Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Bare Sand Patches in the Mu Us Sandy Land, China
Abstract
Highlights
- Post-2000 bare sand area decreased significantly at 530.08 km2/yr.
- Ecological restoration initiatives were key determinants of bare sand decline.
- Developed a comprehensive, efficient, and scalable workflow for accurate extraction and monitoring of bare sand patches.
- Confirmed that ecological restoration policies significantly accelerated the contraction of bare sand patches, providing strong evidence for policy optimization and scale-up.
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
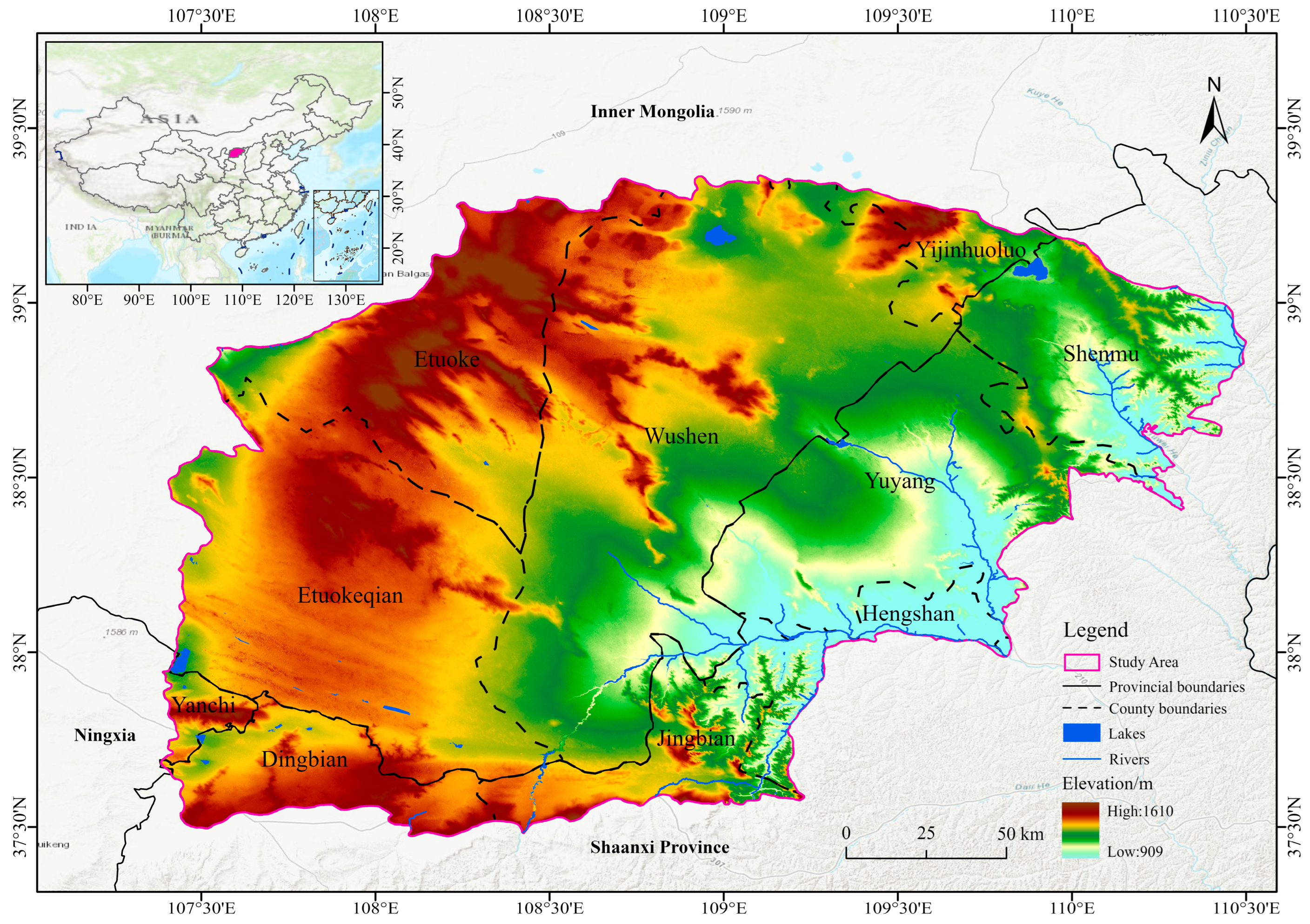
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Source and Preprocessing
2.3. Sample Data
2.4. Methods
2.4.1. Feature Dataset Construction
2.4.2. Random Forest
2.4.3. Accuracy Assessment
2.4.4. Dynamic Analysis of Bare Sand Patches
3. Results
3.1. Accuracy Assessment of Bare Sand Patch Extraction
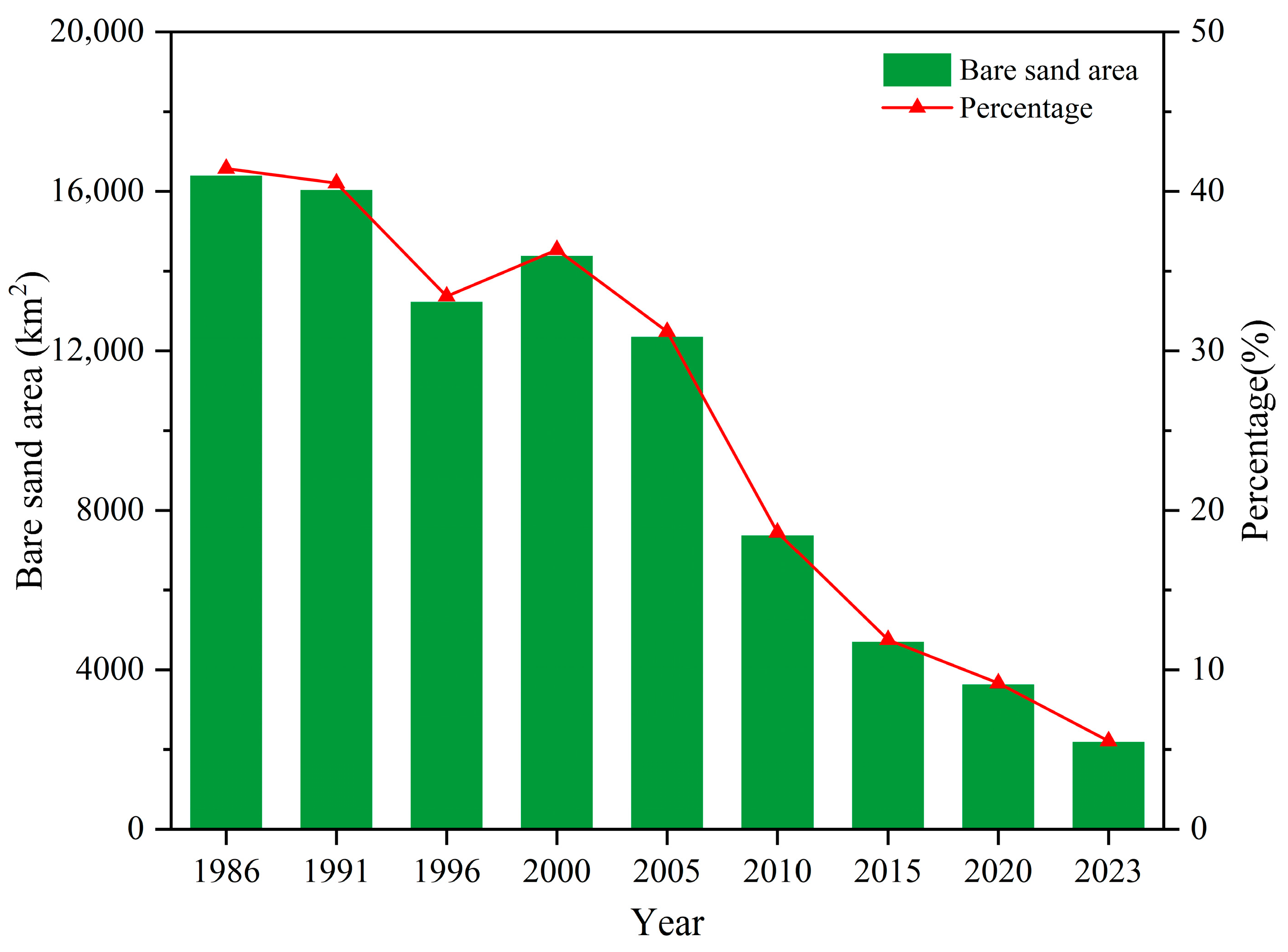
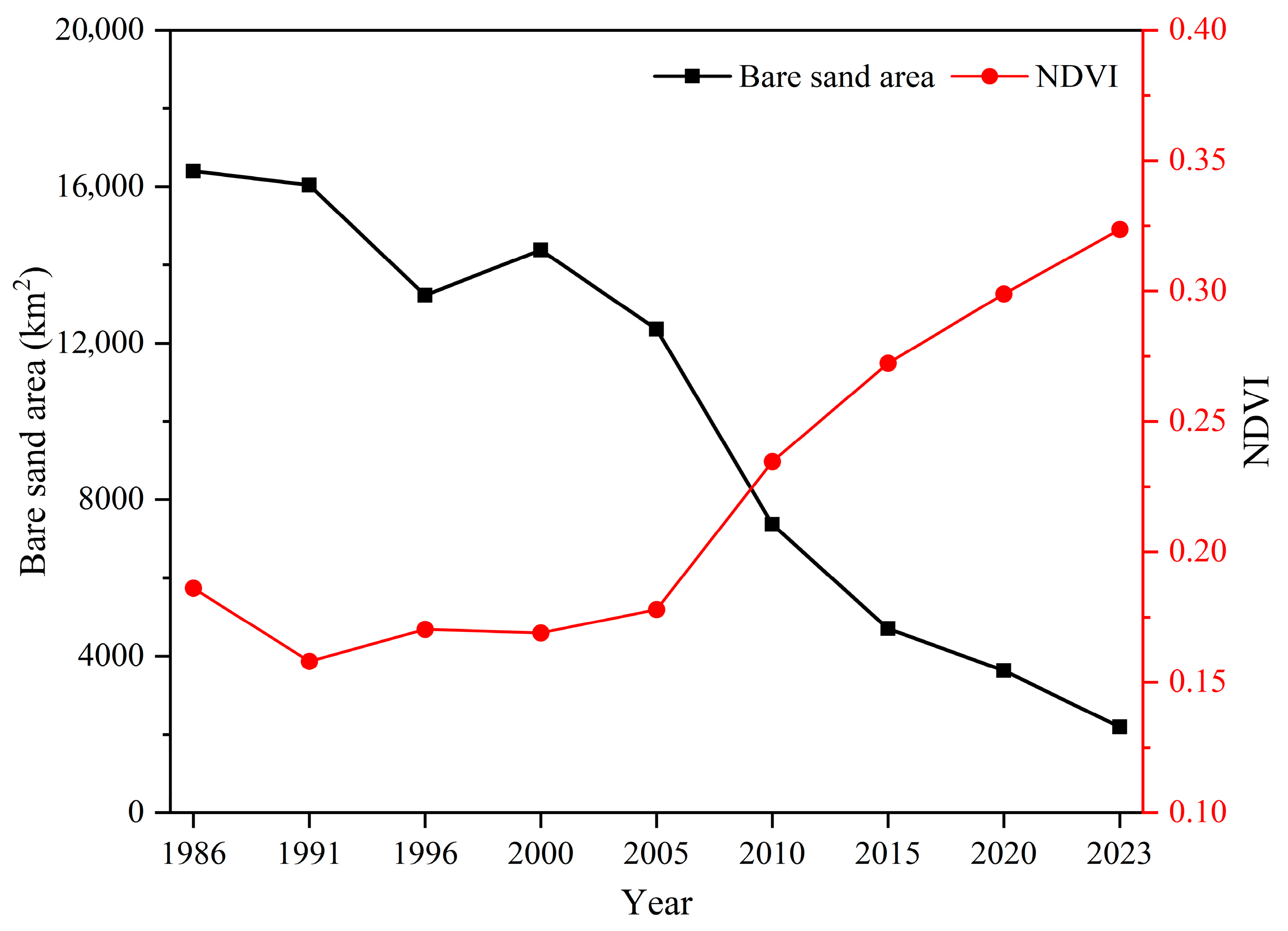
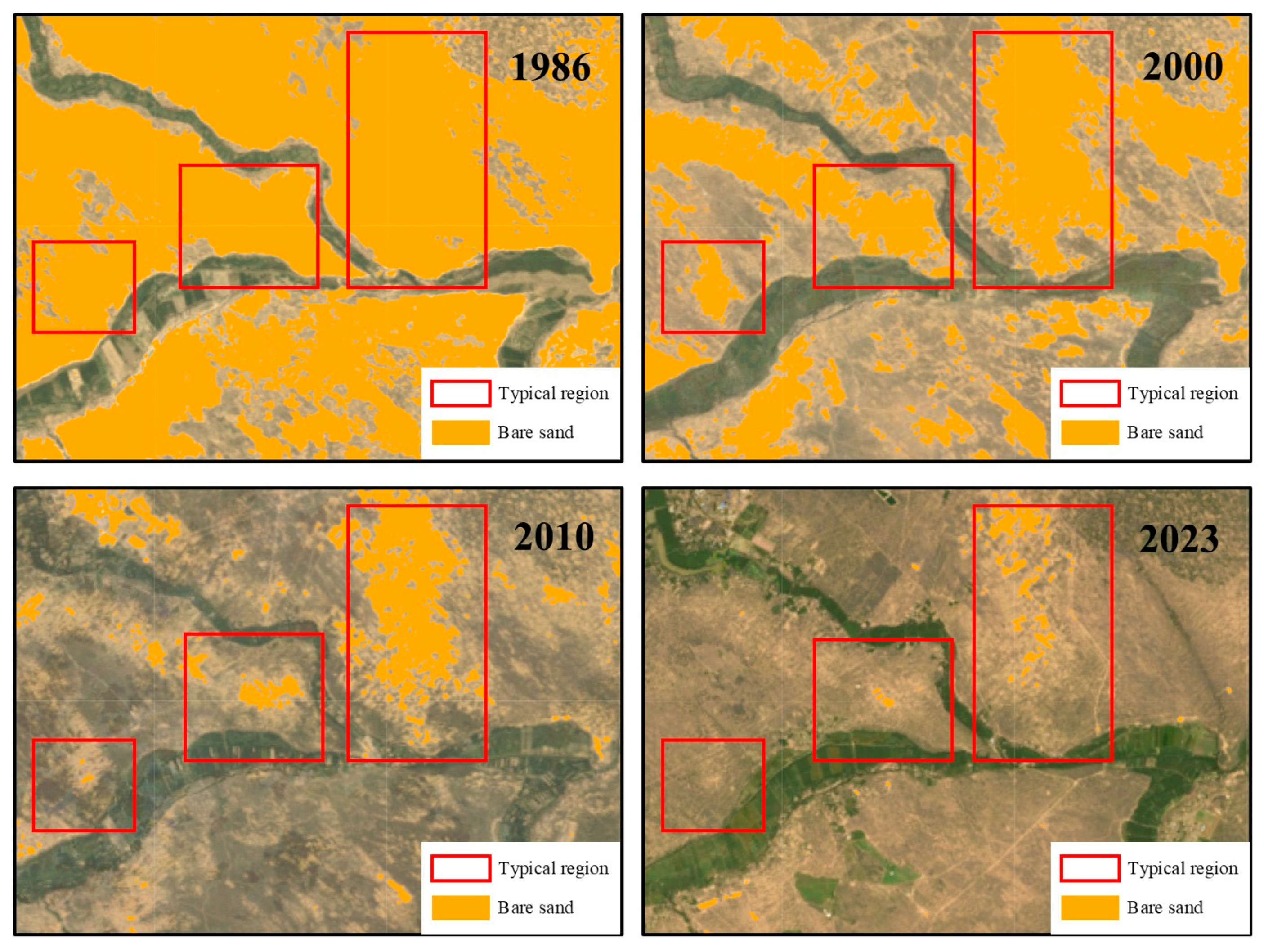
3.2. Temporal Variation Characteristics of Bare Sand in the Mu Us Sandy Land
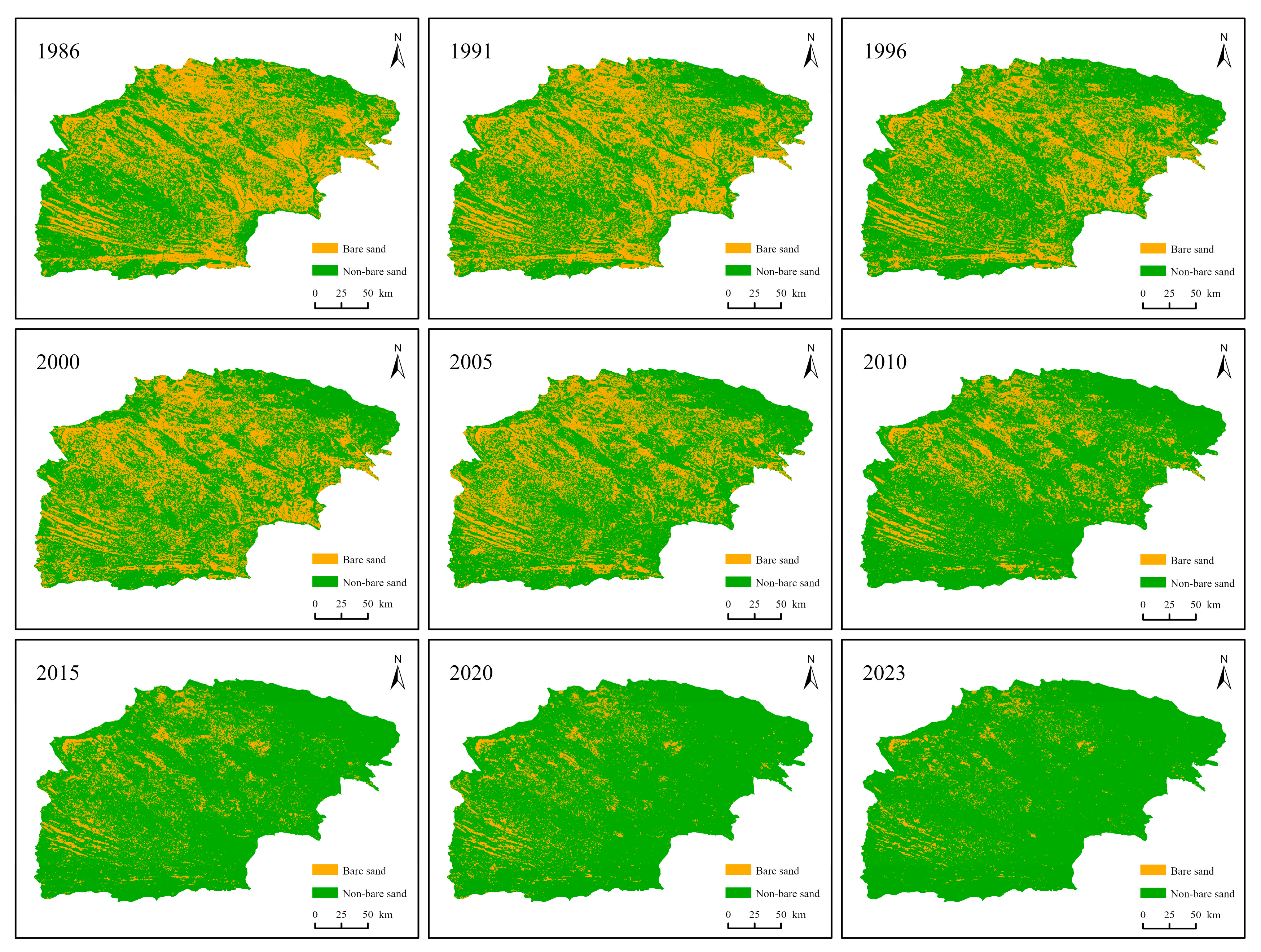
3.3. Spatial Distribution Characteristics of Bare Sand in the Mu Us Sandy Land
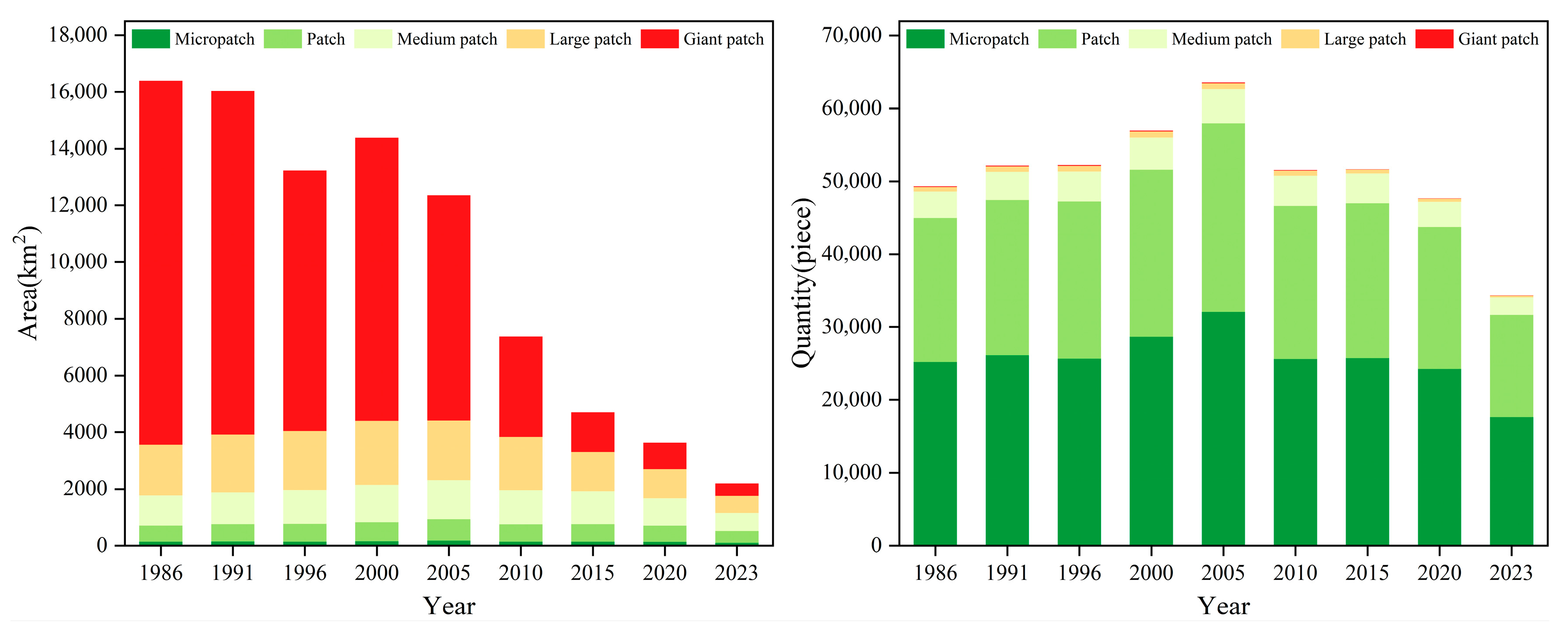
3.4. Dynamic Changes in Bare Sand Patches by Area Class
4. Discussion
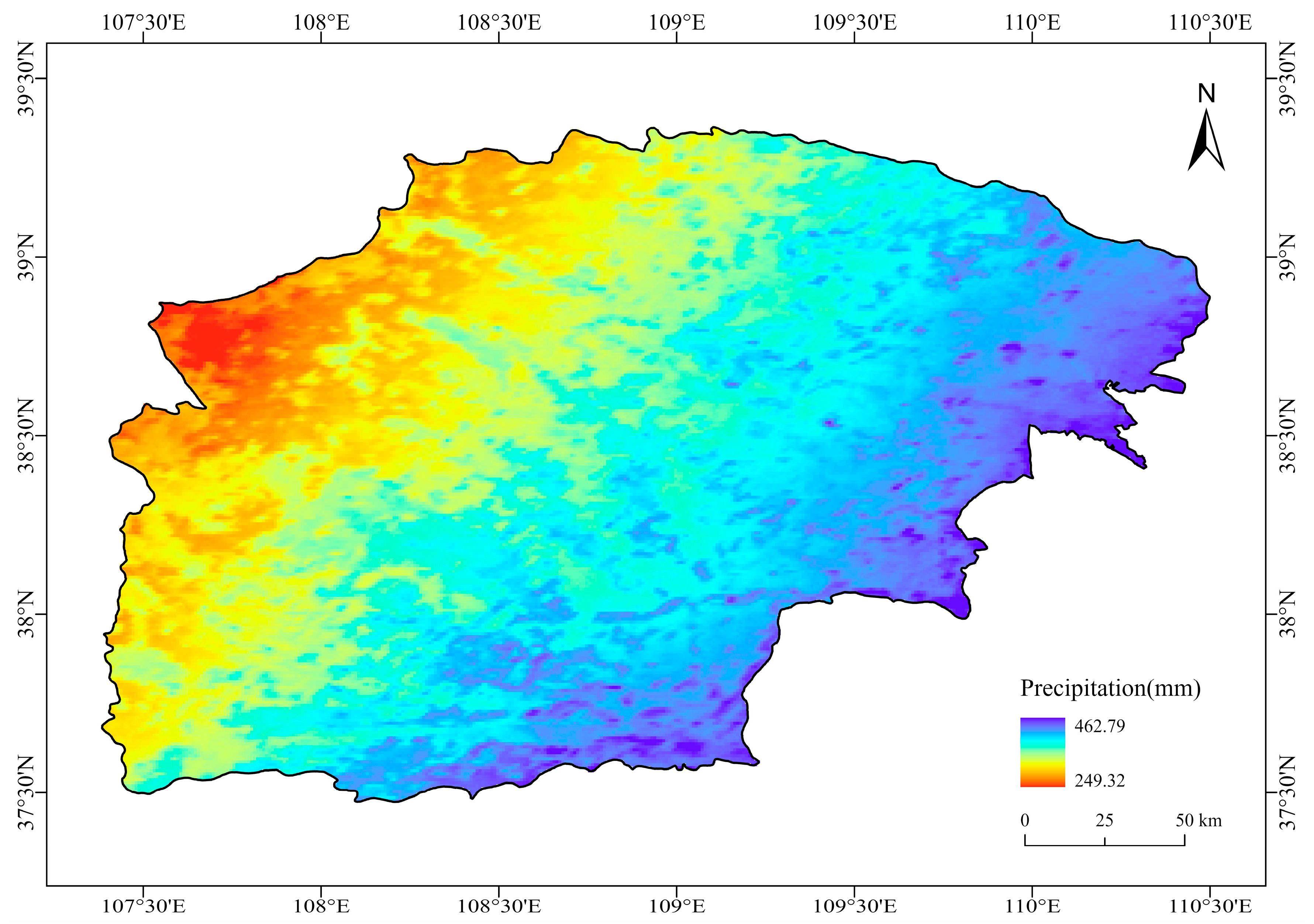
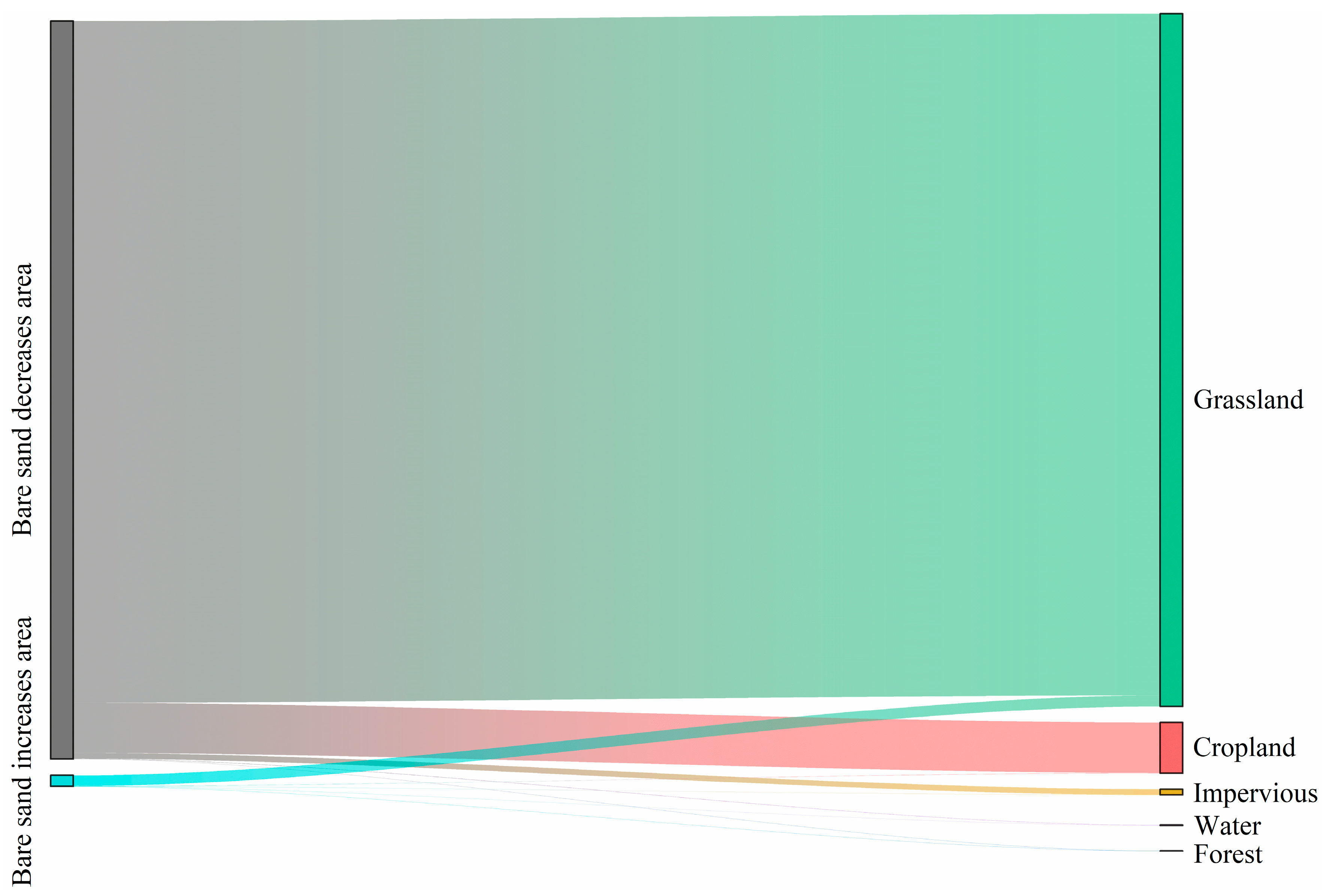
4.1. Factors Affecting the Spatial Distribution of Bare Sand Patches
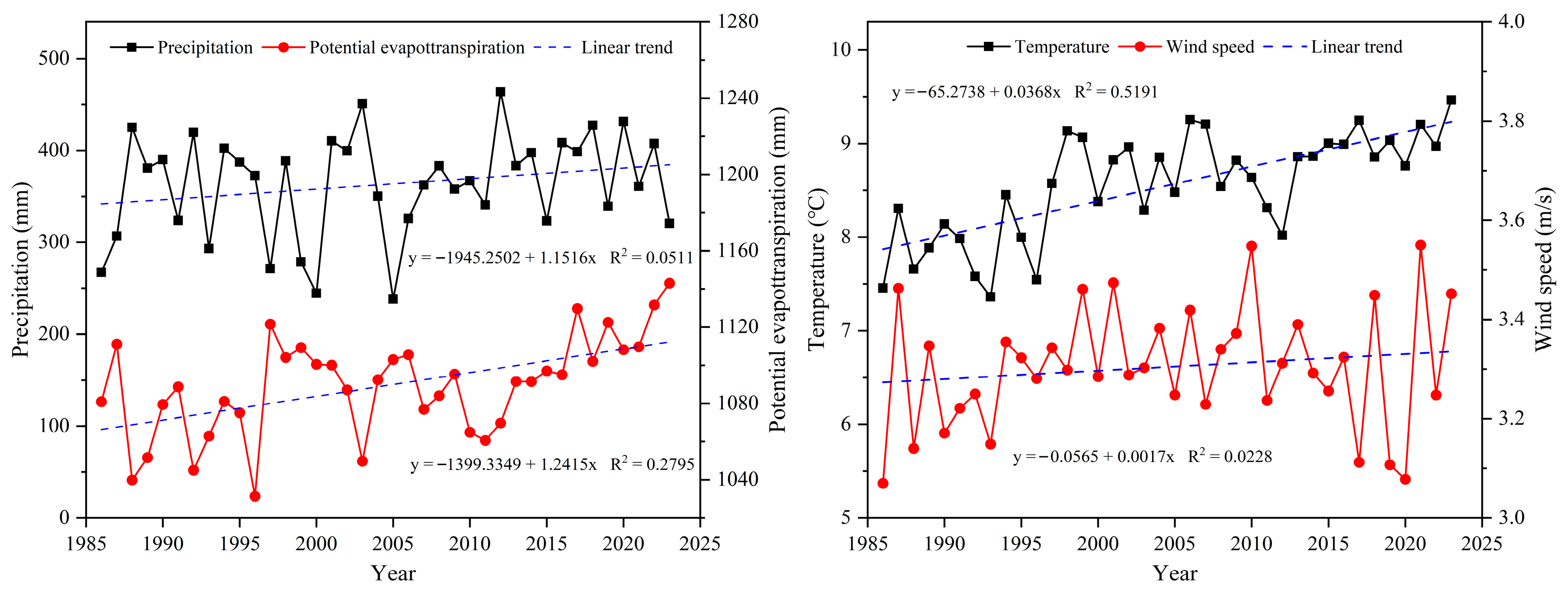
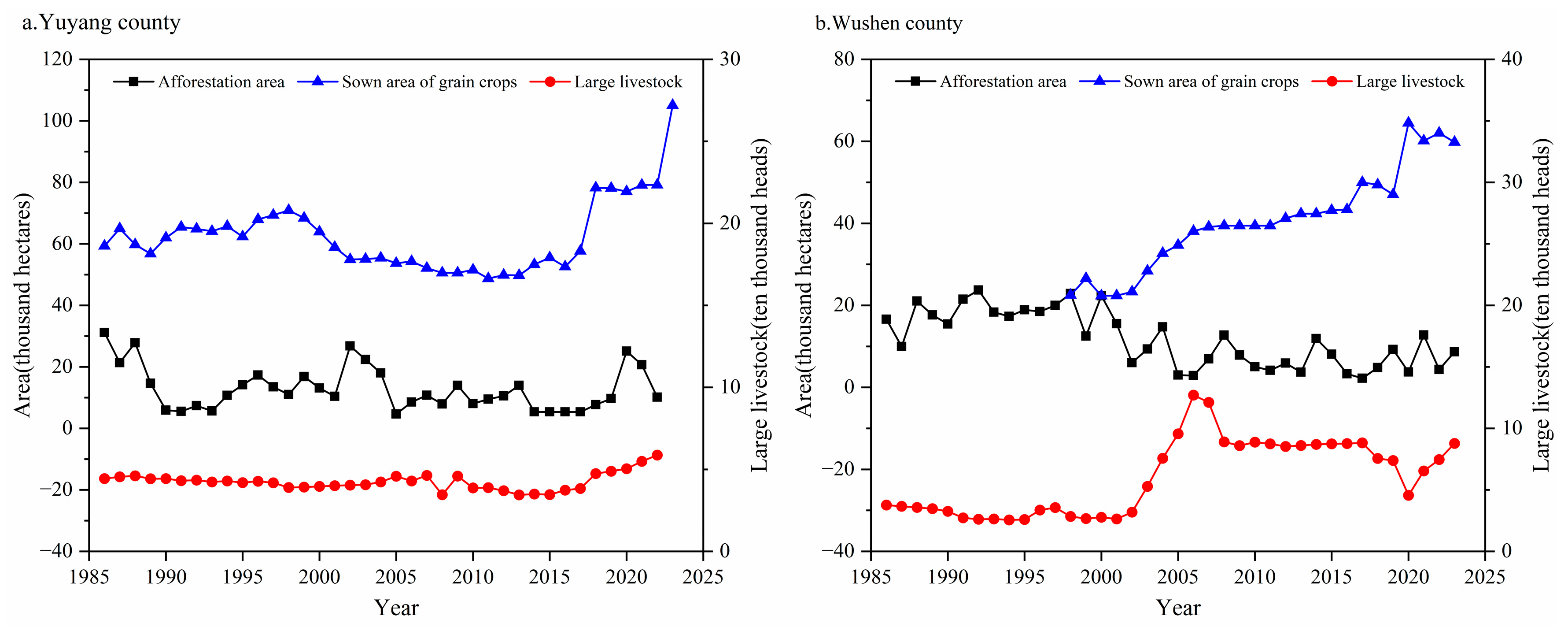
4.2. Factors Affecting the Temporal Variation of Bare Sand Patches
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hassan, R.; Scholes, R.J.; Ash, N. Ecosystems and Human Well-Being: Current State and Trends; Island Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, B.; Stafford-Smith, M.; Wang, Y.; Wu, B.; Yu, X.; Lv, N.; Ojima, D.S.; Lv, Y.; Fu, C.; Liu, Y.; et al. The Global-DEP conceptual framework—Research on dryland ecosystems to promote sustainability. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sustain. 2021, 48, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. Trees, Forests and Land Use in Drylands: The First Global Assessment; FAO Forestry Paper No. 184; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- von Hardenberg, J.; Meron, E.; Shachak, M.; Zarmi, Y. Diversity of Vegetation Patterns and Desertification. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2001, 87, 198101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yizhaq, H.; Ashkenazy, Y.; Tsoar, H. Why Do Active and Stabilized Dunes Coexist under the Same Climatic Conditions? Phys. Rev. Lett. 2007, 98, 188001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayaud, J.R.; Wiggs, G.F.S.; Bailey, R.M. Dynamics of skimming flow in the wake of a vegetation patch. Aeolian Res. 2016, 22, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, Y.; Jin, H.; Cui, J. Human activity accelerating the rapid desertification of the Mu Us Sandy Lands, North China. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 23003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitford, W.G.; Duval, B.D. Ecology of Desert Systems; Academic Press: London, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, X.; Liu, Y.; Yang, C. Study on Influence Upon Agriophyllum squarrosum Population by the Niche Island of Nude Sandy Patches. Acta Sci. Nat. Univ. Neimonggol (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2000, 31, 228–232. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, J.M. Influence of topography, bare sand, and soil pH on the occurrence and distribution of plant species in a lacustrine dune ecosystem. J. Torrey Bot. Soc. 2014, 141, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillette, D.A.; Herrick, J.E.; Herbert, G.A. Wind Characteristics of Mesquite Streets in the Northern Chihuahuan Desert, New Mexico, USA. Environ. Fluid Mech. 2006, 6, 241–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Field, J.P.; Belnap, J.; Breshears, D.D.; Neff, J.C.; Okin, G.S.; Whicker, J.J.; Painter, T.H.; Ravi, S.; Reheis, M.C.; Reynolds, R.L. The ecology of dust. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2010, 8, 423–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludwig, J.A.; Wilcox, B.P.; Breshears, D.D.; Tongway, D.J.; Imeson, A.C. Vegetation patches and runoff-erosion as interacting ecohydrological processes in semiarid landscapes. Ecology 2005, 86, 288–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Xin, X.; Xu, X.; Wang, X.; Yan, R.; Murray, P.J. Vegetation patches increase wind-blown litter accumulation in a semi-arid steppe of northern China. Environ. Res. Lett. 2016, 11, 124008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Yin, Q.; Niu, J.; Yan, Z.; Wang, H.; Wang, Y.; Chen, D. Consistent effects of vegetation patch type on soil microbial communities across three successional stages in a desert ecosystem. Land Degrad. Dev. 2022, 33, 1552–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madurapperuma, B.; Close, P.; Fleming, S.; Collin, M.; Thuresson, K.; Lamping, J.; Dellysse, J.; Cortenbach, J. Habitat Mapping of Ma-le’l Dunes Coupling with UAV and NAIP Imagery. Proceedings 2018, 2, 368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shumack, S.; Hesse, P.; Turner, L. The impact of fire on sand dune stability: Surface coverage and biomass recovery after fires on Western Australian coastal dune systems from 1988 to 2016. Geomorphology 2017, 299, 39–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Secu, C.V.; Stoleriu, C.C.; Lesenciuc, C.D.; Ursu, A. Normalized Sand Index for Identification of Bare Sand Areas in Temperate Climates Using Landsat Images, Application to the South of Romania. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smyth, T.A.G.; Wilson, R.; Rooney, P.; Yates, K.L. Extent, accuracy and repeatability of bare sand and vegetation cover in dunes mapped from aerial imagery is highly variable. Aeolian Res. 2022, 56, 100799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorelick, N.; Hancher, M.; Dixon, M.; Ilyushchenko, S.; Thau, D.; Moore, R. Google Earth Engine: Planetary-scale geospatial analysis for everyone. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 202, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pizarro, S.E.; Pricope, N.G.; Vargas-Machuca, D.; Huanca, O.; Ñaupari, J. Mapping Land Cover Types for Highland Andean Ecosystems in Peru Using Google Earth Engine. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Ni, X.; Xing, M. A Study on Spatial and Temporal Dynamic Changes of Desertification in Northern China from 2000 to 2020. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, K.; Wang, T.; Liu, S.; Yan, C.; Kang, W.; Chen, X.; Guo, Z. Path analysis model to identify and analyse the causes of aeolian desertification in Mu Us Sandy Land, China. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 124, 107386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, T.; Pei, C.; Zhao, X.; Li, Y.; Hu, S.; Bu, C.; Zhang, Q. Multisource Remote Sensing Monitoring and Analysis of the Driving Forces of Vegetation Restoration in the Mu Us Sandy Land. Land 2022, 11, 1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Zhang, Y. Research on temporal and spatial evolution of land use and landscape pattern in Anshan City based on GEE. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 988346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B. The recent evolution of dune landforms and its environmental indications in the mid-latitude desert area (Hexi Corridor). J. Geogr. Sci. 2022, 32, 617–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Z.; Lü, P.; Ma, F.; Cao, M.; Yu, J. Quantifying dune migration patterns and influencing factors in the central Sahara Desert. Catena 2024, 235, 107686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.; Ding, Y.; Liu, W.; Li, Z. 1 km monthly temperature and precipitation dataset for China from 1901 to 2017. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2019, 11, 1931–1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Townshend, J.G.; Goff, T.; Tucker, C. Multitemporal Dimensionality of Images of Normalized Difference Vegetation Index at Continental Scales. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1985, GE-23, 888–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huete, A.R. Vegetation Indices, Remote Sensing and Forest Monitoring. Geogr. Compass 2012, 6, 513–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordan, C.F. Derivation of Leaf-Area Index from Quality of Light on the Forest Floor. Ecology 1969, 50, 663–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, J.; Chehbouni, A.; Huete, A.R.; Kerr, Y.H.; Sorooshian, S. A Modified Soil Adjusted Vegetation Index. Remote Sens. Environ. 1994, 48, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H. Modification of normalised difference water index (NDWI) to enhance open water features in remotely sensed imagery. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2007, 27, 3025–3033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zha, Y.; Gao, J.; Ni, S. Use of normalized difference built-up index in automatically mapping urban areas from TM imagery. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2010, 24, 583–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parracciani, C.; Gigante, D.; Mutanga, O.; Bonafoni, S.; Vizzari, M. Land cover changes in grassland landscapes: Combining enhanced Landsat data composition, LandTrendr, and machine learning classification in google earth engine with MLP-ANN scenario forecasting. GIScience Remote Sens. 2024, 61, 2302221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Feng, S.; Xie, F.; Zhu, S.; Zhang, S. Extraction of long time series wetland information based on Google Earth Engine and random forest algorithm for a plateau lake basin—A case study of Dianchi Lake, Yunnan Province, China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 146, 109813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Guo, P.; Sun, F.; Zhu, J.; Cao, X.; Dong, X.; Lu, Q. Mapping Dryland Ecosystems Using Google Earth Engine and Random Forest: A Case Study of an Ecologically Critical Area in Northern China. Land 2024, 13, 845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiman, L. Random Forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veronesi, F.; Hurni, L. Random Forest with semantic tie points for classifying landforms and creating rigorous shaded relief representations. Geomorphology 2014, 224, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatsumi, K.; Yamashiki, Y.; Canales Torres, M.A.; Taipe, C.L.R. Crop classification of upland fields using Random forest of time-series Landsat 7 ETM+ data. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2015, 115, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, C.; Guo, B.; Fan, Y.; Zang, W.; Ji, J. The Change Pattern and Its Dominant Driving Factors of Wetlands in the Yellow River Delta Based on Sentinel-2 Images. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.; Pan, M.; Hao, Z.; Yang, A.; Xue, W. Variations in aeolian landform patterns in the Gonghe Basin over the last 30 years. J. Mt. Sci. 2021, 18, 2034–2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Chang, X.; Zhang, J.; Cai, M. Spatial analysis of distribution pattern of the mobile dune patches in the typical regions of Korqin Sand land. Sci. Surv. Mapp. 2008, 33, 100–102. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, H.; Wang, Z.; Mao, D. Characteristics of Sand Dune Pattern and Fluvial-aeolian Interaction in Horqin Sandy Land, Northeast Plain of China. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2018, 28, 624–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Y.; Wu, B.; Jia, X.; Xie, S. Wind-proof and sand-fixing effects of Artemisia ordosica with different coverages in the Mu Us Sandy Land, northern China. J. Arid Land 2022, 14, 877–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Cai, Y.; Yang, W.; Yi, Y.; Yang, Z.; Fu, Q. Contributions of climatic and anthropogenic drivers to vegetation dynamics indicated by NDVI in a large dam-reservoir-river system. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 256, 120477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.; Guan, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, H.; Du, Q.; Yuan, T. Investigating the underlying drivers of vegetation dynamics in cold-arid mountainous. Catena 2024, 237, 107831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Cheng, L.; Ding, A.; Yuan, Y.; Li, Z.; Hou, Y.; Ren, L.; Zhang, S. Geodetector model-based quantitative analysis of vegetation change characteristics and driving forces: A case study in the Yongding River basin in China. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2024, 132, 104027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Guan, Q.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, J.; Yang, L.; Yang, E.; Li, H.; Du, Q. Three-dimensional dynamic characteristics of vegetation and its response to climatic factors in the Qilian Mountains. Catena 2022, 208, 105694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Shao, G.; Zhao, G.; Master, D.C.L.; Parker, G.R.; Dunning, J.B., Jr.; Li, Q. China’s Forest Policy for the 21st Century. Science 2000, 288, 2135–2136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Z.; Du, J.; Li, L.; Zhu, X.; Chong, F.; Zhai, G.; Wu, L.; Chen, X.; Han, J. Spatiotemporal Changes of Center Pivot Irrigation Farmland in the Mu Us Region and Its Impact on the Surrounding Vegetation Growth. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Bian, Z.; Zhang, K.; Ahmad, B.; Khan, A. Effects of different fencing regimes on community structure of degraded desert grasslands on Mu Us desert, China. Ecol. Evol. 2019, 9, 3367–3377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Land Use/Land Cover Type | Landsat Image | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bare sand |  | The image is light yellow with an irregular shape and water ripple texture. | |
| Non-bare sand | Water |  | The image is dark green with an irregular shape. |
| Forest/grassland |  | The image is light gray and densely distributed. | |
| Built-up |  | The image is gray and regular in shape. | |
| Cropland |  | The image is green with a regular shape and a smooth texture. | |
| Year | 1986 | 1991 | 1996 | 2000 | 2005 | 2010 | 2015 | 2020 | 2023 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bare sand | 225 | 210 | 222 | 252 | 226 | 178 | 167 | 160 | 126 |
| Non-bare sand | 327 | 307 | 338 | 339 | 319 | 358 | 381 | 393 | 416 |
| Total | 552 | 517 | 560 | 591 | 545 | 536 | 548 | 553 | 542 |
| Year | Cover Type | Producer Accuracy | Consumer Accuracy | Overall Accuracy | Kappa Coefficient |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1986 | Non-bare sand | 0.9906 | 1.0000 | 0.9942 | 0.9878 |
| Bare sand | 1.0000 | 0.9852 | |||
| 1991 | Non-bare sand | 1.0000 | 0.9880 | 0.9929 | 0.9854 |
| Bare sand | 0.9830 | 1.0000 | |||
| 1996 | Non-bare sand | 1.0000 | 0.9908 | 0.9939 | 0.9866 |
| Bare sand | 0.9827 | 1.0000 | |||
| 2000 | Non-bare sand | 0.9900 | 1.0000 | 0.9946 | 0.9893 |
| Bare sand | 1.0000 | 0.9886 | |||
| 2005 | Non-bare sand | 0.9888 | 1.0000 | 0.9936 | 0.9871 |
| Bare sand | 1.0000 | 0.9855 | |||
| 2010 | Non-bare sand | 0.9908 | 0.9908 | 0.9874 | 0.9708 |
| Bare sand | 0.9800 | 0.9800 | |||
| 2015 | Non-bare sand | 0.9909 | 1.0000 | 0.9940 | 0.9870 |
| Bare sand | 1.0000 | 0.9833 | |||
| 2020 | Non-bare sand | 0.9922 | 1.0000 | 0.9936 | 0.9810 |
| Bare sand | 1.0000 | 0.9705 | |||
| 2023 | Non-bare sand | 0.9919 | 1.0000 | 0.9941 | 0.9854 |
| Bare sand | 1.0000 | 0.9791 |
| Year | Micro Patch | Small Patch | Medium Patch | Large Patch | Giant Patch | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Count (Piece) | Area (km2) | Count (Piece) | Area (km2) | Count (Piece) | Area (km2) | Count (Piece) | Area (km2) | Count (Piece) | Area (km2) | |
| 1986 | 25,168 | 134.27 | 19,807 | 578.30 | 3608 | 1051.76 | 642 | 1791.84 | 99 | 12,841.03 |
| 1991 | 26,135 | 139.32 | 21,275 | 625.81 | 3875 | 1118.27 | 743 | 2026.00 | 115 | 12,127.81 |
| 1996 | 25,622 | 137.41 | 21,588 | 639.12 | 4121 | 1190.84 | 770 | 2069.34 | 123 | 9188.94 |
| 2000 | 28,634 | 152.48 | 22,935 | 679.90 | 4431 | 1308.09 | 816 | 2260.35 | 126 | 9981.52 |
| 2005 | 32,072 | 170.49 | 25,889 | 759.49 | 4704 | 1377.39 | 797 | 2104.06 | 119 | 7941.75 |
| 2010 | 25,586 | 136.34 | 21,025 | 620.30 | 4161 | 1205.82 | 671 | 1864.27 | 88 | 3543.38 |
| 2015 | 25,773 | 138.41 | 21,193 | 625.46 | 4097 | 1161.79 | 533 | 1377.84 | 43 | 1398.73 |
| 2020 | 24,213 | 129.85 | 19,505 | 572.63 | 3459 | 960.70 | 431 | 1026.74 | 38 | 941.07 |
| 2023 | 17,631 | 94.49 | 14,038 | 411.30 | 2374 | 644.42 | 245 | 599.56 | 25 | 440.64 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, K.; Cao, Y.; Pang, Y. Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Bare Sand Patches in the Mu Us Sandy Land, China. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 3244. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17183244
Yang K, Cao Y, Pang Y. Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Bare Sand Patches in the Mu Us Sandy Land, China. Remote Sensing. 2025; 17(18):3244. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17183244
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Kang, Yanping Cao, and Yingjun Pang. 2025. "Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Bare Sand Patches in the Mu Us Sandy Land, China" Remote Sensing 17, no. 18: 3244. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17183244
APA StyleYang, K., Cao, Y., & Pang, Y. (2025). Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Bare Sand Patches in the Mu Us Sandy Land, China. Remote Sensing, 17(18), 3244. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17183244







