP) was tested in numerous studies, and the results showed significant improvements over the R(ZH) estimator [62,63,64,65]. In practice, R(KDP) has advantages in the following aspects: (1) KDP is immune to radar miscalibration, attenuation, and partial beam blockage; (2) the presence of hail does not significantly affect the performance of R(KDP) as it does for the R(ZH) and R(ZH, ZDR) estimators [66,67]; and (3) it is less affected by the ground clutter and anomalous propagation [68]. However, shortcomings of R(KDP) include (1) the KDP is noisy in light rain, the performance of the R(KDP) for light rain is pretty poor, and the rain field seems to be “unnatural”; (2) the R(KDP) degrades the radial resolution because KDP is usually estimated using the fitting methods with the differential phase within a certain range, and requires smoothing along the radial; and (3) the accuracy of R(KDP) is strongly influenced by the accuracy of KDP. The “intrinsic” KDP, defined as half of the slope of two adjacent differential phases along the radial, is usually noisy, and should therefore be carefully processed before using it for QPE. Several methods were proposed to estimate KDP with mathematical or/and physical constraints [69,70,71,72].
The R(KDP,ZDR) estimator was proposed by Jameson [73], with the common form of this estimator used nowadays as follows:
Ryzhkov et al. [62] evaluated the performance of R(KDP, ZDR). Their simulation suggested that R(KDP, ZDR) significantly outperformed R(ZH, ZDR) and R(KDP) for moderate and heavy rains. Later, the performance of R(KDP, ZDR) was evaluated against gauges using radars of different bands and in different regions [63,74,75,76]. Theoretically, R(KDP, ZDR) should outperform R(KDP) because it is less sensitive to DSD variability. However, in operational systems, R(KDP, ZDR) shows only modest improvements over R(KDP) [62,63,77], as measurement errors in ZDR may hinder the performance of R(KDP, ZDR). Similarly, R(KDP, ZDR) is prone to ZDR measurement errors such as miscalibration and attenuation. Therefore, in practice, R(KDP, ZDR) will not necessarily outperform R(KDP).
The estimator of R(ZH, Nw) was proposed by Testud et al. [12]. They found that estimating rain rates with ZH and the normalized concentration of raindrops Nw was remarkably insensitive to the DSD variability. The common form of R(ZH, Nw) is as follows:
where Nw is in m−3 mm−1. This estimator was tested using simulation and radar data, with limited results suggesting that it outperforms R(KDP) or R(ZH) [12,78]. Furthermore, this method does not require the smoothing process along the radial as R(KDP) typically does. An accurate estimation of Nw is the critical step in this method. If the radar does not encounter attenuation issues (e.g., for S-band radar or light rain for C-band radar), the “Z-ZDR” technique proposed by Ilingworth et al. [79] can be utilized to estimate Nw. Otherwise, the “ZPHI” method proposed by Testud et al. [12] should be used to estimate Nw [80]. The R(ZH, Nw) method can be performed under attenuation conditions, but it is susceptible to other reflectivity problems, such as miscalibration, bright band contamination, and partial beam blockage.
Similarly, Ryzhkov et al. [81] suggested that R(KDP, Nw) is the least sensitive to the DSD variability. However, to the best of our knowledge, this method has not yet been evaluated with radars and rain gauges.
Atlas et al. [82] suggested that the specific attenuation A is linearly related to the rain rate and is relatively insensitive to the DSD variability. Therefore, Ryzhkov et al. [83] suggested using A to estimate the rain rates. The form of the R(A) estimator is as follows:
where coefficient a depends on the radar wavelength and the temperature, while b is almost constant for a given wavelength but varies with wavelength. The value of A can be estimated with the “ZPHI” method. The coefficients a and b in the R(A) method are practically unaffected by the DSD variability (at least for S-band radars), but not for the estimation of A. In the “ZPHI” method, the estimation of A requires a knowledge of the path-integrated attenuation, which is estimated from the total differential phase along the propagation path:
where PIA is the abbreviation of the path-integrated attenuation and the parameter is the net ratio of A and KDP, and is affected by DSD and temperature. The value of is critical for the estimation of A. Studies showed that depends on the slope of Zdr, and the method to estimate with ZH and Zdr was proposed [84,85]. The performance of R(A) was evaluated with the radar of different bands for different precipitation situations [86,87,88]. The results suggested that the R(A) estimator was able to provide accurate and robust precipitation estimations and outperformed the R(ZH) estimator.
The advantages of the R(A) estimator are as follows: (1) its low sensitivity to the DSD variability; (2) it is immune to radar miscalibration, attenuation, partial beam blockage, and wet radome; (3) it provides high-radial-resolution precipitation estimates (KDP-based estimators degrade radial resolution); and (4) it performs uniformly well in both light and heavy rain (the performance of KDP-based estimators might be unstable in light rain). The main disadvantage of R(A) is that it requires temperature information to estimate attenuation A. Temperature information is usually provided by weather stations or numerical models. If the temperature changes significantly along the propagation path (e.g., crossing fronts), the estimate of A may not be accurate, thereby hindering the performance of the R(A) estimator.
To our knowledge, the polarimetric estimators discussed above currently are applied only to liquid-phase particles in operational systems, meaning that they are only applicable within a limited distance from the radar site in the radar scan domain. Using polarimetric variables in or above the melting layer to estimate surface rain rates is challenging because, when ice or mixed-phase particles fall, their sizes, densities, shapes, orientations, and terminal velocities will also change, while the changes in the polarimetric variables along with them are not yet well understood. Kumjian et al. [89] presented the conceptual vertical profiles of polarimetric variables for ice and snow in different microphysical processes (i.e., vapor deposition, aggregation, riming, sublimation, refreezing, and melting). However, when these processes are combined in the precipitation system, the vertical profiles of polarimetric variables become much more complicated, and more research is needed.
2.3. Composite Methods
Since all estimators discussed above have advantages and disadvantages in different situations, it is natural to utilize different estimators in different situations to promote the advantages of each estimator while avoiding limitations. This idea was first proposed by Chandrasekar et al. [90]. Ryzhkov et al. [75] showed that the composite method they proposed outperformed R(ZH), R(ZH, ZDR), and R(KDP). Since then, many composite methods have been proposed for different wavelength radars in different regions [76,77,91,92,93].
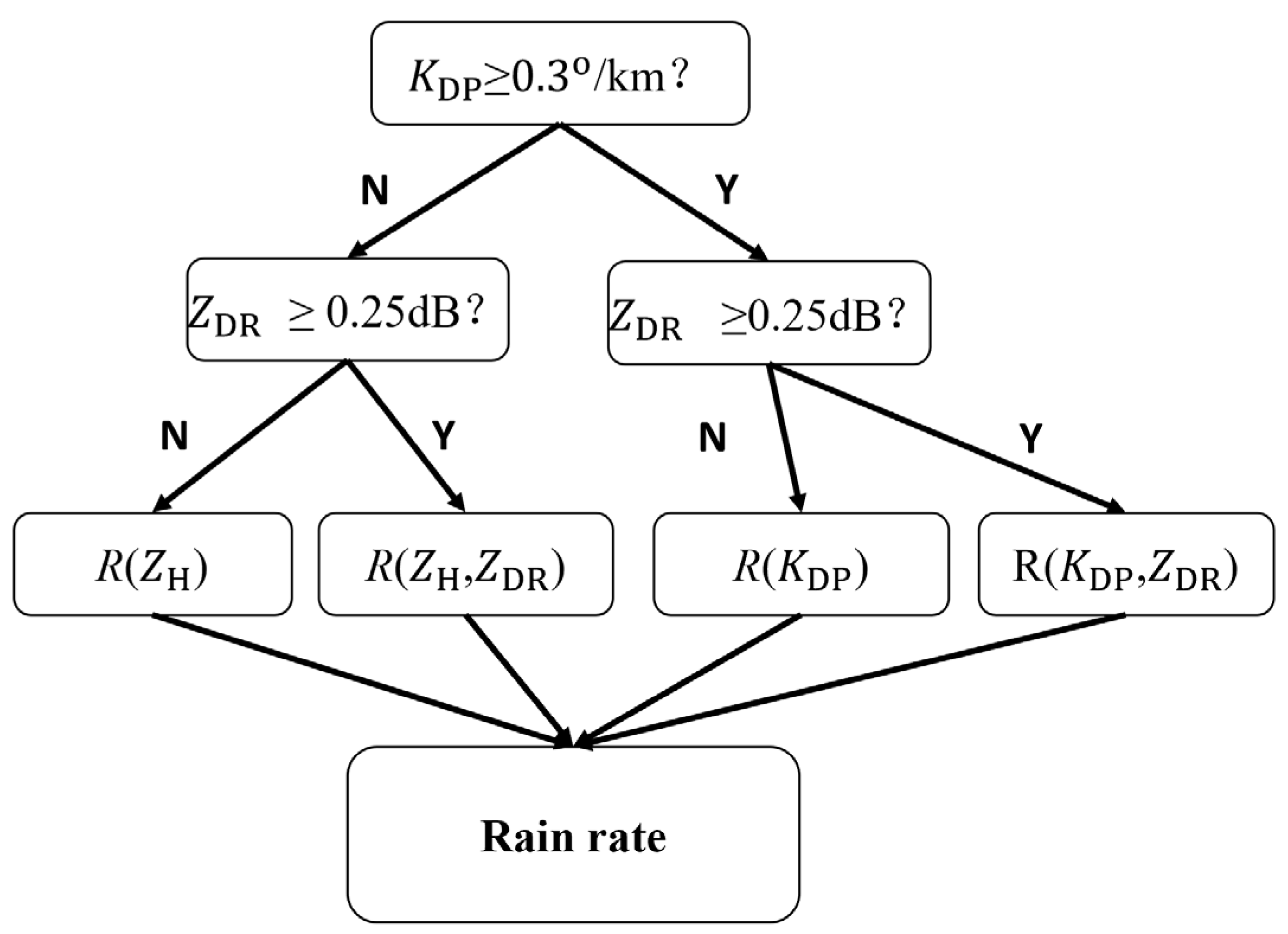
The criteria in those composite methods are different, but the logic behind them is similar. Ryzhkov et al. [75] suggested using different estimators for different rain rates. R(ZH) is used when the rain is light, while polarimetric estimators are used for moderate or heavy rain. In their approach, R(ZH) and polarimetric estimators are combined to produce smooth precipitation fields for light rain and accurate estimation for moderate and heavy precipitation. Cifelli et al. [77] and Chen et al. [92] applied the same approach to radar QPE. Later, Thompson et al. [76] suggested using different estimators depending on the magnitude of the polarimetric variables. KDP-based estimators (i.e., R(KDP) or R(KDP,ZDR)) are used when KDP exceeds a certain threshold (0.3°/km in their paper for the X/C/S band); otherwise, ZH-based estimators (i.e., R(ZH) or R(ZH, ZDR)) are used. If ZDR exceeds a certain threshold (0.25 dB in their work for the X/C/S band), ZDR-based estimators (i.e., R(ZH,ZDR) or R(KDP,ZDR)) are used; otherwise, estimators without ZDR (i.e., R(ZH) or R(KDP)) are used. This method is based on the fact that, when the polarimetric variable signal is weak (i.e., close to 0), the polarimetric variable observation may be contaminated by noise and not accurate, so it should be excluded from QPE. An example of the flowchart for composite methods is shown in Figure 2.
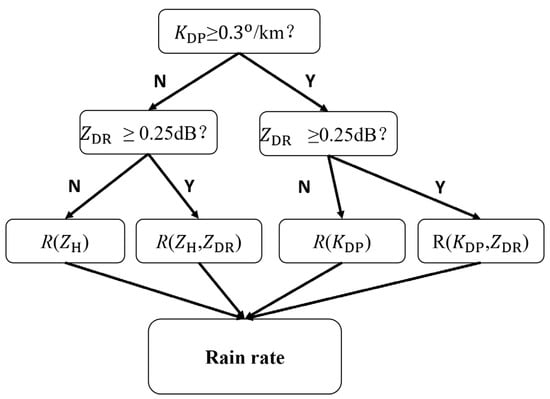
Figure 2.
Flowchart for the composite method adapted from [94].
Composite methods combine the advantages of different estimators, resulting in stable and accurate QPE products. To produce better QPE products, the criteria for composite methods should be carefully set based on the results of numerous tests.
2.4. Hydrometeor Classification-Based Methods
With polarimetric variables, dual-polarization radars can classify radar echoes more accurately than single-polarization radars. Early attempts at hydrometeor classification work can be dated back to the 1980s [95]; they detected hail with ZH and ZDR variables. Since QPE estimators and/or their parameters are different in each hydrometeor, it is natural to generate the radar QPE based on hydrometeor classification results. The hydrometeor classification-based method can be regarded as a kind of composite method, except that it applies different estimators based on the hydrometeor classification results. Giangrande et al. [96] proposed a QPE method based on the echo classification. They classified the radar echo into ten categories. Among these ten categories, two of them are non-meteorological echoes, four of them are rain, and the remaining four are solid-phase particles (e.g., graupel, snow, and ice crystals). The rain rate of non-meteorological echoes is set to 0; R(ZH, ZDR) is used for rain, R(KDP) is used with the presence of hail, and R(ZH) is used with different parameters for different solid-phase particles. The performance of this method was evaluated with different precipitation systems. The results suggest that this method outperformed the composite method proposed by Ryzhkov et al. [75] and all other methods based on a single estimator. A semi-supervised approach was proposed by Besic [97,98]. They used polarimetric radar clustering, guided by microphysical hypotheses, to classify hydrometeors through centroid-based labeling. Then, they extended this by introducing a bin-based de-mixing approach that estimates the proportions of different hydrometeor types in mixed radar volumes using entropy. This semi-supervised approach allows for a better handling of mixed hydrometeor types, improving the classification’s accuracy and operational efficiency. In typhoon events, however, Xia et al. [99] found that the performance of QPE with hydrometeor classification improved only slightly compared to the performance without it. It may be due to the precipitation type they evaluated (i.e., typhoon); rain is the predominant hydrometeor in typhoon systems, so QPE with or without hydrometeor classification has little effect on the accuracy.
Meanwhile, the performance of hydrometeor classification-based methods is highly dependent on the classification accuracy of radar echoes, and numerous methods on hydrometeor classification were proposed [100,101,102,103]. The logics of these methods are very similar: classifying echoes with polarimetric variables (ZH, ZDR, KDP, and CC) and their textures (standard deviation) using fuzzy logic methodology. In recent years, hydrometeor classification methods based on machine learning, neural networks, and deep-learning were proposed [104,105,106].
The disadvantages of hydrometeor classification-based methods are as follows: (1) using different estimators in different hydrometeor regions can lead to a discontinuity in rain rate field, especially when the hydrometeor classification jumps from rain to solid-phase particles; and (2) their performance depends heavily on the accuracy of the hydrometeor classification methods, which is still lacking in many assessments, especially for solid-phase particles due to the lack of observations.
2.5. DSD Retrieval-Based Methods
As stated above, one of the prime errors of QPE comes from the DSD variability. As DSD contains all the information needed to calculate rain rates, it is more natural and accurate to retrieve rain rates using DSD rather than the above QPE methods. In addition to retrieving rain rates, DSD can also be used to calculate other parameters related to rain, such as the number concentration, mean drop diameter, liquid water content, etc., which are crucial for enhancing the knowledge of rain processes and the forecasting ability of numerical weather models.
DSD can be retrieved from polarimetric radar observations because the polarimetric variables can partially represent the raindrop size and concentration information. Polarimetric radar provides ZH, ZDR, KDP, and CC. CC is usually used for hydrometeor classification, but it remains close to 1 in rain and provides little information about DSD, leaving the other three variables to retrieve DSD.
The three-parameter gamma distribution has been widely used to represent DSD in the following form:
where is the number concentration parameter, is the distribution shape parameter, and is the slope parameter; these represent the so-called three-parameter DSD. The two-parameter DSD form and the Marshall–Palmer DSD form [107] can both be regarded as special forms of the three-parameter gamma distribution, with a fixed , and a fixed and , respectively.
Mathematically, it is possible to solve three parameters with three variables. Gorgucci et al. [108] proposed an algorithm (named as the method algorithm) to estimate DSD with ZH, ZDR, and KDP. The magnitude of the slope of the shape–size relationship is calculated with the method described by Gorgucci et al. [109]. Then, three parameters can be estimated. They pointed out that measurement errors of the radar variables are the key for accurate DSD estimation. However, KDP is noisy in low rain rates and could lead to large errors. In addition, KDP is typically estimated with the differential phase over several to dozens of gates, and it does not have the same radial resolution as variables such as ZH or ZDR, which are “gate-to-gate” variables. Therefore, the use of KDP in DSD retrieval may have a negative impact rather than a positive impact.
However, if KDP is excluded for DSD retrieval, only two variables (ZH and ZDR) remain. It is mathematically impossible to solve three parameters with two variables, suggesting that another constraint condition is needed. Illingworth et al. [110] suggested that the three parameters in the gamma distribution model are not independent. Zhang et al. [111] found that and are strongly correlated. They proposed the constrain-gamma (C-G) model, namely to use ZH, ZDR, and the - relation to retrieve DSD; then, this method was modified by Brandes et al. [112].
The - relation has the following form:
where a1, a2, and a3 are parameters that can be derived using a sorting and averaging method [26]. These parameters vary in different locations. For example, the – in Oklahoma has a lower slope than that in Florida [26].
Many studies were conducted based on these two methods. Brandes et al. [113] compared the performance of the method and the C-G model method, and the results suggested that the latter performed better. Cao et al. [114] proposed the Bayesian approach to retrieve DSD to overcome the measurement/model errors. The retrieval of DSD requires ZH and ZDR to be free of attenuation. Since short-band radars (C- or X-band) can be easily affected by attenuation, the variational approach was proposed to overcome this problem [115,116,117]. The double moment normalization approach is also suitable for retrieving the DSD using short-band radars [118,119].
After retrieving the DSD, the rain rates can be derived. The performance of the DSD retrieval-based method is outstanding; it is in good agreement with in situ measurements [111,114]. However, DSD retrieval-based methods also suffer from some deficiencies: (1) when the polarimetric variables are weak, which usually occurs in light rain, the deterministic DSD retrieval may suffer from large measurement errors, and no solution is found; and (2) the Bayesian approach overcomes the previous deficiency, but requires large computational resources, which limits its operational use. So far, the DSD retrieval-based methods have not yet been applied to any operational radar networks for QPE applications.
The rapid advancement of machine learning (ML) and artificial intelligence (AI) has led to the development of numerous ML/AI-based QPE methods in recent years. However, a comprehensive review of these ML/AI-based QPE techniques is beyond the scope of this paper, as the topic itself is substantial enough to warrant a separate, dedicated review. Several innovative works are cited here [120,121,122,123,124,125].
3. Dual-Polarization Radar QPE: Operations
In this section, we demonstrate how the dual-polarization radar observational variables and QPE methods discussed above have been applied in operational practices to generate better QPE products. Many countries around the world have established weather radar networks, making it impractical to review all operational efforts in every nation. In this section, we focus on three representative countries: the United States, which has a large territory and has completed its dual-polarization radar upgrade; China, also vast in territory but still in the process of a dual-polarization upgrade; and France, which has a relatively smaller territory. By examining these three cases, we aim to provide readers with an overview of weather radar operations in different countries.
3.1. The Radar QPE System in the United States
The MRMS (Multi-Radar/Multi-Sensor) system was developed by the National Severe Storms Laboratory and the University of Oklahoma. It is a system that quickly ingests data from radars, satellites, surface observations, upper-air observations, numerical weather models, and other sources to generate seamless and high spatial–temporal resolution mosaics. It was transferred for operational use in 2014 [126,127]. In addition to the QPE product generated with radars, the MRMS system provides other products such as the QPE-gauge merged product, aviation product, and disaster warning product. Here, we will only focus on the QPE product generated with radar observations.
The MRMS system incorporates some components or concepts from the National Mosaic and Multi-Sensor QPE (NMQ) system [128]. The flowchart of the NMQ system was first reviewed thereby. It should be noted that the NMQ system was developed based on single-polarization radar observations, as dual-polarization radars were not yet deployed nationwide at that time. The major modules of NMQ related to QPE are (1) single-radar processing; (2) 2D radar mosaic; and (3) QPE generation.
In the single-radar processing module, the reflectivity field was firstly quality controlled (QC) to remove non-meteorological echoes using a neural network method [129,130]. This QC method was developed for single-polarization radars based on reflectivity. The VPR correction was then applied to eliminate the overestimation caused by the bright band using the method proposed by Zhang et al. [52]. They firstly segregated convection and stratiform based on the vertically integrated liquid water [131]; then, the bright band was delineated from stratiform, and VPR correction was applied in the bright band area. Finally, a single-radar hybrid scan reflectivity (HSR) was obtained based on the reflectivity field after QC and VPR correction. In general, the lower the radar observation is, the more accurate the radar-based precipitation estimates. However, we cannot use only the lowest tilt observation to produce QPE because radars may be blocked by mountains or infrastructures at the low tilts. HSR is the reflectivity field closest to the ground that is not blocked.
Single-radar HSR fields are mosaicked to produce a gridded regional HSR field. This regional HSR field is later used to generate the QPE product. For a specific mosaic grid, all single-radar HSR pixels closest to that grid from different radars are used to generate HSR using both horizontal and vertical interpolations. The mosaicking HSR field produced with this approach has a better continuity than the nearest neighbor method.
The radar QPE is performed with the mosaicking HSR field generated in the previous step. Due to the fact that DSD characteristics vary significantly for different precipitation types, the NMQ system generates QPE according to precipitation types. Surface temperature and wet bulb temperature are checked to distinguish snow from rain. The density of the vertically integrated liquid water is checked for hail. If the precipitation is rain, it is classified into stratiform rain, convective rain, and warm rain, using the classification methods proposed by Xu et al. [37] and Zhang et al. [44]. Then, different R(ZH) relations are applied in different precipitation types to generate the QPE product.
Major modules of the MRMS system related to QPE are the same as NMQ, but the algorithms are different. Here, we present only the algorithms critical to QPE. Dual-polarization radars were already deployed nationwide at the time when the MRMS system was developed. Although the MRMS system did not directly use polarimetric variables to generate the QPE at first, dual-polarization radar made a significant contribution to the development of QPE. QC is more accurate with polarimetric variables, especially with CC. The updated QC algorithm in the MRMS is based on polarimetric variables [132,133,134]. Several types of non-meteorological echoes, such as wind farms, anomalous propagation ground clutter, biological echoes, and chaff scattered for military purposes, are difficult to remove with the single-polarization radar QC, while they can be easily removed with the dual-polarization radar QC. In addition, VPR correction in the MRMS system also benefits from polarimetric variables. In VPR correction, one of the key steps is to determine the bottom of the melting layer, which is more accurate with polarimetric variables [46].
There are also some updated algorithms in the MRMS system that are not related to polarimetric variables, but still contribute to the improvement of QPE. Convection near the radar site was easily misclassified as stratiform, and the strong bright band was easily misclassified as convection with the method of Zhang et al. [44]. Later, Qi et al. [38] proposed a new precipitation classification algorithm, which divides the radar scan domain into several sections with ranges, and different criteria are applied in different sections. This algorithm uses the difference in vertical structures between convection and stratiform for classification, and it separates convection and stratiform more accurately. The correct precipitation classification helps to improve the QPE through (1) the application of correct R(ZH) relations for different precipitation types; and (2) effective VPR correction.
The mosaicking method was also updated in the MRMS system. The mosaicking method in the NMQ introduces false precipitation when the radar detects the cloud anvil or virga, and it underestimates rain rates because high altitude observations are also used for mosaicking. In the method proposed by Qi et al. [135], the lowest radar observation is firstly checked to determine whether a grid has precipitation. This strategy minimizes the false precipitation region due to the cloud anvil or virga. If the grid is flagged as precipitation, the radar quality index [136] is introduced to perform the interpolation. The radar quality index is high if the observation is low above the ground and free from blockage; otherwise, it is low. Only observations with a high radar quality index are used for the interpolation. This strategy reduces the underestimation by excluding the high-altitude observation.
In recent years, the MRMS system has updated QPE methods with polarimetric variables [137]. A composite algorithm using R(A), R(KDP), and R(ZH) is applied to generate an accurate and stable QPE product.
The MRMS system, which ingests 146 WSR-88D S-band radars and 30 Canadian dual-polarization S-band radars (Canadian radars, previously single-polarization C-band radars, which have been replaced in April 2022 with dual-polarization S-band radars), provides high spatial (1 km) and temporal (2 min) resolution QPE products for the contiguous United States and southern Canada, and has become a powerful tool for meteorological application and research.
3.2. The Radar QPE System in China
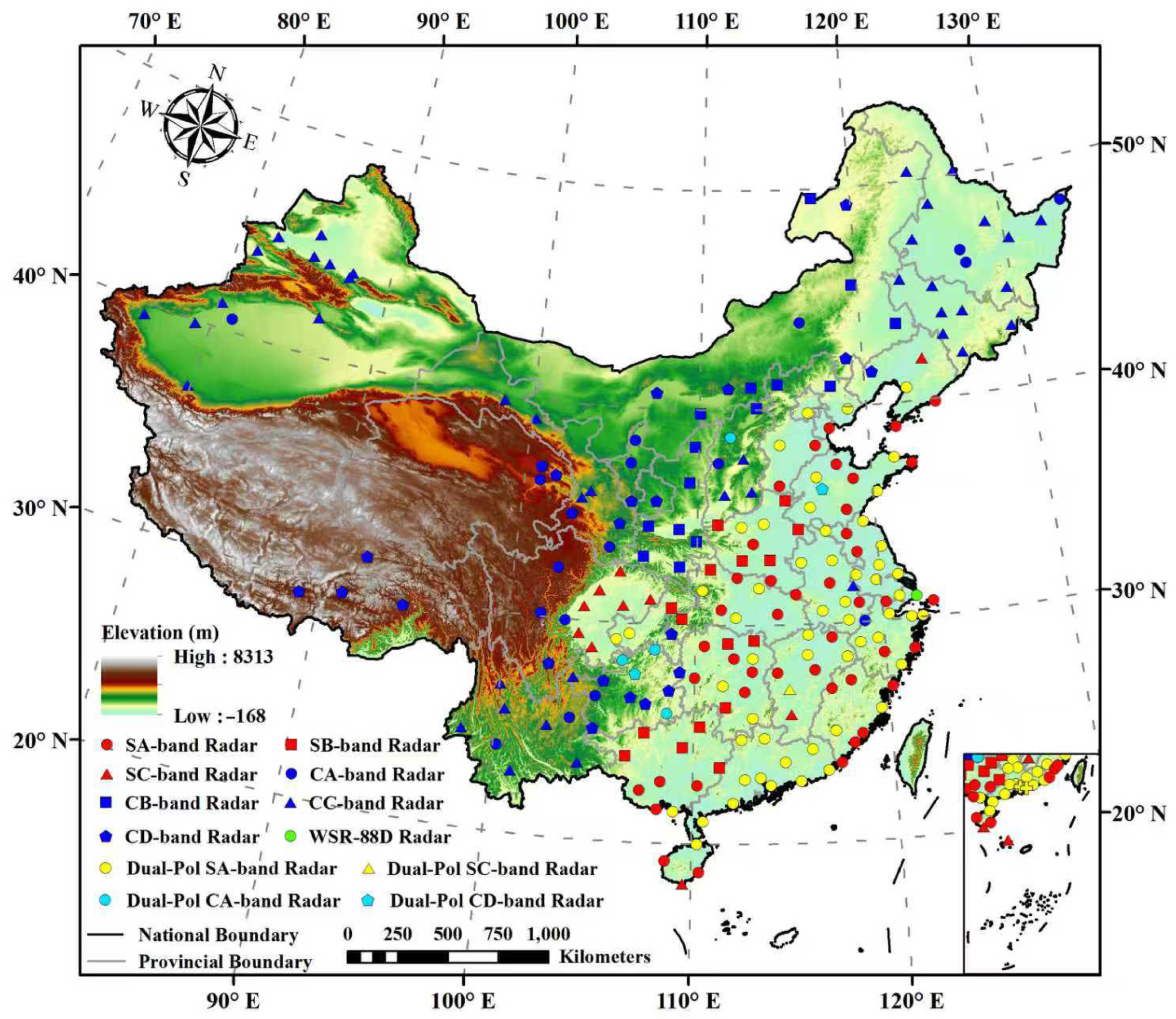
The national territory of China is comparable to that of the United States. China has a national radar network of more than 200 radars covering virtually all its territory, except for some deserts and wilderness areas in the Xinjiang and Tibetan autonomous regions with few inhabitants. The US national radar network consists of S-band radars only, but China’s national radar network has both S-band and C-band radars. S-band radars have been deployed in eastern China and C-band radars in the rest of China (Figure 3). This strategy was adopted because eastern China is more prone to heavy precipitation events due to the Asian monsoon, and S-band radars suffer less from attenuation problems in heavy precipitation. Central and western China receive less annual precipitation with a weaker intensity, and C-band radars were chosen for their lower costs. Dozens of radars have been upgraded to dual-polarization radars, mainly in the southeast and east of the country, with frequently occurring heavy precipitation, while the rest are still single-polarization radars. In recent years, the growing demand for advanced meteorological monitoring has prompted major cities to deploy X-band radars capable of high temporal and spatial resolution. For example, in the Greater Bay Area—one of the most populated and economically developed regions in China—a dense X-band polarimetric phased-array radar network consisting of more than 50 radars has been established [138], and several studies using these radars have been conducted. The results suggest that QPE based on these X-band radars achieves a higher accuracy than S-band radar-based QPE. This enhancement is attributed to the denser network spacing, faster volume scan speed, and more detailed low-level atmospheric precipitation information provided by the X-band radar network [94,139,140,141,142]. These X-band radars are not yet merged into the national radar network.
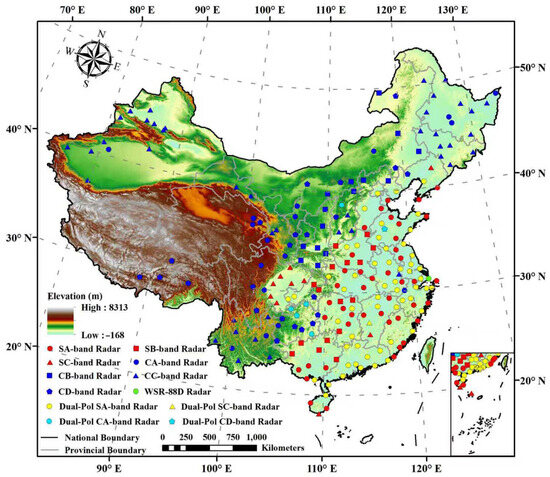
Figure 3.
China weather radar network map.
Since the dual-polarization radar upgrade has not yet been completed, the national QPE system in China uses R(ZH) estimators to generate QPE products. The operational QPE system is a sub-system of the SWAN (Severe Weather Automatic Nowcasting) operational system developed by the National Meteorological Centre. The flowchart of this QPE system is similar to the NMQ system, but the algorithms are different. First, radar QC is performed based on single-polarization radar observations using filters and the fuzzy logic method [143]. Then, single-radar HSR and mosaicking HSR are generated based on the radar blockage information [144], and finally QPE is performed. The QPE system in SWAN does not apply different R(ZH) relations according to precipitation classification as in NMQ. Instead, adjustable regional R(ZH) relations are derived from radar observations and local gauge observations using the method proposed by Smith et al. [145], and later the categorical method proposed by Wang et al. [146]. The R(ZH) relations in both methods are time dependent.
To improve the radar QPE system in China, some research works on radar QPE with polarimetric variables have also been conducted in recent years [93,94,142,147,148,149]. As more radars are upgraded to dual-polarization radars, one can expect future improvements in QPE accuracy with polarimetric QC methods and QPE estimators.
3.3. Radar QPE Systems in France
Many countries have much smaller national territories than the United States or China. A few or a few dozen radars can fully cover their entire territories. Furthermore, such countries usually have denser radar networks than the United States or China, which therefore may have fewer practical problems with DSD variability, radar coverage, and beam broadening effects, etc. To demonstrate QPE systems in countries with small national territories, we take the QPE system in France as an example.
The radar network in France consisted of 18 C-band radars in 2004. All these radars were single-polarization radars [150]. Six new radars had been deployed by 2007, including one C-band and five S-band radars. The S-band radars were deployed in the south of France, where extreme precipitation events occur more frequently because of the Mediterranean climate, a similar strategy to that used in China. X-band radars were then deployed as gap fillers. By 2015, six X-band radars had been deployed, with six located in the Alps, which improved the QPE quality of the Alps significantly [151]. Radars in France completed the upgrade to dual-polarization radars in 2022. Almost all radars in France are less than 200 km apart, much closer than those in the United States or China.
The QPE system in France comprises eight steps to generate the QPE product [150,152].
- (1)
- Ground-clutter identification: Ground clutters are identified using the pulse-to-pulse fluctuation of reflectivity proposed by [153].
- (2)
- R(ZH) relationship: The Marshall–Palmer R(ZH) relationship is applied to generate the rain rates. This single static R(ZH) relationship may result in the underestimation of convection, as the Marshall–Palmer R(ZH) relationship is designed for stratiform.
- (3)
- Correction for partial beam blocking: Partial beam blocking leads to lowered signals of reflectivity and ultimately to the underestimation of rain rates. The correction factor is calculated with high-resolution terrain and radar technical characteristics and sampling strategy. The rain rates are corrected by multiplying the correction factor.
- (4)
- VPR correction: The VPR correction is applied to eliminate the overestimation of QPE in the bright band [154,155]. The correction factor for each of the tilts is computed using VPR information. The rain rate fields are then calculated using the observation from each tilt with correction factors. Note that the sequence of steps 2–4 differs from the MRMS system, which firstly applies partial blocking correction and VPR correction to the reflectivity field, and then retrieves the rain rates using the corrected reflectivity.
- (5)
- Synchronization: Radars in France complete a volume scan every five minutes. When precipitation systems move very fast, such as with convective lines or frontal systems, the vertical structures of the reflectivity might be significantly altered. An advection method is therefore applied to move the observation of different tilts to the same reference time.
- (6)
- Weighted linear combination: This step combines the retrieved rain rates with observations from different tilts to produce 2D surface rain rates.
- (7)
- Accumulation of 5 min of rainfall: The surface rain rate is advected by 1 min increments, and then the 5 min precipitation accumulation is obtained by accumulating a set of five rain rate fields.
- (8)
- QPE field mosaicking: The QPE fields produced by different radars are mosaicked to generate a QPE product covering the whole country of France. The weighted linear combination method similar to the one applied in step (6) is used for mosaicking.
Apart from certain specific methods used for generating the QPE, the logic of the QPE system in France is quite different from that of the MRMS system. The QPE system in France produces a single-radar QPE with observations from all tilts (i.e., a 3D field), whereas, in the MRMS system, the radar QPE is generated by hybrid scan observations (i.e., a 2D field). Both strategies have their advantages and disadvantages. A QPE product based on all tilts produces a more realistic accumulative precipitation field pattern when precipitation systems are moving rapidly. In contrast, the QPE product based on hybrid tilts may produce an unreal precipitation field pattern in such circumstances. However, the QPE product generated by hybrid tilts may be more accurate because it minimizes the effect of vertical changes in raindrops by using the observation closest to the surface. The QPE product generated with observations from all tilts introduces observations from very high above, which could hinder its accuracy, especially for falling raindrops experiencing significant vertical changes.
The polarimetric variables were later introduced into the QPE system in France and contributed significantly to the improved quality of the QPE product [156,157]. In the QPE system of France, polarimetric variables are of great help for the correct identification of non-meteorological echoes and melting layers in the same way as the MRMS system. Polarimetric estimators are then used for QPE. A composite method is applied for the QPE system in France, with the R(ZH) estimator used for solid precipitation, R(KDP) applied for rain when KDP exceeded a certain threshold, and otherwise the R(ZH) estimator. ZDR is not used for QPE due to its insufficient stability at present. This evaluation suggests that the QPE product with polarimetric estimators outperforms QPE with the R(ZH) estimator.
4. Dual-Polarization Radar QPE: Challenges
After reviewing the theories and operational applications of dual-polarization radar QPE, we conclude that the following issues still need to be addressed in the future to further improve the accuracy of dual-polarization radar QPE.
4.1. The Quality of Polarimetric Variables
The quality of polarimetric variables hinders the use of QPE methods.
- (1)
- Attenuation issues: ZH and ZDR suffer from severe attenuation issues in heavy precipitation for short-band (C or X) radars. Attenuation correction must be applied. Otherwise, there will be a large underestimation in QPE. Attenuation correction is more accurate and reliable for dual-polarization radars with polarimetric variables, and numerous methods were proposed [6,7,8,9,10]. The parameters in each of these methods should be carefully adjusted when being applied to a specific radar. Disdrometers could be used to evaluate these methods by comparing corrected ZH and ZDR from the radar with those calculated with the disdrometer data.
- (2)
- Miscalibration: ZH and ZDR can suffer from miscalibration. A hot (cold) ZH will result in an overestimation (underestimation) for QPE estimators with ZH. The QPE estimators with ZDR are sensitive to ZDR, and a miscalibrated ZDR could have a negative impact on QPE, instead of a positive one. That is why both QPE systems in the United States and France exclude ZDR from QPE use. During radar maintenance, ZH and ZDR must be properly calibrated, and disdrometers could be used as references to check whether calibration is needed. One could examine whether radar observation has a systematic bias by comparing the ZH and ZDR observed by the radar with those calculated from the disdrometers.
- (3)
- Partial beam blockage: When radar beams are blocked by obstacles such as terrain and buildings, the accuracy of QPE is compromised. A traditional method of mitigating the partial beam blockage is to estimate the degree of beam blockage using DEM (digital elevation model) data. This method has three shortcomings. Firstly, it may not work well if the radar beams are heavily blocked. Second, building information is not included in the DEM data, and thus the blockage due to buildings cannot be properly mitigated. Third, it can cause large errors if anomalous propagation occurs. The mitigation of partial beam blockage becomes more effective for dual-polarization radars using KDP, since KDP is immune to partial beam blockage. Various methods to mitigate partial beam blockage with KDP were proposed [83,158,159]. In order to obtain good partial beam blockage mitigation results, KDP must be properly processed and parameters in these methods must be carefully adjusted.
- (4)
- Radome effect: A wet radar radome produces a negative bias in ZH and a positive bias in ZDR [160,161,162], thus affecting the accuracy of QPE estimators with ZH and ZDR. To minimize the effects of the wet radome, post-processing methods such as self-consistency principles should be adopted [163]. Radar radomes should also be properly maintained, including the use of hydrophobic paint and cleaning.
- (5)
- Identification of non-meteorological echoes: There are a variety of non-meteorological echoes, such as ground and sea clutter, biological scatterings (e.g., insects and birds), smoke plumes, dust, volcanic ash, electromagnetic interferences, and sun spikes. These echoes should be identified and removed for an accurate QPE. Due to differences in the CC values of meteorological and non-meteorological echoes, the identification of non-meteorological echoes for dual-polarization radars has become more robust and accurate. In general, meteorological echoes have higher CC values than non-meteorological echoes, which could be used to design algorithms to identify non-meteorological echoes [133,134]. However, there is no specific bound for the CC values between meteorological echoes and non-meteorological echoes. CC values in meteorological echoes may decrease when there is a mixing of meteorological and non-meteorological echoes, hailing, melting layers, or non-uniform beam fillings. Under such circumstances, it can be difficult to correctly identify non-meteorological echoes. In recent years, advanced methods such as machine learning and deep learning have been applied to identify non-meteorological echoes [164,165,166]. The use of more physically based information in these advanced methods in the future could make the identification of non-meteorological echoes more reliable and robust.
- (6)
- Noise: When the SNR (signal-to-noise ratio) is low, both ZDR and KDP appear to be very noisy. Subsequently, precipitation fields generated by ZDR-based or KDP-based estimators are noisy, inaccurate, and appear “unnatural” due to their low continuity. To address this issue, both radar hardware and signal processing methods need to be improved.
- (7)
- Degraded radial resolution of the KDP: The “intrinsic” KDP, defined as half of the slope of two adjacent differential phases along the radial, is usually noisy, with fluctuations along the radial, and should therefore be processed carefully. Several methods were proposed to estimate the KDP with mathematical or/and physical constrains [69,70,71,72]. KDP processing is a compromise between accuracy and radial resolution. How to remove the noise and fluctuations of KDP while maintaining its radial resolution is a challenge that needs to be addressed.
4.2. The QPE Quality in Complex Terrain
Radar QPE quality is generally poorer in mountainous areas, such as the Rocky Mountain areas of the western United States, the Alps areas in Europe, and the mountains of central and western China, than that in the plains. There are two reasons for this: (1) the limited radar convergence in these mountainous areas; and (2) the limited knowledge of the vertical structure and microphysical characteristics of precipitation in complex terrain.
It is particularly important to monitor precipitation that occurs over mountainous areas, as it often causes landslides, floods, and debris flows. However, the coverage and quality of radar observations in mountainous areas are poorer than those in the plains. The deployment of radars in mountainous areas is a dilemma. When radars are deployed in valleys, their beams are blocked by the orography and their detection range is limited. Meanwhile, radars at the top of mountains or far away from mountains are unable to detect information close to the ground, which is essential for QPE. In the French Alps area, additional observations are made using X-band radars, which have short ranges, low power consumption, and low cost. This strategy is a great idea to improve the QPE quality over mountainous areas, especially for the European countries around the Alps. However, even with this strategy, it is still a significant cost for countries with large national territories, such as the United States or China, given the number of radars that will be required to cover their mountainous areas.
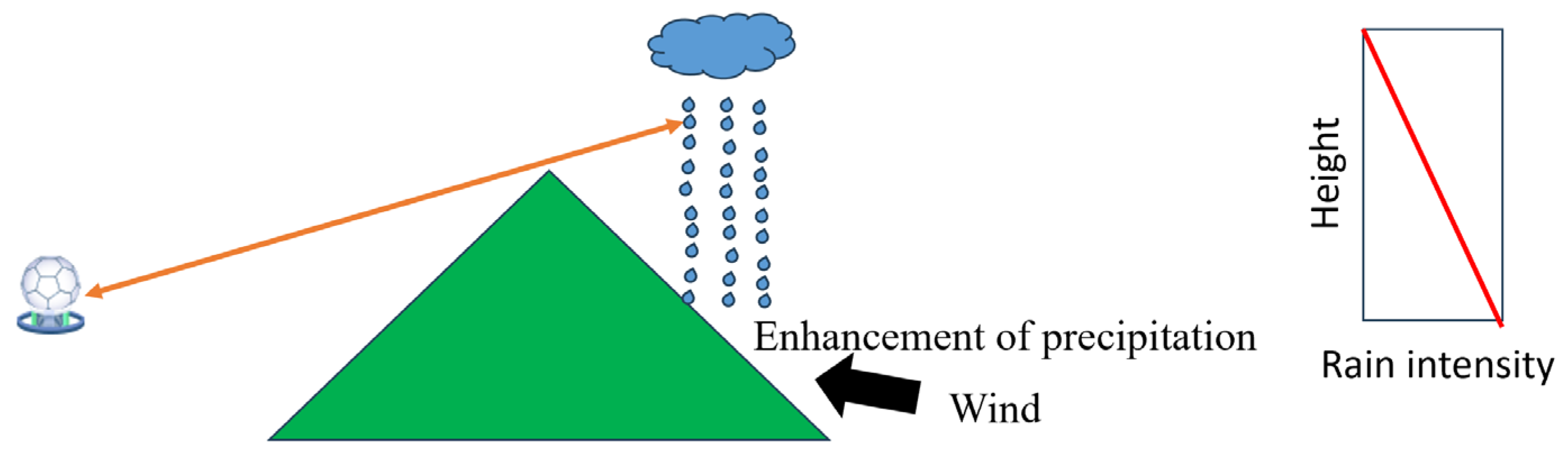
Precipitation tends to enhance over complex terrain due to the lifting of air masses by mountains, which promotes the formation of droplets [167,168]. The enhancement of precipitation is pronounced at low levels. However, ZH observed in complex terrain can usually be well above the surface, since the observation from low tilts is blocked by the orography. Using the ZH well above the surface will underestimate the actual rain rate at the ground (Figure 4). A few QPE techniques were developed to address this issue. Wang et al. [169] utilized the VPR and the vertical profile of specific differential phase (VPSDP) correction technique for QPE in complex terrain, and significantly mitigated the underestimation of QPE in mountainous regions. Crochet [170] proposed a VPR correction technique and a radar adjustment technique compensating for range for QPE over complex terrain, which significantly improved the quality of the QPE.
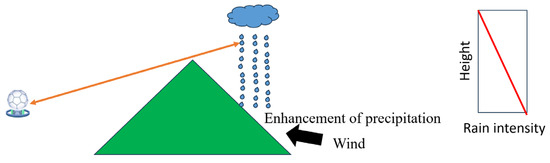
Figure 4.
Schematic diagram illustrating the mechanism of topographic precipitation enhancement and its vertical profile of rain intensity.
In addition, DSD in complex terrain is different from that in the plains. Some studies have shown that raindrops in complex terrain are smaller [171,172,173]. ZH is more sensitive to large drops than to high concentrations of smaller drops, suggesting that parameters a and b in R(ZH) applied in plains may not be appropriate for QPE in complex terrain, resulting in an underestimation of rain rates.
The QPE quality in complex terrain could be improved by (1) deploying more radars; (2) conducting further research on the vertical structure of precipitation in complex terrain with profiler radars, airborne radars, and spaceborne radar observations; and (3) deploying more disdrometers to obtain DSD characteristics. Germann [174] reviewed the challenges and solutions for deploying and operating weather radars in complex terrain, drawing on decades of experience in the Swiss Alps. They proposed a comprehensive approach involving optimized radar siting, dual-polarization technology, advanced scanning strategies, and clutter cancelation algorithms to improve QPE and nowcasting for applications like thunderstorm warnings and flash flood prediction. Readers may refer to their work for further details.
4.3. Estimation of Surface Rain with Observations Within or Above the Melting Layer
Polarimetric estimators are currently only applied to liquid-phase particles in the operational systems reviewed above, implying that they are only applied within a limited distance from a radar site in the radar scan domain. For observations in or above the melting layer, R(ZH) is used instead.
The use of polarimetric variables in or above the melting layer to estimate surface rain rates is challenging because, as ice or mixed-phase particles fall, their sizes, densities, shapes, canting angles, and terminal velocities will also change, resulting in changes in the radar observational variables as well. Therefore, corrections for the vertical profile of radar observational variables should be applied to correctly estimate surface rain rates. Among these vertical profiles, VPR is better understood. VPR usually shows a peak value around the melting layer, and numerous methods of VPR correction were proposed to mitigate the overestimation due to the bright band [51,52,175]. The VPR correction became more effective with polarimetric variables [46,176,177]. Compared to the abundant knowledge and correction methods for VPR, the knowledge of the vertical profile of polarimetric variables is limited. Kumjian et al. [89] presented the conceptual vertical profiles of polarimetric variables for ice and snow in different microphysical processes. However, vertical profiles of polarimetric variables in real precipitation systems can be more complicated than conceptual models [178]. Correction methods for vertical profiles of polarimetric variables need to be developed.
Abundant observations of above-ground DSD information will be of great help in addressing this challenge. Compared to surface DSD observations, above-ground DSD observations are limited and lack long term climatological data because such data are obtained by airborne observations, which are costly and dangerous in severe convective systems [179,180,181]. In recent years, the vertical pointing dual-frequency radars, such as the dual-frequency precipitation radar (DPR) on the Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) core satellite, can provide rich DSD information above the ground [53,182,183,184,185]. Moreover, unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) technologies have been developing rapidly in recent years, and it is promising that these UAVs can be used for airborne DSD observations.
4.4. Polarimetric Radar QPE Methods for Snow
Radar QPE for snow is very difficult due to the large variability of snow particle size distributions, density, shape, structure, terminal velocity, and orientation. Traditionally, the R(ZH) estimator is used to perform QPE for snow. For example, is used for snow estimation in the MRMS system [126]. Evaluations showed that the MRMS QPE product performed worse in the winter than that in warm seasons, with large errors and a poor correlation against gauge observations [186].
A few polarimetric QPE methods for snow have been proposed in recent years. Hassan et al. [187], proposed a QPE estimator for snow using ZH and ZDR. However, it showed only a slight improvement over the R(ZH) estimator. They suggested that low values of ZDR for snow observations limit its contribution to QPE. A QPE estimator for snow using ZH and KDP was proposed by Bukovcic et al. [188]. An evaluation of this estimator against the R(ZH) estimator using disdrometer data showed that it performed better than the R(ZH) estimator. Later, this estimator was applied to S-band polarimetric radar data, and its performance was verified with ground snow measurements. The results also suggested its better performance over the R(ZH) estimator [189,190]. For the four snowfall cases used for evaluations in their paper, this estimator showed a good agreement with gauge observations in three of the cases, but severely underestimated the fourth. Nevertheless, these works are still very encouraging and provide a promising algorithm of snow radar QPE using polarimetric variables. To better understand the polarimetric signal for snow, further research should be conducted on the microphysical structure and processes of snow. It is also necessary to develop and evaluate new polarimetric methods for snow estimation.
5. Conclusions
One of the primary sources of errors in radar QPE comes from DSD variations. The R(ZH) estimator is sensitive to DSD variations, resulting in its insufficient accuracy of QPE. Since the proposal of the theory of using polarimetric variables for QPE in the 1970s, many dual-polarization radar QPE methods were developed using dual-polarization radar observational variables (i.e., ZDR and KDP) or derived variables (i.e., Nw and A). These estimators are less sensitive to DSD variations and thus produce a more accurate QPE. However, these estimators all have drawbacks in practice, so composite methods have been proposed to combine the advantages of each method and to avoid their disadvantages. In addition, the hydrometeor classification became more accurate with polarimetric variables, and QPE methods were developed based on the hydrometeor classification results. The retrieval of DSD also became possible, and QPE could be performed with the retrieved DSD.
It is important to note that polarimetric variables not only contribute directly in improving QPE accuracy with the above methods, but also indirectly, including but not limited to the following: (1) a better identification of non-meteorological echoes [133,134]; (2) a more accurate attenuation correction for ZH [11,13]; (3) a better identification of the melting layer and bright band [46,176,177]; and (4) immunity to partial blockage [83,137].
The QPE systems in various countries and regions are benefiting from the upgrade of dual-polarization radars. The United States completed its upgrade in 2012. Dual-polarization radars improve the accuracy of radar QPE not only directly by using dual-polarization radar QPE methods, but also indirectly through improving non-meteorological echo identification and bright band identification. China has not yet completed the upgrade; the national radar QPE product is still based on R(ZH) estimators, but many studies on dual-polarization radar QPE methods have been conducted. France is expected to complete the upgrade of dual-polarization radars in 2022, and the composite dual-polarization radar QPE method has been applied to its dual-polarization radar observation, significantly improving the accuracy of QPE.
The quality of polarimetric variables is one of the sources of errors in dual-polarization QPE methods, including attenuation, miscalibration, partial beam blockage, the radome effect, contamination of non-meteorological echoes, noise, and degraded radial resolution of the KDP. The radar QPE accuracy in complex terrain is worse than that in the plains. Poor radar coverage and a limited knowledge on the influence of the mountains on precipitation affected the quality of the radar QPE in complex terrain. Estimating surface precipitation with polarimetric variables in or above the melting layer is challenging, and further studies on the correction of vertical profiles of polarimetric variables should be conducted. In addition, new polarimetric methods must be developed and tested for snow estimation, as well as advanced methods for QPE that incorporate artificial intelligence or machine learning. In addiction, the integration of satellite-based precipitation measurements (such as GPM [53,186]) and the use of advanced phased-array radars [191,192,193] with higher temporal and spatial resolution will also improve QPE accuracy.
Author Contributions
Funding
This work was funded by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. U2442201), Shenzhen Science and Technology Program (Grand No. JCYJ20230807154400002), Guidance Project for Science and Technology Plan of Fujian Province (Grant No. 2024Y0076), Key Research and Development Program of Hainan (Grant No. ZDYF2023SHFZ125), and Major Scientific and Technological Special Project of Anyang (Grant No. 2022A02SF005).
Data Availability Statement
All data are available upon request.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the editors and five anonymous reviewers for their thorough comments, which greatly helped improve the manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Seliga, T.A.; Bringi, V. Potential use of radar differential reflectivity measurements at orthogonal polarizations for measuring precipitation. J. Appl. Meteorol. 1976, 15, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doviak, R.; Bringi, V.; Ryzhkov, A.; Zahrai, A.; Zrnić, D. Considerations for polarimetric upgrades to operational WSR-88D radars. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2000, 17, 257–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, J.; Langille, R.; Palmer, W.M.K. Measurement of rainfall by radar. J. Atmos. Sci. 1947, 4, 186–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, J.; Hitschfeld, W.; Gunn, K. Advances in radar weather. In Advances in Geophysics; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1955; Volume 2, pp. 1–56. [Google Scholar]
- Atlas, D. Radar calibration: Some simple approaches. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2002, 83, 1313–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarchilli, G.; Gorgucci, V.; Chandrasekar, V.; Dobaie, A. Self-consistency of polarization diversity measurement of rainfall. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1996, 34, 22–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorgucci, E.; Scarchilli, G.; Chandrasekar, V. A procedure to calibrate multiparameter weather radar using properties of the rain medium. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1999, 37, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorgucci, E.; Scarchilli, G.; Chandrasekar, V. Calibration of radars using polarimetric techniques. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1992, 30, 853–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vivekanandan, J.; Zhang, G.; Ellis, S.M.; Rajopadhyaya, D.; Avery, S.K. Radar reflectivity calibration using differential propagation phase measurement. Radio Sci. 2003, 38, 8049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryzhkov, A.V.; Giangrande, S.E.; Melnikov, V.M.; Schuur, T.J. Calibration issues of dual-polarization radar measurements. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2005, 22, 1138–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bringi, V.; Chandrasekar, V.; Balakrishnan, N.; Zrnić, D. An examination of propagation effects in rainfall on radar measurements at microwave frequencies. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 1990, 7, 829–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Testud, J.; Le Bouar, E.; Obligis, E.; Ali-Mehenni, M. The rain profiling algorithm applied to polarimetric weather radar. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2000, 17, 332–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bringi, V.N.; Keenan, T.; Chandrasekar, V. Correcting C-band radar reflectivity and differential reflectivity data for rain attenuation: A self-consistent method with constraints. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2001, 39, 1906–1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryzhkov, A.V.; Zhang, P.; Hudak, D.; Alford, J.; Knight, M.; Conway, J. Validation of polarimetric methods for attenuation correction at C band. In Proceedings of the 33rd Conference on Radar Meteorology, Cairns, Australia, 6–10 August 2007; American Meteorological Society: Boston, MA, USA, 2007; p. P11B.12. [Google Scholar]
- Rico-Ramirez, M.A. Adaptive attenuation correction techniques for C-band polarimetric weather radars. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2012, 50, 5061–5071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gou, Y.; Chen, H.; Zheng, J. An improved self-consistent approach to attenuation correction for C-band polarimetric radar measurements and its impact on quantitative precipitation estimation. Atmos. Res. 2019, 226, 32–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorgucci, E.; Baldini, L. Attenuation and differential attenuation correction of C-band radar observations using a fully self-consistent methodology. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2007, 4, 326–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vulpiani, G.; Tabary, P.; Parent du Chatelet, J.; Marzano, F.S. Comparison of advanced radar polarimetric techniques for operational attenuation correction at C band. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2008, 25, 1118–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabary, P.; Vulpiani, G.; Gourley, J.J.; Illingworth, A.J.; Thompson, R.J.; Bousquet, O. Unusually high differential attenuation at C band: Results from a two-year analysis of the French Trappes polarimetric radar data. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2009, 48, 2037–2053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, J.-Y.; Ryzhkov, A.; Zhang, P.; Neilley, P.; Knight, M.; Wolf, B.; Lee, D.-I. Polarimetric attenuation correction in heavy rain at C band. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2011, 50, 39–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maki, M.; Keenan, T.D.; Sasaki, Y.; Nakamura, K. Characteristics of the Raindrop Size Distribution in Tropical Continental Squall Lines Observed in Darwin, Australia. J. Appl. Meteorol. 2001, 40, 1393–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bringi, V.; Chandrasekar, V.; Hubbert, J.; Gorgucci, E.; Randeu, W.; Schoenhuber, M. Raindrop size distribution in different climatic regimes from disdrometer and dual-polarized radar analysis. J. Atmos. Sci. 2003, 60, 354–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Yang, J.; Pu, J. Statistical characteristics of raindrop size distribution in the Meiyu season observed in eastern China. J. Meteorol. Soc. Jpn. Ser. II 2013, 91, 215–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Ni, G.; Chandra, C.V.; Tian, F.; Chen, H. Statistical characteristics of raindrop size distribution during rainy seasons in the Beijing urban area and implications for radar rainfall estimation. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2019, 23, 4153–4170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauber, R.M.; Nesbitt, S.W. Radar Meteorology: A First Course; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, Q.; Zhang, G.; Brandes, E.; Schuur, T.; Ryzhkov, A.; Ikeda, K. Analysis of video disdrometer and polarimetric radar data to characterize rain microphysics in Oklahoma. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2008, 47, 2238–2255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calheiros, R.; Zawadzki, I. Reflectivity-rain rate relationships for radar hydrology in Brazil. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 1987, 26, 118–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atlas, D.; Rosenfeld, D.; Wolff, D.B. Climatologically tuned reflectivity-rain rate relations and links to area-time integrals. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 1990, 29, 1120–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenfeld, D.; Wolff, D.B.; Amitai, E. The window probability matching method for rainfall measurements with radar. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 1994, 33, 682–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Brandes, E.A. Optimizing rainfall estimates with the aid of radar. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 1975, 14, 1339–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfieri, L.; Claps, P.; Laio, F. Time-dependent ZR relationships for estimating rainfall fields from radar measurements. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2010, 10, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Liu, L.; Ding, Y. Improvement of radar quantitative precipitation estimation based on real-time adjustments to ZR relationships and inverse distance weighting correction schemes. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2012, 29, 575–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Libertino, A.; Allamano, P.; Claps, P.; Cremonini, R.; Laio, F. Radar estimation of intense rainfall rates through adaptive calibration of the ZR relation. Atmosphere 2015, 6, 1559–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steiner, M.; Houze, R.A., Jr.; Yuter, S.E. Climatological characterization of three-dimensional storm structure from operational radar and rain gauge data. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 1995, 34, 1978–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biggerstaff, M.I.; Listemaa, S.A. An improved scheme for convective/stratiform echo classification using radar reflectivity. J. Appl. Meteorol. 2000, 39, 2129–2150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anagnostou, E.N. A convective/stratiform precipitation classification algorithm for volume scanning weather radar observations. Meteorol. Appl. 2004, 11, 291–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Howard, K.; Zhang, J. An automated radar technique for the identification of tropical precipitation. J. Hydrometeorol. 2008, 9, 885–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, P. A real-time automated convective and stratiform precipitation segregation algorithm in native radar coordinates. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2013, 139, 2233–2240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Qi, Y.; Li, D.; Zhu, Z.; Yang, M.; Wang, N.; Yang, Y.; Hu, Q. A Real-Time Algorithm to Identify Convective Precipitation Adjacent to or within the Bright Band in the Radar Scan Domain. J. Hydrometeorol. 2021, 22, 1139–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Tang, L.; Chang, P.-L.; Tang, Y.-S. Separation of convective and stratiform precipitation using polarimetric radar data with a support vector machine method. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2021, 14, 185–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Diezma, R.; Zawadzki, I.; Sempere-Torres, D. Identification of the bright band through the analysis of volumetric radar data. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2000, 105, 2225–2236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gourley, J.J.; Calvert, C.M. Automated detection of the bright band using WSR-88D data. Weather Forecast. 2003, 18, 585–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matrosov, S.Y.; Clark, K.A.; Kingsmill, D.E. A polarimetric radar approach to identify rain, melting-layer, and snow regions for applying corrections to vertical profiles of reflectivity. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2007, 46, 154–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Langston, C.; Howard, K. Brightband identification based on vertical profiles of reflectivity from the WSR-88D. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2008, 25, 1859–1872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shusse, Y.; Takahashi, N.; Nakagawa, K.; Satoh, S.; Iguchi, T. Polarimetric radar observation of the melting layer in a convective rainfall system during the rainy season over the East China Sea. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2011, 50, 354–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, P.; Cao, Q. VPR correction of bright band effects in radar QPEs using polarimetric radar observations. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 3627–3633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, W.; Rico-Ramirez, M.A.; Krämer, S. Classification and correction of the bright band using an operational C-band polarimetric radar. J. Hydrol. 2015, 531, 248–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Qi, Y. A real-time bright band vertical profile of reflectivity correction using multitilts of reflectivity data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 61, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Loh, J.; Chang, W.-Y.; Liou, Y.-C.; Lin, P.-F.; Chang, P.-L. Detection and Characterization of Polarimetric Radar Bright Band Signatures in Northern Taiwan. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2025, 63, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolfensberger, D.; Scipion, D.; Berne, A. Detection and characterization of the melting layer based on polarimetric radar scans. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2016, 142, 108–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitchen, M.; Brown, R.; Davies, A. Real-time correction of weather radar data for the effects of bright band, range and orographic growth in widespread precipitation. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1994, 120, 1231–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Qi, Y. A real-time algorithm for the correction of brightband effects in radar-derived QPE. J. Hydrometeorol. 2010, 11, 1157–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Qi, Y.; Li, D. A Real-Time Radar QPE Error Correction for Convective Precipitation Using Long-Term TRMM-PR and GPM-DPR Observations. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2024, 62, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seliga, T.; Bringi, V.; Al-Khatib, H. A preliminary study of comparative measurements of rainfall rate using the differential reflectivity radar technique and a raingage network. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 1981, 20, 1362–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulbrich, C.W.; Atlas, D. Assessment of the contribution of differential polarization to improved rainfall measurements. Radio Sci. 1984, 19, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekar, V.; Bringi, V. Error structure of multiparameter radar and surface measurements of rainfall Part I: Differential reflectivity. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 1988, 5, 783–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorgucci, E.; Chandrasekar, V.; Scarchilli, G. Radar and surface measurement of rainfall during CaPE: 26 July 1991 case study. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 1995, 34, 1570–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryzhkov, A.V.; Schuur, T.J.; Burgess, D.W.; Heinselman, P.L.; Giangrande, S.E.; Zrnic, D.S. The Joint Polarization Experiment: Polarimetric rainfall measurements and hydrometeor classification. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2005, 86, 809–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seliga, T.; Bringi, V. Differential reflectivity and differential phase shift: Applications in radar meteorology. Radio Sci. 1978, 13, 271–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sachidananda, M.; Zrnić, D. Rain rate estimates from differential polarization measurements. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 1987, 4, 588–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekar, V.; Bringi, V.; Balakrishnan, N.; Zrnić, D. Error structure of multiparameter radar and surface measurements of rainfall. Part III: Specific differential phase. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 1990, 7, 621–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryzhkov, A.; Zrnić, D. Comparison of dual-polarization radar estimators of rain. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 1995, 12, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandes, E.A.; Zhang, G.; Vivekanandan, J. Experiments in Rainfall Estimation with a Polarimetric Radar in a Subtropical Environment. J. Appl. Meteorol. 2002, 41, 674–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matrosov, S.Y. Evaluating polarimetric X-band radar rainfall estimators during HMT. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2010, 27, 122–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Ryzhkov, A.V.; Tang, L. C-band polarimetric radar QPE based on specific differential propagation phase for extreme typhoon rainfall. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2013, 30, 1354–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balakrishnan, N.; Zrnić, D. Estimation of rain and hail rates in mixed-phase precipitation. J. Atmos. Sci. 1990, 47, 565–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryzhkov, A.V.; Kumjian, M.R.; Ganson, S.M.; Zhang, P. Polarimetric radar characteristics of melting hail. Part II: Practical implications. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2013, 52, 2871–2886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryzhkov, A.V.; Zrnic, D.S. Polarimetric rainfall estimation in the presence of anomalous propagation. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 1998, 15, 1320–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubbert, J.; Bringi, V. An iterative filtering technique for the analysis of copolar differential phase and dual-frequency radar measurements. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 1995, 12, 643–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chandrasekar, V. Algorithm for estimation of the specific differential phase. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2009, 26, 2565–2578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giangrande, S.E.; McGraw, R.; Lei, L. An application of linear programming to polarimetric radar differential phase processing. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2013, 30, 1716–1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Zhang, G.; Zhao, K.; Giangrande, S.E. A hybrid method to estimate specific differential phase and rainfall with linear programming and physics constraints. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2016, 55, 96–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jameson, A.R. A Comparison of Microwave Techniques for Measuring Rainfall. J. Appl. Meteorol. 1991, 30, 32–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, W.A.; Carey, L.D.; Rutledge, S.A.; Knievel, J.C.; Doesken, N.J.; Johnson, R.H.; McKee, T.B.; Haar, T.V.; Weaver, J.F. Mesoscale and radar observations of the Fort Collins flash flood of 28 July 1997. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1999, 80, 191–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryzhkov, A.V.; Giangrande, S.E.; Schuur, T.J. Rainfall estimation with a polarimetric prototype of WSR-88D. J. Appl. Meteorol. 2005, 44, 502–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, E.J.; Rutledge, S.A.; Dolan, B.; Thurai, M.; Chandrasekar, V. Dual-polarization radar rainfall estimation over tropical oceans. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2018, 57, 755–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cifelli, R.; Chandrasekar, V.; Lim, S.; Kennedy, P.C.; Wang, Y.; Rutledge, S.A. A new dual-polarization radar rainfall algorithm: Application in Colorado precipitation events. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2011, 28, 352–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Bouar, E.; Testud, J.; Keenan, T.D. Validation of the rain profiling algorithm “ZPHI” from the C-band polarimetric weather radar in Darwin. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2001, 18, 1819–1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Illingworth, A.J.; Thompson, R. The estimation of moderate rain rates with operational polarisation radar. In Proceedings of the 32nd Conference on Radar Meteorology, Albuquerque, NM, USA, 24–29 October 2005; American Meteorological Society: Boston, MA, USA, 2005; p. P9R.1. [Google Scholar]
- Tabary, P.; Boumahmoud, A.-A.; Andrieu, H.; Thompson, R.J.; Illingworth, A.J.; Le Bouar, E.; Testud, J. Evaluation of two “integrated” polarimetric Quantitative Precipitation Estimation (QPE) algorithms at C-band. J. Hydrol. 2011, 405, 248–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryzhkov, A.V.; Zrnic, D.S. Radar Polarimetry for Weather Observations; Springer Atmospheric Sciences; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Atlas, D.; Ulbrich, C.W. Path-and area-integrated rainfall measurement by microwave attenuation in the 1–3 cm band. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 1977, 16, 1322–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryzhkov, A.; Diederich, M.; Zhang, P.; Simmer, C. Potential utilization of specific attenuation for rainfall estimation, mitigation of partial beam blockage, and radar networking. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2014, 31, 599–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Cocks, S.; Tang, L.; Ryzhkov, A.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, J.; Howard, K. A prototype quantitative precipitation estimation algorithm for operational S-band polarimetric radar utilizing specific attenuation and specific differential phase. Part I: Algorithm description. J. Hydrometeorol. 2019, 20, 985–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cocks, S.B.; Tang, L.; Zhang, P.; Ryzhkov, A.; Kaney, B.; Elmore, K.L.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Howard, K. A prototype quantitative precipitation estimation algorithm for operational S-band polarimetric radar utilizing specific attenuation and specific differential phase. Part II: Performance verification and case study analysis. J. Hydrometeorol. 2019, 20, 999–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, P.; Ryzhkov, A.V.; Zhang, J.; Chang, P.-L. Utilization of specific attenuation for tropical rainfall estimation in complex terrain. J. Hydrometeorol. 2014, 15, 2250–2266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diederich, M.; Ryzhkov, A.; Simmer, C.; Zhang, P.; Trömel, S. Use of specific attenuation for rainfall measurement at X-band radar wavelengths. Part I: Radar calibration and partial beam blockage estimation. J. Hydrometeorol. 2015, 16, 487–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.-Y.; Trömel, S.; Ryzhkov, A.; Simmer, C. Assessing the benefits of specific attenuation for quantitative precipitation estimation with a C-band radar network. J. Hydrometeorol. 2021, 22, 2617–2631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumjian, M.R.; Prat, O.P.; Reimel, K.J.; van Lier-Walqui, M.; Morrison, H.C. Dual-Polarization Radar Fingerprints of Precipitation Physics: A Review. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekar, V.; Gorgucci, E.; Scarchilli, G. Optimization of multiparameter radar estimates of rainfall. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 1993, 32, 1288–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matrosov, S.Y.; Cifelli, R.; Kennedy, P.C.; Nesbitt, S.W.; Rutledge, S.A.; Bringi, V.; Martner, B.E. A comparative study of rainfall retrievals based on specific differential phase shifts at X-and S-band radar frequencies. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2006, 23, 952–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Chandrasekar, V. The quantitative precipitation estimation system for Dallas–Fort Worth (DFW) urban remote sensing network. J. Hydrol. 2015, 531, 259–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Zhao, K.; Zhang, G.; Huang, H.; Liu, S.; Wen, L.; Yang, Z.; Yang, Z.; Xu, L.; Zhu, W. Improving Polarimetric C-Band Radar Rainfall Estimation with Two-Dimensional Video Disdrometer Observations in Eastern China. J. Hydrometeorol. 2017, 18, 1375–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Qi, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Li, D.; Zeng, Q.; Lan, H. Application of radar quantitative precipitation estimation using S-band and X-band polarimetric radars in Shenzhen. Acta Meteorol. Sin. 2021, 79, 786–803. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Aydin, K.; Seliga, T.; Balaji, V. Remote sensing of hail with a dual linear polarization radar. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 1986, 25, 1475–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giangrande, S.E.; Ryzhkov, A.V. Estimation of rainfall based on the results of polarimetric echo classification. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2008, 47, 2445–2462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besic, N.; Figueras i Ventura, J.; Grazioli, J.; Gabella, M.; Germann, U.; Berne, A. Hydrometeor classification through statistical clustering of polarimetric radar measurements: A semi-supervised approach. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2016, 9, 4425–4445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besic, N.; Gehring, J.; Praz, C.; Figueras i Ventura, J.; Grazioli, J.; Gabella, M.; Germann, U.; Berne, A. Unraveling hydrometeor mixtures in polarimetric radar measurements. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2018, 11, 4847–4866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Q.; Zhang, W.; Chen, H.; Lee, W.-C.; Han, L.; Ma, Y.; Liu, X. Quantification of precipitation using polarimetric radar measurements during several typhoon events in Southern China. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Chandrasekar, V. Classification of hydrometeors based on polarimetric radar measurements: Development of fuzzy logic and neuro-fuzzy systems, and in situ verification. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2000, 17, 140–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.; Chandrasekar, V.; Bringi, V.N. Hydrometeor classification system using dual-polarization radar measurements: Model improvements and in situ verification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2005, 43, 792–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.S.; Ryzhkov, A.; Zrnić, D.; Kim, K.-E. The hydrometeor classification algorithm for the polarimetric WSR-88D: Description and application to an MCS. Weather Forecast. 2009, 24, 730–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bechini, R.; Chandrasekar, V. A semisupervised robust hydrometeor classification method for dual-polarization radar applications. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2015, 32, 22–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Ran, Y.; Deng, Y.; Wang, X. Study on deep-learning-based identification of hydrometeors observed by dual polarization Doppler weather radars. EURASIP J. Wirel. Commun. Netw. 2017, 2017, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberto, N.; Baldini, L.; Adirosi, E.; Facheris, L.; Cuccoli, F.; Lupidi, A.; Garzelli, A. A support vector machine hydrometeor classification algorithm for dual-polarization radar. Atmosphere 2017, 8, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Kumar, J. Convolutional Neural Networks for Hydrometeor Classification using Dual Polarization Doppler Radars. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Data Mining Workshops (ICDMW), Beijing, China, 8–11 November 2019; pp. 288–295. [Google Scholar]
- Marshall, J.S.; Palmer, W.M.K. The distribution of raindrops with size. J. Meteorol. 1948, 5, 165–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorgucci, E.; Chandrasekar, V.; Bringi, V.; Scarchilli, G. Estimation of raindrop size distribution parameters from polarimetric radar measurements. J. Atmos. Sci. 2002, 59, 2373–2384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorgucci, E.; Scarchilli, G.; Chandrasekar, V.; Bringi, V. Measurement of mean raindrop shape from polarimetric radar observations. J. Atmos. Sci. 2000, 57, 3406–3413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Illingworth, A.J.; Blackman, T.M. The need to represent raindrop size spectra as normalized gamma distributions for the interpretation of polarization radar observations. J. Appl. Meteorol. 2002, 41, 286–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Vivekanandan, J.; Brandes, E. A method for estimating rain rate and drop size distribution from polarimetric radar measurements. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2001, 39, 830–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandes, E.A.; Zhang, G.; Vivekanandan, J. An evaluation of a drop distribution–based polarimetric radar rainfall estimator. J. Appl. Meteorol. 2003, 42, 652–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandes, E.A.; Zhang, G.; Vivekanandan, J. Comparison of polarimetric radar drop size distribution retrieval algorithms. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2004, 21, 584–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Q.; Zhang, G.; Brandes, E.A.; Schuur, T.J. Polarimetric radar rain estimation through retrieval of drop size distribution using a Bayesian approach. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2010, 49, 973–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Q.; Zhang, G.; Xue, M. A variational approach for retrieving raindrop size distribution from polarimetric radar measurements in the presence of attenuation. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2013, 52, 169–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshikawa, E.; Chandrasekar, V.; Ushio, T. Raindrop size distribution (DSD) retrieval for X-band dual-polarization radar. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2014, 31, 387–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshikawa, E.; Chandrasekar, V.; Ushio, T.; Matsuda, T. A Bayesian approach for integrated raindrop size distribution (DSD) retrieval on an X-band dual-polarization radar network. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2016, 33, 377–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raupach, T.H.; Berne, A. Retrieval of the raindrop size distribution from polarimetric radar data using double-moment normalisation. Atmos. Meas. Tech. Discuss. 2016, 10, 2573–2594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, G.W.; Zawadzki, I.; Szyrmer, W.; Sempere-Torres, D.; Uijlenhoet, R. A general approach to double-moment normalization of drop size distributions. J. Appl. Meteorol. 2004, 43, 264–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolfensberger, D.; Gabella, M.; Boscacci, M.; Germann, U.; Berne, A. RainForest: A random forest algorithm for quantitative precipitation estimation over Swizerland. Atmos. Meas. Tech. Discuss. 2020, 14, 3169–3193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, K.; Song, J.J.; Bang, W.; Lee, G. Quantitative precipitation estimates using machine learning approaches with operational dual-polarization radar data. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Chandrasekar, V.; Tan, H.; Cifelli, R. Rainfall estimation from ground radar and TRMM precipitation radar using hybrid deep neural networks. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2019, 46, 10669–10678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huangfu, J.; Hu, Z.; Zheng, J.; Wang, L.; Zhu, Y. Study on quantitative precipitation estimation by polarimetric radar using deep learning. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2024, 41, 1147–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Chen, H.; Han, L. Polarimetric radar quantitative precipitation estimation using deep convolutional neural networks. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 61, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yo, T.S.; Su, S.H.; Chu, J.L.; Chang, C.W.; Kuo, H.C. A deep learning approach to radar-based QPE. Earth Space Sci. 2021, 8, e2020EA001340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Howard, K.; Langston, C.; Kaney, B.; Qi, Y.; Tang, L.; Grams, H.; Wang, Y.; Cocks, S.; Martinaitis, S. Multi-Radar Multi-Sensor (MRMS) quantitative precipitation estimation: Initial operating capabilities. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2016, 97, 621–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, T.M.; Lakshmanan, V.; Stumpf, G.J.; Ortega, K.L.; Hondl, K.; Cooper, K.; Calhoun, K.M.; Kingfield, D.M.; Manross, K.L.; Toomey, R. Multi-Radar Multi-Sensor (MRMS) severe weather and aviation products: Initial operating capabilities. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2016, 97, 1617–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Howard, K.; Langston, C.; Vasiloff, S.; Kaney, B.; Arthur, A.; Van Cooten, S.; Kelleher, K.; Kitzmiller, D.; Ding, F.; et al. National Mosaic and Multi-Sensor QPE (NMQ) System: Description, Results, and Future Plans. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2011, 92, 1321–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakshmanan, V.; Fritz, A.; Smith, T.; Hondl, K.; Stumpf, G. An automated technique to quality control radar reflectivity data. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2007, 46, 288–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakshmanan, V.; Zhang, J.; Howard, K. A technique to censor biological echoes in radar reflectivity data. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2010, 49, 453–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Greene, D.R.; Clark, R.A. Vertically Integrated Liquid Water—A New Analysis Tool. Mon. Weather Rev. 1972, 100, 548–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Zhang, J.; Qi, Y.; Langston, C.; Howard, K.W. Non-standard blockage mitigation for national radar QPE products. In Proceedings of the 36th Conference on Radar Meteorology, Breckenridge, CO, USA, 16–20 September 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, L.; Zhang, J.; Langston, C.; Krause, J.; Howard, K.; Lakshmanan, V. A physically based precipitation–nonprecipitation radar echo classifier using polarimetric and environmental data in a real-time national system. Weather Forecast. 2014, 29, 1106–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Zhang, J.; Simpson, M.; Arthur, A.; Grams, H.; Wang, Y.; Langston, C. Updates on the radar data quality control in the MRMS quantitative precipitation estimation system. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2020, 37, 1521–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.; Zhang, J. A physically based two-dimensional seamless reflectivity mosaic for radar QPE in the MRMS system. J. Hydrometeorol. 2017, 18, 1327–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Qi, Y.; Howard, K.; Langston, C.; Kaney, B. Radar quality index (RQI)—A combined measure of beam blockage and VPR effects in a national network. IAHS Publ. 2011, 351, 388–393. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Tang, L.; Cocks, S.; Zhang, P.; Ryzhkov, A.; Howard, K.; Langston, C.; Kaney, B. A dual-polarization radar synthetic QPE for operations. J. Hydrometeorol. 2020, 21, 2507–2521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, K.; Huang, H.; Lu, Y.; Chen, H.; Wu, C.; Zhao, G.; Zhu, Y.; Tan, Z.-M.; Zhang, Y.; Fu, P. Operational Phased Array Radar Network for Natural Hazard Monitoring and Warnings in Urban Environments over the Greater Bay Area, China. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2024, 105, E2152–E2174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Min, J.; Yang, G.; Cao, Y. Contrasting the Effects of X-Band Phased Array Radar and S-Band Doppler Radar Data Assimilation on Rainstorm Forecasting in the Pearl River Delta. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 2655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Xian-Tong, L.; Bing-Hong, C.; Jia-Bao, F.; Lin, C.; Cong-Cong, T. Application of X-band Polarimetric Phased-array Radars in Quantitative Precipitation Estimation. J. Trop. Meteorol. 2023, 29, 142–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Huang, H.; Yu, Y.; Zhao, K.; Yang, Z.; Chen, G.; Zhang, Y. Study on the quantitative precipitation estimation of X-band dual-polarization phased array radar from specific differential phase. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Qi, Y.; Lan, H.; Zhu, Z.; Zeng, Q.; Luo, M.; Liu, A.; Zong, R. Introduction to a radar mosaicking system for quantitative precipitation estimation based on the S-band and X-band phase-array polarimetric radars in Shenzhen. Acta Meteorol. Sin. 2023, 81, 506–519. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wu, T.; Wan, Y.; Wo, W.; Leng, L. Design and Application of Radar Reflectivity Quality Control Algorithm in SWAN. Meteorol. Sci. Technol. 2013, 41, 809–817. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, Y.; Liu, L.; Yang, H. Technique for generating hybrid reflectivity field based on 3-D mosaicked reflectivity of weather radar network. Acta Meteorol. Sin. 2008, 66, 470–473. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Smith, P.; Joss, J. Use of a fixed exponent in ‘‘adjustable’’ Z-R relationships. In Proceedings of the 28th Conference on Radar Meteorology, Austin, TX, USA, 7–12 September 1997; American Meteorological Society: Boston, MA, USA, 1997; p. 255. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Feng, Y.; Cai, J.; Hu, S. An approach for radar quantitative precipitation estimate based on categorical Z-I relations. J. Trop. Meteorol. 2011, 27, 601–608. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Gou, Y.; Ma, Y.; Chen, H.; Yin, J. Utilization of a C-band polarimetric radar for severe rainfall event analysis in complex terrain over eastern China. Remote Sens. 2018, 11, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Zhao, K.; Zhang, G.; Lin, Q.; Wen, L.; Chen, G.; Yang, Z.; Wang, M.; Hu, D. Quantitative precipitation estimation with operational polarimetric radar measurements in Southern China: A differential phase–based variational approach. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2018, 35, 1253–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, K.; Huang, H.; Wang, M.; Lee, W.-C.; Chen, G.; Wen, L.; Wen, J.; Zhang, G.; Xue, M.; Yang, Z.; et al. Recent Progress in Dual-Polarization Radar Research and Applications in China. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2019, 36, 961–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabary, P. The new French operational radar rainfall product. Part I: Methodology. Weather Forecast. 2007, 22, 393–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faure, D.; Gaussiat, N.; Dupuy, P.; Delrieu, G.; Yu, N.; Sarter, F. Quality analysis of the 2016 quantitative precipitation estimates in the French Alps. In Proceedings of the 38th Conference on Radar Meteorology, Chicago, IL, USA, 28 August–1 September 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Tabary, P.; Desplats, J.; Do Khac, K.; Eideliman, F.; Gueguen, C.; Heinrich, J. The new French operational radar rainfall product. Part II: Validation. Weather Forecast. 2007, 22, 409–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugier, J.; du Chatelet, J.P.; Roquain, P.; Smith, A. Detection and removal of clutter and anaprop in radar data using a statistical scheme based on echo fluctuation. Proc. ERAD (2002) 2002, 17–24. [Google Scholar]
- Andrieu, H.; Creutin, J.D. Identification of vertical profiles of radar reflectivity for hydrological applications using an inverse method. Part I: Formulation. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 1995, 34, 225–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrieu, H.; Creutin, J.D. Identification of vertical profiles of radar reflectivity for hydrological applications using an inverse method. Part II: Formulation. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 1995, 34, 240–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Figueras i Ventura, J.; Boumahmoud, A.-A.; Fradon, B.; Dupuy, P.; Tabary, P. Long-term monitoring of French polarimetric radar data quality and evaluation of several polarimetric quantitative precipitation estimators in ideal conditions for operational implementation at C-band. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2012, 138, 2212–2228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueras i Ventura, J.; Tabary, P. The new French operational polarimetric radar rainfall rate product. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2013, 52, 1817–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, T.J.; Nesbitt, S.W.; Carey, L.D. On the correction of partial beam blockage in polarimetric radar data. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2009, 26, 943–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Zrnić, D.; Ryzhkov, A. Partial beam blockage correction using polarimetric radar measurements. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2013, 30, 861–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurri, M.; Huuskonen, A. Measurements of the transmission loss of a radome at different rain intensities. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2008, 25, 1590–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frech, M. The effect of a wet radome on dualpol data quality. In Proceedings of the 34th Conference on Radar Meteorology, Williamsburg, VA, USA, 5–9 October 2009; American Meteorological Society: Boston, MA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Frasier, S.J.; Kabeche, F.; i Ventura, J.F.; Al-Sakka, H.; Tabary, P.; Beck, J.; Bousquet, O. In-place estimation of wet radome attenuation at X band. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2013, 30, 917–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorgucci, E.; Bechini, R.; Baldini, L.; Cremonini, R.; Chandrasekar, V. The influence of antenna radome on weather radar calibration and its real-time assessment. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2013, 30, 676–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, T.; Rico-Ramirez, M.A.; Han, D.; Srivastava, P.K. Artificial intelligence techniques for clutter identification with polarimetric radar signatures. Atmos. Res. 2012, 109, 95–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakshmanan, V.; Karstens, C.; Krause, J.; Tang, L. Quality control of weather radar data using polarimetric variables. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2014, 31, 1234–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husnoo, N.; Darlington, T.; Torres, S.; Warde, D. A Neural Network Quality-Control Scheme for Improved Quantitative Precipitation Estimation Accuracy on the UK Weather Radar Network. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2021, 38, 1157–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frei, C.; Schär, C. A precipitation climatology of the Alps from high-resolution rain-gauge observations. Int. J. Climatol. A J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1998, 18, 873–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porcacchia, L.; Kirstetter, P.; Gourley, J.; Maggioni, V.; Cheong, B.; Anagnostou, M. Toward a polarimetric radar classification scheme for coalescence-dominant precipitation: Application to complex terrain. J. Hydrometeorol. 2017, 18, 3199–3215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Chang, P.-L.; Langston, C.; Kaney, B.; Tang, L. Operational C-band dual-polarization radar QPE for the subtropical complex terrain of Taiwan. Adv. Meteorol. 2016, 2016, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Crochet, P. Enhancing radar estimates of precipitation over complex terrain using information derived from an orographic precipitation model. J. Hydrol. 2009, 377, 417–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwiebel, J.; Van Baelen, J.; Anquetin, S.; Pointin, Y.; Boudevillain, B. Impacts of orography and rain intensity on rainfall structure. The case of the HyMeX IOP7a event. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2016, 142, 310–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Guo, J.; Yun, Y.; Li, J.; Guo, X.; Lv, Y.; Wang, D.; Li, L.; Zhang, Y. Regional variability of summertime raindrop size distribution from a network of disdrometers in Beijing. Atmos. Res. 2021, 257, 105591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Li, H.; Li, D.; Qi, Y. Spatial Variability of Raindrop Size Distribution at Beijing City Scale and Its Implications for Polarimetric Radar QPE. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 3964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Germann, U.; Boscacci, M.; Clementi, L.; Gabella, M.; Hering, A.; Sartori, M.; Sideris, I.V.; Calpini, B. Weather radar in complex orography. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van den Heuvel, F.; Foresti, L.; Gabella, M.; Germann, U.; Berne, A. Learning about the vertical structure of radar reflectivity using hydrometeor classes and neural networks in the Swiss Alps. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2020, 13, 2481–2500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryzhkov, A.; Zhang, P.; Bukovčić, P.; Zhang, J.; Cocks, S. Polarimetric radar quantitative precipitation estimation. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanft, W.; Zhang, J.; Simpson, M. Dual-Pol VPR Corrections for Improved Operational Radar QPE in MRMS. J. Hydrometeorol. 2023, 24, 353–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Ryzhkov, A. Climatology of the vertical profiles of polarimetric radar variables and retrieved microphysical parameters in continental/tropical MCSs and landfalling hurricanes. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2022, 127, e2021JD035498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorgensen, D.P.; Willis, P.T. A ZR relationship for hurricanes. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 1982, 21, 356–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willis, P.T. Functional fits to some observed drop size distributions and parameterization of rain. J. Atmos. Sci. 1984, 41, 1648–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuter, S.E.; Houze, R.A. Measurements of raindrop size distributions over the Pacific warm pool and implications for Z–R relations. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 1997, 36, 847–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, A.Y.; Kakar, R.K.; Neeck, S.; Azarbarzin, A.A.; Kummerow, C.D.; Kojima, M.; Oki, R.; Nakamura, K.; Iguchi, T. The global precipitation measurement mission. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2014, 95, 701–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iguchi, T.; Seto, S.; Meneghini, R.; Yoshida, N.; Awaka, J.; Le, M.; Chandrasekar, V.; Kubota, T. GPM/DPR Level-2 Algorithm Theoretical Basis Document; NASA Goddard Space Flight Center: Greenbelt, MD, USA, 2010.
- Zhu, Z.; Qi, Y.; Cao, Q.; Li, D.; Zhang, Z.; Cao, J.; Xue, M. Particle Size Distribution Characteristics Within Different Regions of Mature Squall-Line Based on the Analysis of Global Precipitation Measurement Dual-Frequency Precipitation Radar Retrieval. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2020, 19, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Qi, Y.; Li, D. Improving CINRAD Radar QPE Through GPM-DPR Reflectivity Bias Correction. Water Resour. Res. 2023, 59, e2022WR033719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cocks, S.B.; Martinaitis, S.M.; Kaney, B.; Zhang, J.; Howard, K. MRMS QPE performance during the 2013/14 cool season. J. Hydrometeorol. 2016, 17, 791–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, D.; Taylor, P.A.; Isaac, G.A. Snowfall rate estimation using C-band polarimetric radars. Meteorol. Appl. 2017, 24, 142–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bukovčić, P.; Ryzhkov, A.; Zrnić, D.; Zhang, G. Polarimetric radar relations for quantification of snow based on disdrometer data. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2018, 57, 103–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bukovčić, P.; Ryzhkov, A.; Zrnić, D. Polarimetric relations for snow estimation—Radar verification. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2020, 59, 991–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanft, W.; Zhang, J.; Bukovčić, P.; Ryzhkov, A.V.; Cocks, S.B.; Martinaitis, S.M.; Howard, K.W. Dual-Polarization Radar Snow QPE in MRMS. In Proceedings of the 100th American Meteorological Society Annual Meeting, Boston, MA, USA, 12–16 January 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Palmer, R.D.; Schvartzman, D. Emerging Trends in Radar: Phased Arrays for Weather Observations. IEEE Aerosp. Electron. Syst. Mag. 2025, 40, 60–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, R.D.; Yeary, M.B.; Schvartzman, D.; Salazar-Cerreno, J.L.; Fulton, C.; McCord, M.; Cheong, B.; Bodine, D.; Kirstetter, P.; Sigmarsson, H.H. Horus—A fully digital polarimetric phased array radar for next-generation weather observations. IEEE Trans. Radar Syst. 2023, 1, 96–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, R.D.; Fulton, C.J.; Salazar, J.; Sigmarsson, H.; Yeary, M. The ”Horus” Radar—An All-Digital Polarimetric Phased Array Radar for Multi-Mission Surveillance. In Proceedings of the 99th Annual AMS Meeting 2019, Phoenix, AZ, USA, 6–10 January 2019; p. 8A.6. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).