Studying Long-Term Nutrient Variations in Semi-Enclosed Bays Using Remote Sensing and Machine Learning Methods: A Case Study of Laizhou Bay, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Study Area
3. Data and Methods
3.1. In Situ Measurement Data
3.2. Satellite Data
3.3. Machine Learning Method
3.4. Design of Machine Learning Models for Nutrient Concentration in the Sea Surface
3.5. Evaluation of Machine Learning Models
4. Results
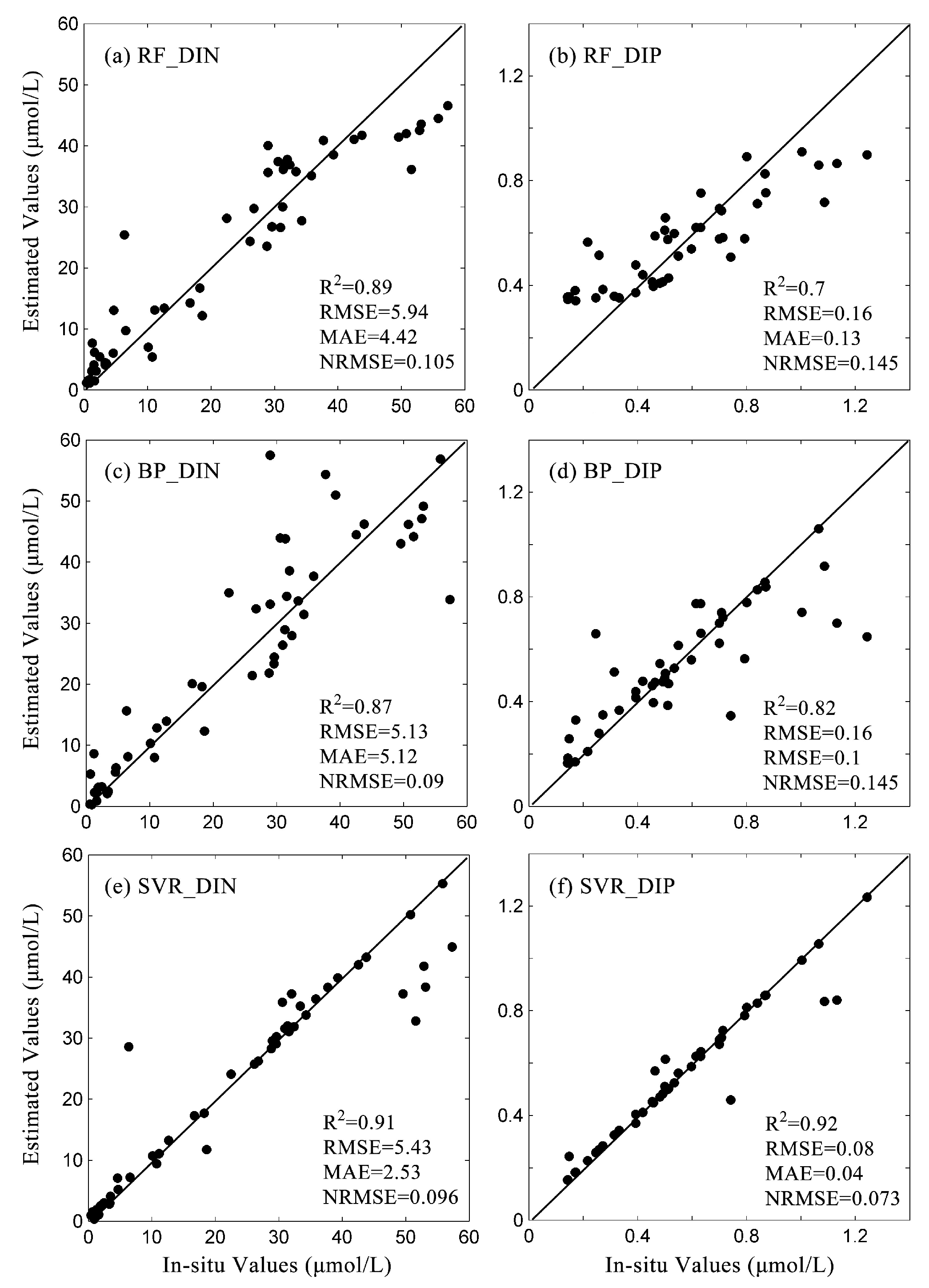
4.1. Machine Learning Model Evaluation
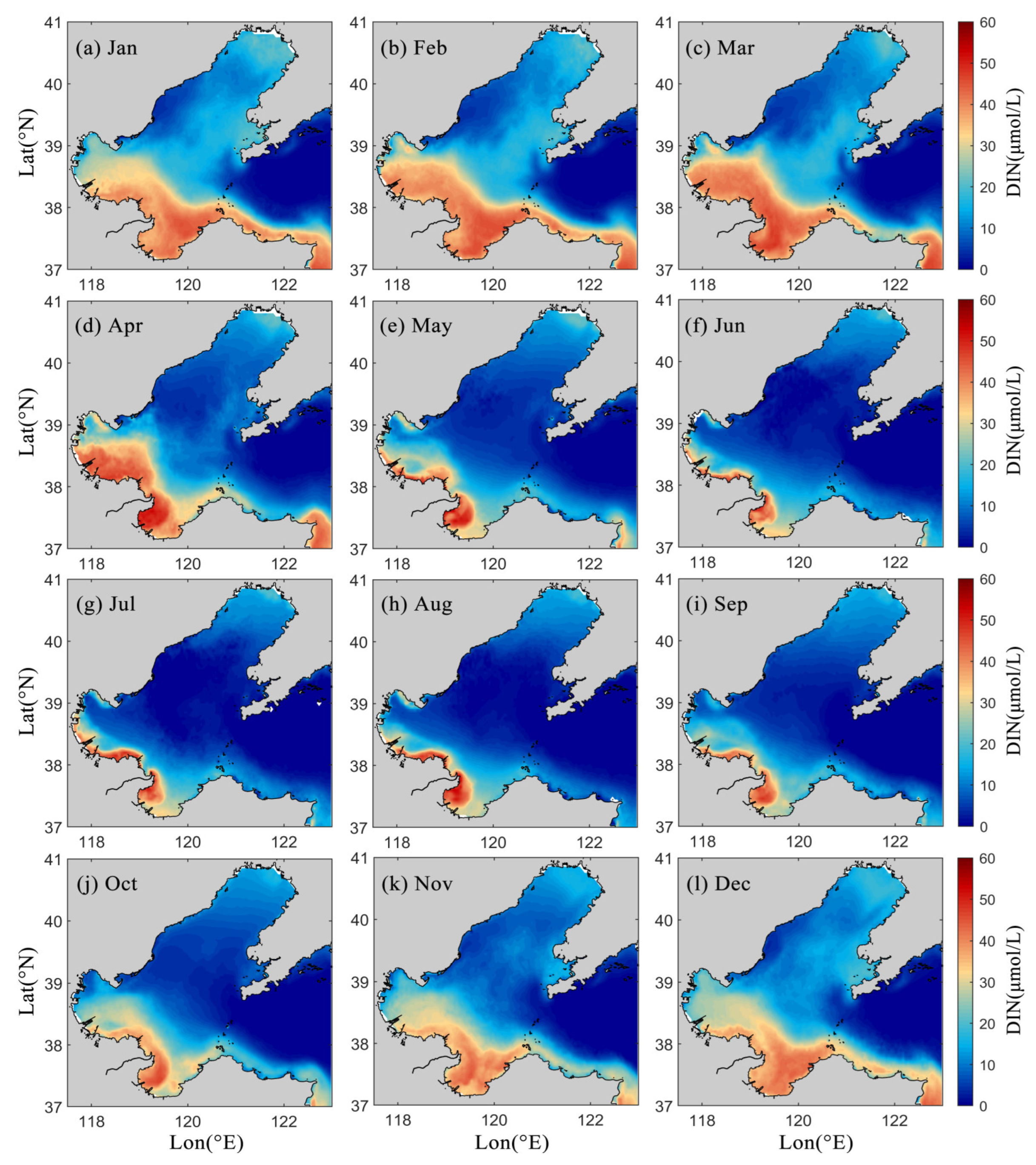
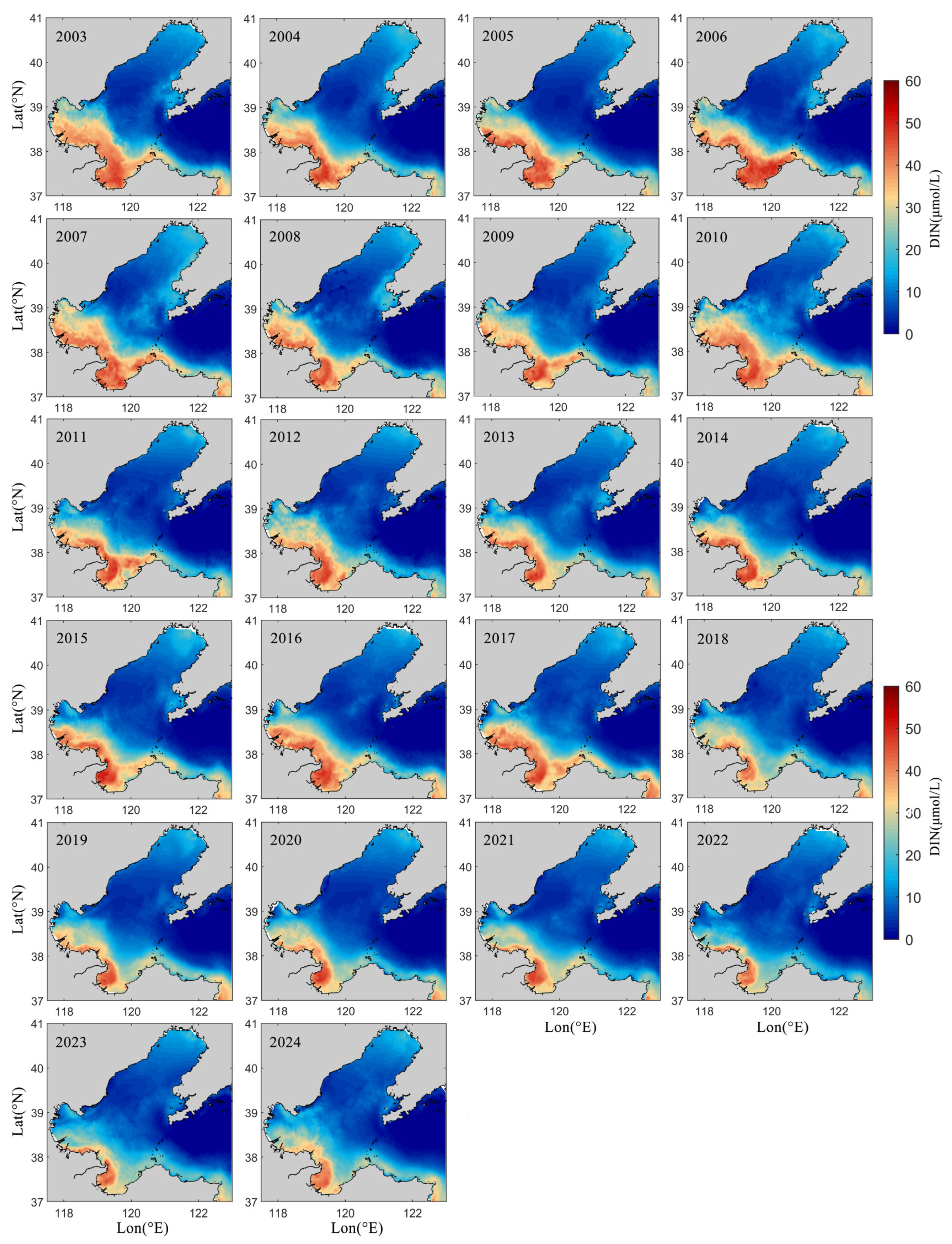
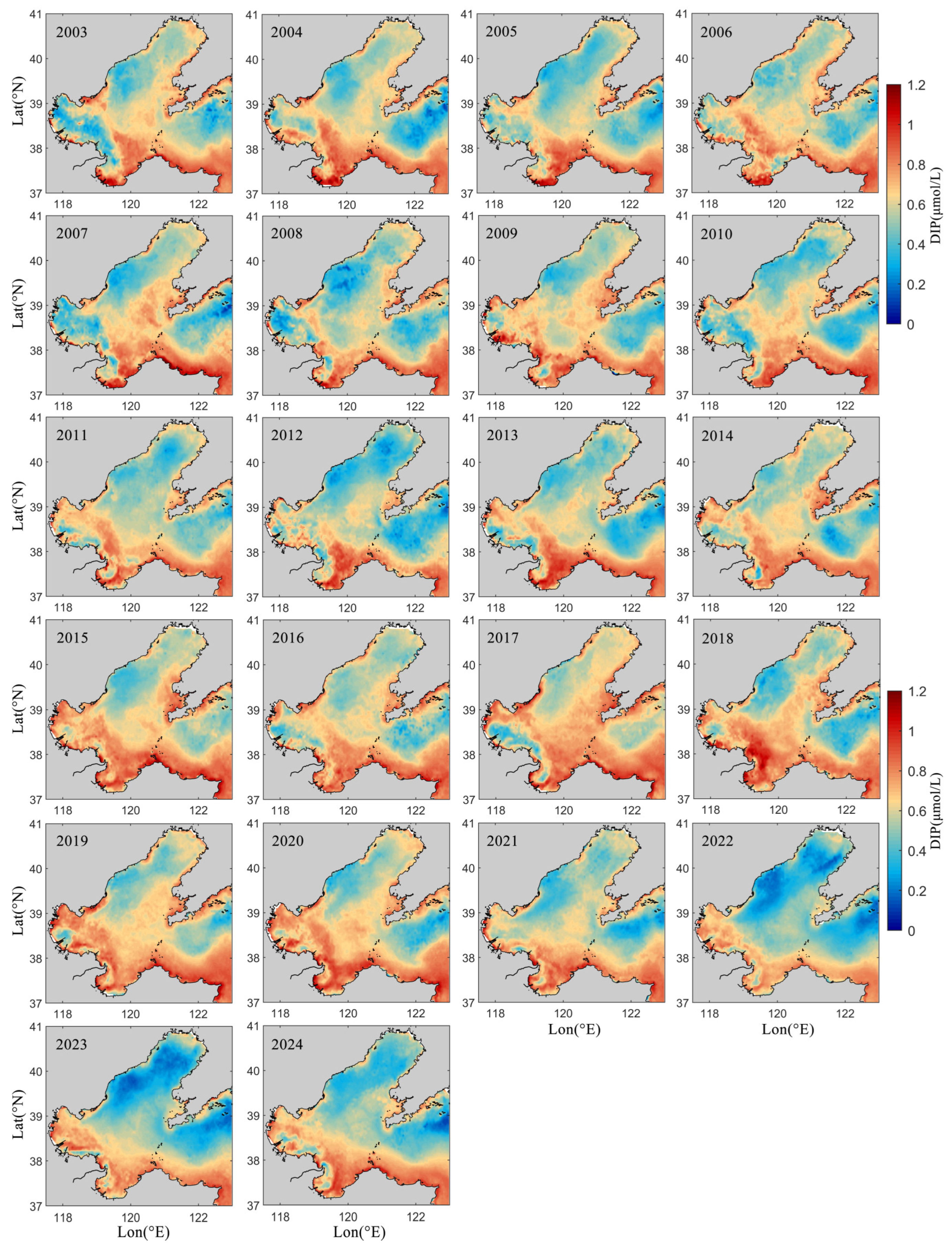
4.2. Regional and Seasonal Variations in Nutrients in LZB
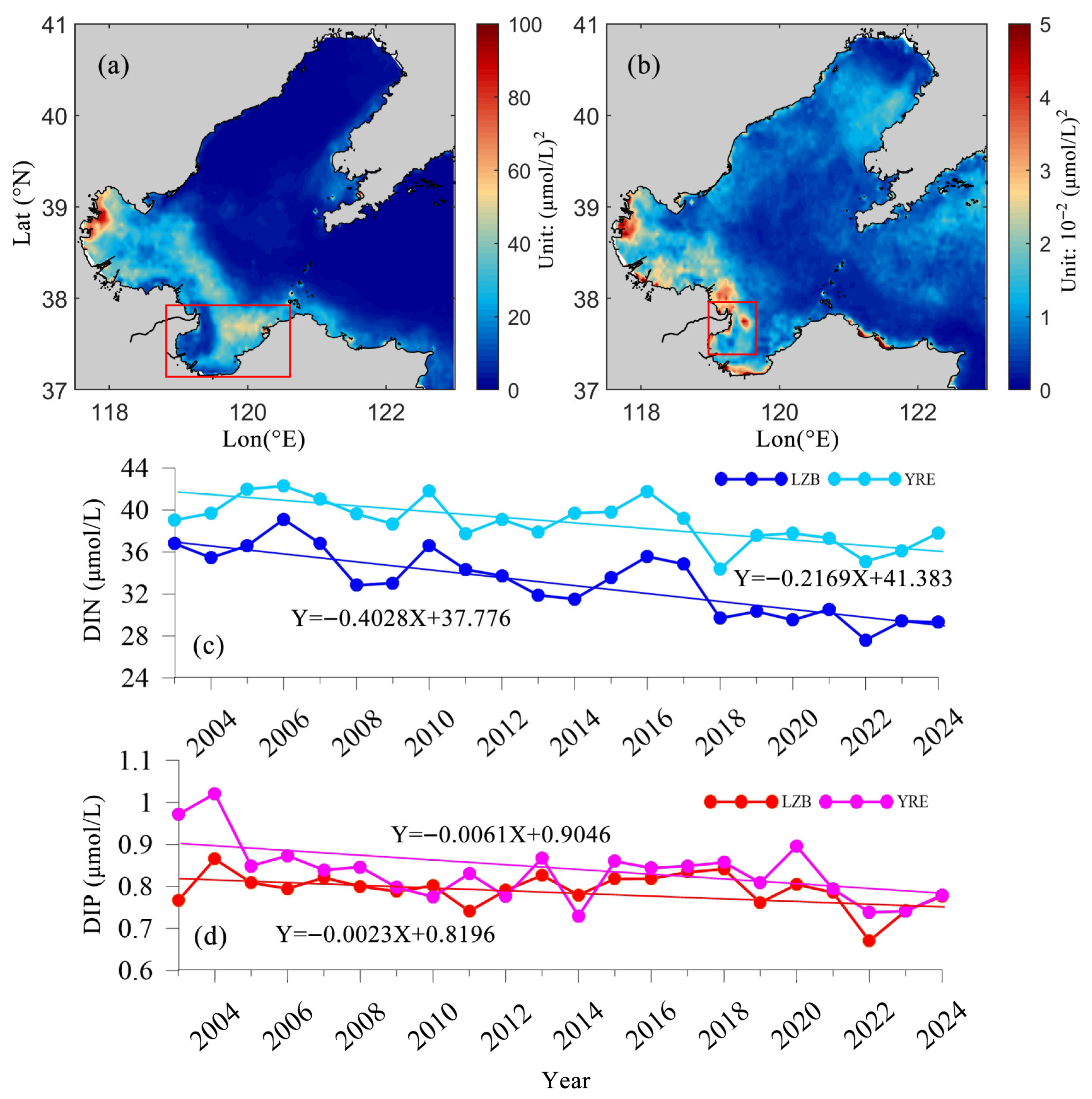
4.3. Interannual Variation in Nutrients in LZB
5. Discussion
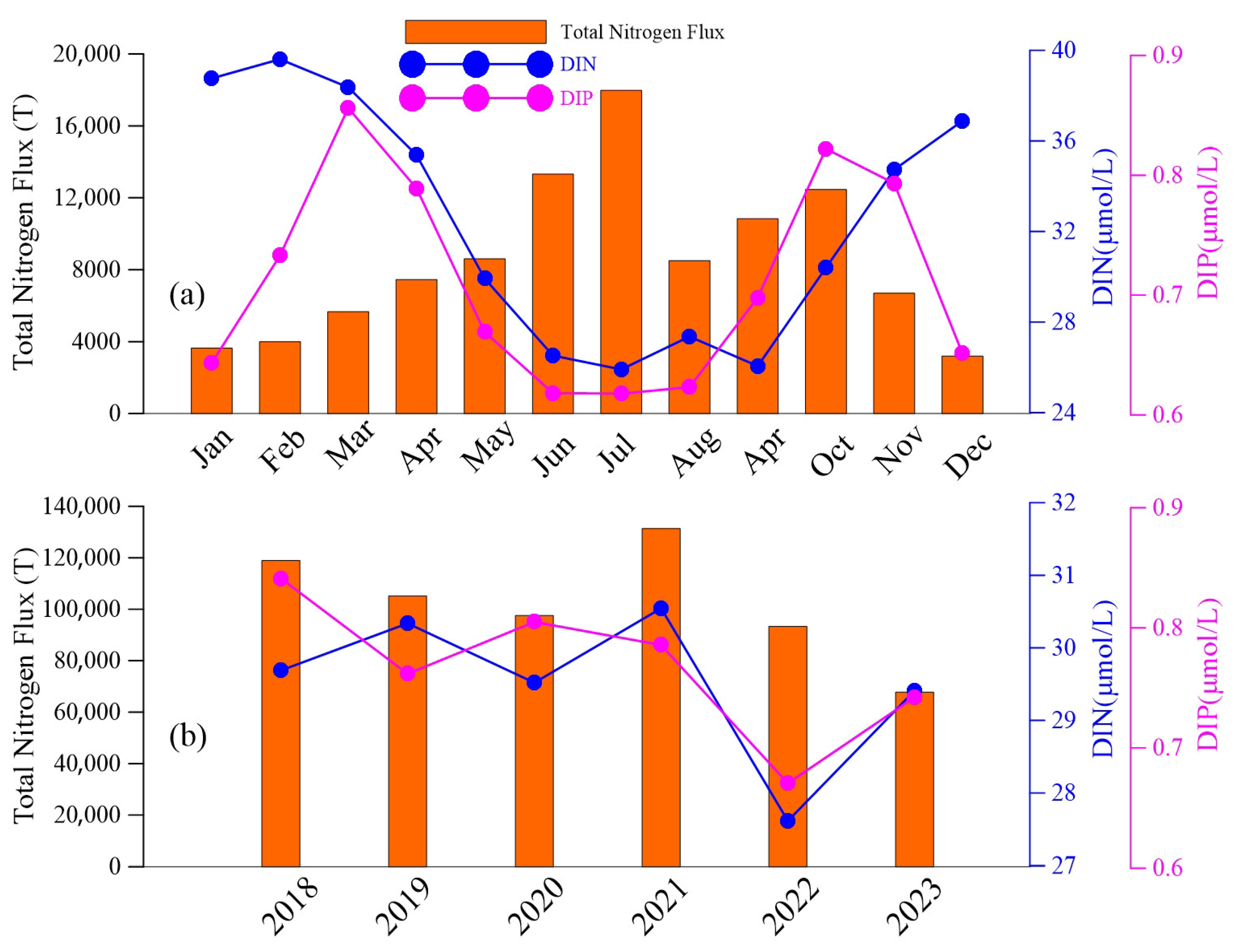
5.1. Factors Affecting Seasonal Variations in Nutrient Concentrations in LZB
5.2. Factors Affecting Interannual Variation in Nutrient Concentrations in LZB
5.3. Future Work
6. Conclusions
- (1)
- Three machine learning algorithms were evaluated for their suitability in the retrieval of surface nutrients in LZB, with SVR showing better performance than BP and RFR. The DIN and DIP retrieval results based on the SVR algorithm achieved R2 values of 0.91 and 0.92, with RMSE values of 5.43 and 0.08 μmol/L, respectively.
- (2)
- Seasonal variations in nutrient concentrations in LZB show higher concentrations in the winter half of the year compared to the summer half, which is hypothesized to be mainly due to the uptake of nutrients by phytoplankton growth and reproduction.
- (3)
- From 2003 to 2024, DIN concentrations in LZB decreased at a rate of 0.4 μmol/L/yr, mainly due to changes in riverine nutrient flux and the implementation of environmental policies by the government.
- (4)
- Changes in hydrodynamic conditions also significantly affected nutrient concentrations in LZB.
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhu, G.; Noman, M.; Narale, D.; Feng, W.; Pujari, L.; Sun, J. Evaluation of ecosystem health and potential human health hazards in the Hangzhou Bay and Qiantang Estuary region through multiple assessment approaches. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 264, 114791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, L.; Wai, O.W.H.; Chen, X.L.; Liu, Y.; Feng, L.; Li, J.; Huang, J. Assessment of total suspended sediment distribution under varying tidal conditions in deep bay: Initial results from HJ1A/1B satellite CCD images. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 9911–9929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, A.; Corbett, D.; Fitzgerald, A.; Lemley, D.A.; Quigg, A.; Steppe, C.N. Impacts of urbanization and development on estuarine ecosystems and water quality. Estuaries Coasts 2019, 42, 1821–1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cloern, J.; Foster, S.; Kleckner, A. Phytoplankton primary production in the world’s estuarine-coastal ecosystems. Biogeosciences 2014, 11, 1726–4170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, J.; Chen, L.; Cao, Z.; Hu, M.; Xue, K.; Chen, X.; Ma, R. Development of remote sensing algorithm for total phosphorus concentration in eutrophic lakes: Conventional or machine learning? Water Res. 2022, 215, 118213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, J.; Chen, L.; Ma, R.; Wang, X.; Xue, K.; Cao, Z.; Hu, M.; Chen, L.; Lin, C. The Remote Sensing Observations of Phosphorus in Eutrophic Lakes: From Concentration to Storage. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2025, 63, 4203182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyrrell, T. The Relative Influences of Nitrogen and Phosphorus on Oceanic Primary Production. Nature 1999, 400, 525–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristiansen, S.; Hoell, E. The Importance of Silicon for Marine Production. Hydrobiologia 2002, 484, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Lin, L.; Wang, Y.; Du, L.; Wang, S.; Zhou, P.; Yu, Y.; Gong, X.; Lu, X. Reconstruction of Monthly Surface Nutrient Concentrations in the Yellow and Bohai Seas from 2003–2019 Using Machine Learning. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabalais, N.N.; Turner, R.E.; Díaz, R.J.; Justić, D. Global change and eutrophication of coastal waters. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2009, 66, 1528–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Wang, D.; Gong, F.; Bai, Y.; He, X. Changes in Nutrient Concentrations in Shenzhen Bay Detected Using Landsat Imagery between 1988 and 2020. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Anil, A.; Kumar, V.; Kapoor, D.; Subramanian, S.; Singh, J.; Ramamurthy, P.C. Nitrates in the environment: A critical review of their distribution, sensing techniques, ecological effects and remediation. Chemosphere 2022, 287 Pt 1, 131996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, T.; Deutsch, C. Ocean nutrient ratios governed by plankton biogeography. Nature 2010, 467, 550–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamun, M.; Lee, S.; An, K. Temporal and spatial variation of nutrients, suspended solids, and chlorophyll in Yeongsan watershed. J. Asia-Pac. Biodivers. 2018, 11, 206–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Wang, D.; Pan, S.; Li, H.; Gong, F.; Hu, H.; He, X.; Bai, Y.; Zheng, Z. A New High-Resolution Remote Sensing Monitoring Method for Nutrients in Coastal Waters. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 61, 4206315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Lu, Q.; Wang, D.; Ding, D.; Cui, Z.; Shi, H. Spatiotemporal evolution of nutrients and the influencing factors in Laizhou Bay over the past 40 years. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 184, 114186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Y.; Cui, H.; Hu, Q.; Bai, Y.; Qu, K.; Sun, J.; Cui, Z. Eutrophication status assessment in the Laizhou Bay, Bohai Sea: Further evidence for the ecosystem degradation. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 181, 113867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Qiao, L.; Zhong, Y.; Wan, X.; Xue, W.; Liu, P. Pathways of suspended sediments transported from the Yellow River mouth to the Bohai Sea and Yellow Sea. Estuarine. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2020, 236, 106639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Qiao, L.; Zhong, Y.; Xue, W.; Liu, P. Multi-Year Winter Variations in Suspended Sediment Flux through the Bohai Strait. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 4066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Cui, Q.; Gong, F.; Wang, L.; He, X.; Bai, Y. Satellite Retrieval of Surface Water Nutrients in the Coastal Regions of the East China Sea. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Li, X.; Song, D.; Nie, J.; Liang, S. Prediction on daily spatial distribution of chlorophyll-a in coastal seas using a synthetic method of remote sensing, machine learning and numerical modeling. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 910, 168642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C.; Zheng, W.; Shi, H.; Ding, D.; Wang, Z. Assessment and regulation of ocean health based on ecosystem services: Case study in the Laizhou Bay, China. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2015, 34, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Zhu, M.; Chen, W.; Wang, X.; Liu, X.; Qiao, S.; Su, B.; Yang, Y. Unveiling the effects of environmental factors and Yellow River inputs on the ichthyoplankton community structure in typical bays. Mar. Environ. Res. 2024, 201, 106677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Cao, L.; Dou, S. Bioaccumulation of heavy metals and health risk assessment in three benthic bivalves along the coast of Laizhou Bay, China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 117, 98–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Wang, Z.; Cui, Q.; Sun, X.; Huang, H. Coastal ecological disasters triggered by an extreme rainfall event thousands of kilometers inland. Commun. Earth Environ. 2024, 5, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, D.; Tang, D. Application of a Generalized Additive Model (GAM) for Estimating Chlorophyll-a Concentration from MODIS Data in the Bohai and Yellow Seas, China. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2017, 38, 639–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Mi, T.; Yu, Z.; Yang, F.; Wang, K.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Yuan, L.; Yao, Q. Upwelling of cold water in the South Yellow Sea alleviates phosphorus and silicon limitations. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2025, 70, 553–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Bian, C.; Wang, C.; Jiang, W.; Bi, R. Quantitative assessment on multiple timescale features and dynamics of sea surface suspended sediment concentration using remote sensing data. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2017, 122, 8739–8752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noble, W. What Is a Support Vector Machine? Nat. Biotechnol 2006, 24, 1565–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Werner, A.; Yao, J. Investigating a complex lake-catchment-river system using artificial neural networks: Poyang Lake (China). Hydrol. Res. 2015, 46, 912–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, M.; Wang, B.; Xie, L.; Sun, X.; Wei, Q.; Liang, S.; Chen, K. Long-term changes in nutrient regimes and their ecological effects in the Bohai Sea China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 146, 562–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Tian, C.; Zong, Z.; Wang, X.; Jiang, W.; Chen, Y.; Ma, J.; Luo, Y.; Li, J.; Zhang, G. Flux and source-sink relationship of heavy metals and arsenic in the Bohai Sea, China. Environment. Pollut. 2018, 242 Pt B, 1353–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Chen, H.Y.; Karl, D.; Takahashi, M. Nitrogen modulates phytoplankton growth in spring in the South China Sea. Cont. Shelf Res. 2004, 24, 527–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Jia, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Shan, H. Influence of seepage flows on the erodibility of fluidized silty sediments: Parameterization and mechanisms. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2018, 123, 3307–3321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Li, L.; Zhang, Z. Inventory of nutrients in the Bohai. Cont. Shelf Res. 2011, 31, 1790–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Wang, Y.; Liu, D. Vertical Average Irradiance Shapes the Spatial Pattern of Winter Chlorophyll-a in the Yellow Sea. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2019, 224, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Li, L.; Zhang, G.; Liu, Z.; Yu, Z.; Ren, J.L. Impacts of human activities on nutrient transports in the Huanghe (Yellow River) estuary. J. Hydrol. 2012, 430–431, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Cao, J.; Yang, Y. Variation of wind speed and its influencing factors around the Bohai coastal areas from 1971 to 2012. J. Meteorol. Environ. 2015, 31, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Jiang, W.; Wang, T.; Chen, S.; Bian, C. Decadal variation and regulation mechanisms of the suspended sediment concentration in the Bohai Sea, China. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2022, 127, e2021JC017699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Qiao, L.; Li, G.; Zhong, Y.; Miao, H.; Hu, R. Discontinuity of sediment transport from the Bohai Sea to the open sea dominated by the wind direction. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2023, 293, 108486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
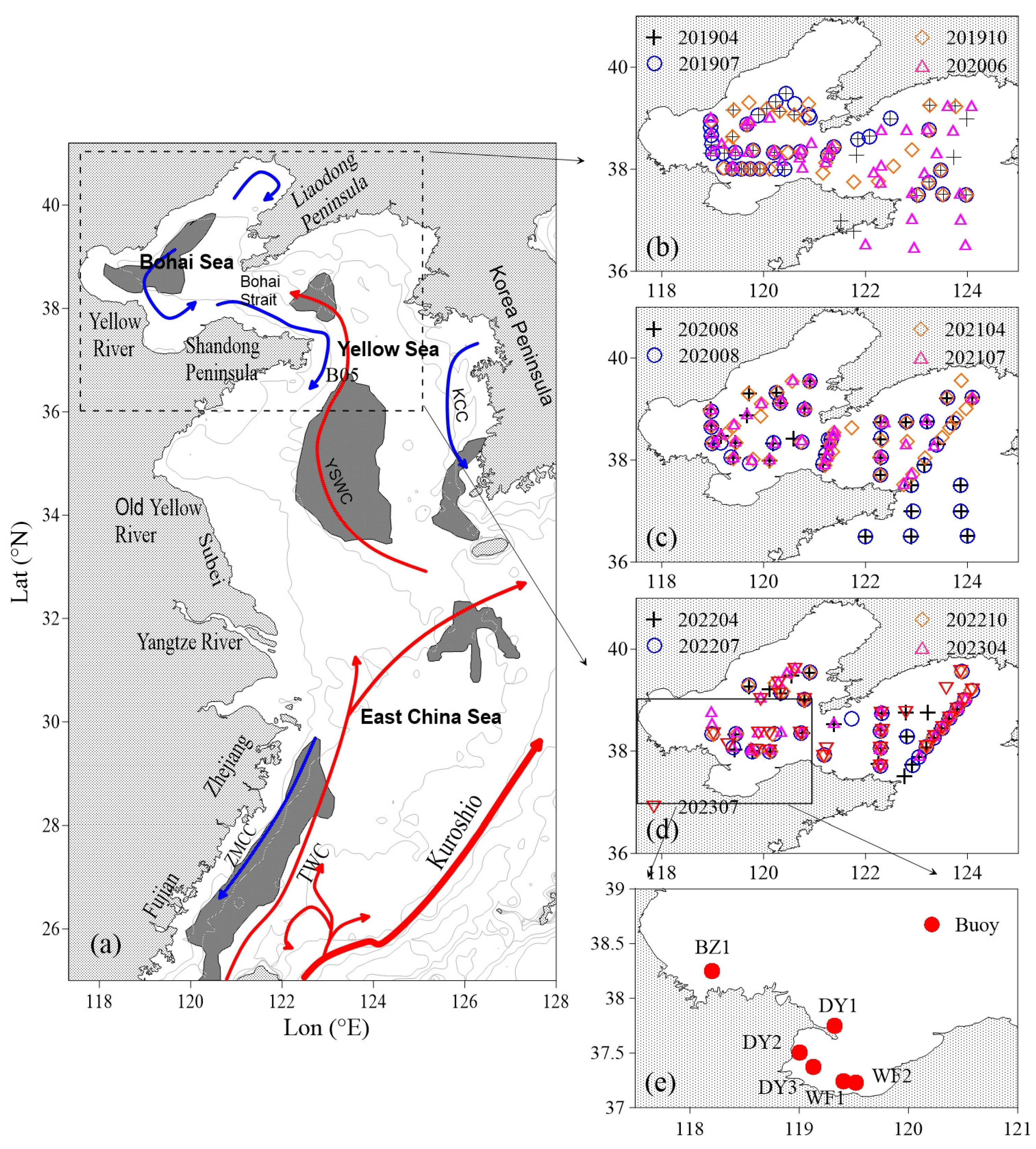
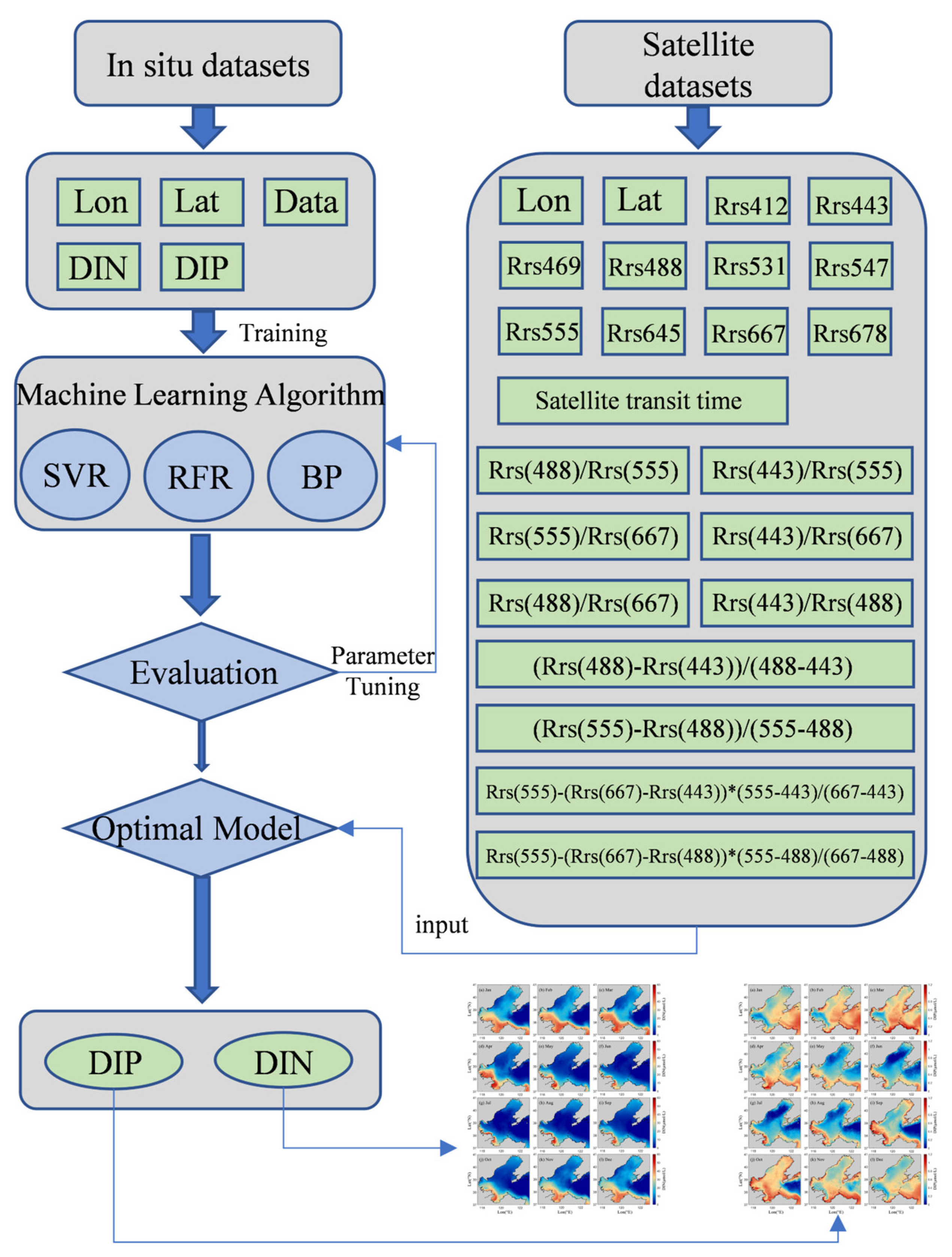

| Station Name | Time | Time Resolution |
|---|---|---|
| BZ1 | 19 March 2024–19 April 2024 | 4 h |
| DY1 | 26 May 2024–18 November 2024 | 6 h |
| DY2 | 26 May 2024–18 November 2024 | 6 h |
| DY3 | 26 May 2024–21 November 2024 | 6 h |
| WF1 | 1 July 2022–16 September 2022 | 6 h |
| WF2 | 1 July 2022–19 September 2022 | 6 h |
| Parameter | RF | BP | SVR | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DIN | DIP | DIN | DIP | DIN | DIP | |
| R2 | 0.89 | 0.7 | 0.87 | 0.82 | 0.91 | 0.92 |
| RMSE | 5.94 | 0.16 | 5.13 | 0.16 | 5.43 | 0.08 |
| MAE | 4.42 | 0.13 | 5.12 | 0.1 | 2.53 | 0.04 |
| NRMSE | 0.105 | 0.145 | 0.09 | 0.145 | 0.096 | 0.073 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, X.; Qiao, L.; Song, D.; Yu, X.; Zhong, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y. Studying Long-Term Nutrient Variations in Semi-Enclosed Bays Using Remote Sensing and Machine Learning Methods: A Case Study of Laizhou Bay, China. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 2857. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17162857
Liu X, Qiao L, Song D, Yu X, Zhong Y, Wang J, Wang Y. Studying Long-Term Nutrient Variations in Semi-Enclosed Bays Using Remote Sensing and Machine Learning Methods: A Case Study of Laizhou Bay, China. Remote Sensing. 2025; 17(16):2857. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17162857
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Xingmin, Lulu Qiao, Dehai Song, Xiaoxia Yu, Yi Zhong, Jin Wang, and Yueqi Wang. 2025. "Studying Long-Term Nutrient Variations in Semi-Enclosed Bays Using Remote Sensing and Machine Learning Methods: A Case Study of Laizhou Bay, China" Remote Sensing 17, no. 16: 2857. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17162857
APA StyleLiu, X., Qiao, L., Song, D., Yu, X., Zhong, Y., Wang, J., & Wang, Y. (2025). Studying Long-Term Nutrient Variations in Semi-Enclosed Bays Using Remote Sensing and Machine Learning Methods: A Case Study of Laizhou Bay, China. Remote Sensing, 17(16), 2857. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17162857







