Dynamic Monitoring of Soil Salinization in Oasis Regions Using Spatiotemporal Fusion Algorithms
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- To explore whether images generated through spatiotemporal fusion can be applied to soil salinization inversion modeling in arid zone oases.
- (2)
- To determine which fusion strategy is more effective for different vegetation and salinity indices.
- (3)
- To assess whether spatiotemporal fusion-based modeling strategies can improve the accuracy of traditional soil salinization inversion models.
2. Materials and Methods
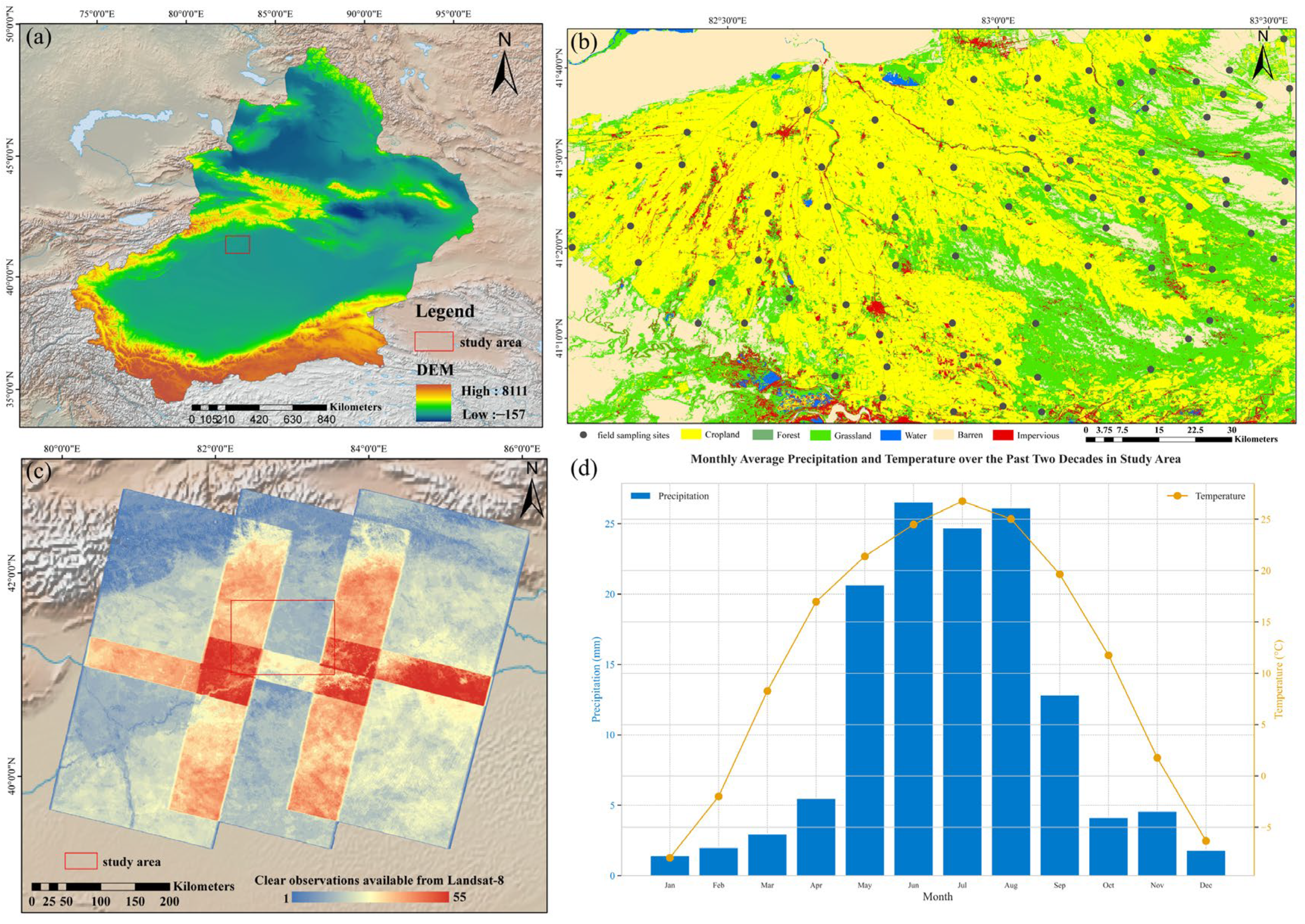
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Collection of Field Data
2.3. Acquisition and Preprocessing of Remote-Sensing Images
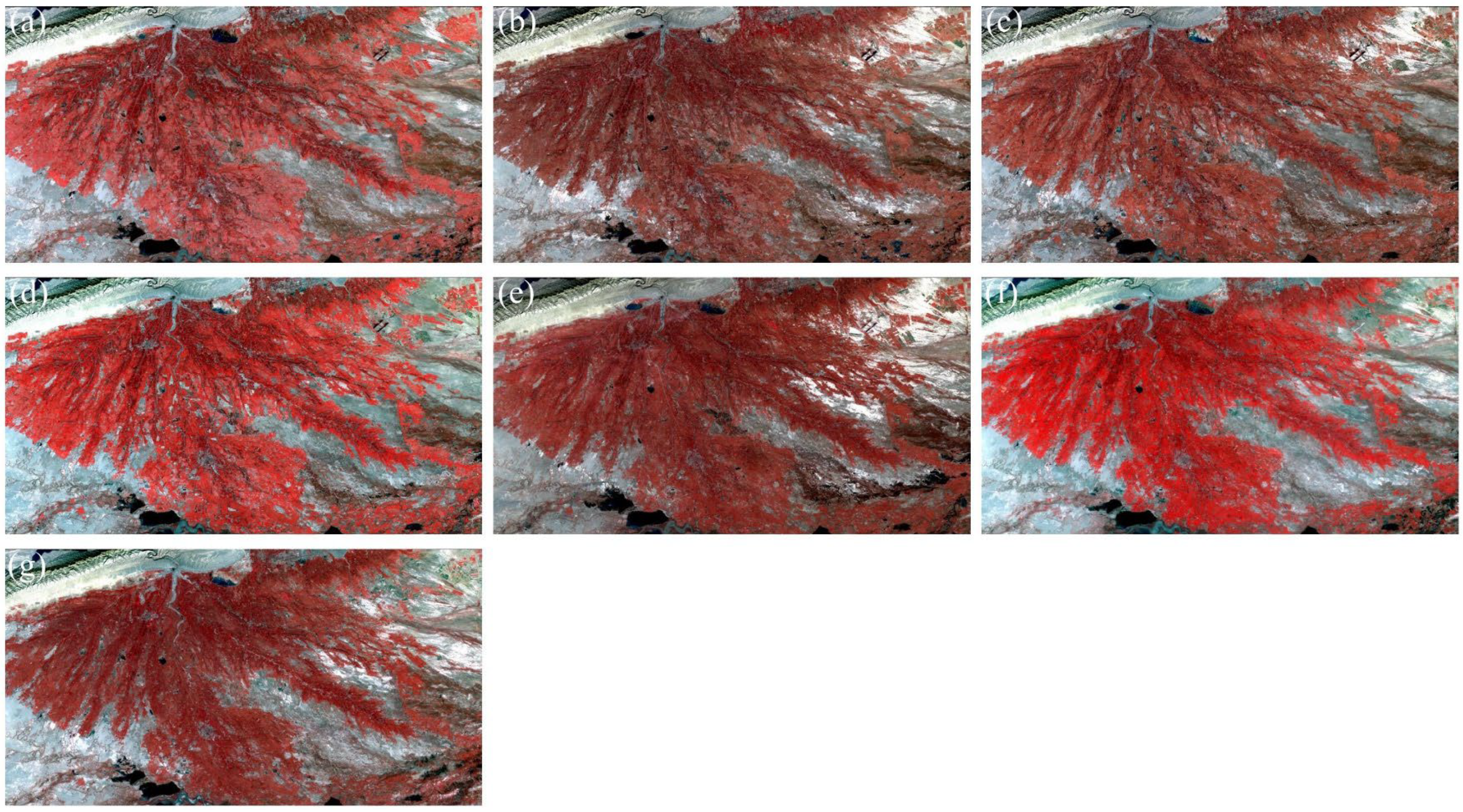
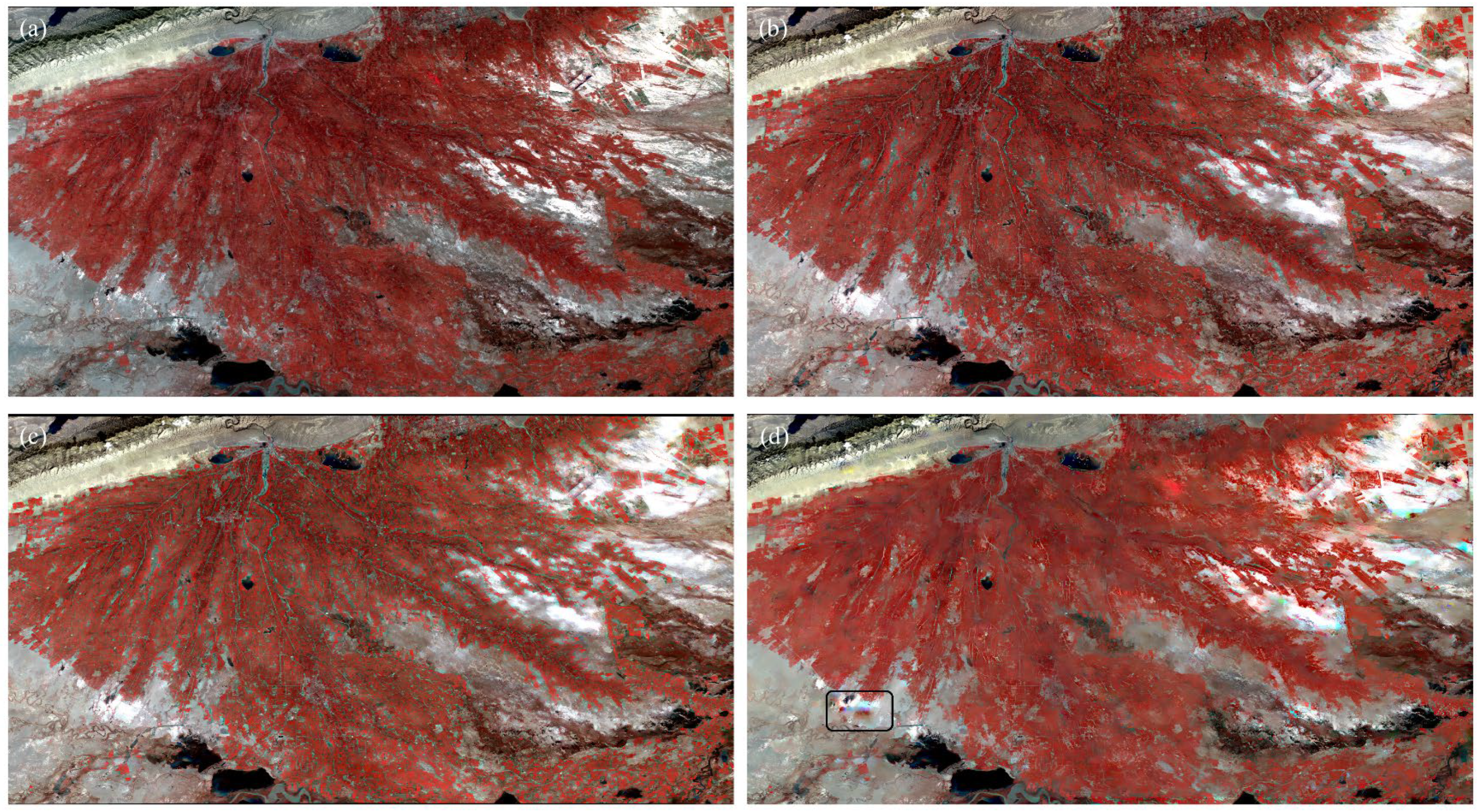
2.4. Spatiotemporal Fusion Methods, Strategies, and Accuracy Assessment
2.5. Soil Salinization Inversion Model and Accuracy Assessment
2.6. Composition of Multi-Temporal Remote-Sensing Images
3. Results
3.1. Statistical Description of Soil Samples
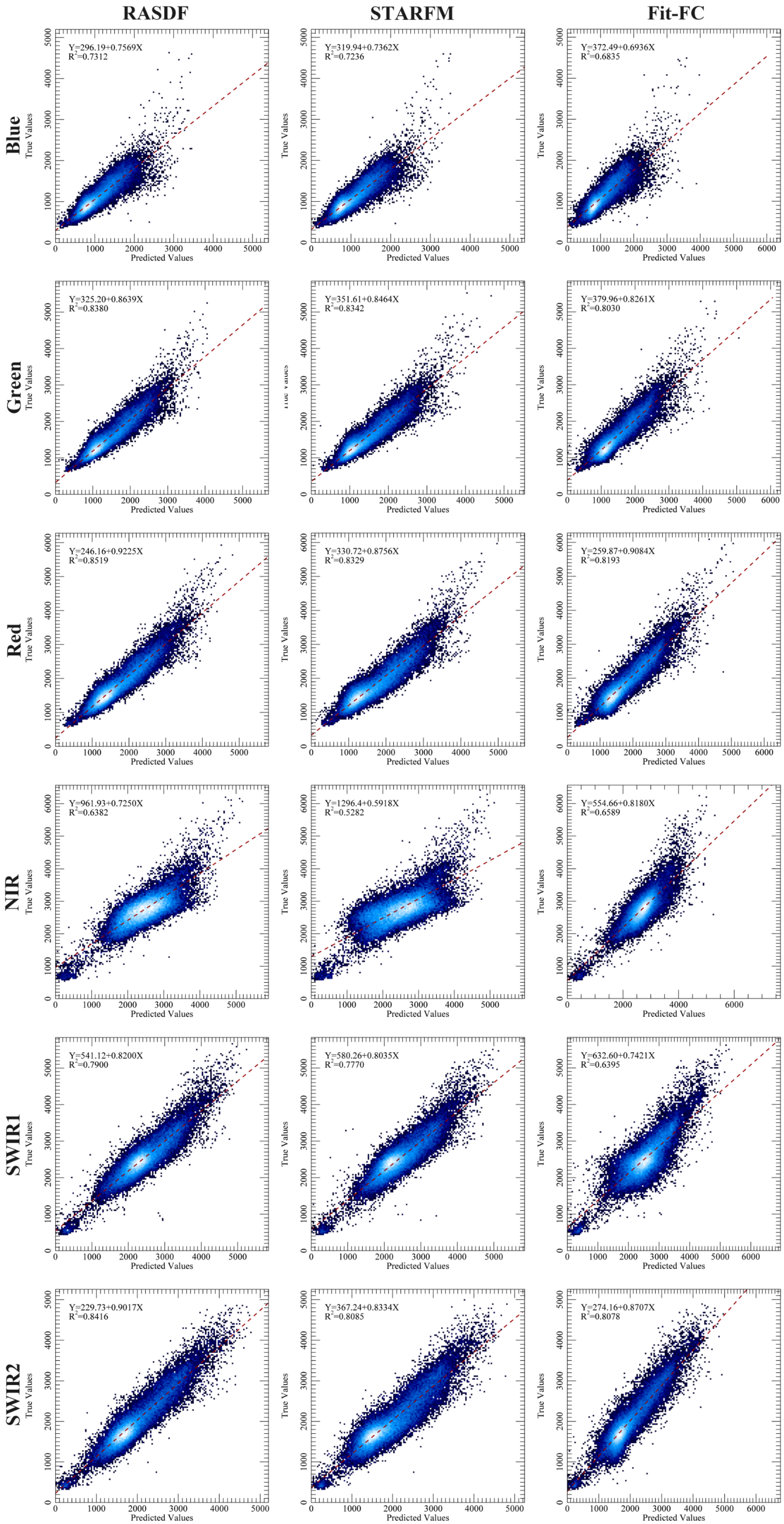
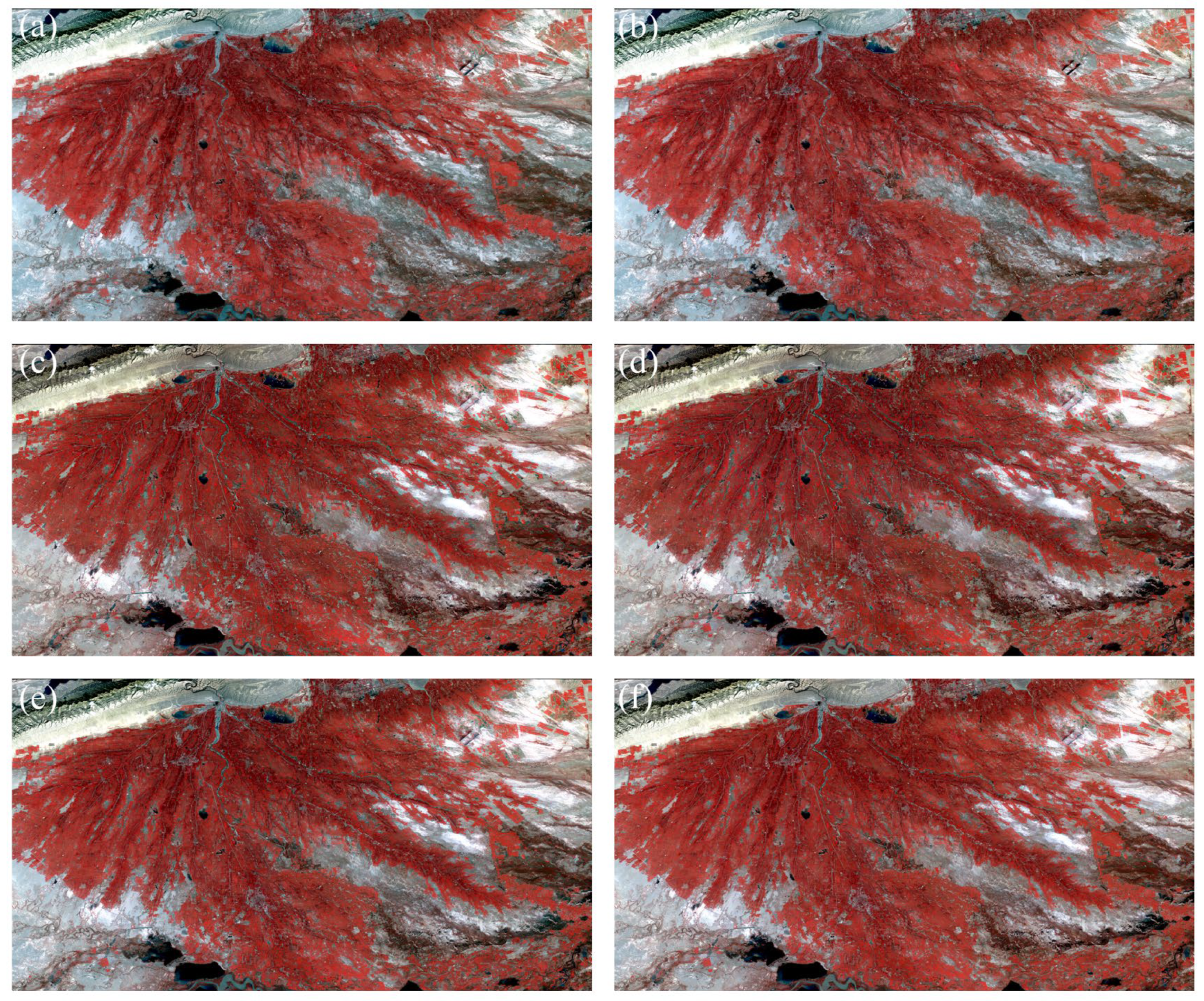
3.2. Comparison of Spatiotemporal Fusion Methods
3.3. Selection of Fusion Strategies
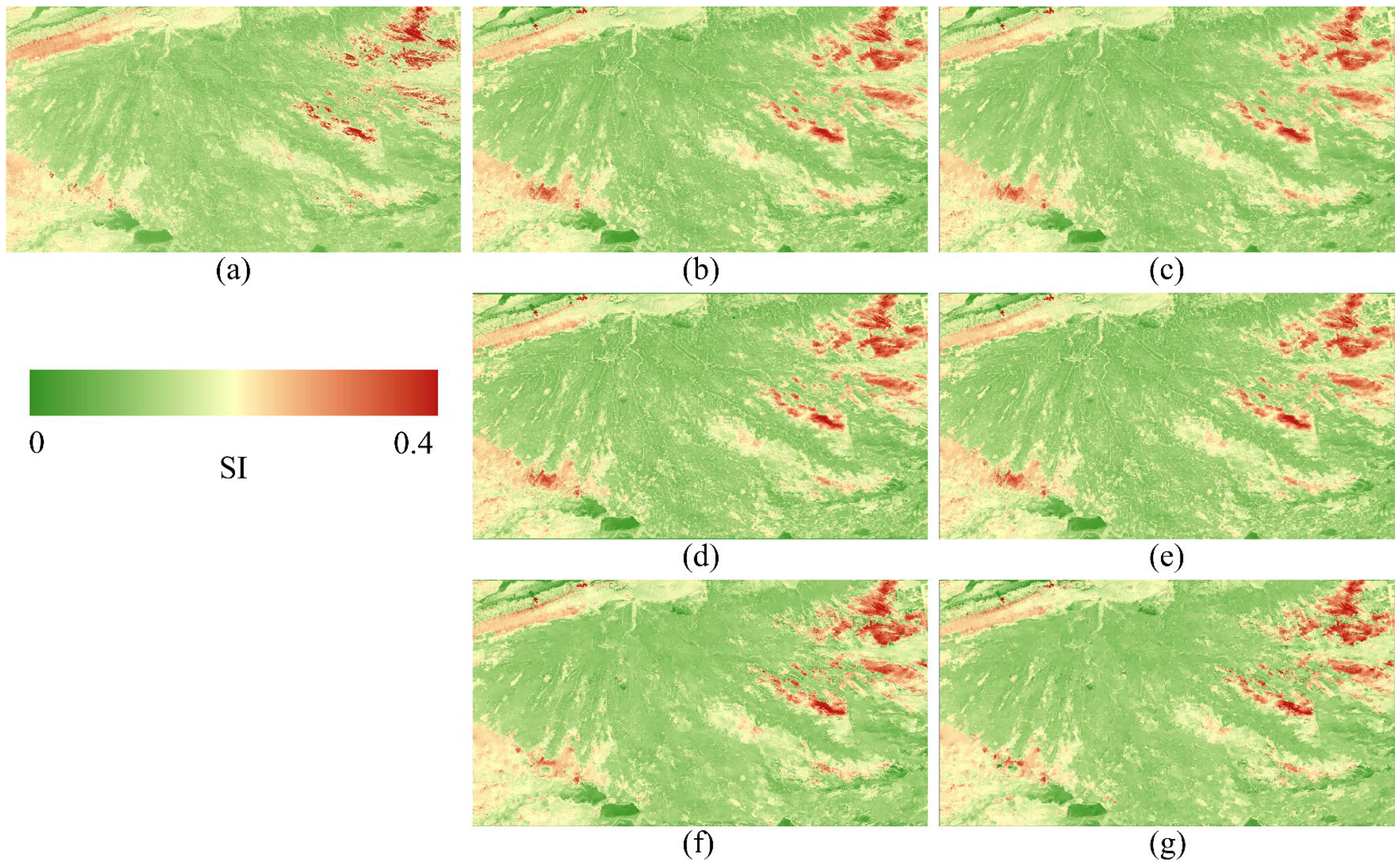
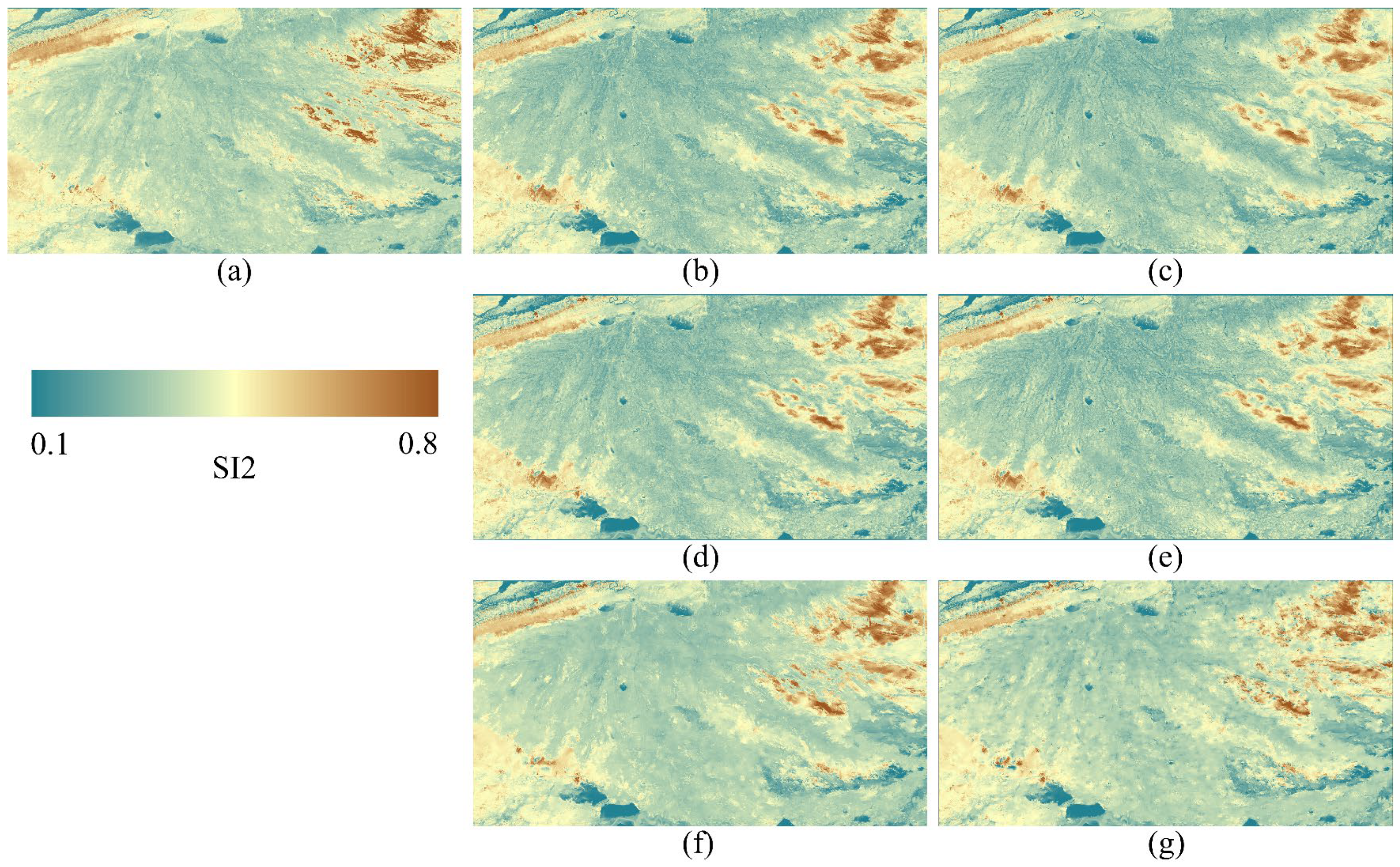
3.4. Applicability of Spatiotemporal Fusion Images
3.5. Comparison of Modeling Results for Multi-Temporal Composite Images
4. Discussion
4.1. Simulated Image Experiments
4.2. Incorporating Auxiliary Datasets and Variables
- (1)
- When additional high-resolution images are input as auxiliary datasets, the temporal proximity of the images leads to high sample correlation (strong autocorrelation), causing the model to learn more noise than useful features during training, thus reducing its generalization ability. Additionally, errors or inconsistencies introduced during the spatiotemporal fusion process may accumulate, affecting the model’s performance.
- (2)
- When used as auxiliary features, the new features may have high redundancy with the existing ones, offering little additional useful information and increasing model complexity, which leads to more noise during training. Furthermore, the increase in feature numbers introduces high-dimensional data issues, especially when the sample size remains unchanged, making it difficult for the model to capture the underlying structure and reducing predictive performance.
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hassani, A.; Azapagic, A.; Shokri, N. Predicting Long-Term Dynamics of Soil Salinity and Sodicity on a Global Scale. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 33017–33027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassani, A.; Azapagic, A.; Shokri, N. Global Predictions of Primary Soil Salinization under Changing Climate in the 21st Century. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 6663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vincent, F.; Maertens, M.; Bechtold, M.; Jobbágy, E.; Reichle, R.H.; Vanacker, V.; Vrugt, J.A.; Wigneron, J.-P.; De Lannoy, G.J.M. L-Band Microwave Satellite Data and Model Simulations over the Dry Chaco to Estimate Soil Moisture, Soil Temperature, Vegetation, and Soil Salinity. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2022, 15, 6598–6614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewitte, O.; Jones, A.; Elbelrhiti, H.; Horion, S.; Montanarella, L. Satellite Remote Sensing for Soil Mapping in Africa: An Overview. Prog. Phys. Geogr. Earth Environ. 2012, 36, 514–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khosravichenar, A.; Aalijahan, M.; Moaazeni, S.; Lupo, A.R.; Karimi, A.; Ulrich, M.; Parvian, N.; Sadeghi, A.; von Suchodoletz, H. Assessing a Multi-Method Approach for Dryland Soil Salinization with Respect to Climate Change and Global Warming—The Example of the Bajestan Region (NE Iran). Ecol. Indic. 2023, 154, 110639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Hu, P.; Zheng, H.; Bai, J.; Liu, Y.; Hellwich, O.; Liu, T.; Chen, X.; Bao, A. An Automated Framework for Interaction Analysis of Driving Factors on Soil Salinization in Central Asia and Western China. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tweed, S.; Grace, M.; Leblanc, M.; Cartwright, I.; Smithyman, D. The Individual Response of Saline Lakes to a Severe Drought. Sci. Total Environ. 2011, 409, 3919–3933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Biswas, A.; Jiang, Q.; Zhao, R.; Hu, J.; Hu, B.; Shi, Z. Estimating Soil Salinity from Remote Sensing and Terrain Data in Southern Xinjiang Province, China. Geoderma 2019, 337, 1309–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A. Soil Salinization Management for Sustainable Development: A Review. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 277, 111383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Gaurav, K. Deep Learning and Data Fusion to Estimate Surface Soil Moisture from Multi-Sensor Satellite Images. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 2251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Z.; Chen, J.; Chen, Y.; Qiu, Y.; Zhu, X.; Chen, X. Agri-Fuse: A Novel Spatiotemporal Fusion Method Designed for Agricultural Scenarios with Diverse Phenological Changes. Remote Sens. Environ. 2023, 299, 113874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Y.; Van Niel, T.G.; McVicar, T.R. Reconstructing Cloud-Contaminated NDVI Images with SAR-Optical Fusion Using Spatio-Temporal Partitioning and Multiple Linear Regression. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2023, 198, 115–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Tang, Y.; Tong, X.; Atkinson, P.M. Filling Gaps in Cloudy Landsat LST Product by Spatial-Temporal Fusion of Multi-Scale Data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2024, 306, 114142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Ye, D.; Xu, H.; Bruzzone, L. OBSUM: An Object-Based Spatial Unmixing Model for Spatiotemporal Fusion of Remote Sensing Images. Remote Sens. Environ. 2024, 304, 114046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, S.; Sun, W.; Guo, B.; Li, X.; Zhang, J.; Xu, C.; Li, X.; Shao, Y.; Li, C. RFSDAF: A New Spatiotemporal Fusion Method Robust to Registration Errors. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Aggarwal, A.K.; Duc, N.H.; Arya, A.; Rage, U.K.; Avtar, R. A Review of Remote Sensing Image Spatiotemporal Fusion: Challenges, Applications and Recent Trends. Remote Sens. Appl. Soc. Environ. 2023, 32, 101005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Zhan, W.; Zhou, J.; Chen, X.; Liang, Z.; Xu, S.; Chen, J. A Novel Framework to Assess All-Round Performances of Spatiotemporal Fusion Models. REMOTE Sens. Environ. 2022, 274, 113002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Cai, F.; Tian, J.; Williams, T.K.-A. Spatiotemporal Fusion of Multisource Remote Sensing Data: Literature Survey, Taxonomy, Principles, Applications, and Future Directions. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Huang, B.; Xu, B. Multi-Source Remotely Sensed Data Fusion for Improving Land Cover Classification. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2017, 124, 27–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Ling, F.; Foody, G.M.; Ge, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Du, Y. Generating a Series of Fine Spatial and Temporal Resolution Land Cover Maps by Fusing Coarse Spatial Resolution Remotely Sensed Images and Fine Spatial Resolution Land Cover Maps. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 196, 293–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, D.; Shi, W.; Hao, M.; Zhu, X. FSDAF 2.0: Improving the Performance of Retrieving Land Cover Changes and Preserving Spatial Details. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 248, 111973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Gao, W.; Jia, J.; Tao, S.; Ren, Y. Developing and Evaluating the Feasibility of a New Spatiotemporal Fusion Framework to Improve Remote Sensing Reflectance and Dynamic LAI Monitoring. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2022, 198, 107037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Yang, W.; Zhu, X.; Chen, J.; Chen, X.; Yang, L.; Helmer, E.H. An Improved Flexible Spatiotemporal DAta Fusion (IFSDAF) Method for Producing High Spatiotemporal Resolution Normalized Difference Vegetation Index Time Series. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 227, 74–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abowarda, A.S.; Bai, L.; Zhang, C.; Long, D.; Li, X.; Huang, Q.; Sun, Z. Generating Surface Soil Moisture at 30 m Spatial Resolution Using Both Data Fusion and Machine Learning toward Better Water Resources Management at the Field Scale. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 255, 112301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Peng, J.; Xue, J.; Zhang, X.; Huang, J.; Biswas, A.; He, Y.; Shi, Z. A Framework for Determining the Total Salt Content of Soil Profiles Using Time-Series Sentinel-2 Images and a Random Forest-Temporal Convolution Network. Geoderma 2022, 409, 115656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Renzullo, L.J.; McVicar, T.R.; Malone, B.P.; Tian, S. Generating Daily 100 m Resolution Land Surface Temperature Estimates Continentally Using an Unbiased Spatiotemporal Fusion Approach. Remote Sens. Environ. 2023, 297, 113784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Ding, J.; Ge, X.; He, B.; Wang, J.; Xie, B.; Zhang, Z. Using Spatiotemporal Fusion Algorithms to Fill in Potentially Absent Satellite Images for Calculating Soil Salinity: A Feasibility Study. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2022, 111, 102839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Yu, D. Monitoring and Evaluating Spatial Variability of Soil Salinity in Dry and Wet Seasons in the Werigan–Kuqa Oasis, China, Using Remote Sensing and Electromagnetic Induction Instruments. Geoderma 2014, 235–236, 316–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Li, M.; Wang, H.; Jiang, P.; Luo, K. Zoning Management Framework for Comprehensive Land Consolidation in Oasis Rural in Arid Area: Case Study of the Ugan-Kuqa River Delta Oasis in Xinjiang, China. Land Degrad. Dev. 2024, 35, 1124–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Yang, S.; Simayi, Z.; Gu, Q.; Li, J.; Yang, X.; Ding, J. Modeling Variations in Soil Salinity in the Oasis of Junggar Basin, China. Land Degrad. Dev. 2018, 29, 551–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uuemaa, E.; Ahi, S.; Montibeller, B.; Muru, M.; Kmoch, A. Vertical Accuracy of Freely Available Global Digital Elevation Models (ASTER, AW3D30, MERIT, TanDEM-X, SRTM, and NASADEM). Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Huang, X. The 30 m Annual Land Cover Dataset and Its Dynamics in China from 1990 to 2019. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2021, 13, 3907–3925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.; Ding, Y.; Li, Z. High-Spatial-Resolution Monthly Temperature and Precipitation Dataset for China for 1901–2017. Earth Syst. Sci. Data Discuss. 2019, 2019, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Yang, S.; Shi, Q.; Wei, Y.; Wang, F. Using Apparent Electrical Conductivity as Indicator for Investigating Potential Spatial Variation of Soil Salinity across Seven Oases along Tarim River in Southern Xinjiang, China. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, D.; Cheng, C.; Song, C.; Shen, S.; Ning, L.; Zhang, T. A Hybrid Deep Learning-Based Spatiotemporal Fusion Method for Combining Satellite Images with Different Resolutions. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Cheng, Q.; Li, H.; Li, S.; Guan, X.; Shen, H. Spatiotemporal Fusion With Only Two Remote Sensing Images as Input. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2020, 13, 6206–6219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouse, J.W.; Haas, R.H.; Deering, D.W.; Schell, J.A.; Harlan, J.C. Monitoring the Vernal Advancement and Retrogradation (Green Wave Effect) of Natural Vegetation; NASA: Washington, DC, USA; GSFC: Greenbelt, MD, USA, 1974. [Google Scholar]
- Huete, A.; Didan, K.; Miura, T.; Rodriguez, E.P.; Gao, X.; Ferreira, L.G. Overview of the Radiometric and Biophysical Performance of the MODIS Vegetation Indices. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 83, 195–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douaoui, A.E.K.; Nicolas, H.; Walter, C. Detecting Salinity Hazards within a Semiarid Context by Means of Combining Soil and Remote-Sensing Data. Geoderma 2006, 134, 217–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Masek, J.; Schwaller, M.; Hall, F. On the Blending of the Landsat and MODIS Surface Reflectance: Predicting Daily Landsat Surface Reflectance. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2006, 44, 2207–2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, K.; Wang, Q.; Tang, Y.; Tong, X.; Atkinson, P.M. Geographically Weighted Spatial Unmixing for Spatiotemporal Fusion. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobler, W.R. A Computer Movie Simulating Urban Growth in the Detroit Region. Econ. Geogr. 1970, 46, 234–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, D.; Chen, B.; Wang, J.; Zhu, X.; Hilker, T. An Improved Image Fusion Approach Based on Enhanced Spatial and Temporal the Adaptive Reflectance Fusion Model. Remote Sens. 2013, 5, 6346–6360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, C.; Wang, J.; Pritchard, I.; Liu, J.; Shang, J. A Spatio-Temporal Data Fusion Model for Generating NDVI Time Series in Heterogeneous Regions. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Onojeghuo, A.O.; Zhu, X.; Atkinson, P.M. Enhancing Spatio-Temporal Fusion of MODIS and Landsat Data by Incorporating 250 m MODIS Data. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2017, 10, 4116–4123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.; Shen, H.; Zhang, L.; Göttsche, F.-M. Integrated Fusion of Multi-Scale Polar-Orbiting and Geostationary Satellite Observations for the Mapping of High Spatial and Temporal Resolution Land Surface Temperature. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 156, 169–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Chen, J.; Gao, F.; Chen, X.; Masek, J.G. An Enhanced Spatial and Temporal Adaptive Reflectance Fusion Model for Complex Heterogeneous Regions. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 2610–2623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Atkinson, P.M. Spatio-Temporal Fusion for Daily Sentinel-2 Images. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 204, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Huang, B.; Xu, Y.; Cao, K.; Guo, C.; Meng, D. Spatial and Temporal Image Fusion via Regularized Spatial Unmixing. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2015, 12, 1362–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Tang, Y.; Tong, X.; Atkinson, P.M. Virtual Image Pair-Based Spatio-Temporal Fusion. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 249, 112009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Peng, K.; Tang, Y.; Tong, X.; Atkinson, P.M. Blocks-Removed Spatial Unmixing for Downscaling MODIS Images. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 256, 112325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Guo, D.; Zhang, H. A Reliable and Adaptive Spatiotemporal Data Fusion Method for Blending Multi-Spatiotemporal-Resolution Satellite Images. Remote Sens. Environ. 2022, 268, 112770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Shi, K.; Ge, Y.; Zhou, Y. Spatiotemporal Remote Sensing Image Fusion Using Multiscale Two-Stream Convolutional Neural Networks. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Q.; Liu, H.; Shen, H.; Wu, P.; Zhang, L. A Spatial and Temporal Nonlocal Filter-Based Data Fusion Method. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2017, 55, 4476–4488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Zhou, J.; Qiu, Y.; Chen, J.; Zhu, X.; Chen, H. The FIRST Model: Spatiotemporal Fusion Incorrporting Spectral Autocorrelation. Remote Sens. Environ. 2022, 279, 113111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Deng, C.; Chanussot, J.; Hong, D.; Zhao, B. StfNet: A Two-Stream Convolutional Neural Network for Spatiotemporal Image Fusion. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 6552–6564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, C.; Tian, A.; Zhu, D.; Zhao, J.; Xiong, H. Estimation of Salinity Content in Different Saline-Alkali Zones Based on Machine Learning Model Using FOD Pretreatment Method. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 5140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, C.; Ji, Q.; Chen, J.; Zhang, F.; Li, Y.; Fan, J.; Hou, X.; Yan, F.; Wang, H. Prediction of Soil Salinity Parameters Using Machine Learning Models in an Arid Region of Northwest China. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2023, 204, 107512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Ding, J.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, J.; Chen, X.; Han, L.; Shi, H.; Wang, J. Soil Salinity Dynamics in Arid Oases during Irrigated and Non-Irrigated Seasons. Land Degrad. Dev. 2023, 34, 3823–3835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, C.; Zhang, X.; Meng, X.; Zhu, H.; Ni, C.; Chen, M.; Liu, H. Regional Mapping of Soil Organic Matter Content Using Multitemporal Synthetic Landsat 8 Images in Google Earth Engine. CATENA 2022, 209, 105842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; He, B.; Ge, X.; Luo, X. Spatial Prediction of Soil Salinity Based on the Google Earth Engine Platform with Multitemporal Synthetic Remote Sensing Images. Ecol. Inform. 2023, 75, 102111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Chen, J.; Chen, X.; Zhu, X.; Qiu, Y.; Song, H.; Rao, Y.; Zhang, C.; Cao, X.; Cui, X. Sensitivity of Six Typical Spatiotemporal Fusion Methods to Different Influential Factors: A Comparative Study for a Normalized Difference Vegetation Index Time Series Reconstruction. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 252, 112130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Wang, J.; Gong, P. ROBOT: A Spatiotemporal Fusion Model toward Seamless Data Cube for Global Remote Sensing Applications. Remote Sens. Environ. 2023, 294, 113616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Cao, R.; Chen, J.; Zhu, X.; Zhou, J.; Wang, G.; Shen, M.; Chen, X.; Yang, W. A New Cross-Fusion Method to Automatically Determine the Optimal Input Image Pairs for NDVI Spatiotemporal Data Fusion. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 58, 5179–5194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.; Meng, X.; Zhang, L. An Integrated Framework for the Spatio–Temporal–Spectral Fusion of Remote Sensing Images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2016, 54, 7135–7148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pôças, I.; Calera, A.; Campos, I.; Cunha, M. Remote Sensing for Estimating and Mapping Single and Basal Crop Coefficientes: A Review on Spectral Vegetation Indices Approaches. Agric. Water Manag. 2020, 233, 106081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
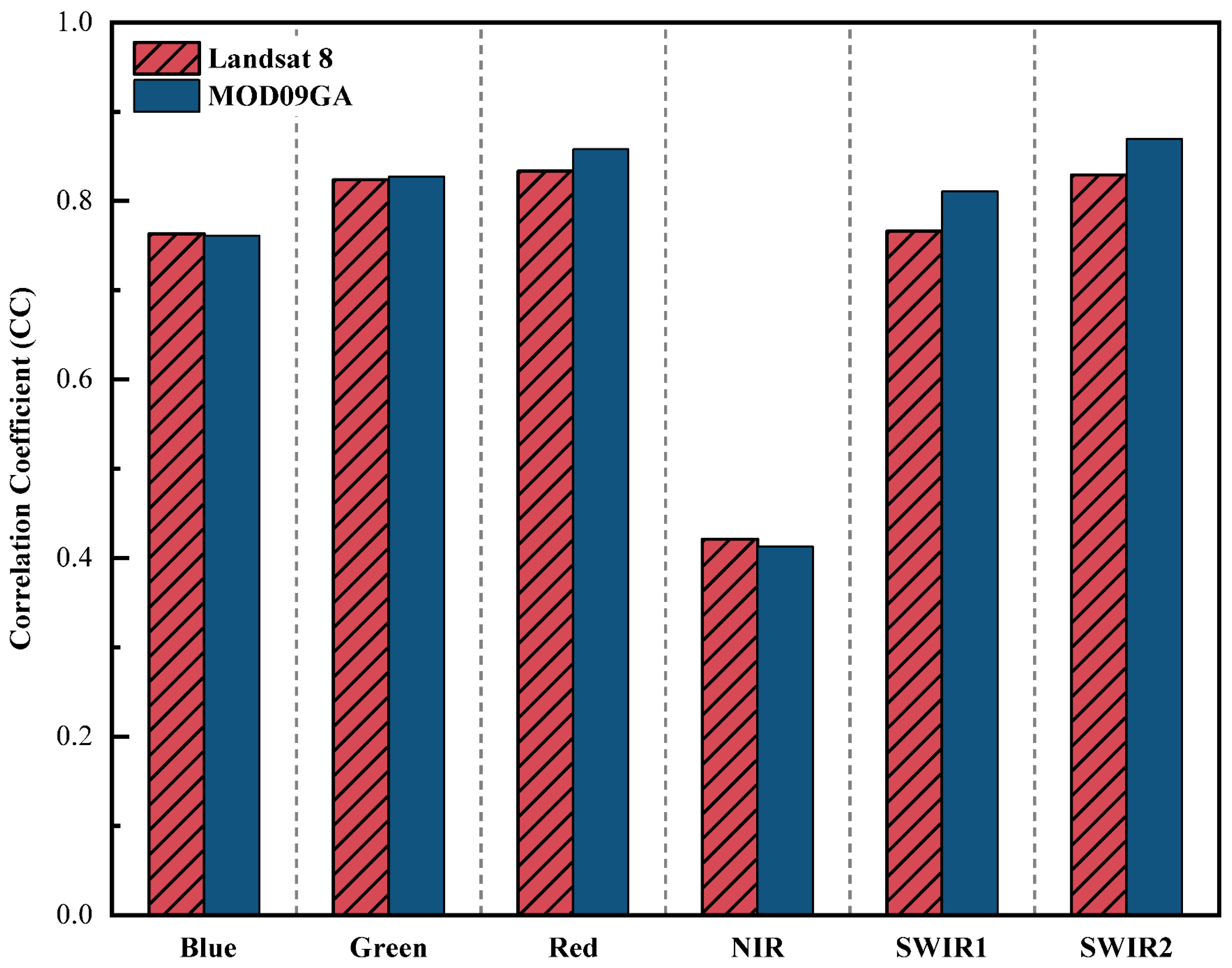





| Landsat 8 | MOD09GA | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Band Name | Wavelength (nm) | Resolution (m) | Band Name | Wavelength (nm) | Resolution (m) |
| SR_B2(Blue) | 452–512 | 30 | sur_ref1_b03 | 459–479 | 500 |
| SR_B3 (Green) | 533–590 | 30 | sur_ref1_b04 | 545–565 | 500 |
| SR_B4 (Red) | 636–673 | 30 | sur_ref1_b01 | 620–670 | 500 |
| SR_B5 (NIR) | 851–879 | 30 | sur_ref1_b02 | 841–876 | 500 |
| SR_B6 (SWIR 1) | 1566–1651 | 30 | sur_ref1_b06 | 1628–1652 | 500 |
| SR_B7 (SWIR 2) | 2107–2294 | 30 | sur_ref1_b07 | 2105–2155 | 500 |
| N | Min. | Max. | Mean | Median | IQR | SD | CV | Skewness | Kurtosis |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 83 | 0.113 | 114.200 | 17.295 | 5.940 | 15.308 | 25.847 | 1.495 | 2.057 | 3.641 |
| Band | RASDF | STARFM | Fit-FC | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AD | CC | SSIM | AD | CC | SSIM | AD | CC | SSIM | |
| Blue | −0.002 | 0.855 | 0.896 | −0.003 | 0.851 | 0.883 | −0.003 | 0.827 | 0.874 |
| Green | −0.012 | 0.915 | 0.886 | −0.013 | 0.913 | 0.878 | −0.013 | 0.896 | 0.872 |
| Red | −0.011 | 0.923 | 0.867 | −0.012 | 0.913 | 0.840 | −0.020 | 0.905 | 0.849 |
| NIR | −0.027 | 0.799 | 0.705 | −0.029 | 0.727 | 0.626 | −0.006 | 0.812 | 0.772 |
| SWIR1 | −0.003 | 0.889 | 0.814 | −0.011 | 0.882 | 0.806 | 0.010 | 0.800 | 0.766 |
| SWIR2 | −0.002 | 0.917 | 0.843 | −0.005 | 0.899 | 0.803 | −0.003 | 0.899 | 0.812 |
| Strategy | Index | RASDF | STARFM | Fit-FC | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AD | CC | SSIM | AD | CC | SSIM | AD | CC | SSIM | ||
| FI | NDVI | −0.029 | 0.796 | 0.678 | −0.033 | 0.722 | 0.538 | 0.015 | 0.821 | 0.760 |
| EVI | −0.027 | 0.808 | 0.721 | −0.023 | 0.719 | 0.573 | 0.007 | 0.809 | 0.805 | |
| SI | −0.004 | 0.890 | 0.919 | −0.005 | 0.863 | 0.903 | −0.004 | 0.864 | 0.905 | |
| SI2 | −0.006 | 0.882 | 0.863 | −0.017 | 0.841 | 0.807 | −0.007 | 0.875 | 0.831 | |
| IF | NDVI | −0.008 | 0.877 | 0.799 | −0.008 | 0.837 | 0.624 | 0.000 | 0.912 | 0.833 |
| EVI | −0.013 | 0.857 | 0.817 | −0.013 | 0.756 | 0.602 | −0.002 | 0.921 | 0.890 | |
| SI | −0.004 | 0.884 | 0.918 | −0.008 | 0.880 | 0.911 | −0.004 | 0.851 | 0.895 | |
| SI2 | −0.017 | 0.845 | 0.780 | −0.018 | 0.815 | 0.759 | −0.017 | 0.798 | 0.792 |
| Training R2 | Validation R2 | Training RMSE | Validation RMSE | Training RPD | Validation RPD | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reference | 0.815 | 0.652 | 11.035 | 15.214 | 2.322 | 1.696 |
| STARFM | 0.821 | 0.548 | 11.772 | 13.295 | 2.362 | 1.487 |
| RASDF | 0.831 | 0.714 | 11.214 | 11.469 | 2.434 | 1.870 |
| Fit-FC | 0.829 | 0.543 | 11.537 | 13.026 | 2.416 | 1.480 |
| Training R2 | Validation R2 | Training RMSE | Validation RMSE | Training RPD | Validation RPD | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reference image | 0.815 | 0.652 | 11.035 | 15.214 | 2.322 | 1.696 |
| Fused images–median | 0.863 | 0.614 | 10.263 | 11.717 | 2.699 | 1.609 |
| Fused images–mean | 0.797 | 0.726 | 12.048 | 12.011 | 2.221 | 1.910 |
| Multi-year images–median | 0.862 | 0.600 | 10.251 | 12.447 | 2.687 | 1.581 |
| Multi-year images–mean | 0.857 | 0.724 | 10.505 | 10.347 | 2.640 | 1.905 |
| Combined images–median | 0.866 | 0.807 | 10.500 | 6.525 | 2.734 | 2.275 |
| Combined images–mean | 0.818 | 0.676 | 11.426 | 13.056 | 2.342 | 1.757 |
| Training R2 | Validation R2 | Training RMSE | Validation RMSE | Training RPD | Validation RPD | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reference image | 0.815 | 0.652 | 11.035 | 15.214 | 2.322 | 1.696 |
| Auxiliary datasets | 0.892 | 0.636 | 8.555 | 14.983 | 3.044 | 1.657 |
| Auxiliary features | 0.826 | 0.626 | 11.155 | 14.022 | 2.399 | 1.636 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, J.; Zeng, A.; Ding, J.; Qin, S. Dynamic Monitoring of Soil Salinization in Oasis Regions Using Spatiotemporal Fusion Algorithms. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 2905. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17162905
Wang J, Zeng A, Ding J, Qin S. Dynamic Monitoring of Soil Salinization in Oasis Regions Using Spatiotemporal Fusion Algorithms. Remote Sensing. 2025; 17(16):2905. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17162905
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Jinjie, Annan Zeng, Jianli Ding, and Shaofeng Qin. 2025. "Dynamic Monitoring of Soil Salinization in Oasis Regions Using Spatiotemporal Fusion Algorithms" Remote Sensing 17, no. 16: 2905. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17162905
APA StyleWang, J., Zeng, A., Ding, J., & Qin, S. (2025). Dynamic Monitoring of Soil Salinization in Oasis Regions Using Spatiotemporal Fusion Algorithms. Remote Sensing, 17(16), 2905. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17162905








