Estimating Methane Emissions by Integrating Satellite Regional Emissions Mapping and Point-Source Observations: Case Study in the Permian Basin
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
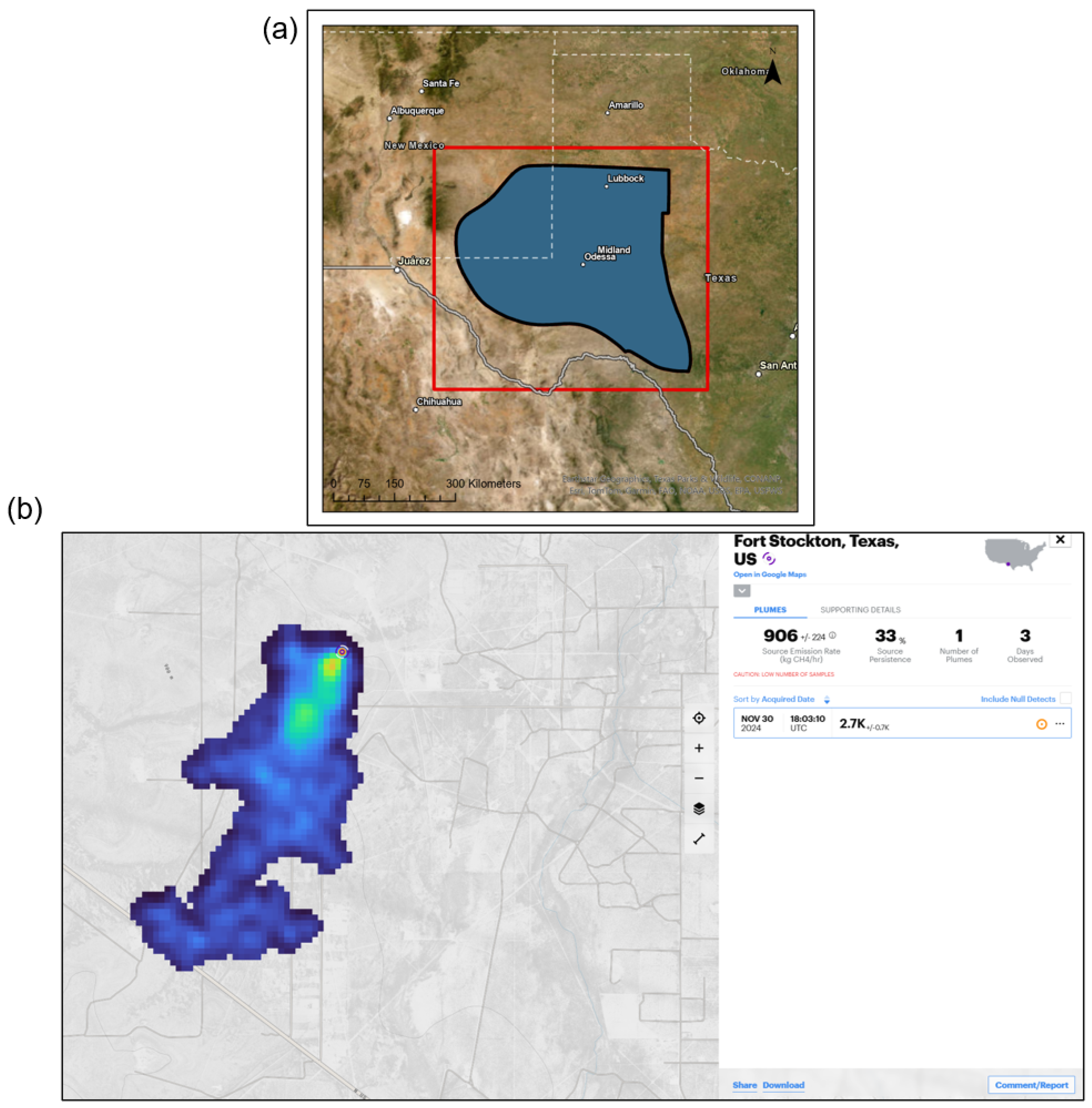
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Regional CH4 Emission Estimate—The Divergence Method
2.2.1. TROPOMI Level 2 Data Product
2.2.2. Reanalysis Data from CAMS EAC4
2.2.3. The Divergence Method
2.3. Event-Based CH4 Emissions Estimate
2.3.1. CH4 Plumes from Carbon Mapper
2.3.2. Event Creation
2.3.3. Calculate Event-Based Emissions
3. Results
3.1. Divergence of CH4 Emissions
3.2. Event-Based CH4 Emissions
4. Discussion
Implications for Emission Reconciliation
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
Root Mean Square Error
Appendix B
| Emission Event Type | Definition | Duration Determination | Emissions Quantity from Events | Uncertainty |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Resolved Event (RE) | Events with durations determined using operational data/log | Extracted from operational data/log | Calculated | Only quantification uncertainty is considered |
| Partially Resolved Event (PRE) | Events with duration that are either measured by remote sensing technologies or estimated using null-detection and rules | Simulated by using proceedings and succeeding null-detection times | Calculated | Quantification uncertainty and duration estimation uncertainty |
| Unresolved Event (UE) | Events that are missing from annual emissions data | Simulated | (1) Simulate emissions that are not detected using POD checks (2) Simulate emissions by random sample RE and PRE | Estimated in the simulations |
| References | Year of Investigation | Emission Rate | Uncertainty | Method | Unit | Doi |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [49] | 2010–2015 | 2.01 | 0.01 | GOSAT inverse flux estimate—derived from [61] | Tg/year | https://doi.org/10.1038/s43247-021-00312-6 |
| [20] | 2018–2019 | 2.68 | 0.5 | TROPOMI inverse flux estimate—O&G production | Tg/year | https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.aaz5120 |
| 2018–2019 | 2.9 | 0.5 | TROPOMI inverse flux estimate—basin total | Tg/year | ||
| [50] | 2018–2020 | 2.9 | 0.4 | TROPOMI inverse flux estimate | Tg/year | https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-22-11203-2022 |
| 2018–2020 | 3.7 | 0.5 | TROPOMI inverse flux estimate with an adjusted prior | Tg/year | ||
| [7] | 2019 | 3.06 | 2.82—3.78 | Divergence method: the continuity equation connecting the divergence (D), emission (E) and sink (S) for steady state. | Tg/year | https://doi.org/10.1029/2021GL094151 |
| [52] | 2018–2019 | 3.18 | 1.13 | Gaussian integral mass balance method—TROPOMI/WFMD v1.2 | Tg/year | https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-20-9169-2020 |
| [53] | 2018–2021 | 4.1 | 1.1 | Automated detection of regions with persistently enhanced methane concentrations (TROPOMI) coupled with mass balance quantification method. | Tg/year | https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-24-10441-2024 |
| [51] | 2018–2020 | 3.7 | 0.9 | Weekly TROPOMI inverse flux estimate | Tg/year | https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-23-7503-2023 |
| [54] | 2022–2023 | 2.69 | 0.86 | Aggregation from GF-4 plume mapping | Tg/year | https://doi.org/10.1029/2024JD040870 |
| [55] | 2021 | 335 (2.9) | 274–428 (2.4–3.7) | Measurement-based methane emissions inventory (EI-ME) | t/h (Tg/year) | https://doi.org/10.5194/essd-16-3973-2024 |
References
- Jacob, D.J.; Varon, D.J.; Cusworth, D.H.; Dennison, P.E.; Frankenberg, C.; Gautam, R.; Guanter, L.; Kelley, J.; McKeever, J.; Ott, L.E.; et al. Quantifying methane emissions from the global scale down to point sources using satellite observations of atmospheric methane. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2022, 22, 9617–9646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, H.; Neethirajan, S. Satellite data and machine learning for benchmarking methane concentrations in the Canadian dairy industry. Sustainability 2024, 16, 10400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Jacob, D.; Gautam, R.; Omara, M.; Stavins, R.N.; Stowe, R.C.; Nesser, H.; Sulprizio, M.P.; Lorente, A.; Varon, D.J.; et al. Satellite quantification of methane emissions and oil–gas methane intensities from individual countries in the Middle East and North Africa: Implications for climate action. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2023, 23, 5945–5967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cusworth, D.H.; Duren, R.M.; Ayasse, A.K.; Jiorle, R.; Howell, K.; Aubrey, A.; Green, R.O.; Eastwood, M.L.; Chapman, J.W.; Thorpe, A.K.; et al. Quantifying methane emissions from United States landfills. Science 2024, 383, 1499–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irakulis-Loitxate, I.; Guanter, L.; Liu, Y.-N.; Varon, D.J.; Maasakkers, J.D.; Zhang, Y.; Chulakadabba, A.; Wofsy, S.C.; Thorpe, A.K.; Duren, R.M.; et al. Satellite-based survey of extreme methane emissions in the Permian Basin. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabf4507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irakulis-Loitxate, I.; Guanter, L.; Maasakkers, J.D.; Zavala-Araiza, D.; Aben, I. Satellites detect abatable super-emissions in one of the world’s largest methane hotspot regions. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 2143–2152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; van der A, R.; van Weele, M.; Eskes, H.; Lu, X.; Veefkind, P.; de Laat, J.; Kong, H.; Wang, J.; Sun, J.; et al. A new divergence method to quantify methane emissions using observations of Sentinel-5P TROPOMI. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2021, 48, e2021GL094151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maasakkers, J.D.; Varon, D.J.; Elfarsdóttir, A.; McKeever, J.; Jervis, D.; Mahapatra, G.; Pandey, S.; Lorente, A.; Borsdorff, T.; Foorthuis, L.R.; et al. Using satellites to uncover large methane emissions from landfills. Sci. Adv. 2022, 8, eabn9683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacLean, J.-P.W.; Girard, M.; Jervis, D.; Marshall, D.; McKeever, J.; Ramier, A.; Strupler, M.; Tarrant, E.; Young, D. Offshore methane detection and quantification from space using sun glint measurements with the GHGSat constellation. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2024, 17, 863–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorpe, A.K.; Green, R.O.; Thompson, D.R.; Brodrick, P.G.; Chapman, J.W.; Elder, C.D.; Irakulis-Loitxate, I.; Cusworth, D.H.; Ayasse, A.K.; Duren, R.M.; et al. Attribution of individual methane and carbon dioxide emission sources using EMIT observations from space. Sci. Adv. 2023, 9, eadh2391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dogniaux, M.; Maasakkers, J.D.; Varon, D.J.; Aben, I. Report on Landsat 8 and Sentinel-2B observations of the Nord Stream 2 pipeline methane leak. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2024, 17, 2777–2787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, S.; Gautam, R.; Houweling, S.; van der Gon, H.D.; Sadavarte, P.; Borsdorff, T.; Hasekamp, O.; Landgraf, J.; Tol, P.; van Kempen, T.; et al. Satellite observations reveal extreme methane leakage from a natural gas well blowout. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 26376–26381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherwin, E.D.; Rutherford, J.S.; Chen, Y.; Aminfard, S.; Kort, E.A.; Jackson, R.B.; Brandt, A.R. Single-blind validation of space-based point-source detection and quantification of onshore methane emissions. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 3836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hancock, S.E.; Jacob, D.J.; Chen, Z.; Nesser, H.; Davitt, A.; Varon, D.J.; Sulprizio, M.P.; Balasus, N.; Estrada, L.A.; Cazorla, M.; et al. Satellite quantification of methane emissions from South American countries: A high-resolution inversion of TROPOMI and GOSAT observations. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2025, 25, 797–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Wang, C.; Gao, P.; Zhao, B.; Jin, C.; Zhao, L.; He, B.; Xue, Y. High-spatial-resolution methane emissions calculation using TROPOMI data by a divergence method. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; van der A, R.; van Weele, M.; Bryan, L.; Eskes, H.; Veefkind, P.; Liu, Y.; Lin, X.; de Laat, J.; Ding, J. Current potential of CH4 emission estimates using TROPOMI in the Middle East. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2024, 17, 5261–5277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maasakkers, J.D.; Jacob, D.J.; Sulprizio, M.P.; Scarpelli, T.R.; Nesser, H.; Sheng, J.-X.; Zhang, Y.; Hersher, M.; Bloom, A.A.; Bowman, K.W.; et al. Global distribution of methane emissions, emission trends, and OH concentrations and trends inferred from an inversion of GOSAT satellite data for 2010–2015. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 7859–7881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Z.; Jacob, D.J.; Shen, L.; Lu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Scarpelli, T.R.; Nesser, H.; Sulprizio, M.P.; Maasakkers, J.D.; Bloom, A.A.; et al. Global distribution of methane emissions: A comparative inverse analysis of observations from the TROPOMI and GOSAT satellite instruments. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2021, 21, 14159–14175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wecht, K.J.; Jacob, D.J.; Frankenberg, C.; Jiang, Z.; Blake, D.R. Mapping of North American methane emissions with high spatial resolution by inversion of SCIAMACHY satellite data. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2014, 119, 7741–7756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Gautam, R.; Pandey, S.; Omara, M.; Maasakkers, J.D.; Sadavarte, P.; Lyon, D.; Nesser, H.; Sulprizio, M.P.; Varon, D.J.; et al. Quantifying methane emissions from the largest oil-producing basin in the United States from space. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaaz5120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EDF. Environmental Defense Fund—MethaneSAT. Google Earth Engine Data Catalog. 2024. Available online: https://developers.google.com/earth-engine/datasets/publisher/edf-methanesat-ee (accessed on 23 May 2025).
- South, D.W. Methane emissions, nowhere to hide from detection and compliance monitoring with newly launched satellite. Clim. Energy 2024, 40, 28–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Foy, B.; Schauer, J.J.; Lorente, A.; Borsdorff, T. Investigating high methane emissions from urban areas detected by TROPOMI and their association with untreated wastewater. Environ. Res. Lett. 2023, 18, 044004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauvaux, T.; Giron, C.; Mazzolini, M.; d’Aspremont, A.; Duren, R.; Cusworth, D.; Shindell, D.; Ciais, P. Global assessment of oil and gas methane ultra-emitters. Science 2022, 375, 557–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuit, B.J.; Maasakkers, J.D.; Mahapatra, G.; Pandey, S.; Lorente, A.; Borsdorff, T.; Houweling, S.; Varon, D.J.; McKeever, J.; Jervis, D.; et al. Automated detection and monitoring of methane super-emitters using satellite data. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2023, 23, 9071–9098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Z.; Barchyn, T.E.; Vollrath, C.; Gao, M.; Hugenholtz, C. Satellite-derived estimate of city-level methane emissions from Calgary, Alberta, Canada. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, L.; Cooper, J.; Hawkes, A. Minimum detection limits of the TROPOMI satellite sensor across North America and their implications for measuring oil and gas methane emissions. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 872, 162222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finman, L. Satellites are no silver bullet for methane monitoring. Nature 2024, 636, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, M.; Xing, Z.; Vollrath, C.; Hugenholtz, C.H.; Barchyn, T.E. Global observational coverage of onshore oil and gas methane sources with TROPOMI. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 16759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buchwitz, M.; Schneising, O.; Reuter, M.; Heymann, J.; Krautwurst, S.; Bovensmann, H.; Burrows, J.P.; Boesch, H.; Parker, R.J.; Somkuti, P.; et al. Satellite-derived methane hotspot emission estimates using a fast data-driven method. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 5751–5774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joyce, P.; Villena, C.R.; Huang, Y.; Webb, A.; Gloor, M.; Wagner, F.H.; Chipperfield, M.P.; Guilló, R.B.; Wilson, C.; Boesch, H. Using a deep neural network to detect methane point sources and quantify emissions from PRISMA hyperspectral satellite images. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2023, 16, 2627–2640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estrada, L.A.; Varon, D.J.; Sulprizio, M.; Nesser, H.; Chen, Z.; Balasus, N.; Hancock, S.E.; He, M.; East, J.D.; Mooring, T.A.; et al. Integrated Methane Inversion (IMI) 2.0: An improved research and stakeholder tool for monitoring total methane emissions with high resolution worldwide using TROPOMI satellite observations. Geosci. Model Dev. 2025, 18, 3311–3330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varon, D.J.; Jacob, D.J.; Sulprizio, M.; Estrada, L.A.; Downs, W.B.; Shen, L.; Hancock, S.E.; Nesser, H.; Qu, Z.; Penn, E.; et al. Integrated Methane Inversion (IMI 1.0): A user-friendly, cloud-based facility for inferring high-resolution methane emissions from TROPOMI satellite observations. Geosci. Model Dev. 2022, 15, 5787–5805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaughn, T.L.; Bell, C.S.; Pickering, C.K.; Schwietzke, S.; Heath, G.A.; Pétron, G.; Zimmerle, D.J.; Schnell, R.C.; Nummedal, D. Temporal variability largely explains top-down/bottom-up difference in methane emission estimates from a natural gas production region. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 11712–11717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zavala-Araiza, D.; Lyon, D.R.; Alvarez, R.A.; Davis, K.J.; Harriss, R.; Herndon, S.C.; Karion, A.; Kort, E.A.; Lamb, B.K.; Lan, X.; et al. Reconciling divergent estimates of oil and gas methane emissions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 15597–15602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Saunois, M.; Bousquet, P.; Lin, X.; Hegglin, M.I.; Canadell, J.G.; Jackson, R.B.; Zheng, B. Reconciling the bottom-up and top-down estimates of the methane chemical sink using multiple observations. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2023, 23, 789–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.; Ashena, Z.; Liang, S.H.; Kiaei, S.; Saeedi, S. An event-based framework for estimating annual methane emissions and managing emissions data from oil and gas facilities. EarthArXiv 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarpelli, T.R.; Roy, E.; Jacob, D.J.; Sulprizio, M.P.; Tate, R.D.; Cusworth, D.H. Using new geospatial data and 2020 fossil fuel methane emissions for the Global Fuel Exploitation Inventory (GFEI) v3. Earth Syst. Sci. Data Discuss. 2025, 2025, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EIA. Drilling Productivity Report; U.S. Energy Information Administration: Washington, DC, USA, 2024. Available online: https://www.eia.gov/petroleum/drilling/archive/2024/05/pdf/dpr-full.pdf (accessed on 3 April 2025).
- Hu, H.; Hasekamp, O.; Butz, A.; Galli, A.; Landgraf, J.; Aan de Brugh, J.; Borsdorff, T.; Scheepmaker, R.; Aben, I. The operational methane retrieval algorithm for TROPOMI. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2016, 9, 5423–5440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorente, A.; Borsdorff, T.; Butz, A.; Hasekamp, O.; aan de Brugh, J.; Schneider, A.; Wu, L.; Hase, F.; Kivi, R.; Wunch, D.; et al. Methane retrieved from TROPOMI: Improvement of the data product and validation of the first 2 years of measurements. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2021, 14, 665–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inness, A.; Ades, M.; Agustí-Panareda, A.; Barré, J.; Benedictow, A.; Blechschmidt, A.-M.; Dominguez, J.J.; Engelen, R.; Eskes, H.; Flemming, J.; et al. The CAMS reanalysis of atmospheric composition. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 3515–3556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirkland, E.J. Bilinear interpolation. In Advanced Computing in Electron Microscopy; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2010; pp. 261–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, C.; IJzermans, R.; Randell, D.; Jones, M.; Jonathan, P.; Mandel, K.; Hirst, B.; Shorttle, O. Avoiding methane emission rate underestimates when using the divergence method. Environ. Res. Lett. 2023, 18, 114033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duren, R.; Cusworth, D.; Ayasse, A.; Howell, K.; Diamond, A.; Scarpelli, T.; Kim, J.; O’Neill, K.; Lai-Norling, J.; Thorpe, A.; et al. The Carbon Mapper emissions monitoring system. EGUsphere 2025, 2025, 1–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbon Mapper. Product Guide: Data Definition & Specification; Carbon Mapper: Pasadena, CA, USA, 2025; Available online: https://carbonmapper.org/articles/product-guide (accessed on 14 April 2025).
- Allen, J.F. Maintaining knowledge about temporal intervals. Commun. ACM 1983, 26, 832–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bureau of Economic Geology. Permian Basin GIS Projects and Databases; University of Texas at Austin: Austin, TX, USA, 2024; Available online: https://www.beg.utexas.edu/resprog/permianbasin/gis.htm (accessed on 3 April 2025).
- Cusworth, D.H.; Bloom, A.A.; Ma, S.; Miller, C.E.; Bowman, K.; Yin, Y.; Maasakkers, J.D.; Zhang, Y.; Scarpelli, T.R.; Qu, Z.; et al. A Bayesian framework for deriving sector-based methane emissions from top-down fluxes. Commun. Earth Environ. 2021, 2, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.; Gautam, R.; Omara, M.; Zavala-Araiza, D.; Maasakkers, J.D.; Scarpelli, T.R.; Lorente, A.; Lyon, D.; Sheng, J.; Varon, D.J.; et al. Satellite quantification of oil and natural gas methane emissions in the US and Canada including contributions from individual basins. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2022, 22, 11203–11215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varon, D.J.; Jacob, D.J.; Hmiel, B.; Gautam, R.; Lyon, D.R.; Omara, M.; Sulprizio, M.; Shen, L.; Pendergrass, D.; Nesser, H.; et al. Continuous weekly monitoring of methane emissions from the Permian Basin by inversion of TROPOMI satellite observations. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2023, 23, 7503–7520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneising, O.; Buchwitz, M.; Reuter, M.; Vanselow, S.; Bovensmann, H.; Burrows, J.P. Remote sensing of methane leakage from natural gas and petroleum systems revisited. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 9169–9182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanselow, S.; Schneising, O.; Buchwitz, M.; Reuter, M.; Bovensmann, H.; Boesch, H.; Burrows, J.P. Automated detection of regions with persistently enhanced methane concentrations using Sentinel-5 Precursor satellite data. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2024, 24, 10441–10473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Bai, S.; Lin, K.; Feng, C.; Sun, S.; Zhao, S.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, W.; Zhou, C.; Zhang, Y. Satellite-based surveys reveal substantial methane point-source emissions in major oil & gas basins of North America during 2022–2023. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2024, 129, e2024JD040870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omara, M.; Himmelberger, A.; MacKay, K.; Williams, J.P.; Benmergui, J.; Sargent, M.; Wofsy, S.C.; Gautam, R. Constructing a measurement-based spatially explicit inventory of US oil and gas methane emissions (2021). Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2024, 16, 3973–3991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherwin, E.; Kruguer, J.; Wetherley, E.B.; Yakovlev, P.V.; Brandt, A.; Deiker, S.; Berman, E.S.F.; Biraud, S. Comprehensive aerial surveys find a reduction in Permian Basin methane intensity from 2020–2023. SSRN Prepr. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leblanc, R. Cleaning Up: Overflight Data Show Permian Methane Emissions Intensity down Further 28% in 2024. S&P Global Commodity Insights. 2025. Available online: https://view.highspot.com/viewer/992ecc322aa7c4d80d5f6b15a4a0f2c4#1 (accessed on 15 August 2025).
- Koene, E.F.M.; Brunner, D.; Kuhlmann, G. On the theory of the divergence method for quantifying source emissions from satellite observations. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2024, 129, e2023JD039904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beirle, S.; Borger, C.; Dörner, S.; Li, A.; Hu, Z.; Liu, F.; Wang, Y.; Wagner, T. Pinpointing nitrogen oxide emissions from space. Sci. Adv. 2019, 5, eaax9800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ECMWF. L60 Model Level Definitions—User Documentation. ECMWF Confluence Wiki. 2024. Available online: https://confluence.ecmwf.int/display/UDOC/L60+model+level+definitions (accessed on 28 May 2025).
- Maasakkers, J.D.; Jacob, D.J.; Sulprizio, M.P.; Scarpelli, T.R.; Nesser, H.; Sheng, J.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, X.; Bloom, A.A.; Bowman, K.W.; et al. 2010–2015 North American methane emissions, sectoral contributions, and trends: A high-resolution inversion of GOSAT satellite observations of atmospheric methane. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2021, 21, 4339–4356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, M.; Xing, Z. Estimating Methane Emissions by Integrating Satellite Regional Emissions Mapping and Point-Source Observations: Case Study in the Permian Basin. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 3143. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17183143
Gao M, Xing Z. Estimating Methane Emissions by Integrating Satellite Regional Emissions Mapping and Point-Source Observations: Case Study in the Permian Basin. Remote Sensing. 2025; 17(18):3143. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17183143
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Mozhou, and Zhenyu Xing. 2025. "Estimating Methane Emissions by Integrating Satellite Regional Emissions Mapping and Point-Source Observations: Case Study in the Permian Basin" Remote Sensing 17, no. 18: 3143. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17183143
APA StyleGao, M., & Xing, Z. (2025). Estimating Methane Emissions by Integrating Satellite Regional Emissions Mapping and Point-Source Observations: Case Study in the Permian Basin. Remote Sensing, 17(18), 3143. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17183143







