PolarFormer: A Registration-Free Fusion Transformer with Polar Coordinate Position Encoding for Multi-View SAR Target Recognition
Highlights
- A novel multi-view polar coordinate position encoding is proposed to accurately model the complex geometric relationships among unaligned SAR images.
- A spatially aware self-attention mechanism is designed to inject this geometric information as an inductive bias into the Transformer, enhancing its ability to perceive spatial structures.
- The proposed registration-free paradigm demonstrates that precise geometric modeling can completely supplant physical image registration, simplifying the processing pipeline and avoiding feature distortion.
- This work provides a more effective and robust pathway for early fusion of multi-view SAR data, significantly improving target recognition accuracy in complex scenarios.
Abstract
1. Introduction
- We introduce a novel multi-view polar coordinate position encoding. This encoding scheme decouples and precisely describes the local position of any patch within its view, as well as the position and rotational offset of its host view relative to a global reference frame. This allows us, for the first time, to establish a unified and consistent spatial coordinate system for unaligned multi-view images at the feature level.
- We design a spatially aware self-attention mechanism. This mechanism converts the polar encoding into a position-aware score matrix, which quantifies the true spatial distance between any two patches, regardless of whether they originate from the same view. By integrating this score matrix as a learnable bias term into the Transformer’s self-attention computation, we inject a powerful and explicit spatial inductive bias into the model.
- We build an end-to-end, registration-free early fusion framework. Leveraging these innovations, we construct a complete recognition network that requires no image preprocessing. The network learns features directly from spatially concatenated multi-view images, thereby retaining the advantages of early fusion while fundamentally circumventing the problems associated with registration.
2. Related Works
2.1. Multi-View SAR Target Recognition
2.2. Position Encoding in Vision Transformers
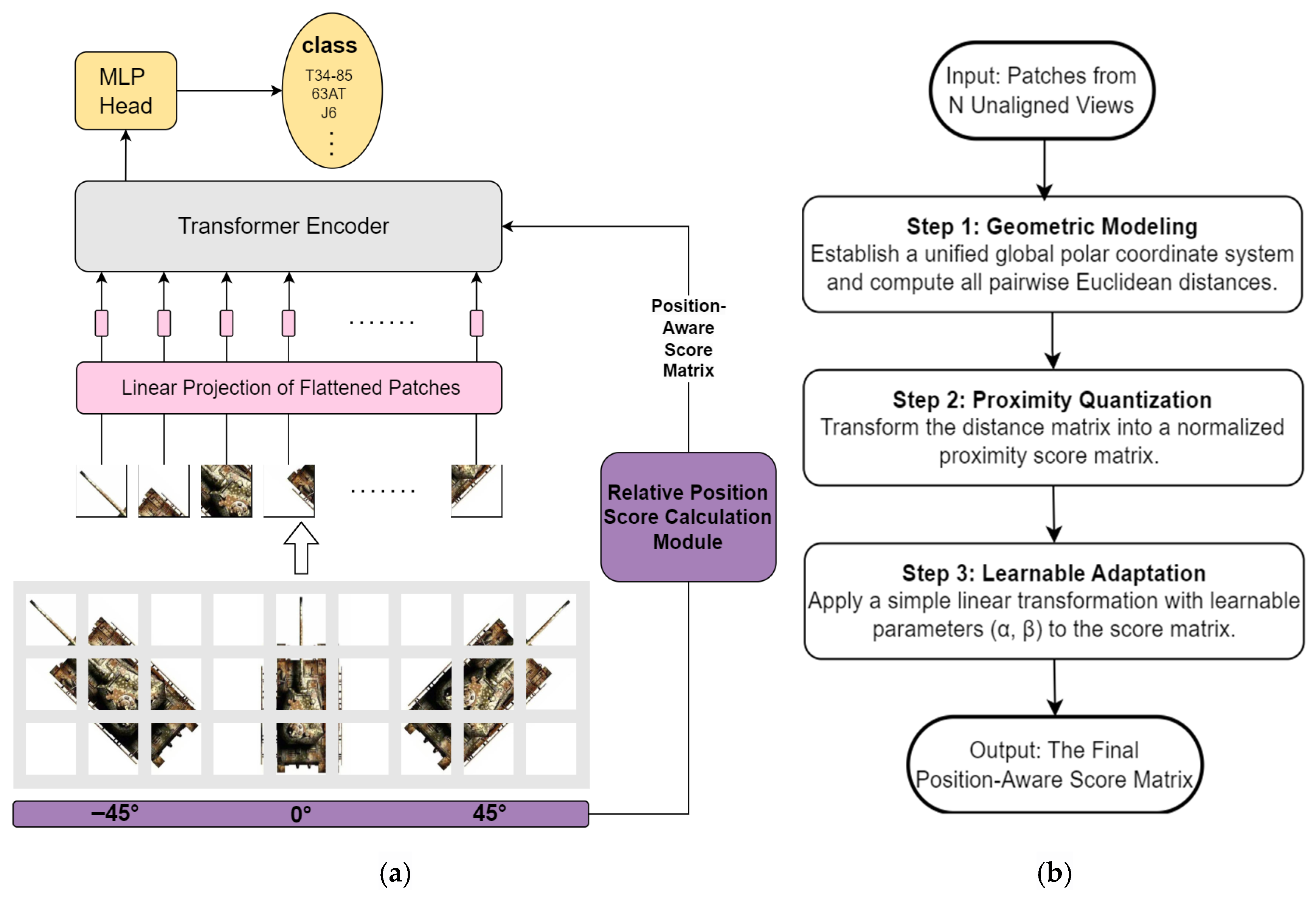
3. Proposed Method
3.1. Spatial-Dimension Concatenation and the Global Feature Extraction Framework
3.1.1. Image Patching and Linear Embedding
3.1.2. Feature and Positional Information Fusion
3.1.3. Transformer Encoder
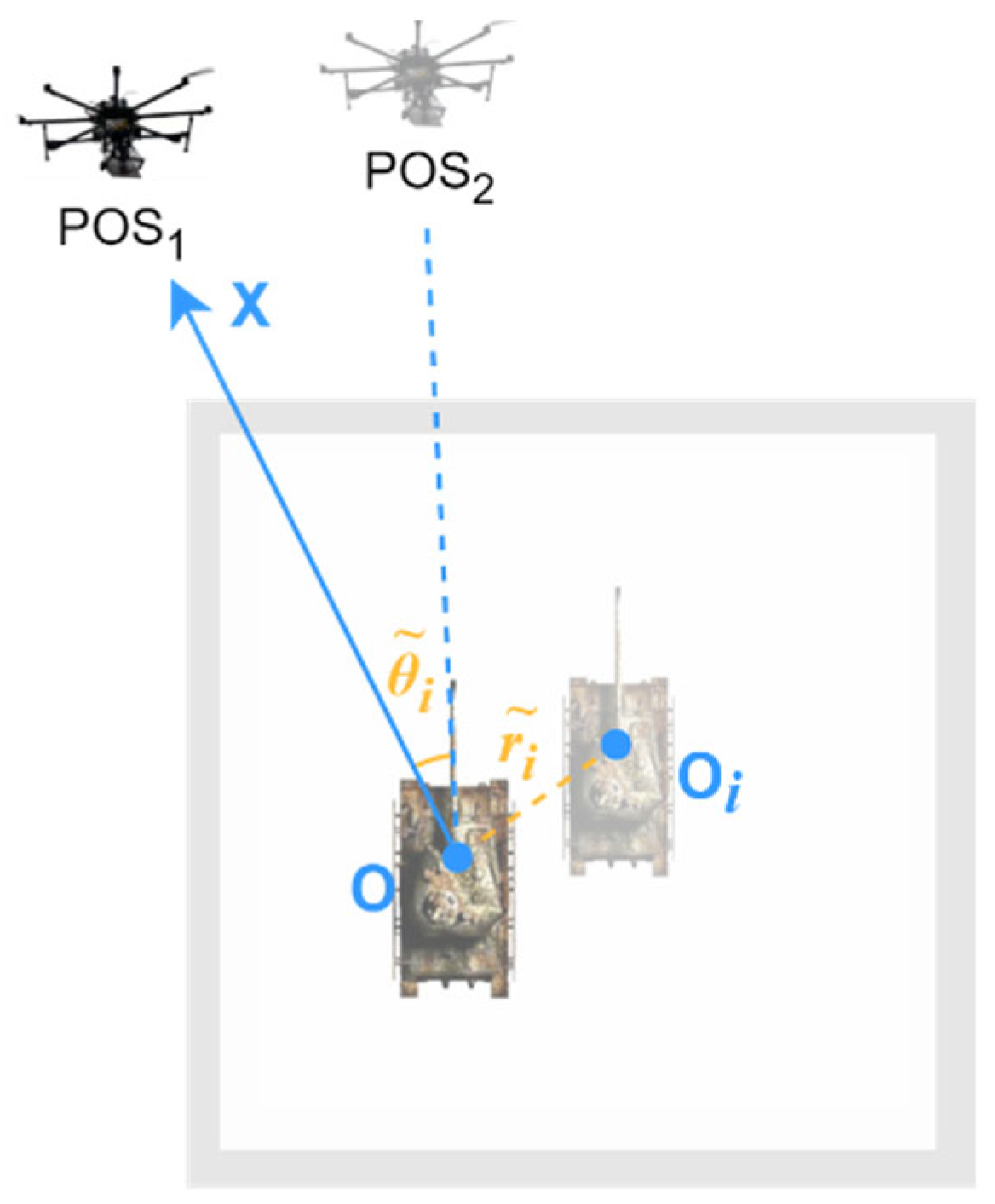
3.2. Polar Coordinate Relative Position Encoding
3.2.1. Local Polar Coordinates Within a Single View
3.2.2. Global Polar Coordinates for Multiple Views
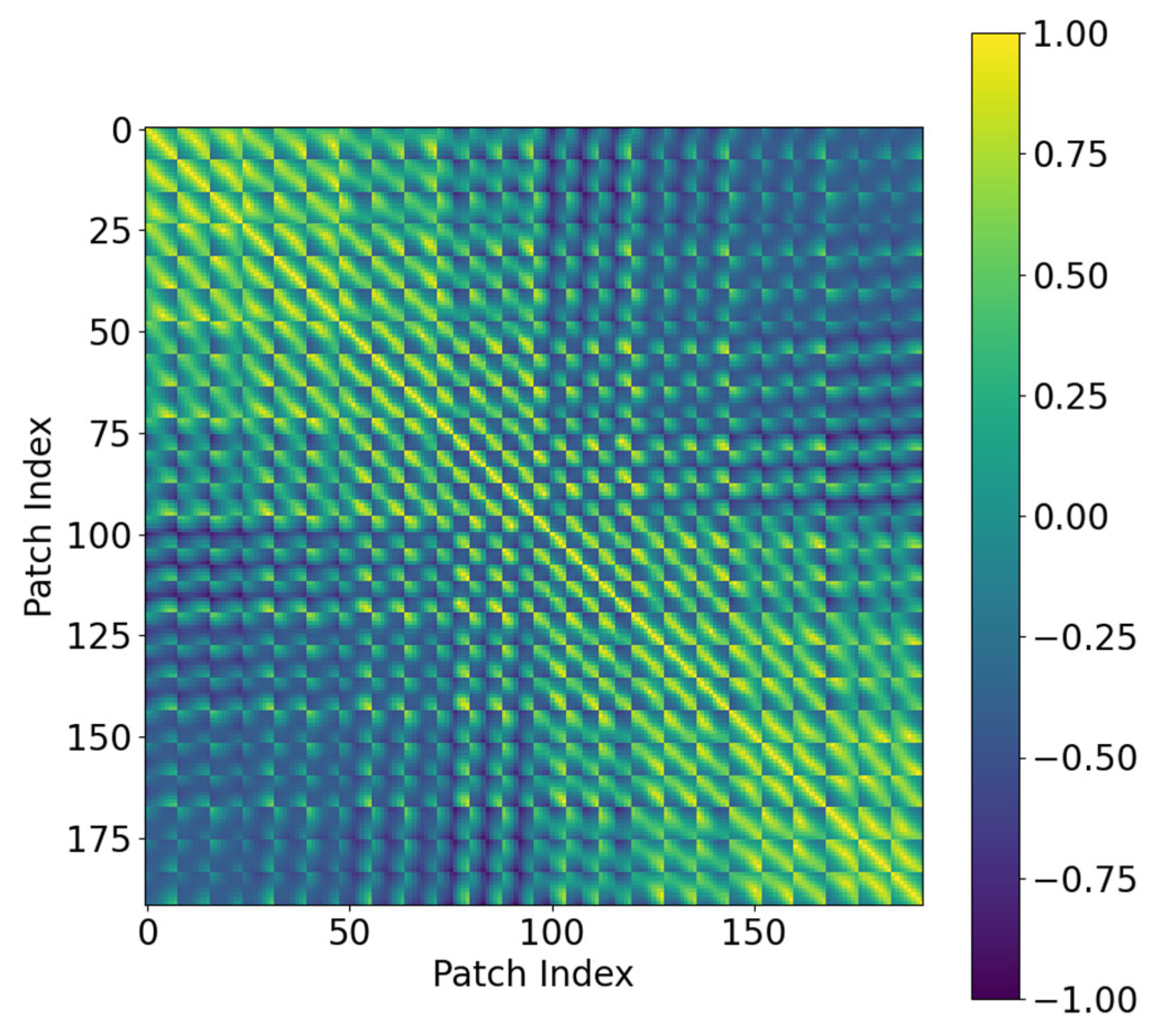
3.3. The Position-Aware Score Matrix and Its Injection Method
3.3.1. Distance Matrix Construction from Position Encodings
3.3.2. Distance Matrix Normalization
3.3.3. Spatially Aware Self-Attention Mechanism
4. Experiments and Analysis
4.1. Dataset and Experimental Setup
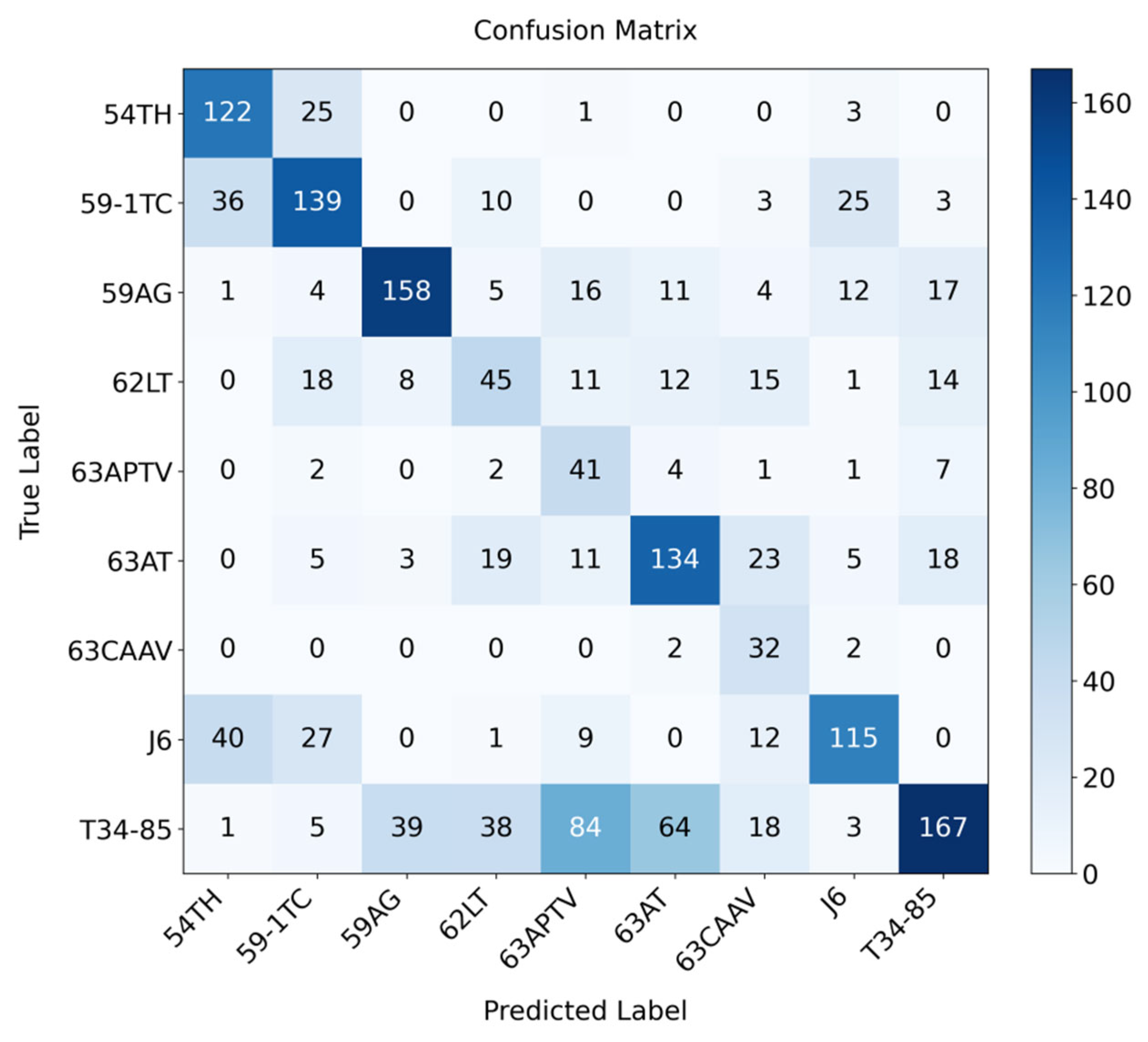
4.2. Comparative Experiments and Analysis
4.2.1. Comparison of Different Position Encoding Strategies
4.2.2. Comparison with Image Registration Strategies
4.3. Ablation Study
4.3.1. Efficacy of the Polar Coordinate Position Encoding
4.3.2. Analysis of the Impact of View-Angle Separation
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tang, Y.; Chen, J. A multi-view SAR target recognition method using feature fusion and joint classification. Remote Sens. Lett. 2022, 13, 631–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, B.; Wen, G. Exploiting multi-view SAR images for robust target recognition. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, G.; Zhu, D.; Dai, Q. Multi-view rotation double-layer fusion CNN-LSTM for SAR target recognition. In Proceedings of the 2024 2nd International Conference on Algorithm, Image Processing and Machine Vision (AIPMV), Zhenjiang, China, 12–14 July 2024; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2024; pp. 349–353. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, C.; Pei, J.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, H.; Xing, Z. Multi-view SAR automatic target recognition based on deformable convolutional network. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium IGARSS, Brussels, Belgium, 11–16 July 2021; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2021; pp. 3585–3588. [Google Scholar]
- Lv, J.; Zhu, D.; Geng, Z.; Han, S.; Wang, Y.; Ye, Z.; Zhou, T.; Chen, H.; Huang, J. Recognition for SAR deformation military target from a new MiniSAR dataset using multi-view joint transformer approach. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2024, 210, 180–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huan, R.; Pan, Y. Decision fusion strategies for SAR image target recognition. IET Radar Sonar Navig. 2011, 5, 747–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Zhang, G.; Zhu, D. Multi-view SAR target recognition using bidirectional Conv-LSTM network. In Proceedings of the 2022 14th International Conference on Signal Processing Systems (ICSPS), Zhenjiang, China, 18–20 November 2022; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2022; pp. 410–413. [Google Scholar]
- Zijun, W.; Gong, Z.; Daiyin, Z.; Qijun, D. MV-ResFPN: A residual network deeply combining multi-view and multiscale fusion for SAR target recognition. In Proceedings of the SPIE 13539, Sixteenth International Conference on Graphics and Image Processing (ICGIP 2024), Nanjing, China, 8–10 November 2024; p. 135390V. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, Z.; Zhang, G.; Dai, Q.; Wang, Z. A multi-view stable feature extraction network for SAR target recognition. In Proceedings of the 2023 International Conference on Image Processing, Computer Vision and Machine Learning (ICICML), Chengdu, China, 3–5 November 2023; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2023; pp. 114–117. [Google Scholar]
- Yifei, S.; Sihang, D.; Boda, Q.; Shuliang, G.; Xiaoyue, J.; Xiaoyi, F. Synthetic aperture radar target recognition using multi-view feature enhancement-based contrastive clustering. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2024, 19, 16503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Q.; Zhang, G.; Xue, B.; Fang, Z. Capsule-guided multi-view attention network for SAR target recognition with small training set. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2023, 20, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Wang, L.; Li, Y.; Zhu, D. Relation aware network for multi-view SAR target recognition. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE International Conference on Signal, Information and Data Processing (ICSIDP), Zhuhai, China, 22–24 November 2024; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2024; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- He, L.; Ohbuchi, R.; Jiang, M.; Furuya, T.; Zhang, M. Cascaded multi-channel feature fusion for object detection. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Control and Computer Vision, Macau, China, 23–25 August 2020; pp. 11–16. [Google Scholar]
- Teepe, T.; Wolters, P.; Gilg, J.; Herzog, F.; Rigoll, G. EarlyBird: Early-fusion for multi-view tracking in the bird’s eye view. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision Workshops (WACVW), Waikoloa, HI, USA, 1–6 January 2024; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2024; pp. 102–111. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, S.; Yang, J.; Gou, S.; Jiao, L.; Xiong, T.; Xiong, L. Multi-scale fused SAR image registration based on deep forest. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Ding, J.; Guo, Q. Unsupervised image registration for video SAR. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2021, 14, 1075–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, S.; Pati Umesh, C. Automatic optical-to-SAR image registration using a structural descriptor. IET Image Process. 2020, 14, 62–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Guan, D.; Xie, Y.; Zheng, X.; Chen, Z.; Pan, L.; Zhao, W.; Xiang, D. Global optical and SAR image registration method based on local distortion division. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, B.; Jiao, R.; Wang, J.; Han, Y.; Hang, H. SAR image registration based on KECA-SAR-SIFT operator. In Proceedings of the 2022 2nd International Conference on Computer Science, Electronic Information Engineering and Intelligent Control Technology (CEI), Nanjing, China, 23–25 September 2022; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2022; pp. 114–119. [Google Scholar]
- Geng, J.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, W. Polarimetric SAR image classification based on hierarchical scattering-spatial interaction transformer. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2024, 62, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, S.; Chen, S. SAR image recognition Using ViT network and contrastive learning framework with unlabeled samples. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2024, 21, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Xu, W.; Yao, Y.; Huang, X. SAR-3DTR: A novel feature hybrid transformer network for end-to-end 3-D target reconstruction from SAR images. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2024, 21, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Wu, Q.; Wu, F.; Huang, J.; Wang, C. A Lightweight pyramid transformer for high-resolution SAR image-based building classification in port regions. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 3218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yataka, R.; Wang, P.P.; Boufounos, P.; Takahashi, R. Multi-view radar detection transformer with differentiable positional encoding. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2025—2025 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Hyderabad, India, 6–11 April 2025; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2025; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Tang, M.; Rong, Y.; Ni, M.; Li, F. Multi-view SAR image classification through decision fusion of adaptive dictionary learning and CNN. In Proceedings of the 2024 Photonics & Electromagnetics Research Symposium (PIERS), Chengdu, China, 21–25 April 2024; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2024; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, T. A Multi-view SAR target recognition method based on adaptive weighted decision fusion. Remote Sens. Lett. 2023, 14, 1196–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juan, L. Synthetic aperture radar target recognition based on adaptive decision fusion of multiple views. J. Electron. Imaging 2024, 33, 23015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Bruzzone, L. Self-supervised SAR-optical data fusion of sentinel-1/-2 Images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Guo, X.; Ren, H.; Wan, Q.; Shen, X. Multi-View fusion based on expectation maximization for SAR target recognition. In Proceedings of the IGARSS 2020—2020 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Waikoloa, HI, USA, 26 September–2 October 2020; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2020; pp. 778–781. [Google Scholar]
- Ettinger, G.J.; Snyder, W.C. Model-based fusion of multi-look SAR for ATR. In Proceedings of the Algorithms for Synthetic Aperture Radar Imagery IX, Orlando, FL, USA, 1–5 April 2002; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2002; pp. 277–289. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, W.; Chen, N. Pixel level fusion approach based on optimizing visual perception for multi-band SAR image. Syst. Eng. Electron. 2004, 9, 1299–1301. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.L.; Wang, J. Performance analysis of SIFT feature extraction algorithm in application to registration of SAR image. In Proceedings of the MATEC Web of Conferences, Lucerne, Switzerland, 6–10 July 2016; EDP Sciences: London, UK, 2016; p. 01063. [Google Scholar]
- Sreeja, G.; Saraniya, O. A comparative study on image registration techniques for SAR images. In Proceedings of the 2019 5th International Conference on Advanced Computing & Communication Systems (ICACCS), Coimbatore, India, 15–16 March 2019; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 947–953. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Q.; Pang, B.; Wu, P.; Zhang, Y. Automatic coarse-to-precise subpixel multi-band SAR images co-registration based affine SIFT and radial base function(RBF). In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE 5th Asia-Pacific Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar (APSAR), Singapore, 1–4 September 2015; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 684–687. [Google Scholar]
- Li, N.; Hu, X. UltraWideband Mutual RFI Mitigation Between SAR Satellites: From the Perspective of European Sentinel-1A. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2024, 62, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Wang, F.; Wang, H. A transformer-based coarse-to-fine wide-swath SAR image registration method under weak texture conditions. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, R.; Wang, G.; Xu, H.; Zhang, Z. A sub-second method for SAR image registration based on hierarchical episodic control. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 4941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Mao, S.; Yang, J.; Lu, S.; Gou, S.; Zhou, Y.; Jiao, L. Multi-class double-transformation network for SAR image registration. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 2927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dosovitskiy, A.; Beyer, L.; Kolesnikov, A.; Weissenborn, D.; Zhai, X.; Unterthiner, T.; Dehghani, M.; Minderer, M.; Heigold, G.; Gelly, S. An image is worth 16x16 words: Transformers for image recognition at scale. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2010.11929. [Google Scholar]
- Chu, X.; Tian, Z.; Zhang, B.; Wang, X.; Shen, C. Conditional positional encodings for vision transformers. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2102.10882. [Google Scholar]
- Foumani, N.M.; Tan, C.W.; Webb, G.I.; Salehi, M. Improving position encoding of transformers for multivariate time series classification. Data Min. Knowl. Discov. 2024, 38, 22–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.; Peng, H.; Chen, M.; Fu, J.; Chao, H. Rethinking and improving relative position encoding for vision transformer. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2021; pp. 10013–10021. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Y.; Wang, R. Relative-position embedding based spatially and temporally decoupled transformer for action recognition. Pattern Recognit. 2024, 145, 109905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, Ł.; Polosukhin, I. Attention is all you need. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2017, 30, 261–272. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Lin, Y.; Cao, Y.; Hu, H.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, S.; Guo, B. Swin transformer: Hierarchical vision transformer using shifted windows. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2021; pp. 9992–10002. [Google Scholar]


| Types | Training Set (July) | Test Set (March) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Depression Angle | Number | Depression Angle | Number | |
| 62LT | 26°, 31°, 37°, 45° | 1103 | 15°, 31°, 45° | 385 |
| 63APTV | 26°, 31°, 37°, 45° | 1101 | 15°, 31°, 45° | 414 |
| 63CAAV | 26°, 31°, 37°, 45° | 1104 | 15°, 31°, 45° | 357 |
| 63AT | 26°, 31°, 37°, 45° | 1102 | 15°, 31°, 45° | 488 |
| T34-85 | 26°, 31°, 37°, 45° | 1084 | 15°, 31°, 45° | 1810 |
| 59-1TC | 26°, 31°, 37°, 45° | 1105 | 15°, 31°, 45° | 854 |
| 54TH | 26°, 31°, 37°, 45° | 1094 | 15°, 31°, 45° | 446 |
| 59AG | 26°, 31°, 37°, 45° | 1093 | 15°, 31°, 45° | 2027 |
| J6 | 26°, 31°, 37°, 45° | 1101 | 15°, 31°, 45° | 416 |
| View(s) | Position Encoding | Training Samples | Test Samples | Parameters (M) | Accuracy (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Single-view | Learnable | 9592 | 7197 | 9.546 | 54.6 |
| 3-view | Polar Coordinates (ours) | 8284 | 1654 | 43.102 | 57.6 |
| 3-view | Absolute (2D sin/cos) | 8284 | 1654 | 43.102 | 53.4 |
| 3-view | Relative (2D) | 8284 | 1654 | 43.104 | 53.7 |
| 3-view | Learnable | 8284 | 1654 | 43.255 | 52.8 |
| 3-view | MV-DCN | 8284 | 1654 | 35.536 | 56.8 |
| Position Encoding | Training Samples | Test Samples | Parameters (M) | Accuracy (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polar Coordinates (ours) | 8284 | 1654 | 43.102 | 57.6 |
| Image Registration (Absolute) | 8284 | 1654 | 43.102 | 54.2 |
| Position Encoding Source | Training Samples | Test Samples | Parameters (M) | Accuracy (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polar Coordinates (ours) + Score Matrix | 8284 | 1654 | 43.102 | 57.6 |
| Learnable + Score Matrix | 8284 | 1654 | 43.104 | 53.6 |
| Azimuthal Angle Separation (°) | Accuracy (%) |
|---|---|
| 6 | 53.8 |
| 12 | 55.3 |
| 18 | 57.6 |
| 24 | 54.4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, X.; Qian, Y.; Jin, G.; Geng, Z.; Zhu, D. PolarFormer: A Registration-Free Fusion Transformer with Polar Coordinate Position Encoding for Multi-View SAR Target Recognition. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 3559. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17213559
Yu X, Qian Y, Jin G, Geng Z, Zhu D. PolarFormer: A Registration-Free Fusion Transformer with Polar Coordinate Position Encoding for Multi-View SAR Target Recognition. Remote Sensing. 2025; 17(21):3559. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17213559
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Xiang, Ying Qian, Guodong Jin, Zhe Geng, and Daiyin Zhu. 2025. "PolarFormer: A Registration-Free Fusion Transformer with Polar Coordinate Position Encoding for Multi-View SAR Target Recognition" Remote Sensing 17, no. 21: 3559. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17213559
APA StyleYu, X., Qian, Y., Jin, G., Geng, Z., & Zhu, D. (2025). PolarFormer: A Registration-Free Fusion Transformer with Polar Coordinate Position Encoding for Multi-View SAR Target Recognition. Remote Sensing, 17(21), 3559. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17213559







