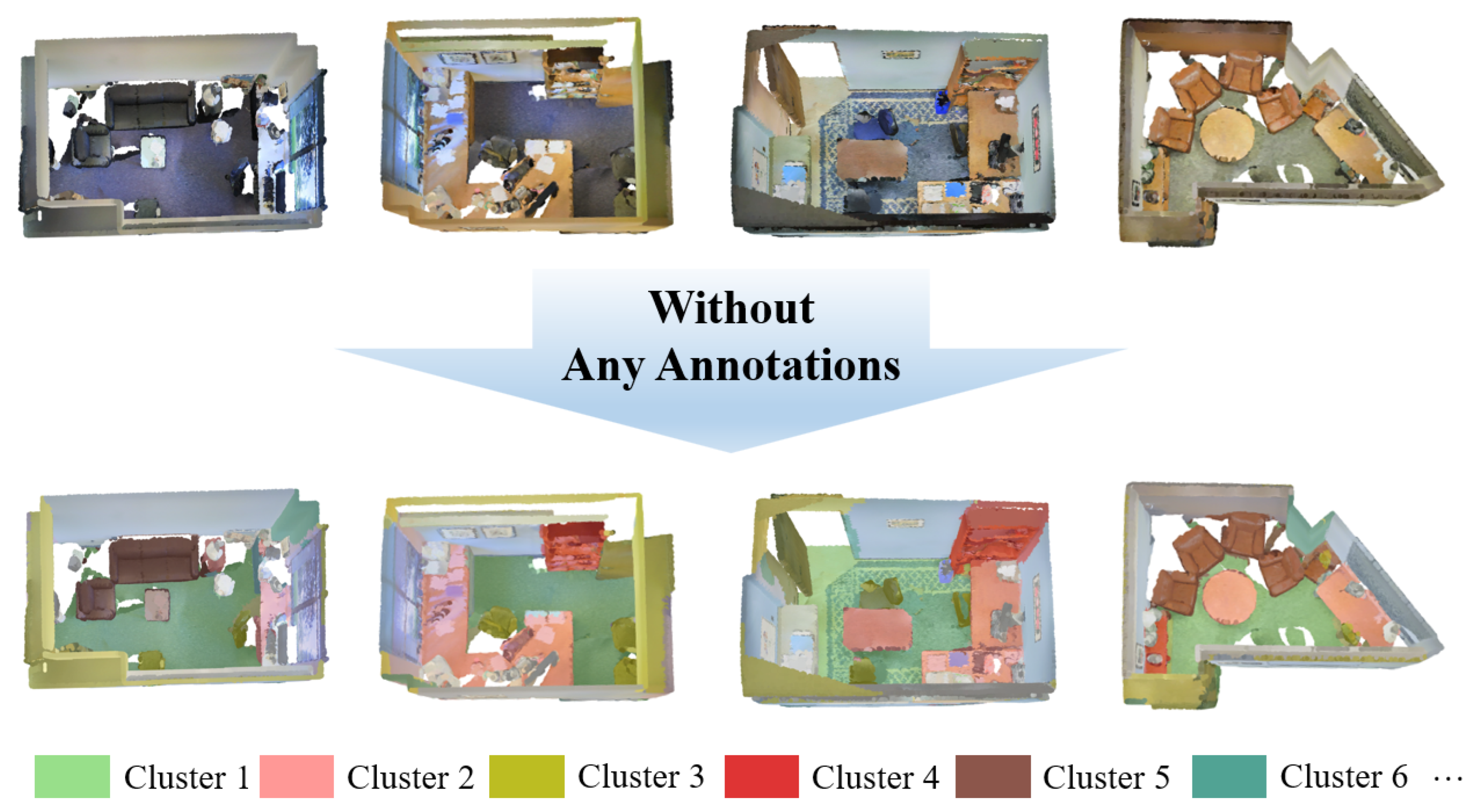
Highlights
What are the main findings?
- We propose CGHP, a component-guided hierarchical progressive framework that achieves unsupervised 3D point cloud segmentation without any manual annotations, 2D data, or pre-trained models.
- The framework integrates component-level descriptors with an adjacency-constrained progressive clustering strategy, enabling effective transition from component- to object-level semantics and achieving competitive results on benchmark datasets.
What is the implication of the main finding?
- The results demonstrate that structured priors and hierarchical learning can substantially enhance unsupervised 3D semantic segmentation, effectively narrowing the gap with supervised methods.
- The framework provides a scalable solution for processing massive airborne and terrestrial point clouds, enabling broader applications in smart city development and scene understanding.
Abstract
With the rapid development of airborne LiDAR and photogrammetric techniques, massive amounts of high-resolution 3D point cloud data have become increasingly available. However, extracting meaningful semantic information from such unstructured and noisy point clouds remains a challenging task, particularly in the absence of manually annotated labels. We present CGHP, a novel component-guided hierarchical progressive framework that addresses this challenge through a two-stage learning approach. Our method first decomposes point clouds into components using geometric and appearance consistency, constructing comprehensive geometric-appearance descriptors that capture shape, scale, and gravity-aligned distribution information to guide initial feature learning. These component-level features then undergo progressive growth through an adjacency-constrained clustering algorithm that gradually merges components into object-level semantic clusters. Extensive experiments on publicly available point cloud datasets S3DIS and ScanNet++ datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed method. On the S3DIS dataset, our method achieves state-of-the-art performance, with 48.69% mIoU and 79.68% OA, without using any annotations, closely approaching the results of fully supervised PointNet++ (50.1% mIoU, 77.5% OA). On the more challenging ScanNet++ benchmark, our approach also demonstrates competitive performance in terms of both mAcc and mIoU.
1. Introduction
Three-dimensional point cloud semantic segmentation serves as a foundational technology for robotic navigation, scene understanding, and virtual reality applications [1] and has also become essential in autonomous driving and marine navigation, where vehicle- or ship-mounted LiDAR systems enable perception, obstacle detection, and situational awareness [2,3,4,5]. Moreover, 3D semantic segmentation techniques have also found growing use in human-centered applications such as intelligent rehabilitation and human–machine interaction, highlighting their broad applicability across diverse fields [6,7]. While fully supervised approaches [8,9,10] have demonstrated remarkable progress, their reliance on extensive point-level annotations (requiring up to 22.3 min per scene in ScanNet [11]) considerably impedes practical deployment. Although contemporary semi-supervised [12,13,14,15] and weakly supervised [16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25] methods reduce annotation requirements, they still necessitate partial human intervention.
Consequently, unsupervised point cloud semantic segmentation, which completely eliminates annotation requirements, has emerged as a frontier challenge in this domain. This challenge is particularly formidable due to its inherent circular dependency: generating high-quality feature representations demands supervision with accurate labels, while obtaining accurate labels requires models capable of producing meaningful feature representations—a classic chicken-and-egg dilemma. In this study, we aim to develop an unsupervised framework for 3D semantic segmentation that automatically learns to discover and disentangle semantic concepts from raw point cloud data, without relying on any manual annotations, as presented in Figure 1.

Figure 1.
From raw point cloud data, our framework is designed to identify meaningful segments automatically without any supervisory signals. Different color blocks indicate distinct semantic clusters generated by the proposed method.
Traditional clustering methods exhibit considerable limitations. Kmeans [26] struggles to form coherent clusters in the presence of uneven data distributions, noise, and outliers. DBSCAN [27] demonstrates poor performance in detecting clusters of varying densities, requires reduced density thresholds for boundary identification, and suffers from substantial performance degradation in high-dimensional spaces. However, other classical clustering algorithms, such as HDBSCAN [28], Mean Shift [29], Gaussian Mixture Models (GMM) [30], and Euclidean distance-based hierarchical clustering [31], also face scalability and computational efficiency challenges when applied to high-dimensional, irregular point clouds. Specifically, they suffer from density degradation, high computational cost, and difficulty handling non-Gaussian and non-convex spatial distributions.
Existing 2D approaches, such as IIC [32] and PiCIE [33], employ self-supervised learning to extract semantically meaningful features through transformation invariance and equivariance while optimizing semantic cluster compactness. However, their direct adaptation to 3D point clouds encounters substantial challenges: (1) clustering ambiguity arising from the typically smaller data volume, limited diversity, and imbalanced class distribution in 3D data, leading to ambiguous cluster boundaries; (2) spatial density irregularity, where point clouds exhibit highly non-uniform density distributions, severely impacting clustering effectiveness. Consequently, direct adaptations of methods [34,35] to 3D scenarios have shown limited improvements. For instance, on the S3DIS [36] dataset, IIC [32] achieves only 28.5% OA and 6.4% mIoU, while PiCIE [33] reaches 61.6% OA and 17.9% mIoU when applied to 3D data, highlighting the difficulty of transferring 2D self-supervised clustering paradigms to irregular and sparse 3D domains.
Recent 3D approaches have attempted to address these limitations. PointDC [35] employs cross-modal distillation and supervoxel clustering, yet its reliance on 2D data for cross-modal distillation restricts generalization. Its supervoxel clustering module, based on classical superpoint segmentation algorithms, overlooks spatial regularization constraints, resulting in either highly homogeneous but undersized superpoints or large volumes lacking semantic consistency, thus failing to fully leverage point cloud local consistency. While GrowSP [34] utilizes PFH [37] descriptors for training guidance and implements region growing for high-quality oversegmentation without 2D data dependency, the PFH descriptors’ inherent limitation in capturing spatial distribution and scale information, along with the region growing process that solely relies on geometric consistency constraints in superpoint generation, renders it inadequate for achieving optimal semantic segmentation in complex scenarios.
For unsupervised semantic segmentation, direct object-level semantic learning proves exceptionally challenging. Inspired by recognition-by-components theory [38] and Gestalt laws [39], human visual systems first identify geometrically and appearance-consistent adjacent points as components, subsequently combining these components into complete objects based on proximity principles and statistical co-occurrence. However, prior studies have overlooked the explicit utilization of this “component-to-object” hierarchical structure in guiding unsupervised 3D semantic segmentation.
In this study, we propose a novel component-guided hierarchical progressive (CGHP) unsupervised segmentation framework encompassing (I) component-level semantic learning and (II) component- to object-level learning, capable of discovering semantic objects without any labels, 2D data, or pre-trained models. Phase I partitions the original point cloud into components based on geometric and appearance consistency, incorporating physical descriptors that integrate shape, scale, and gravity direction information to enhance component features and guide learning. Phase II introduces a heuristic component graph progressive aggregation module that facilitates the transition from component-level to object-level semantics through adaptive component-graph growth.
The core insight of our approach lies in its progressive learning paradigm, advancing from lower-level component semantics to higher-level object semantics. Our method fully exploits point cloud local consistency by decomposing point clouds into components, providing reliable component-level priors while incorporating physical descriptors to guide model learning with comprehensive consideration of component shape and scale distribution information. Additionally, we develop a strategy for component-level to object-level semantic learning that effectively promotes object-level semantic understanding. We conduct extensive experimental validation on S3DIS and ScanNet++ datasets, demonstrating the efficacy of our proposed approach.
In summary, our primary contributions are fourfold:
- We propose CGHP, a novel component-guided unsupervised point cloud semantic segmentation framework that incorporates component recognition theory and Gestalt laws, establishing a “component-to-object” hierarchical optimization paradigm.
- We introduce an elegant component construction strategy and component descriptors for guiding component-level semantic learning.
- We develop a heuristic adjacent component graph progressive aggregation module to facilitate the transition from component-level to object-level semantics.
- Our CGHP approach achieves substantial improvements over existing unsupervised methods in 3D semantic segmentation, validating its effectiveness.
2. Related Work
In this section, we review prior art in two main streams: (1) supervised 3D semantic segmentation, covering point-based, voxel-based, and self-supervised pre-training methods; and (2) unsupervised segmentation learning, starting from 2D clustering-based frameworks and extending to 3D techniques.
2.1. Three-Dimensional Semantic Segmentation
With the public availability of point cloud datasets [11,36,40,41,42,43,44,45,46,47,48,49], supervised methods for point cloud analysis have witnessed rapid advancement in recent years. These approaches can be broadly categorized into point-based [9,50,51,52,53,54,55] and voxel-based methods [56,57,58]. In point-based approaches, PointNet [59] as a seminal work directly learns per-point features using shared MLP and max-pooling operations. Subsequent works have largely followed this paradigm. For voxel-based methods, unstructured point clouds are voxelized into regular spheres, cubes or cylinders, enabling the application of existing convolutional networks. Given the inherent sparsity of point clouds, sparse convolution techniques [10,60,61] have been developed to process voxelized representations effectively. With the advancement of self-supervised learning, methods such as PointContrast [62], CSC [63], and MSC [64] have demonstrated that feature representations learned through self-supervised pre-training on unlabeled data can effectively capture local geometric structures and spatial consistency information in point clouds. This prior knowledge provides more discriminative feature representations for semantic segmentation tasks, enhancing model generalization and overall performance [65,66,67,68,69,70,71,72]. Despite their impressive performance, these methods require expensive dense point annotations for training, which is time consuming and labor intensive.
2.2. Unsupervised Segmentation Learning
2.2.1. Two-Dimensional Unsupervised Methods
Remarkable progress has been made in 2D unsupervised semantic segmentation. DeepCluster [73] iteratively groups feature vectors of the entire dataset using Kmeans [26] to assign pseudo-labels, utilizing these assignments as supervision to update network weights. IIC [32] introduces invariant-information clustering in pixel-level representation, learning by maximizing mutual information between class assignments of paired samples after random transformations. PICIE [33] extends clustering from images to pixels, assigning separate cluster membership to different instances within each image by incorporating geometric consistency as an inductive bias to learn invariance and equivariance for photometric and geometric variations. However, these methods have proven ineffective when directly applied to 3D point clouds due to the fundamental domain gap between images and point clouds [34,35].
2.2.2. Three-Dimensional Unsupervised Methods
In the 3D domain, several approaches have been proposed to address the limitations of 2D methods, achieving notable improvements in performance. GrowSP [34] employs a progressive region-growing scheme to generate high-quality over-segmentation. However, this method does not fully leverage the intrinsic geometric and appearance information of point clouds, resulting in suboptimal semantic partitioning in complex scenes. PointDC [35] addresses clustering ambiguity caused by limited data magnitude and imbalanced class distribution through cross-modal distillation, while utilizing super-voxel clustering to mitigate irregularity ambiguity stemming from point cloud sparsity. Nevertheless, their reliance on 2D data constrains generalization capability. OGC [74] can simultaneously identify multiple 3D objects in a single forward pass without human annotations by leveraging dynamic motion patterns over sequential point clouds as supervision signals for automatic object discovery. However, OGC requires dynamic information from consecutive point cloud frames as input priors.
3. Method
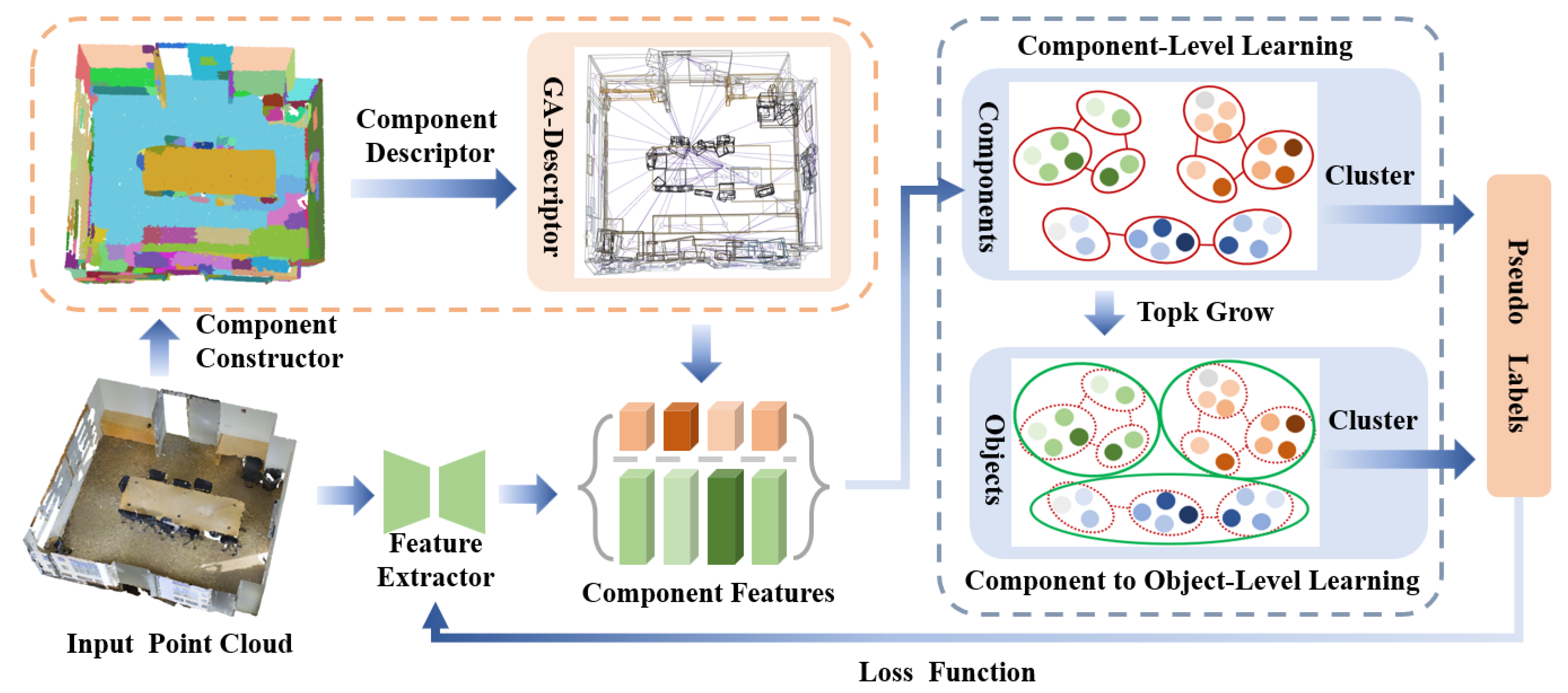
In this section, we propose a novel unsupervised framework for 3D point cloud semantic segmentation that progressively discovers semantic structures through a two-stage learning approach. Our CGHP framework first decomposes point clouds into components using geometric and appearance consistency, and constructs geometry–appearance (GA) descriptors to guide initial feature learning. These component-level features then undergo progressive growth through an adjacency-constrained clustering algorithm that gradually merges components into object-level semantic clusters. The entire framework is trained end-to-end without any manual annotations, leveraging an expectation–maximization (EM)-based [75] optimization strategy that alternates between clustering for pseudo-label generation and model parameter updates.
The remainder of this section details our technical approach as follows: We first formulate the problem and introduce our optimization objective (Section 3.1), followed by preliminaries on EM-based clustering framework that forms the theoretical foundation of our method (Section 3.2). To address the challenges of direct point-level clustering, we propose component-level learning (Section 3.3) that constructs semantically meaningful components guided by geometric and appearance descriptors. We then present a progressive clustering algorithm (Section 3.4) that bridges component-level and object-level semantics through adjacency-constrained growth. Finally, we detail the implementation and training process of our framework Section 3.5. The overview of the CGHP is shown in Figure 2.
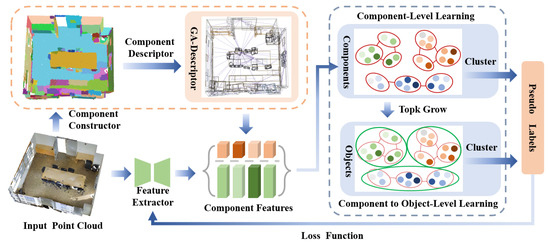
Figure 2.
General framework of our CGHP. The training comprises two steps: component-level learning and component to object-level learning.
3.1. Problem Formulation
Given a point cloud dataset containing R point clouds, where each point cloud represents both coordinate and color information, our objective is to train a feature extractor and classifier in an unsupervised manner (without ground truth labels Y) to predict the semantic category of each point.
3.2. Preliminaries
In the unsupervised setting, directly optimizing model parameters and the classifier poses considerable challenges. Inspired by DeepCluster [73], we adopt an alternating learning approach that iteratively learns features and generates pseudo-labels through cluster-based learning. Theoretically grounded in the EM, this approach iteratively maximizes the lower bound by leveraging weak signals to optimize the backbone feature extractor and classifier parameters.
While existing unsupervised semantic segmentation methods generally follow the DeepCluster paradigm, the constantly evolving pseudo-labels make learning a parametric classifier difficult and unstable. Therefore, following DeepCluster-v2 [76], we employ a non-parametric classifier based on Kmeans centroids for pseudo-label assignment.
We formulate this as an EM optimization problem where the point cloud data serve as observed variables, model parameters as parameters to be optimized, and pointwise semantic labels as latent variables. The optimization proceeds in two main steps:
- (1)
- E-step: With fixed model parameters , we optimize the distribution of latent variables by clustering the current features using Kmeans to obtain cluster labels for each point. Let i and denote the indices of a point and its corresponding point cloud, respectively.where denotes the k-th cluster centroid, and represents the assigned cluster label of the i-th point in the i’-th point cloud.
- (2)
- M-step: With fixed latent variables, we optimize the model parameters by training with cluster assignments as pseudo-labels:where is the cross-entropy loss function, and represents the non-parametric classifier parameterized by cluster centroids .
3.3. Component-Level Learning
3.3.1. Component Constructor
According to recognition-by-components theory [38] and the Gestalt law of proximity [39], humans perceive point clouds with consistent geometric and appearance properties as components before recognition, considerably simplifying the recognition process. Motivated by this observation, we propose to decompose point clouds into components, transforming the pointwise classification task into a component-level classification task to facilitate subsequent model learning.
However, directly extracting components from point clouds poses considerable challenges. While existing unsupervised superpoint segmentation algorithms offer a straightforward approach, their spatial regularization constraints (e.g., VCCS’s [77] uniformly distributed voxel seed points with voxel connectivity regularization, or cut-pursuit’s [78] spatial regularization parameter) make it difficult to extract meaningful components. This difficulty results in either over-segmented superpoints with high homogeneity but small size or under-segmented superpoints that are large but semantically mixed.
Given the massive and irregular distribution of points in point cloud data , we propose an efficient component construction method. To simplify component extraction, we leverage existing superpoint segmentation algorithms to obtain small superpoints with high geometric-appearance purity, transforming the complex task of extracting components from points into extracting components from superpoints. Specifically, we employ VCCS [77] as the baseline superpoint segmentation algorithm. VCCS integrates geometric, appearance, and spatial connectivity cues through voxel-based seed initialization and local region growing, which effectively maintains local geometric consistency and yields compact superpoints with high purity. This characteristic aligns well with our component construction goal—starting from fine-grained, homogeneous superpoints and progressively merging them into semantically consistent components. Preliminary experiments across various scenes further confirm that VCCS consistently generates stable and reliable over-segmentation results, providing a robust foundation for subsequent hierarchical learning. On the basis of these superpoints, we compute adjacency relationships and merge adjacent superpoints with consistent geometric and appearance properties into components.
Our component construction process consists of two main stages: initial superpoint partitioning and component formation through merging. Given a room point cloud , we first decompose it into superpoints with geometric and appearance homogeneity , where represents the j-th superpoint in the i-th point cloud. Subsequently, we merge these superpoints into larger components based on geometric-appearance consistency through a two-step procedure. The first step identifies adjacent superpoint pairs by computing their spatial proximity. Specifically, we define the adjacency set for each superpoint as follows:
where represents the Euclidean distance between the closest points of superpoints, and serves as a distance threshold.
The second step examines both appearance and geometric consistency between adjacent superpoints. We establish the criteria for merging:
Here, for each superpoint containing points, we compute its mean color and mean normal as follows: , , where indexes the adjacent superpoints in , the notation denotes the L2 norm measuring color difference, and represents the cosine similarity between normal vectors.
Adjacent superpoints satisfying these consistency criteria are merged to form components , expressed as follows:
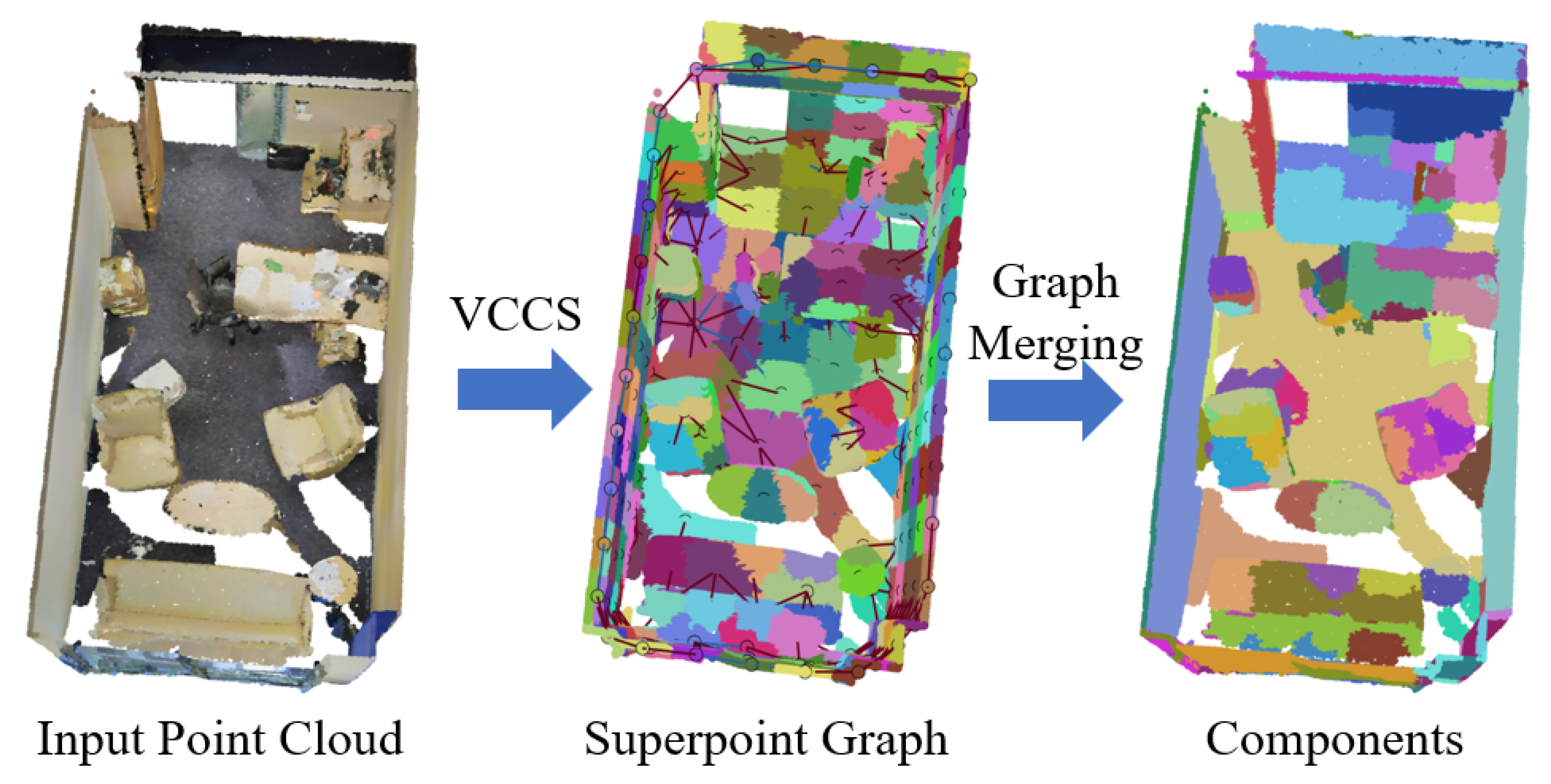
This comprehensive component construction approach addresses several limitations of existing superpoint segmentation algorithms. Notably, it fully incorporates appearance information, distinguishing it from traditional VCCS [77] and region-growing [79] methods. The resulting components provide reliable prior knowledge that substantially benefits subsequent model learning stages. Figure 3 shows an example of components for the raw point cloud.
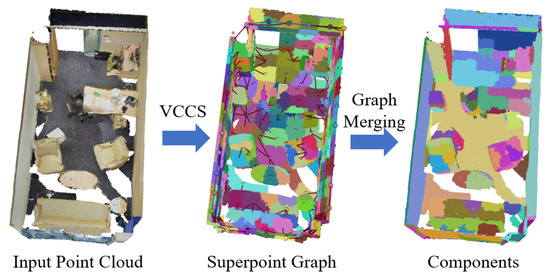
Figure 3.
Example of components constructed by superpoint partitioning and superpoint graph merging. In the superpoint graph, different colors represent distinct superpoints segmented by VCCS, which are subsequently merged through the graph structure. In the resulting components map, different colors correspond to higher-level components obtained after the merging process.
3.3.2. Component Descriptor
The core idea of DeepCluster [73] leverages the inductive bias of 2D ConvNets through EM optimization to enhance feature representation. For 3D point clouds, we employ 3D sparse convolutional networks as feature extractors. However, given the sparsity of 3D point cloud data and considerably smaller dataset sizes compared with carefully curated 2D images, relying solely on 3D network inductive bias makes it challenging for models to learn to distinguish different component categories from scratch. While PointDC employs cross-modal distillation requiring 2D information, such methods are difficult to extend to scenarios with only 3D data.
Therefore, we propose constructing component descriptors as prior knowledge to guide model learning, helping the model understand unlabeled data in unsupervised settings. Intuitively, components with the same semantics share similar geometric and appearance properties. Thus, we design our component descriptor to capture both aspects.
Geometric Properties
Component geometric properties encompass shape, size, and spatial distribution. For shape-size characteristics, considering that components consist of points with normal consistency and to simplify feature description, we represent shape using cuboids, describing shape-size information through bounding box (BB) dimensions length (l), width (w), and height (h). A key observation is that gravity’s downward force determines objects’ vertical (z-axis) distribution characteristics, which are crucial for their structure and function. On the basis of this observation, we aim to preserve components’ vertical distribution information.
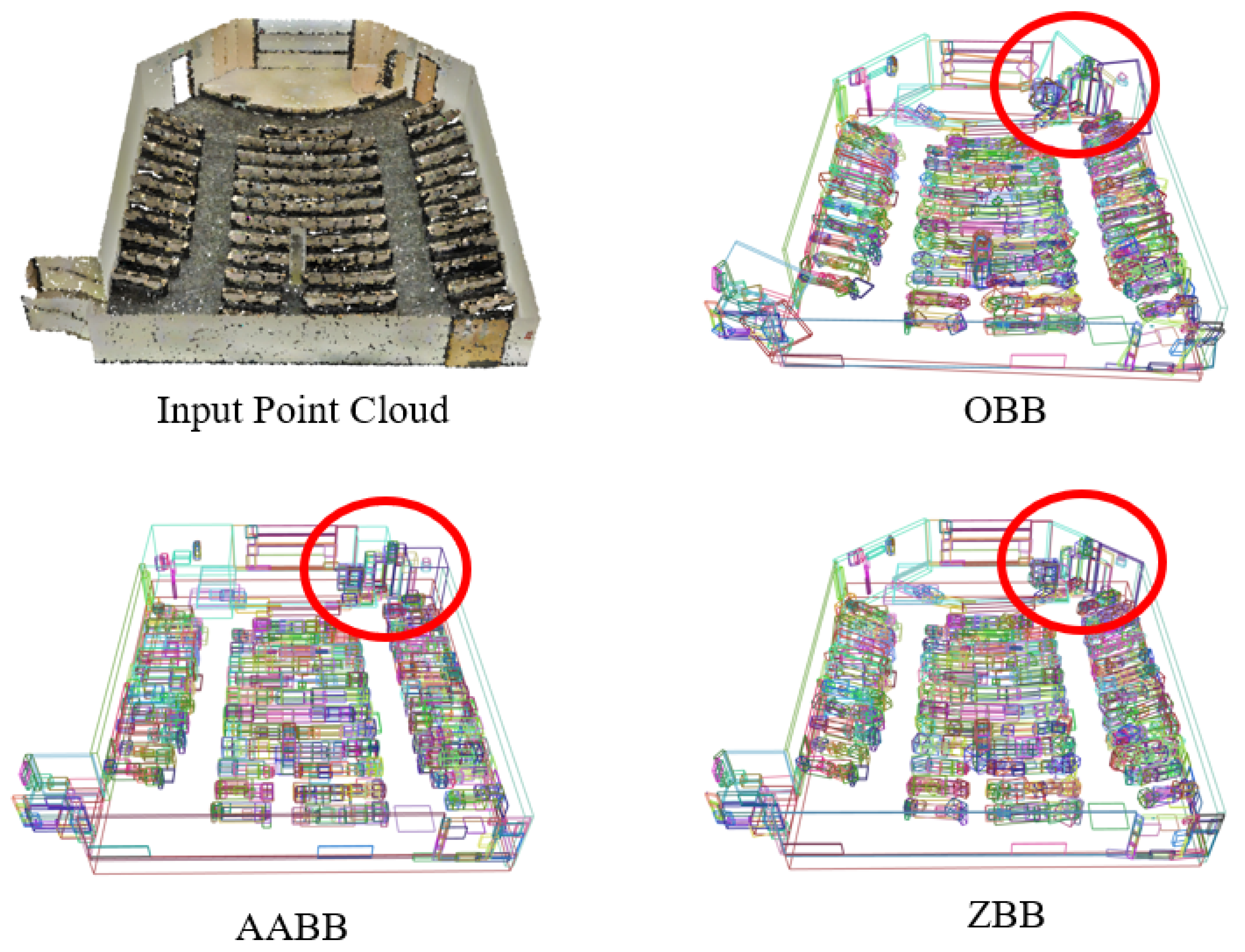
Common approaches for representing component shape-size properties using bounding boxes include axis-aligned bounding box (AABB) and oriented bounding box (OBB). While AABB preserves height information along the vertical z-axis (gravity direction), its axis alignment may overestimate actual component size for rotated or tilted objects. OBB preserves size properties well but poorly maintains vertical height information. To overcome these limitations, we design a novel bounding box, termed ZBB, that simultaneously preserves height attributes and size information. In our experimental setting, the datasets are pre-aligned with gravity, ensuring that the global z-axis corresponds to the true vertical direction. Under this setup, most objects remain approximately upright, and ZBB is thus designed to be yaw-invariant: it maintains vertical extent along z while determining the in-plane orientation and dimensions via PCA on the projection. This design effectively balances the vertical stability of AABB with the in-plane accuracy of OBB, providing a consistent and comparable geometric reference across different scenes.
For spatial distribution, component categories should be invariant to -plane distribution, focusing primarily on vertical distribution information. Specifically, given a component obtained from Section 3.3.1, our approach consists of several computational steps. We first compute the principal component in the -plane to determine the BB orientation, followed by projecting the component onto this principal direction to obtain length and width dimensions (). Subsequently, we utilize the difference between and along the vertical direction to compute the height, while also employing and as spatial distribution features, denoted by H. The ZBB dimensional parameters are computed as follows:
where represents component points projected onto the XY plane, denotes the PCA principal direction in the XY plane with as its orthogonal direction, and , are the maximum and minimum height values, respectively. Figure 4 demonstrates ZBB’s remarkable advantages over conventional bounding boxes (AABB/OBB) in preserving geometric fidelity.
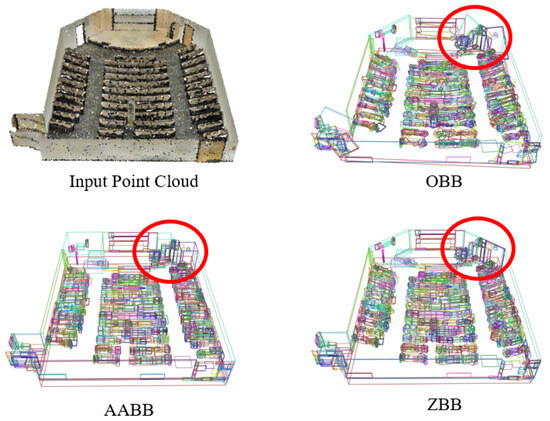
Figure 4.
An example of component bounding box construction, including OBB, AABB, and ZBB. Each color-coded bounding box represents a component.
The spatial distribution feature H and the complete geometric descriptor are defined as follows:
We denote the component dimensions as ZBB and the vertical spatial distribution as H, combining them as the geometric descriptor.
Appearance Properties
We use the mean color of points within the component as the appearance descriptor:
The final component descriptor combines geometric and appearance representations, termed the descriptor.
Our geometric representation incorporates vertical attributes, providing rotational invariance around the z-axis while helping the model better understand physical principles in real-world scenarios, improving comprehension of complex scenes and classification accuracy. The GA descriptor guides model learning by explicitly considering components’ geometric-appearance features, helping identify different components and reducing learning difficulty. To ensure numerical consistency among physical attributes, each component’s GA descriptor is normalized before being concatenated with neural network features to form enhanced component representations for subsequent clustering.
How can we obtain component-level semantic information from these components? A direct strategy would be to cluster the enhanced component features into the actual number of object categories using existing clustering algorithms. However, considering that different instance objects comprise one or more components, and some components belonging to different category objects may be similar, this approach is too aggressive and prone to early-stage misclassification which is difficult to correct. Therefore, we cluster components into a larger number of categories. By clustering components across all scenes, we obtain component-level semantic information.
3.4. Component to Object-Level Learning
How do we transform component-level semantic information into actual object-level semantic information? A straightforward approach would be to re-cluster the obtained component semantic classifier into the number of object categories as the final classifier. However, considering that instance objects consist of multiple components, directly applying this method leads to suboptimal performance. We observe that different components constituting a complete instance object are adjacent and exhibit feature correlation. We aim to address this through adjacent component growth. However, without explicit supervision labels to constrain component growth into instance objects, achieving accurate one-step growth is challenging. Therefore, we propose a heuristic progressive clustering algorithm based on adjacent component growth.
Our approach begins with a pre-training phase following the EM algorithm described in Section 3.2, where component descriptors guide the training of a feature extractor with enhanced representation capability. The subsequent progressive growth process consists of three main steps that iterate until reaching a predetermined maximum ratio .
At time step t with growth ratio , we first obtain meaningful representations of current components through the feature extractor. Component adjacency is determined by computing pairwise distances and applying a threshold :
where denotes the Euclidean distance between the closest points of components. For adjacent components, we compute feature similarity using their neural representations:
On the basis of these computations, we construct a component adjacency graph where edge weights correspond to feature similarities. The growth process starts from an initial graph at each iteration. We sort edge weights in descending order and merge the top-k adjacent component pairs, as formulated by
where represents the number of component pairs to merge, adaptively scaled by the current growth ratio.
Following the component growth phase, we execute the EM steps: clustering current component features to obtain pseudo-labels (E-step) and training the model with these labels for a fixed number of epochs (M-step). The growth ratio increases with each iteration () until reaching .
Our approach avoids cross-spatial region merging errors through explicit adjacency constraints and adaptively adjusts merging granularity for different scenes. While previous work such as GrowSP employed similar ideas, our approach differs in the following ways: First, while GrowSP relies on Kmeans clustering for superpoint reduction within individual rooms, our method explicitly leverages adjacency relations for component growth. Second, instead of applying fixed cluster numbers across all rooms, we adaptively adjust growth based on room-specific component counts, providing increased flexibility in handling varying scene complexities.
3.5. Implementation
3.5.1. Training Phase
We first construct components from given point clouds and generate component descriptors. The components then enter the clustering phase where component descriptors promote model learning. Additionally, we leverage more meaningful neural features for progressive growth of adjacent components to obtain improved quality representations.
3.5.2. Inference Phase
We cluster the component-level classifier into the actual category classifier, predicting one of C categories for each point. Given that true semantic labels are unknown, clustered labels have a random order compared with true semantic labels. For evaluation, we use the Hungarian algorithm to match and align them.
4. Experiment
This section introduces the datasets utilized in this study and describes the training configuration of the proposed model. In terms of assessing model performance, the accuracy of the proposed model was determined by comparing it with those of other state-of-the-art methods. Ablation studies conducted within this work demonstrated the rationality of the proposed model design.
4.1. Dataset Description and Experimental Setup
We conduct extensive experiments on two benchmark datasets: S3DIS [36] and ScanNet++ [80].
S3DIS [36] contains 271 scenes with 13 semantic classes. Following the official protocol, we train on Areas 1, 2, 3, 4, and 6 then evaluate on Area 5. For fair comparison with GrowSP [34], we exclude the clutter class and evaluate on the remaining 12 classes.
ScanNet++ [80] is a large-scale scene dataset featuring high-fidelity 3D geometry and high-resolution RGB images. The dataset comprises 360 training scenes, 50 validation scenes and 50 test scenes. While the dataset includes over 1000 unique semantic classes, we focus on the official top 100 classes and evaluate against existing clustering and unsupervised methods on the validation set.
Implementation Details: Following GrowSP [34], we employ a 3D sparse UNet [60] as our backbone architecture. During the construction of components from superpoints, we empirically set the spatial distance threshold to 0.05,m, the normalized color difference threshold to 0.1, and the normal vector similarity threshold to 0.98. These values are chosen based on geometric intuition and preliminary validation. Specifically, corresponds to approximately 5–10 times the average inter-point distance, allowing adjacent superpoints to be connected while avoiding merges across large gaps. (after RGB normalization to [0, 1]) represents a perceptible color difference of roughly 25/255 per channel, which effectively distinguishes materials (e.g., walls vs. doors) while remaining robust to illumination variation. corresponds to an angular deviation of about 10°, providing a reasonable tolerance for planar structures such as walls and floors, ensuring coplanar regions are merged while tilted surfaces remain distinct. A preliminary sensitivity analysis conducted within small parameter variations (: 0.04–0.06 m; : 0.08–0.12; : 0.96–0.99) indicated consistent segmentation behavior, suggesting that the chosen settings are relatively robust. For progressive component growing, the initial growth ratio is set to 5%.
For evaluation metrics, we adopt the standard mean intersection-over-union (mIoU), overall accuracy (OA), and mean accuracy (mAcc) across all classes. All the evaluation indices are defined as follows:
where represents the number of correctly classified points in class i, denotes the number of points from other classes misclassified as class i, denotes the number of points in class i misclassified into other classes, and N is the total number of categories.
Specifically, OA measures the overall classification correctness of all points, mAcc measures the average classification accuracy across categories to reduce the effect of class imbalance, and mIoU measures the overlap ratio between predictions and ground-truth labels, which is widely used in semantic segmentation evaluation.
4.2. Comparison with Current Methods
We conduct a comprehensive evaluation of our approach against established baselines and state-of-the-art methods in unsupervised point cloud segmentation. The baseline comparisons include RandCluster, which employs Kmeans clustering on per-point features extracted from a randomly initialized backbone network, and Vanilla Kmeans, which directly clusters raw 3D points incorporating spatial coordinates and color information. We further compare against leading unsupervised methods, specifically GrowSP [34] (implemented with original settings as reported) and MSC [64] (utilizing Kmeans clustering with MSC pre-trained features). To validate our methodological contributions rigorously, we augment evaluation by incorporating our proposed component-level constraints and descriptors into vanilla Kmeans and MSC frameworks, denoted as van Kmeans-M and MSC-M, respectively. We also evaluate variants that integrate our GA features, termed van Kmeans-M-GA and MSC-M-GA. This systematic evaluation framework enables us to assess the efficacy of our innovations independently and in combination across different clustering paradigms.
Table 1 and Table 2 demonstrate the effectiveness of our unsupervised approach across two challenging datasets. On the S3DIS dataset, our method achieves state-of-the-art unsupervised performance with 79.68% overall accuracy and 48.69% mIoU, approaching the performance of fully supervised methods such as PointNet++ [50] (77.5% OA, 50.1% mIoU) without requiring any annotations. Compared with the previous best unsupervised method GrowSP [34], we achieve improvements of 4.29% in mIoU and 2.64% in mean accuracy. The effectiveness of our methodological components is evidenced by consistent improvements when integrating them into baseline methods: incorporating component-level constraints and GA descriptors enhances vanilla KMeans’ mIoU from 7.90% to 22.13% and, similarly, improves MSC from 19.55% to 32.15%. We also compare our method with a concurrent work, U3DS3 [81], which reports 42.8% mIoU, 55.8% mAcc, and 75.5% OA on S3DIS, and our approach achieves better performance.

Table 1.
Quantitative results of our method and baselines on the Area-5 of S3DIS dataset.

Table 2.
Semantic segmentation results on ScanNet++ dataset [80]. We evaluate 100 categories on the validation set.
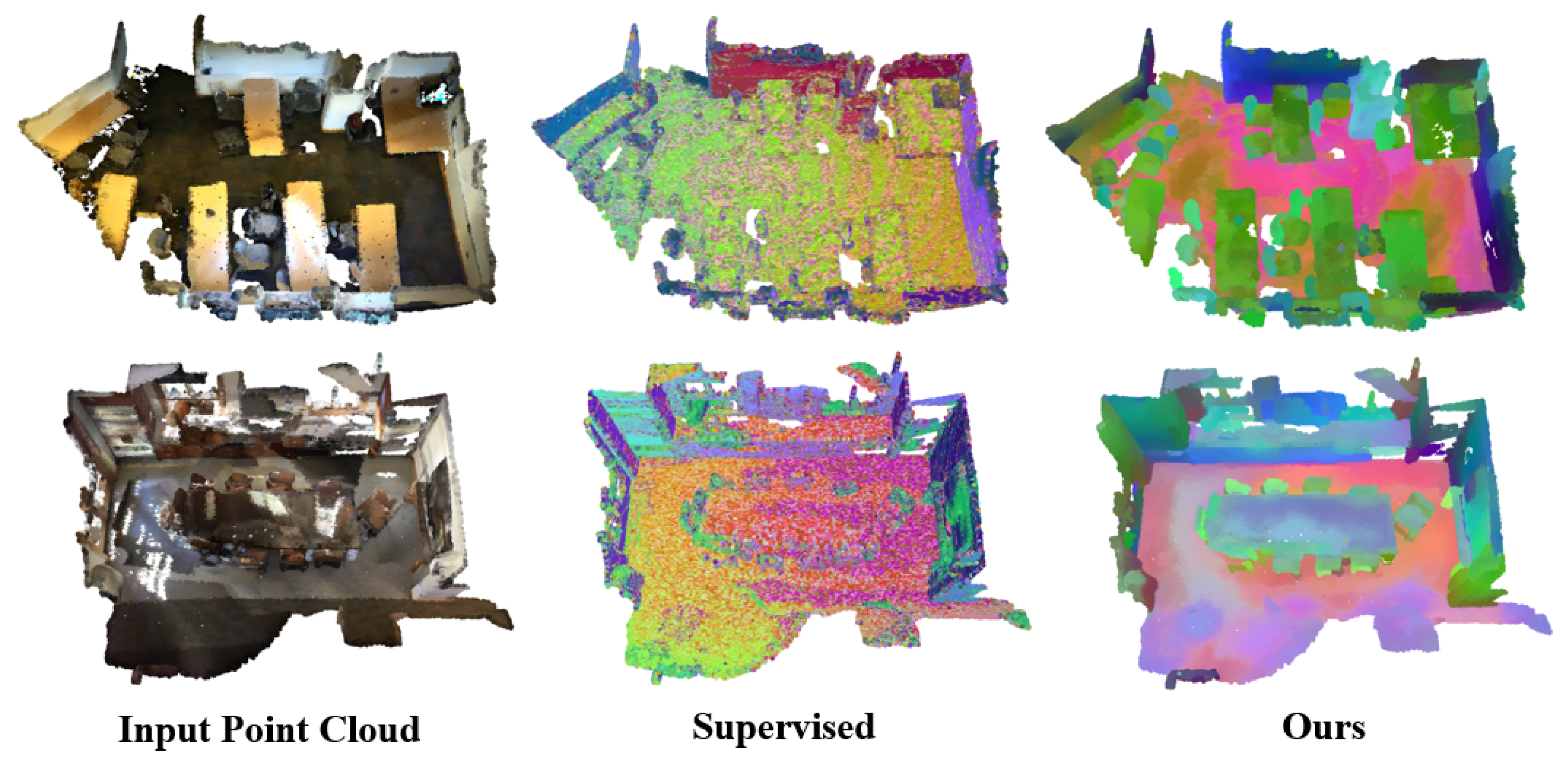
On the more challenging ScanNet++ dataset with a much larger semantic space, our method achieves superior performance, with 17.51% mean accuracy and 9.19% mIoU compared with previous unsupervised approaches. While experiencing a slight decrease in overall accuracy, we demonstrate improved performance in mean accuracy and mIoU, indicating more balanced performance across all categories. Compared with S3DIS, the performance shows a noticeable decline on the more challenging ScanNet++ dataset. This performance degradation is largely attributed to the significantly greater complexity of ScanNet++, which encompasses 100 semantic categories (compared to 13 in S3DIS) and highly cluttered, fine-grained scenes. Despite this increased difficulty, our method still achieves competitive results, comparable to fully supervised methods such as PointNet [59] (7% mIoU) and PointNet++ [50] (15% mIoU), on this complex dataset.
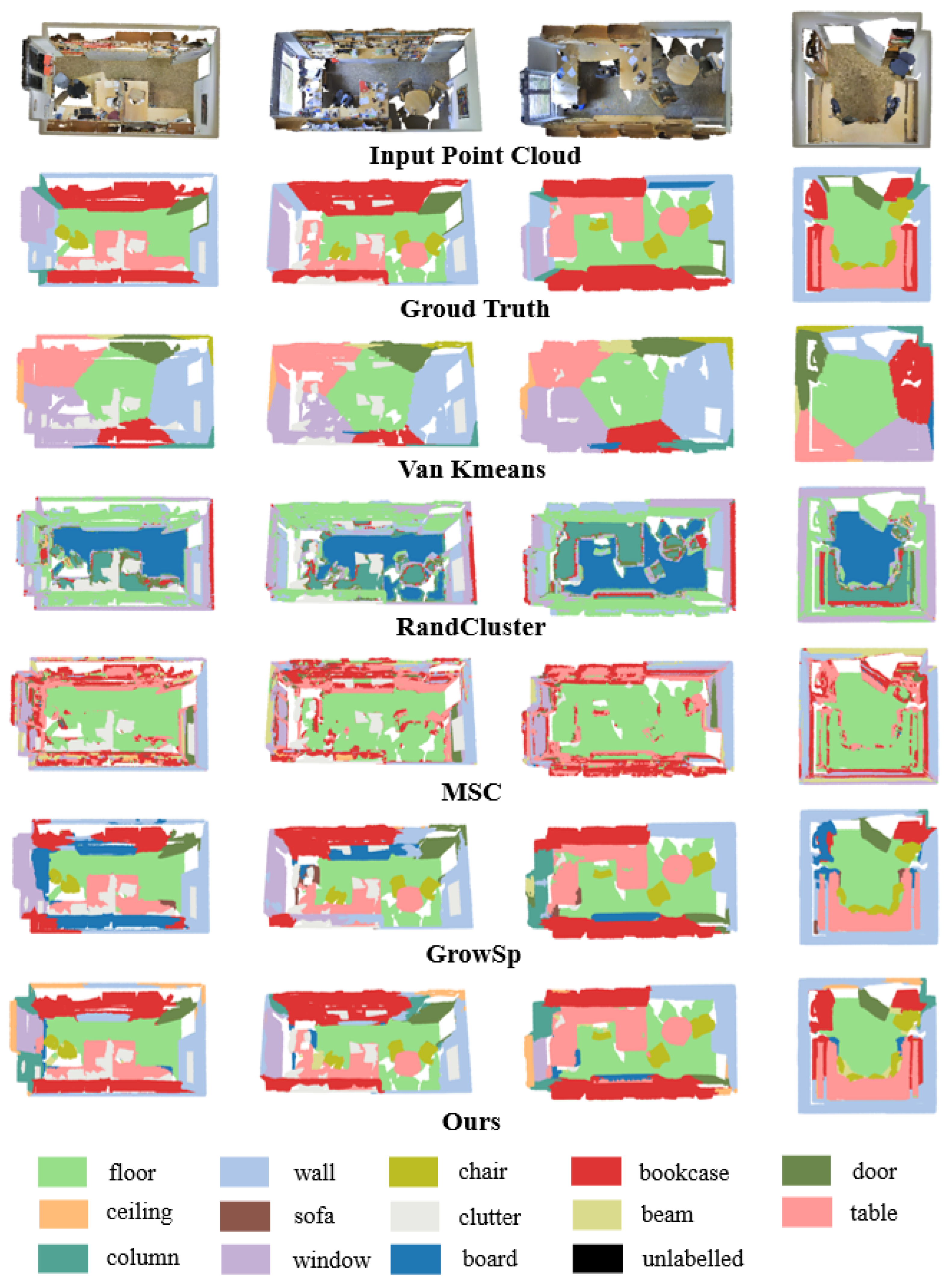
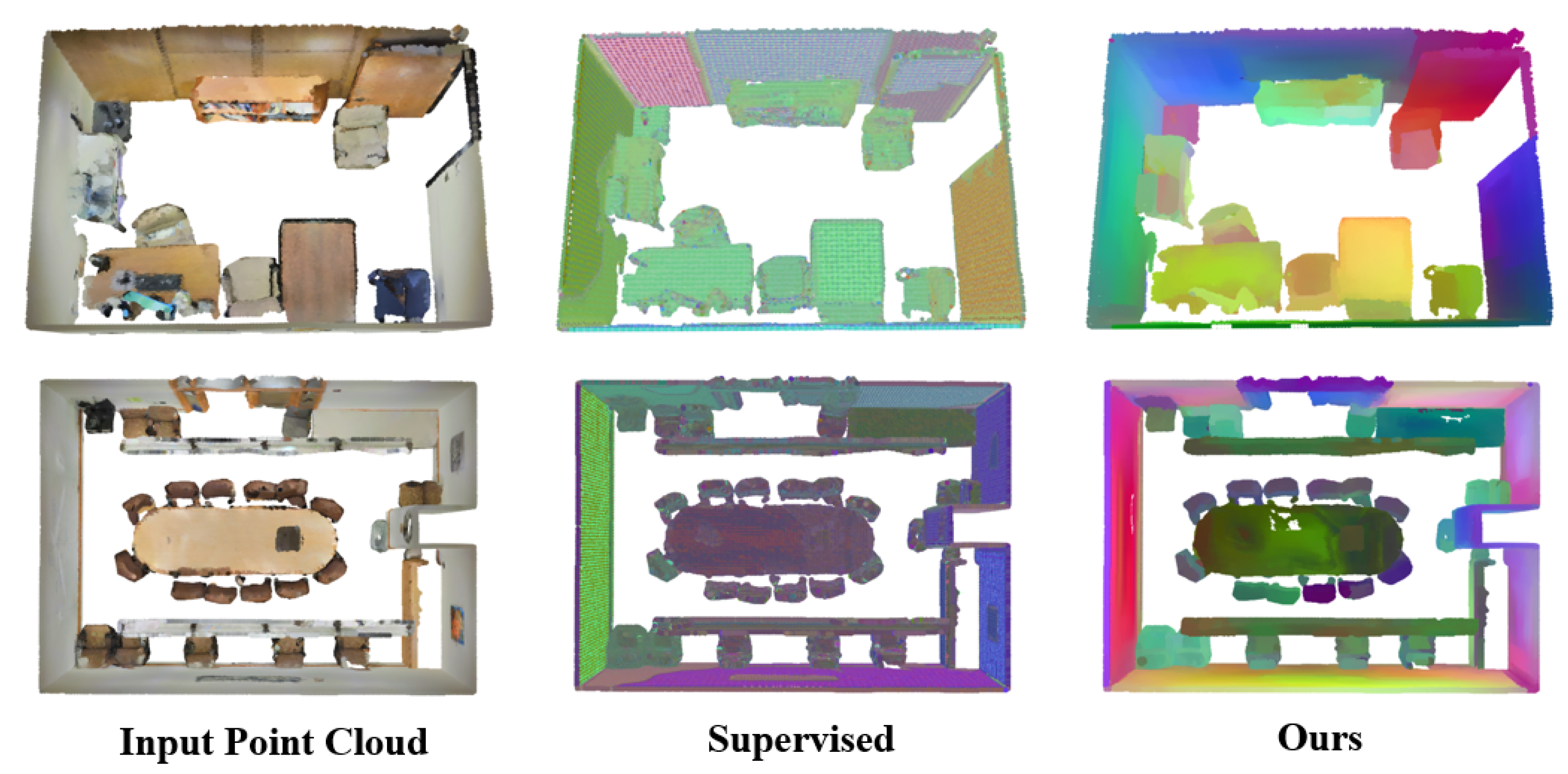
These results validate our two-stage learning approach, demonstrating robust performance on standard benchmarks and generalization to more challenging scenarios with larger semantic spaces. Qualitative results (Figure 5) further validate the superiority of our approach.
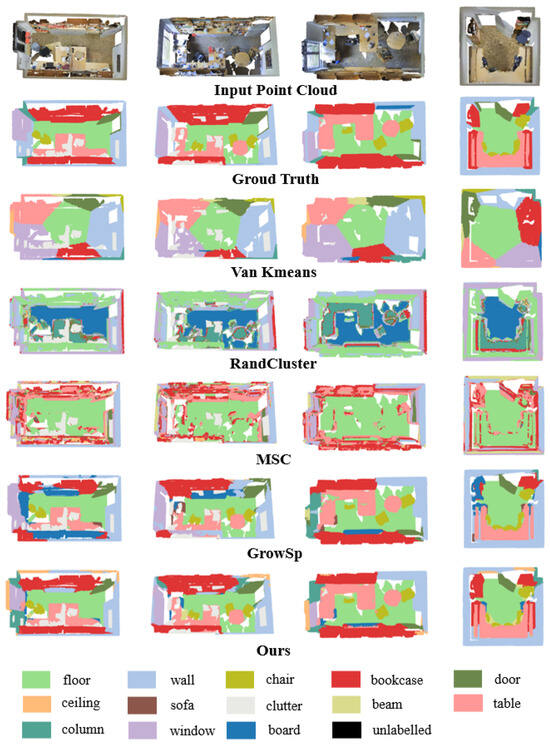
Figure 5.
Qualitative comparison of unsupervised segmentation on S3DIS validation set (Area 5). Ground truth labels and predicted clusters are color-matched for comparison. Corresponding semantic mappings are annotated in the legend.
4.3. Ablation Studies
To validate each module of our pipeline, we conduct comprehensive ablation experiments on the S3DIS dataset, as summarized in Table 3.

Table 3.
Ablation study on S3DIS Area-5.
First, we examine the necessity of our component descriptor by removing it while maintaining all other settings. Second, we investigate the importance of the progressive growth mechanism by eliminating the component-to-object growth phase. Third, we study the impact of different component clustering numbers by evaluating three settings: 100, 300, and 500 clusters. Finally, we analyze the sensitivity to growth ratios by testing four different values: 10%, 15%, 20%, 25%, and 30%.
The ablation results demonstrate the critical role of each component in our framework. Removing the component descriptor leads to a considerable decrease in mIoU from 48.69% to 40.46%, while eliminating the component-to-object growth mechanism results in a performance drop to 42.24% mIoU. These substantial degradations highlight the essential nature of both components in achieving optimal performance. Hyperparameter analysis reveals that the framework performs optimally with 300 component clusters, achieving 48.69% mIoU, while maintaining stable performance with 500 clusters. Regarding the growth ratio, the best segmentation performance is achieved at 15%, while both smaller and larger ratios lead to degradation. This trend arises from the unsupervised nature of our framework: when the growth ratio becomes too large, the merging process loses fine-grained control, causing semantically inconsistent components to be combined incorrectly. Conversely, overly small ratios restrict the merging of semantically related regions, resulting in fragmented object representations.
These results clearly validate the importance of each component in our pipeline, particularly highlighting the importance of the component descriptor and growth mechanism in achieving superior performance.
5. Discussion
The proposed CGHP framework sheds light on how structured priors can be systematically integrated into unsupervised point cloud analysis. Unlike prior unsupervised methods that either rely heavily on handcrafted geometric cues or adapt 2D self-supervised paradigms, CGHP explicitly incorporates a hierarchical learning process that more closely mirrors human perception. This design demonstrates that progressively bridging local consistency and global semantics can be a powerful alternative to direct object-level clustering.
One notable implication of our results is that unsupervised 3D segmentation can significantly benefit from hybrid strategies that combine descriptive priors with data-driven learning. While fully supervised methods depend on exhaustive annotations, and purely self-supervised methods often struggle with ambiguity in irregular point clouds, CGHP shows that leveraging component-level structures as intermediaries can mitigate both extremes. This perspective opens up opportunities to rethink the role of domain knowledge in unsupervised representation learning.
We further observe that our unsupervised method achieves comparable mIoU performance to the fully supervised PointNet++ on S3DIS, and to better understand this phenomenon, we visualize the learned feature spaces. We employ UMAP [82] to reduce the backbone features of a fully supervised 3D sparse UNet [60], which is adopted here to maintain architectural consistency with our unsupervised framework, into three dimensions and project them onto the point cloud. Similarly, we apply the same dimensionality reduction to the backbone features learned by our unsupervised framework. As shown in Figure 6, both feature spaces exhibit strong semantic consistency—points belonging to the same semantic category tend to cluster together. However, their spatial distributions differ significantly. The supervised model forms compact, label-driven clusters organized explicitly by semantic annotations, whereas our unsupervised method arranges features according to component-level geometric and spatial regularities. These regularities, such as the separation of walls, doors, and furniture, naturally align with semantic boundaries, which explains why CGHP can achieve performance comparable to supervised methods despite the absence of labels. This finding suggests that the component structure representations learned by CGHP capture spatial and geometric cues that partially overlap with the semantic features learned in supervised networks. Rather than replicating label-based semantics, CGHP derives highly interpretable and semantically coherent structural representations directly from the data through component construction and hierarchical aggregation, serving as an implicit bridge between structural regularities and semantic understanding.
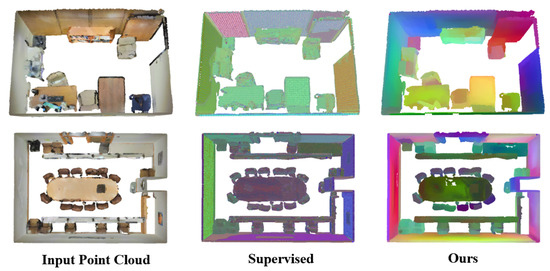
Figure 6.
Visualization of learned feature spaces on the S3DIS dataset. Colors represent feature similarities in the projected three-dimensional UMAP space, where points with similar colors correspond to features with higher semantic or structural consistency.
To further evaluate the generalization ability of CGHP, we transfer the backbone trained on the S3DIS dataset to another dataset, ScanNet, which contains diverse scene structures and object arrangements. We visualize the learned feature spaces using UMAP to examine semantic consistency across datasets. As shown in Figure 7, the supervised backbone exhibits weak generalization, with feature clusters becoming less coherent when applied to unseen data. In contrast, our unsupervised CGHP maintains clear and well-clustered semantic structures, indicating that it effectively captures dataset-invariant geometric–structural regularities rather than overfitting to dataset-specific semantics. These findings demonstrate that CGHP learns transferable structural representations that generalize across diverse 3D scenes without requiring any label supervision.
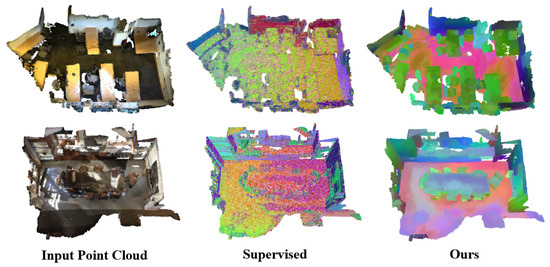
Figure 7.
Visualization of learned feature spaces on the ScanNet dataset. Colors represent feature similarities in the projected three-dimensional UMAP space, where points with similar colors correspond to features with higher semantic or structural consistency.
Nevertheless, several challenges remain. The reliance on heuristic aggregation may limit robustness across diverse datasets, and the descriptors employed, though effective, cannot fully capture higher-level semantic relations such as functional similarity between different objects. In addition, our framework is primarily designed for static datasets; extending it to dynamic environments requires further research. In dynamic scenarios, point clouds often contain moving objects and suffer from temporal inconsistency and occlusion, which complicate component construction and semantic consistency. Future extensions of CGHP could incorporate temporal information to maintain coherence across frames or leverage multimodal data (e.g., LiDAR–camera fusion) to provide complementary cues for robust dynamic scene understanding.
Future efforts could focus on integrating CGHP with adaptive thresholding and attention-based mechanisms to dynamically balance geometric and appearance constraints, thereby improving robustness across datasets with varying densities, noise levels, and illumination conditions. In addition, incorporating graph-based reasoning modules could further enhance scalability and generalization by enabling more explicit modeling of structural dependencies among components. Another promising direction is to explore cross-modal extensions, such as integrating point clouds with textual or multimodal cues, which could reduce reliance on handcrafted descriptors while maintaining annotation-free learning.
6. Conclusions
We have presented a novel component-guided hierarchical progressive framework for unsupervised 3D point cloud semantic segmentation. Our approach introduces several key innovations: (1) a component construction strategy that effectively leverages geometric and appearance consistency; (2) comprehensive GA descriptors that capture crucial physical properties including gravity-aligned distribution information; and (3) an adjacency-constrained progressive growth mechanism that bridges component-level and object-level semantics. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method achieves competitive performance on S3DIS and ScanNet++ datasets, approaching the performance of supervised methods in some metrics.
The success of our approach highlights the importance of incorporating human visual perception principles and physical constraints in unsupervised learning frameworks. The component-level learning strategy, guided by GA descriptors, provides reliable prior knowledge that remarkably enhances feature learning, while the progressive growth mechanism effectively addresses the challenges of direct object-level semantic learning.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.S. and H.Z.; methodology, H.Z.; validation, S.B.; formal analysis, W.G.; investigation, S.S.; resources, S.B. and S.S.; data curation, H.Z.; writing—original draft preparation, H.Z.; writing—review and editing, S.S., H.Z., W.G. and S.B.; visualization, H.Z.; supervision, S.S. and W.G.; project administration, S.S. and W.G.; funding acquisition, S.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (42471413), Natural Science Foundation of Hubei Province (2024AFA069) and LIESMARS Special Research Funding.
Data Availability Statement
The Stanford Large-Scale 3D Indoor Spaces (S3DIS) data set can be found at: https://opendatalab.org.cn/OpenDataLab/S3DIS (accessed on 30 October 2023). The ScanNet++ data set can be found at https://kaldir.vc.in.tum.de/scannetpp/ (accessed on 1 November 2024).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| PFH | Point Feature Histograms |
| GA | Geometry Appearance |
| VCCS | Voxel Cloud Connectivity Segmentation |
| MLP | Multi-Layer Perception |
| EM | Expectation Maximization |
References
- Bello, S.A.; Yu, S.; Wang, C.; Adam, J.M.; Li, J. Deep learning on 3D point clouds. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponzini, F.; Zaccone, R.; Martelli, M. LiDAR target detection and classification for ship situational awareness: A hybrid learning approach. Appl. Ocean Res. 2025, 158, 104552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Bhattarai, N.; Zhao, J.; Liu, H.; Xu, H. An unsupervised clustering method for processing roadside LiDAR data with improved computational efficiency. IEEE Sens. J. 2022, 22, 10684–10691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roriz, R.; Cabral, J.; Gomes, T. Automotive LiDAR technology: A survey. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2021, 23, 6282–6297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leong, P.Y.; Ahmad, N.S. LiDAR-based obstacle avoidance with autonomous vehicles: A comprehensive review. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 164248–164261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Z.; Ma, G.; Wang, L.; Yang, L.; Guo, X.; Chen, S. Towards visual interaction: Hand segmentation by combining 3D graph deep learning and laser point cloud for intelligent rehabilitation. IEEE Internet Things J. 2025, 12, 21328–21338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Z.; Meng, Z.; Zheng, G.; Ma, G.; Yang, L.; Guo, X.; Tan, L.; Jiang, Y.; Wu, H. Intelligent rehabilitation in an aging population: Empowering human-machine interaction for hand function rehabilitation through 3D deep learning and point cloud. Front. Comput. Neurosci. 2025, 19, 1543643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Lao, Y.; Jiang, L.; Liu, X.; Zhao, H. Point transformer v2: Grouped vector attention and partition-based pooling. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2022, 35, 33330–33342. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, X.; Jiang, L.; Wang, P.S.; Liu, Z.; Liu, X.; Qiao, Y.; Ouyang, W.; He, T.; Zhao, H. Point transformer v3: Simpler faster stronger. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 16–22 June 2024; pp. 4840–4851. [Google Scholar]
- Choy, C.; Gwak, J.; Savarese, S. 4d spatio-temporal convnets: Minkowski convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 3075–3084. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, A.; Chang, A.X.; Savva, M.; Halber, M.; Funkhouser, T.; Nießner, M. Scannet: Richly-annotated 3d reconstructions of indoor scenes. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 5828–5839. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, L.; Shi, S.; Tian, Z.; Lai, X.; Liu, S.; Fu, C.W.; Jia, J. Guided point contrastive learning for semi-supervised point cloud semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021; pp. 6423–6432. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, S.; Dong, Q.; Liu, B.; Hu, Z. Superpoint-guided semi-supervised semantic segmentation of 3D point clouds. In Proceedings of the 2022 International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Philadelphia, PA, USA, 23–27 May 2022; pp. 9214–9220. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, M.; Hui, L.; Xie, J.; Yang, J. Sspc-net: Semi-supervised semantic 3d point cloud segmentation network. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Virtually, 2–9 February 2021; pp. 1140–1147. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Dong, Q. Density-guided semi-supervised 3d semantic segmentation with dual-space hardness sampling. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 16–22 June 2024; pp. 3260–3269. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Qu, Y.; Xie, Y.; Li, Z.; Zheng, S.; Li, C. Perturbed self-distillation: Weakly supervised large-scale point cloud semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021; pp. 15520–15528. [Google Scholar]
- Lei, J.; Deng, C.; Schmeckpeper, K.; Guibas, L.; Daniilidis, K. Efem: Equivariant neural field expectation maximization for 3d object segmentation without scene supervision. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 4902–4912. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.; Liu, W.; Zhu, J.; Cui, M.; Hua, X.S.; Zhang, L. Box-supervised instance segmentation with level set evolution. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Tel Aviv, Israel, 23–27 October 2022; pp. 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Q.; Yang, B.; Fang, G.; Guo, Y.; Leonardis, A.; Trigoni, N.; Markham, A. Sqn: Weakly-supervised semantic segmentation of large-scale 3d point clouds. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Tel Aviv, Israel, 23–27 October 2022; pp. 600–619. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Qi, X.; Fu, C.W. One thing one click: A self-training approach for weakly supervised 3d semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 1726–1736. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, X.; Lee, G.H. Weakly supervised semantic point cloud segmentation: Towards 10x fewer labels. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 13706–13715. [Google Scholar]
- Chibane, J.; Engelmann, F.; Anh Tran, T.; Pons-Moll, G. Box2mask: Weakly supervised 3d semantic instance segmentation using bounding boxes. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Tel Aviv, Israel, 23–27 October 2022; pp. 681–699. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, K.; Zhao, Y.; Nie, Q.; Gao, Z.; Chen, B.M. Weakly supervised 3d scene segmentation with region-level boundary awareness and instance discrimination. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Tel Aviv, Israel, 23–27 October 2022; pp. 37–55. [Google Scholar]
- Tao, A.; Duan, Y.; Wei, Y.; Lu, J.; Zhou, J. SegGroup: Seg-level supervision for 3D instance and semantic segmentation. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2022, 31, 4952–4965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Lin, G.; Yap, K.H.; Hung, T.Y.; Xie, L. Multi-path region mining for weakly supervised 3D semantic segmentation on point clouds. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 4384–4393. [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd, S. Least squares quantization in PCM. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 1982, 28, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ester, M.; Kriegel, H.P.; Sander, J.; Xu, X. A density-based algorithm for discovering clusters in large spatial databases with noise. In Proceedings of the KDD, Portland, OR, USA, 2–4 August 1996; pp. 226–231. [Google Scholar]
- McInnes, L.; Healy, J.; Astels, S. hdbscan: Hierarchical density based clustering. J. Open Source Softw. 2017, 2, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comaniciu, D.; Meer, P. Mean shift: A robust approach toward feature space analysis. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2002, 24, 603–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, D. Gaussian mixture models. In Encyclopedia of Biometrics; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; pp. 659–663. [Google Scholar]
- Murtagh, F.; Contreras, P. Algorithms for hierarchical clustering: An overview. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Data Min. Knowl. Discov. 2012, 2, 86–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, X.; Henriques, J.F.; Vedaldi, A. Invariant information clustering for unsupervised image classification and segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 9865–9874. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, J.H.; Mall, U.; Bala, K.; Hariharan, B. Picie: Unsupervised semantic segmentation using invariance and equivariance in clustering. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 16794–16804. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Yang, B.; Wang, B.; Li, B. Growsp: Unsupervised semantic segmentation of 3d point clouds. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 17619–17629. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.; Xu, H.; Chen, W.; Zhou, Z.; Xiao, H.; Sun, B.; Xie, X. PointDC: Unsupervised semantic segmentation of 3D point clouds via cross-modal distillation and super-voxel clustering. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Paris, France, 1–6 October 2023; pp. 14290–14299. [Google Scholar]
- Armeni, I.; Sax, S.; Zamir, A.R.; Savarese, S. Joint 2d-3d-semantic data for indoor scene understanding. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1702.01105. [Google Scholar]
- Rusu, R.B.; Blodow, N.; Marton, Z.C.; Beetz, M. Aligning point cloud views using persistent feature histograms. In Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Nice, France, 22–26 September 2008; pp. 3384–3391. [Google Scholar]
- Biederman, I. Recognition-by-components: A theory of human image understanding. Psychol. Rev. 1987, 94, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, D.B.; Wertheimer, M.; Keller, H.; Crochetière, K. The legacy of Max Wertheimer and Gestalt psychology. Soc. Res. 1994, 61, 907–935. [Google Scholar]
- Behley, J.; Garbade, M.; Milioto, A.; Quenzel, J.; Behnke, S.; Stachniss, C.; Gall, J. Semantickitti: A dataset for semantic scene understanding of lidar sequences. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 9297–9307. [Google Scholar]
- Hackel, T.; Savinov, N.; Ladicky, L.; Wegner, J.D.; Schindler, K.; Pollefeys, M. Semantic3d. net: A new large-scale point cloud classification benchmark. ISPRS Ann. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2017, IV-1/W1, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.; Yang, B.; Khalid, S.; Xiao, W.; Trigoni, N.; Markham, A. Towards semantic segmentation of urban-scale 3D point clouds: A dataset, benchmarks and challenges. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 4977–4987. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, L.; Liu, Y.; Hu, Y.; Yan, X.; Xie, K.; Huang, H. Capturing, reconstructing, and simulating: The urbanscene3d dataset. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Tel Aviv, Israel, 23–27 October 2022; pp. 93–109. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, W.; Qin, N.; Ma, L.; Li, Y.; Du, J.; Cai, G.; Yang, K.; Li, J. Toronto-3D: A large-scale mobile LiDAR dataset for semantic segmentation of urban roadways. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Seattle, WA, USA, 14–19 June 2020; pp. 202–203. [Google Scholar]
- Varney, N.; Asari, V.K.; Graehling, Q. DALES: A large-scale aerial LiDAR data set for semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Seattle, WA, USA, 14–19 June 2020; pp. 186–187. [Google Scholar]
- Kölle, M.; Laupheimer, D.; Schmohl, S.; Haala, N.; Rottensteiner, F.; Wegner, J.D.; Ledoux, H. The Hessigheim 3D (H3D) benchmark on semantic segmentation of high-resolution 3D point clouds and textured meshes from UAV LiDAR and Multi-View-Stereo. ISPRS Open J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2021, 1, 100001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Yu, J.; Tan, L.; Su, W.; Zhao, L.; Tao, W. Semantic segmentation of 3D point cloud based on spatial eight-quadrant kernel convolution. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, N.; Yu, H.; Huo, Z.; Liu, J.; Wang, Q.; Xu, Y.; Gao, Y. KVGCN: A KNN searching and VLAD combined graph convolutional network for point cloud segmentation. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Wu, J.; Luo, Y.; Xu, G. PointMM: Point cloud semantic segmentation CNN under multi-spatial feature encoding and multi-head attention pooling. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, C.R.; Yi, L.; Su, H.; Guibas, L.J. Pointnet++: Deep hierarchical feature learning on point sets in a metric space. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2017, 30, 5099–5108. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, M.H.; Cai, J.X.; Liu, Z.N.; Mu, T.J.; Martin, R.R.; Hu, S.M. Pct: Point cloud transformer. Comput. Vis. Media 2021, 7, 187–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Jiang, L.; Jia, J.; Torr, P.H.; Koltun, V. Point transformer. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021; pp. 16259–16268. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Q.; Yang, B.; Xie, L.; Rosa, S.; Guo, Y.; Wang, Z.; Trigoni, N.; Markham, A. Randla-net: Efficient semantic segmentation of large-scale point clouds. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 11108–11117. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, H.; Qi, C.R.; Deschaud, J.E.; Marcotegui, B.; Goulette, F.; Guibas, L.J. Kpconv: Flexible and deformable convolution for point clouds. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 6411–6420. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Bu, R.; Sun, M.; Wu, W.; Di, X.; Chen, B. Pointcnn: Convolution on x-transformed points. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2018, 31, 828–838. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, X.; Zhou, H.; Wang, T.; Hong, F.; Ma, Y.; Li, W.; Li, H.; Lin, D. Cylindrical and asymmetrical 3d convolution networks for lidar segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 9939–9948. [Google Scholar]
- Lei, H.; Akhtar, N.; Mian, A. Octree guided cnn with spherical kernels for 3d point clouds. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 9631–9640. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, H.Y.; Gao, L.; Lai, Y.K.; Manocha, D. Vv-net: Voxel vae net with group convolutions for point cloud segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 8500–8508. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, C.R.; Su, H.; Mo, K.; Guibas, L.J. Pointnet: Deep learning on point sets for 3d classification and segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 652–660. [Google Scholar]
- Graham, B.; Engelcke, M.; Van Der Maaten, L. 3d semantic segmentation with submanifold sparse convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 9224–9232. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, B.; Wu, X.; Jiang, L.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, H.; Tian, Z.; Jia, J. Oa-cnns: Omni-adaptive sparse cnns for 3d semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 16–22 June 2024; pp. 21305–21315. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, S.; Gu, J.; Guo, D.; Qi, C.R.; Guibas, L.; Litany, O. Pointcontrast: Unsupervised pre-training for 3d point cloud understanding. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020; pp. 574–591. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, J.; Graham, B.; Nießner, M.; Xie, S. Exploring data-efficient 3d scene understanding with contrastive scene contexts. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 15587–15597. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, X.; Wen, X.; Liu, X.; Zhao, H. Masked scene contrast: A scalable framework for unsupervised 3d representation learning. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 9415–9424. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Liu, J.; Ni, B.; Wang, H.; Yang, J.; Liu, N.; Li, T.; Tian, Q. Shape self-correction for unsupervised point cloud understanding. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021; pp. 8382–8391. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, S.; Xie, Y.; Zhu, S.C.; Zhu, Y. Spatio-temporal self-supervised representation learning for 3d point clouds. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021; pp. 6535–6545. [Google Scholar]
- Pang, Y.; Tay, E.H.F.; Yuan, L.; Chen, Z. Masked autoencoders for 3d point cloud self-supervised learning. World Sci. Annu. Rev. Artif. Intell. 2023, 1, 2440001. [Google Scholar]
- Rao, Y.; Lu, J.; Zhou, J. Global-local bidirectional reasoning for unsupervised representation learning of 3d point clouds. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 5376–5385. [Google Scholar]
- Thabet, A.; Alwassel, H.; Ghanem, B. Self-supervised learning of local features in 3d point clouds. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Seattle, WA, USA, 14–19 June 2020; pp. 938–939. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Liu, Q.; Yue, X.; Lasenby, J.; Kusner, M.J. Unsupervised point cloud pre-training via occlusion completion. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021; pp. 9782–9792. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, Z.; Wang, P.; Wang, F.; Xu, X.; Zhang, H.; Li, H.; Jin, R. Transfgu: A top-down approach to fine-grained unsupervised semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Tel Aviv, Israel, 23–27 October 2022; pp. 73–89. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Girdhar, R.; Joulin, A.; Misra, I. Self-supervised pretraining of 3d features on any point-cloud. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021; pp. 10252–10263. [Google Scholar]
- Caron, M.; Bojanowski, P.; Joulin, A.; Douze, M. Deep clustering for unsupervised learning of visual features. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 132–149. [Google Scholar]
- Song, Z.; Yang, B. Ogc: Unsupervised 3d object segmentation from rigid dynamics of point clouds. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2022, 35, 30798–30812. [Google Scholar]
- Dempster, A.P.; Laird, N.M.; Rubin, D.B. Maximum likelihood from incomplete data via the EM algorithm. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B (Methodol.) 1977, 39, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caron, M.; Misra, I.; Mairal, J.; Goyal, P.; Bojanowski, P.; Joulin, A. Unsupervised learning of visual features by contrasting cluster assignments. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2020, 33, 9912–9924. [Google Scholar]
- Papon, J.; Abramov, A.; Schoeler, M.; Worgotter, F. Voxel cloud connectivity segmentation-supervoxels for point clouds. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Portland, OR, USA, 23–28 June 2013; pp. 2027–2034. [Google Scholar]
- Landrieu, L.; Obozinski, G. Cut pursuit: Fast algorithms to learn piecewise constant functions on general weighted graphs. SIAM J. Imaging Sci. 2017, 10, 1724–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, R.; Bischof, L. Seeded region growing. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 1994, 16, 641–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeshwanth, C.; Liu, Y.C.; Nießner, M.; Dai, A. Scannet++: A high-fidelity dataset of 3d indoor scenes. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Paris, France, 1–6 October 2023; pp. 12–22. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Yu, Z.; Breckon, T.P.; Shum, H.P. U3ds3: Unsupervised 3d semantic scene segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, Waikoloa, HI, USA, 3–8 January 2024; pp. 3759–3768. [Google Scholar]
- McInnes, L.; Healy, J.; Melville, J. Umap: Uniform manifold approximation and projection for dimension reduction. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1802.03426. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).