M4MLF-YOLO: A Lightweight Semantic Segmentation Framework for Spacecraft Component Recognition
Abstract
1. Introduction
- 1.
- A lightweight backbone network based on MobileNetV4, which reduces parameters and computational complexity through structural optimization, making it suitable for resource-constrained space environments while maintaining good segmentation performance.
- 2.
- Linear Deformable Convolution, which can adaptively adjust sampling point density and distribution based on regional characteristics, enhancing feature extraction capabilities in complex regions while reducing redundant computations in flat backgrounds.
- 3.
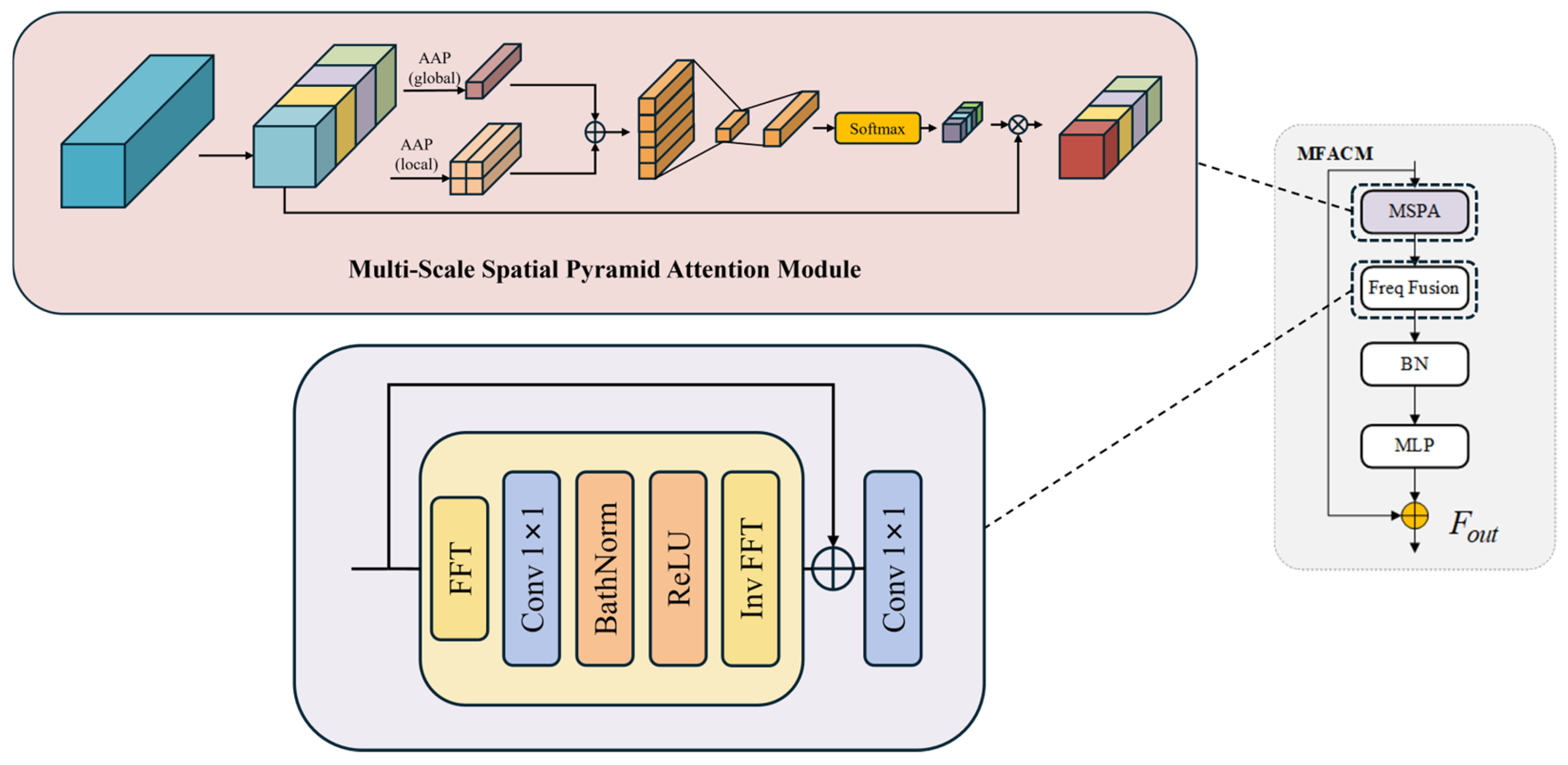
- Multi-Scale Fourier Adaptive Calibration Module (MFAC), which leverages frequency domain characteristics and multi-scale fusion strategies to improve boundary segmentation accuracy and background suppression capabilities for spacecraft components.
- 4.
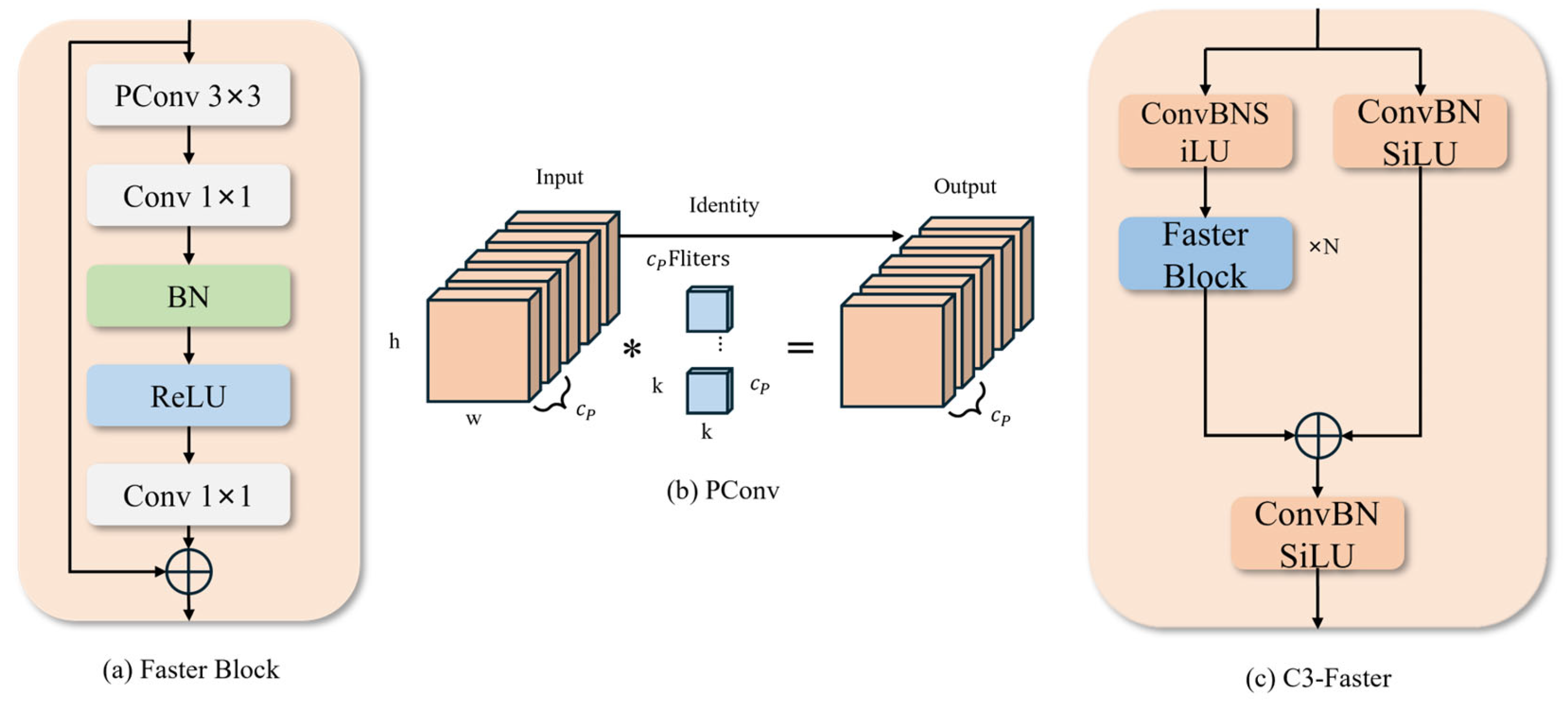
- C3-Faster module, which performs lightweight reconstruction of the original C3 structure, introduces efficient residual units based on FasterNet, and adopts a partial convolution strategy to perform spatial modeling on only some channels, effectively reducing the number of parameters and computational load. This module significantly improves inference efficiency and edge deployment adaptability while retaining channel interaction and multi-scale fusion capabilities.
2. Related Work
2.1. Semantic Segmentation Based on Deep Learning
2.2. Model Lightweighting Technology
3. Methods
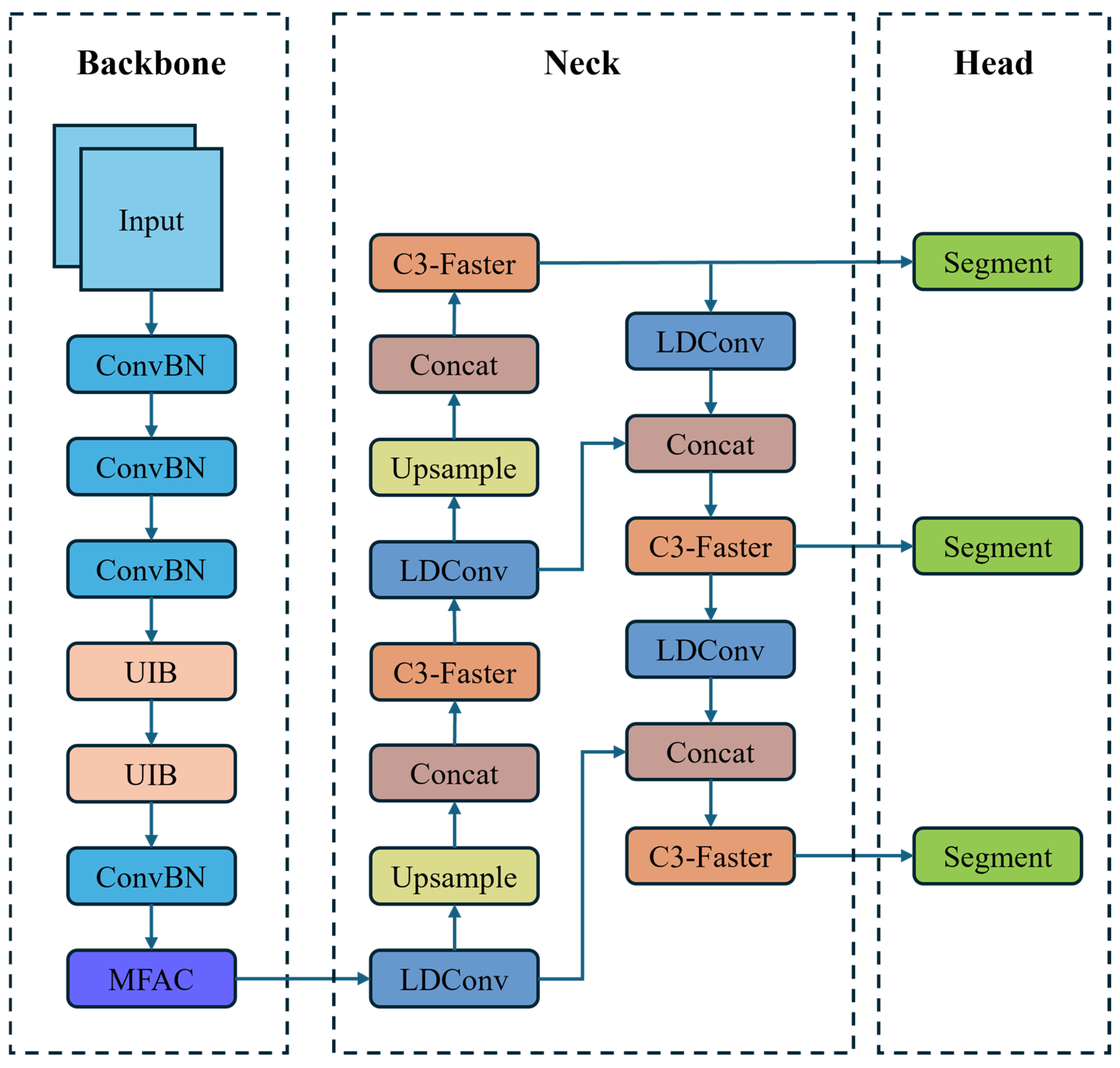
3.1. M4MLF-YOLO Network Architecture
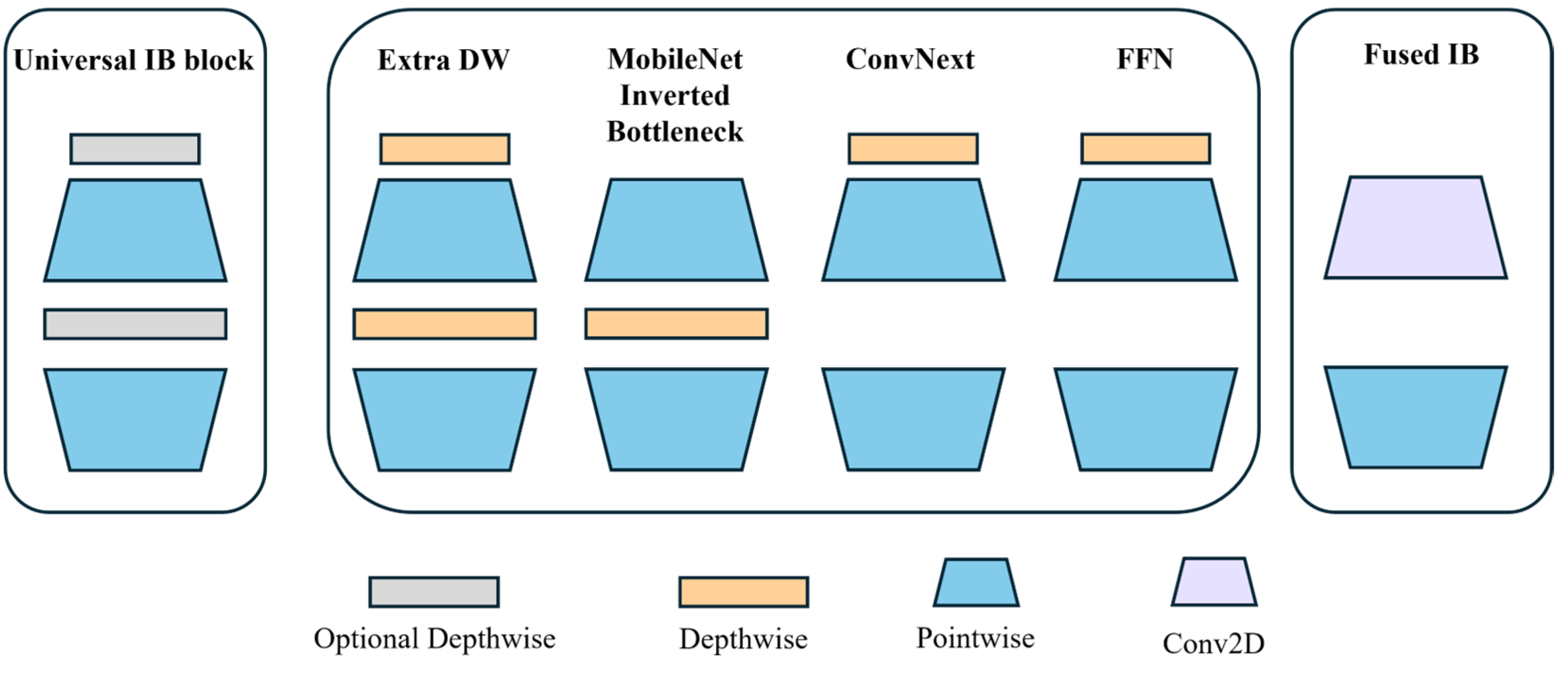
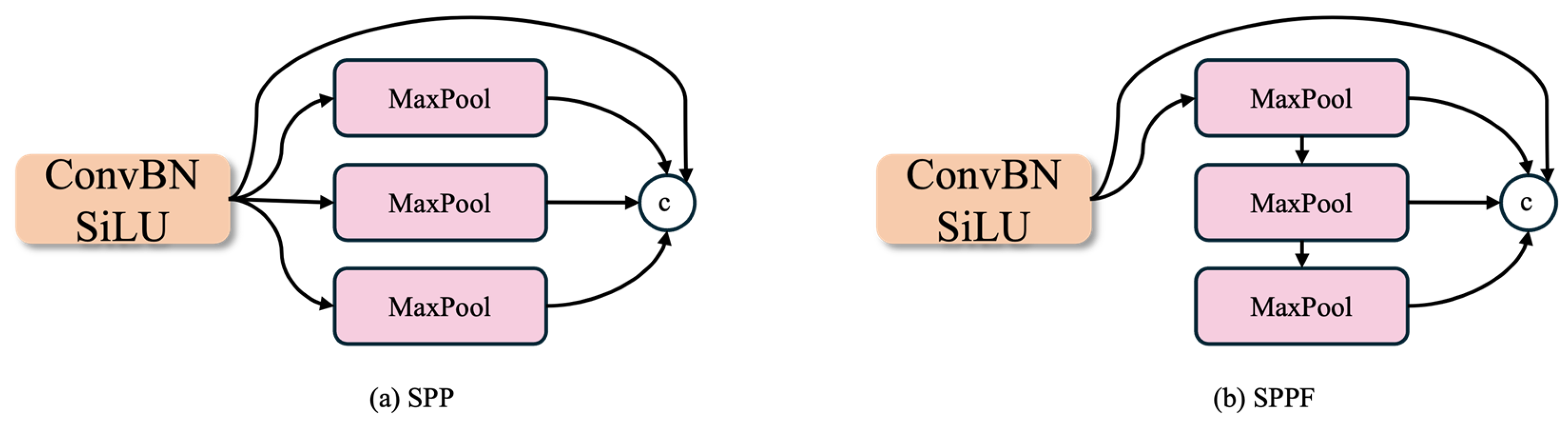
3.2. Backbone Network Improvement
3.3. MFACM
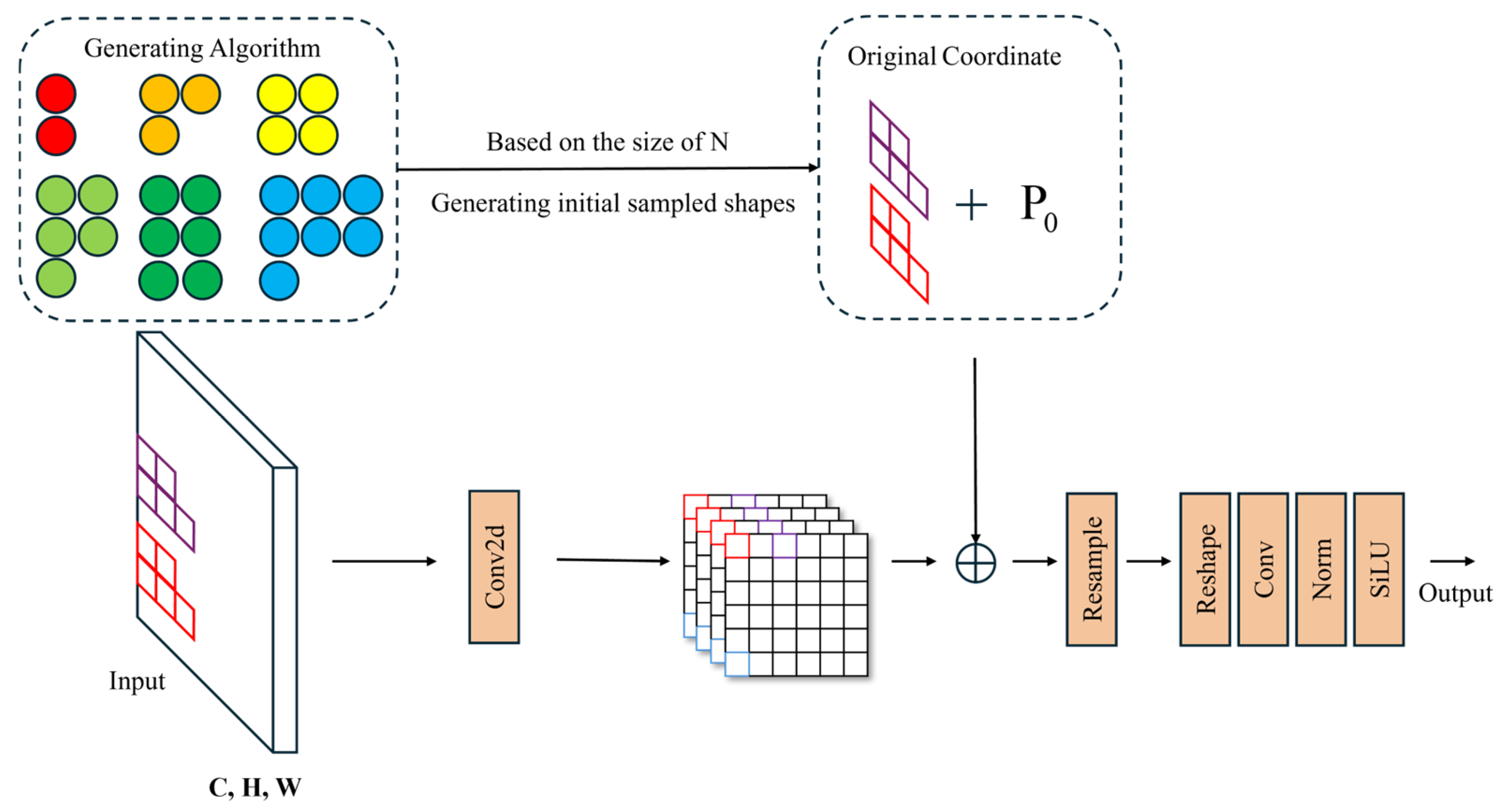
3.4. LDConv
3.5. C3-Faster
4. Experimental Results and Analyses
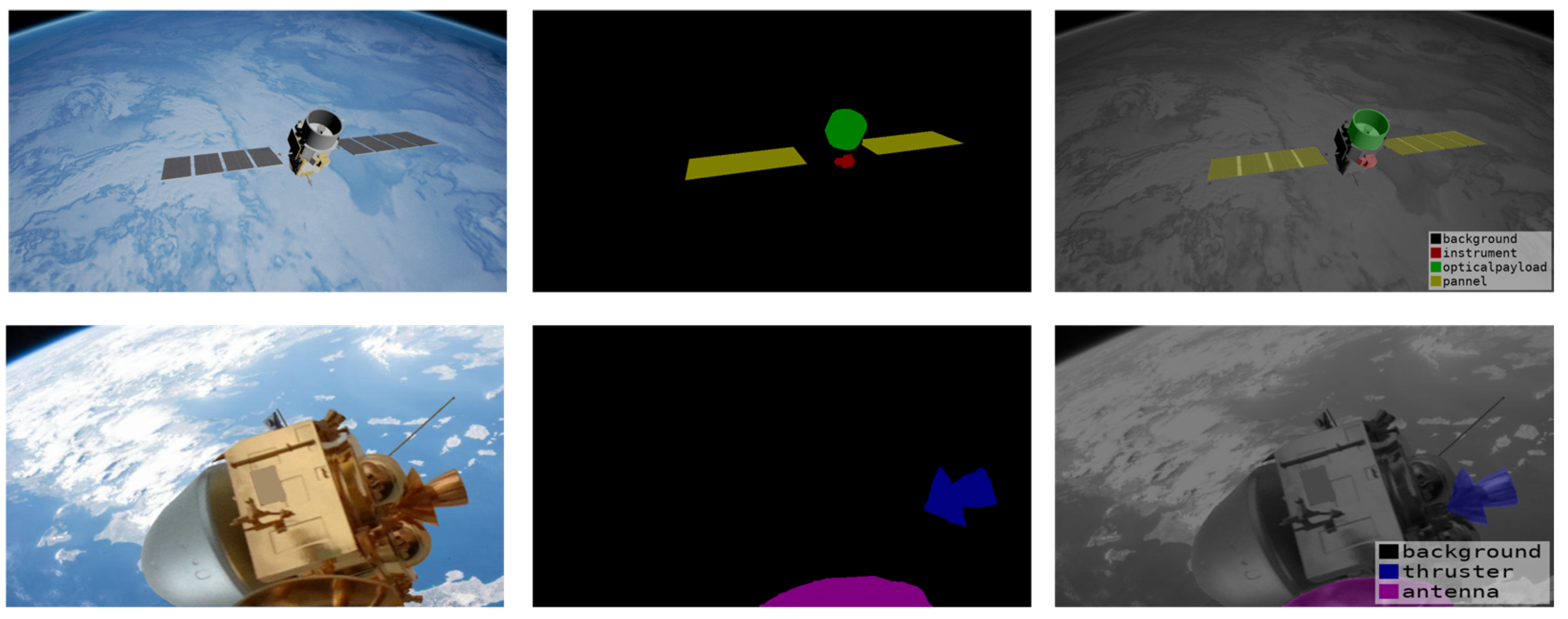
4.1. Dataset Construction
4.2. Experimental Environment and Metrics
4.3. Comparison of Lightweight Backbone Network Effects
4.4. Ablation Experiment
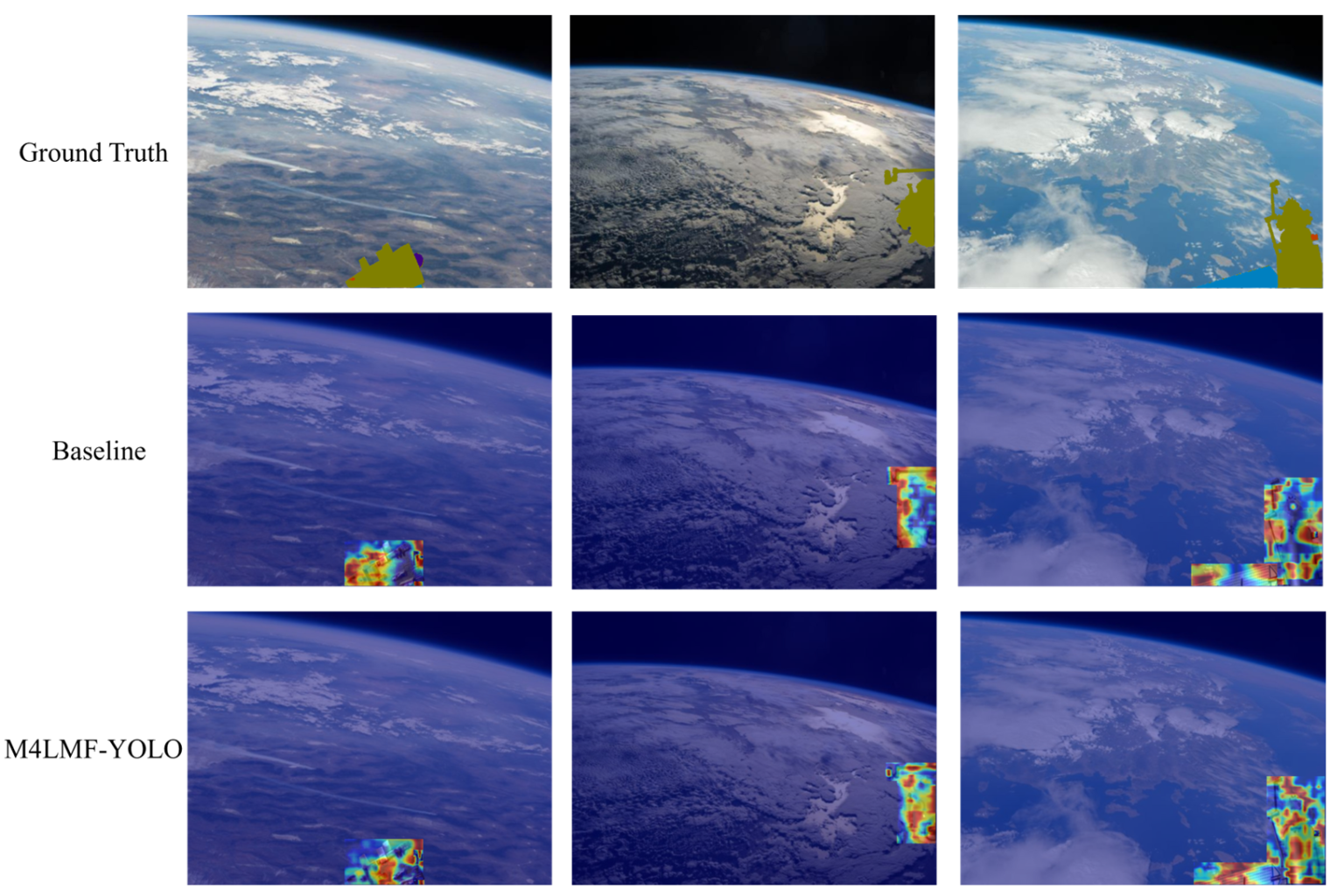
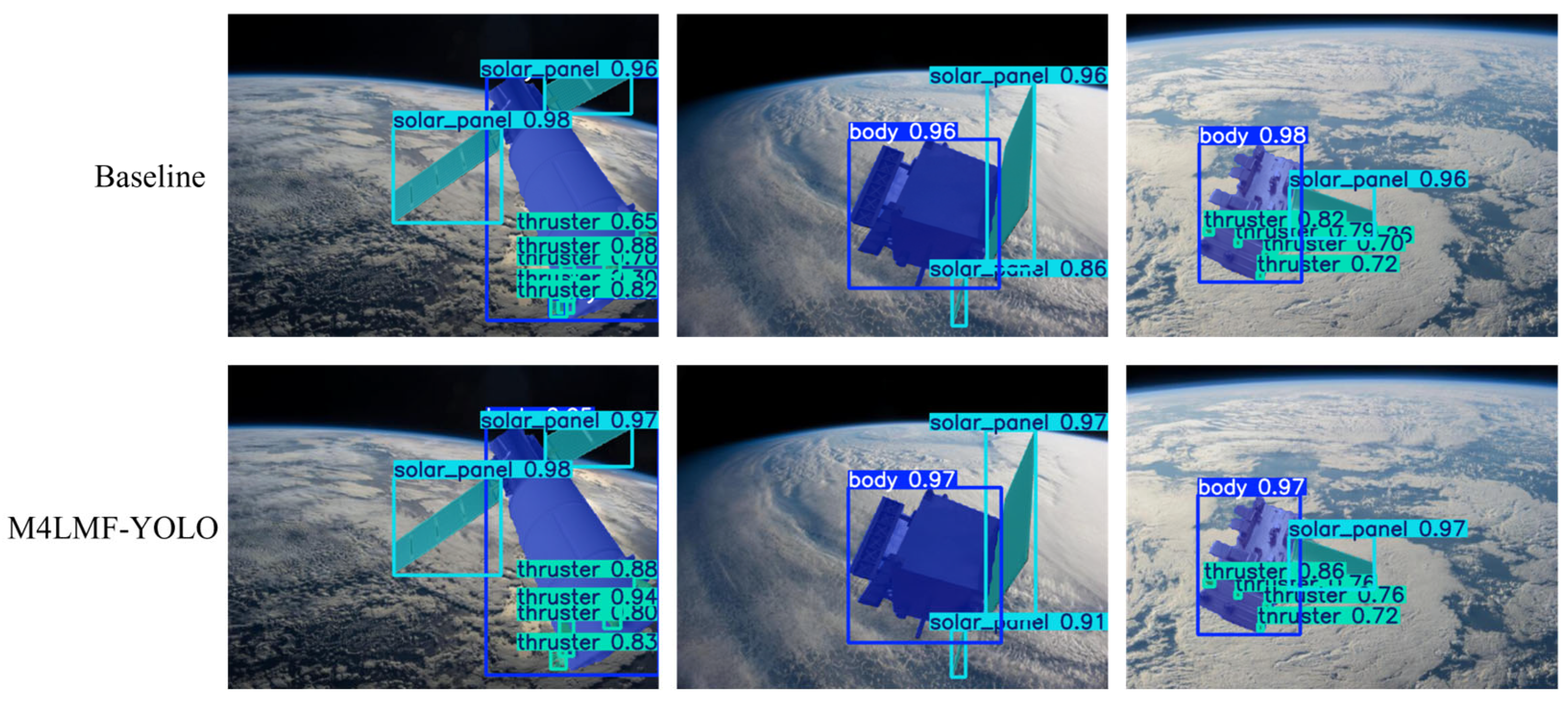
4.5. Visualization Experiment
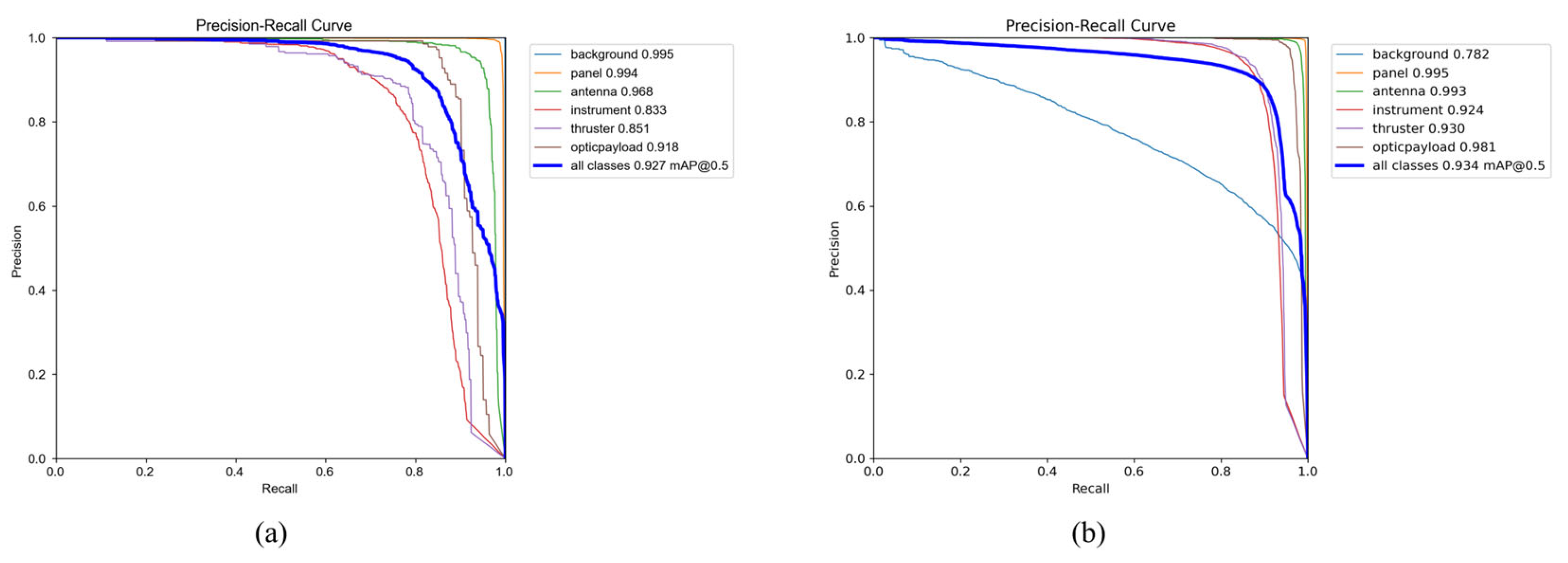
4.6. Network Comparative Experiment
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Henshaw, C. The DARPA Phoenix Spacecraft Servicing Program: Overview and Plans for Risk Reduction. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Artificial Intelligence, Robotics and Automation in Space (i-SAIRAS), Montreal, QC, Canada, 17–19 June 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Volpe, R.; Circi, C. Optical-Aided, Autonomous and Optimal Space Rendezvous with a Non-Cooperative Target. Acta Astronaut. 2019, 157, 528–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, B.B.; Smith, R.C.; Naasz, B.J.; Pellegrino, J.F.; Bacon, C.E. The Restore-L Servicing Mission. In Proceedings of the AIAA SPACE 2016, Long Beach, CA, USA, 13–16 September 2016; American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics: Reston, VA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Canny, J. A Computational Approach to Edge Detection. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 1986, PAMI-8, 679–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Beierle, C.; D’Amico, S. Pose Estimation for Non-Cooperative Spacecraft Rendezvous Using Convolutional Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Aerospace Conference, Big Sky, MT, USA, 3–10 March 2018; pp. 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Ballard, D.H. Generalizing the Hough transform to detect arbitrary shapes. Pattern Recognit. 1981, 13, 111–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, L.; Goshtasby, A. On the Canny edge detector. Pattern Recognit. 2001, 34, 721–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yin, T.; Chen, X.; Hauwa, A.S.; Deng, B.; Zhu, Y.; Gao, S.; Zang, H.; Zhao, H. A Steel Defect Detection Method Based on Edge Feature Extraction via the Sobel Operator. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 27694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.; Liu, Y.; Yang, J.; Li, B.; Wang, Y.; An, W. Graph Laplacian regularization for fast infrared small target detection. Pattern Recognit. 2025, 158, 111077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Yuan, S.; Pan, J. Building Detection in High Resolution Satellite Urban Image Using Segmentation, Corner Detection Combined with Adaptive Windowed Hough Transform. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium—IGARSS, Melbourne, VIC, Australia, 21–26 July 2013; pp. 508–511. [Google Scholar]
- Girshick, R.; Donahue, J.; Darrell, T.; Malik, J. Rich Feature Hierarchies for Accurate Object Detection and Semantic Segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Columbus, OH, USA, 23–28 June 2014. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Spatial Pyramid Pooling in Deep Convolutional Networks for Visual Recognition. In Proceedings of the 13th European Conference on Computer Vision, ECCV 2014, Zurich, Switzerland, 6–12 September 2014; Volume 8691, pp. 346–361. [Google Scholar]
- Girshick, R. Fast R-CNN. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 7–13 December 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, Z.; Vasconcelos, N. Cascade R-CNN: High Quality Object Detection and Instance Segmentation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2019, 43, 1483–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Anguelov, D.; Erhan, D.; Szegedy, C.; Reed, S.; Fu, C.-Y.; Berg, A.C. SSD: Single Shot MultiBox Detector. In Proceedings of the 14th European Conference on Computer Vision, ECCV 2016, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 11–14 October 2016; Volume 9905, pp. 21–37. [Google Scholar]
- Redmon, J.; Farhadi, A. YOLOv3: An Incremental Improvement. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1804.02767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redmon, J.; Divvala, S.; Girshick, R.; Farhadi, A. You Only Look Once: Unified, Real-Time Object Detection. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; IEEE: Las Vegas, NV, USA, 2016; pp. 779–788. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Li, L.; Jiang, H.; Weng, K.; Geng, Y.; Li, L.; Ke, Z.; Li, Q.; Cheng, M.; Nie, W.; et al. YOLOv6: A Single-Stage Object Detection Framework for Industrial Applications. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2209.02976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.-Y.; Bochkovskiy, A.; Liao, H.-Y.M. YOLOv7: Trainable Bag-of-Freebies Sets New State-of-the-Art for Real-Time Object Detectors. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; IEEE: Vancouver, BC, Canada, 2023; pp. 7464–7475. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, A.; Chen, H.; Liu, L.; Chen, K.; Lin, Z.; Han, J.; Ding, G. YOLOv10: Real-Time End-to-End Object Detection. In Proceedings of the 38th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 10–15 December 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Bochkovskiy, A.; Wang, C.-Y.; Liao, H.-Y.M. YOLOv4: Optimal Speed and Accuracy of Object Detection. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2004.10934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.-Y.; Maire, M.; Belongie, S.; Bourdev, L.; Girshick, R.; Hays, J.; Perona, P.; Ramanan, D.; Zitnick, C.L.; Dollár, P. Microsoft COCO: Common Objects in Context. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1405.0312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.; Zhao, H.; Puig, X.; Fidler, S.; Barriuso, A.; Torralba, A. Scene Parsing Through ADE20K Dataset. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 633–641. [Google Scholar]
- Cordts, M.; Omran, M.; Ramos, S.; Rehfeld, T.; Enzweiler, M.; Benenson, R.; Franke, U.; Roth, S.; Schiele, B. The Cityscapes Dataset for Semantic Urban Scene Understanding. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 3213–3223. [Google Scholar]
- Ultralytics/Yolov5 at v6.1. Available online: https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5 (accessed on 30 June 2025).
- Chen, J.; Wei, L.; Zhao, G. An Improved Lightweight Model Based on Mask R-CNN for Satellite Component Recognition. In Proceedings of the 2020 2nd International Conference on Industrial Artificial Intelligence (IAI), Shenyang, China, 23–25 October 2020; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Cao, Y.; Li, J. A Detection Algorithm Based on Improved Faster R-CNN for Spacecraft Components. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing and Computer Applications (ICIPCA), Changchun, China, 11–13 August 2023; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Zhu, M.; Wang, J.; Guo, X.; Yang, Y.; Wang, J. Multi-Scale Deep Neural Network Based on Dilated Convolution for Spacecraft Image Segmentation. Sensors 2022, 22, 4222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Feng, Z.; Song, B.; Li, X. SSP: A Large-Scale Semi-Real Dataset for Semantic Segmentation of Spacecraft Payloads. In Proceedings of the 2023 8th International Conference on Image, Vision and Computing (ICIVC), Dalian, China, 27–29 July 2023; pp. 831–836. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhong, R.; Cui, L. Intelligent Recognition of Spacecraft Components from Photorealistic Images Based on Unreal Engine 4. Adv. Space Res. 2023, 71, 3761–3774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Mu, J.; Cheng, X.; Liu, F. Spacecraft-DS: A Spacecraft Dataset for Key Components Detection and Segmentation via Hardware-in-the-Loop Capture. IEEE Sens. J. 2024, 24, 5347–5358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, Y.; Gang, S.; Guan, C. FCIHMRT: Feature Cross-Layer Interaction Hybrid Method Based on Res2Net and Transformer for Remote Sensing Scene Classification. Electronics 2023, 12, 4362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wang, H.; Wang, Z.; Chen, X.; Chen, W.; Xie, Z. Filtering and Regret Network for Spacecraft Component Segmentation Based on Gray Images and Depth Maps. Chin. J. Aeronaut. 2024, 37, 439–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proença, P.F.; Gao, Y. Deep Learning for Spacecraft Pose Estimation from Photorealistic Rendering. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Paris, France, 31 May–31 August 2020; pp. 6007–6013. [Google Scholar]
- Sandler, M.; Howard, A.; Zhu, M.; Zhmoginov, A.; Chen, L.-C. MobileNetV2: Inverted Residuals and Linear Bottlenecks. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 4510–4520. [Google Scholar]
- Howard, A.; Sandler, M.; Chu, G.; Chen, L.-C.; Chen, B.; Tan, M.; Wang, W.; Zhu, Y.; Pang, R.; Vasudevan, V.; et al. Searching for MobileNetV3. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 1314–1324. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, D.; Leichner, C.; Delakis, M.; Fornoni, M.; Luo, S.; Yang, F.; Wang, W.; Banbury, C.; Ye, C.; Akin, B.; et al. MobileNetV4—Universal Models for the Mobile Ecosystem. In Proceedings of the ECCV 2024: 18th European Conference, Milan, Italy, 29 September–4 October 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Zhou, X.; Lin, M.; Sun, J. ShuffleNet: An Extremely Efficient Convolutional Neural Network for Mobile Devices. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, N.; Zhang, X.; Zheng, H.-T.; Sun, J. ShuffleNet V2: Practical Guidelines for Efficient CNN Architecture Design. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 116–131. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, M.; Le, Q.V. EfficientNet: Rethinking Model Scaling for Convolutional Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the 36th International Conference on Machine Learning, ICML 2019, Long Beach, CA, USA, 9–15 June 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, M.; Le, Q.V. EfficientNetV2: Smaller Models and Faster Training. In Proceedings of the 38th International Conference on Machine Learning, PMLR 139, Virtual, 18–24 July 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, Z.; Li, X.; Li, M.; Zuo, W.; Shan, S. Shift-Net: Image Inpainting via Deep Feature Rearrangement. In Proceedings of the ECCV 2018: 15th European Conference, Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; Wang, Y.; Xu, C.; Shi, B.; Xu, C.; Tian, Q.; Xu, C. AdderNet: Do We Really Need Multiplications in Deep Learning? arXiv 2021, arXiv:1912.13200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, L.; Polosukhin, I. Attention Is All You Need. arXiv 2023, arXiv:1706.03762. [Google Scholar]
- Chi, L.; Jiang, B.; Mu, Y. Fast Fourier Convolution. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 6–12 December 2020; Curran Associates, Inc.: Red Hook, NY, USA, 2020; Volume 33, pp. 4479–4488. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, Z.; Yang, H.; Fu, J.; Fu, D. Learning Spatiotemporal Frequency-Transformer for Compressed Video Super-Resolution. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision—ECCV 2022, Tel Aviv, Israel, 23–27 October 2022; Avidan, S., Brostow, G., Cissé, M., Farinella, G.M., Hassner, T., Eds.; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 257–273. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, L.; Dong, J.; Ge, J.; Li, M.; Pan, J. Efficient Frequency Domain-Based Transformers for High-Quality Image Deblurring. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 5886–5895. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, M.; Huang, J.; Guo, C.-L.; Li, C. Fourmer: An Efficient Global Modeling Paradigm for Image Restoration. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Honolulu, HI, USA, 23–29 July 2023; pp. 42589–42601. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, H.; Li, Y.; Li, Z.; Yang, R.; Xu, Z.; Dou, J.; Qi, H.; Chen, H. Fourier Convolution Block with global receptive field for MRI reconstruction. Med. Image Anal. 2025, 99, 103349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suvorov, R.; Logacheva, E.; Mashikhin, A.; Remizova, A.; Ashukha, A.; Silvestrov, A.; Kong, N.; Goka, H.; Park, K.; Lempitsky, V. Resolution-Robust Large Mask Inpainting with Fourier Convolutions. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV), Waikoloa, HI, USA, 3–8 January 2022; pp. 3172–3182. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Cheng, Z.; Song, Z.; Tang, C. Multi-Scale Spatial Pyramid Attention Mechanism for Image Recognition: An Effective Approach. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2024, 133, 108261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, N.; Jiang, X.; Zhang, X.; Deng, Y. Efficient Frequency-Domain Image Deraining with Contrastive Regularization. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision—ECCV 2024, Milan, Italy, 29 September–4 October 2024; Leonardis, A., Ricci, E., Roth, S., Russakovsky, O., Sattler, T., Varol, G., Eds.; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2025; Volume 15099, pp. 240–257, ISBN 978-3-031-72939-3. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, J.; Qi, H.; Xiong, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, G.; Hu, H.; Wei, Y. Deformable Convolutional Networks. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Song, Y.; Song, T.; Yang, D.; Ye, Y.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, L. LDConv: Linear Deformable Convolution for Improving Convolutional Neural Networks. Image Vision Comput. 2024, 149, 105190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Kao, S.; He, H.; Zhuo, W.; Wen, S.; Lee, C.-H.; Chan, S.-H.G. Run, Don’t Walk: Chasing Higher FLOPS for Faster Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Chattopadhyay, A.; Sarkar, A.; Howlader, P.; Balasubramanian, V.N. Grad-CAM++: Improved Visual Explanations for Deep Convolutional Networks. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1710.11063. [Google Scholar]
- Selvaraju, R.R.; Cogswell, M.; Das, A.; Vedantam, R.; Parikh, D.; Batra, D. Grad-CAM: Visual Explanations from Deep Networks via Gradient-Based Localization. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 618–626. [Google Scholar]
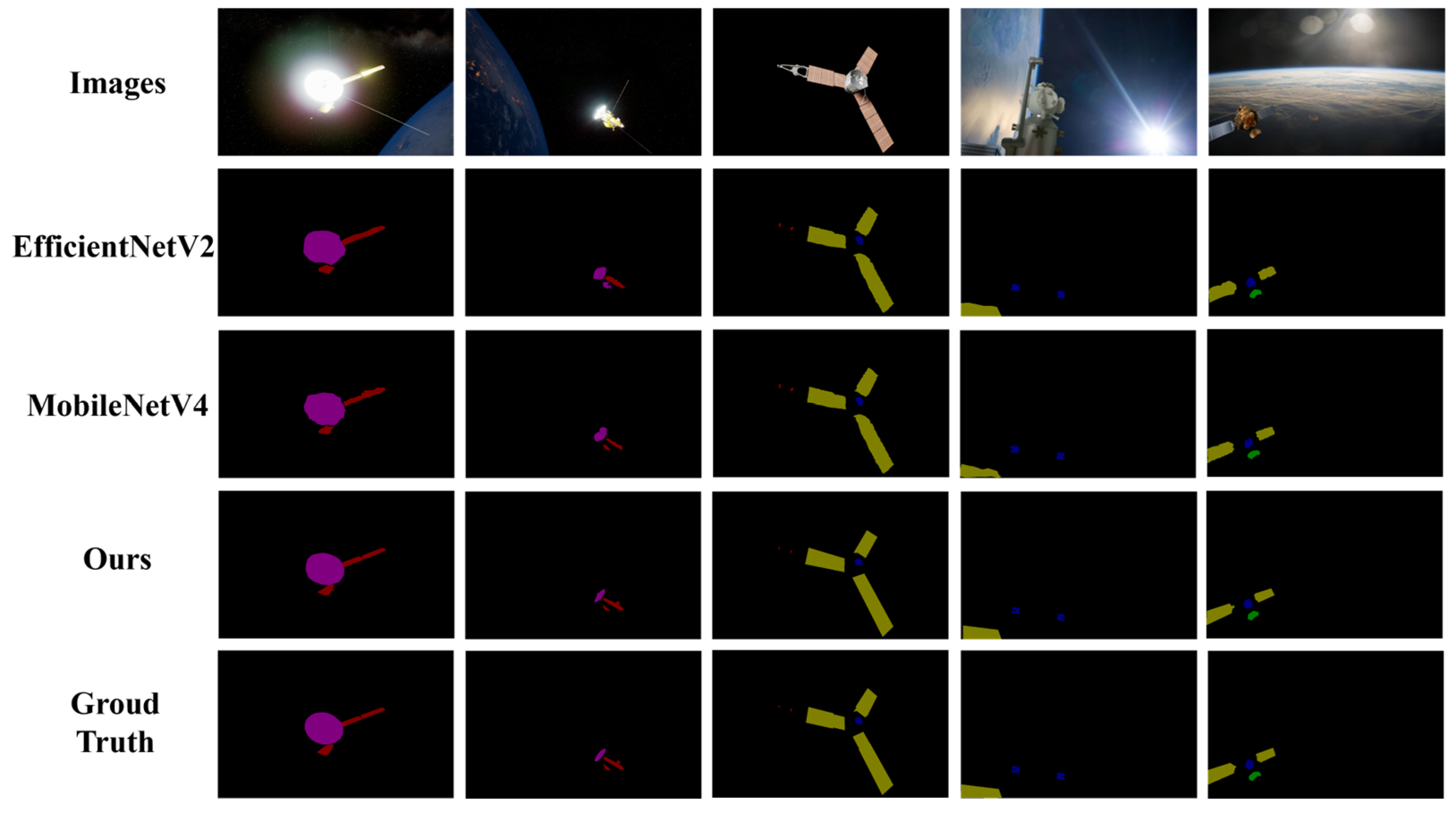

| Configuration Name | Environment Parameters |
|---|---|
| Operating system | Windows 10 |
| CPU | Intel(R) Xeon(R) w5-3425 |
| GPU | 2xNVIDIA GTX 3090 |
| Memory | 128 G |
| Programming language | Python3.9.21 |
| Framework | PyTorch 2.12 + CUDA 11.8 |
| IDE | VSCode |
| Backbone Network | Precision | Recall | mAP | GFLOPs | Parameter |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ShuffleNetv2 | 91.2 | 85.3 | 89.3 | 16.0 | 5.94 M |
| GhostNetv2 | 92.1 | 86.4 | 91.0 | 19.1 | 8.24 M |
| EfficientFormer v2 | 93.7 | 87.4 | 92.7 | 26.0 | 7.42 M |
| MobileViTv3-S | 92.8 | 86.7 | 92.6 | 22.4 | 7.71 M |
| MobileNetv4 | 93.5 | 87.6 | 93.0 | 23.1 | 6.01 M |
| MobileNetV4 | LDConv | MFAC | C3-Faster | Precision | Recall | mAP | GFLOPs | Parameter |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| √ | 91.9 | 79.1 | 91.5 | 18.4 | 5,834,531 | |||
| √ | 93.4 | 85.2 | 92.8 | 22.5 | 5,943,707 | |||
| √ | 94.8 | 83.5 | 93.1 | 25.8 | 6,802,430 | |||
| √ | 93.7 | 87.5 | 92.6 | 23.1 | 6,013,745 | |||
| √ | √ | 94.4 | 85.3 | 93.2 | 20.1 | 5,818,481 | ||
| √ | √ | 94.6 | 87.4 | 92.9 | 20.8 | 4,551,241 | ||
| √ | √ | √ | √ | 95.1 | 88.3 | 93.4 | 19.6 | 4,713,179 |
| - | - | - | - | 93.2 | 84.4 | 92.7 | 26.0 | 7,421,699 |
| Backbone Network | Precision | Recall | mAP | GFLOPs | Parameter |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EfficientNetV2 | 94.3 | 87.7 | 93.2 | 15.1 | 5.72 M |
| MobileNetV4 | 93.0 | 86.8 | 92.4 | 18.3 | 6.34 M |
| Ours | 95.1 | 88.3 | 93.4 | 19.6 | 4.71 M |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yi, W.; Zhang, Z.; Chang, L. M4MLF-YOLO: A Lightweight Semantic Segmentation Framework for Spacecraft Component Recognition. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 3144. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17183144
Yi W, Zhang Z, Chang L. M4MLF-YOLO: A Lightweight Semantic Segmentation Framework for Spacecraft Component Recognition. Remote Sensing. 2025; 17(18):3144. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17183144
Chicago/Turabian StyleYi, Wenxin, Zhang Zhang, and Liang Chang. 2025. "M4MLF-YOLO: A Lightweight Semantic Segmentation Framework for Spacecraft Component Recognition" Remote Sensing 17, no. 18: 3144. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17183144
APA StyleYi, W., Zhang, Z., & Chang, L. (2025). M4MLF-YOLO: A Lightweight Semantic Segmentation Framework for Spacecraft Component Recognition. Remote Sensing, 17(18), 3144. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17183144





